Plastic Processing Equipment
Find innovative plastics equipment and connect directly with world-leading technology suppliers
Can it be said that we live in the Plastic age? Basically, yes. From pillows over toothbrushes, and packaging to utensils, plastic is a widely used material in our day-to-day lives. But what is it? Plastics are synthetic or semi-synthetic materials built of polymers that are easily shaped into various structures with the help of plastic processing equipment such as extruders and molders.
Top picks for plastic production
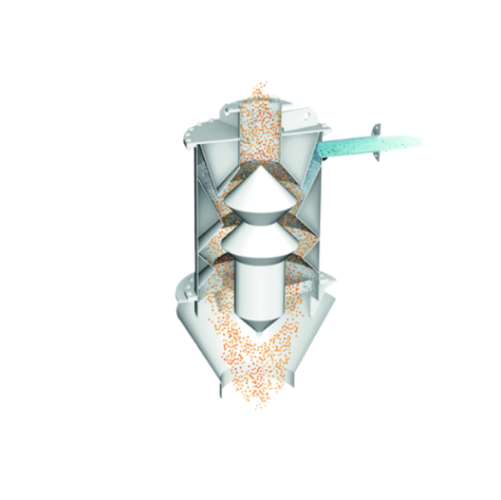

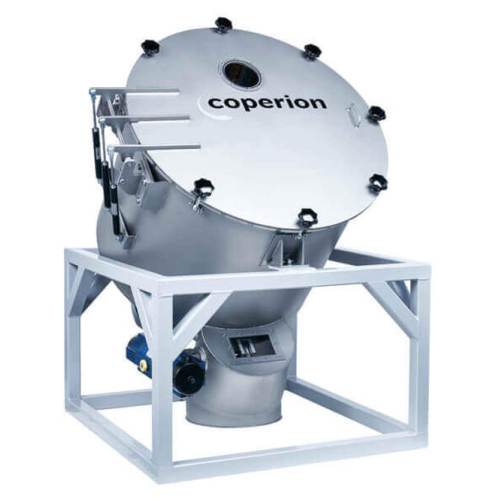
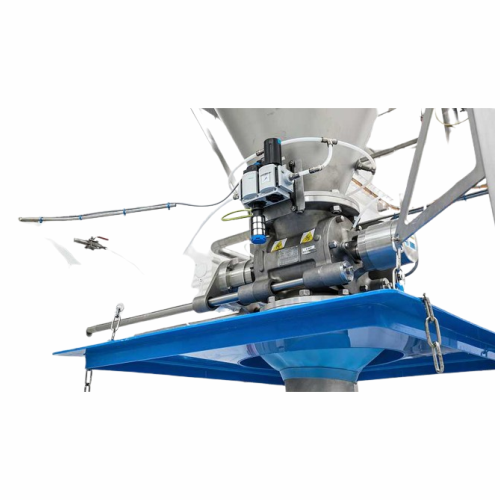
Air separator for polymers and plastics
Ensure high-purity plastic pellets by efficiently separating fine dust and streamer...
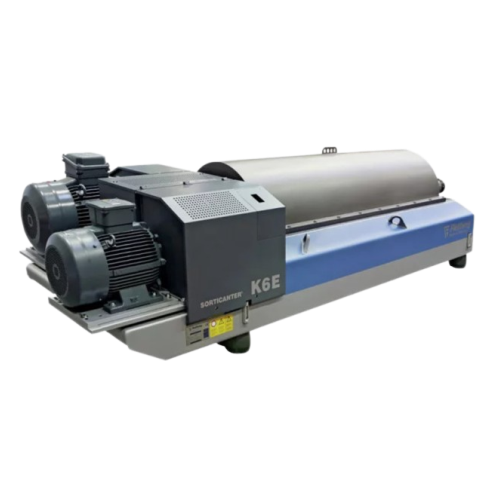

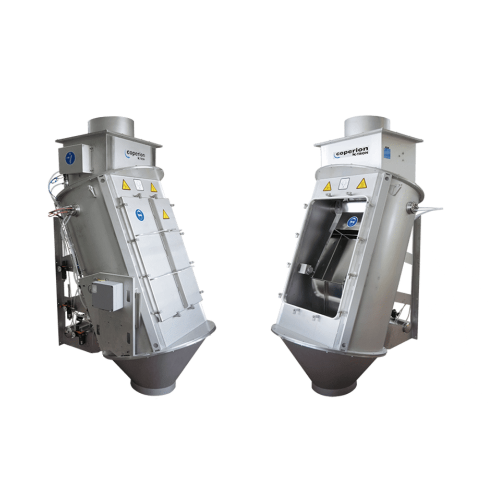
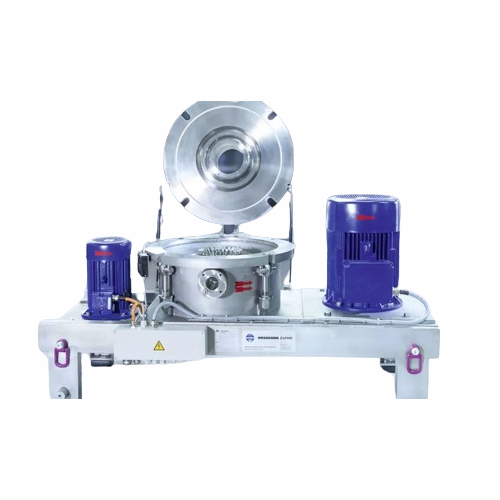
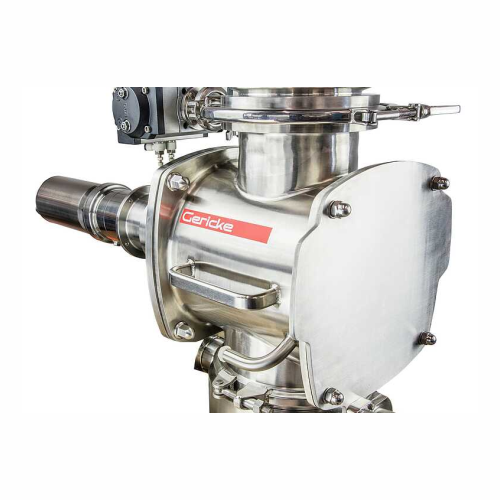
Centrifuge for plastics recycling
Enhance your recycling process with a centrifuge designed to efficiently separate and dew...
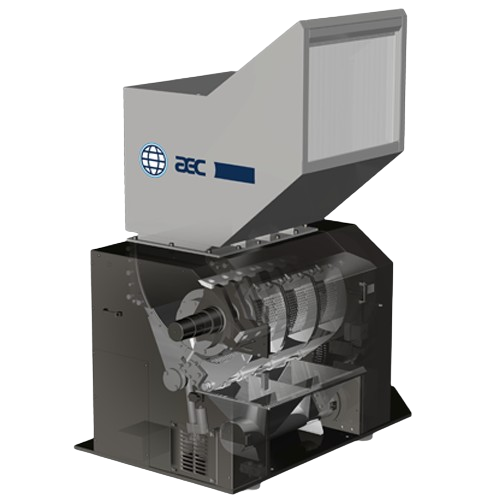

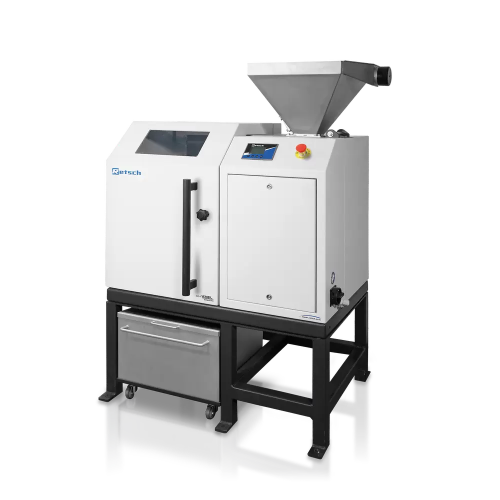
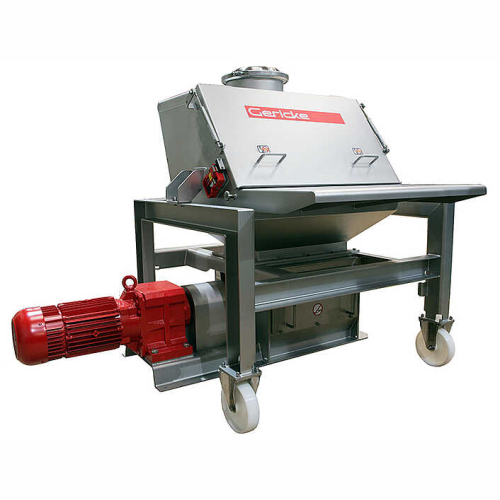
Central granulators for high-volume plastics recycling
Efficiently process large volumes of recycled plastics and industr...
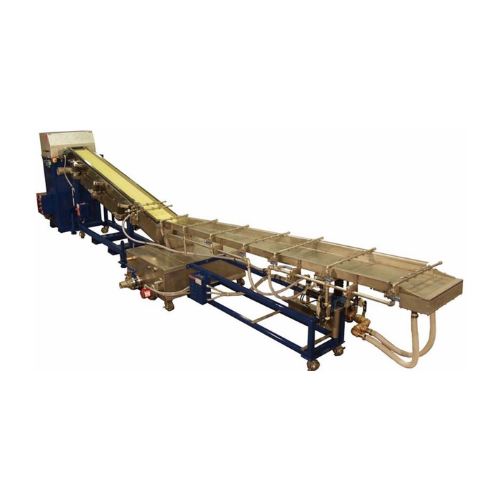

Automatic strand pelletizer for reinforced and filled polymers
Optimize your polymer production with precise pelletizing...
Select your plastics process
What are you making?

Biodegradable polymers

Biodegradable plastics
Biopolymers

Synthetic polymers

Tire treads

Thermoplastics

Textile fibers

Textile

Synthetic fibers

Pvc pipes

Pvc pellets

Rubber tires

Rubber seals

Rubber

Resin

Polyurethane foam

Polypropylene films

Polypropylene containers

Polypropylene

Polyolefins

Polymer resins

Polyethylene film

Polyethylene

Polyester resin

Plastics recycling

Plastic resins

Plastic intermediates

Plastic containers

Mdf boards

Optical lenses

Nylon pellets

Nylon fibers

Liquid crystal displays

Moped tires
Injection molding

Engineering plastics

Elastomers

Fiberglass

Anti-reflective coated lenses
Composite materials

Color masterbatches

Recycled plastic

Masterbatches

Silicone

Polymers

Bioplastics

Synthetic rubber
Latex
Tell us about your production challenge
Making plastics – from crude oil to plastic pellets
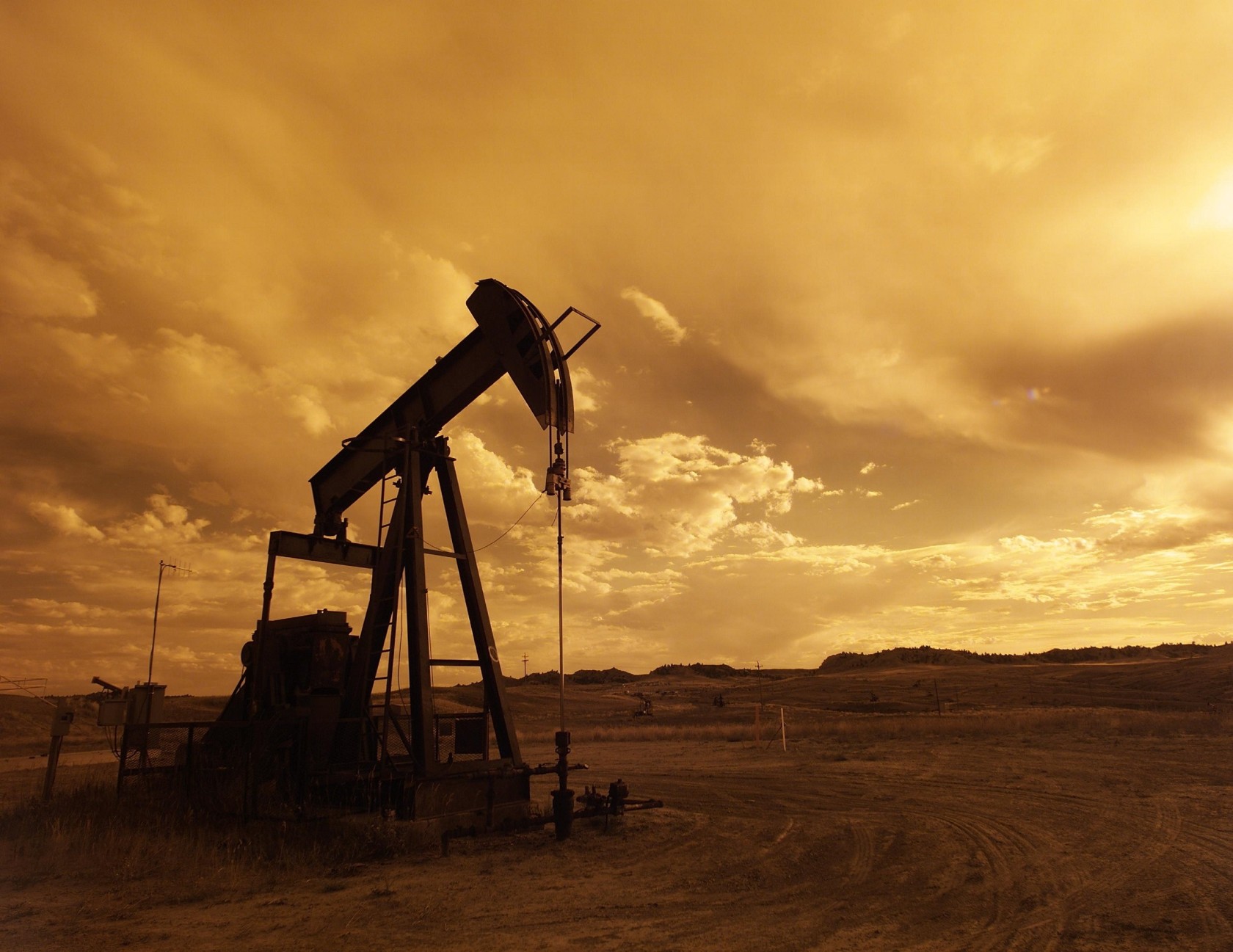

Although originally a natural product, nowadays plastic is mostly synthetic and widely produced. The production starts with extracting oil from the underground with the help of pumps that produce between 5 and 40 liters of oil per stroke, which is then transported to an oil refiner through pipelines. The crud oil is poured into preheater, where it is boiled and sent to a furnace. There, according to its molecular weight, oil is separated into several groups of chemicals — petroleum, gasoline, paraffin, etc.

For plastic manufacturing, what’s essential is naphtha. Naphta has to be broken down into smaller units in a cracking process to get ethene. There are two types of cracking processes. Stem cracking is done at high temperatures and pressure, which is not required for catalytic cracking, which uses catalyst instead. Ethene is forwarded into a reaction chamber where the process of polymerization links the hydrocarbon monomers together into thick, viscous substances used to make plastics. The resulting product, polythene, is processed into strings in an extruder before being ground into pellets dispatched to factories to be molded into end products using various plastic machinery.
Plastic processing equipment and transformation of pellets into usable products
Forming usable plastic products, for instance, bottles, hoses, or toys, is executed using various processes: compounding, forming, thermoforming, extrusion and molding. Compounding is the first step – mixing liquids with other ingredients according to the desired recipe in conventional stirred tanks. Other essential plastic processing equipment includes two types of mixers; the workhorse mixer, which applies heat and pressure simultaneously, and the Banbury mixer which reminds of a robust dough mixer with two interrupted spiral rotors.
The next step is forming plastics into various shapes by melting, shaping, and solidifying. Extrusion and molding processes create finished or semi-finished products. During extrusion, the melted polymer is continuously forced through an orifice in an extruder for products such as sheets, tubing, and grocery bags. Various types of molding rely on molds to create the desired shape.
To illustrate, rotational molding produces large, hollow products such as kayaks. On the contrary, blow molding is used for small hollow pieces – bottles or fuel tanks. With compression molding, plastic parts can replace metal in the automotive industry. Finally, the most common type, injection molding, has virtually limitless uses with a large production capacity.

Classification of plastics
Plastics are classified according to their unique properties acquired during production processes. The main classification is based on how plastic responds to heat – it is differentiated between thermoplastics and thermosets. Thermoplastics are more common than thermosets. They can be heated without burning, melted, cooled and reheated without losing their properties. On the other hand, thermosets can be heated only, typically during injection molding, once due to irreversible chemical changes.
Any further heating would result in burning. For this reason, thermosets are not recycling-friendly. Further categorization is between amorphous, also known as shapeless, material and semi-crystalline material. While the former gradually softens when exposed to heat, the latter maintains its shape until a certain temperature point, when it rapidly becomes liquid. Finally, according to their monomer composition, plastics can be classified as homopolymers, made of a single type of monomer, or, on the contrary, copolymers.
Bioplastics, biodegradable plastics and recycled plastics – ecological alternatives?
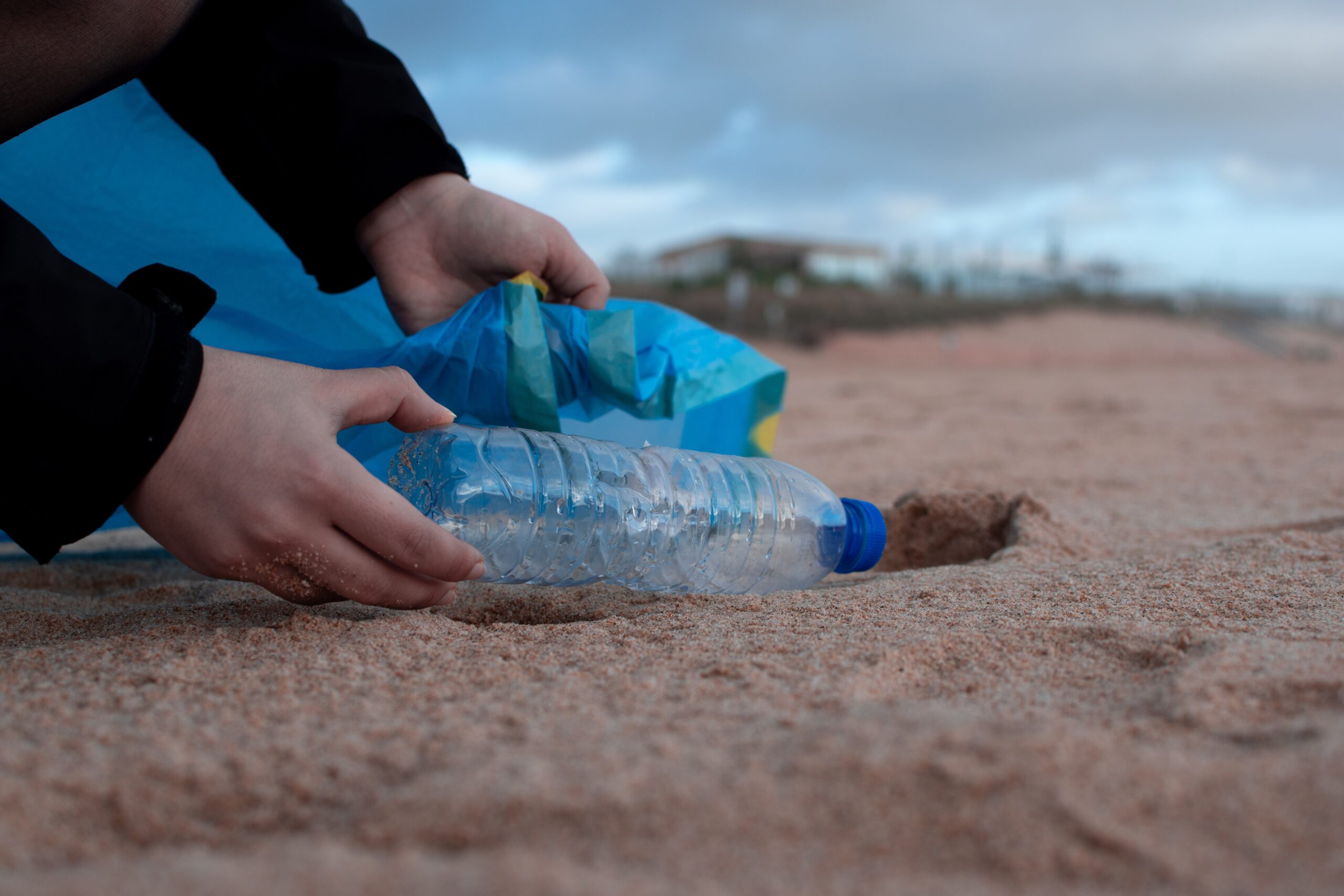

The environmental effects of plastic are a widely known topic. It takes up to 450 years for a plastic bottle and 50 to 80 years for a plastic cup to decompose. Alternatives to traditional plastics are biodegradable, bio-based and recycled plastics. Biodegradable plastics are made of petrochemicals but degraded by microorganisms. However, it can be safely done under warm conditions; otherwise, it degrades into harmful microplastic.

Bioplastic is sourced from renewable natural materials (corn, sugarcane, cellulose), which are compostable. The downside is that using food sources, as well as that, owing to chemical and mechanical differences, can be challenging to recycle. Finally, recycled plastic does not exploit raw material, but it can be used only to produce lower-grade products. Furthermore, it uses energy, water and emits gases. However, it is important to recycle already existing materials as replacing them with mass production of non-reusable lower-quality products is not the ideal solution either.

Green innovations - plastic-eating waxworms
Considering that bioplastics, biodegradable plastics and recycled plastics have downsides, scientists from Canada’s Brandon University have found a unique possible solution. Namely, they discovered that waxworms could live off polyethylene. Their guts contain bacteria that biodegrade plastics and turn them into glycol. In the lab-controlled environment, 60 waxworms can eat more than 30 square centimeters of a plastic bag in less than a week. While it is unrealistic to expect that waxworms can solve the plastic pollution issue, understanding the symbiosis of waxworms and gut bacteria could lead to the development of better plastic biodegradation systems.
Which plastics technology do you need?

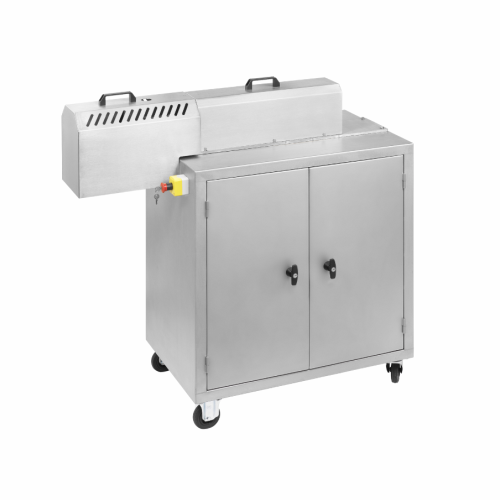
Fine cutting mill for soft to medium-hard plastics
Achieve precise size reduction and smooth particle shapes in plastic p...

Centrifuge for plastics recycling
Enhance your recycling process with a centrifuge designed to efficiently separate and dew...
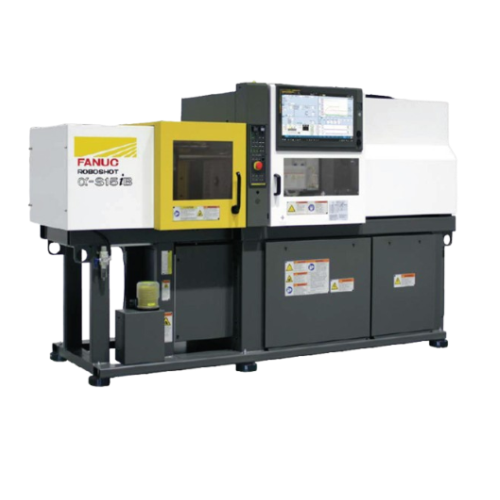

Electric injection molding for precision plastics
Ideal for precision molding, this electric injection system enhances ef...
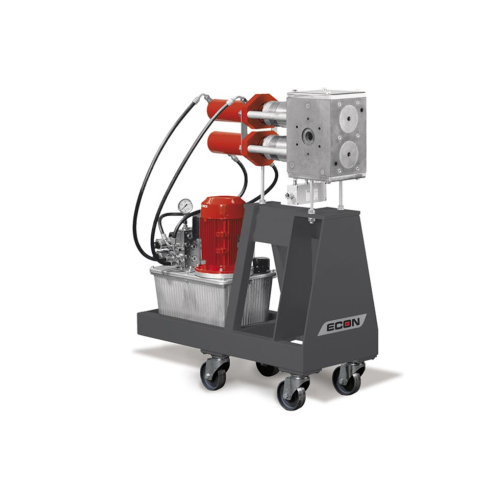

Inline screen changer for thermoplastics
Effortlessly swap filter screens during thermoplastic processing without halting o...
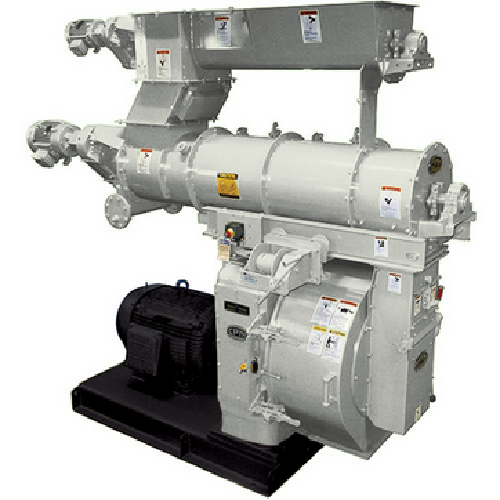

Pellet mills for feed, plastics, and industrial products
Optimize pelleting output across diverse materials with precisio...
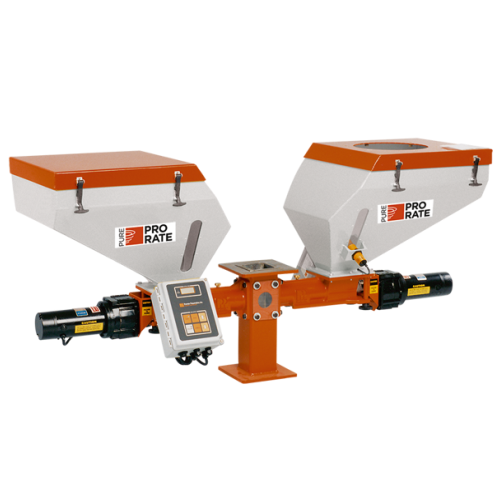

Precision feeders and mixers for plastics processing
Achieve precise blending and feeding for plastics processing with mo...
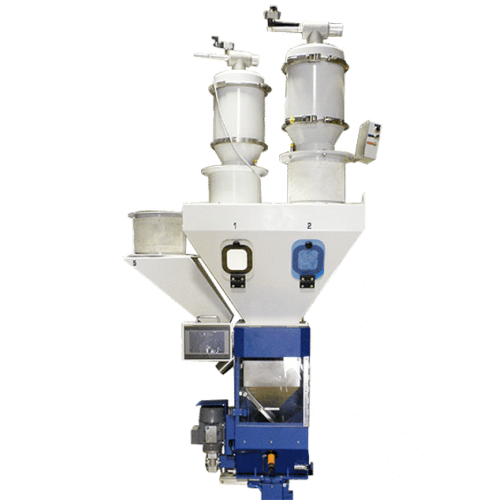

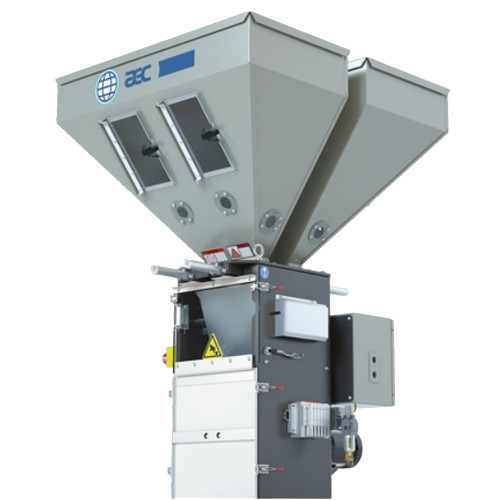
Gravimetric batch blender for plastics compounding
Achieve precise batch blending with high accuracy, ensuring consistenc...
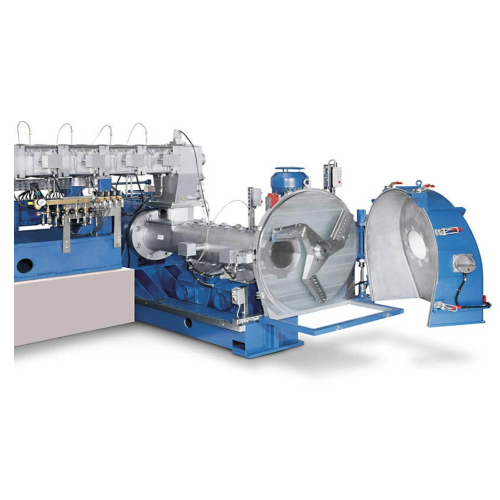

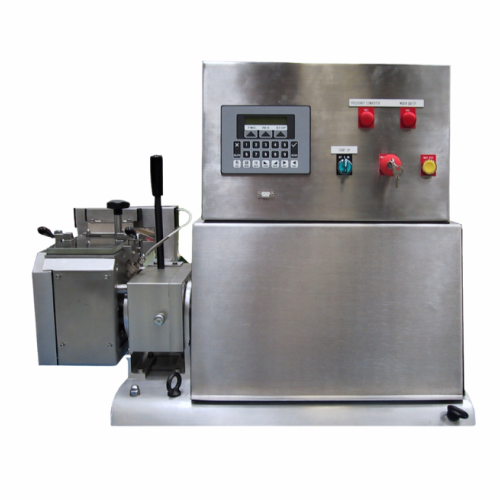
Pelletizer for temperature and shear-sensitive plastics
Optimize your production line efficiency with a pelletizing solut...
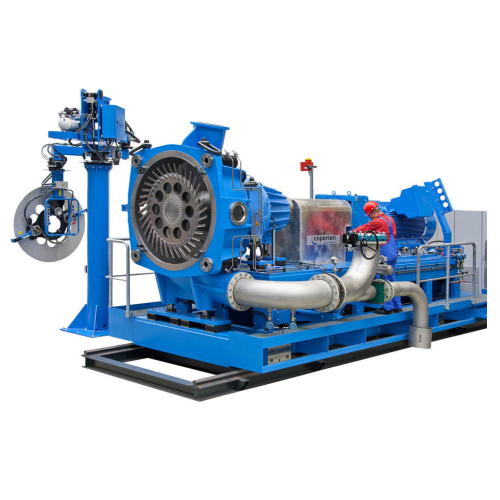

Underwater pelletizer for sticky thermoplastics
Enhance pelletizing efficiency for challenging products with optimal therm...
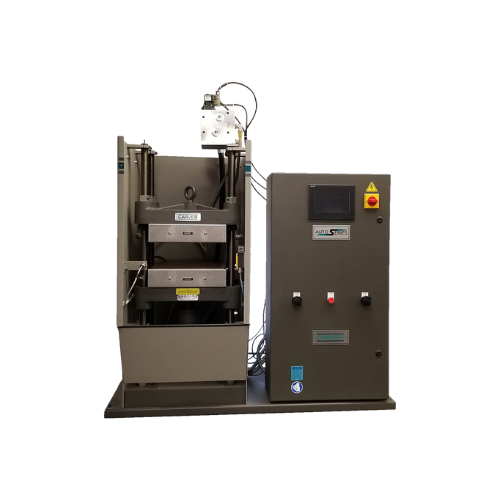

Bench top press for Astm testing of plastics and rubber
Streamline your material testing with precision-controlled bench ...

Optical sorter for grains, coffee, nuts, and plastics
Ensure consistent product quality and minimize waste with advanced ...

Optical sorter for grains, seeds, and plastics
Enhance sorting efficiency with cutting-edge optical technology that distin...

Modular torque rheometer for plastics and plastifiable substances
Optimize your material development and testing with a...

Modular torque rheometer for plastics and rubbers
Optimize your material testing and process development with a versatile...
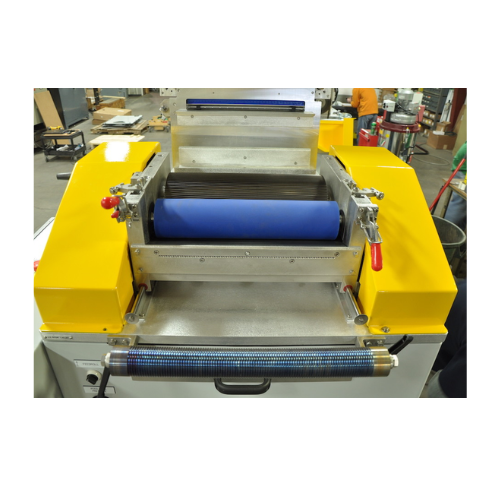

Micro pelletizer for thermoplastics
Achieve precision in micro pelletizing with a solution engineered to reduce turbulence,...
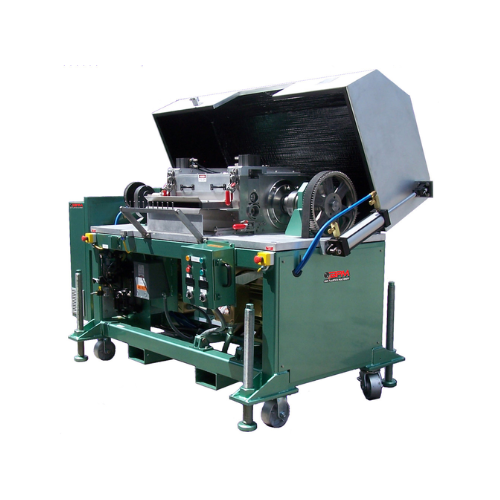

Pultrusion pelletizer for long glass fiber thermoplastics
Engineered to tackle the challenges of cutting and pelletizing...

Central granulators for high-volume plastics recycling
Efficiently process large volumes of recycled plastics and industr...
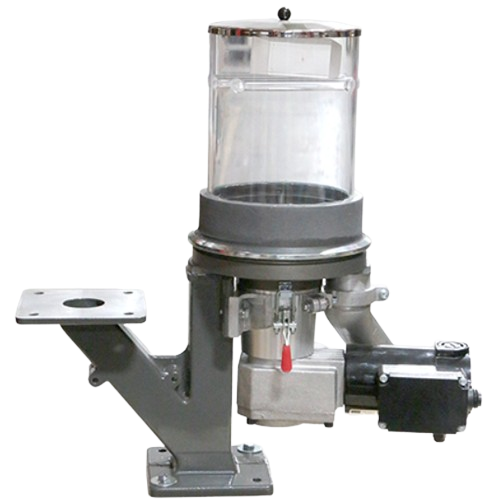

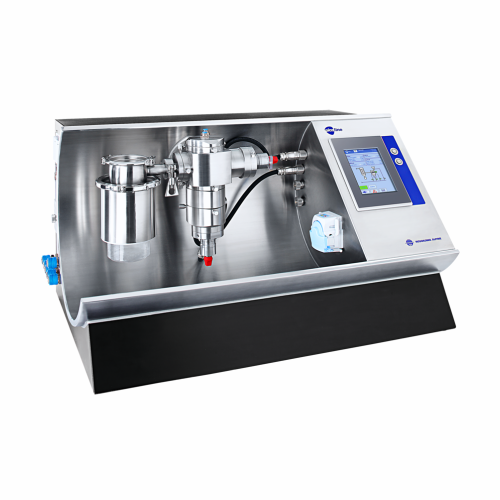
Digital doser system for plastics additive feeding
Achieve precise additive dosing for plastics, ensuring consistent qual...
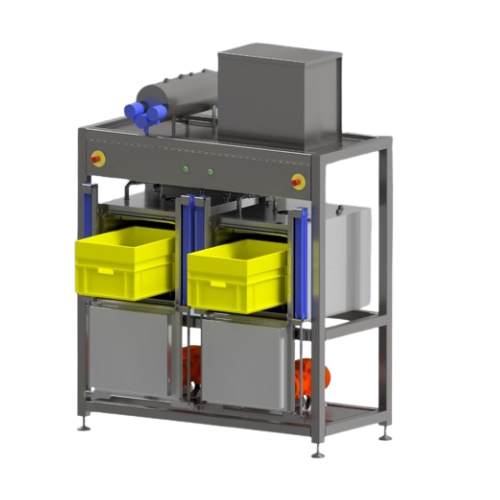

Steam conditioning plants for polyamide plastics
Enhance the durability and assembly readiness of polyamide components wit...

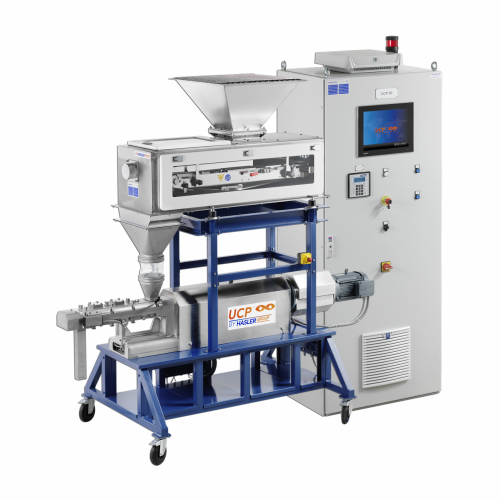
Technical plastics production system
Optimize your production line by integrating a versatile system capable of precise mix...

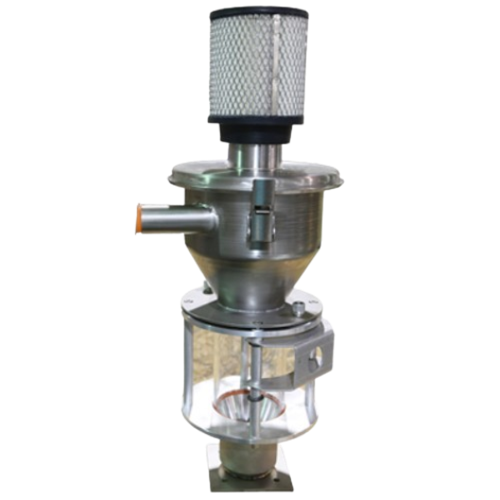
Air separator for polymers and plastics
Ensure high-purity plastic pellets by efficiently separating fine dust and streamer...
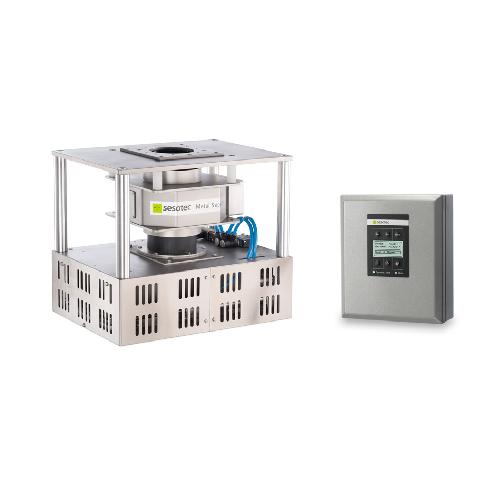

In-line metal detector for plastics processing
Prevent costly breakdowns in plastics production with an in-line metal dete...
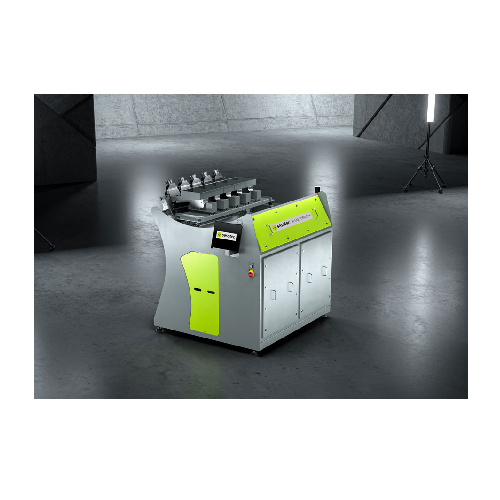

Chute sorting systems for recycling plastics and glass
Streamline your recycling operations by efficiently sorting and pu...
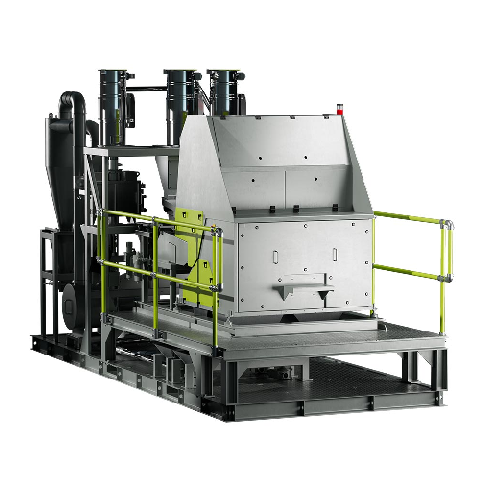

Mobile regrind sorting platform for plastics
Struggling with inconsistent regrind quality? This mobile sorting platform ef...
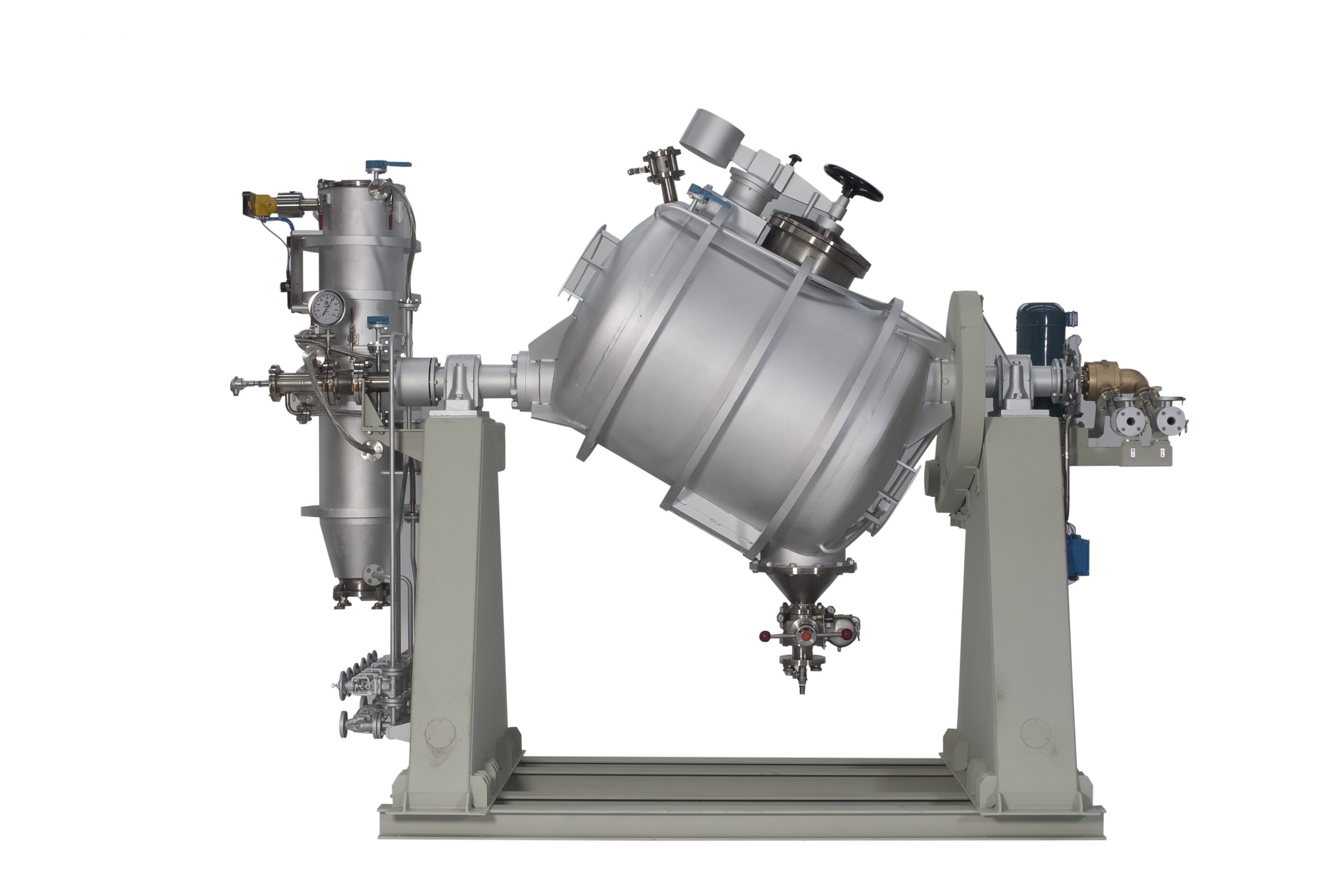

Tumble dryer for granulated plastics
Vacuum drying at high temperatures is important in the production of granulated plasti...
Sieve analysis software for automated evaluation
Streamline your sieving processes with automated data evaluation and prec...
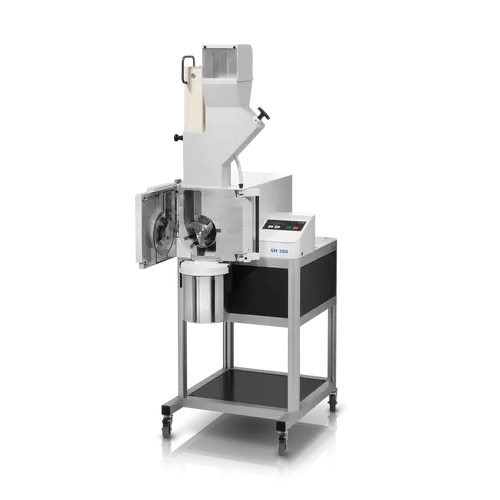

High-torque cutting mill for tough and fibrous materials
Tackle the toughest materials and ensure consistent particle siz...
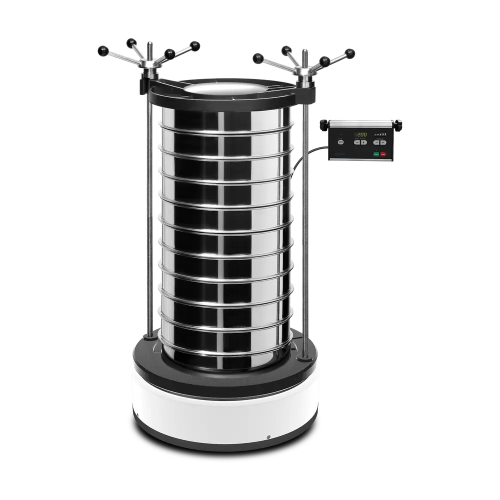

Laboratory sieve shaker for accurate particle size analysis
Streamline your material testing with a robust vibratory sie...
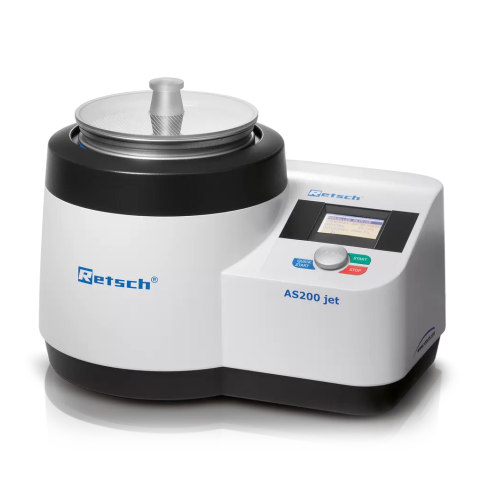

Air jet sieving system for powdered materials
Optimize particle distribution with precision air jet sieving, designed to e...
Continuous ploughshare mixer for diverse industrial applications
Enhance mixing efficiency and achieve precise particle ...
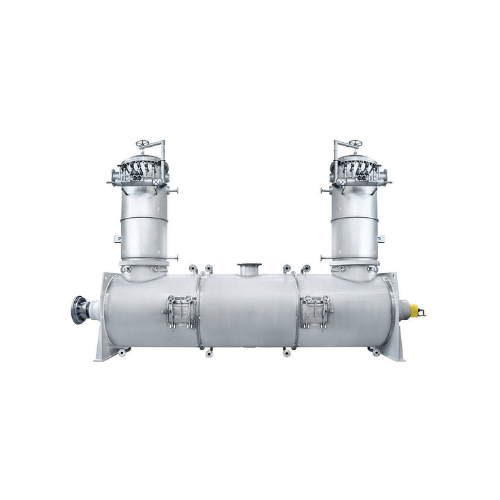

Vacuum paddle dryer for chemical and pharmaceutical applications
Achieve precise moisture control and efficient drying i...
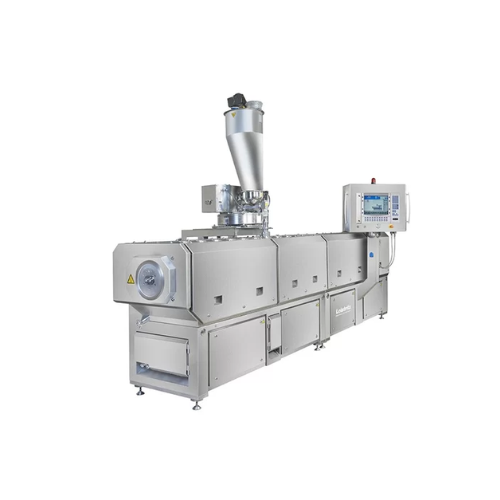

High torque twin screw extruder for industrial applications
Enhance your production capabilities with advanced twin scre...
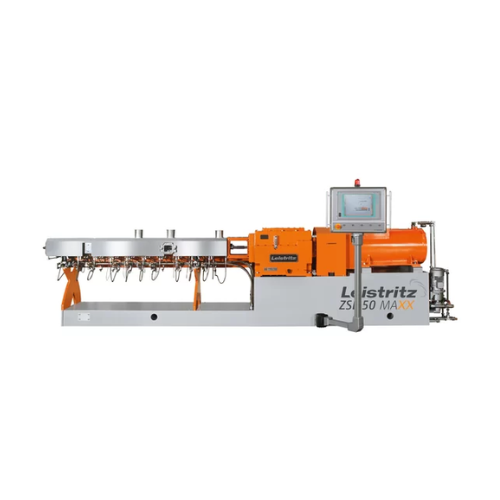

Industrial twin screw extruders for high torque and volume applications
Optimize your extrusion processes with high tor...
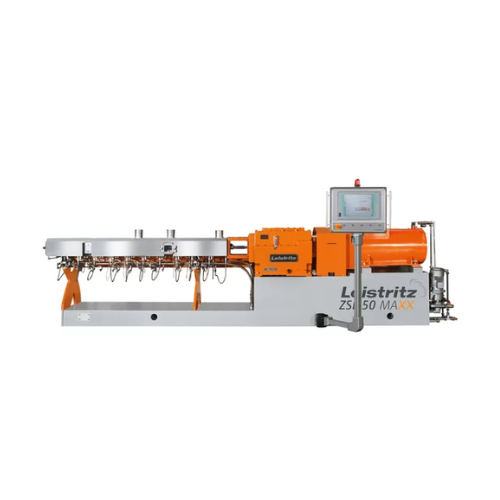

High torque and volume twin screw extruder
Maximize processing adaptability and efficiency across diverse applications wit...
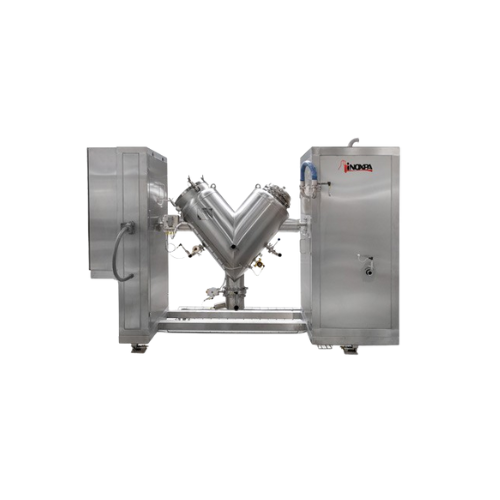

Industrial v-type solids blender for homogeneous mixture
Achieve precise blending of diverse powders and solids using the...
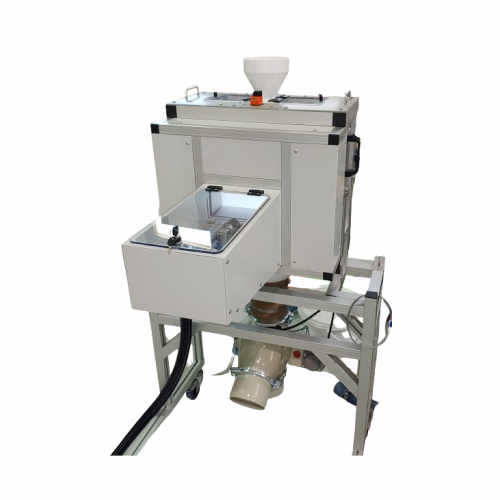

Plastic pellets inspection system
Ensure product quality by accurately detecting impurities and variations in plastic pelle...
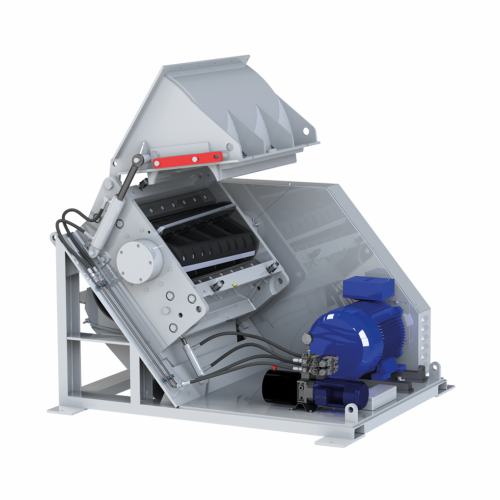

Low-dust granulator for plastic parts recycling
Achieve efficient comminution with minimized dust generation, ideal for pr...
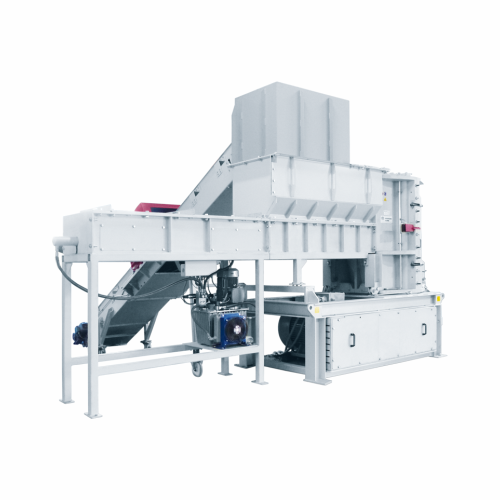

Shredder-granulator for plastic recycling
Simplify your plastic recycling process by integrating shredding and granulating...
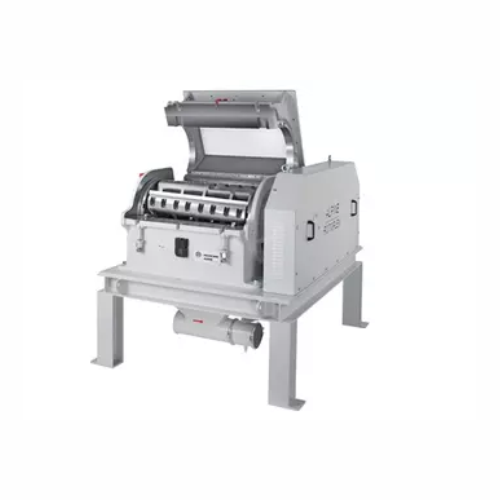

Industrial granulator for high-throughput plastic recycling
Facing challenges in efficiently recycling high-volume plast...
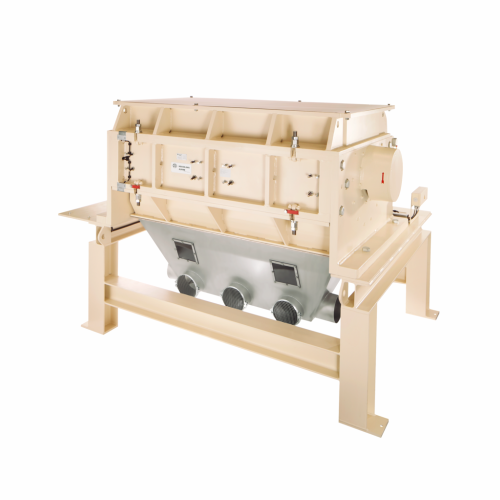

Compact granulator for plastic comminution
Optimize your plastic recycling operations with a compact granulator designed t...
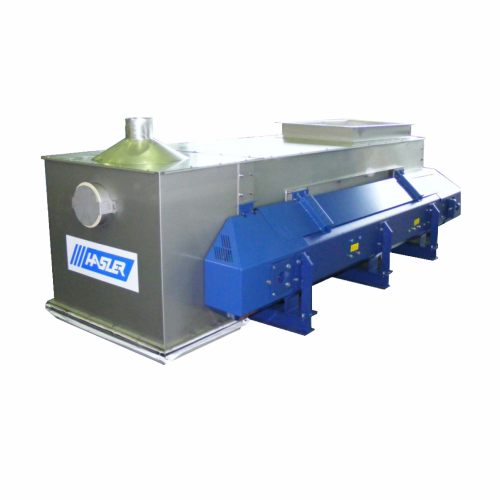

Belt feeder for alternative fuels
Maximize fuel efficiency with this belt feeder designed for seamless dosing of alternativ...
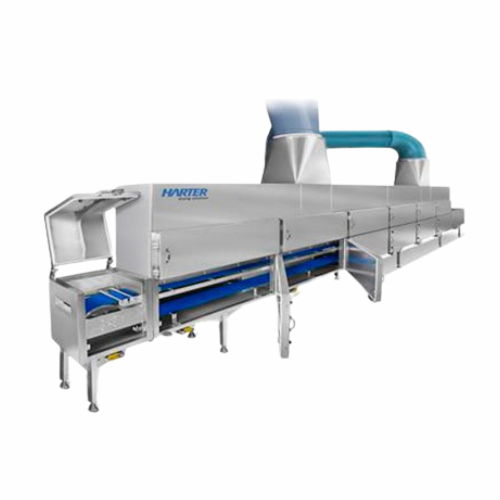

Continuous conveyor belt dryer for endless products
Optimize your continuous production line with a high-speed drying sol...
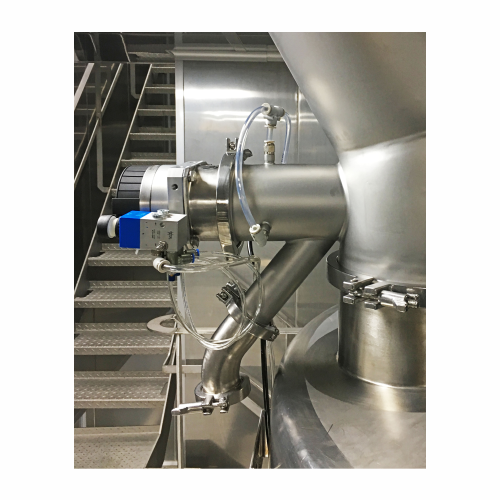

Sampling valve for secure sample extraction
Ensure product quality by safely extracting representative samples without hal...

Cutting mill for dry sample comminution
Achieve precise comminution of dry materials, from plastics to dried plants, with e...
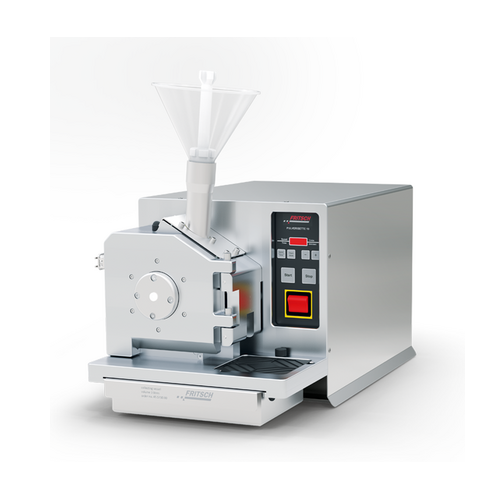

High-speed cutting mill for versatile material comminution
Efficiently transform diverse materials like plastics, textil...
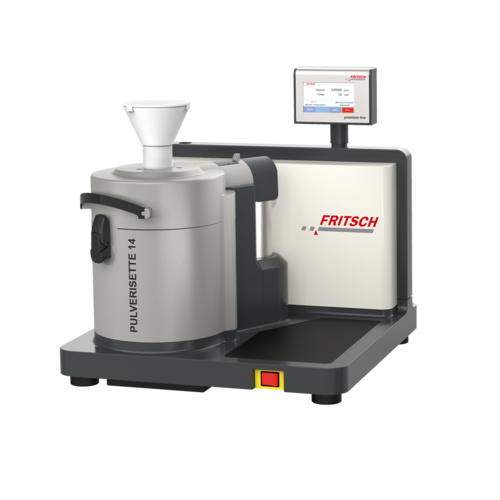

Variable speed rotor mill for sample preparation
Achieve rapid and precise grinding of various materials with a versatile ...
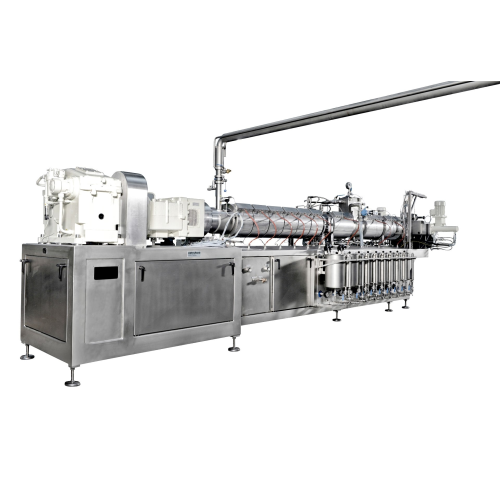

Cooking extruders for low shear confectionery production
For producers looking to create high-quality confectionery, this...
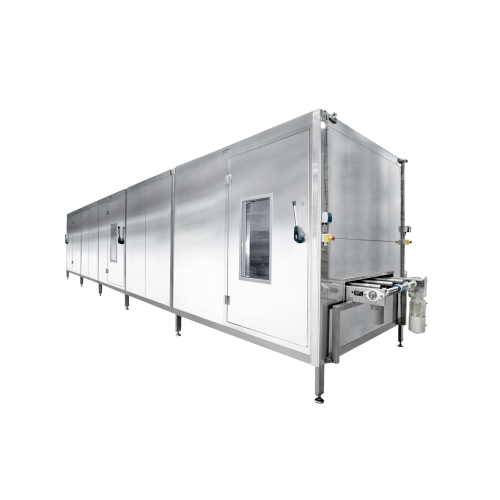

Cooling tunnel for confectionery extrusion
Optimize your production line with a versatile cooling tunnel capable of effici...
Extrusion system for color changing confectionery strands
Easily switch colors in confectionery strands mid-production, ...
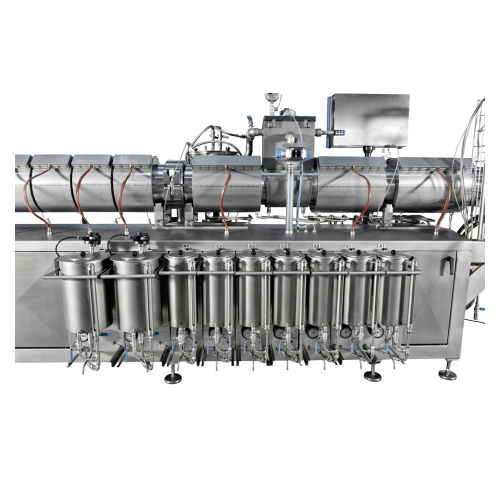

High precision dosing system for color, flavor, and acid
Achieve precision and reliability in dosing color, flavor, and a...
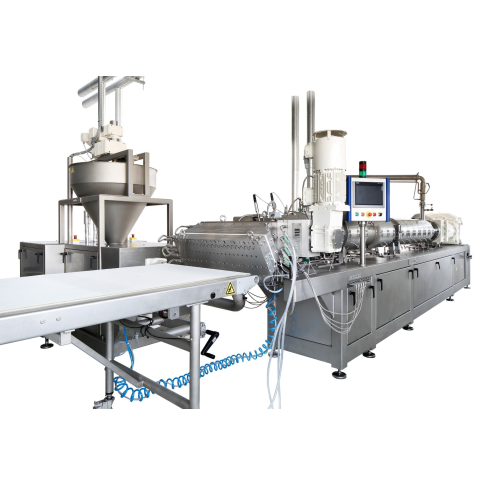

Screen changer for extrusion lines
Prevent clogs and maintain quality with this screen changer, designed to filter out soli...
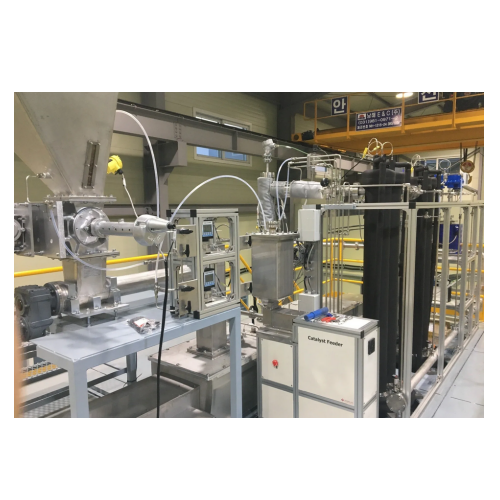

Pyrolysis for biomass conversion
Transform diverse waste materials into valuable bio-commodities and energy through advanced...
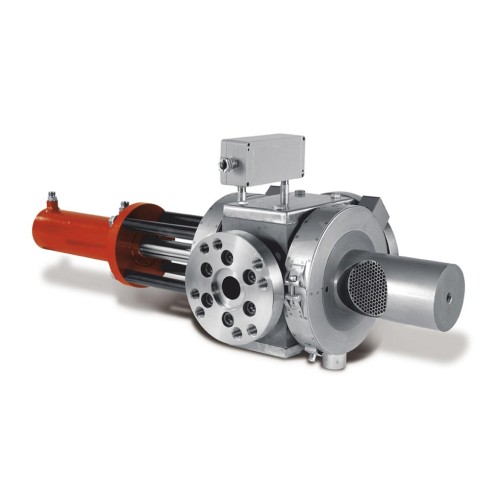

Discontinuous screen changer for low viscosity melts
Optimize your filtration process with a discontinuous screen changer...
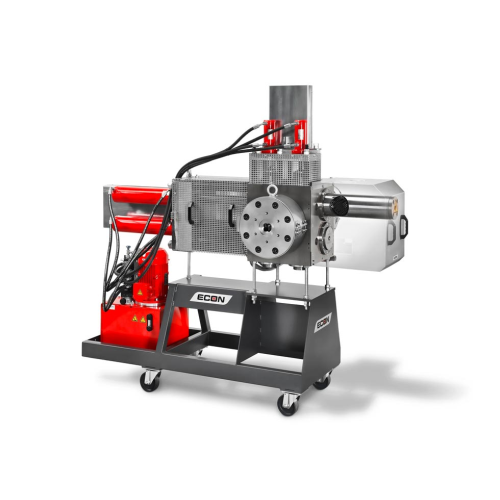

Continuous screen changer for thermoplastic materials
Eliminate downtime caused by blockages with a continuous screen cha...

Underwater pelletizing system for thermoplastic materials
Optimize your thermoplastic pellet production with a reliable ...
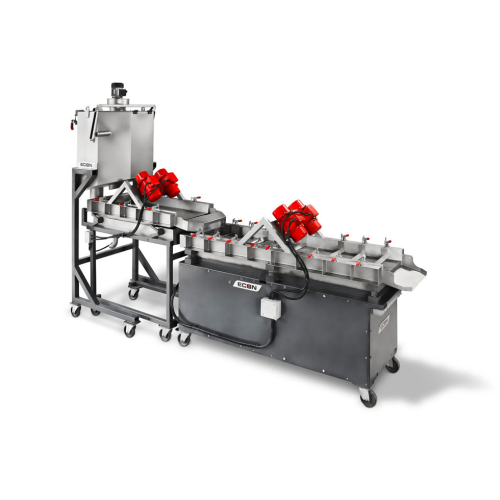

Vibration drying system for pellets
Achieve precise moisture control for pellets with high filler content, enhancing final ...
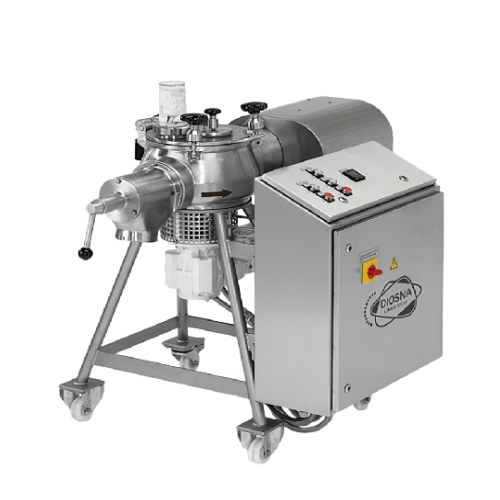

Versatile entry-level mixer granulator
Solve complex mixing and granulating challenges with this compact solution, offering...

Bulk material mixer for high-speed homogenization
Achieve fast and gentle homogenization of bulk materials with a high-sp...
Pellet dedusting elutriators
Achieve superior purity in your production line by effectively removing dust and streamers with...

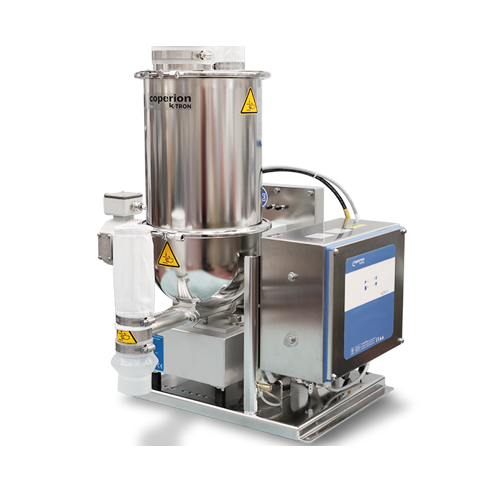
Industrial smart flow meter
Ensure precise metering and smooth handling of bulk materials with a device that eliminates movi...

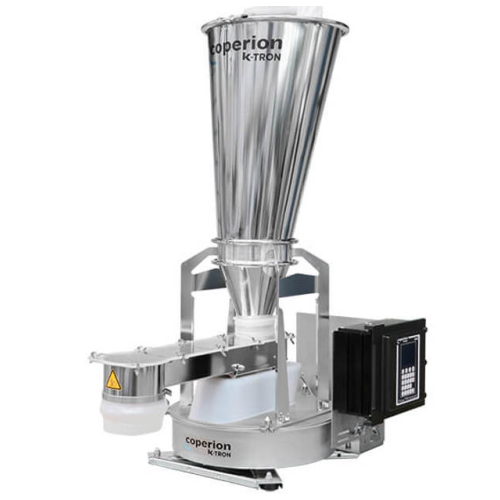
Twin screw feeders for difficult bulk materials
For manufacturers handling sticky or fine powders, twin screw feeders ensu...

Industrial vibratory feeder for bulk solids
Ensure precise and gentle handling of delicate bulk materials with a cutting-e...

Aerolock surge hopper for precise bulk material management
Optimize your production with a surge hopper designed to ensu...

Feed bins for pre-conditioning materials
Optimize your material flow by pre-conditioning bulk solids for efficient vacuum c...

Scale hopper for bulk material processing
Optimize your bulk material handling with precise control in separation, filling...

Industrial strand pelletizer for polymer processing
Optimize polymer pellet production with precision engineering, ensuri...
Filtration compounder for polymer recycling
Streamline your recycling process by integrating filtration and compounding in...

Laboratory twin screw extruder for small batch processing
Efficiently develop formulations and conduct precise research ...
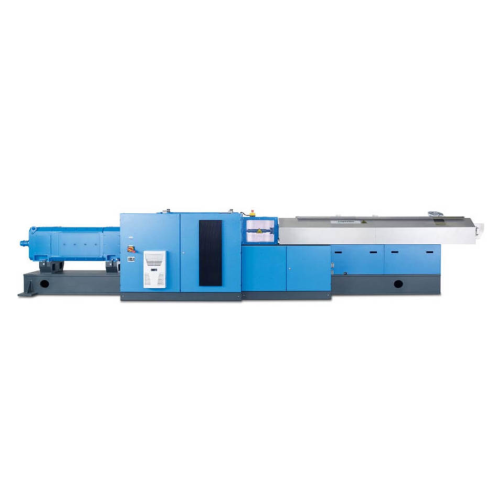

High throughput twin screw extruder for low bulk density products
When handling low bulk density materials, achieving m...
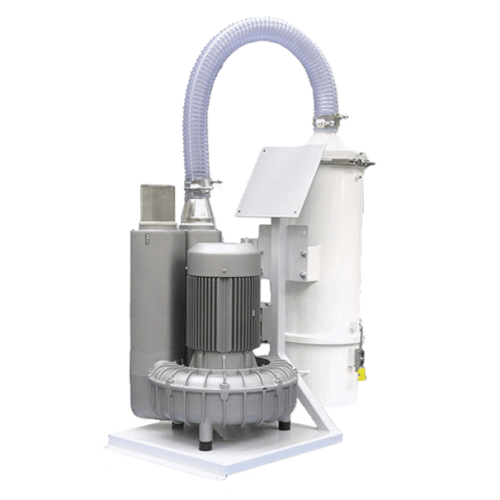

Regenerative vacuum blower for pneumatic conveying
Optimize your material handling with a compact regenerative vacuum blo...
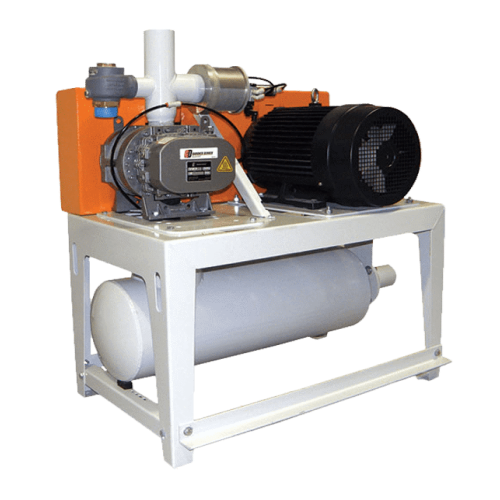

Industrial vacuum blower for continuous pressure conveying
Optimize your production line with reliable vacuum conveying,...
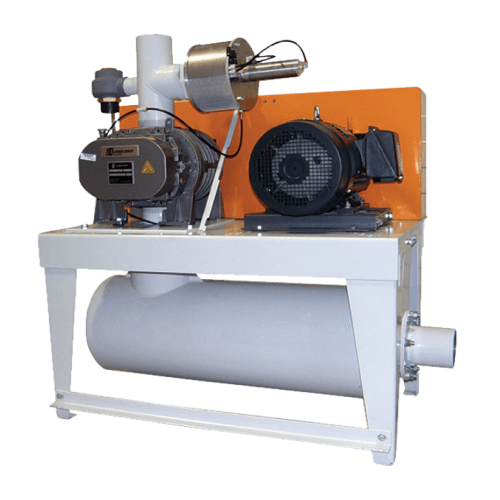

Vacuum sequencing blower for industrial conveying systems
For manufacturers handling bulk materials like powders and gra...
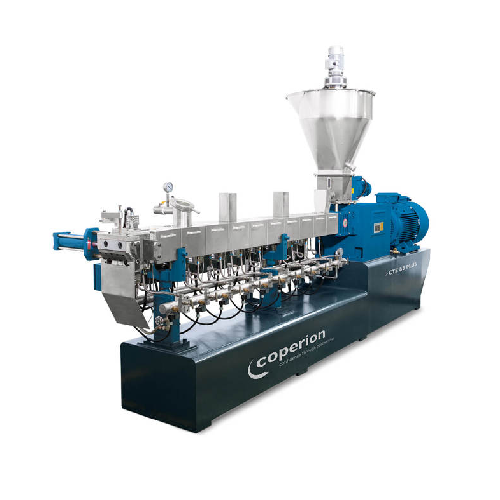

High-performance compounding extruder
Achieve precision in compounding and pelletizing with advanced extruders that ensure ...
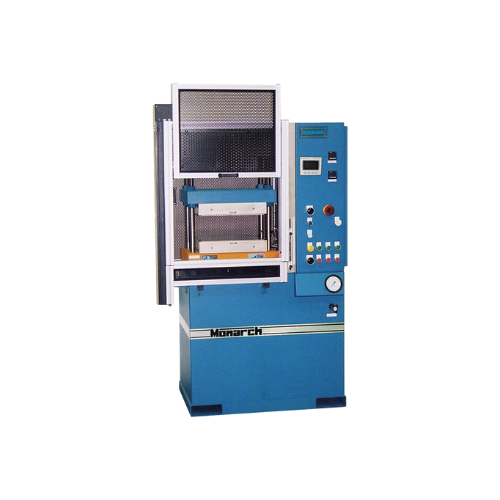

Hydraulic compression press for Astm plastic sample preparation
Achieve precision in molding and testing with this hydra...

Ashing furnace for complete combustion
Ensure precise sample combustion with a furnace designed for optimal ash analysis, p...
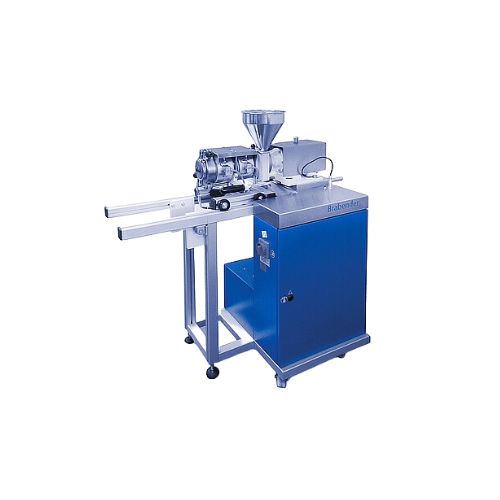

Twin screw compounder for polymer processing
Achieve superior polymer blends with optimized shear forces and consistent ma...
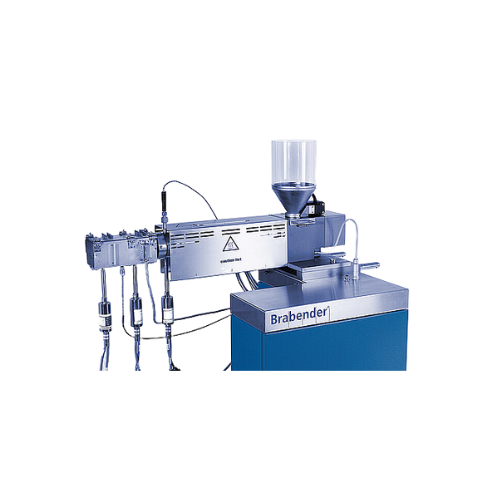

Single-screw extruder for material analysis
Ideal for material testing and development, this single-screw extruder enhance...
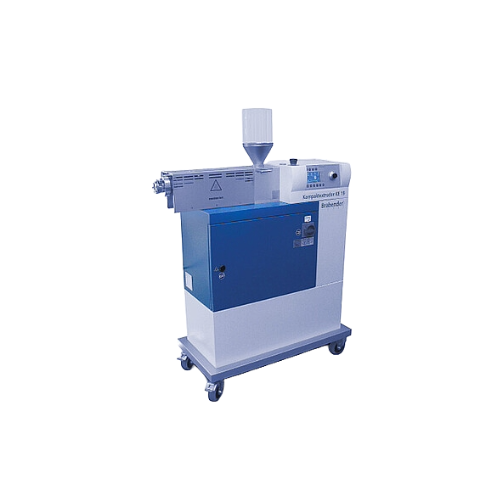

Stand-alone extruder for lab-scale testing
Optimize your lab-scale extrusion testing with a compact solution that handles ...
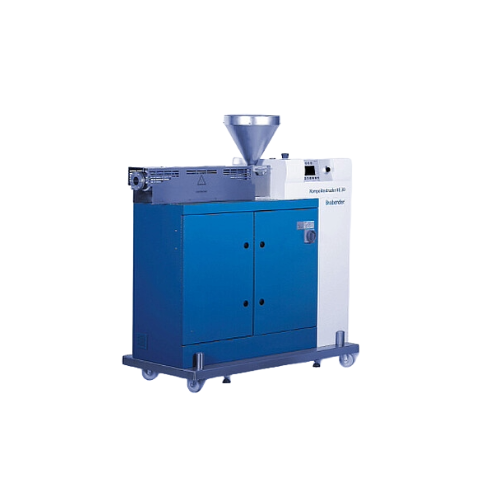

Stand-alone extruder for polymer and food processing
Optimize your extrusion process with a versatile and efficient machi...
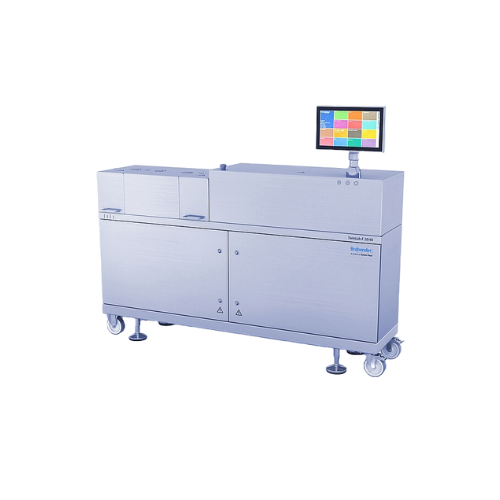

Small twin screw extruder
Optimize your lab and pilot production with a versatile twin screw extruder, designed for precise ...
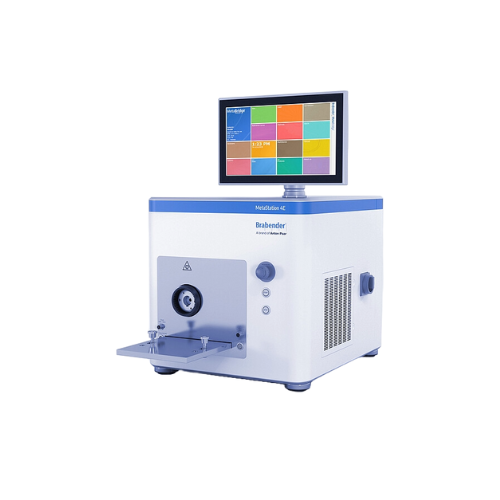

Modular torque rheometer for polymer testing
Gain deep insights into the processability and material characteristics of po...
Mini-compounder for laboratory polymer processing
Streamline your polymer development process with a compact compounding ...
Measuring extruder for small sample simulation
Optimize your production process with this precise extruder, designed to si...
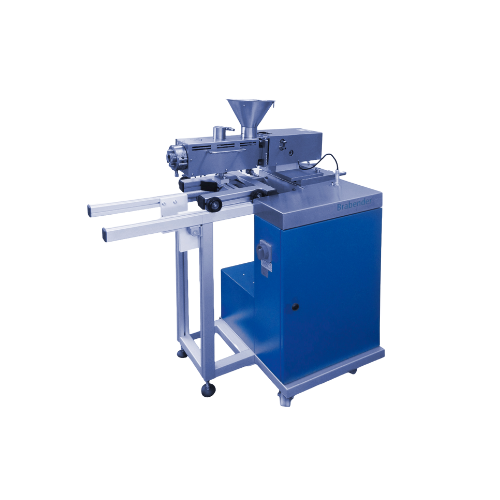

Conical twin screw extruder for shear-sensitive materials
Optimize the extrusion process for shear-sensitive materials w...

Lab extruder for elastomer extrudability testing
Optimize your small-scale testing with an innovative extruder designed to...
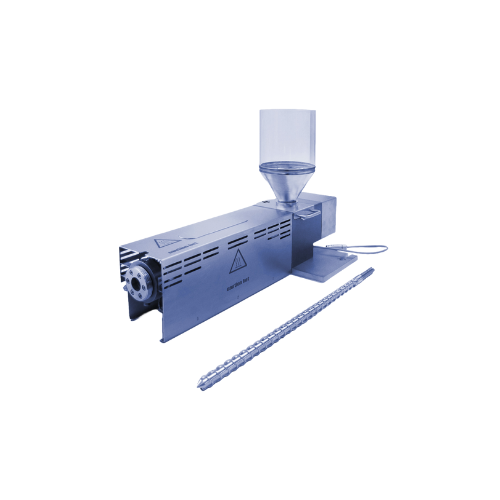
Polymer testing extruder
Effortlessly evaluate polymer and plastic product properties with precision, ensuring your materials...
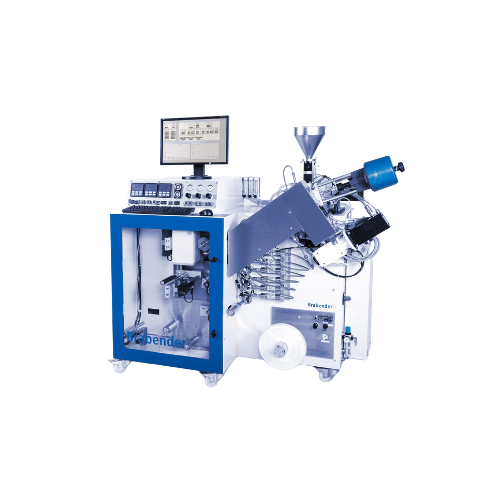

Automated polymer melt flow rate measurement system
Achieve precise polymer quality control by continuously analyzing mel...
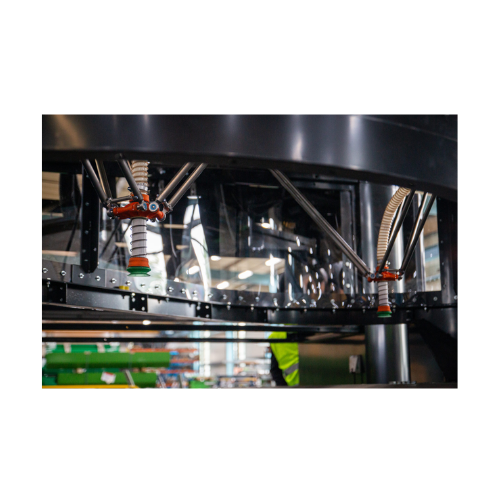

Automated sorting robot for material recovery facilities
Enhance your material recovery operations with AI-driven precisi...
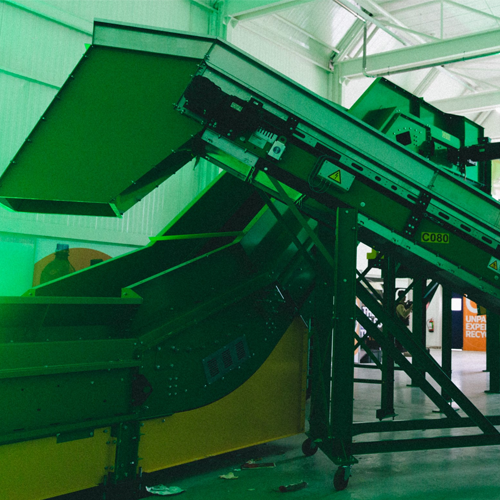

Belt feeder for waste sorting applications
Efficiently handle diverse waste streams and optimize resource recovery with a ...
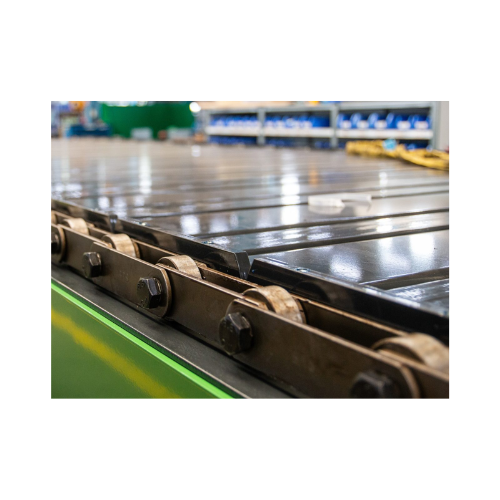

Chain belt conveyor for waste paper and industrial waste
Optimize your waste processing with a robust chain belt conveyor...
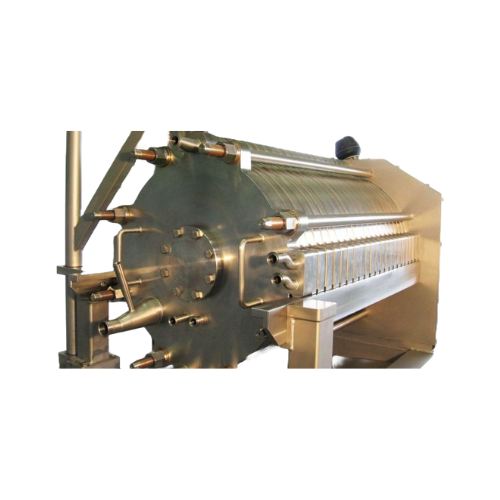

Crossflow filtration for microfine to nanoscale suspensions
Optimize your production line with advanced crossflow filtra...

Automatic strand pelletizer for reinforced and filled polymers
Optimize your polymer production with precise pelletizing...
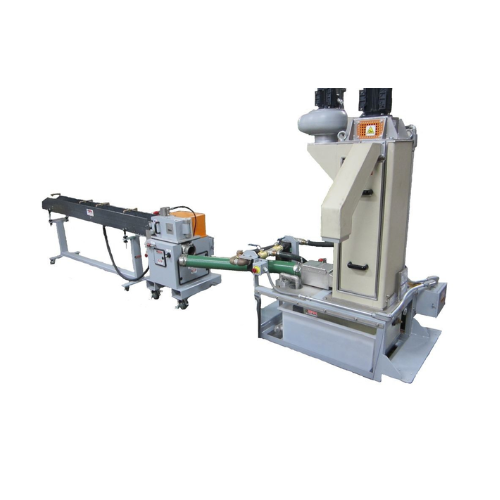

Automatic wet cut strand pelletizer for thermoplastic pellet production
Streamline your polymer pellet production with ...
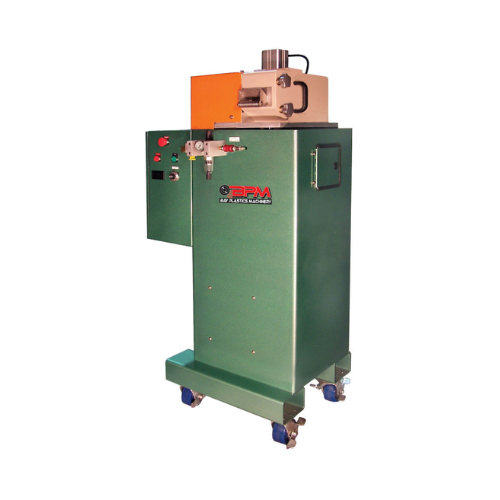

Strand pelletizer for small production lines
Achieve consistent and precise pellet sizes with our strand pelletizer, ideal...
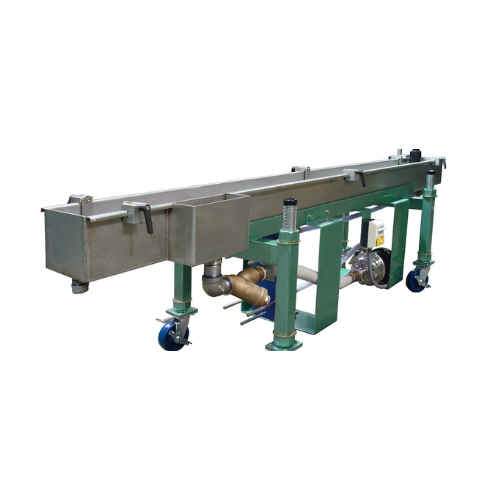

Industrial water bath for pelletizing processes
Enhance pellet quality and efficiency with a customizable water bath desig...
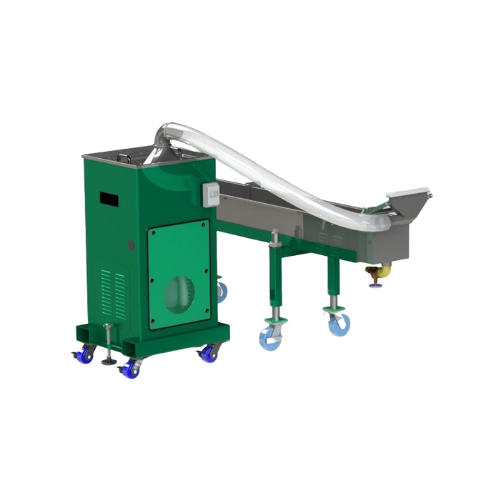

Advanced vacuum air dryer for pelletizing strands
Efficiently remove residual water from polymer strands with a vacuum ai...
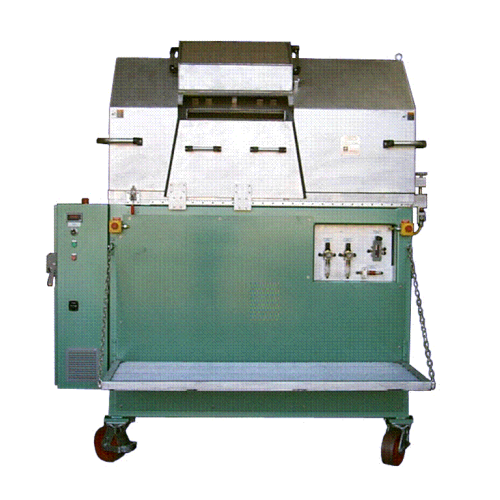

Dx strand pelletizer for plastic pellet production
Reduce operational noise while precision-cutting a wide array of therm...

Bag feeding hopper for bulk solids
Optimize your material handling with a robust feeding hopper that seamlessly integrates ...
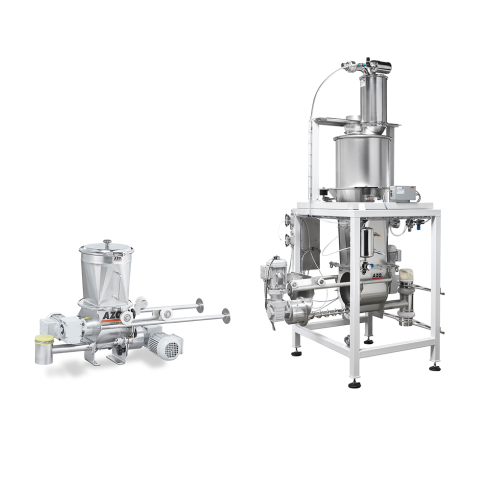

Accurate dosing for powder products
Ensure precise dosing and consistent flow of bulk powders in your production line to en...
Robotic dosing system for accurate micro quantities
Achieve precise and reproducible micro dosing of challenging raw mate...
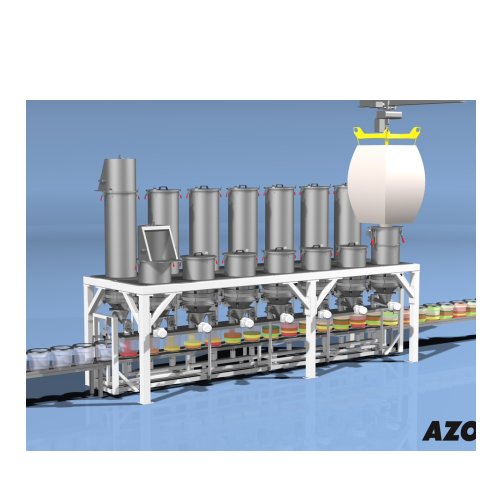

Automatic minor components weighing system
Streamline precision in your production by automating the weighing of minor and...
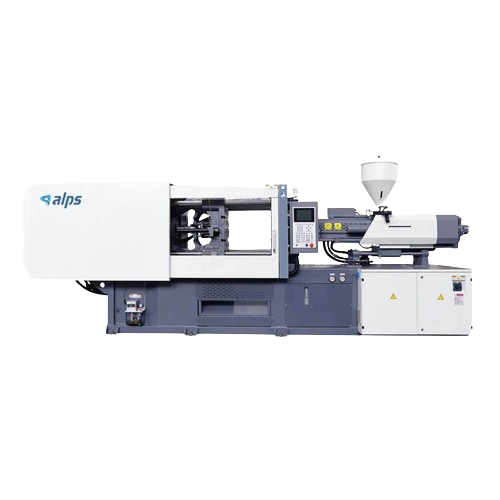

Automatic Pet preform injection moulding
Optimize your production with high-speed injection molding capable of shaping dive...
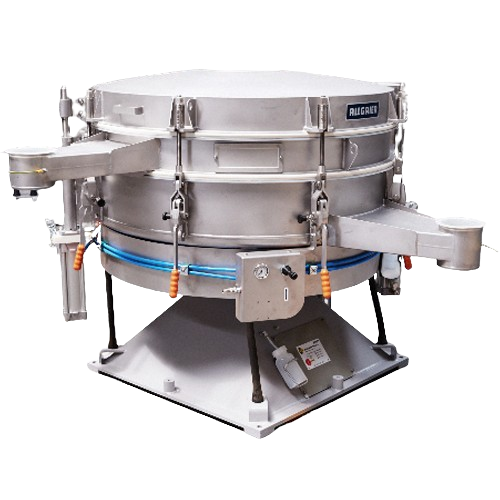

Tumbler screening for fine and ultra-fine sieving
For operations demanding precise particle separation, this solution off...
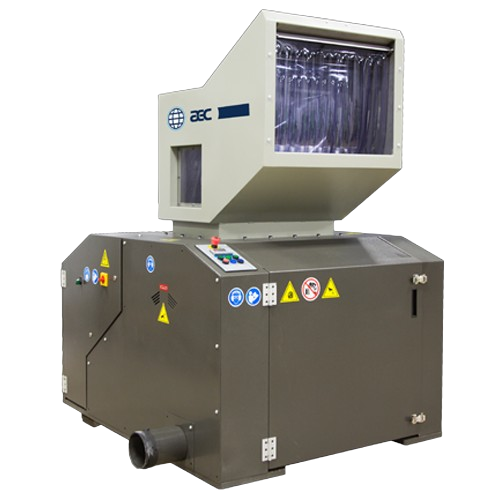

Beside-the-press granulators for injection molding
Optimize your plastic production by efficiently reclaiming resin with ...
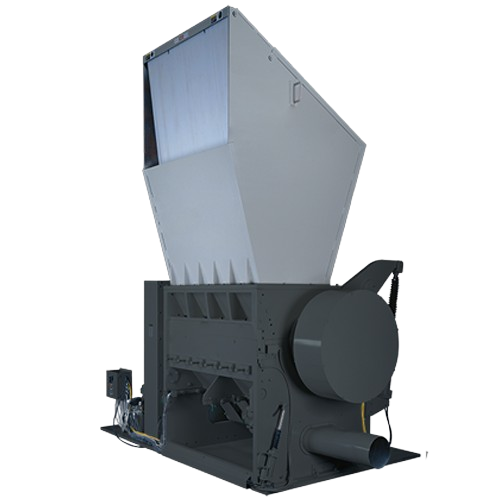

Heavy duty granulator for high-capacity size reduction
When tackling high-volume materials, rely on these industrial-grad...
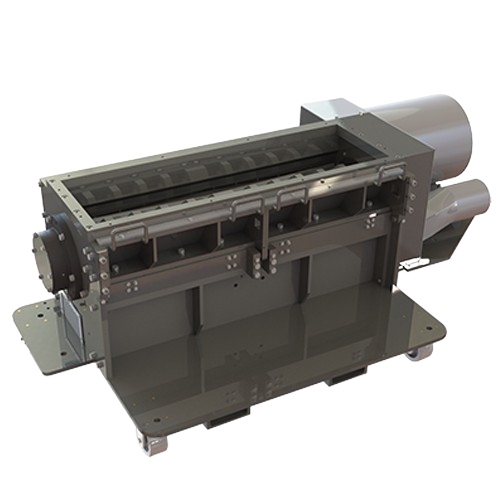

Thermoforming granulators for efficient material processing
Efficiently recycle and optimize your plastic waste by trans...
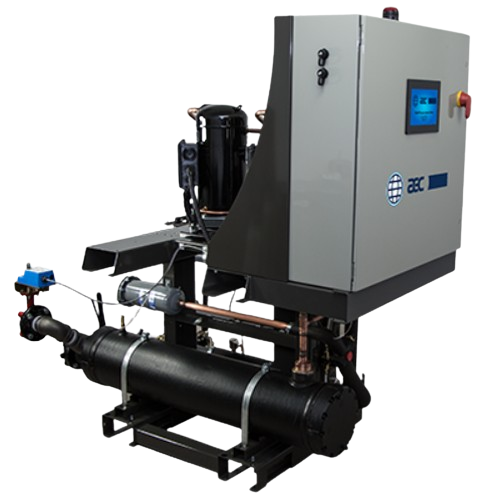

High efficiency central chiller for industrial cooling
Achieve remarkable energy savings with this modular chiller system...

Powder hopper loaders for free-flowing materials
Efficiently transport free-flowing powders, including PVC and polyethylen...

3.5 Hp air-cooled chiller for industrial cooling
Optimize your production with high-efficiency cooling, essential for main...

Central chiller for consistent process cooling
Optimize your production with modular central chillers offering scalable co...

Industrial shredder for recycling and waste management
Efficiently transform challenging waste streams into valuable raw ...
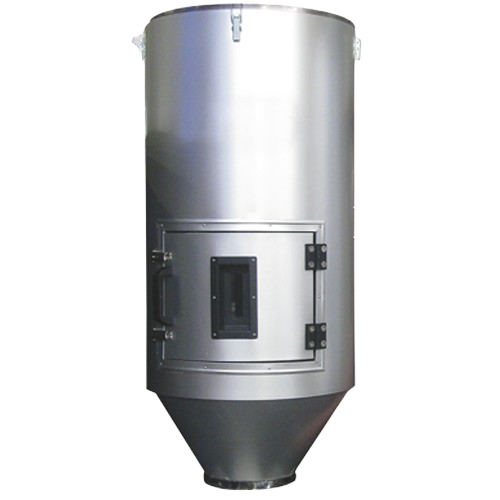

Stainless steel drying hoppers for plastic processing
Optimize moisture control for thermoplastics with robust drying hop...
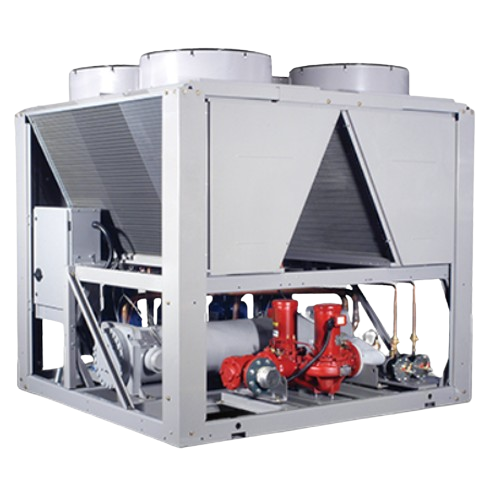

Outdoor central chiller for process cooling
For facilities needing reliable process cooling without sacrificing indoor spa...
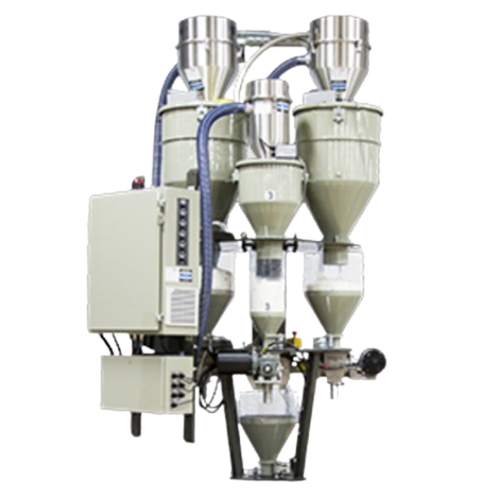

Continuous loss-in-weight blender for extrusion applications
Ensure precise ingredient ratios for extrusion processes wi...
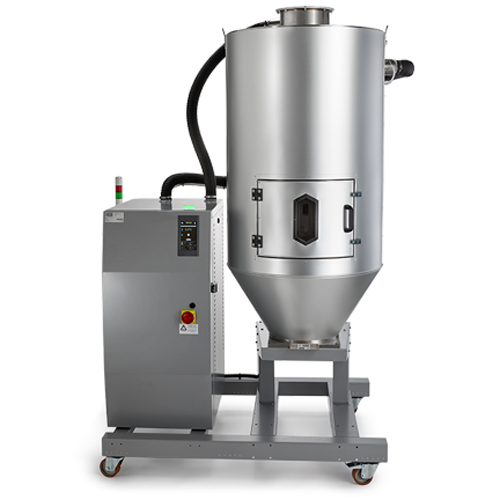

Desiccant wheel dryer for plastic processing
Optimize drying processes in plastic manufacturing with a system designed for...

Compressed air loaders for material conveying
Efficiently convey diverse materials with minimal operator intervention, usi...

Gravimetric batch blender for injection molding and extrusion
Enhance your polymer blending precision with a solution ta...

Hot air dryers for non-hygroscopic material
Ensure reliable material quality by effectively reducing moisture in non-hygro...

Industrial ring dryer for efficient particle processing
Control particle size and drying efficiency with precise recircul...

Traditionally welded silos for constrained installation sites
Ideal for facilities with limited space, these traditional...
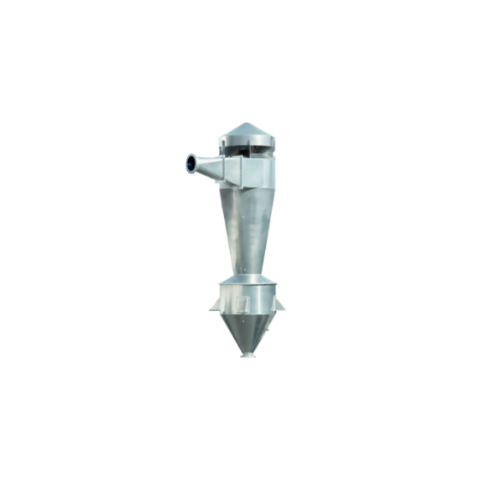

Cyclone separator for pneumatic conveyor systems
Enhance efficiency in pneumatic conveyor systems by effectively separatin...

Automated process controllers for industrial plants
Enhance your production line’s efficiency and adaptability with...

Autonomous process control for petrochemical and food industries
Streamline your production with autonomous control syst...

Pneumatic conveying diverter valve for abrasive bulk materials
Streamline the flow of abrasive materials in your pneumat...
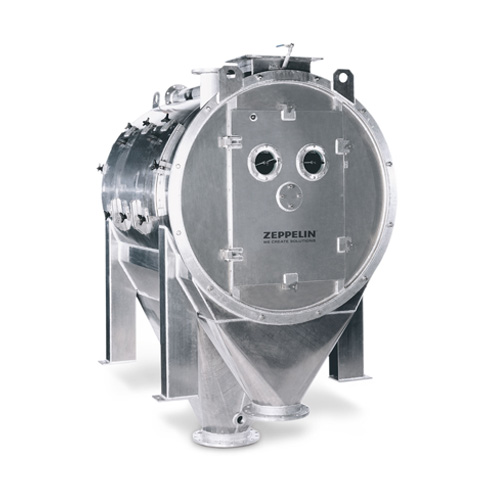

Industrial rotary sifter for bulk materials
Ensure precision and quality in your production line with a robust solution de...
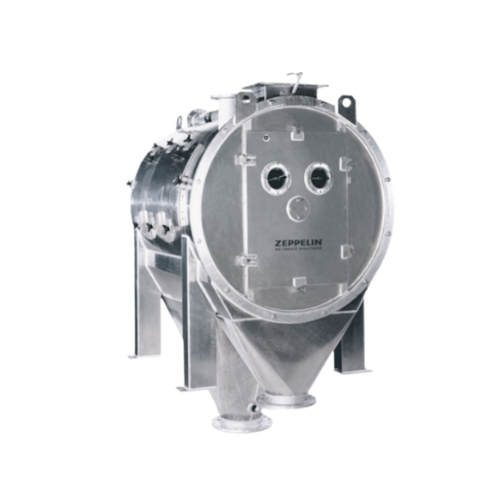

Drum screen for streamer and bird’s nest removal in plastic pellets
Ensure the highest quality of plastic pellets by ef...
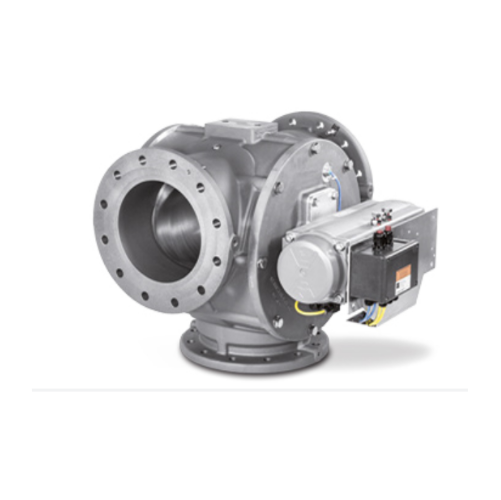

Pneumatic conveying diverter valve for multi-silo feeding
Optimize your pneumatic conveying system by efficiently direct...

Turnkey plant solutions for industrial applications
Enhance your production line with seamless integration and optimized ...

Negative pressure bin vent filter for dust control
Ensure optimal air quality and operational safety by effectively captu...

Vibratory bottom discharge system for bulk materials
Ensure consistent flow of challenging bulk materials with a vibrator...
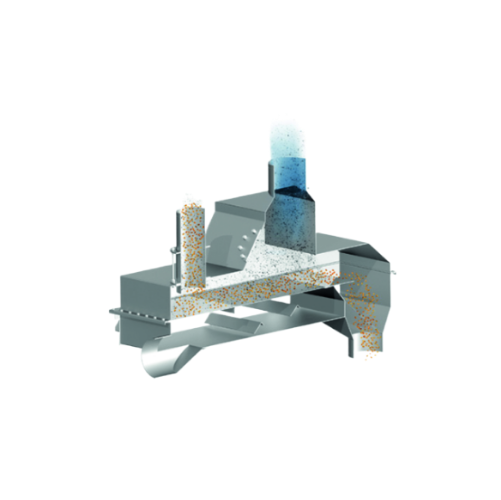
Vibratory pellet separator for dust and streamer removal
Achieve high-efficiency separation of dust and streamers from po...

Pneumatic conveying systems diverter valve
Effortlessly manage bulk material flow with precision, ensuring seamless transi...

Plant refurbishment services for industrial operations
Optimize your existing plant’s performance and extend its li...

Rotary sifter for bulk material preparation
Ensure precise material preparation and protect downstream processes by integr...

Screw belt mixer for dry materials
Achieve uniform mixing of bulk dry materials with variable speed control, ensuring preci...

Vacuum hopper loader for automatic feeding of powders and pellets
Optimize your material handling with seamless automat...

Special chemical plant safety systems
Ensure operational safety and regulatory compliance in chemical processing with advan...

Industrial multi-chamber silos
Optimize spatial efficiency and streamline your production with versatile multi-chamber silos...
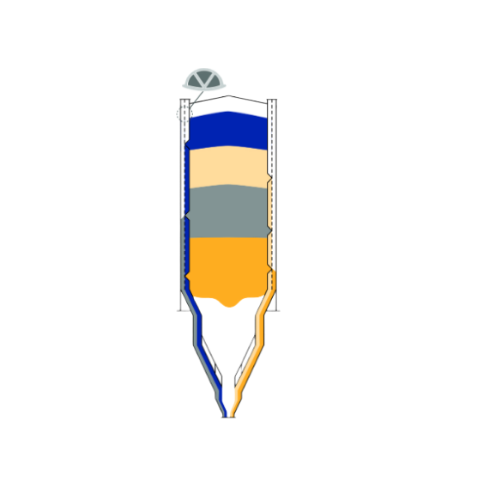
Multi-channel blending silo for free-flowing bulk materials
Achieve precise homogenization and mixing of free-flowing bu...

Blending silo for free-flowing and poorly flowing bulk materials
Achieve precise blending and mixing of diverse bulk mat...

High-speed paddle mixer for food industry blends
Achieve rapid, high-energy blending of varied particulate materials with ...

Prefabricated panel silo construction
Designed for efficient assembly, this silo construction system reduces installation t...

Industrial rotary feeder for powder and agglomerates
Achieve seamless integration in your production line with a robust s...

Process control for baked goods production
Enhance your production line with precise process control designed to optimize ...

Pta and Pet production systems
Maximize throughput while minimizing dust fines in your production of PTA and PET pellets wit...

Bin vent filter with anti-static filter cartridges
Optimize your production line’s air quality by removing fine dus...

Vertical cooler mixer for industrial cooling mixing
Enhance your production line with efficient temperature control and r...

Precise discharge and dosing module for silos and containers
Ensure seamless material flow and accurate dosing with adva...

Industrial discharge and dosing module
Optimize material flow and prevent blockages in silo discharge and dosing processes,...
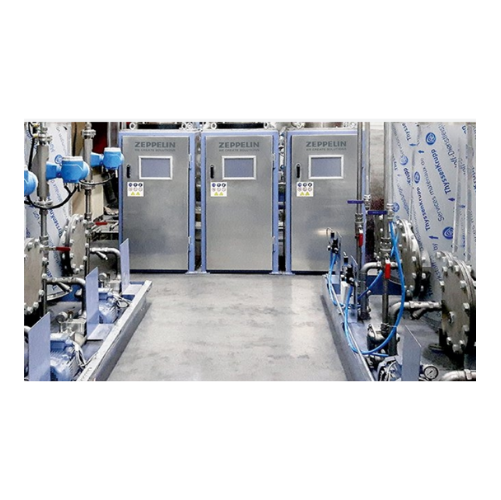

Liquid additive dosing system for industrial mixers
Achieve unparalleled precision in liquid ingredient integration with ...
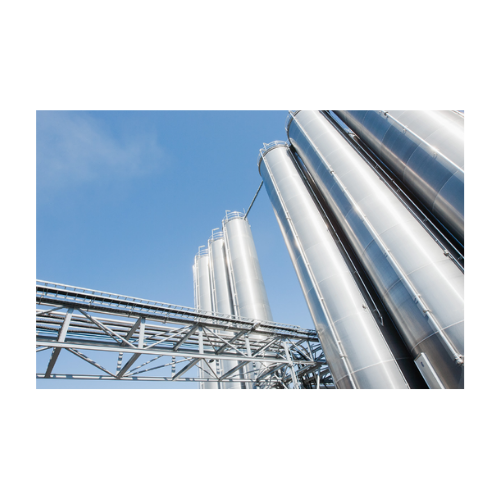

Storage silo with long base skirt for processing industry
Optimize your bulk material storage with a silo that offers du...

High precision mixer for metallic powder paints
Achieve unparalleled precision and uniformity in producing high-gloss and ...
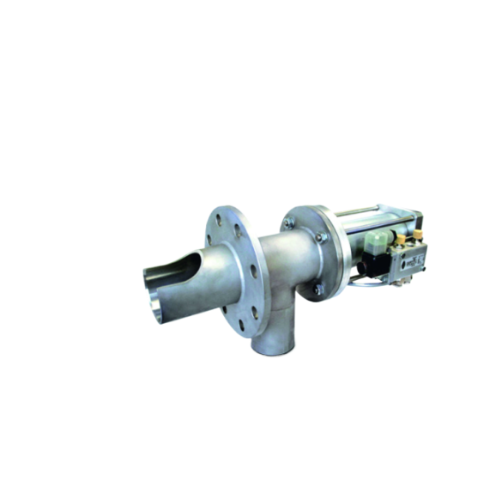

Sampler for powdered and granular bulk materials
Ensure precise sampling of powdered and granular materials under varied o...
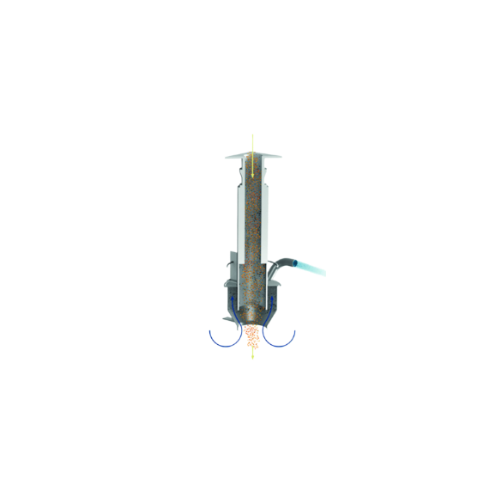

Gravimetric loading sifter for dust and streamer removal
Optimal for removing dust and streamers, this compact sifter ens...

Sampler for free-flowing granular bulk materials
Efficient and precise sampling of granular bulk materials and coarse powd...

Counterflow separator for polymer pellet cleaning
Achieve unparalleled pellet purity with efficient dust and streamer rem...

Horizontal cooling mixer for industrial applications
Efficient cooling in your production line enhances material quality ...

Horizontal homogenizing mixer for all-purpose applications
Achieve uniformity and consistency in your products with a ve...

Horizontal cooling mixer
Ensure consistent batch temperatures and reduce production costs with this robust cooling mixer, des...

High-pressure rotary feeder for continuous powder handling
Optimize your production line with reliable powder handling, ...
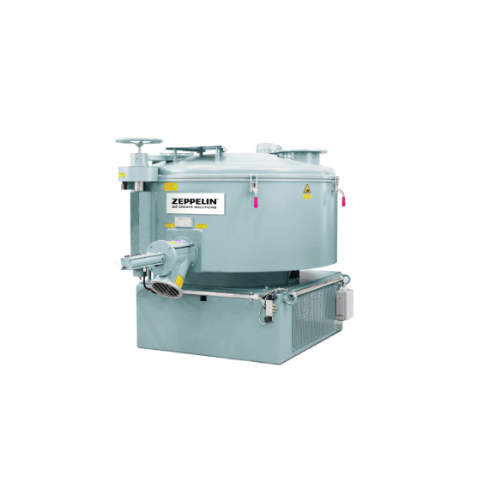

Universal mixer for diverse industrial mixing needs
Achieve precise homogenization and optimal emptying with a versatile ...
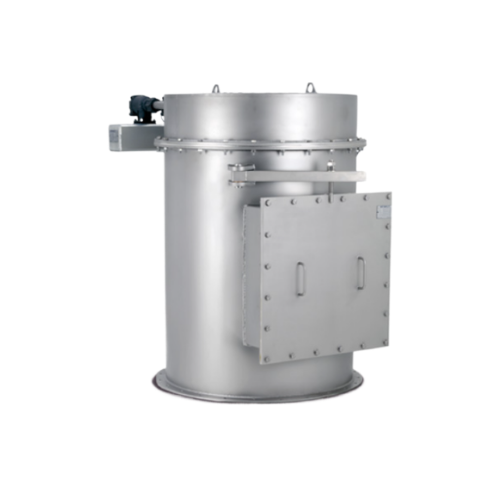

Industrial bin vent filter for fine dust particles
Enhance your production line with efficient fine dust filtration to en...
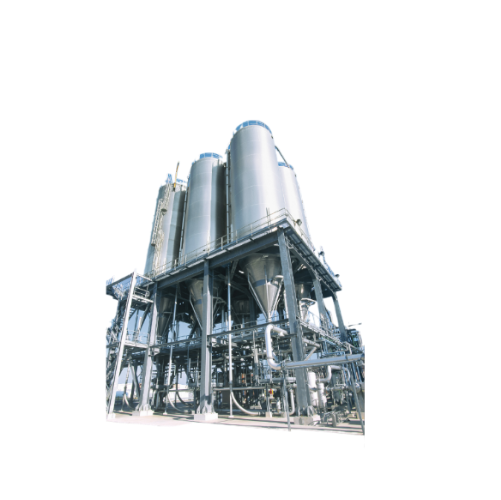

Advanced degassing and temperature control solution for process silos
Optimize your production line with precise contro...
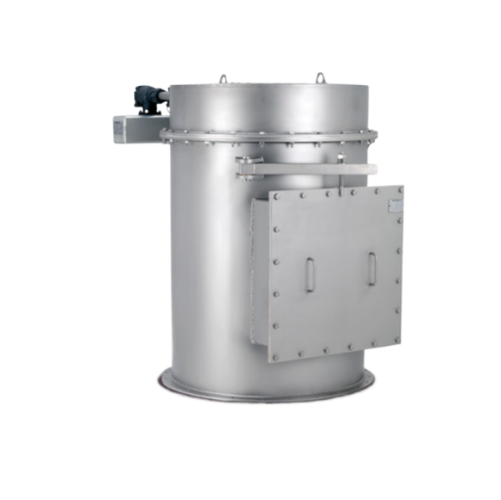

Bin vent filter for dust control in modular systems
Optimize your production line by efficiently controlling dust and fin...
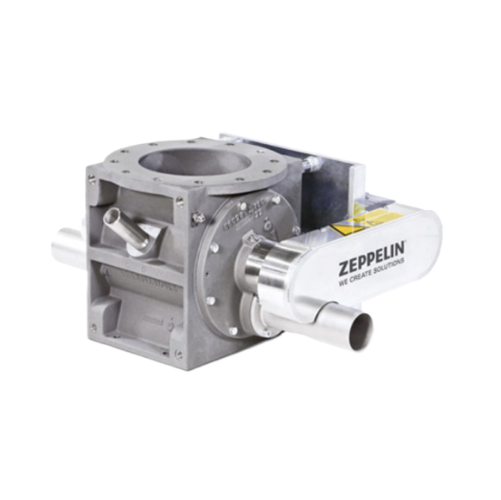

Rotary feeder for powdered bulk materials
Achieve precise control in feeding and discharging powdered materials with a rot...

Advanced plant engineering services
Optimize your production line with seamless integration of high-efficiency mixing, dosi...
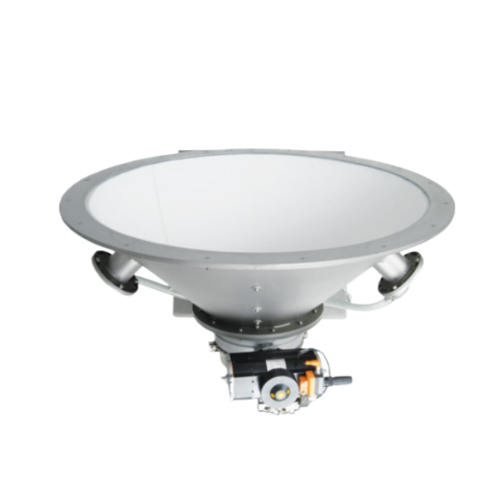

Fluidizing bed for bulk material discharge
Optimize your material flow with a fluidizing bed designed for seamless dischar...

Fluidizing bed blending silo for powder mixing
Optimize your batch mixing process with a fluidizing bed blending silo, des...
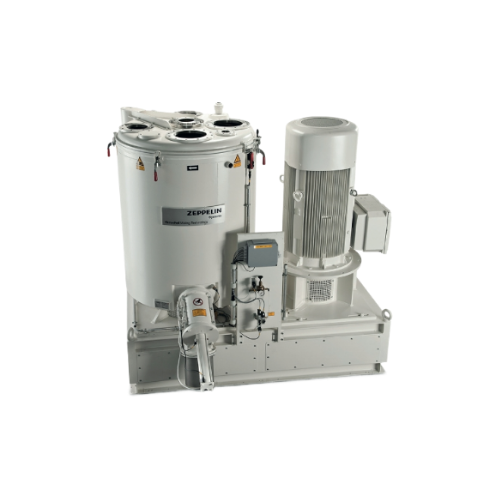

High intensity industrial mixer
Achieve rapid homogenization and outstanding dispersion with this versatile mixer, designed ...

Bulk materials discharge solution for silos and containers
Ensure reliable material flow with a robust discharge solutio...

Industrial conveying system for carbon black and silica
Ensure dust-free conveyance of sensitive materials like carbon bl...
Blending silo for poorly flowing bulk material
Enhance your bulk material processing with a blending solution that ensures...

High-pressure rotary feeder for powder and agglomerates
Optimize your production line with a high-torque solution that ef...

High-pressure rotary feeder for bulk material handling
Manage high-pressure bulk material distribution with precision, en...

Continuous material handling in compounding plants
Enhance your production line efficiency with advanced dosing, mixing, ...
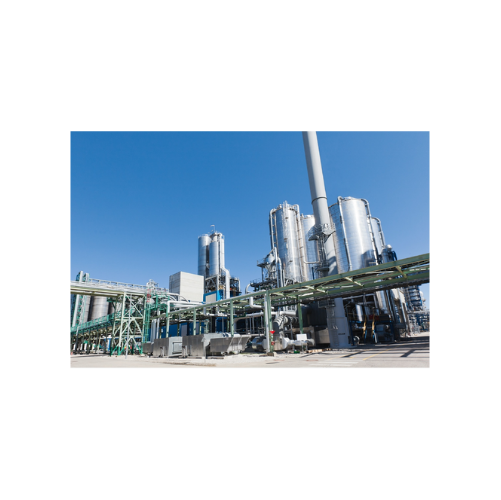

Turnkey manufacturing and processing systems management
Streamline your production line with comprehensive assembly and c...
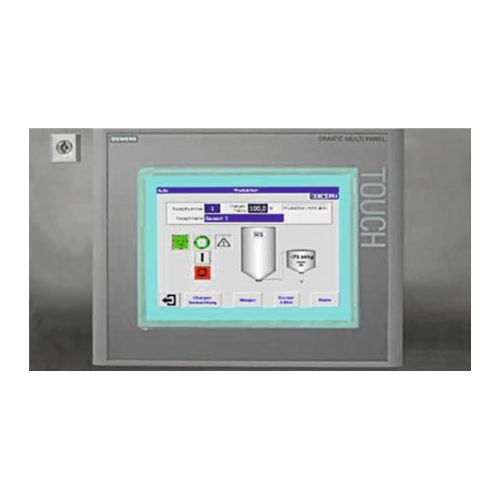

Industrial control cabinets and control stations
Streamline your plant operations with customizable control cabinets and s...
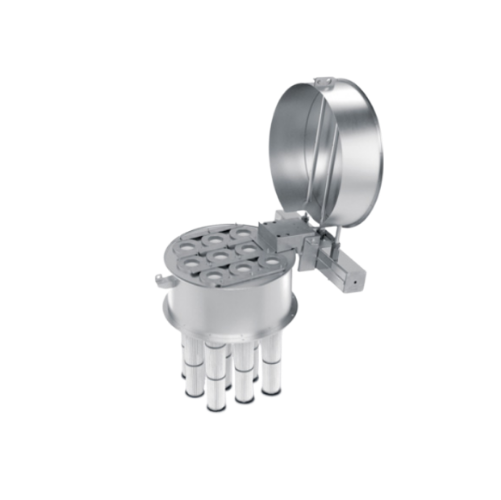

Continuous pneumatic silo air filtering system
Ensure clean and efficient pneumatically conveyed materials by integrating ...
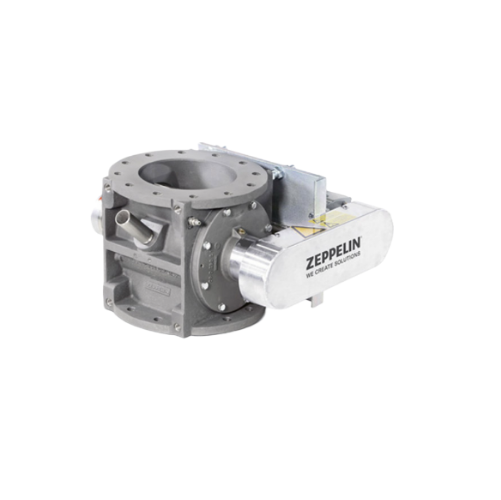

A-type rotary feeder for powder and pelleted bulk materials
Ensure precise feeding and discharging of powdered and pelle...
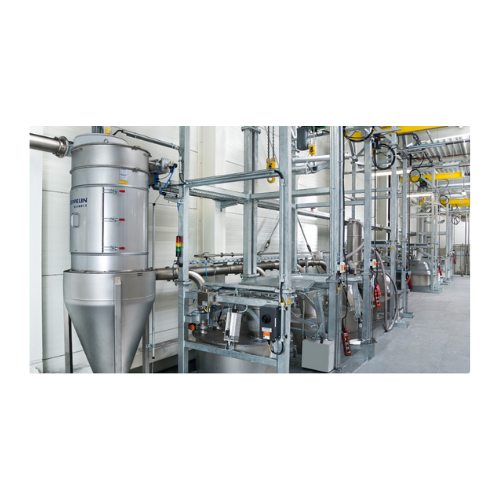

Battery production facilities with precision weighing
Achieve maximum product purity and precision in your production pro...
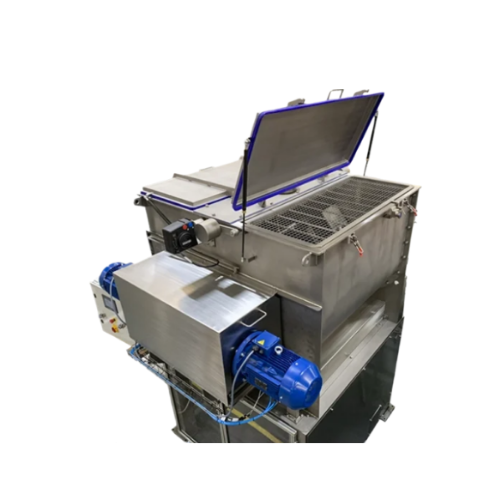

Twin shaft mixers for fragile and high throughput applications
Maximize mixing efficiency and protect delicate materials...
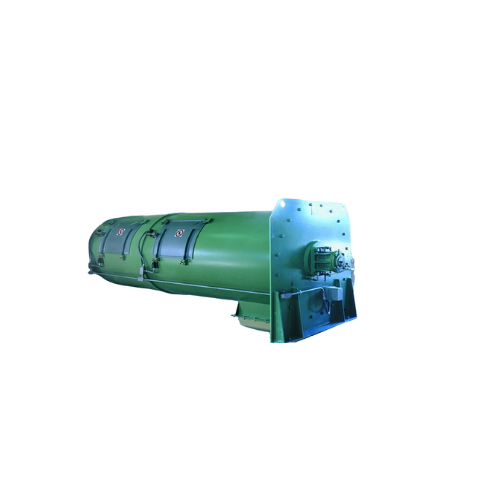

Continuous single shaft mixer for waste treatment
Achieve consistent mixing homogeneity and prevent dead spots in your pr...
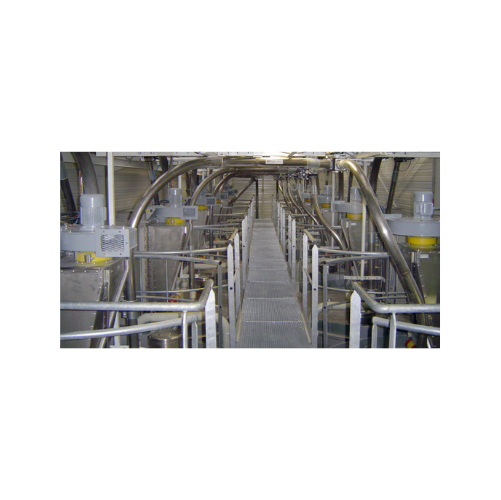

Atex certified flanged round dust collectors
Designed for potentially explosive environments, these flanged round dust col...
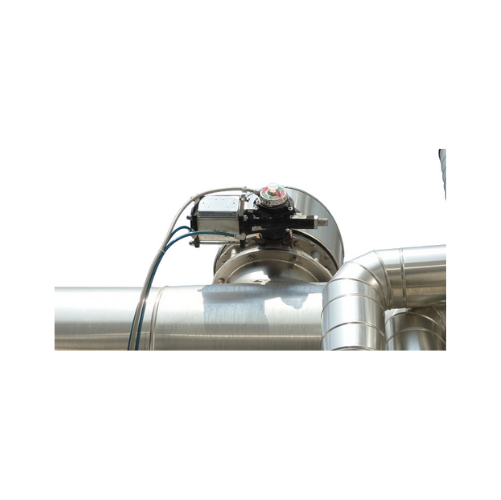

Fit-frame butterfly valves for dry bulk solids
Achieve precise control and minimize contamination in your dry bulk materia...
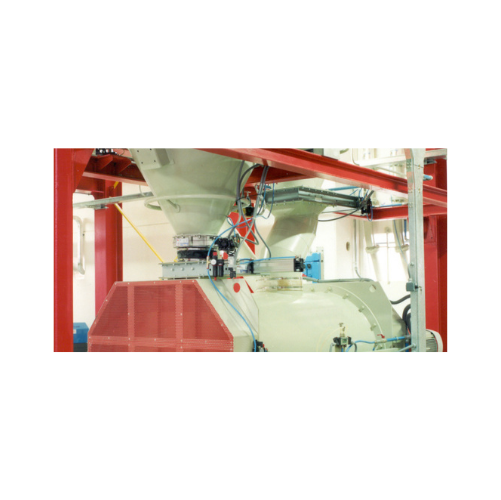

Butterfly valves for powder and granular material handling
Experience seamless material control with advanced butterfly ...
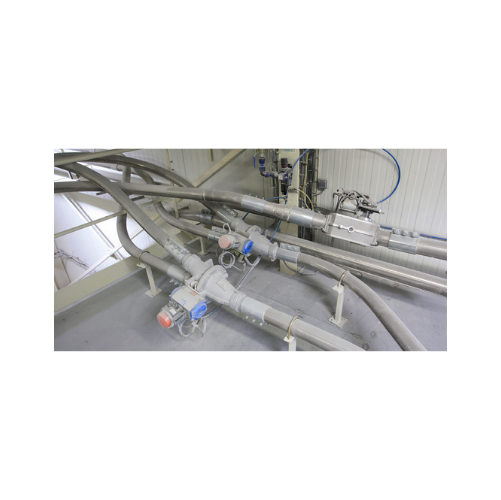

Flap diverter valves for pneumatic conveying
Streamline material flow in your pneumatic conveying system by effortlessly r...

Diverter valves for pneumatic conveying lines
Experience precise flow control in pneumatic conveying with diverter valves ...
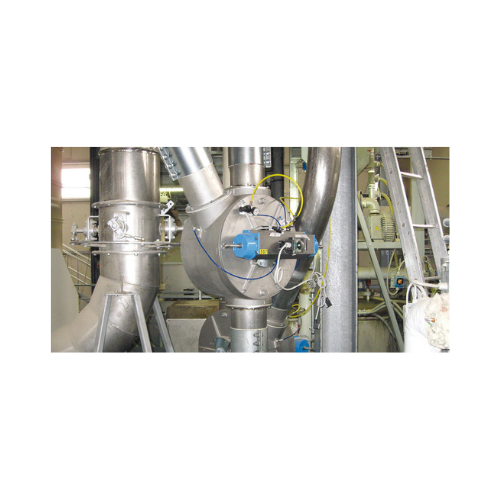

Drum-type diverter valves for pneumatic conveying
Optimize your pneumatic conveying system by effortlessly controlling th...

Stainless steel tubular screw conveyor for bulk solids handling
Ensure precise material handling with stainless steel tu...
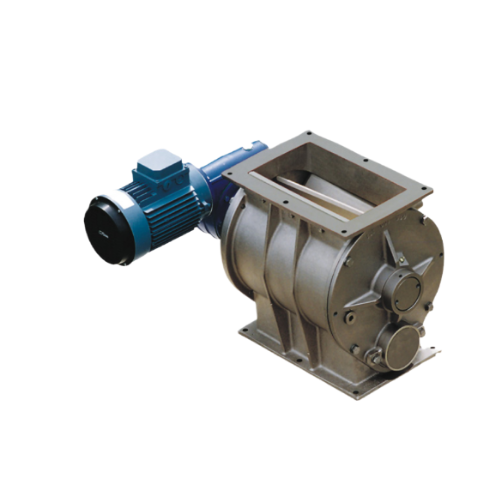

Drop-through rotary valve for precise powder and granule feeding
Ensure precise material handling with this drop-through...

High flow rate Fibc discharger
Optimize your bulk material handling with a system designed for efficient and dust-free FIBC ...

Single impact pneumatic hammers for flow aids
Combat material clogs and ensure smooth flow in your production line with pn...

Industrial vibrator for high-frequency vibration
Achieve efficient material flow and compaction across various production ...

External electric motovibrators for bulk solids conveying
Enhance material flow efficiency and solve challenging dischar...

External electric motovibrator for increased safety in hazardous environments
Designed for environments with explosive...

Micro-batch feeders for powder and granular material
Struggling with clog-prone powders? Gain precise control and consist...
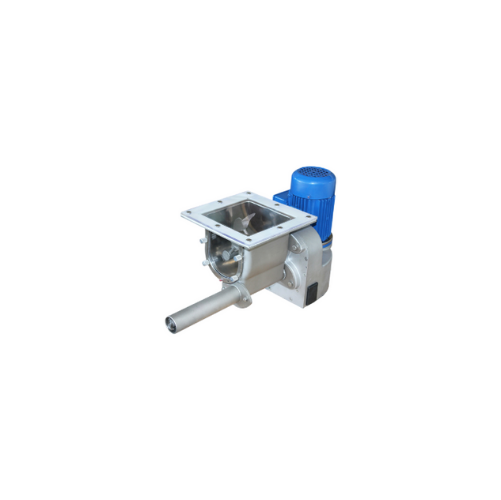

High efficiency micro-batch feeder for powdery or granular materials
Achieve precise volumetric feeding and metering of...
Loading bellows for drums and Ibcs
Ensure dust-free loading of bulk solids into confined spaces with compact, pneumatically...
Bin level indicators for wastewater treatment
Ensure reliable material level monitoring in your silos and hoppers with ILT...
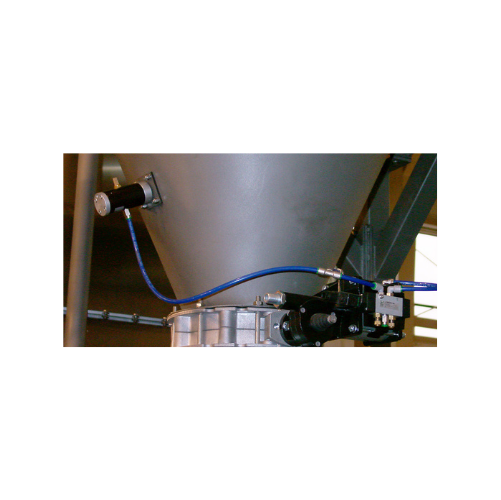

Cushioned pneumatic linear vibrators for bulk solids
Combat material bridging and rat-holing with silent vibratory techno...
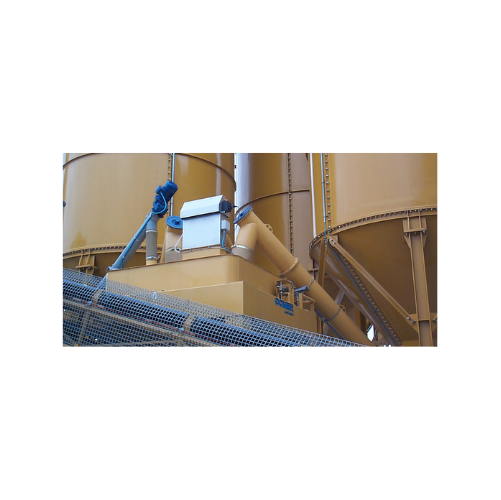

Hopper venting filter for efficient dust filtration
Achieve superior dust control and efficient material handling with a ...
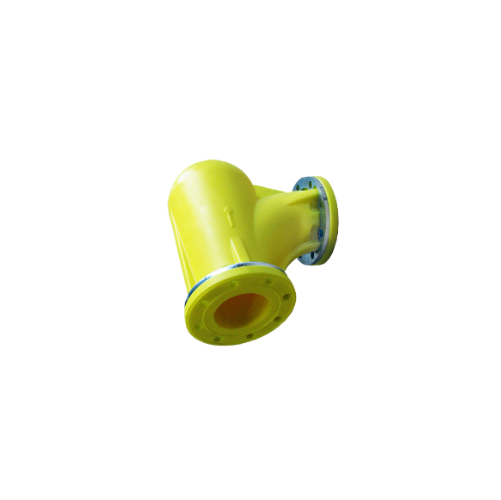

Anti-wear elbows for pneumatic conveying systems
Reduce wear and extend the lifespan of your pneumatic conveying systems w...
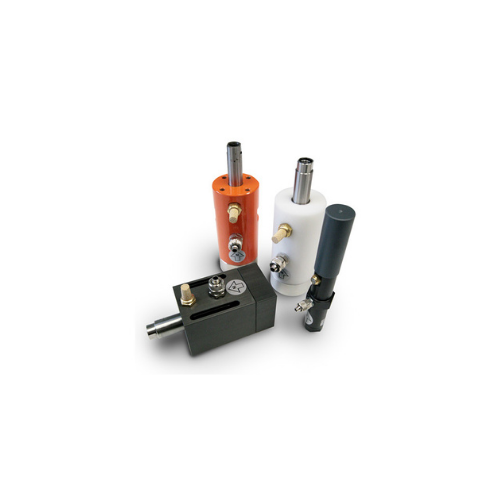

Cushioned pneumatic vibrators for coarse particle materials compaction
Enhance your material flow and compaction proces...

Waste bag compactor for bulk solids
Efficiently compact waste bags to a fraction of their volume, streamlining disposal whi...

Rotary bin discharger for bulk solids
Efficiently manage bulk solids with a rotary bin discharger that minimizes residue an...

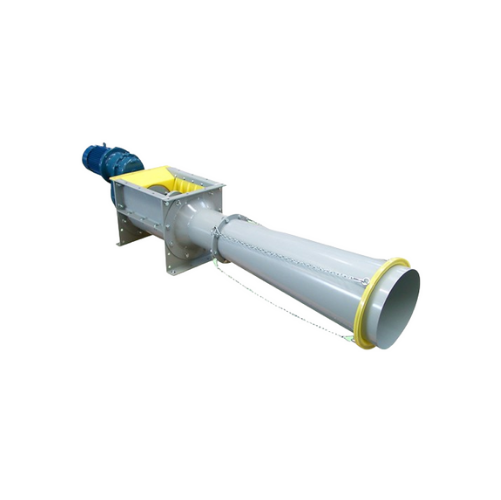
Trough screw conveyors for powdery and granular materials
Optimize your material handling process with a flexible screw ...
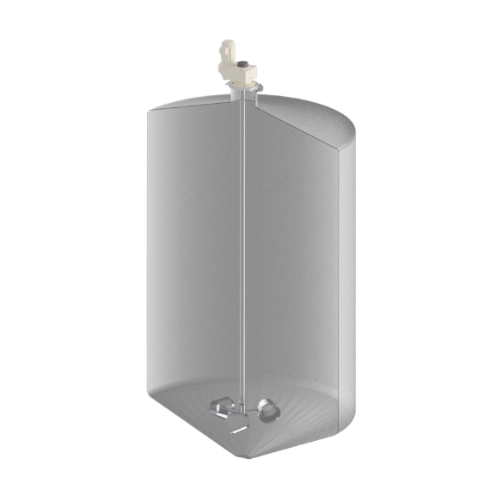

Industrial tank mixer for high-volume containers
Optimize your mixing processes with a robust solution designed for high-v...
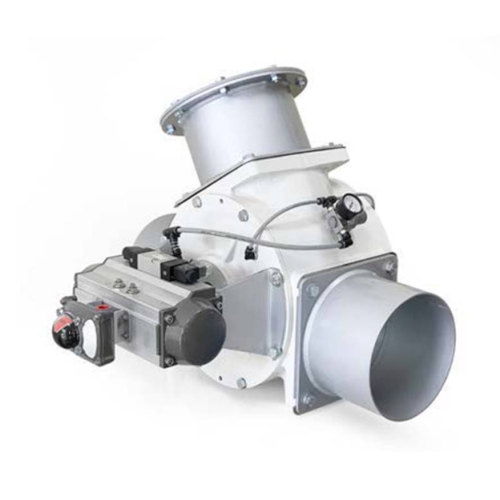

Pneumatic diverting valve for powder and granule transfer
Efficiently redirect bulk materials from one point to another ...
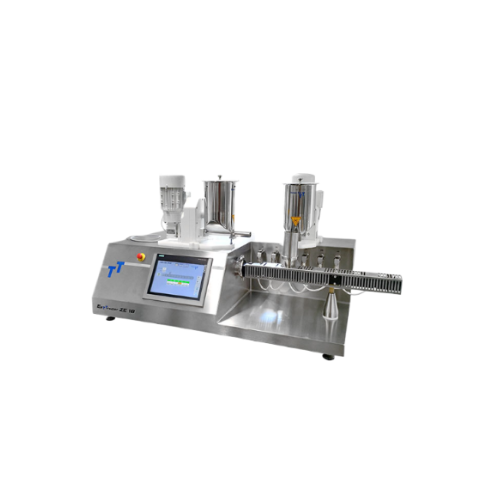

Table top extruder for customizable extrusion processes
Discover versatile extrusion capabilities for developing complex ...
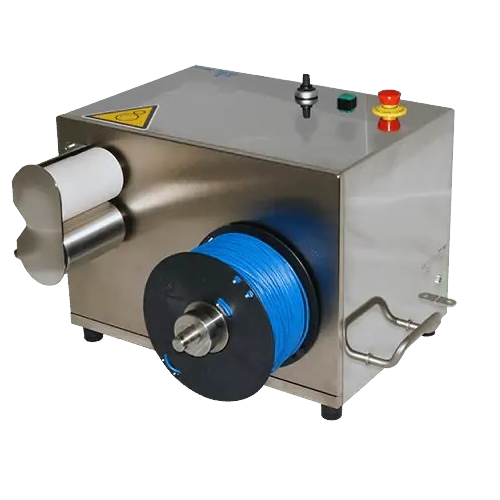

Rewinder for extrudates
Achieve precise winding of extrudates with adjustable tension control, ensuring consistent spooling f...
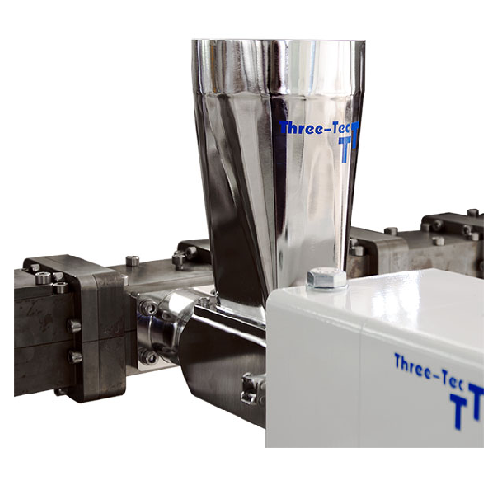

Side feeding device for extruders
Enhance your extrusion process with a side feeding device that gently introduces powders,...
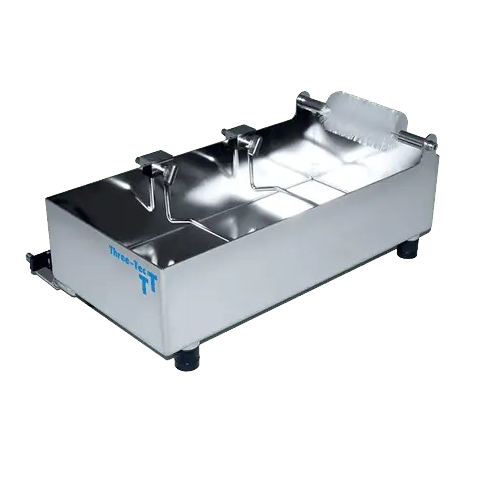

Cooling bath for efficient extrudate processing
Ensure optimal cooling for extrudates to maintain product integrity and en...
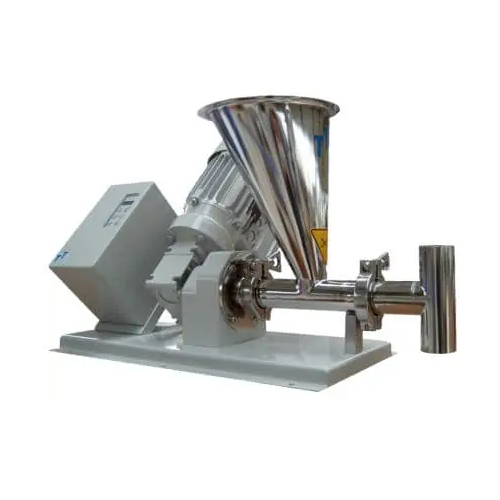

Single screw feeders for granules
Optimize the feeding of well-flowing granules with precision and consistency—key for main...
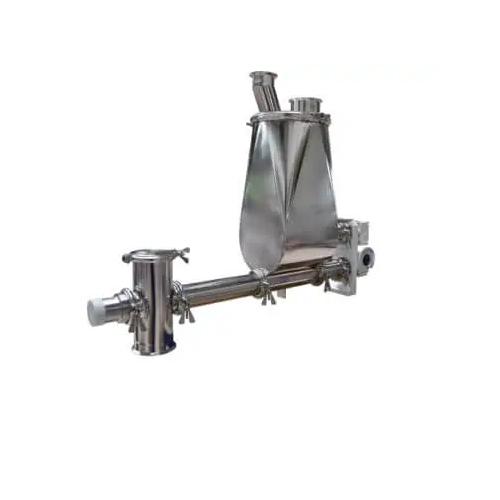

Quick change volumetric and gravimetric single-screw dosing device
Simplify your dosing process with a quick-change sin...
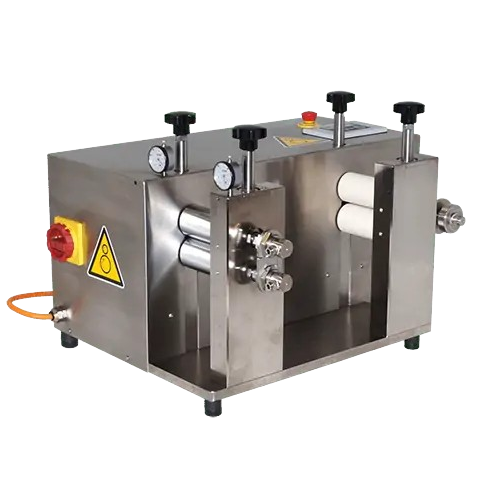

Foil roller for precise extrudate calibration
Achieve uniform film thickness and precise calibration of extrudates with an...
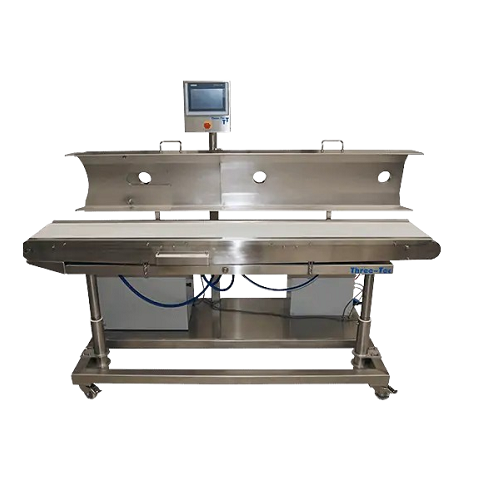

Cooling conveyor belt for extrudates and granules
Efficiently cool and convey extrudates and granules with precise temper...
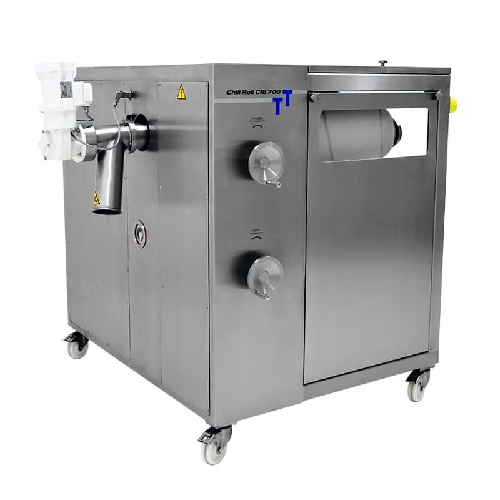

Continuous cooling roller for extrudates
Ensure rapid and efficient cooling of high-heat capacity extrudates with a compact...
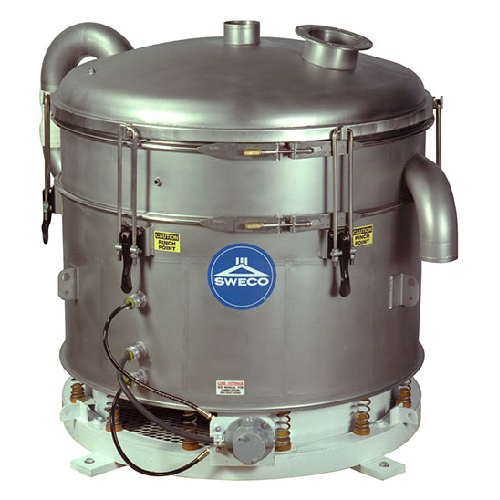

Pneumatic inline sifter for dry flowing material
Ensure precise particle segregation and foreign matter removal with this ...
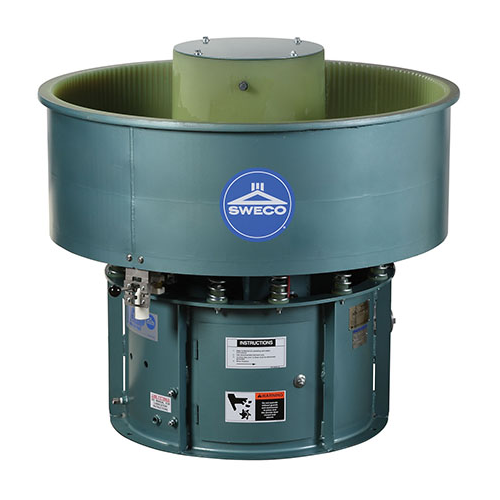

Vibratory finishing and deburring technology
Achieve precise surface finishing and deburring with advanced vibratory motio...
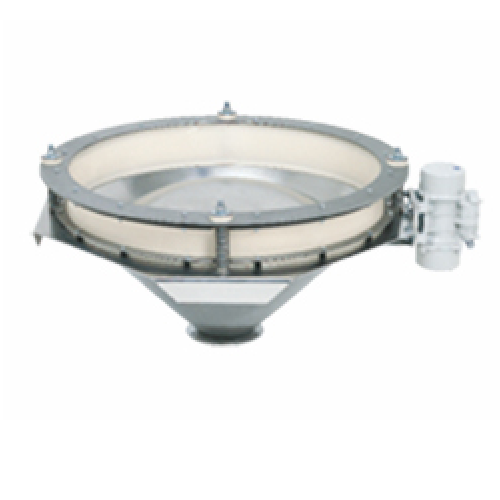

Bin activator for reliable bulk solids discharge
Ensure reliable flow and prevent compaction in your production line with ...
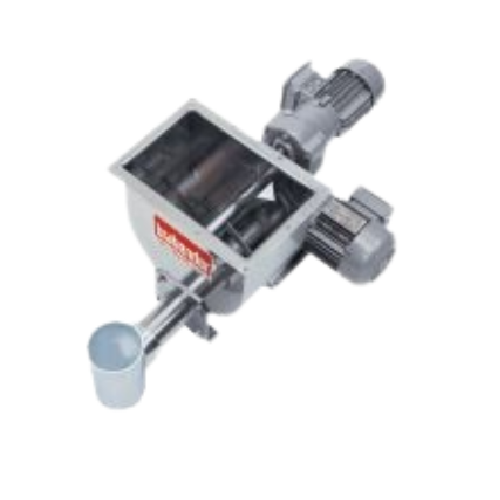

Single screw feeder with stirring agitator for powders and pellets
Ensure consistent mass flow and precise dosing with ...
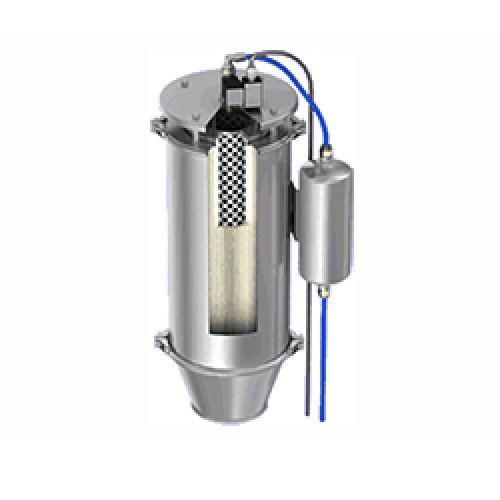

Dust filter for loss-in-weight feeder refill
Optimize your feeder operations by effectively filtering displaced air and mi...

Bigbag discharge station
Efficiently manage bulk material unloading with this solution, which facilitates seamless dischargin...
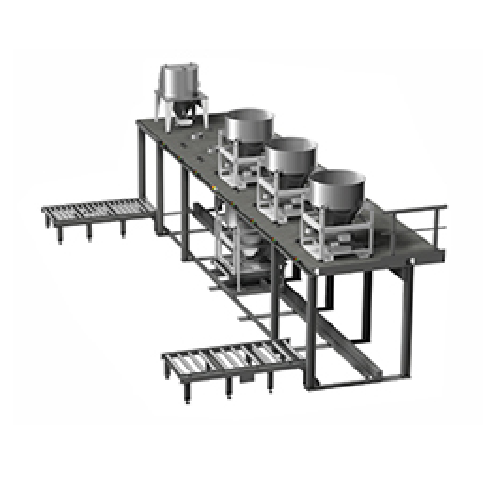

Batch ingredient dosing system for high-accuracy weight control
Achieve precise weight measurement for multi-ingredient ...
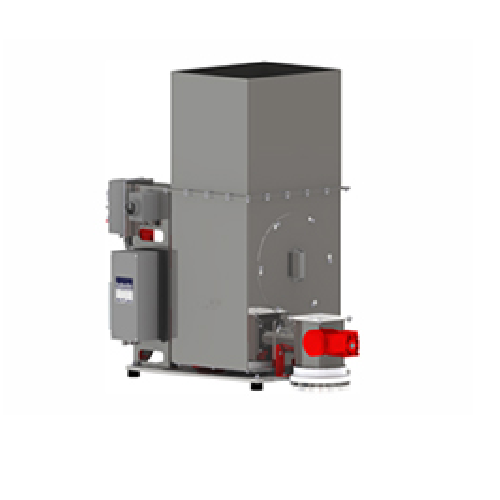

Loss-in-weight feeder for long and uneven fibers
Optimize feeding precision for challenging materials like long and uneven...
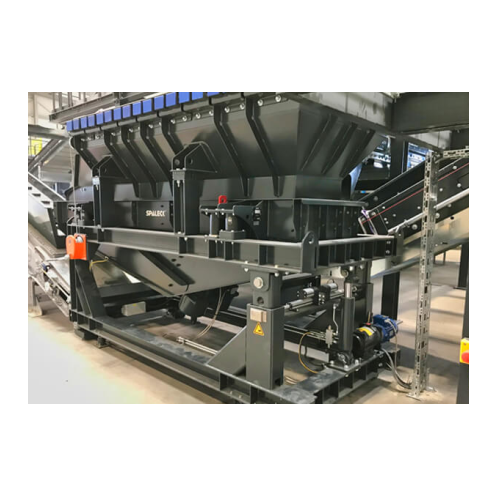

Self-regulating material feeder for recycling lines
Experience enhanced efficiency in recycling operations with a feeder ...
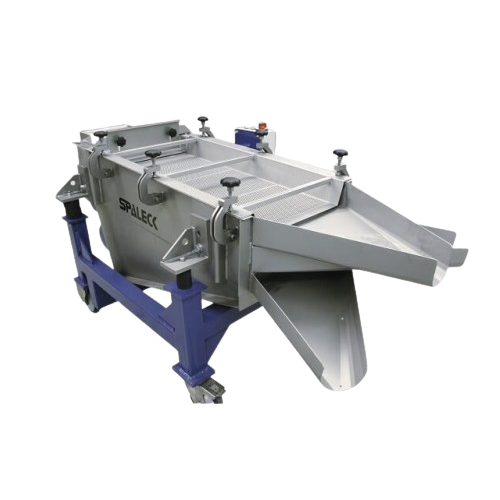

Granulate screening technology for precise particle size separation
Achieve exceptional sorting precision and maintain ...
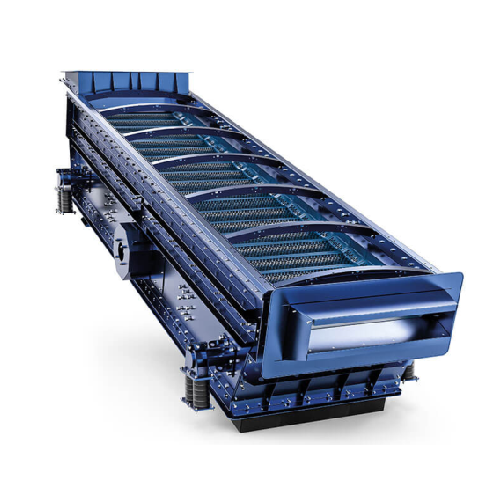

Vibrating screen for sticky and moist materials
Efficiently tackle the challenges of processing wet and sticky materials w...
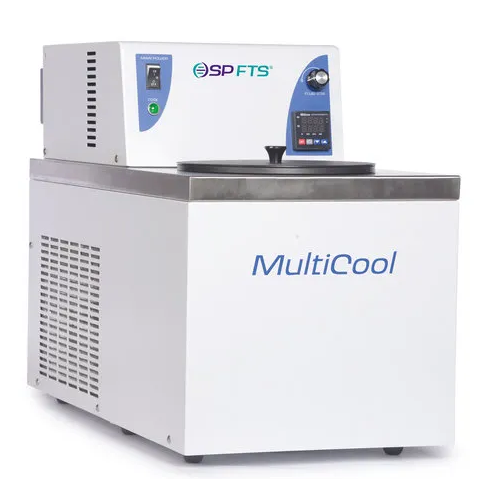

Low temperature bath for sample freezing and temperature control
Achieve precise temperature control from -80°C to +100°...

Metal detection system for powders & granules
Ensure product integrity and protect your machinery from metallic contaminan...
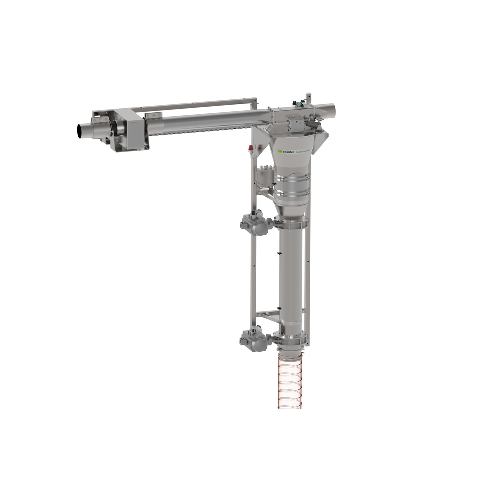

In-line metal detector for pneumatic systems
Ensure product purity and operational efficiency with a solution that effecti...

Conveyor belt metal detection system
Ensure seamless product safety with a system that detects and separates metallic conta...
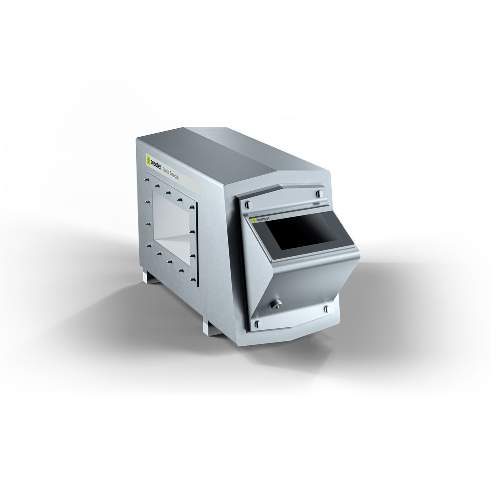

Metal detector systems for conveyor belts and chutes
Ensure the integrity of your production line by efficiently detectin...
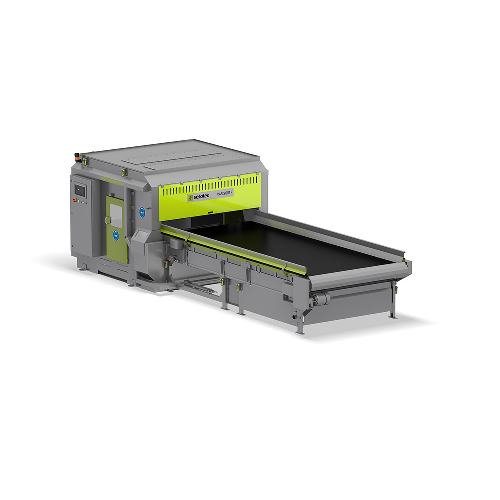

Sorting conveyor systems for recyclables
Efficiently sort and reclaim diverse materials from mixed waste streams with high-...

X-ray inspection system for unpackaged bulk products
Ensure product purity and safety in high-speed production lines with...
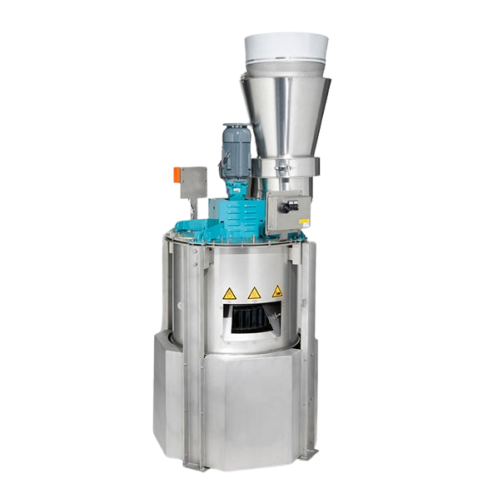

Mass flow rate feeder for bulk powders
Achieve precise control and consistent material flow in high-speed manufacturing env...
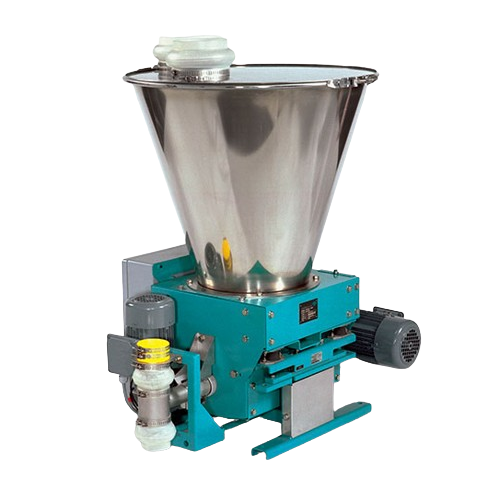

Loss-in-weight feeder for bulk solids
Ensure precise and reliable dosing of bulk solids with a compact feeder that eliminat...
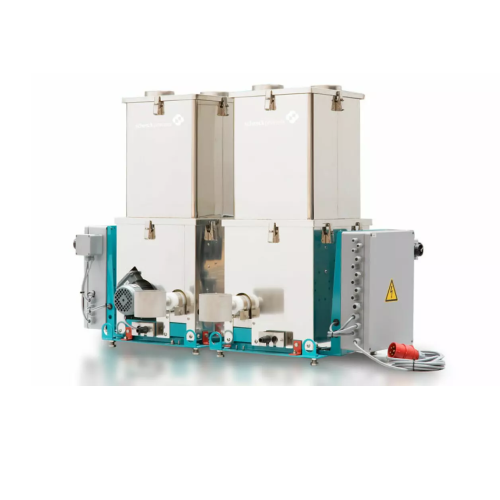

Loss-in-weight feeder for plastic compounding
Achieve precise material flow and improved production efficiency with an ada...

Continuous and batch feeding system for bulk materials
Achieve precise bulk material feeding with seamless integration in...
Injected density stabilizer for pneumatic conveying
Optimize your dense phase pneumatic conveying with a stabilizer desig...

Multipurpose feed station for bulk solids
Optimize your production line with a versatile feeding station designed for simu...

Industrial pellet mill
At the industrial level, the application areas of pellets range widely in fields such as feeds, biomas...

Laboratory aerator for food products
Successful innovators in the food, chemicals, and plastics industries need reliable mi...

Macro ingredient dosing system
Traditional dosing systems do not have a very long operational life and are hard and expensiv...

DAF wastewater treatment
The food and beverage industry requires the total removal of suspended solids (TSS), biochemical oxy...

Laboratory granule dedusting analyzer
High quality clean bulk materials are used in many industries including plastics, foo...

Small scale deduster for plastic granules
Industries that use bulk plastics see better product quality and decreased equip...

Deduster for injection moulding
High quality injection molded plastic parts require clean bulk resins free of dust and strea...

Pusher centrifuge
Pusher centrifuges are continuously operating filter centrifuges and can have several basket stages dependi...
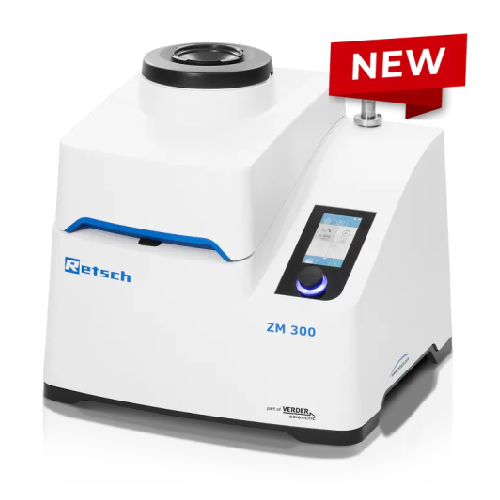

Ultra centrifugal mill for size reduction of soft and medium-hard materials
Achieve precise particle size reduction an...
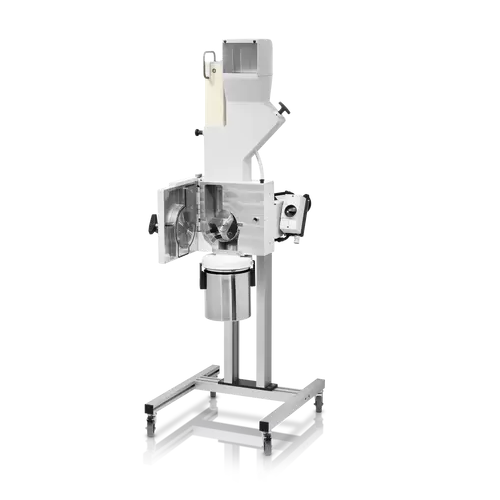

Cutting mill for soft and medium-hard materials
Efficiently reduce the size of diverse materials with precision cutting an...
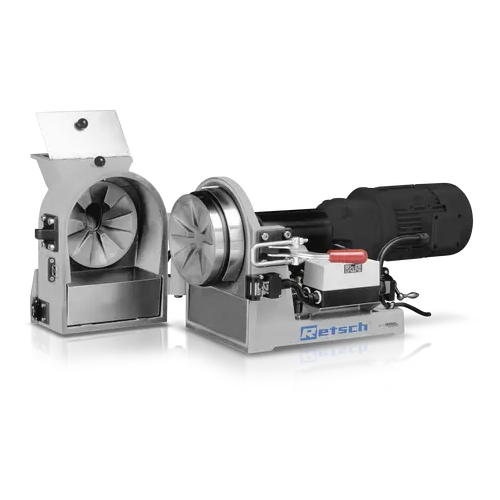

Disc mill for industrial laboratory grinding
Streamline your sample preparation with a robust disc mill designed for preci...
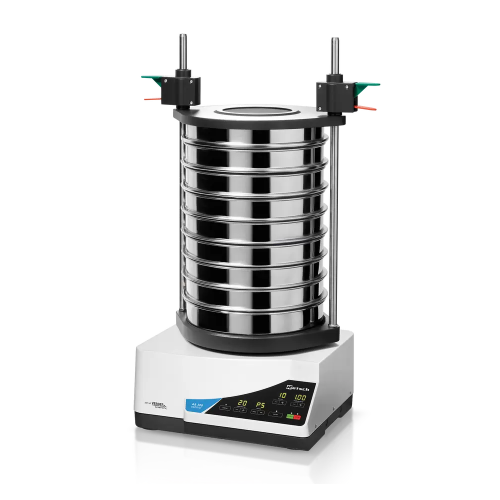

Electromagnetic sieve shaker for quality control
Achieve precise particle size distribution with this advanced electromagn...
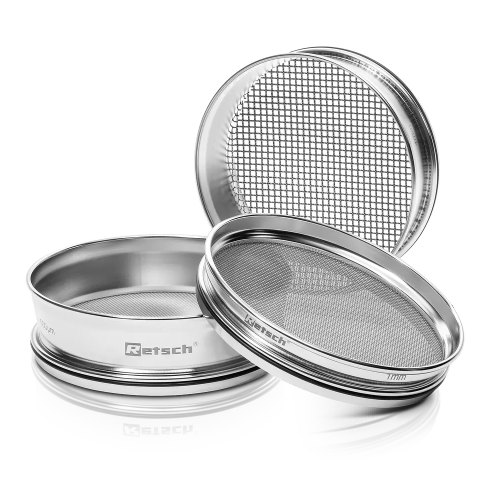

Mesh sieves for laboratory particle size analysis
Ensure precise particle size control for a wide range of materials with...
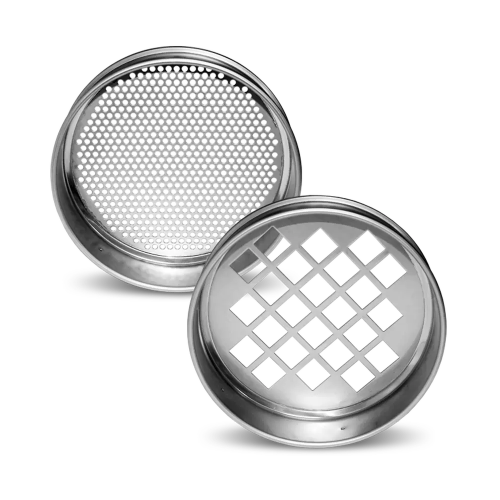

Perforated plate sieves for particle size determination
Optimize your particle size separation with high-stability stainl...
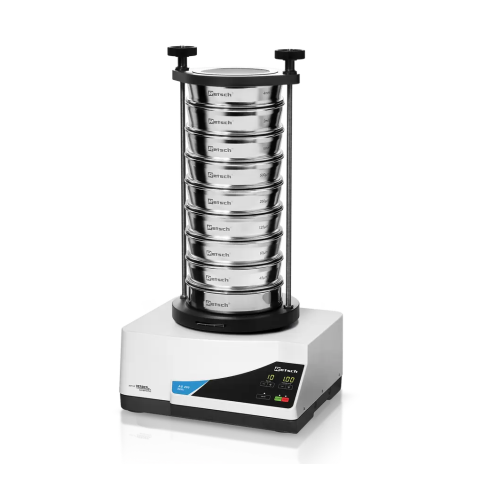

Vibratory sieve shaker
Enhance your quality control processes with this versatile sieve shaker, designed to efficiently separ...
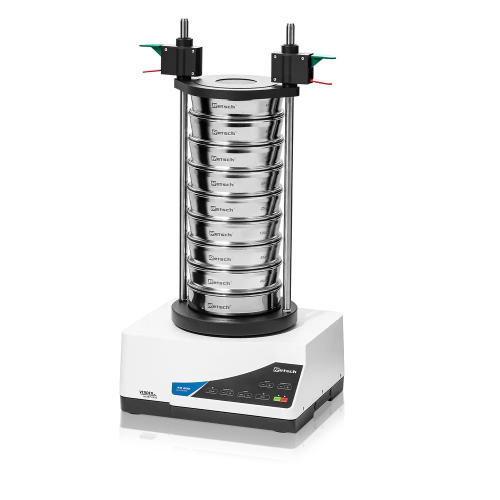

Vibratory sieve shaker for particle size determination
Achieve precise particle size analysis with rapid, reproducible re...
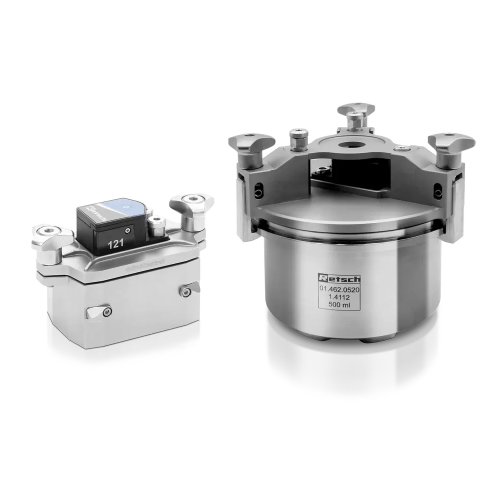

Pressure and temperature monitoring system for ball mills
Ensure optimal grinding conditions and enhance product quality...
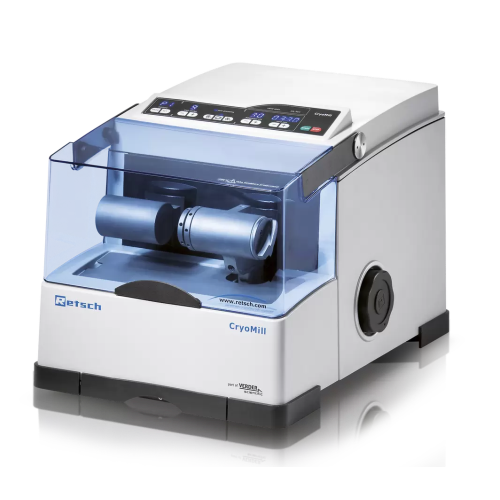

Cryogenic ball grinder for laboratory use
Achieve precise temperature-controlled grinding with advanced cryogenic technolo...
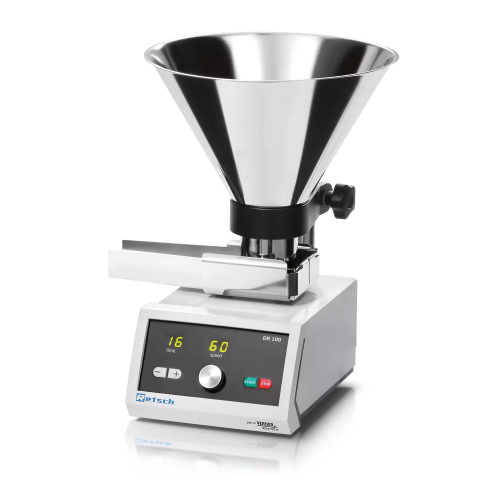

Vibratory feeder for bulk materials and fine powders
Ensure consistent material flow and precise feeding for optimized pr...
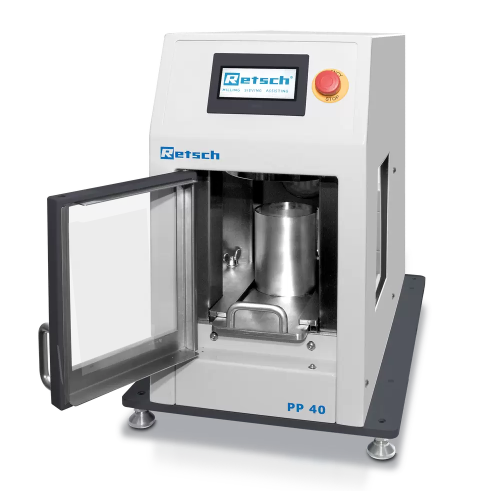

Pellet press for Xrf analysis
Ensure precise spectral analysis with strong, smooth-surfaced pellets by utilizing adjustable ...

Rotating sample divider for large bulk materials
Achieve precise, dust-free division and volume reduction of bulk material...
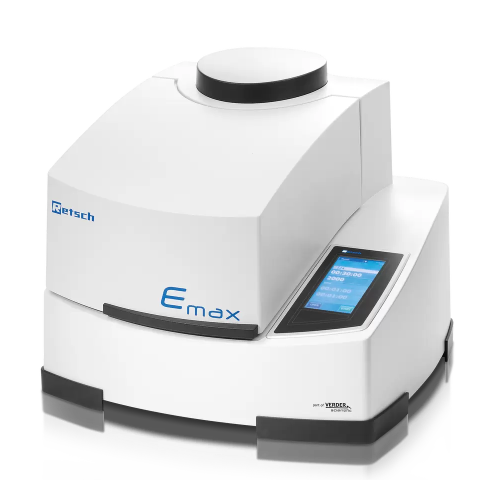

High energy untra fine ball mill
Achieve ultra-fine particle sizes rapidly with this high energy milling solution, designed ...
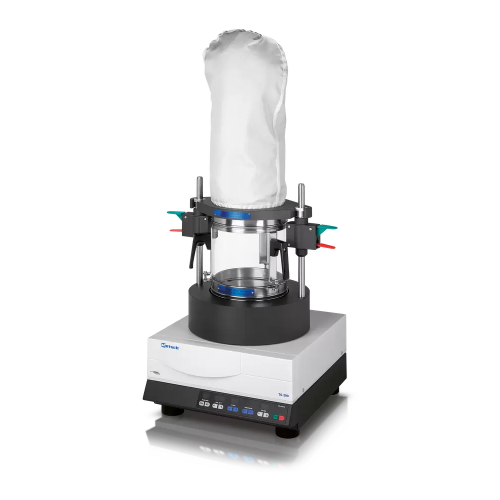

Fluid bed dryer for bulk material laboratory drying
Efficiently dry and mix organic and inorganic materials with precise ...
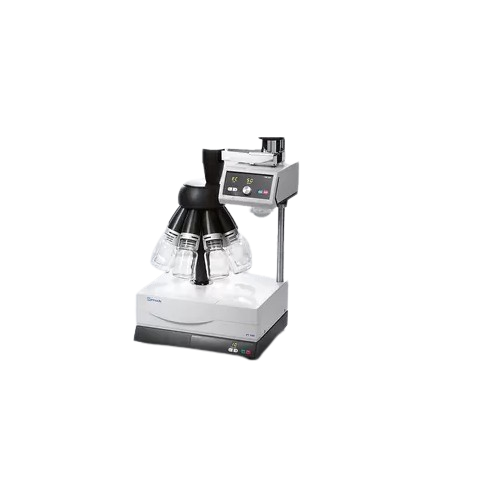

Sample dividing solutions for laboratory applications
Streamline your lab’s precision in sample preparation with so...
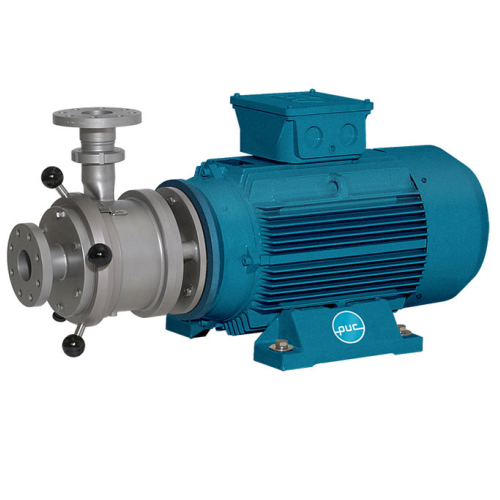

Colloid mill for emulsifying and wet milling applications
Achieve precise mixing and grinding with our colloid mill, des...
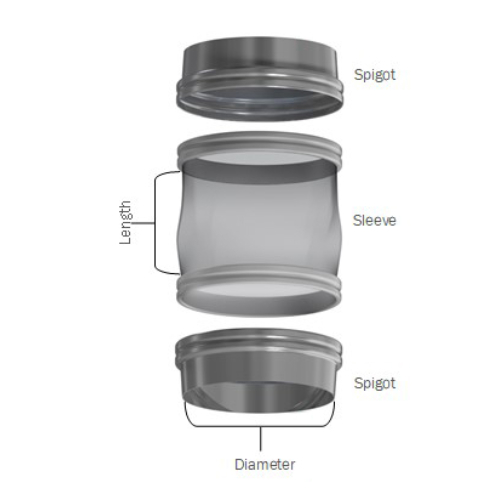
Flexible connector for bulk powder manufacturing
Eliminate leakage and enhance hygiene in your powder processing with a sn...
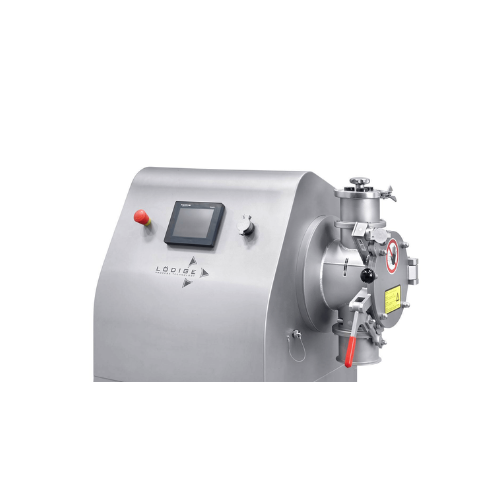

Laboratory ploughshare mixer for small-scale production
Achieve precise mixing and granulation for R&D and small-bat...
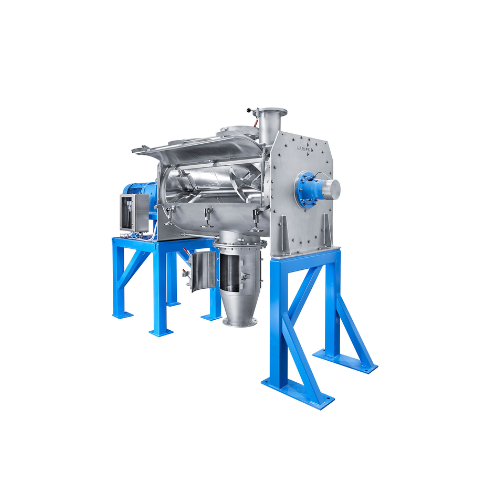

Ploughshare mixer for batch operation
Achieve superior mixing quality with a system designed for rapid batch operations. Ex...
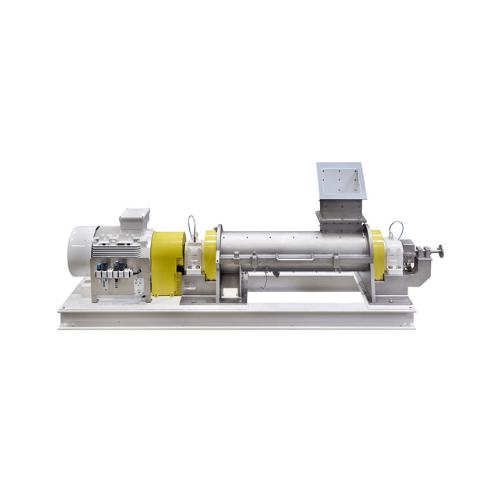

High-speed mixer for continuous high throughputs
Achieve exceptional homogeneity in mixing liquid and pasty components int...
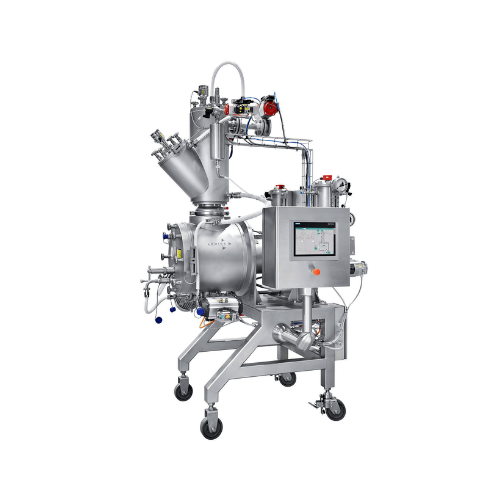

Vacuum paddle dryer for laboratory use
Achieve precise temperature and moisture control in your batches with this vacuum sh...
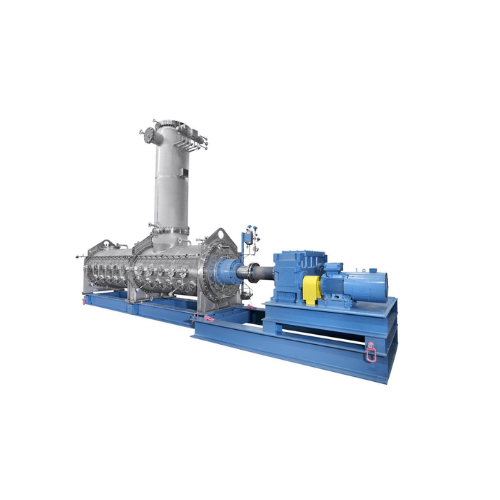

Continuous granulation dryer for chemical and polysaccharide applications
Enhance your production with precise drying ...
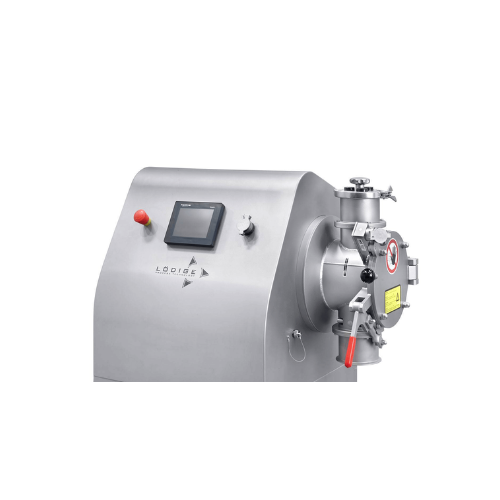

Laboratory mixer granulator
Achieve high-quality mixtures in R&D and small-batch production with versatile laboratory m...
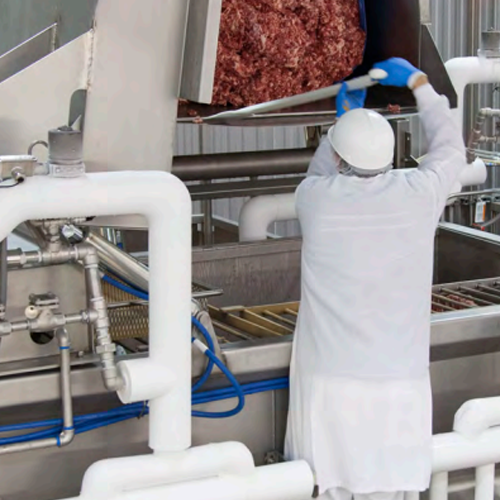

Cryogenic cooling system for meat mixing
Efficiently manage heat during meat mixing to enhance product quality and ensure s...
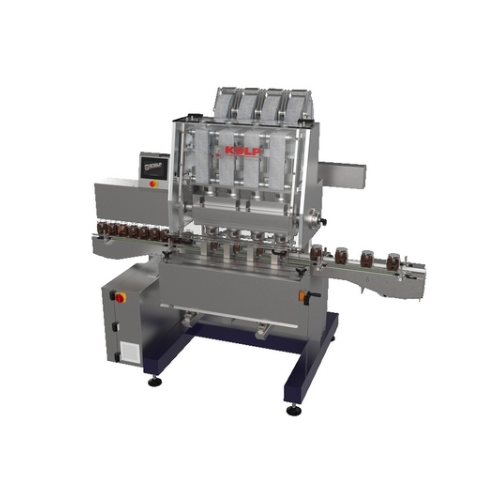

4 head sealing system for plastic and glass jars
Achieve precision sealing for jars of various materials with this high-sp...
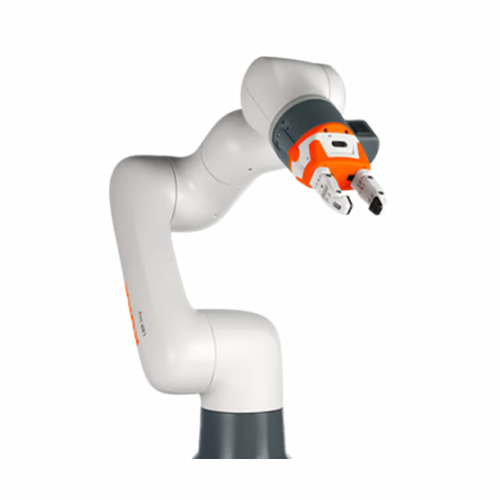

Collaborative robot for fast and intuitive automation
Accelerate your production line with a versatile and intuitive cobo...

Sanitary bulk bag filling system
Streamline your powder handling process with a system designed to improve stability and acc...
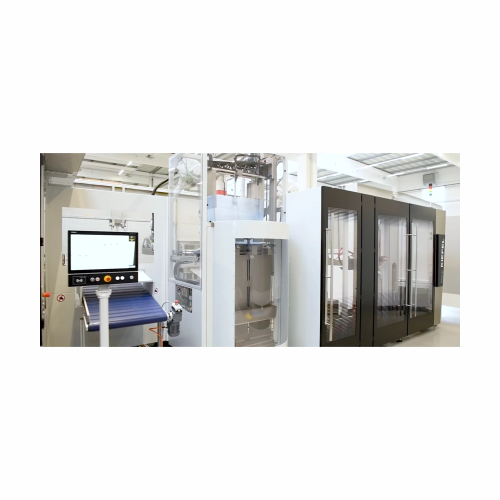

Modular stacking and automation for polymer packaging
Addressing the needs of flexible food packaging, this solution offe...
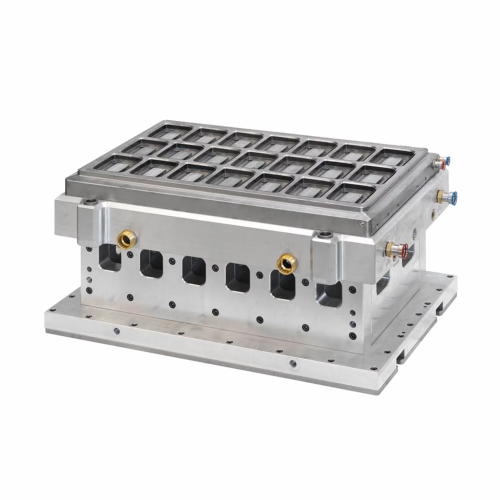

Thermoforming tools for polymer packaging
Optimize your production line with versatile thermoforming tools that enhance fl...

360° palletizing and depalletizing robot
Optimize your packaging flow with a robot offering seamless 360° operation for pre...

180° palletizing robot for automated palletizing and depalletizing
Optimize your production line with a versatile solut...

Vibrating tumbler screener for dry and wet screening
Achieve efficient dry and wet material separation with a high-capaci...

Double cone blender for homogeneous solid-solid mixtures
Need uniform blending for complex solid mixtures with diverse de...

Rotary unscrambler for plastic bottles
Streamline your bottling process with a solution that efficiently sorts, orients, an...
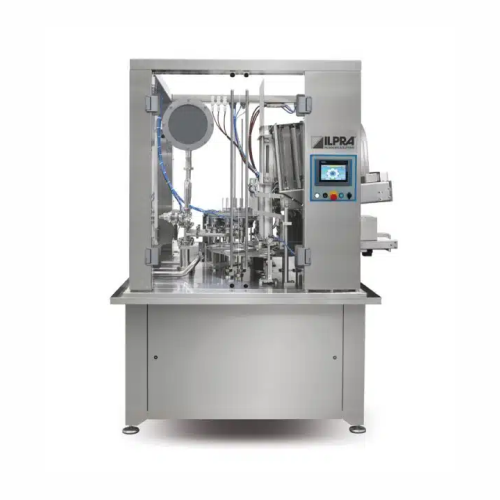

Automatic filling and sealing solution for medium to large production
Streamline your high-capacity filling and sealing...
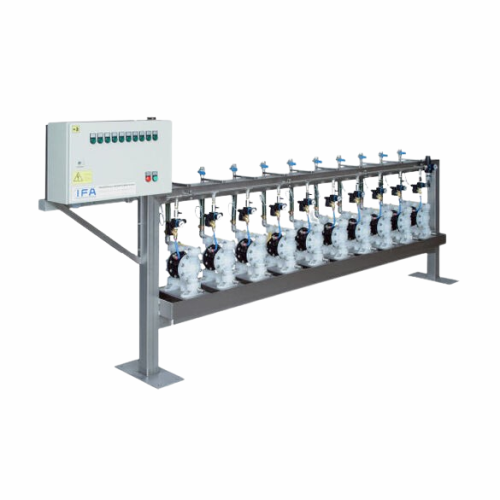

Pneumatic conveying systems for industrial applications
Efficiently transport bulk materials or liquids across your produ...
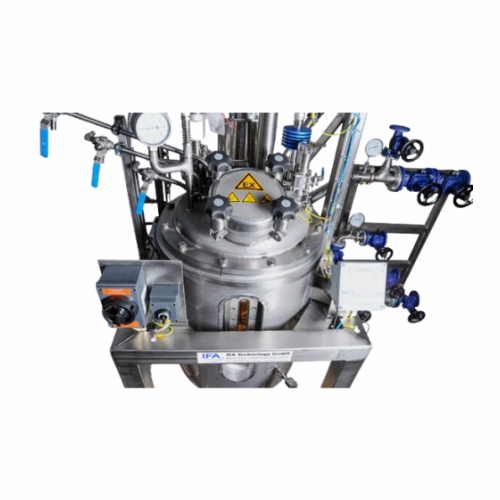

Wastewater treatment system for industrial applications
Optimize resource management and environmental impact by integrat...
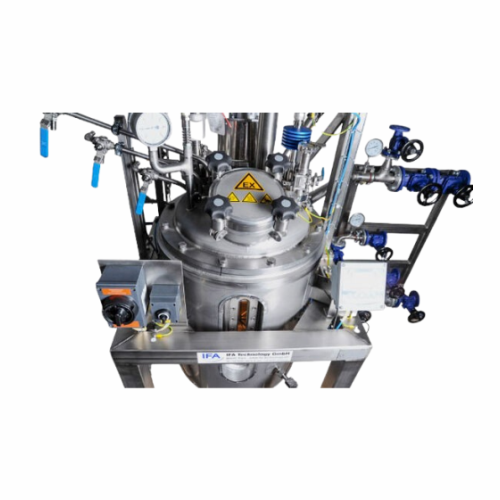

Turnkey resin synthesis plant system
Streamline resin production with a comprehensive turnkey system designed to efficientl...

Gravimetric dosing systems for precise material measurement
Achieve precise material measurement with gravimetric dosing...
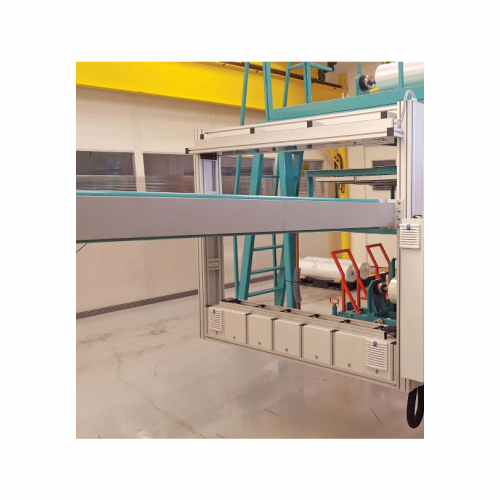

Optical sheet inspection system for industrial manufacturing
Enhance your sheet production quality with accurate defect ...
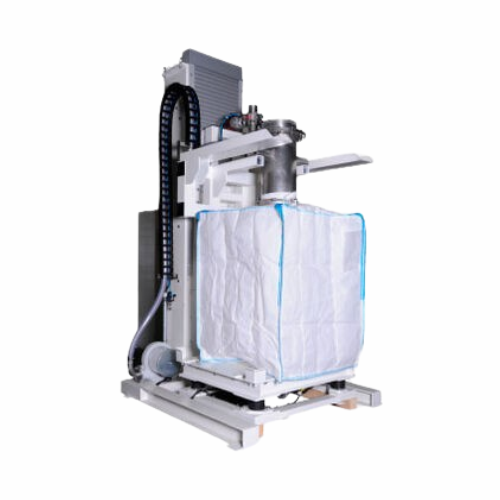

Customised tank systems for liquid and bulk material storage
Ensure safe and compliant storage of liquids and bulk mater...
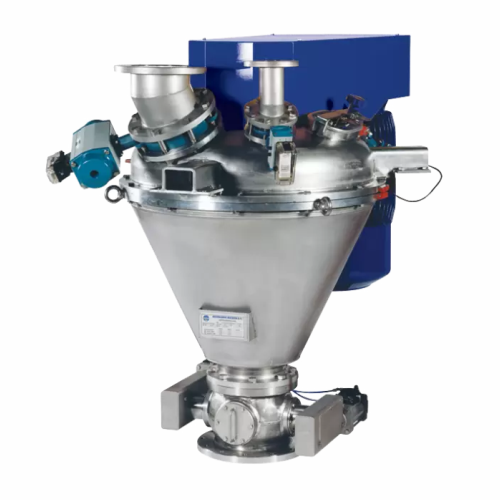

High shear impact mixer for agglomeration and dispersion
Achieve precise homogeneity and efficient agglomeration with a h...
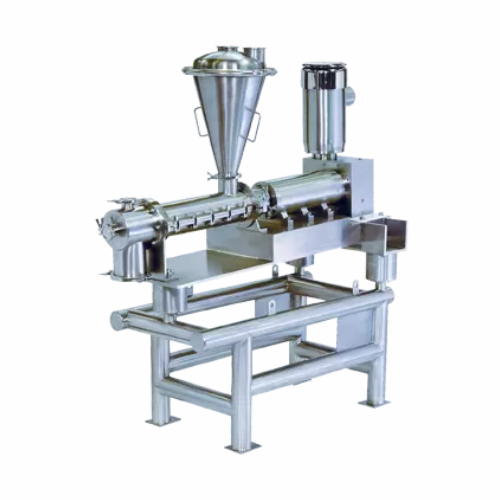

Mixer/extruder for viscous pastes and plastic masses
Achieve seamless mixing, kneading, and extrusion of viscous material...
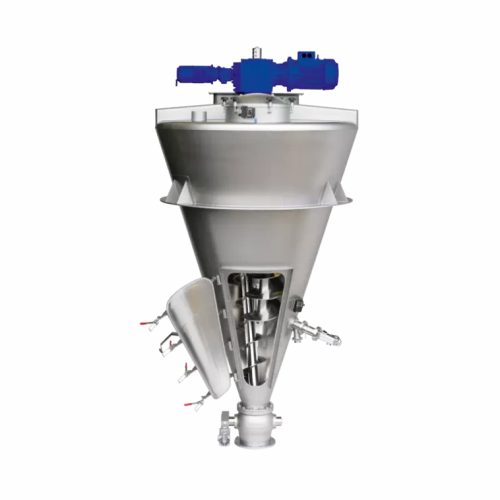

Batch mixer for segregative, free-flowing powders and pastes
Achieve precise and gentle batch mixing for delicate produc...
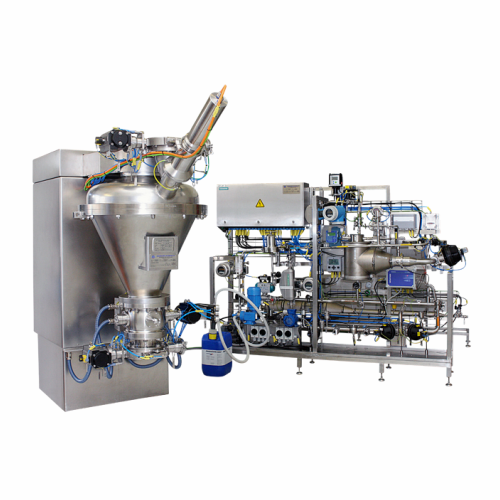

Cip/sip cleaning for solids processing systems
Ensure seamless transitions and maintain hygienic production environments w...
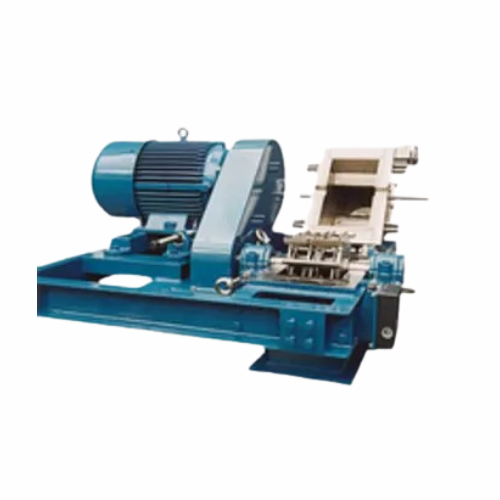

High-speed pulverizer for carbon black production
Achieve consistent particle size and optimal homogenization with high-s...
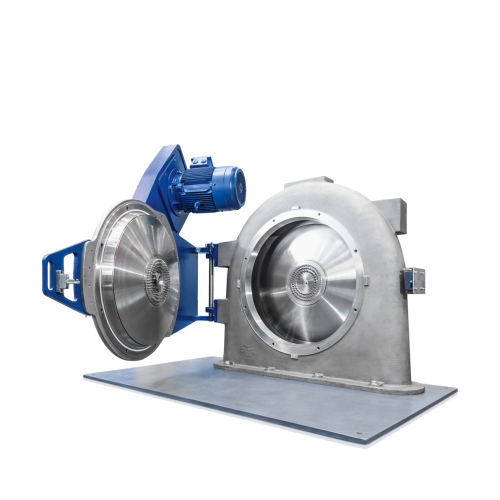

Pin mill for fine grinding of sticky materials
Achieve ultra-fine grinding of challenging materials with high speed and pr...
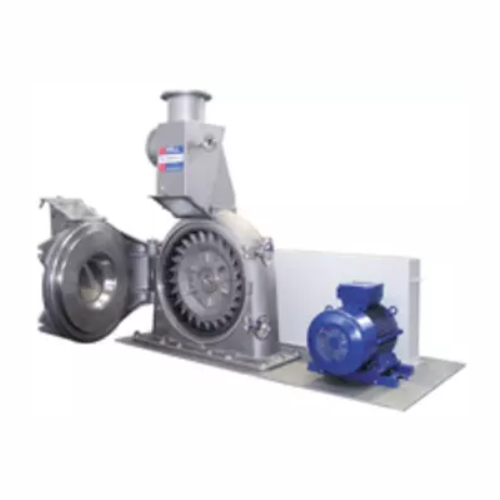

Versatile fine impact mill for soft materials
Achieve precision grinding with flexibility for a wide range of materials, e...
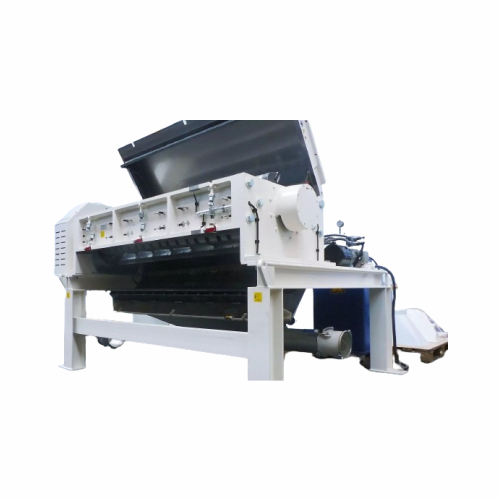

Industrial granulators for plastic recycling
Streamline your recycling operations with a solution that not only reduces en...
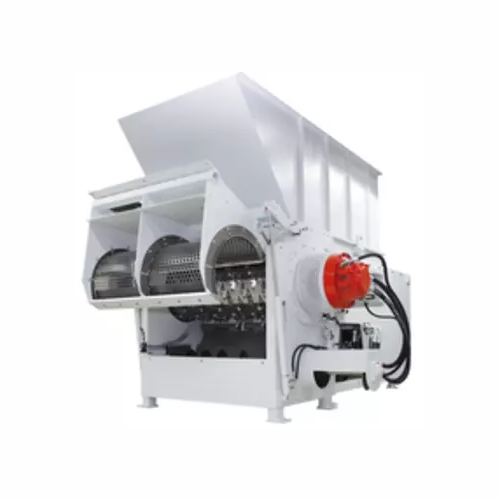

Heavy-duty shredder for difficult materials
Struggling with stubborn materials that resist conventional shredding? This ro...
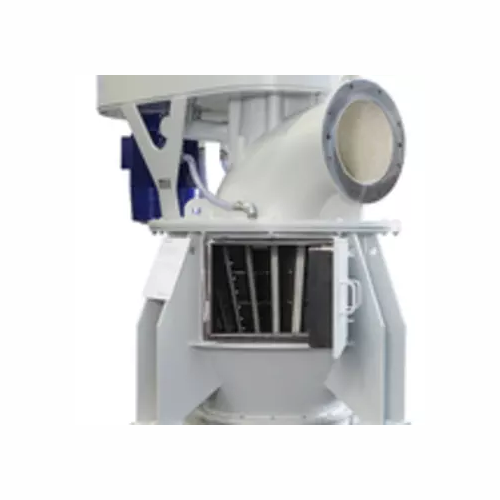

Ultrafine classifier for precise particle separation
Gain precise control over particle size with this ultrafine classifi...
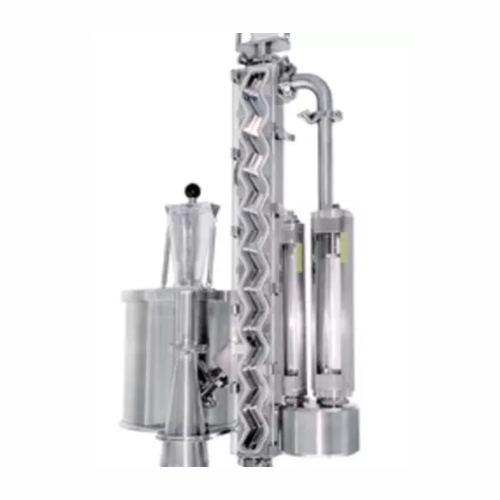

Gravity classifier for precise particle separation
Achieve sharp separations in particle processing with minimal maintena...

Fine impact mills for particle size reduction
Achieve precise particle size reduction with fine impact mills, essential fo...

Classifier mill for ultrafine grinding
Achieve precise particle size distribution and contamination-free processing with th...

Laboratory system for powder and particle processing
When precision in powder processing is crucial, this versatile labor...

Filtration system for Cip cleaning in food production
Optimize your cleaning processes with a state-of-the-art filtration...

Continuous kneader for viscous applications
For engineers tackling high-viscosity challenges, this continuous kneader stre...

Stationary entry packaging system for valve bags
Optimize your packaging workflow with a high-speed, modular filling syste...

High-viscosity continuous industrial kneader for small volumes
Achieve consistent high-viscosity material processing wit...

Laboratory z-arm kneader for high-viscosity materials
Ideal for R&D, this advanced Z-arm kneader efficiently handles...
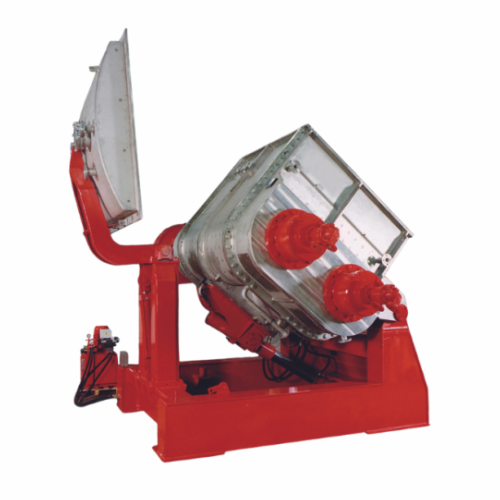

Double z-arm industrial extrusion kneader for high-viscosity processes
Optimize high-viscosity material processing with...
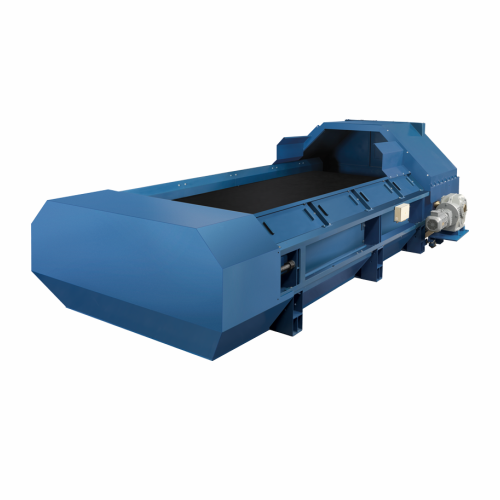

High-speed industrial belt feeder for granular materials
Achieve precise and consistent material dosing in high-flow envi...
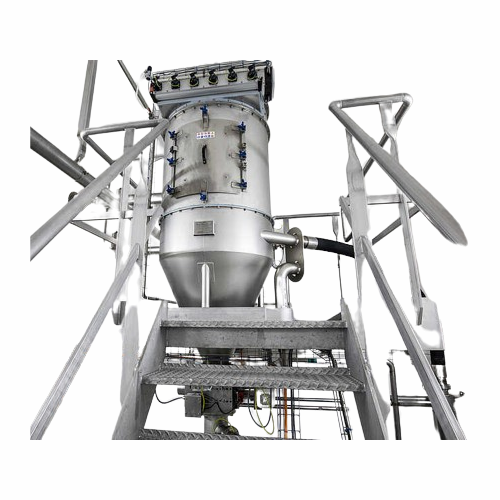

Vacuum pneumatic conveying for infant nutrition
Ensure efficient handling of delicate powders with a versatile vacuum pneu...
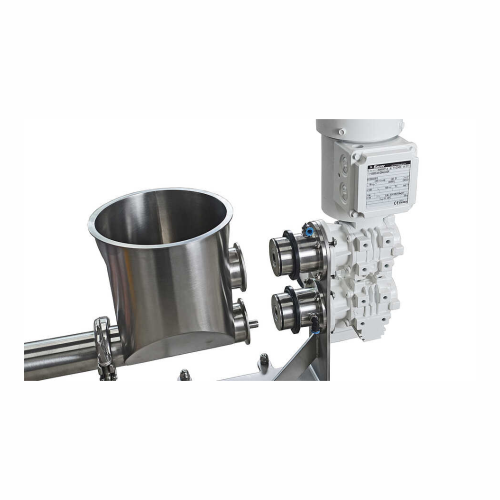

High-precision volumetric feeder for bulk materials
Achieve precise bulk material flow with a solution that ensures consi...

Mini batch blender for pharmaceutical solids
Achieve precise mixing homogeneity with the mini batch blender, perfect for l...

Heavy duty rotary valves for powder handling
Ensure precise material flow and safety in harsh processing environments with...

Contact detection system for rotary valves
Prevent product contamination and equipment damage with instant contact detecti...

Sack tipping station for dust-free bulk material handling
Efficiently manage bulk materials while minimizing dust exposu...
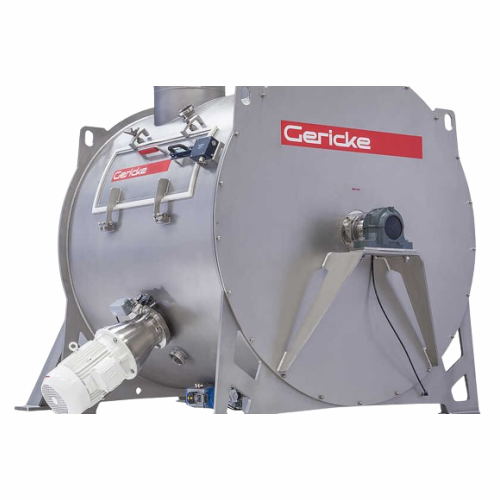

Single shaft batch mixer for chemical and pharmaceutical applications
Optimize mixing efficiency with rapid batch proce...
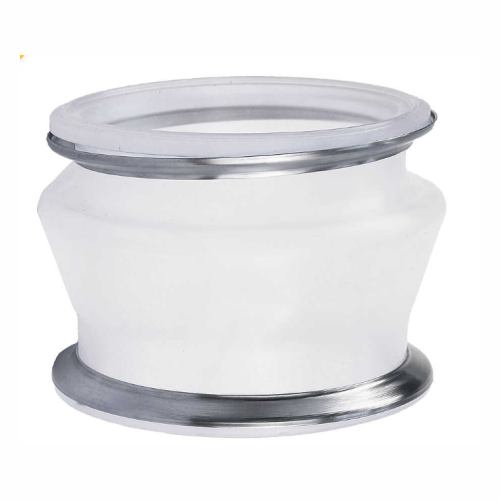

Hygienic flexible sleeves for tri-clamp connections
Ensure seamless, contamination-free transitions between processing st...
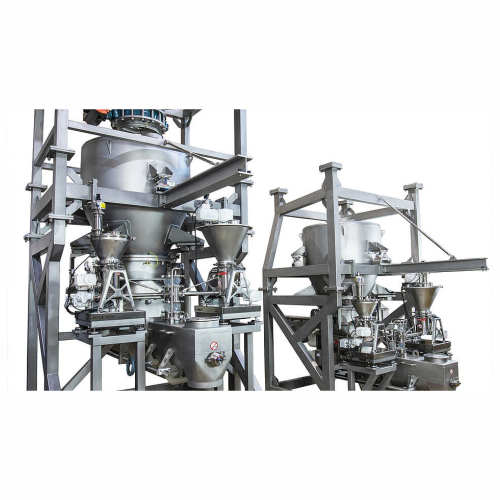

Continuous inline mixing for late product differentiation
Achieve seamless product differentiation with compact inline m...
Conveying controller for dense phase conveying
Streamline your dense phase conveying operations with precise control and m...
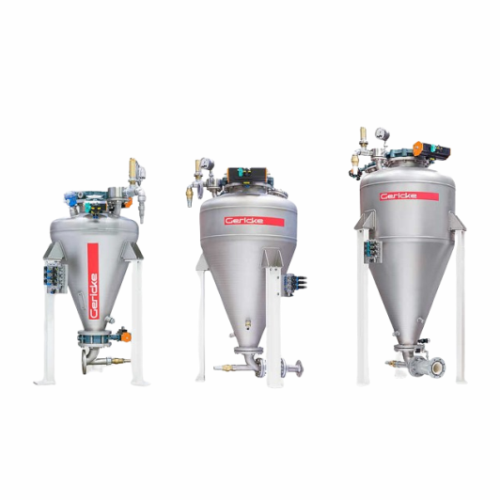

Dense phase pneumatic conveying system for powder transfer
Ensure gentle and efficient material transport with minimal m...
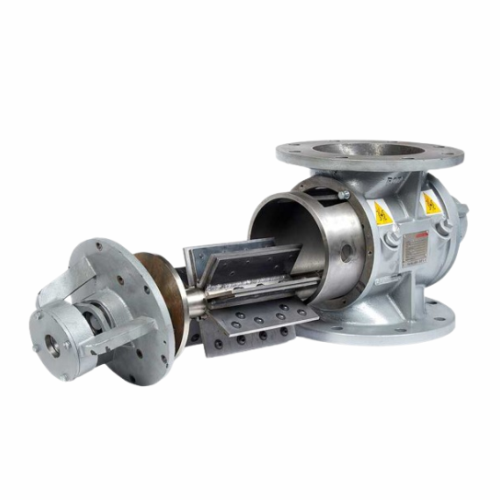

Pneumatic dilute phase conveying system for powders and bulk materials
Optimize your production line’s efficiency...
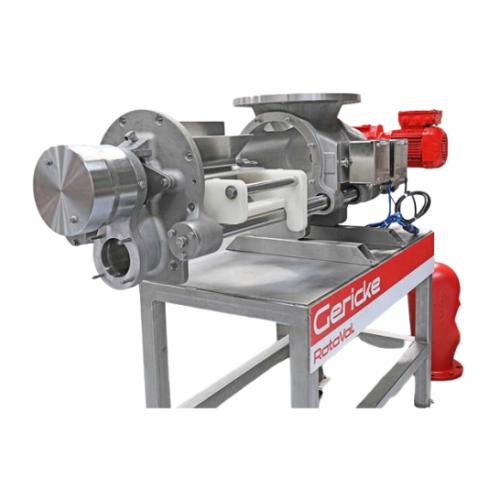

Quick-clean hygienic rotary valves
Ensure seamless cleaning and minimal downtime in your production line with rotary valves...
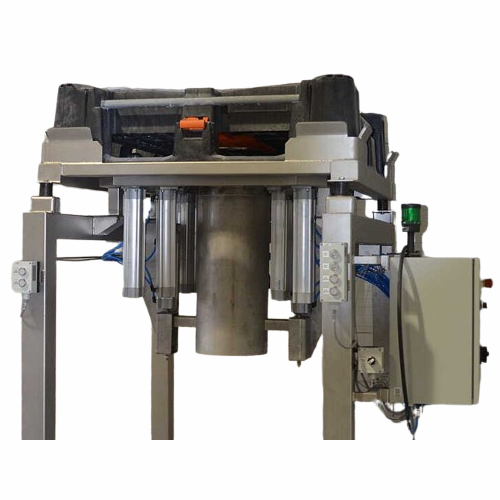

Big bag pallet unloader for bulk products
Efficient and reliable solution for unloading and transporting powders and bulk ...
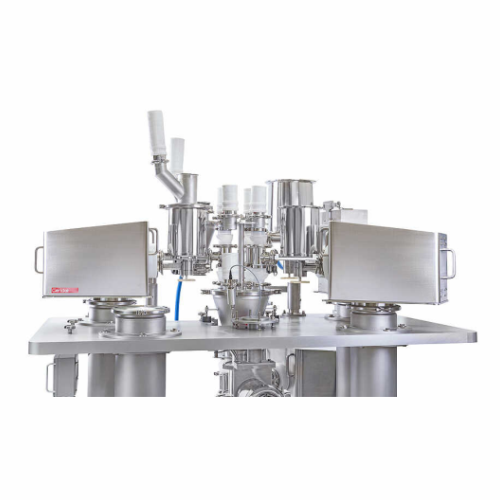

High-precision gravimetric feeders for industrial bulk solids
Achieve unparalleled accuracy in your production line with...
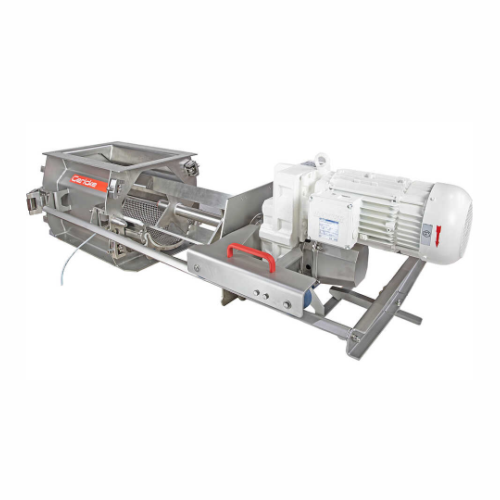

Deagglomerator for consistent particle size reduction
Struggling with inconsistent particle sizes or unwanted lumps in yo...

Continuous mixer for homogeneous blending
Achieve consistent product quality with precise mixing and blending, ideal for a...
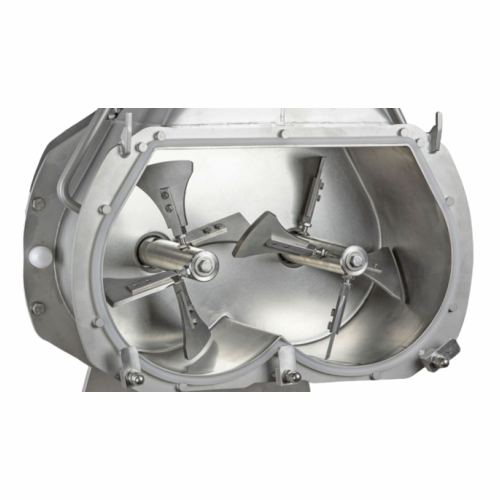

Laboratory mixer for r&d and small batch production
Achieve superior mixing precision for R&D and pilot production w...
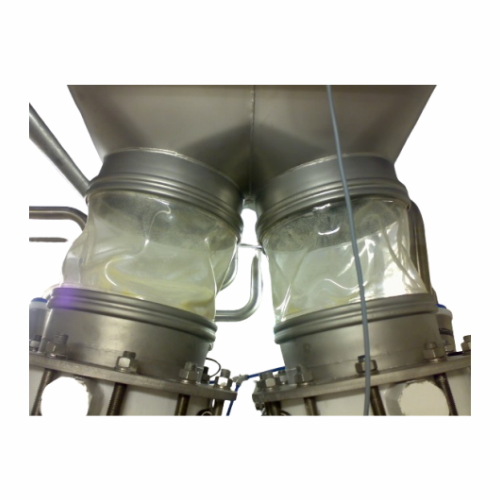

Hygienic flexible sleeves for food and pharmaceutical use
Say goodbye to contamination risks with this tool-free, quick-...
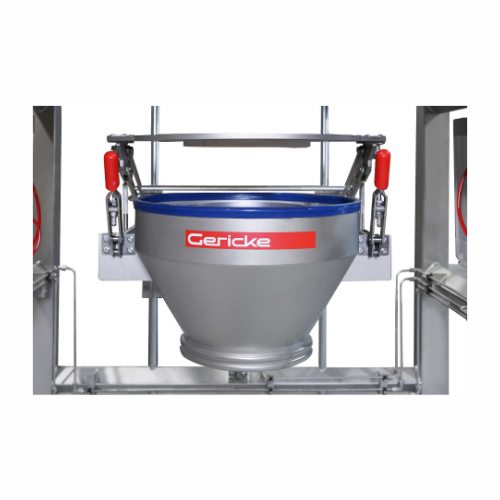

Big bag unloader for industrial bulk materials
Efficiently handle bulk materials with this modular unloading system, desig...
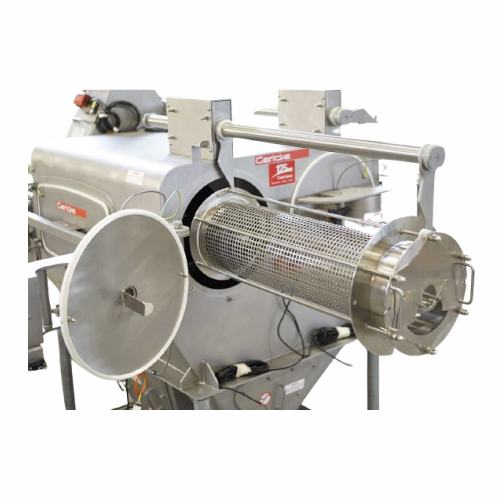

Centrifugal sifter for bulk solids and powders
Achieve precise particle separation and enhance product quality with a solu...
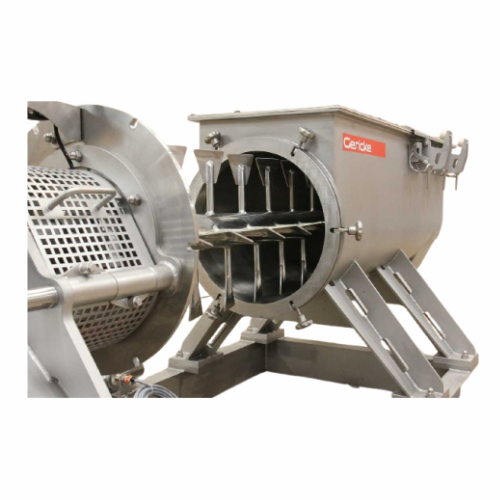

Continuous powder mixer for industrial applications
Achieve precise and efficient integration of powders, granules, and l...
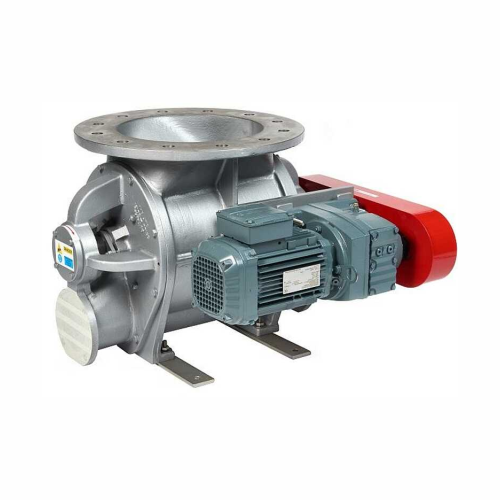

Heavy duty blowing seals for abrasive products
For operations dealing with abrasive materials under high pressure, these r...
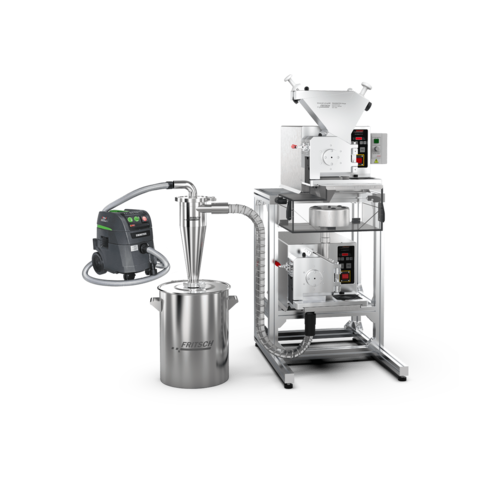

Cutting mill combination for heterogeneous material reduction
Achieve precise size reduction and material separation in ...
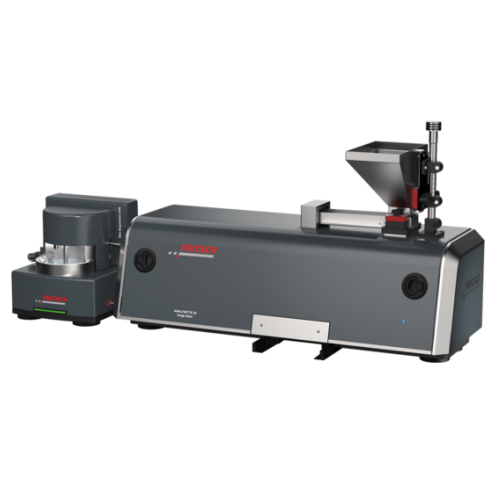

Particle sizing for powders and suspensions
Optimize particle shape and size analysis with rapid, reproducible results for...
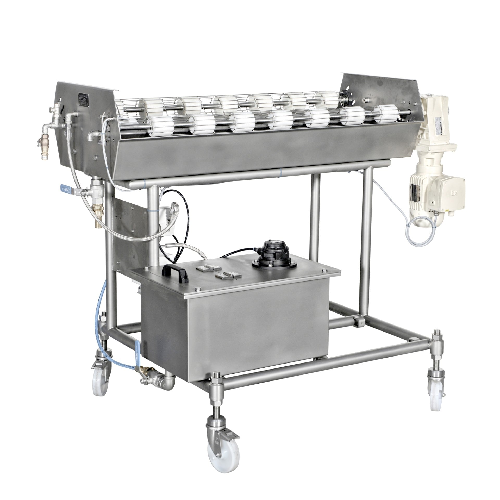

Waxing station for confectionery products
Optimize your product’s final presentation and quality by applying a preci...
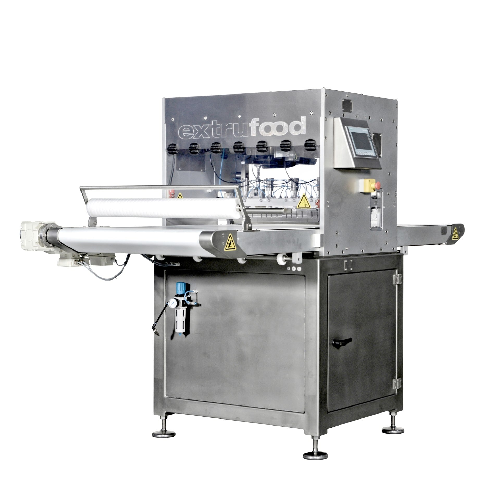

Confectionery cutting system for accurate results
Achieve precision and flexibility in modern confectionery production wi...
Multi-color and flavor confectionery production system
Maximize production flexibility with a single extruder that seamle...
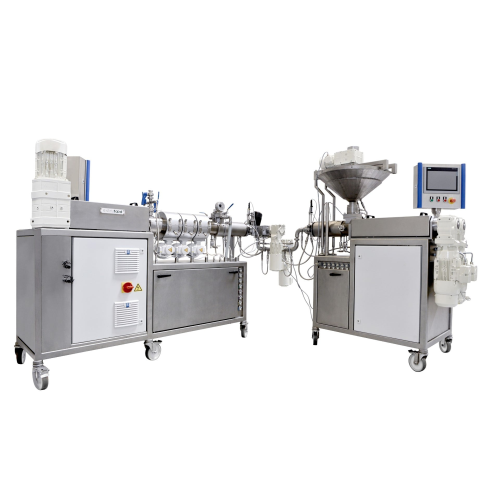

Lab cooking and forming extruders for r&d
Optimize your R&D processes by testing new recipes and improving formulatio...
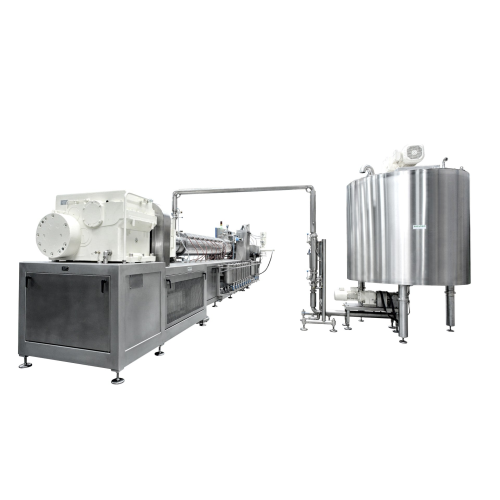

Slurry preparation for licorice production
Ensure a continuous and homogeneous feed of licorice slurry to your extruder, o...
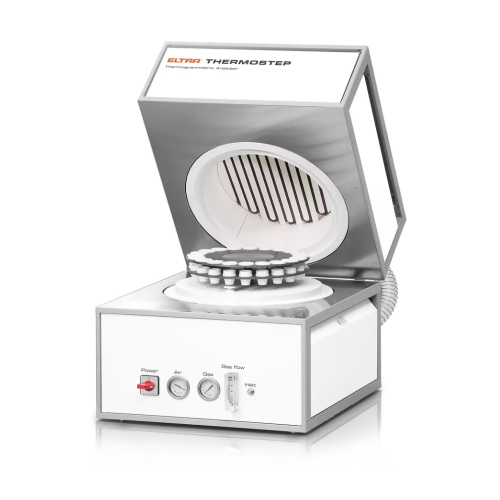

Thermogravimetric analyzer for moisture, ash, and volatiles analysis
Streamline your laboratory analysis with this solu...
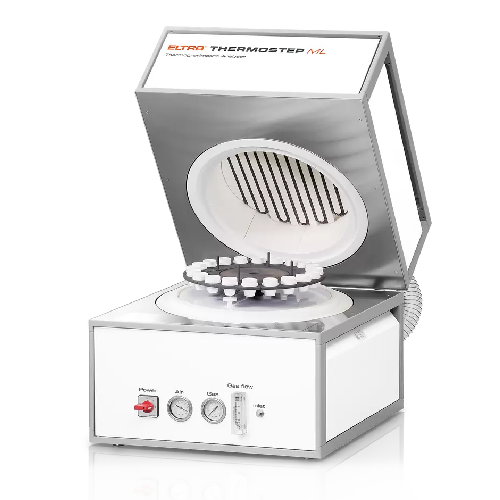

Thermogravimetric analyzer for ash and moisture content analysis
Optimize your production with precise weight loss analy...
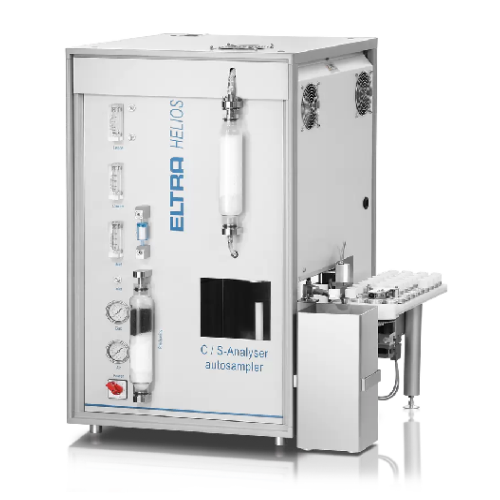

Carbon and sulfur analyzer for organic and inorganic samples
Achieve precise and simultaneous carbon and sulfur analysis...
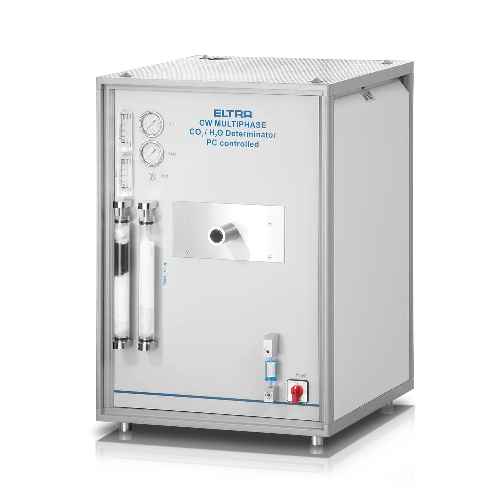

Carbon and water analysis for lime and gypsum
Achieve precise carbon and water measurement in diverse materials like cemen...
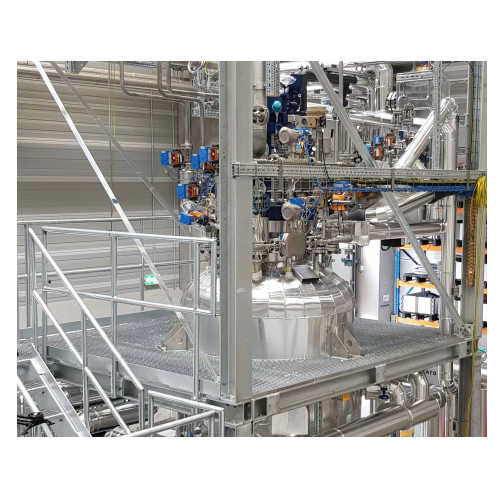

Industrial hydrogenation plant for pharmaceutical raw materials
Optimize your hydrogenation processes with a modular pla...

Laboratory mixer and dryer for solids
Enhance your laboratory capabilities with precision mixing and drying for small batch...
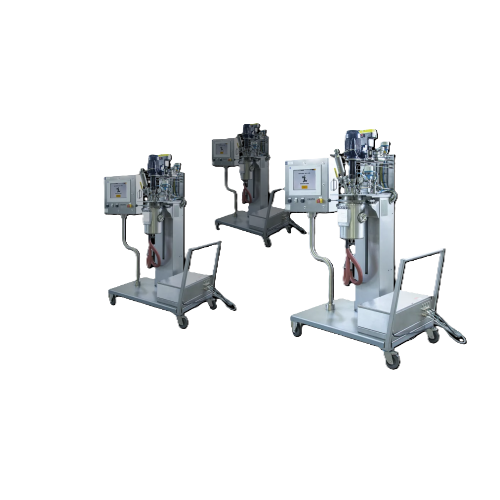

Portable process development unit for gas-liquid reactions
Optimize your gas-liquid reaction processes with a versatile,...
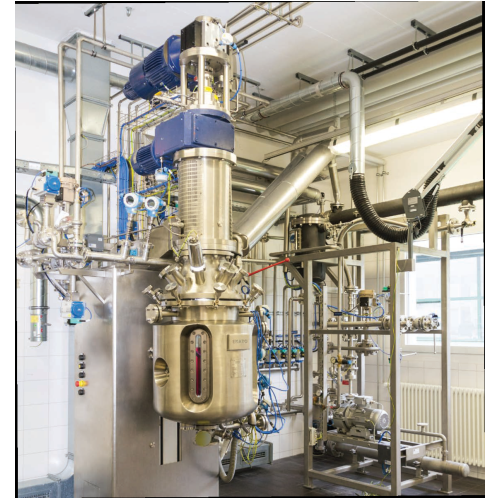

Pilot plant for highly viscous applications
Perfect for R&D, this pilot plant efficiently handles complex mixing and ...
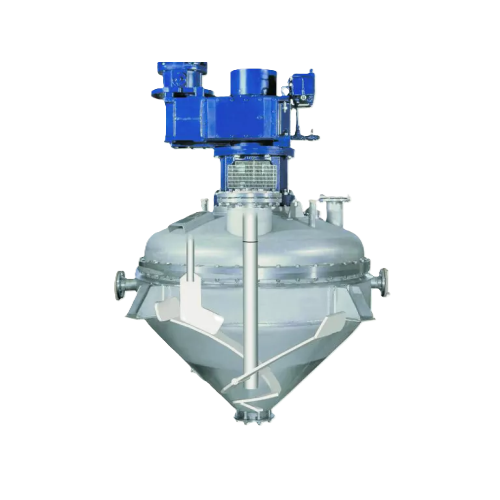

Vacuum dryer for free-flowing and pasty solids
Achieve precise drying and mixing with this vacuum dryer, optimizing heat t...
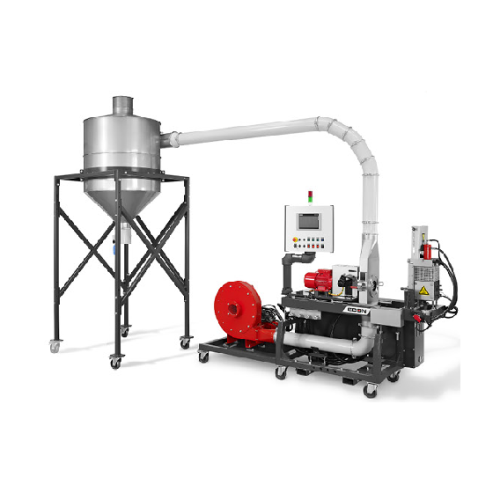

Air pelletizer for wood and natural fiber compounds
Optimize your pelletizing process with air-based cooling and conveyin...
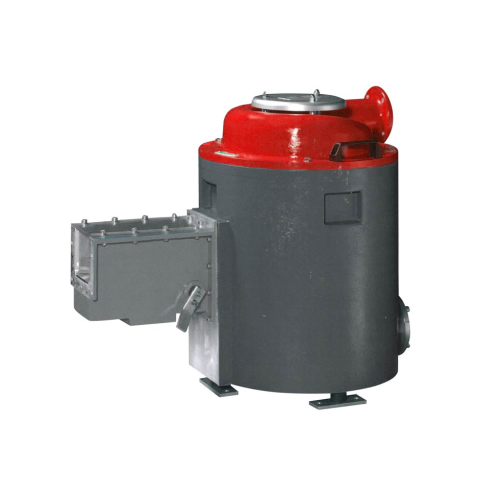

Pellet dryer for industrial recycling applications
Ensure precise moisture control for recycled plastic pellets and flake...
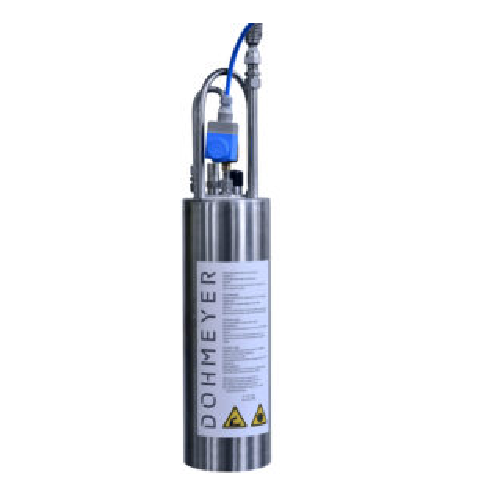

In situ dry-ice snow generator for food and pharma applications
Achieve precise cooling and deburring with this versatil...
Cryogenic immersion bath for rapid freezing
Achieve rapid and intense cooling by immersing products in liquid nitrogen, id...
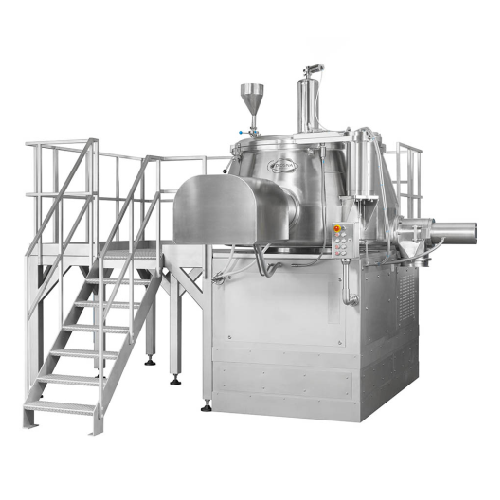

High-capacity universal mixer for industrial applications
Optimize your batch processing with a versatile high-speed mix...
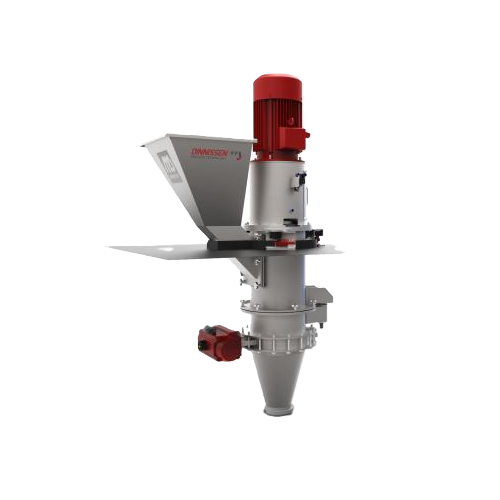

Industrial shredder for diverse material reduction
Achieve precise and efficient material resizing for diverse applicatio...
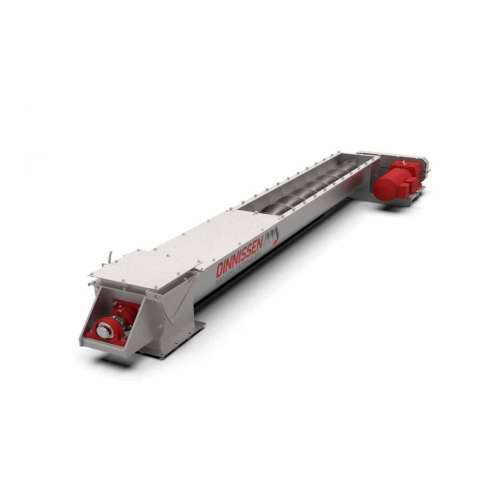

Vertical transport for bulk goods
Efficiently move bulk goods vertically with minimal energy usage, ensuring seamless integ...
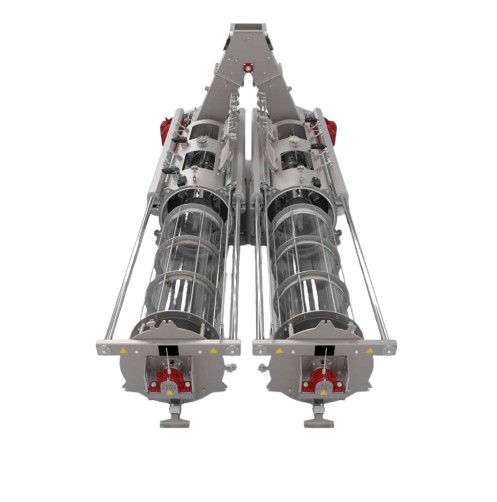

Industrial centrifugal sifter for solid particulate materials
Quickly and accurately sift a wide range of powders and gr...

Surge bins for material handling
Ensure efficient material flow and storage in your production line with surge bins that fea...

Batch weigh vacuum receiver
Optimize precision in ingredient batching and streamline your production line with advanced vacu...

Hydrocarbon liquefaction process for plastic waste
Transform plastic waste into valuable liquid hydrocarbons with a conti...

Optical sorter for coffee, grains, nuts, and plastic flakes
Ensure precise defect detection and foreign material removal...
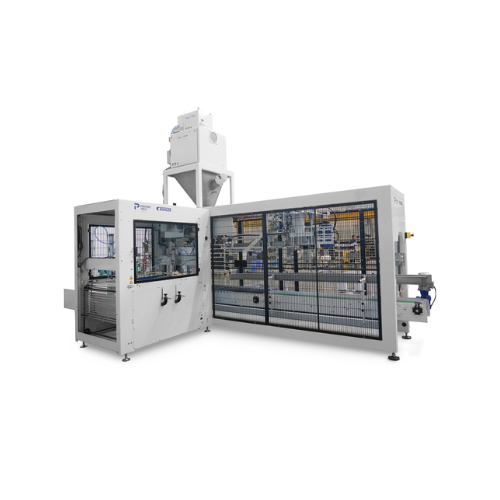

Fully automatic bagging station for granular products
Streamline your packaging line with a high-speed solution designed ...
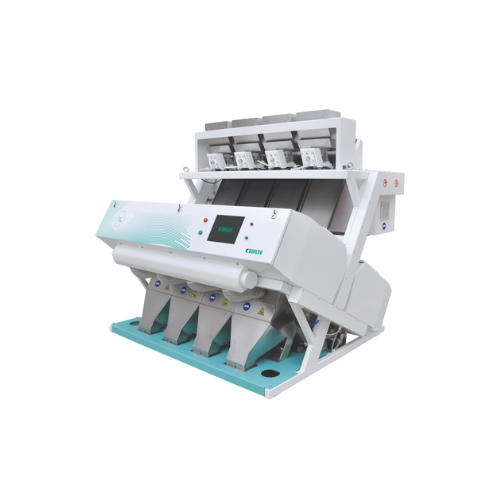

Optical sorter for grain and seed sorting
Ensure precise defect detection and efficient sorting of grains, pulses, and see...
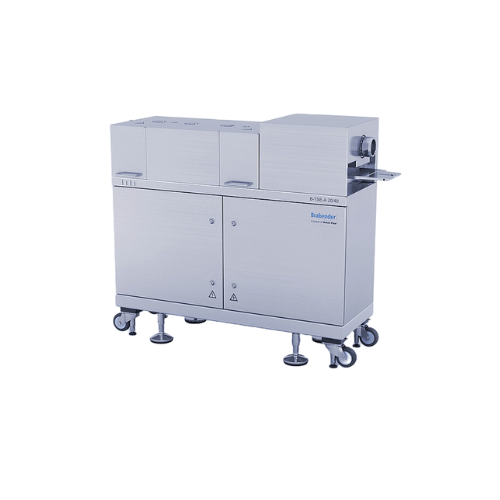

Lab-scale twin screw extruder
Optimize your material testing and production efficiency with our versatile twin screw extrude...
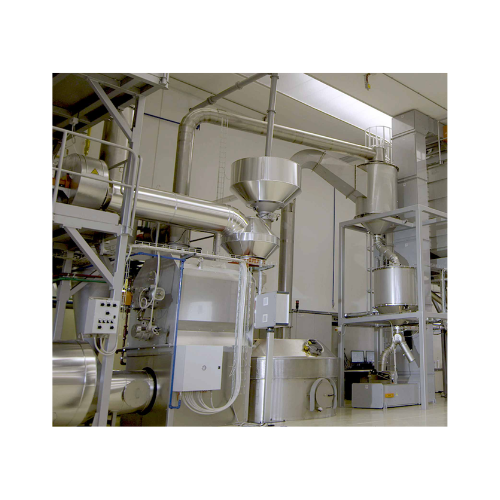

Coffee roasting system
Optimize your coffee production from green beans to finely ground espresso with this versatile system,...

Flour handling plant for pasta production
Streamline your production with precision handling and processing of flour for p...

Raw material handling systems for plastic and pharmaceutical industries
Effortlessly manage and optimize the handling a...

Rotary mill for tough and fibrous materials
Achieve precise material reduction with our Rotary Mill, ideal for transformin...
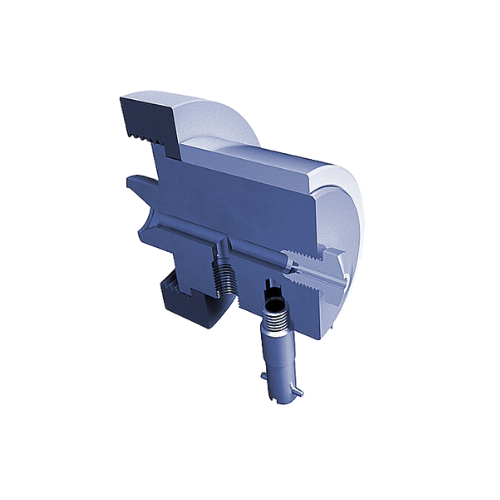
Round strand die head for precision extrusion
Achieve precise extrusion control across varied applications with our custom...

Lab- and pilot-scale twin screw extruders
Optimize your material development and testing with versatile extruders, ideal f...
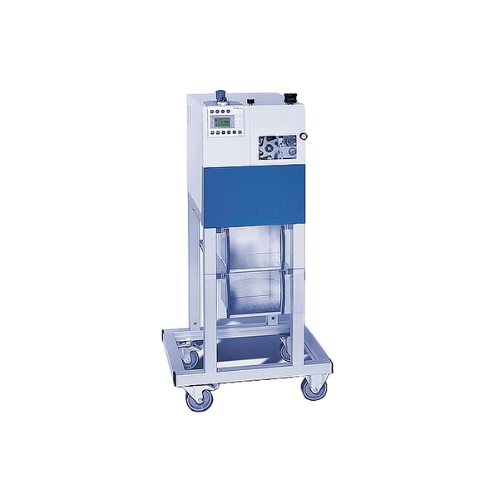

Pelletizer for consistent plastic pellet production
Achieve precise pellet sizes consistently with this flexible solution...
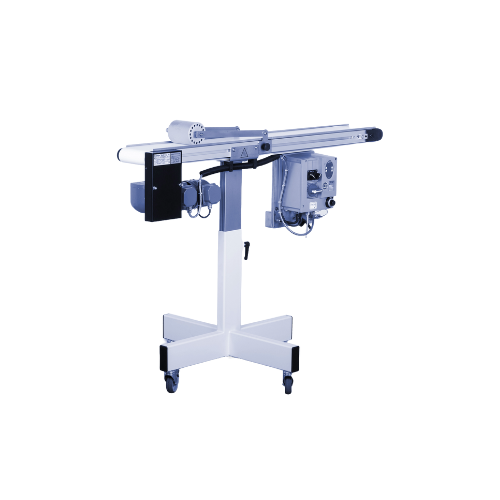

Conveyor belt for extruded profiles
Efficiently transport and convey extruded profiles with precision through adjustable sp...
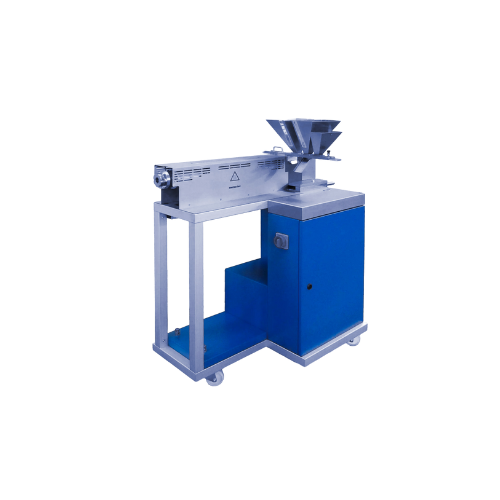

Polymer extrusion testing extruder
Optimize your polymer and plastic production with precise extrusion testing, simulating ...
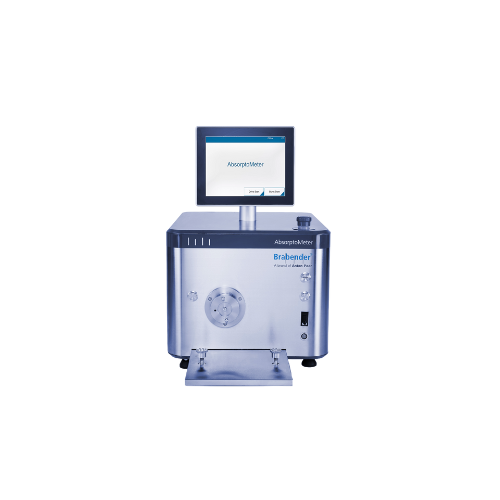

Oil absorption testing instrument for carbon black and silica
Accurately measure oil absorption in powders to enhance fo...
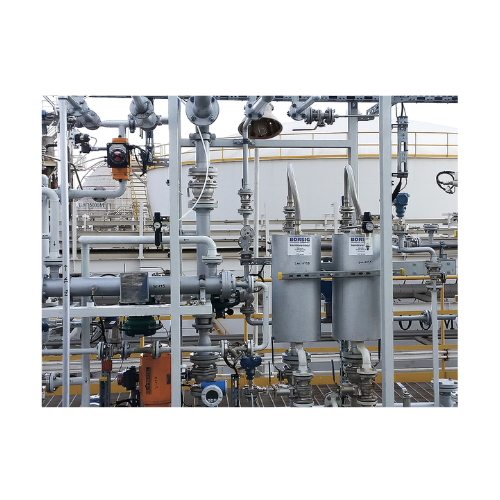

Monomer recovery unit
Effectively recover valuable monomers while ensuring high purity and low operating pressures, ideal for...
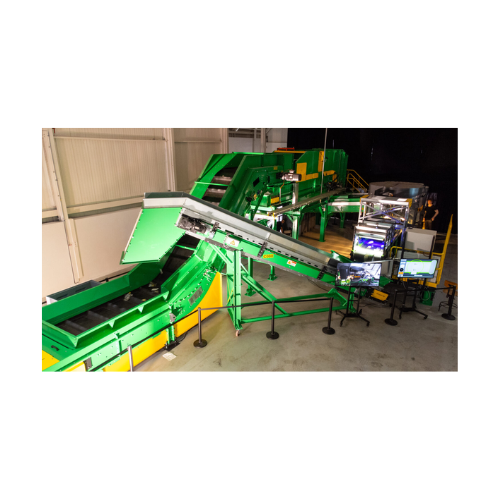

Troughed belt conveyor for efficient material transport
Effortlessly transport a variety of materials, from glass to muni...
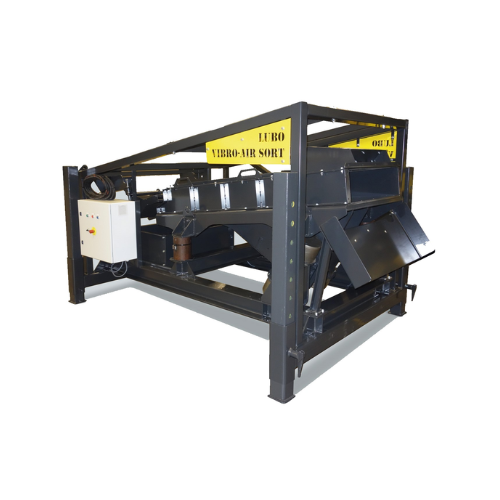

Density separator for recycling applications
Efficiently separate light and heavy materials with minimal density differenc...
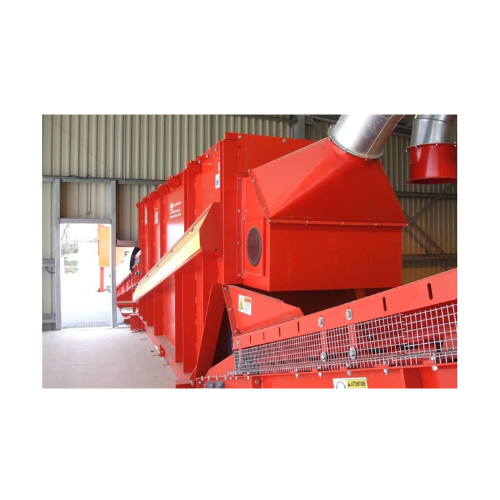

Fines starscreen for construction and demolition waste
Efficiently separate construction and demolition waste into valuab...
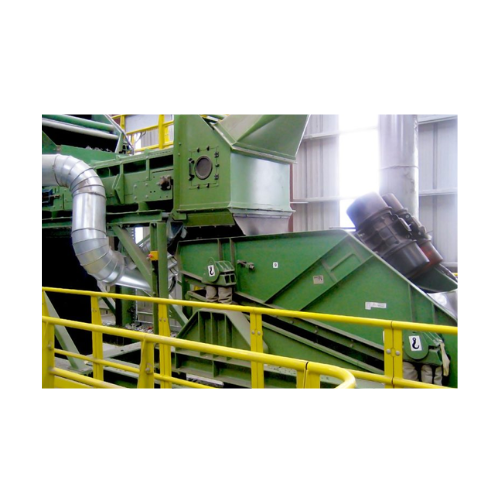

Glass cleaning system for recycling applications
Optimize glass recycling by efficiently removing contaminants and minimiz...
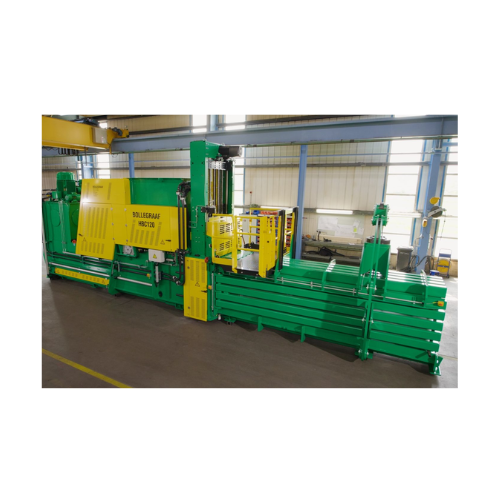

Industrial balers for recycling applications
Effortlessly transform various waste streams into compact, export-ready bales...
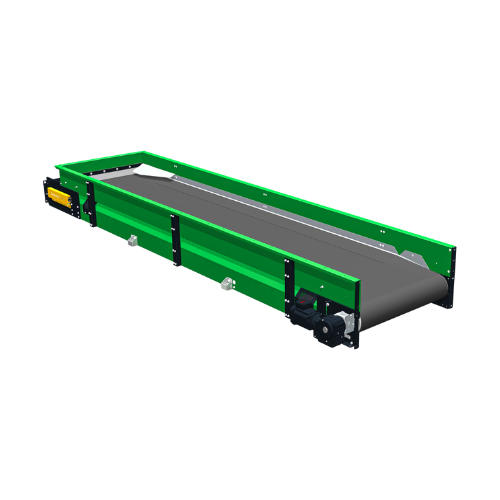

Sliding belt conveyor for sorting light, voluminous materials
Efficiently sort and convey light, voluminous materials wi...
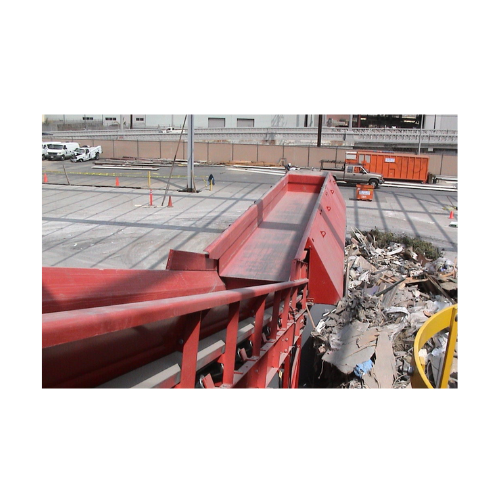

Vibrating feeder for sorting system
Efficiently manage waste streams with a vibrating feeder that optimizes material flow f...
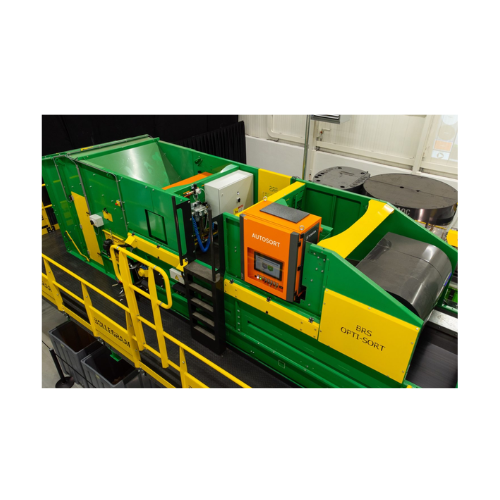

Integrated optical sorting unit for lightweight materials
Optimize your processing of lightweight materials by achieving...
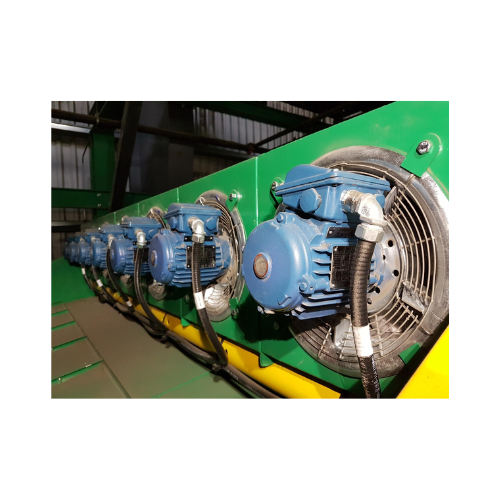

Optimize optical sorter performance
Enhance your optical sorting line capacity and material purity with advanced air displa...
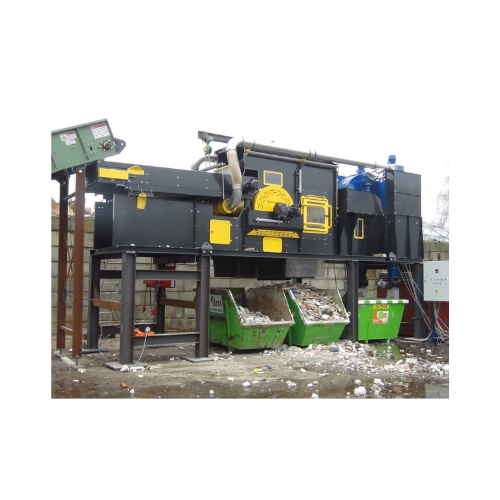

Air drum separator for heavy and light material separation
Effectively separate heavy and light materials with minimal e...
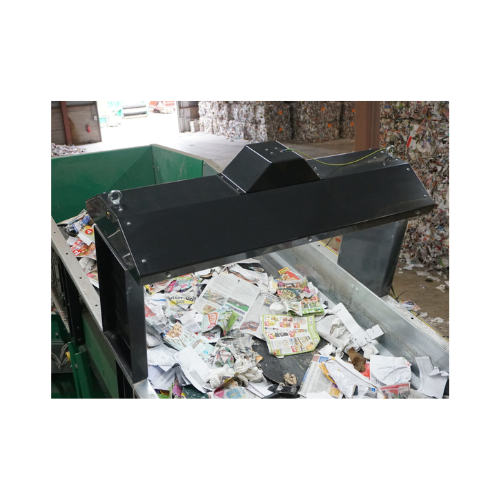

Optical analytics tool for material flow and composition
Optimize your waste management with real-time data analysis and ...

Anti-wrapping starscreen for material sorting
Tackle film, tape, and textile wrapping issues in your sorting process with ...

Commingled material separator
Streamline your recycling operations with precise separation of paper, cans, and glass, reduci...

Film separation system for recycling processes
Facing challenges with film removal in recycling streams? Optimize your pre...

V shape mixer for solids and powders
Ideal for preserving the delicate structures of fragile materials, this mixer ensures ...
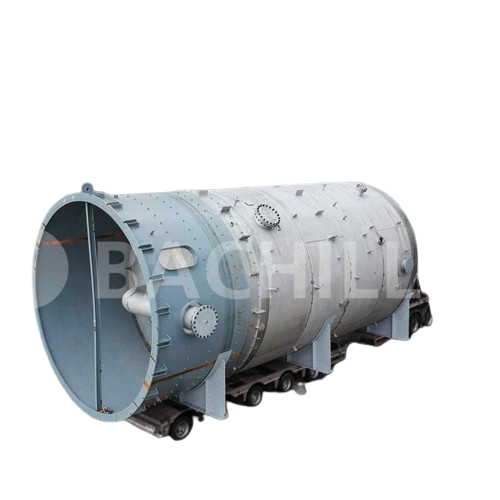

Custom pressure vessels and tanks
For industries demanding precise storage and processing, our tailor-made pressure vessels...

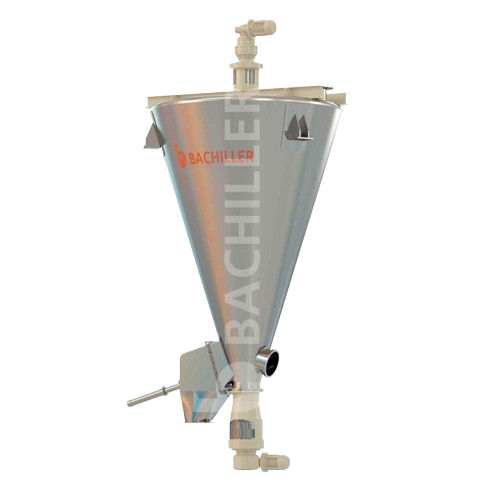
Vertical ribbon mixer for solids and powders
Achieve rapid, uniform mixing of powders and solids while preserving particle...
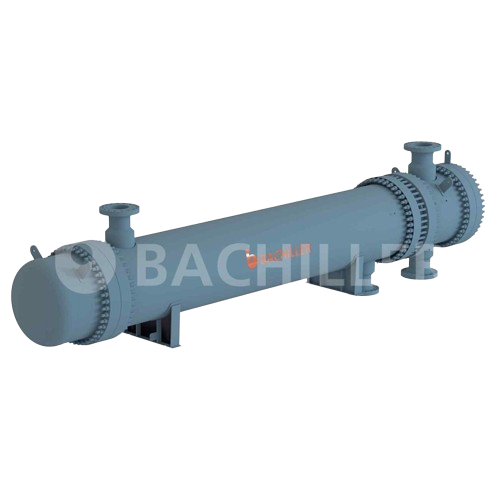

Shell and tube heat exchangers
Efficiently manage heat transfer in your production line with custom-engineered shell and tub...

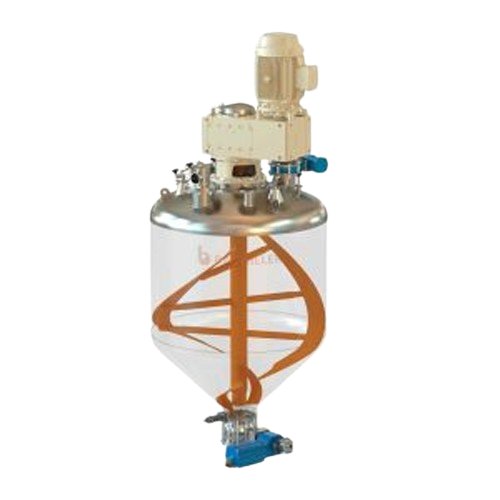
Conical screw mixer for solids and powders
Achieve precise homogenization of your solid and powder mixtures with minimal e...
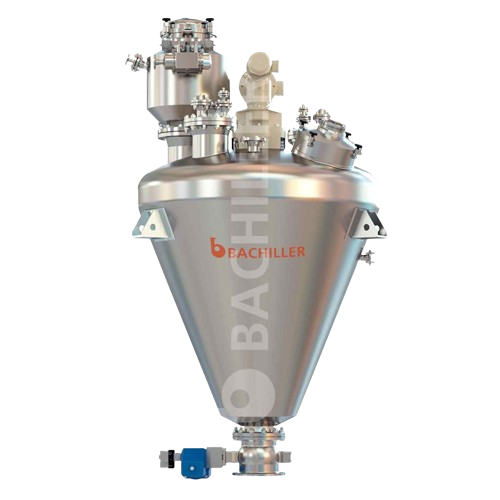

Vertical conical screw vacuum dryer
Achieve precise moisture control with ultra-vacuum batch drying, ideal for thermo-sensi...
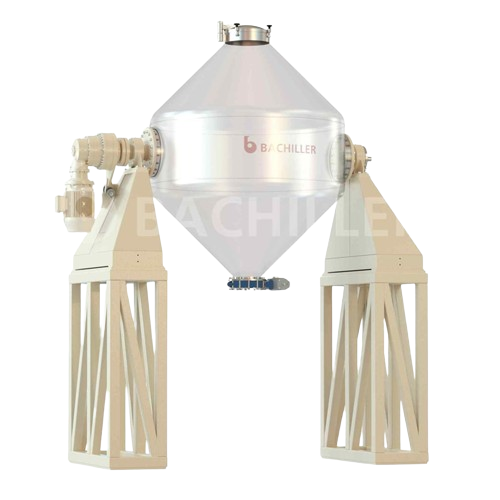

Double cone mixer for powders and solids
Ensure gentle mixing of fragile powders and solids with a low-speed, non-forced bl...
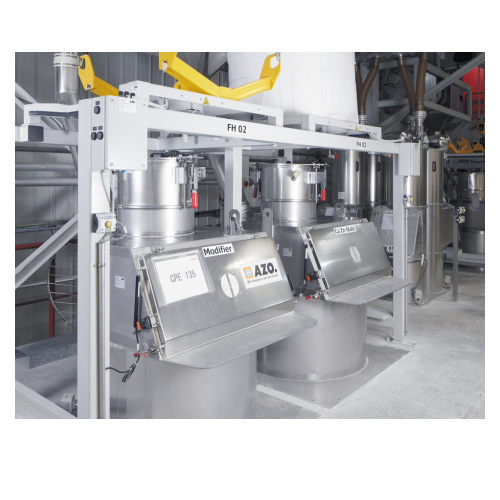

Integrated pickup station for bagged products and big bags
Streamline the handling and transition of bulk materials with...
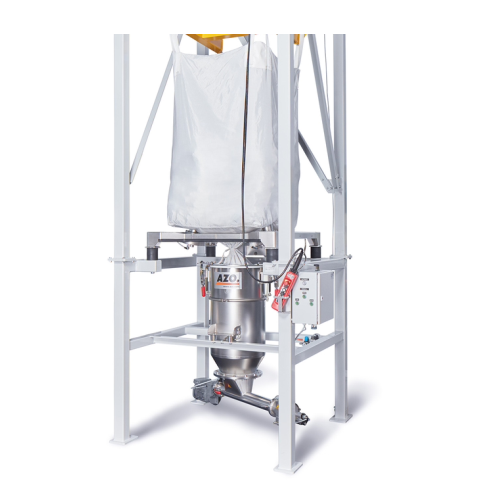

Modular big bag discharge station for bulk material handling
Streamline your bulk material handling with a customizable ...
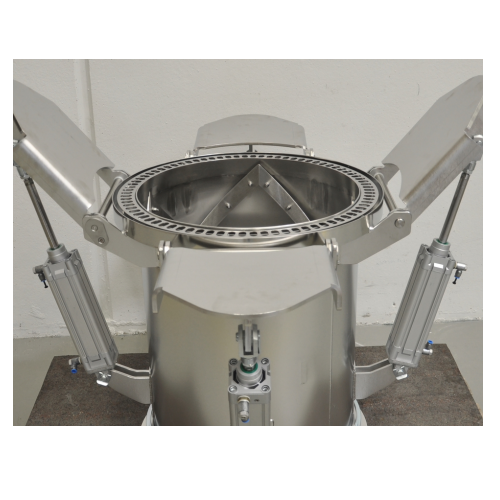

Dust-free big bag connection system for bulk solids
Eliminate dust and ensure reliable discharge with this vacuum docking...
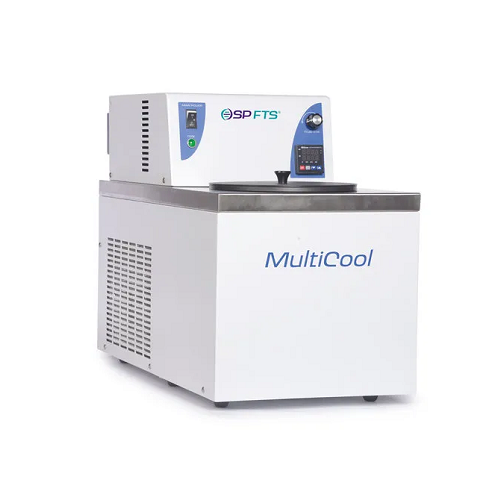

Low temperature bath for precise temperature control
Achieve precise sample freezing from -80°C to 100°C with this low te...
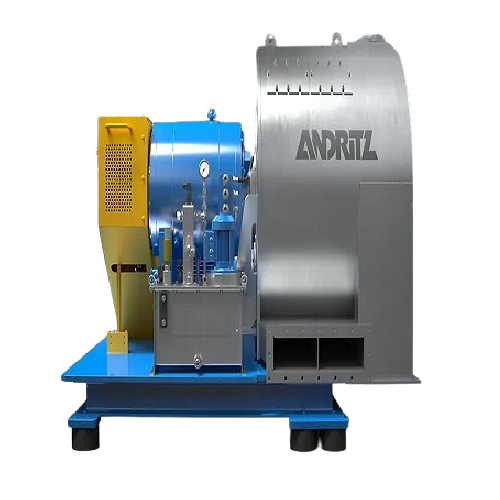

Screen scroll centrifuge for flexible dewatering
Ensure maximum uptime and consistent dewatering performance amidst variab...
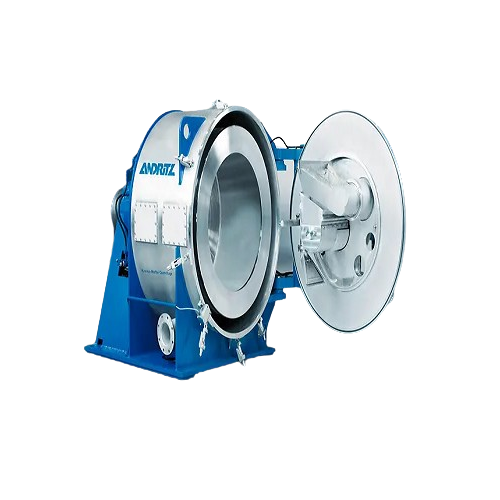

Horizontal peeler centrifuge for filtration
Optimize your batch processing with a centrifuge designed for high-speed, effi...

Vertical vacuum dryer and mixing reactor
Achieve precise control over drying and mixing processes with a versatile unit des...
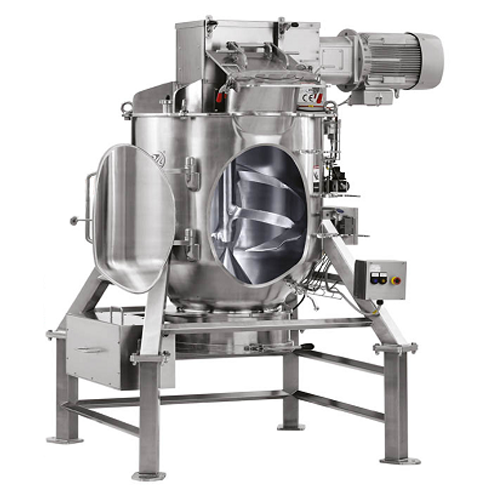

Precision powder mixer for baby formula
Achieve consistent texture and rapid homogenization for sensitive powder blends lik...
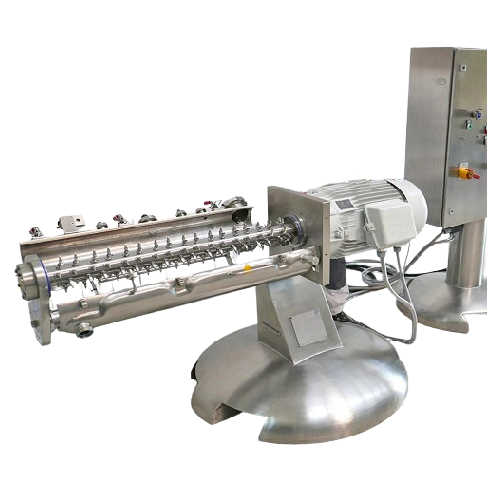

Continuous granulator for powdery goods
Achieve uniform particle size and structure with a continuous granulation process t...
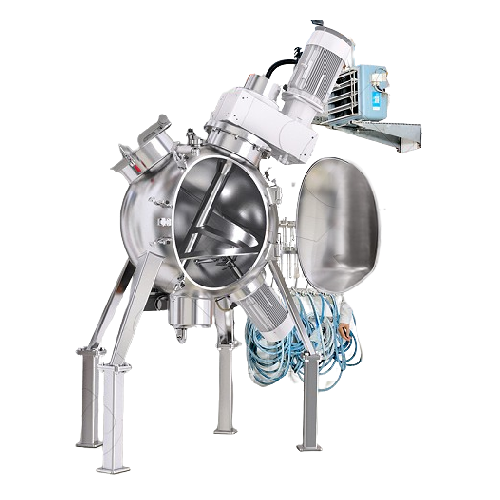

Spherical mixer for industrial mixing applications
Experience precise and efficient mixing with this hollow spherical mix...
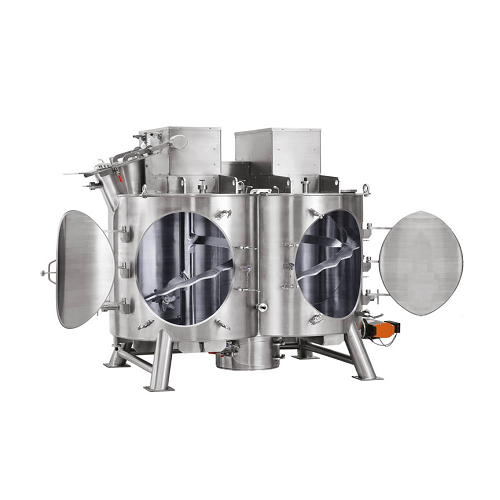

Vertical twin-shaft mixer for dry, moist, and viscous materials
Achieve consistent mixing and blending of diverse materi...
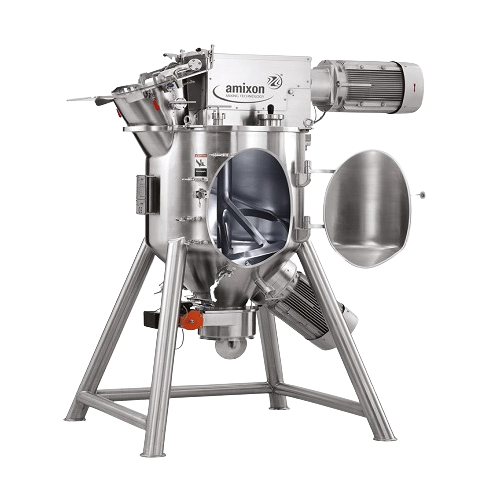

Conical mixer for dry, moist, and viscous materials
Achieve optimal mixing consistency and precision for diverse material...
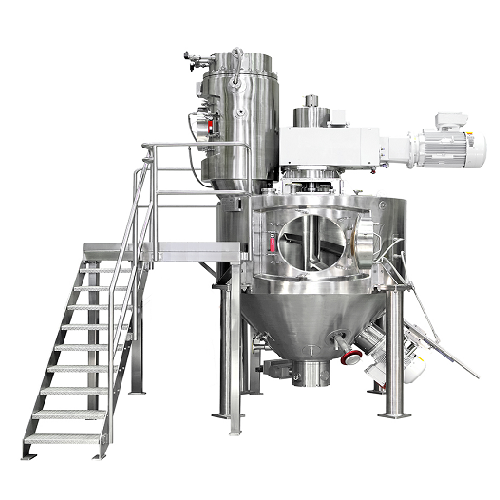

Conical vacuum dryer for viscous materials
Achieve precise drying and mixing of moist and viscous materials, ensuring cons...
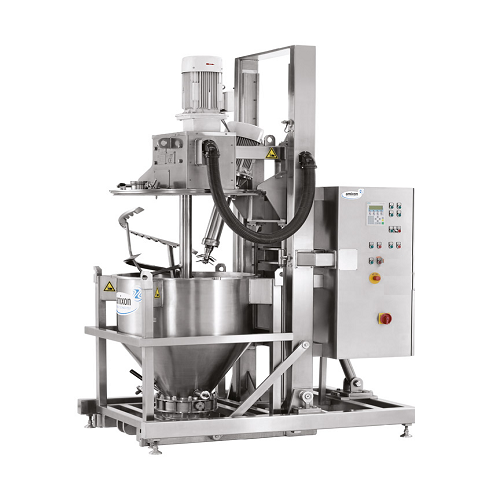

Container mixer for dry and moist materials
Achieve exceptional mixing quality with variable filling levels, ensuring cons...
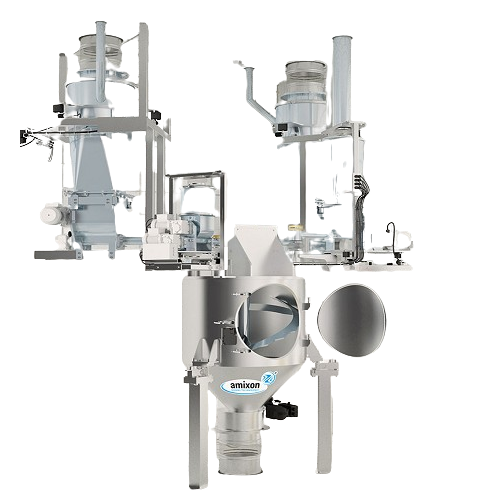

Continuous powder mixer for dry, moist and suspended goods
Achieve precise homogenization and deagglomeration with a con...
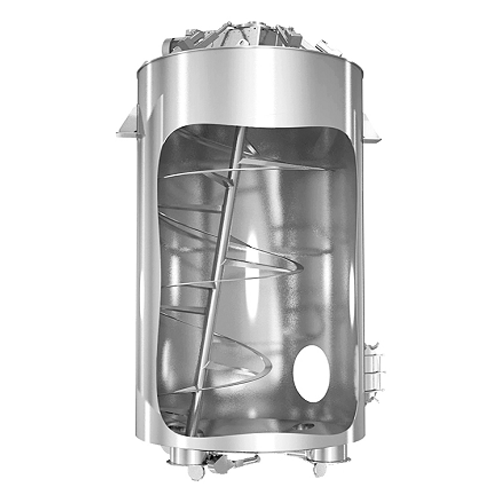

Large batch gyraton® mixer for homogenizing moist and poorly flowing materials
Optimize your production line with this...
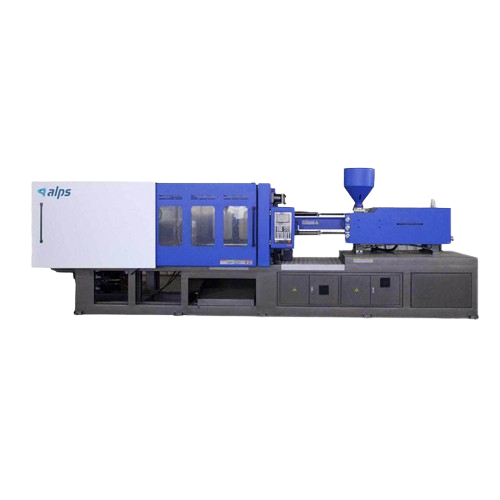

Automatic plastic injection moulding machine
Enhance your production line with this high-precision injection moulding mach...

Indirect drying drums for solvent-based products
Optimize energy use and safety with our indirect drying drums, ideal for ...
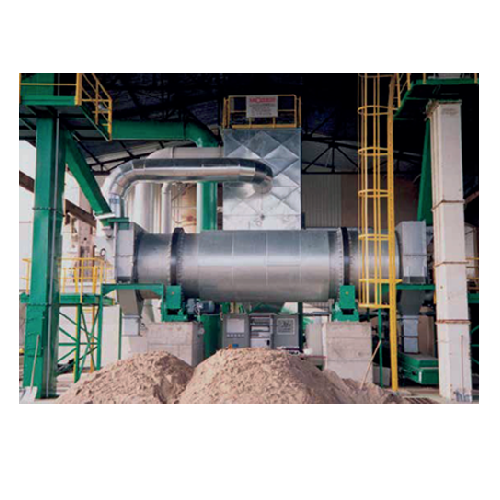

Industrial drum dryer for bulk solids
Optimize your production line with high-throughput drying for varied particle sizes, ...

Flash dryer for high-moisture bulk materials
Tackle high-moisture challenges head-on with rapid drying solutions that effi...
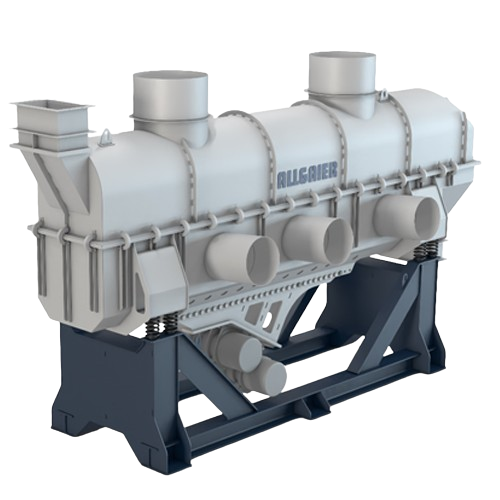
Fluidized bed dryer for industrial materials
Enhance product quality and energy efficiency with fluidized bed dryers, opti...

Industrial auger sack filler for large bags
Designed to efficiently fill large bags and sacks, this advanced filling machi...

Compact marine boiler economizer for auxiliary engines
Efficiently reclaim waste heat from auxiliary engine exhaust to bo...

Oil and gas-fired industrial boiler
Enhance steam production efficiency with a robust three-pass combustion system designed...

High-efficiency brazed plate heat exchanger
Optimize your thermal processes with compact, high-efficiency heat exchangers,...
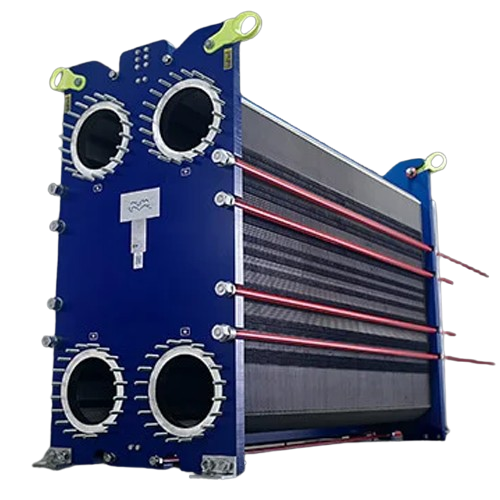
Gasketed plate-and-frame heat exchangers for industrial applications
Optimize your production with precise thermal mana...

Gravimetric batch blender for precise material handling
Achieve precision in blending complex regrind materials and polym...

Positive/negative pressure temperature control unit for cooling circuits
Ensure precise temperature regulation and prev...

Compact water temperature control unit
Achieve precise temperature control in cramped production spaces, enabling consisten...

Water temperature control unit for production applications
Enhance your production efficiency by precisely managing wate...

Volumetric additive feeders for injection and extrusion processes
Ensure precise and consistent blending of color conce...

Extrusion control units for high precision manufacturing
Optimize your extrusion process with precision control over thro...

Industrial vibrating extractor for homogeneous product conveyance
Ensure consistent flow of dry bulk materials with a v...

Food product sifter
Ensure precise separation with vibratory sifters designed for continuous operation, delivering gentle han...

Big bag loading station for bulk product handling
Efficiently manage big bag handling with a system that combines hoistin...
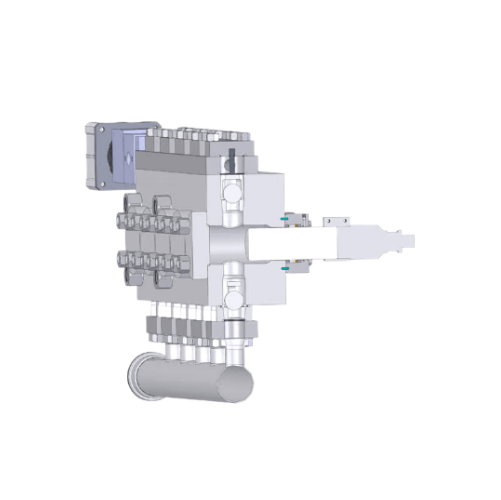
High pressure homogenization for polymer nanodispersions
Effortlessly handle challenging products with fibers or solid pa...

Fluid bed drying system for wet powder chemicals
Achieve efficient large-scale drying and cooling of wet powder chemicals ...

Negative pressure filter for fine dust particles
Ensure efficient air purification and dust collection in your production ...

Short base skirt silo for bulk material storage
Optimize your bulk material handling with adaptable discharge and rapid lo...
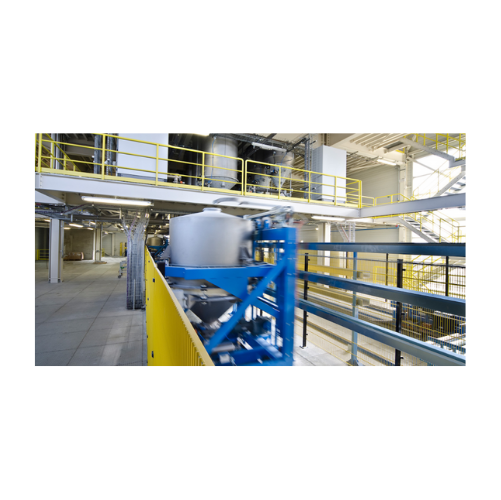

Plastic processing systems for high plant availability
Achieve unparalleled throughput and efficiency in your production ...
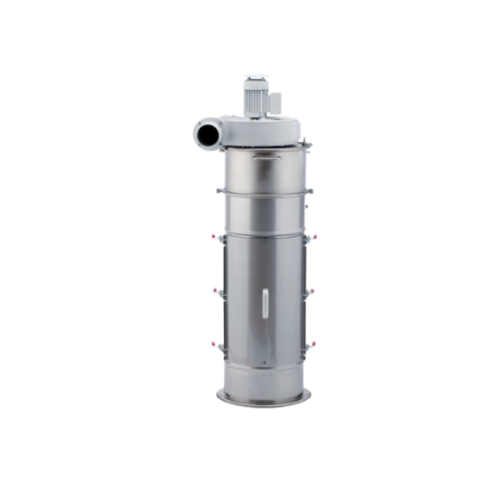

Industrial fine dust particle ventilation filter
Optimize your production line with a modular filtration system designed t...
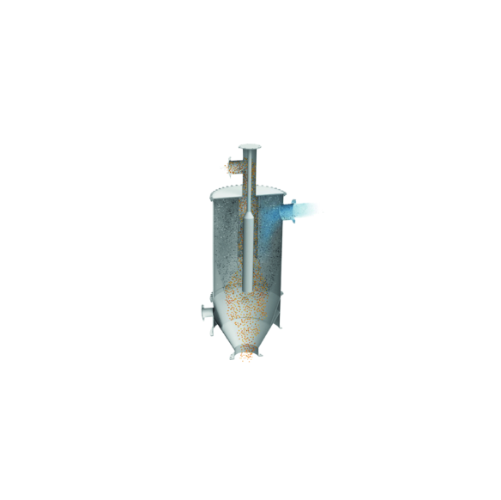
High-efficiency pellet dust separator
Achieve unparalleled separation efficiency in your polymer production line by removin...
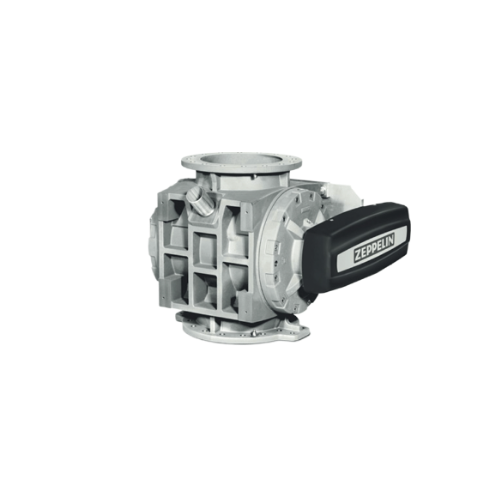

Rotary feeder for bulk material conveying
Enhance your material flow with precise metering and efficient conveying, ensuri...
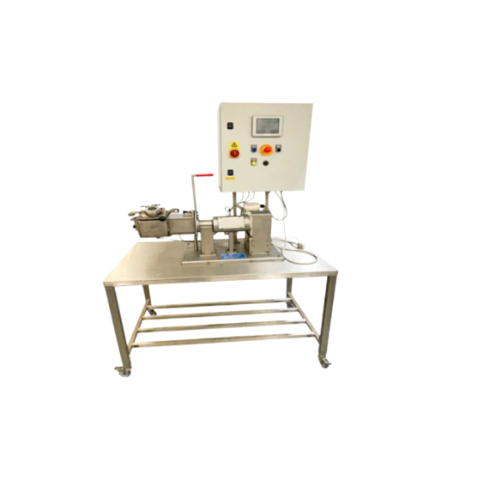

Processing vessel for liquid, sauce, or cream products
Efficiently mix and integrate liquid, cream, or slurry products wi...
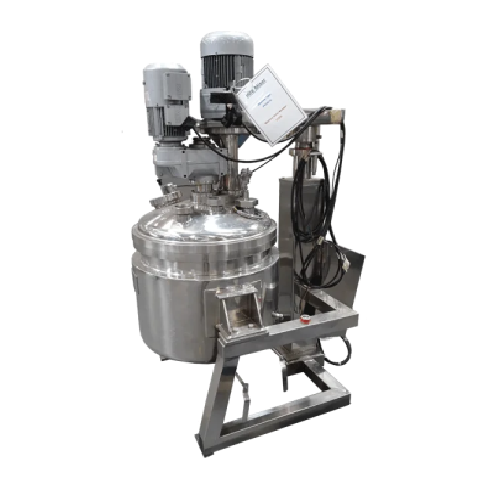

Mixing vessel for liquid, sauce, and cream products
Maximize efficiency in your production line with a versatile solution...
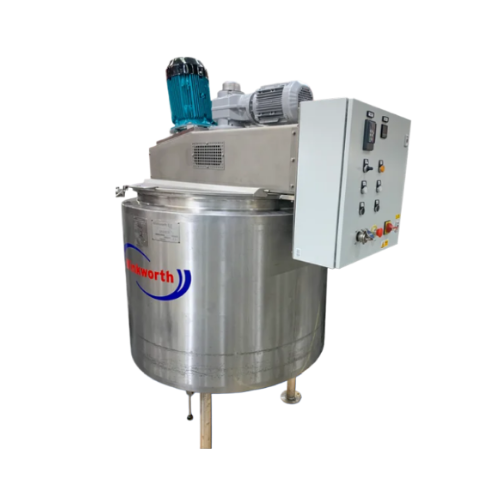

Pv processing vessels for liquid and cream mixing
Optimize your mixing operations with versatile processing vessels desig...
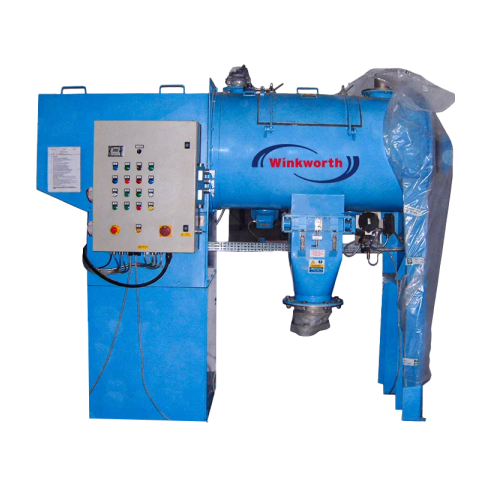

High-speed mixer for homogenous mixing of powders and pastes
Achieve rapid and precise mixing with high-speed dispersion...
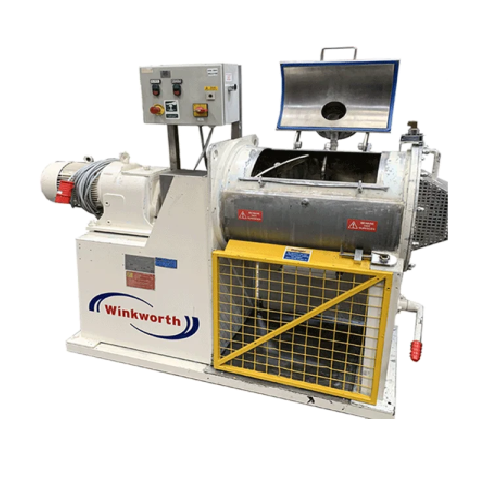

Industrial rapid turbulent mixer for homogeneous mixing
Achieve unparalleled homogeneity with rapid turbulent mixing, ess...
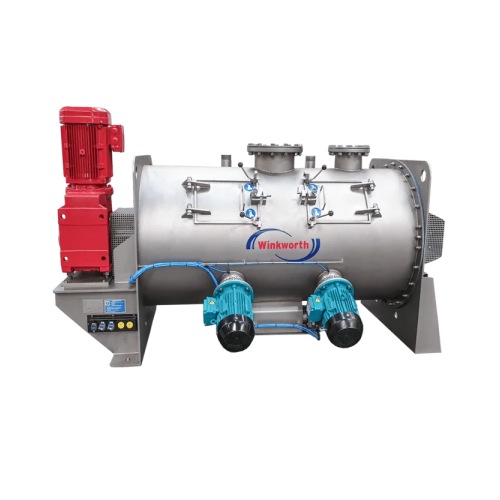

High-speed mixer for industrial mixing applications
Achieve rapid, consistent mixing and dispersion across diverse materi...
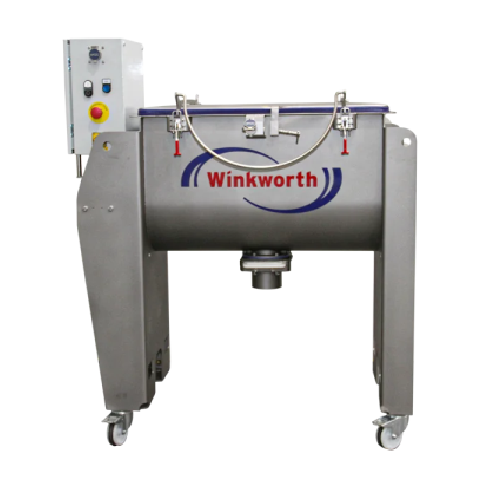

Horizontal shaft mixer for free-flowing materials
Achieve consistent mixing of diverse free-flowing materials with a reli...
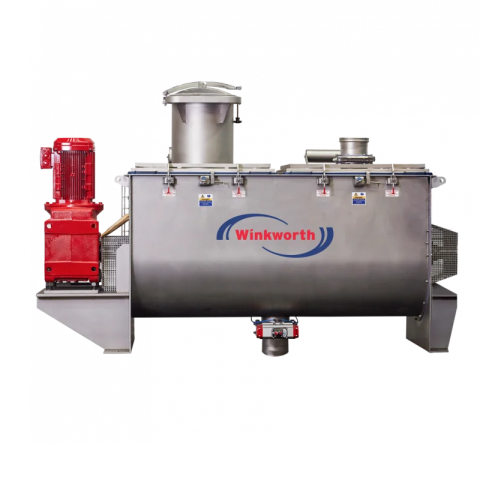

Efficient ribbon mixers for precise powder blending
Achieve consistent and uniform blending with this advanced U-Trough m...
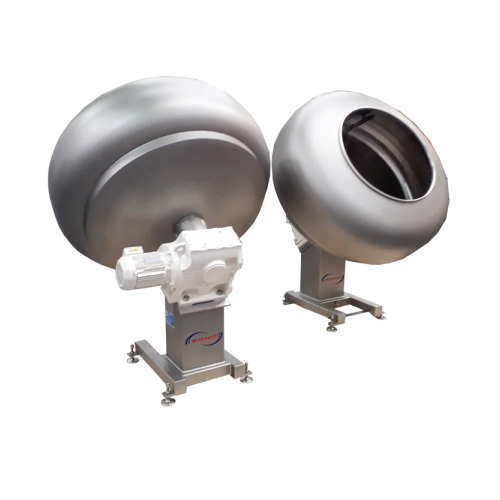

Industrial coating pans for sweets and confectionery
Ensure even and consistent coatings with high-capacity pans designed...
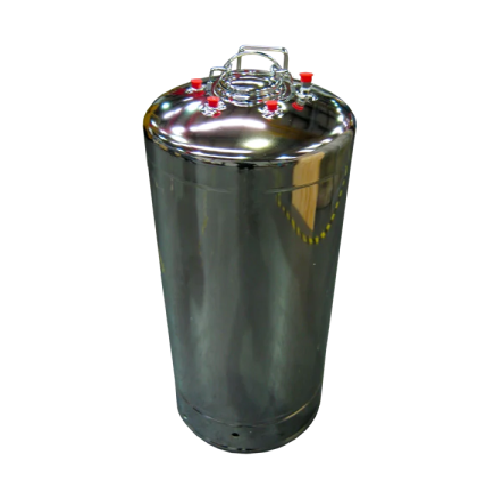

Pressure vessel for hazardous and non-hazardous liquids and gases
Ensure safety and compliance when handling hazardous ...
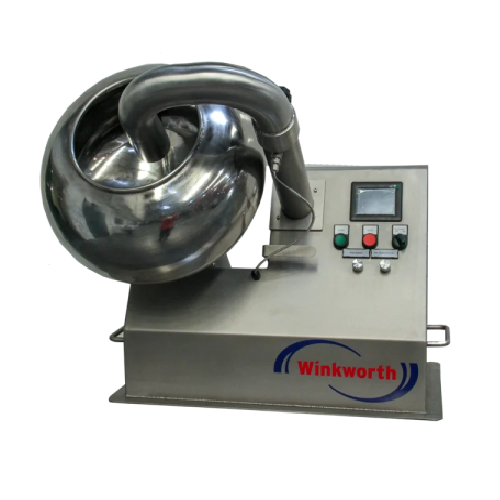

Industrial coating pan for food and pharmaceutical products
Optimize your production with precision mixing and coating, ...
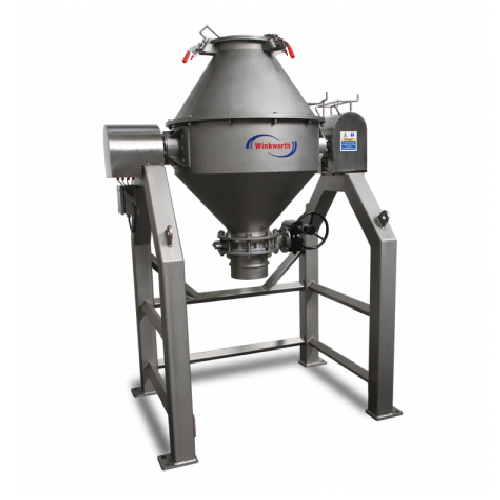

Double cone mixer for free-flowing material blending
Optimize your production with precision blending and gentle drying o...
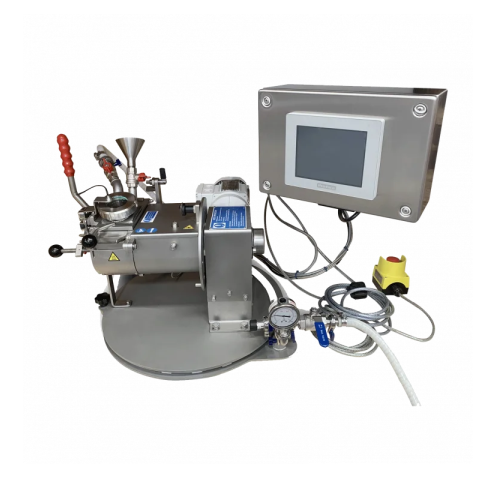

Laboratory mixers for product development and research
Optimize your R&D efforts with advanced mixing solutions desi...
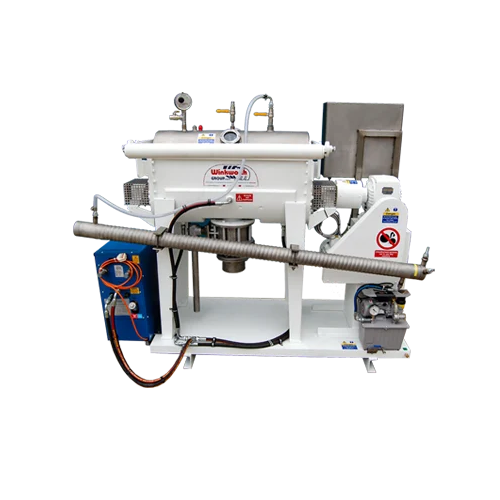

Industrial blenders for powder and granule mixing
Optimize your production line with advanced mixing solutions designed f...
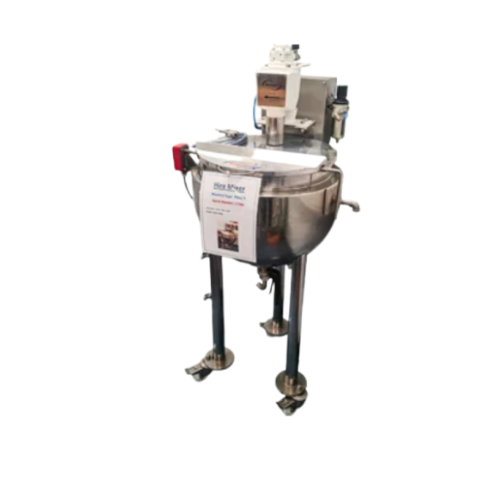

Pv mixing vessels for industrial hire
Optimize your production mix with vessels that ensure precise blending, heating, and ...
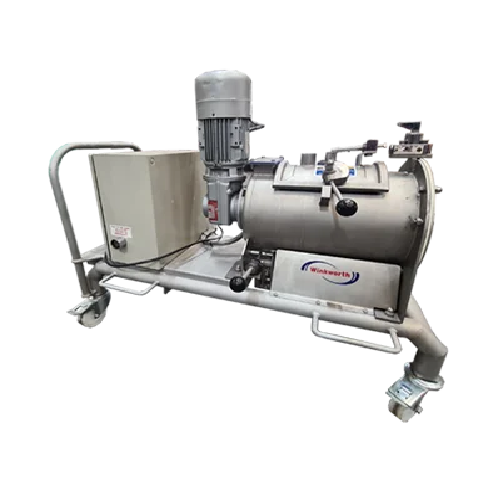

Industrial mixers for hire
Optimize your production line with versatile mixers designed for precision blending, heating, and...
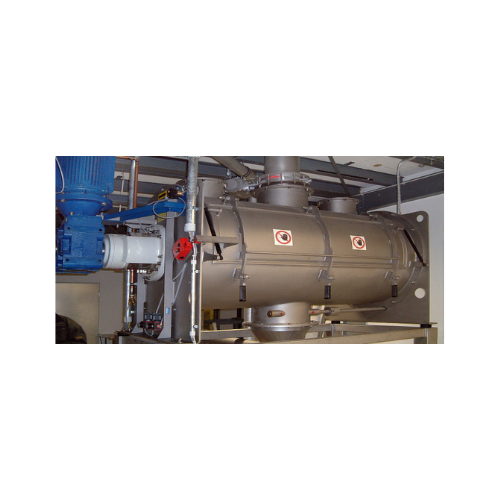

Batch-type single shaft mixer for efficient discharging
Optimize your material mixing and discharging processes with a sy...
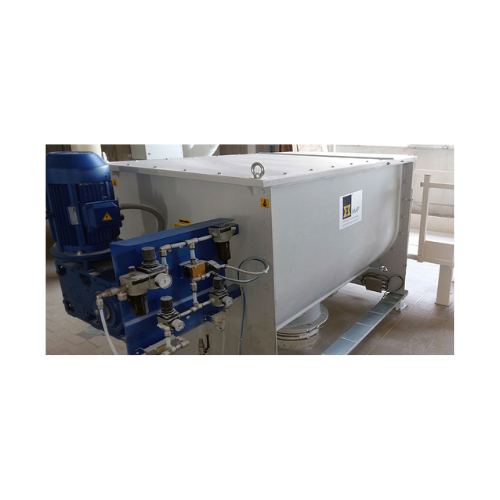

Single-shaft ribbon blender for homogeneous mixing
Achieve high-quality, precise blending of delicate and temperature-sen...
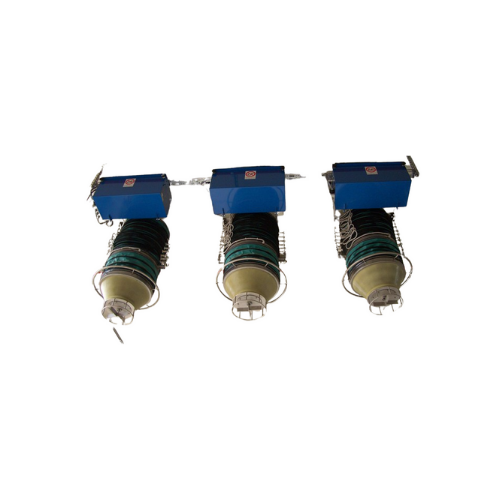

Tanker loading bellow for dust-free bulk solids loading
Optimize tanker loading while minimizing dust emissions with this...
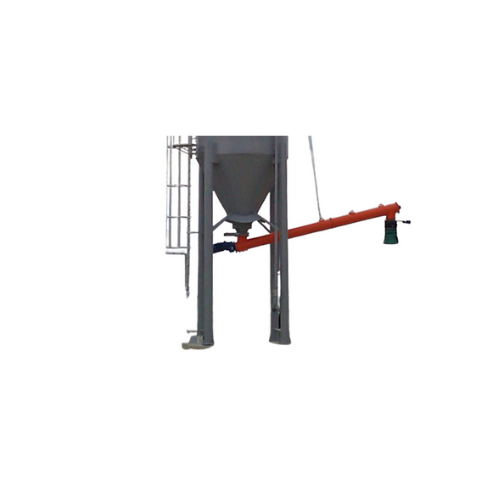

Bulk solids tanker loading bellows
For industries looking to efficiently load dry, non-dusty bulk solids into tankers, thes...
Bulk solids conveying systems
Efficiently move and manage bulk materials with precision and reliability, ensuring seamless i...
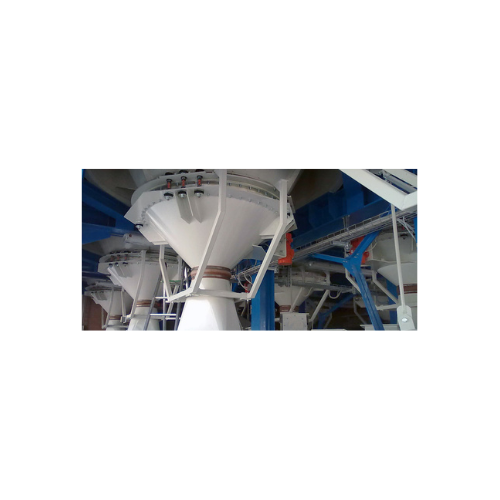

Bulk solids discharging and loading solution
Optimize your bulk material handling with equipment that ensures efficient an...
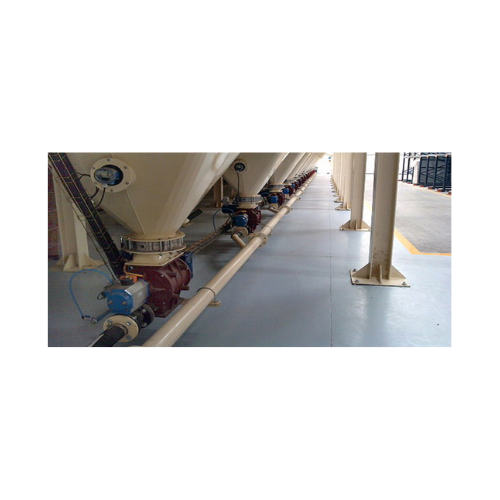

Pneumatic conveying system for bulk solids
Ensure efficient and dust-free transport of bulk materials with a pneumatic con...
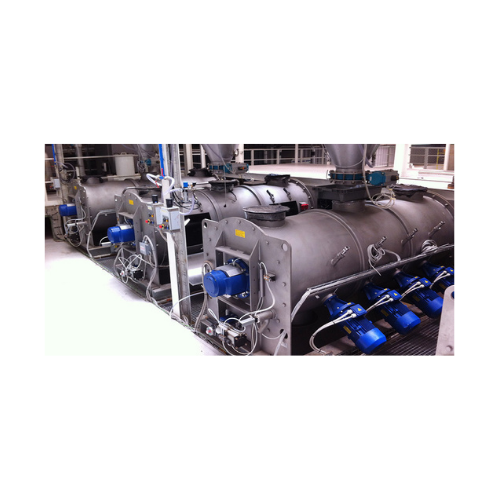

Batch-type single shaft mixer for industrial mixing
Achieve precise and uniform mixing with high-speed, single-shaft mixe...
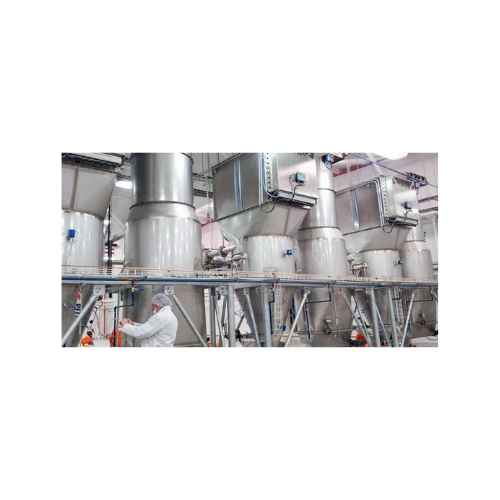

Atex-certified flanged polygonal dust collectors
Ensure dust control and compliance in explosive environments with our com...
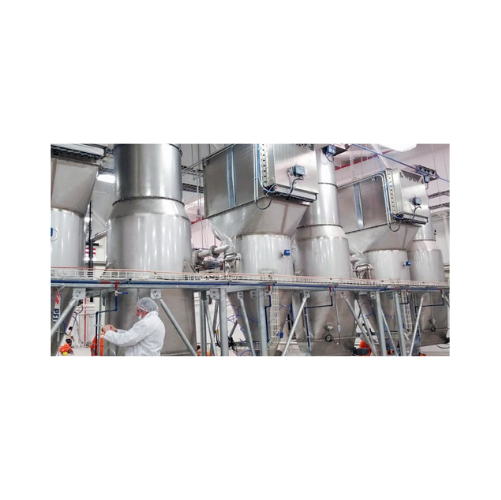

Industrial dust collection system for air filtration
Optimize air quality in your production line with this compact dust ...
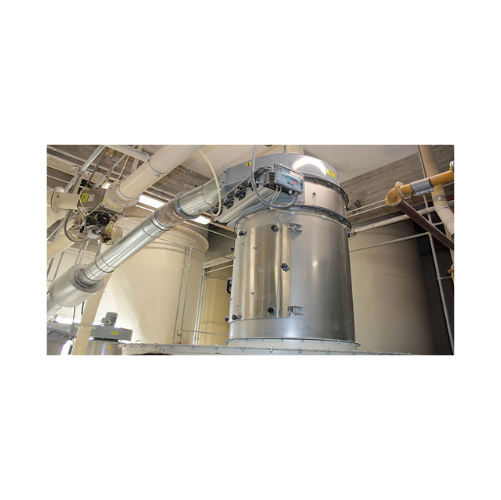

Food-grade round dust collectors
Maintain a clean production environment with this food-grade dust collector, designed to ma...
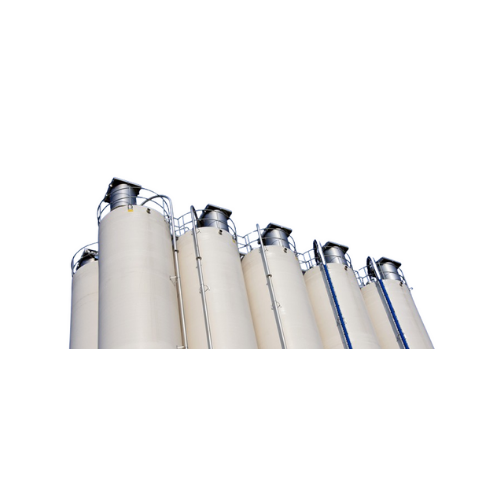

Flanged round dust collectors for industrial air filtration
Optimize your industrial processes with a dust collection sy...
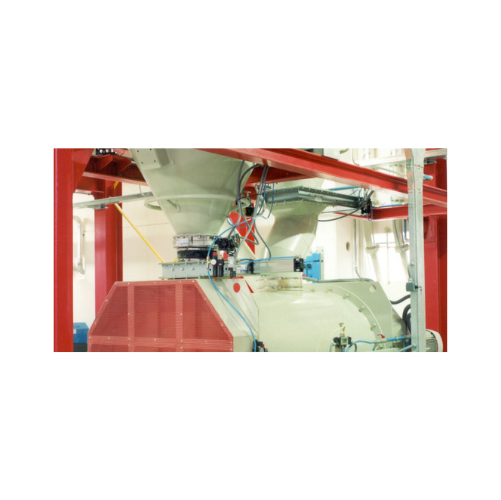

Butterfly valves for powders and granules
Ensure precise flow control and reliable sealing for gravity-fed or pneumatic sy...
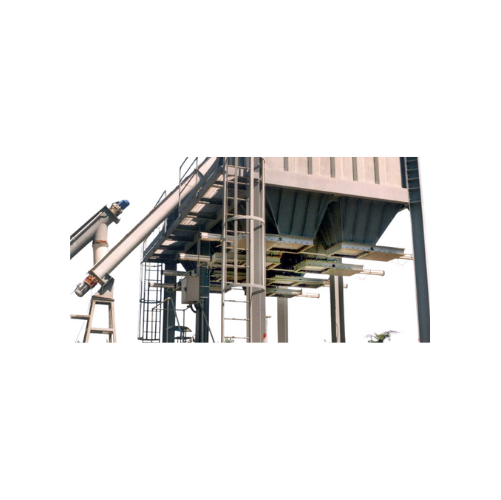

Industrial slide valve for heavy-duty applications
When managing gravity material flow in abrasive environments, achievin...
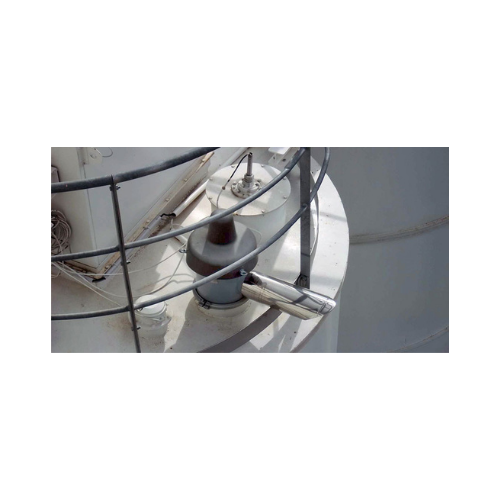

Membrane pressure relief valve for silos and bins
Ensure silo safety with our valve that instantly balances internal pres...
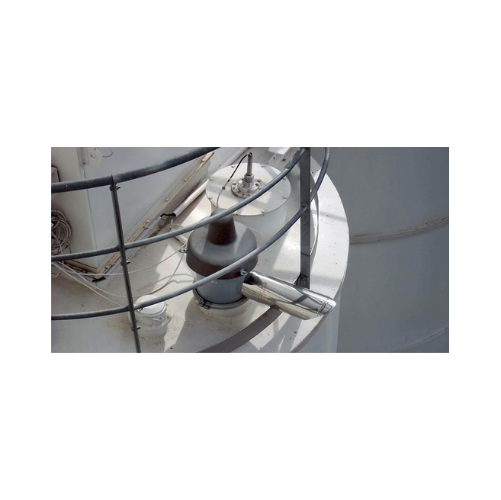

Membrane pressure relief valve for silo protection
Ensure immediate pressure stabilization in your bulk storage silos wit...

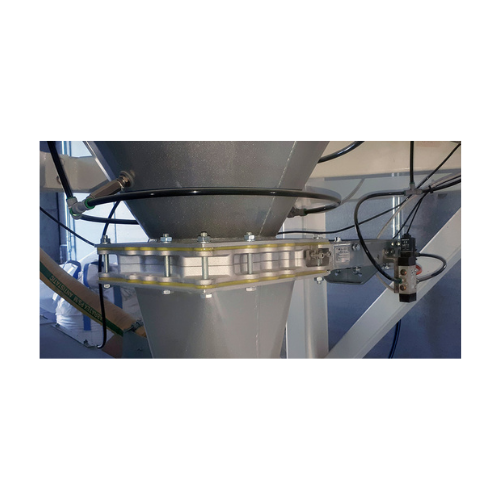
Low profile slide valve for controlling powder flow
Optimize your powder and granule flow management with precision-engin...

Slide valves for flow interception in powder and granular materials
Effectively manage the flow of powdery and granular...

Vibro-aerators for bulk solids discharging
Optimize your powder flow and ensure consistent discharge with this advanced ae...

Silo overfill protection valves
When abnormal pressure threatens your silo’s integrity, reliable pressure relief becom...

Spring-loaded pressure relief valves for silo overfill protection
Ensure safety and prevent costly overfills with press...

Double dump valves for high temperature granules
Ensure precise material flow and withstand extreme temperatures with thes...
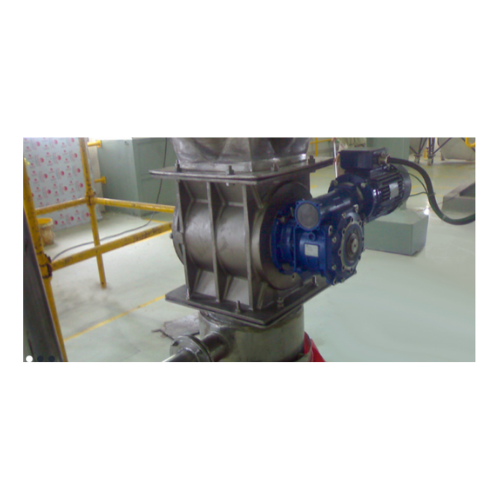

Drop-through rotary valve for powder and granular material feeding
Achieve precise control in discharging and feeding p...
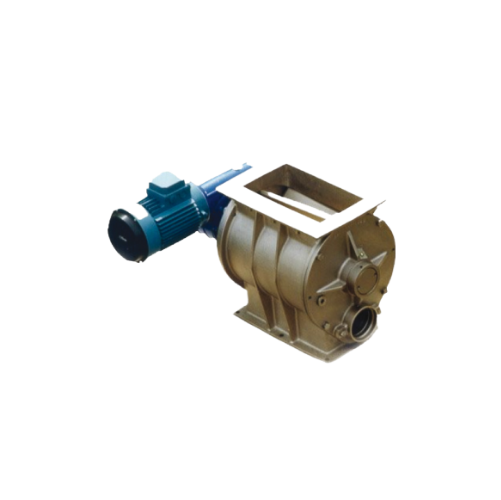

Blow-through rotary valves for pneumatic conveying
Optimize your pneumatic conveying systems with high-efficiency blow-th...
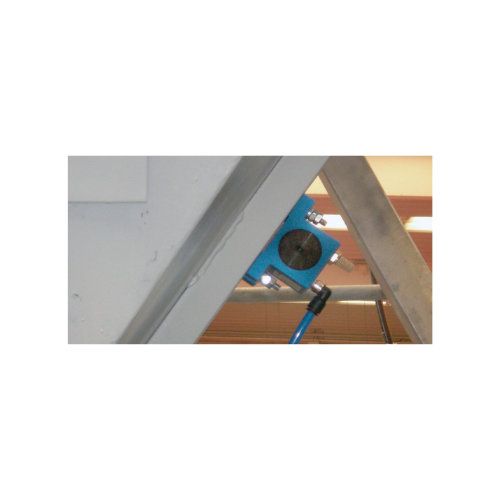

Rotary ball vibrators for bulk solids discharging
Ideal for enhancing material flow, this equipment efficiently handles f...
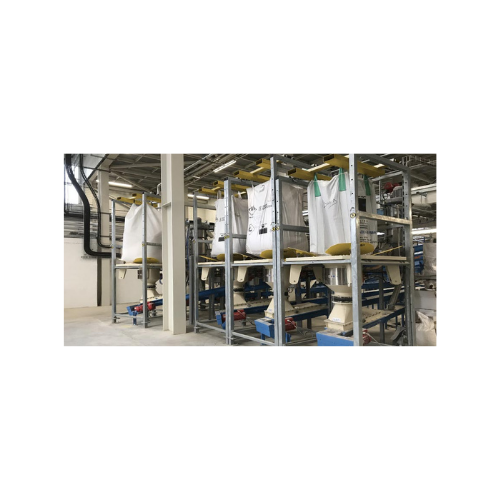

High flow rate Fibc dischargers for wastewater treatment
Optimize your material handling with efficient, dust-proof disch...
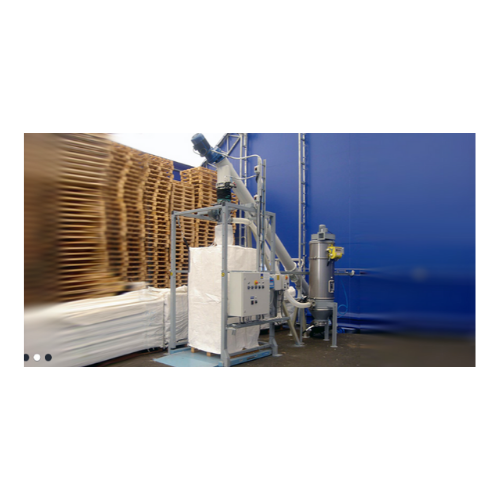

Dust-free bulk bag filling system
Achieve efficient, dust-free filling of bulk bags with our innovative system, ensuring se...
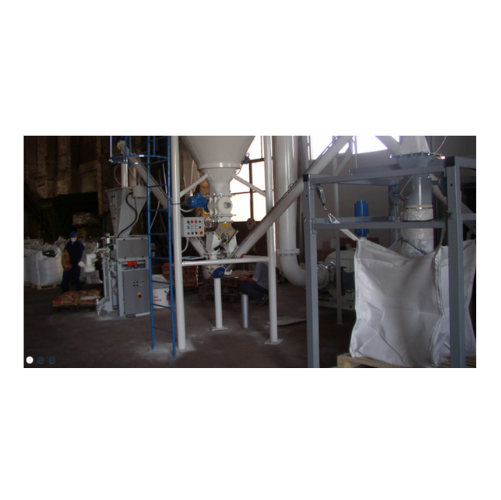

Manual Fibc bag filling station
Achieve dust-free filling of bulk bags with an efficient system designed to handle compacted...
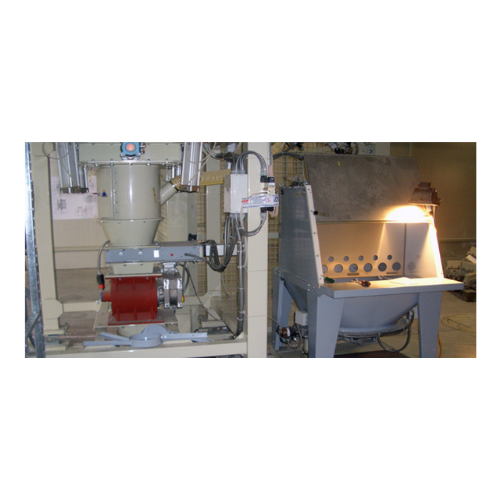

Manual bag opener for bulk solids discharging
Effortlessly open and empty bags while containing dust emissions, ensuring a...
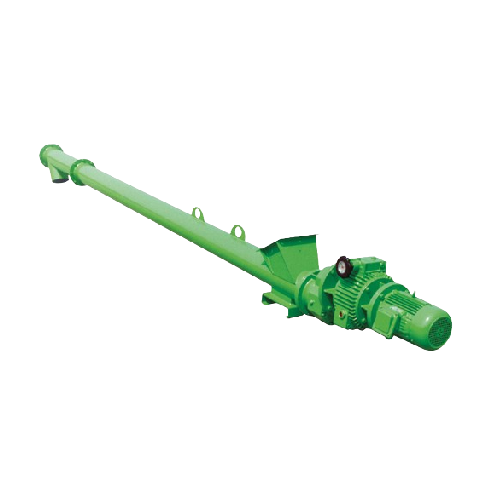

Tubular ribbon flight screw feeder for lime feeding
Experience uniform material flow and precise dosing with this special...

Pneumatic hammers for bulk solids discharging
Optimize your production efficiency and solve material flow challenges with ...

Pneumatic hammers for aiding material flow
Optimize material flow and eliminate blockages in your processing line with pne...

Rotary turbine vibrators for bulk solids discharging
Enhance the efficiency of material handling with high-speed, low-noi...

Rotary turbine vibrators for material flow aid
Optimize your production efficiency with high-speed, silent operation vibra...
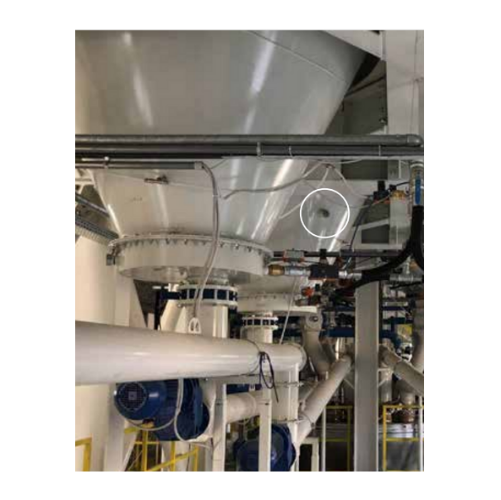

Continuous impact vibrators for bulk material removal
Combat material flow issues like bridging and rat-holing with our i...
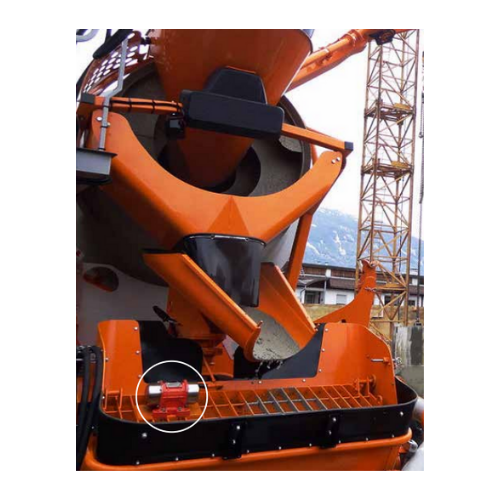

Continuous impact vibrator for aggregate reclaiming
Tackle material flow challenges head-on by preventing common issues l...
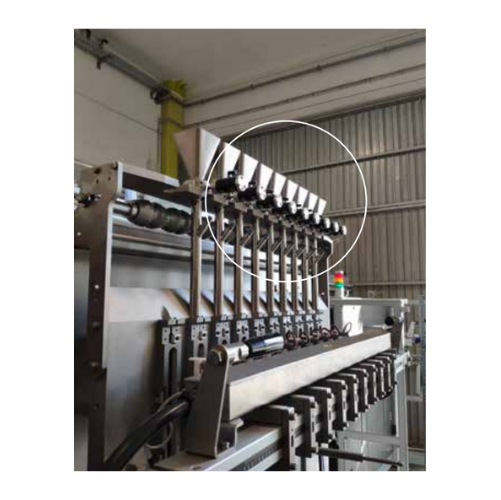

Continuous impact vibrators for bulk solids discharging
Optimize your discharging process with vibrators that effectively...
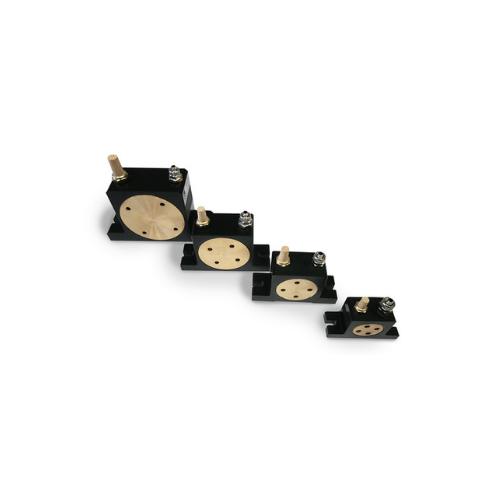

Rotary roller vibrators for concrete compacting and hopper emptying
Achieve higher compaction and efficient emptying wi...

External electric motovibrators for industrial applications
Optimize material movement and improve discharge efficiency ...

Industrial electric vibrator for bulk solids discharging
Enhance material flow efficiency and ensure consistent output ac...

External electric motovibrators for industrial material flow
Experience enhanced material flow and precise material disc...

Silo overfilling safety system
Ensure safe silo filling with our system that prevents overfilling and excess pressurization,...

Lump breaking feeder valve for bulk material processing
Tackle bulk material flow challenges with a feeder valve engineer...
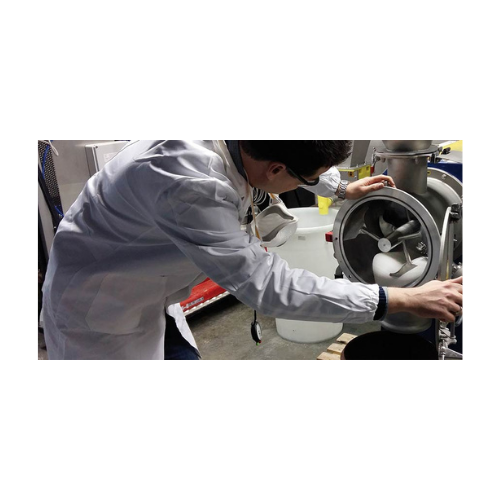

Laboratory batch mixer for small scale production
Achieve rapid and reproducible mixing results with this laboratory batc...
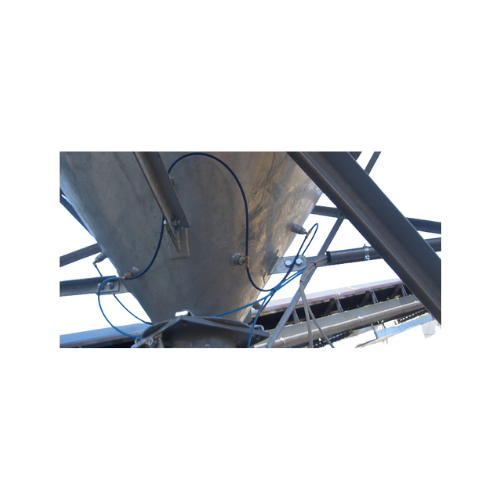

Aeration pads for powdery material flow in silos
Ensure consistent material flow in your silos and bins with a reliable ae...
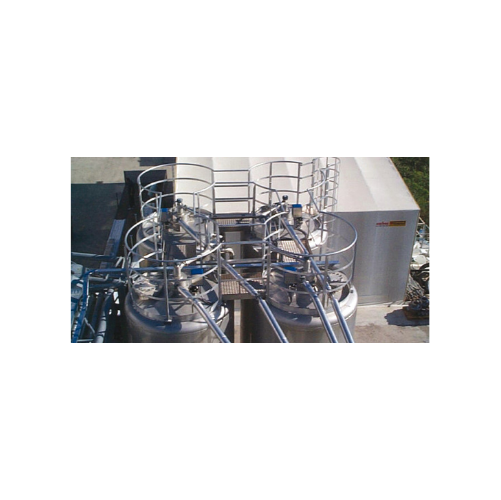

Continuous level measurement system for powdery or granular materials
Ensure precise inventory management and enhanced ...
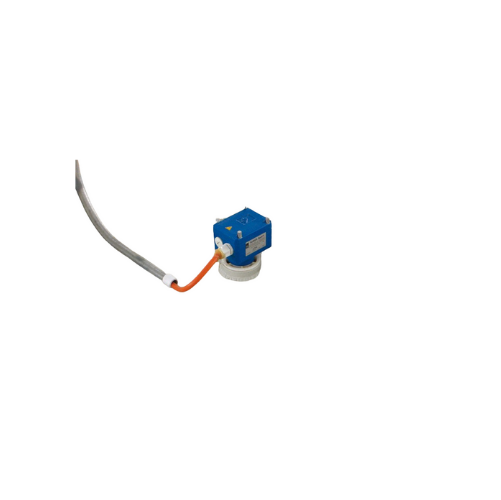
Bin level indicator for bulk solids
Ensure precise material level detection across your production processes, minimizing th...
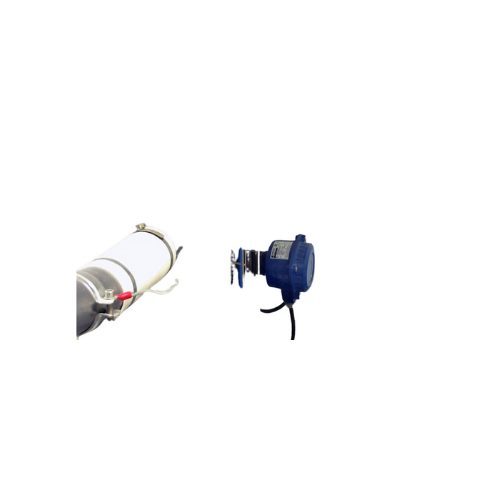

Bin level indicators for powder and granular material
Ensure precise inventory management and prevent overflows in your p...

Electronic pressure meter for silo safety
Ensure the safety of your silos by efficiently monitoring internal pressure chan...

Electronic pressure meters for silo safety monitoring
Ensure precise pressure management in your systems with this advanc...

Pneumatic linear vibrators for bulk material flow
Prevent bridging and rat-holing in your production process with silent,...

Pipe couplings for pneumatic conveying lines
Ensure a secure and quick connection for your pneumatic lines with these pipe...

Cushioned pneumatic vibrators for bulk solids conveying
Streamline your material handling with precision vibration contro...

Pneumatic actuators for industrial valves
Optimize valve control in your production line with precision-engineered actuato...

Stainless steel trough screw conveyor
Ideal for precise handling of powdery and granular materials, this solution ensures m...

Hand wheel actuators for Vg slide valves
Effortlessly control flow interception in high-demand settings with these hand whe...
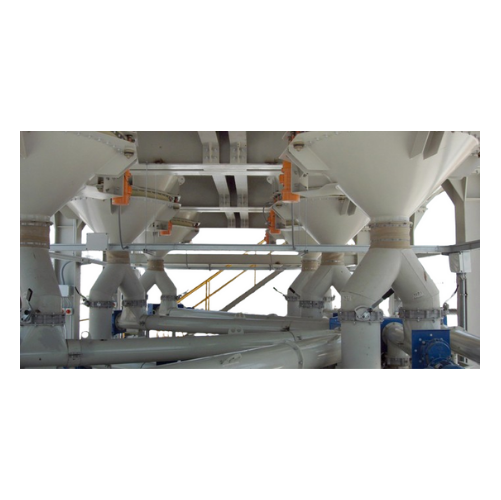

Vibratory outlet hopper for bulk material discharge
Struggling with material bridging and inconsistent discharge? Enhance...
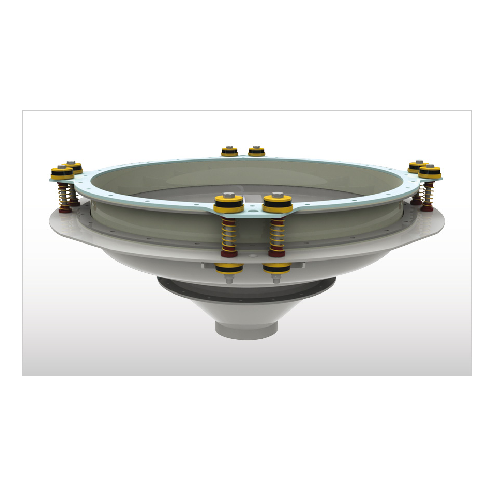
Industrial bin activator for smooth material flow
Enhance your material handling process with a solution that ensures con...
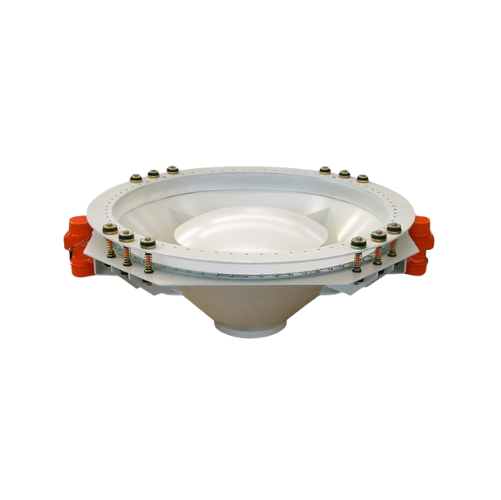

Vibratory hopper for bulk solids discharge
Ensure consistent material flow and prevent bridging in storage silos with this...
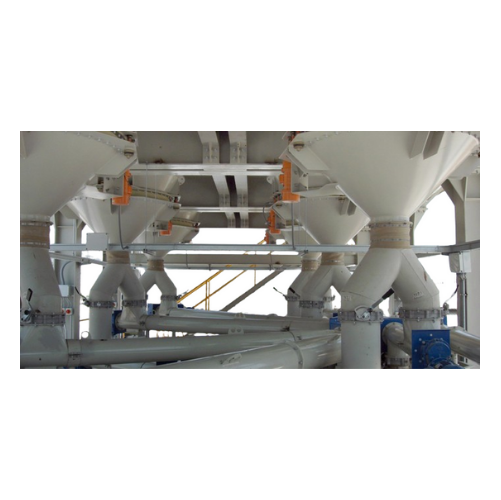

Bin activator for silo and hopper discharge
Ensure optimal material flow and prevent blockages in your storage systems wit...

Pharmaceutical vacuum conveyors for hygienic transport
Ensure contamination-free transport of sensitive pharmaceuticals a...
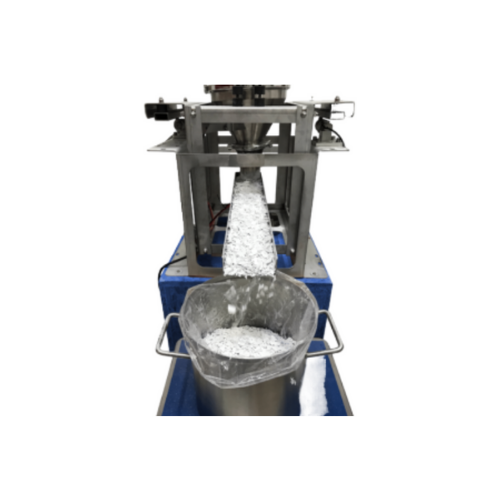

Vibratory feeder for dosing powders and bulks
Ensure precise feeding of powders and bulk materials with a system that inte...
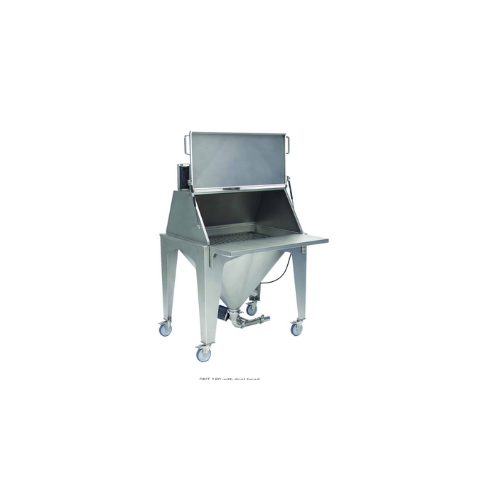

Bag rip-and-tip dump stations for bag emptying
Efficiently manage bag emptying operations with advanced dust containment a...
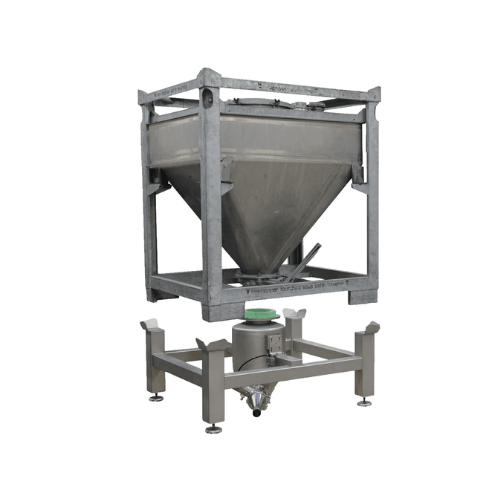

Ibc docking and discharge stations
Ensure seamless material transfer with dust-free docking and effective discharge, mainta...
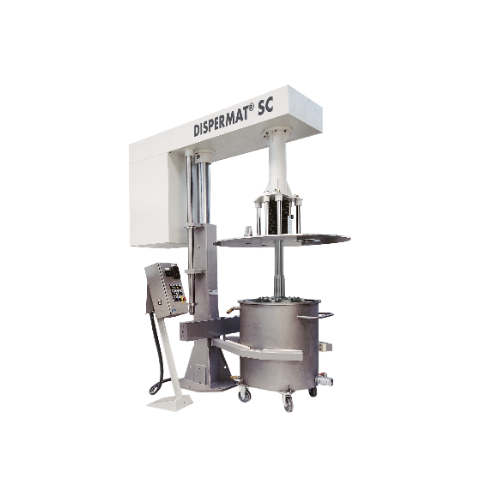

Explosion-proof dissolver for chemical processing
Ensure safe and efficient dispersion in volatile environments with this...
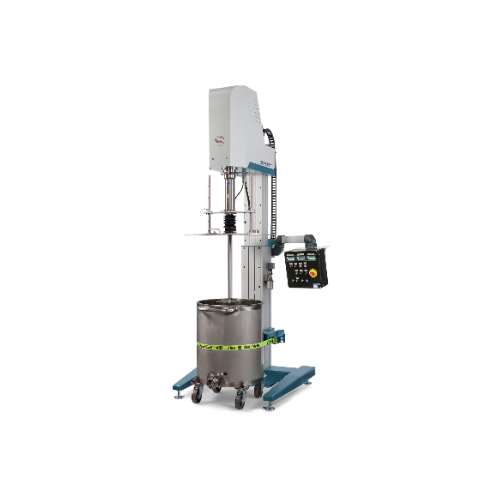

High-performance dissolver for large-scale production
Optimize your production line with precision-controlled dispersion ...
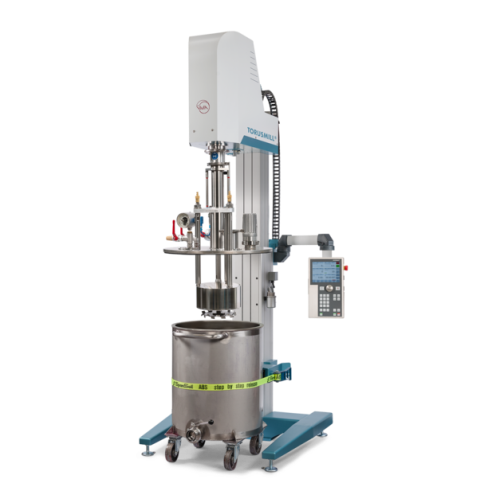

Vacuum basket mill for high-viscosity product processing
Achieve exceptional fine milling results while preventing air in...

Vacuum dissolver for high viscosity products
Optimize your production with a vacuum dissolver designed to efficiently prev...

Vacuum disperser for high-viscosity products
Optimize high-viscosity product dispersion and prevent air inclusions with a ...
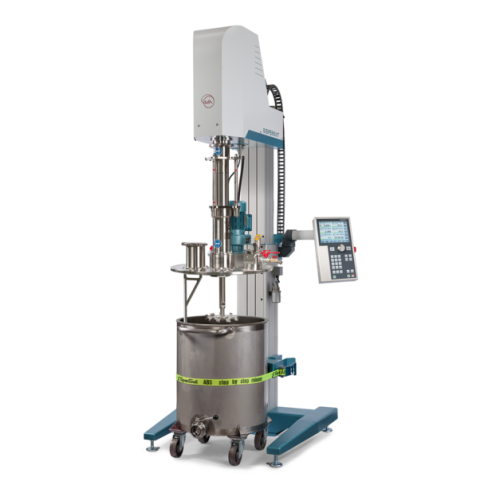

Vacuum dissolving system for high-viscosity products
Achieve flawless dispersion of high-viscosity substances under vacuu...

Production dissolver for high-viscosity products
Achieve optimal dispersion and grinding of high-viscosity substances with...

Explosion-proof production vacuum disperser for viscous products
Achieve precise and reliable dispersion of high-viscosi...

High-performance production dissolver for large batches
Achieve precise and repeatable dispersion for complex formulation...

Dissolving system for high-viscosity products
Optimize the dispersion of high-viscosity liquids and pastes with this versa...
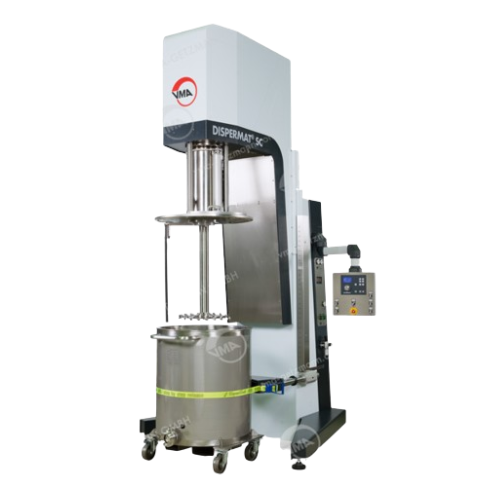

Production dissolver with scraper for high-viscosity products
Efficiently tackle high-viscosity material processing with...
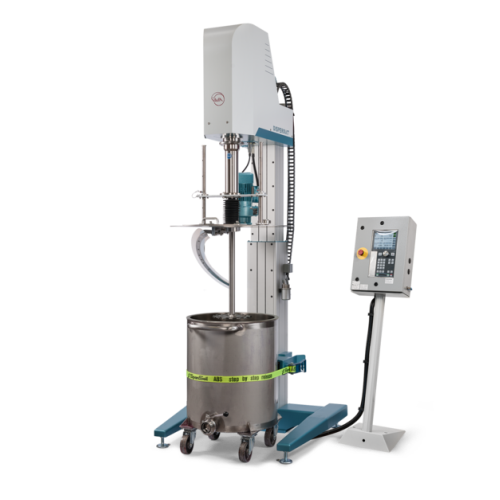

Explosion-proof dissolver with scraper for high viscosity substances
Ensure flawless dispersion with enhanced safety, d...
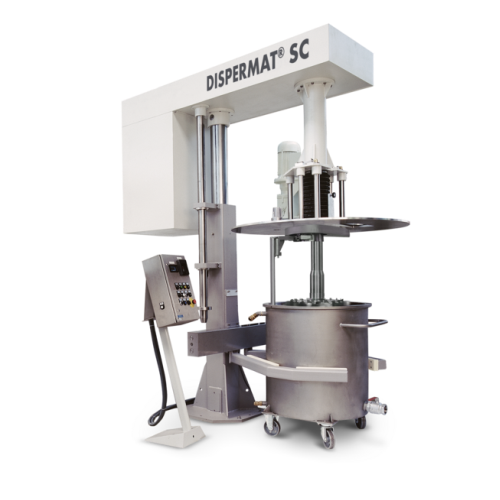

Explosion-proof dissolver for high viscosity products
Optimize your high-viscosity material processing with an explosion-...
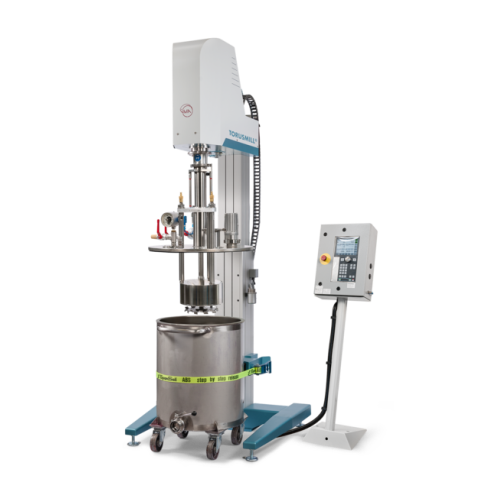

Vacuum basket mill for highly viscous products
Achieve precision in fine milling under vacuum to prevent air inclusions in...
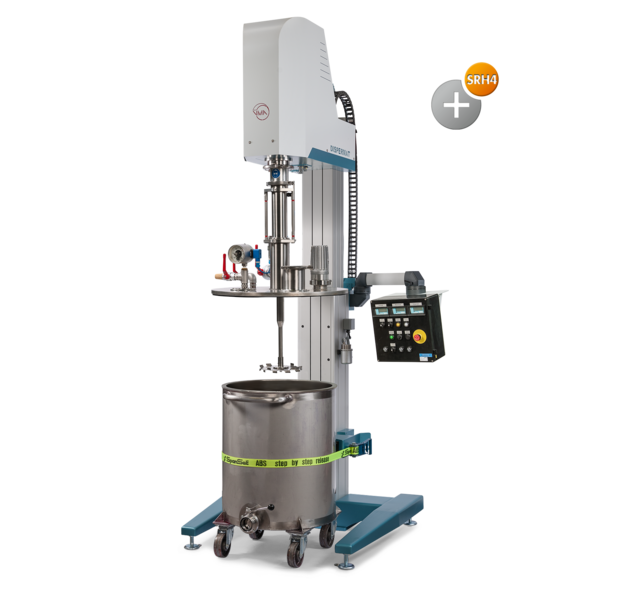

ATEX vacuum dissolver for high viscosity products
Ensure safe and efficient dispersion of high-viscosity materials under...
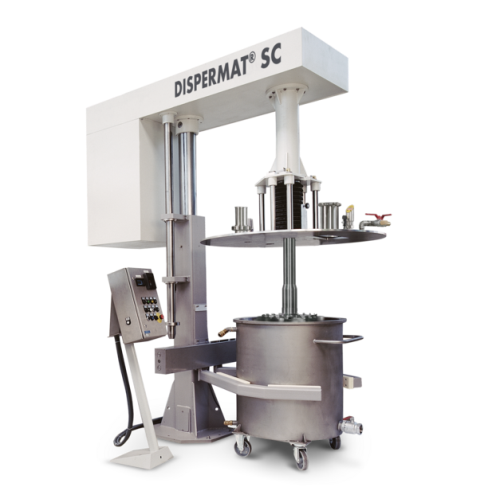

Explosion-proof vacuum dissolver for high viscosity products
Achieve precise dispersion of high-viscosity products under...
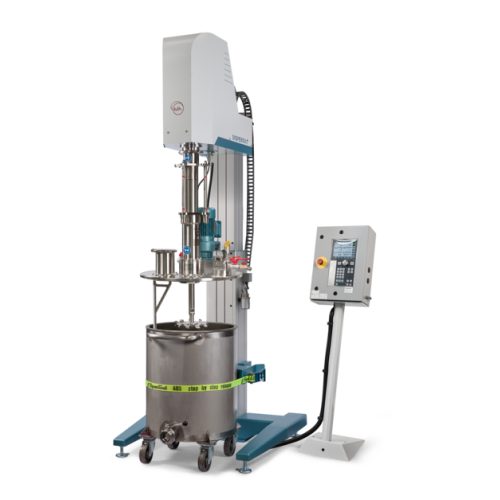

Explosion-proof vacuum dissolver for high viscosity applications
For operations requiring precise control in high-viscos...
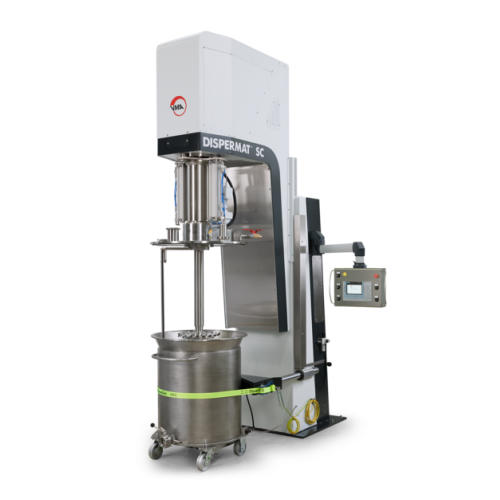

Explosion-proof vacuum disperser for high-viscosity substances
Achieve precise dispersion and eliminate air inclusions w...
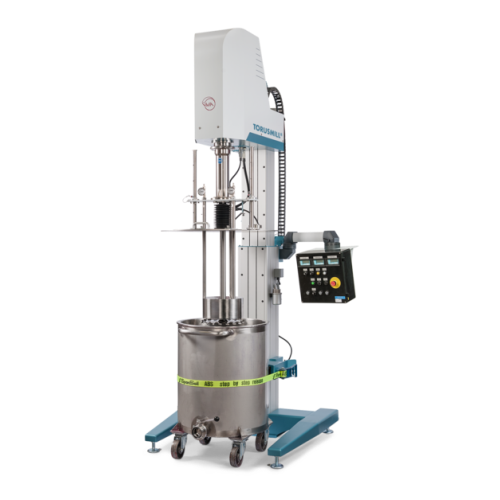

Explosion-proof basket mill for fine grinding
Achieve efficient and safe fine grinding with this innovative explosion-proo...
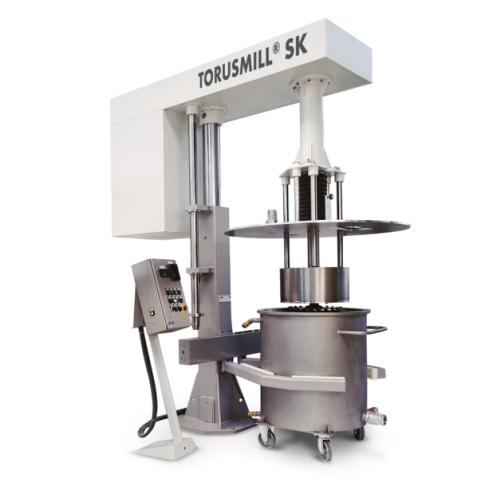

Explosion-proof basket mill for large scale production
Enhance your production line with an explosion-proof basket mill t...

Laboratory stirrer for small batch mixing
Achieve consistent mixing and blending in small-scale environments with minimal ...
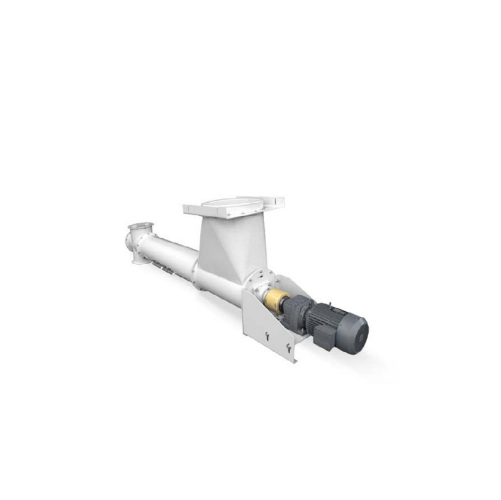

Tube screw conveyor for flour and fine-milled materials
Optimize your production line by efficiently transporting flour a...

Pneumatic cyclone for effective product-air separation
Optimize particle separation with high-speed pneumatic cyclones, e...

Industrial airlock for pneumatic systems
Ensure precise air and product separation in your pneumatic systems, maintaining m...

Table-top mini extruder for precision material processing
Achieve precise control over complex formulations with this fl...

Hybrid laboratory extruders for reproducible scale-up applications
Easily switch between screw diameters to enhance fle...
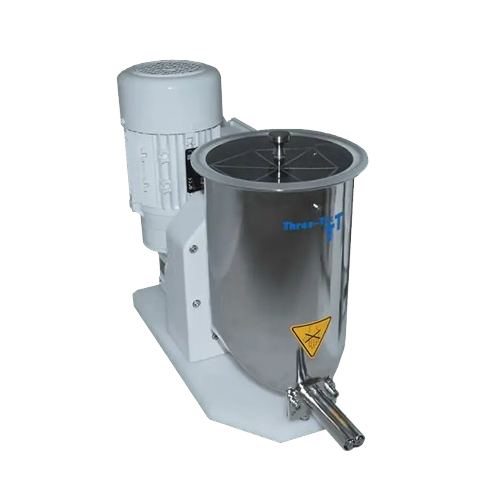

Twin screw feeder for dosing bulk solids
Ideal for precise bulk solids dosing, this twin screw feeder ensures consistent fl...
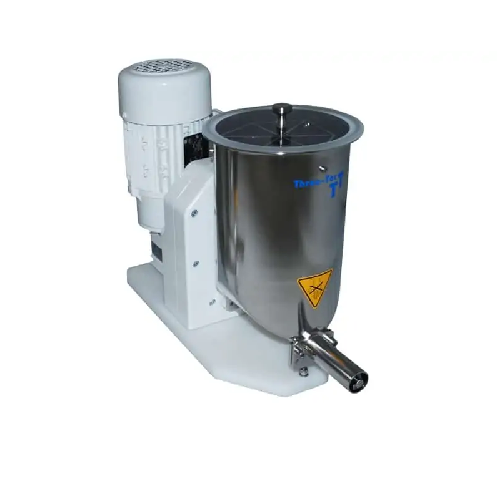

Volumetric single-screw feeders for free-flowing products
Achieve precise and continuous feeding of free-flowing powders...
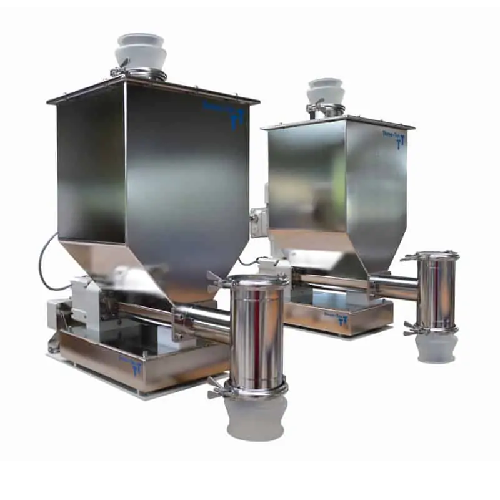

Volumetric single-screw feeder for free-flowing products
Optimize your production line with precise feeding and metering ...
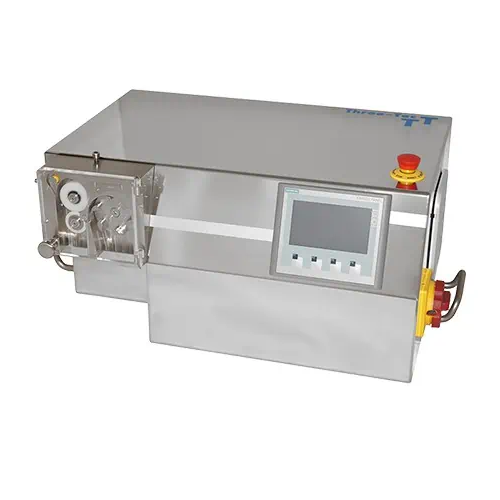

Granulator for processing strands into granulate
Optimize granule production with precise control over pellet size and ext...
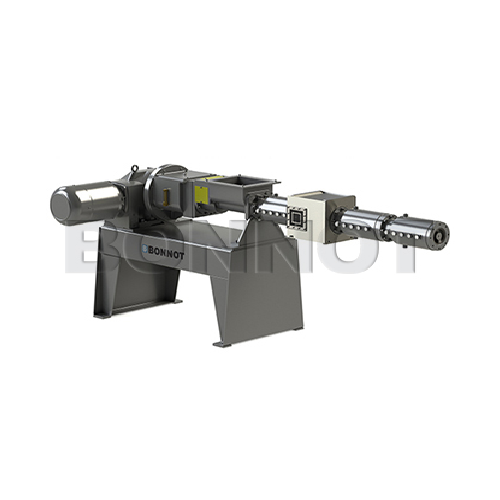

Vacuum extruder for high-viscosity materials
Optimize material processing with precision de-airing and temperature control...
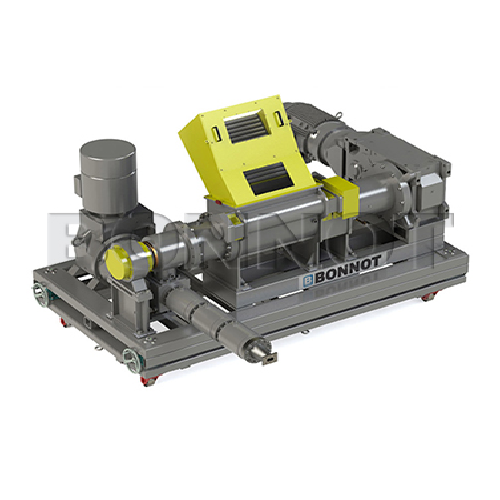

Horizontal bale feeder for high viscosity rubbers
Efficiently process full rubber bales into granules or compound materia...
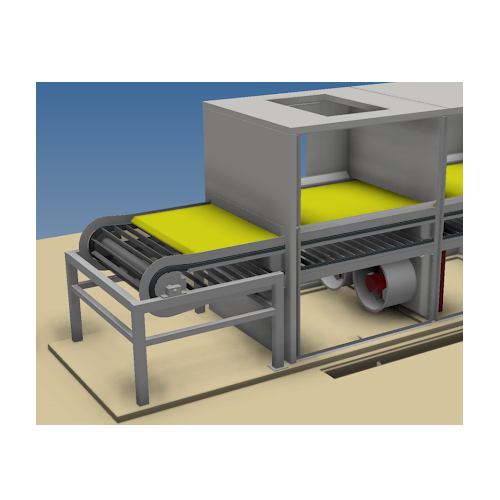
Belt dryer for large-scale continuous drying
Achieve precise moisture control and energy-efficient processing with this be...
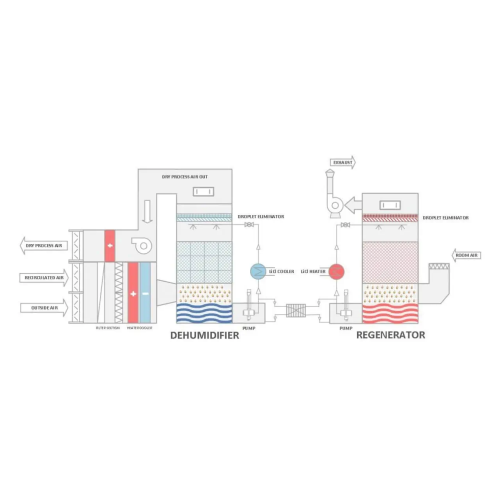
Industrial lithium chloride dehumidifier
Efficiently control air moisture and temperature with a solution that ensures prec...

Industrial dust collection system
Optimize your process by efficiently capturing and removing airborne dust particles, ensu...

Continuous bulk fluid bed dryer
Achieve rapid and energy-efficient moisture removal across diverse materials with our advanc...
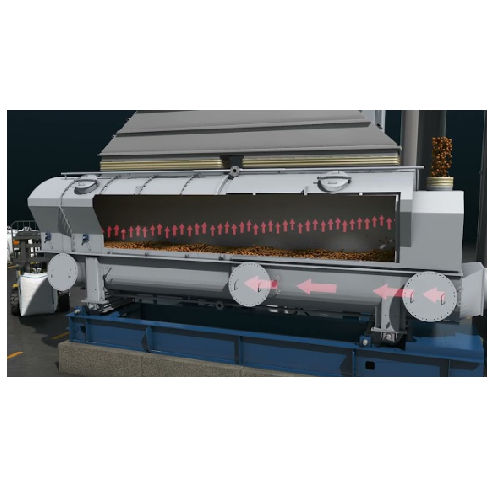

Continuous fluid bed dryers for various industrial applications
Achieve precise moisture control with fluid bed dryers, ...
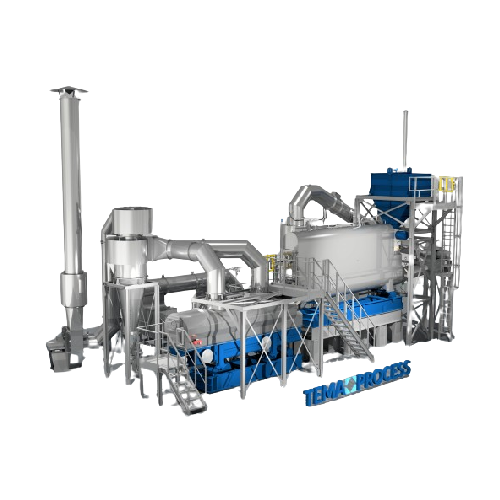

Vibrating fluid bed dryer for bulk materials
Ensure efficient moisture removal and thermal processing with this fluid bed ...

Horizontal laminar flow bench for particle-free environment
Ensure contamination-free workspaces with a horizontal lamin...

Vertical laminar air flow cabinet for non-hazardous material handling
Achieve a particle-free environment crucial for s...
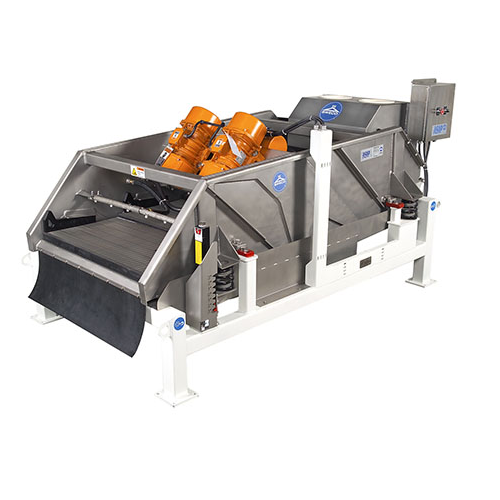

Multi-motion rectangular separator
Solve screen blinding effortlessly with an innovative system that combines elliptical an...
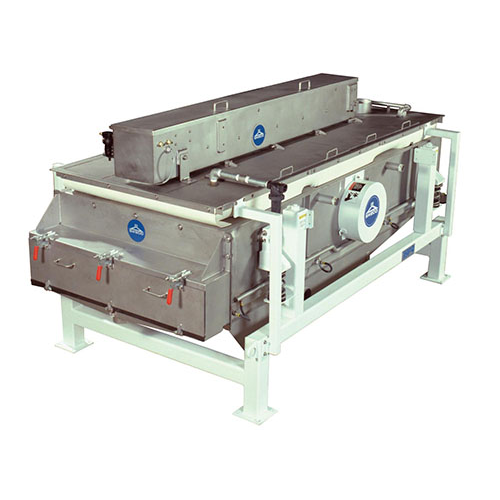

Round motion separator for dry and wet screening
Optimize your production line with an efficient solution for precise scre...
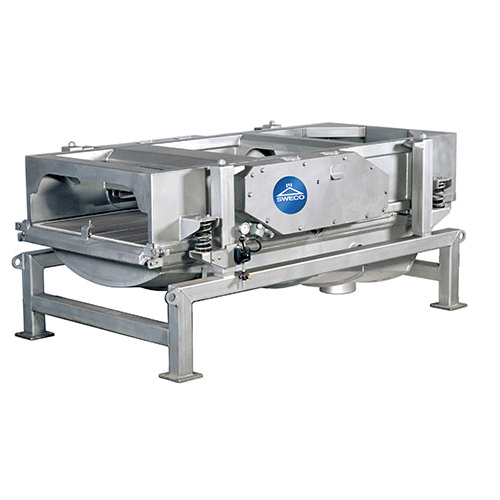

Universal motion rectangular separator for pulp and paper
Achieve precise motion adjustments with a versatile separator ...
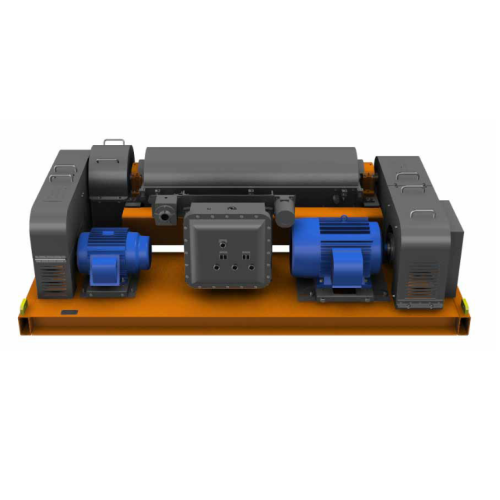
Industrial decanter centrifuge for solids separation
Optimize your production line with high-speed decanter centrifuges t...
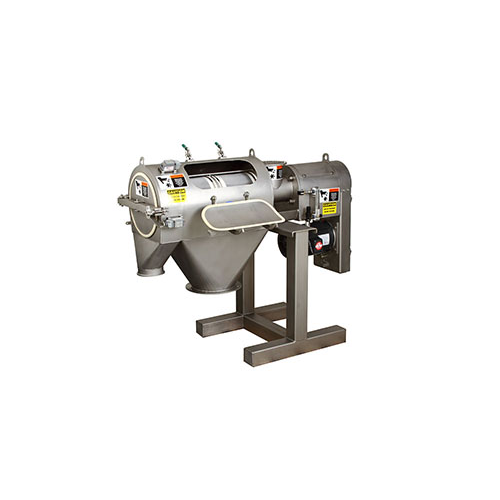

Centrifugal sifter for efficient particle separation
Enhance your material throughput by efficiently separating particles...
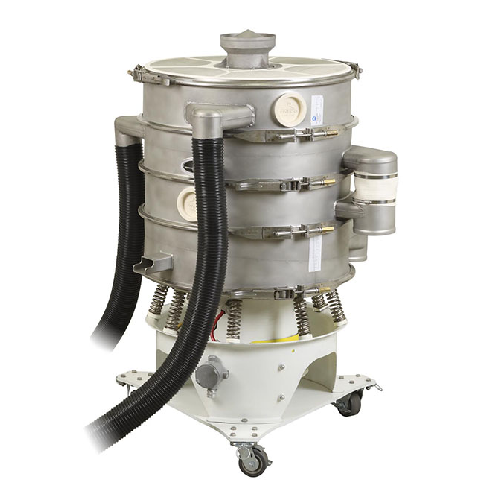

Drying and cooling classifier for plastic pellets
This solution enhances efficiency by combining drying, cooling, and cla...
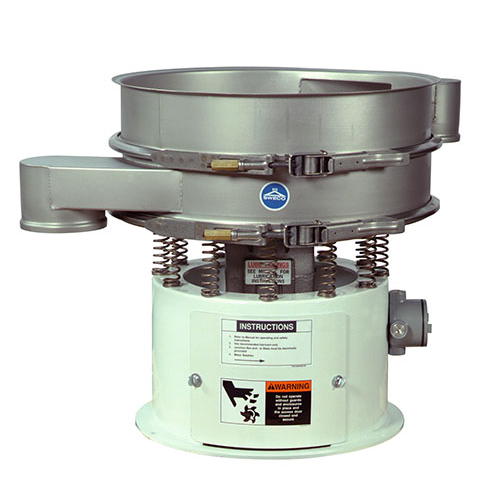

Lab scale round separator for particle classification
Optimize lab-scale processes with this compact separator, ideal for...
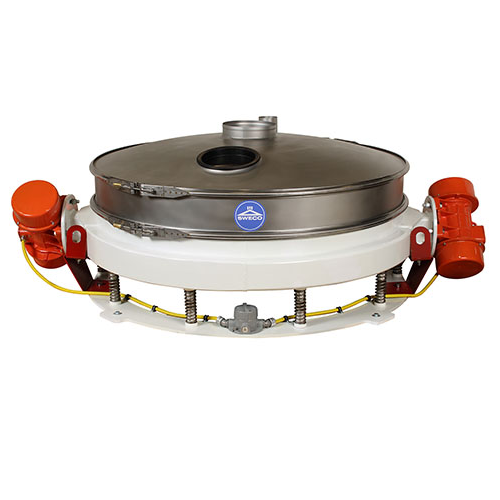

Low profile flow-thru separator for wet or dry scalping
Efficiently handle high-capacity separation with a compact design...
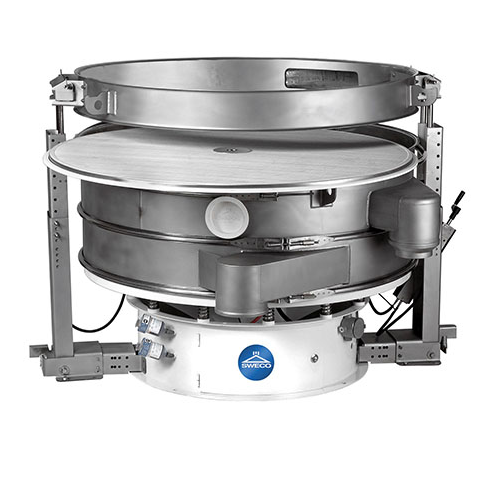

Quickchange systems for vibratory separator screen changes
Streamline your production with a system that enables rapid s...

Vibratory separator for efficient solid-liquid separation
Maximize throughput and efficiency in your production line wit...

Sanitary separator for food processing applications
Ensure efficient separation and prevent contamination in food product...

Ultrasonic round vibratory separator for fine powders
Efficiently prevent screen blinding during powder separation proces...

High-capacity industrial sifter for chemical and food processing
Achieve unparalleled screening precision and efficiency...
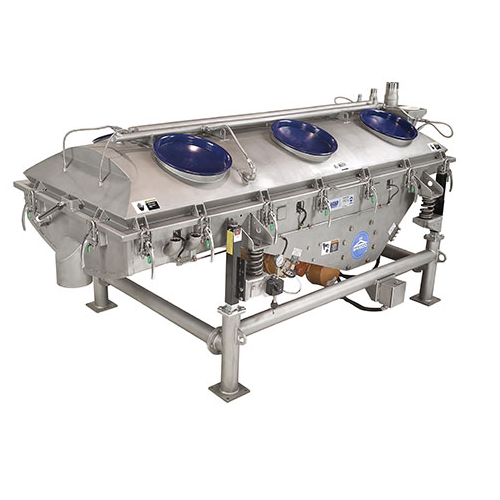

Dual-motion rectangular separator for pulp and paper industry
Optimize your production line with a versatile separation ...
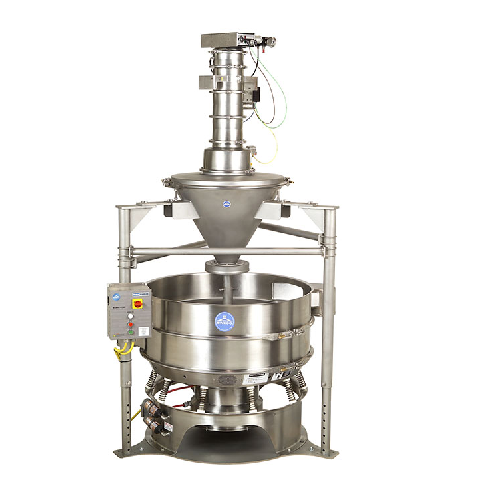

Accu-feed system for dry material separation
Boost efficiency by combining storage, feeding, and screening into one space-...
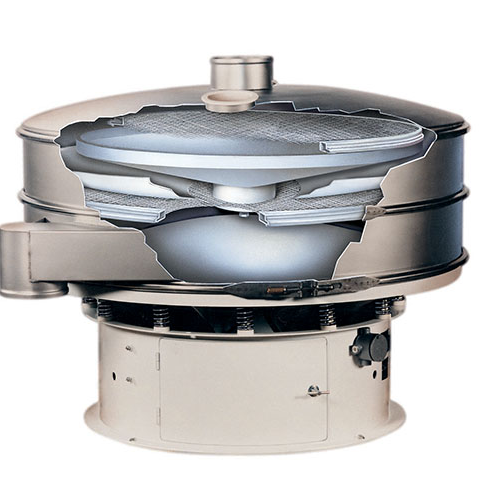

Round vibratory separation for high capacity screening
Maximize screening efficiency with dual screen vibratory technolog...
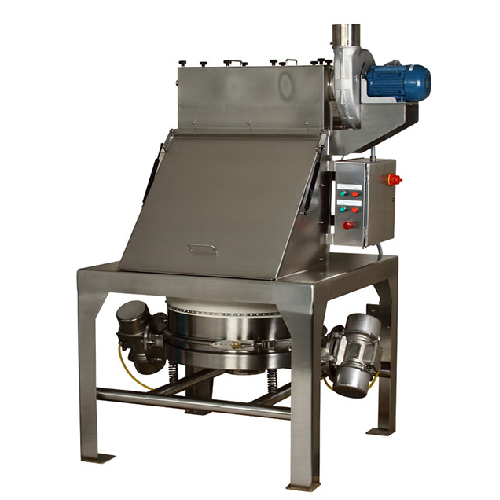

Round vibratory separation equipment - bag dump screener system
Enhance your material handling and safety by efficiently...
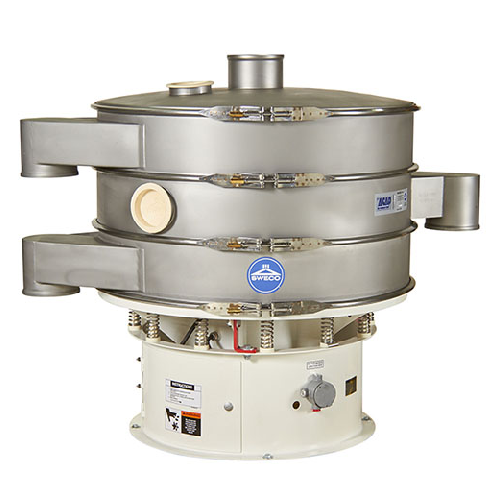

Round vibratory separation for various industrial applications
Ensure accurate material separation with a robust solutio...
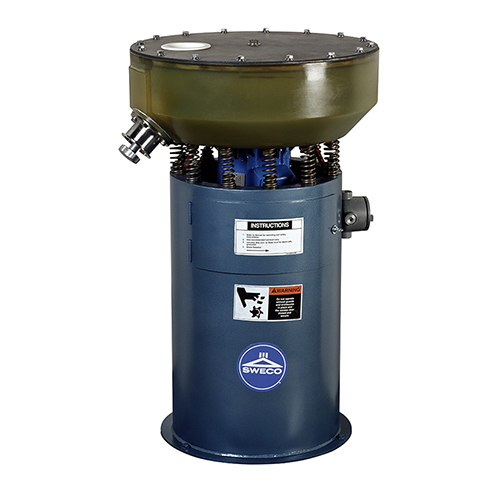

Sub-micron particle size reduction grinding mill
Achieve precise particle size reduction effortlessly with advanced vibrat...

Scraped surface heat exchangers for high viscosity products
Ideal for continuous processing, these heat exchangers effic...

Portable and fixed mount mixing system
Optimize your mixing operations with a versatile system that adapts seamlessly betwe...

Bigbag discharge station with dust-free docking system
Streamline your production line with an efficient solution for man...

Volumetric feeder for flowable ingredients
Ensure consistent and precise dosing of diverse materials in your production li...

Volumetric feeder for consistent ingredient flow
Achieve precise and consistent ingredient dosing in your production line ...

Twin screw feeder with stirring agitator for poor flowing powders
Optimize your processing line with a highly adaptable...

Loss-in-weight feeder for flowable ingredients
Achieve precise ingredient delivery with this feeder, designed to handle a ...

Laboratory loss-in-weight feeder for powders or pellets
Achieve precise dosing for lab-scale trials with this versatile f...

Loss-in-weight feeder for liquids
Achieve precise and continuous liquid dosing with high accuracy, adapting seamlessly to y...

Loss-in-weight feeder for non-hygroscopic ingredients
Ensure precision in your dosing and weighing processes with this ad...

Single screw loss-in-weight feeder for powders and pellets
Ensure precise dosing and mixing in continuous automated oper...
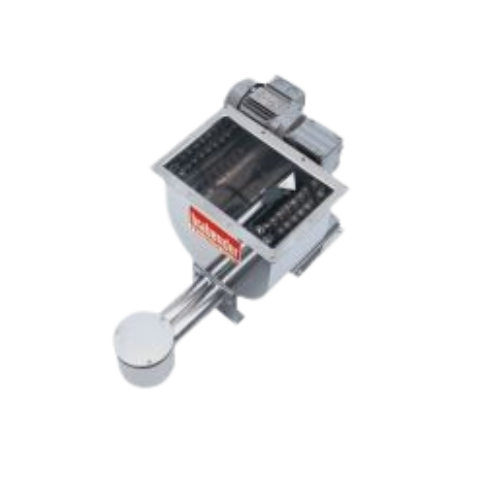

Twin screw volumetric feeder for poor flowing powders
Struggling with poor flowing or floodable powders? This twin screw ...
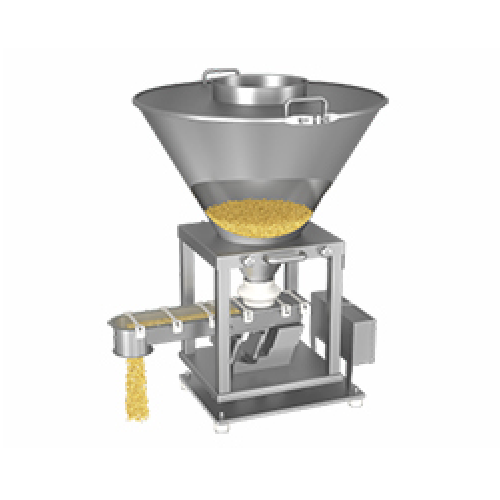

Vibrating tray loss-in-weight feeder for grained ingredients
Achieve precise and continuous dosing of free-flowing solid...
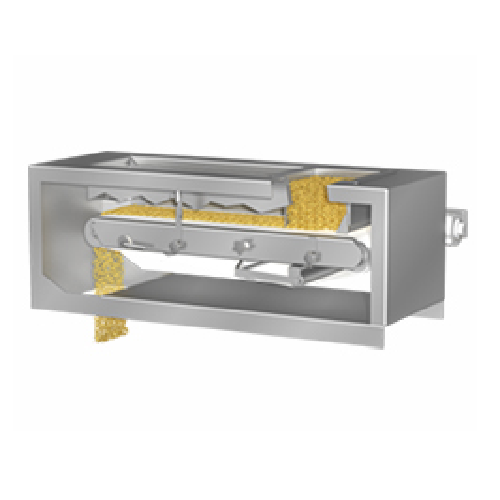

Weigh-belt feeder for industrial processes
Efficiently manage material flow and precision with a dependable weigh-belt fee...
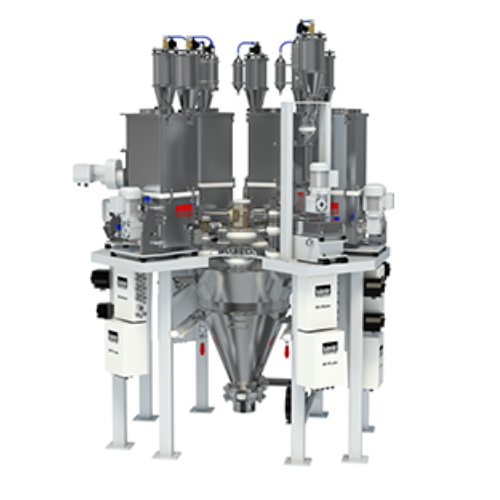

Hopper scale for precision batching
Achieve high batch accuracy with a central weighing hopper engineered for seamless inte...
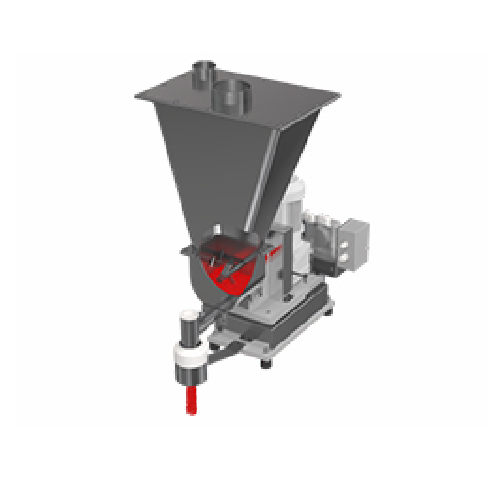

Single screw batch feeder with stirring agitator for powders and pellets
Ensure precise ingredient control and consiste...
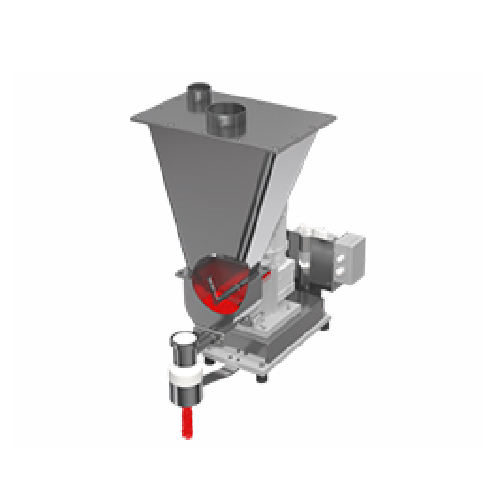

Double screw batch feeder for poorly flowing powders
Effectively manage challenging powders with precise batch dosing and...

Feeder controller for gravimetric feeders
Optimize your dosing precision and monitoring accuracy with a versatile feeder c...

Gravimetric feeder operator interface
Efficiently manage up to 16 gravimetric feeders with a user-friendly interface, enabl...

Single feeder operator interface for gravimetric feeders
Enhance precision in your dosing operations with an intuitive to...
Speed controller for feeders
Ensure precise material flow by integrating this speed controller, ideal for managing both volu...

Loss-in-weight feeder for flowable particles
Ensure precise ingredient delivery with a feeder designed for high accuracy a...

Batch feeder for bulk solids processing
Achieve precise batch dosing with this advanced feeder, designed to handle a variet...

Precision batch feeder for flowable ingredients
Achieve precise ingredient control with a batch feeder designed for versat...

Microbatch dosing for precision ingredient measurement
Achieve precise ingredient dosing with our MicroBatch system, desi...

3d screening solution for recycling facilities
For facilities handling diverse recycling materials, a solution that effect...

Precision temperature cycling system for semiconductor testing
Achieve rapid, precise temperature control from -80°C to ...

Plastic bag sealing system for batch production
Effortlessly seal and pack various films and plastic bags in batch product...

Single-stage plastic container production system
Eliminate multiple steps and minimize production costs with an integrated...
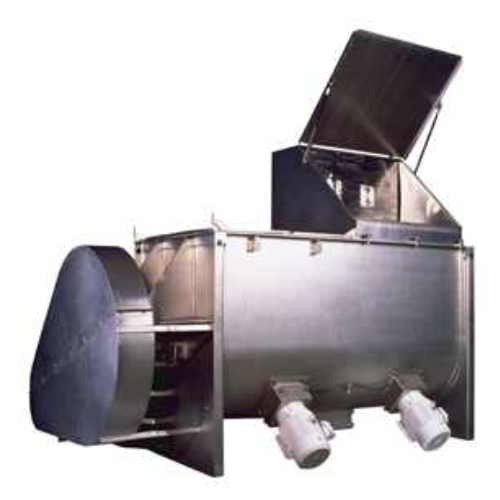

Single shaft horizontal batch mixer
Achieve consistent, high-quality blends with precise homogenization using a single shaf...
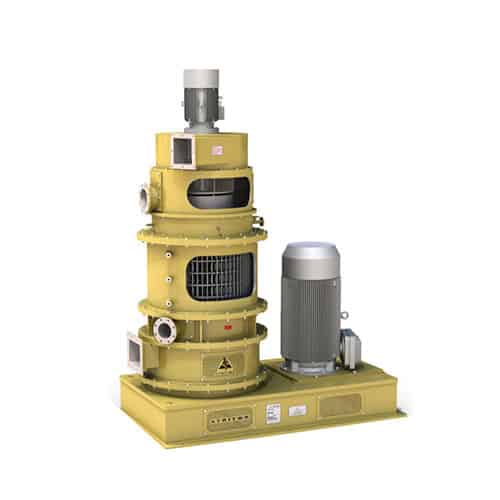

Efficient grinding and drying mill
Transform your production line with a versatile mill that simultaneously grinds, dries, ...
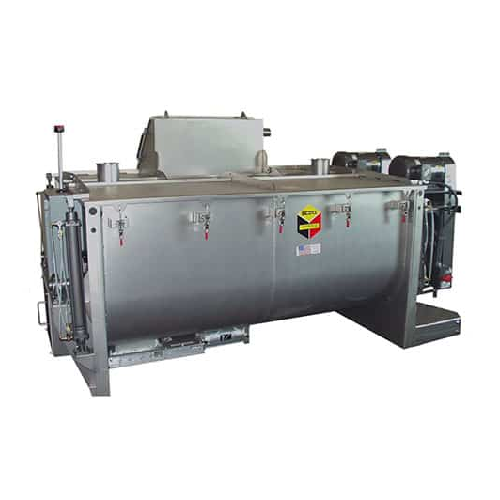

Twin shaft horizontal batch mixers for homogenous material mixing
Achieve consistent and rapid mixing of diverse materi...

Sanitary modular bulk silos for efficient storage
Maximize your storage capacity and streamline assembly with a modular s...

Modular bulk storage bins for efficient material handling
Maximize your storage efficiency with bolt-together solutions ...

Industrial high-speed turbo blender
Achieve homogeneous blending with high-speed precision, ideal for creating fine product...

Continuous blending system for fragile materials
Ideal for operations requiring gentle handling, this system seamlessly in...

High-speed container loading system for granulated bulk materials
Optimize your loading operations with a robust system...
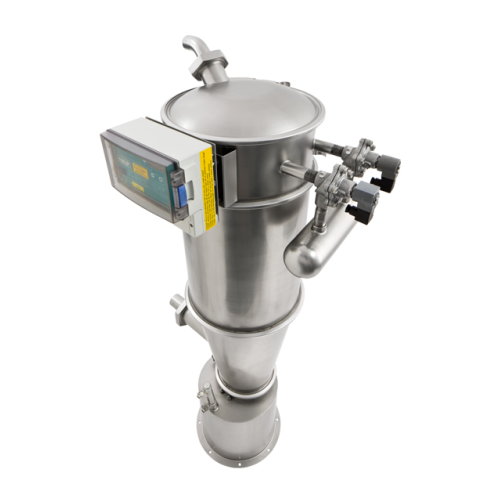

Industrial vacuum conveying system
Simplify bulk material movement and separation with a versatile vacuum conveying system,...
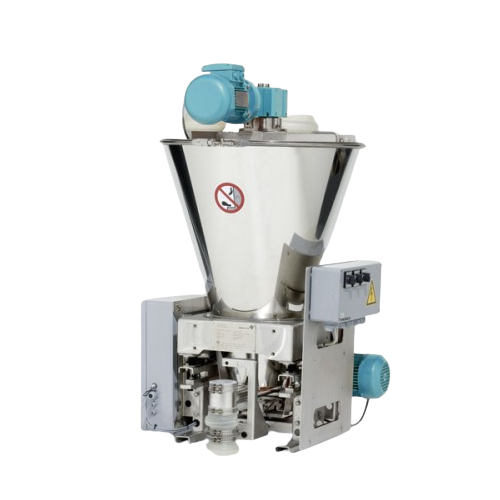

Loss-in-weight feeder for poor flowing bulk solids
Efficiently handle poorly flowing bulk solids with unparalleled precis...

Infrared moisture analyzer for lab and production use
Achieve precise and reliable moisture analysis with minimal time an...

Fast and accurate moisture meter for various samples
Quickly determine moisture content in solids, liquids, and pastes wi...
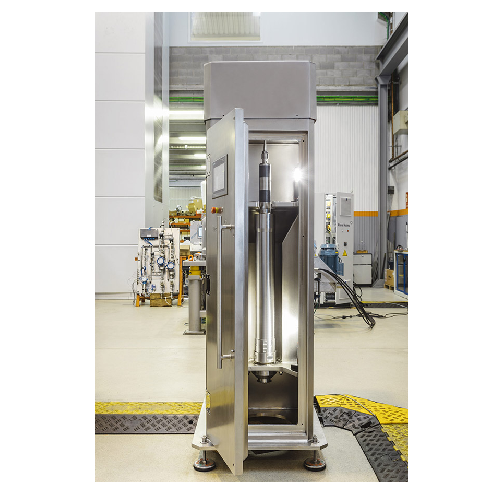

Supercentrifuge for solid-liquid separation and liquid phase separation
Optimize your separation processes with advance...

R&D shaker mixer for battery powders and chemicals
Material heterogeneity, agglomeration, and contamination are key param...
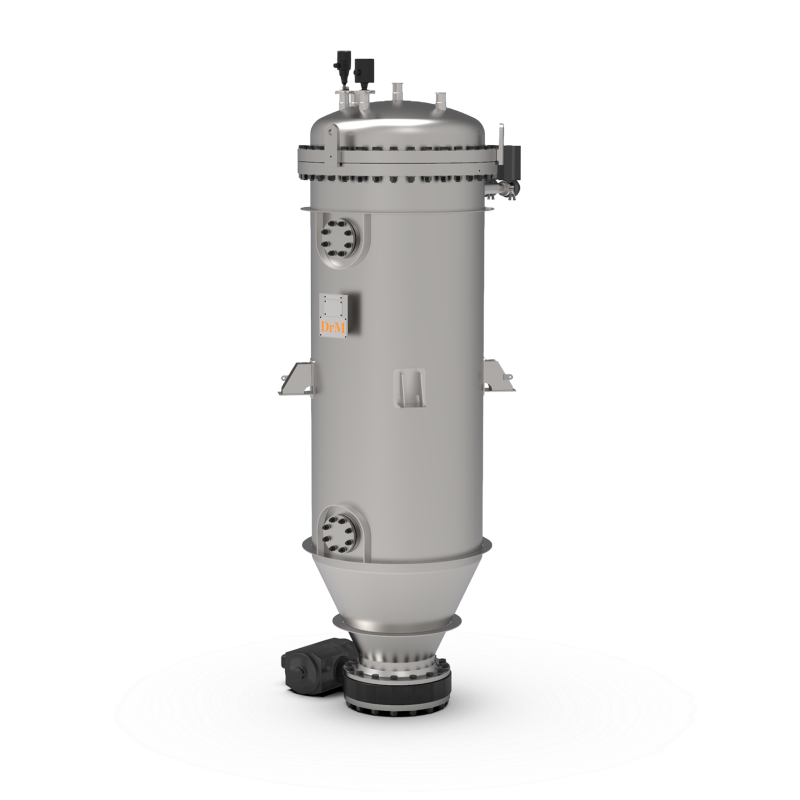

Self-cleaning candle filtration system
Separating solids from liquids by filtration requires frequent cleaning or replaceme...
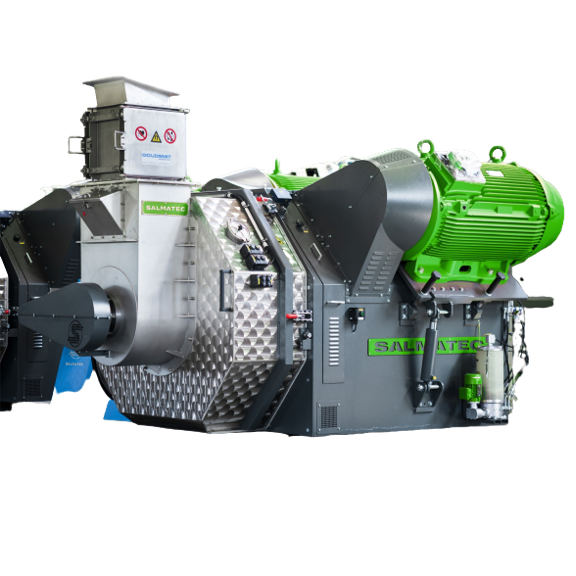
Complete pellet line
Large industries are shifting towards more environment-friendly technology, such as recycling wastes and...
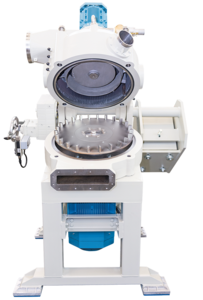
Classifier mill for recovered carbon black
Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) can be recycled back to the tire production chain ...
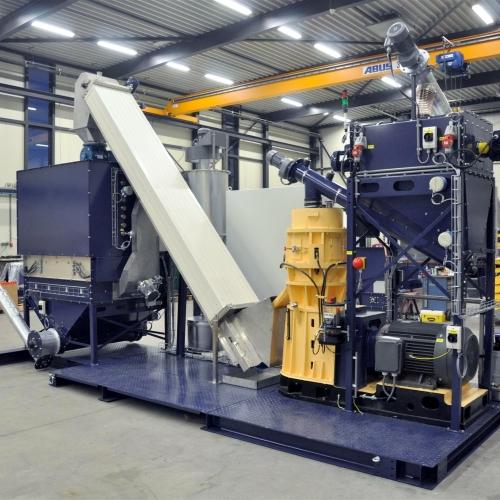

Pelleting line for manure fertilizer
Manure fertilizer needs to be made marketable by making them visually attractive, with...
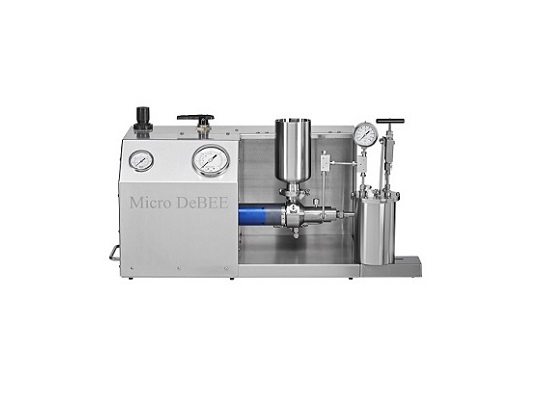

High pressure air powered laboratory homogenizer
Offering lab-scale to small pharmaceutical production scale output for in...
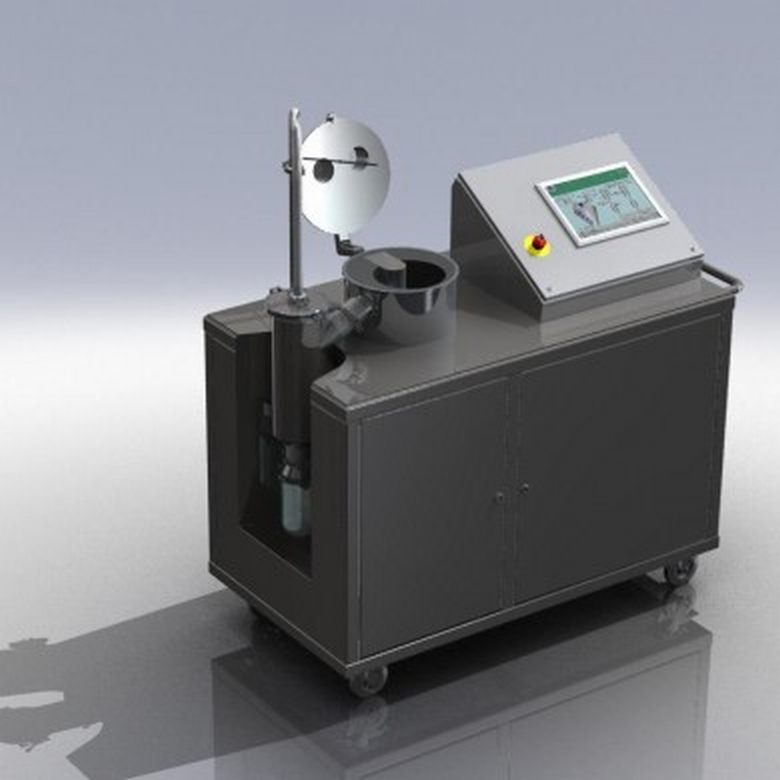

Laboratory scale active freeze dryer
The laboratory-scale active freeze-drying is used for dehydrating high-value products ...

Feeder with flexible wall hopper
The varying properties of dry powder products mean that specialized feeders are required fo...

Hygienic FIBC handling line
There are many considerations when handling FIBC’s (Flexible Intermediate Bulk Containers)...

Wiped film evaporator
With wiped film distillation, a substantial decrease of boiling temperature is obtained by reducing the...
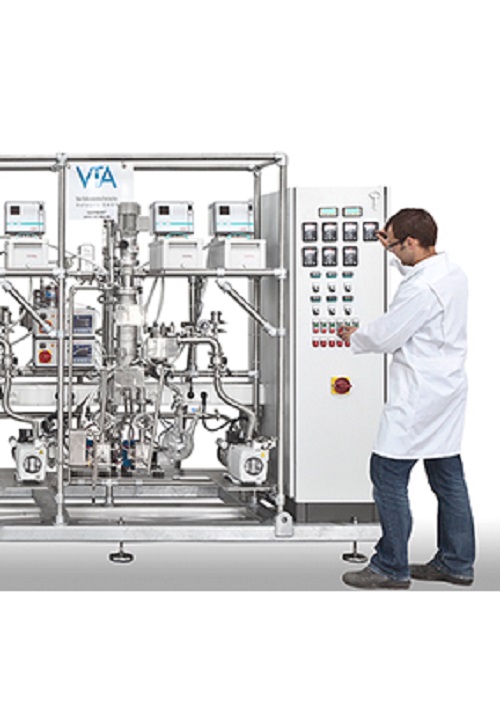

Pilot multi-stage distiller
If generating an scalable data and bring in results with small sample quantities of high-boiling...
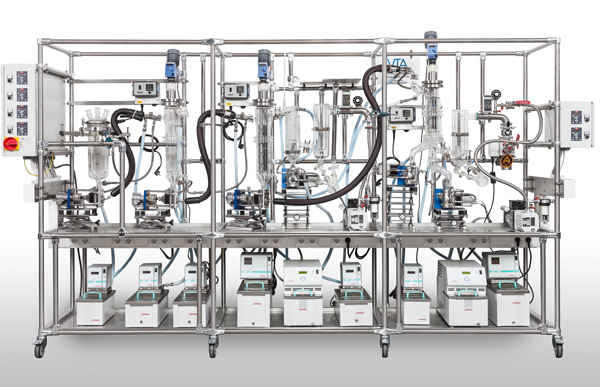
Laboratory multi-stage distiller
A laboratory multi-stage distillers that combines the wiped film and short path distillatio...

Laboratory wiped film distiller
Reach reliable conclusions testing the distillation of high-boiling or highly viscous materi...
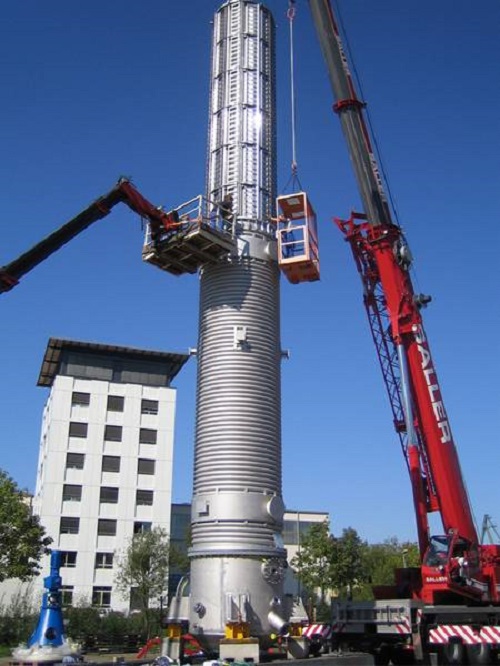

Short path evaporators
With short path distillation, a substantial decrease of boiling temperature is obtained by reducing th...
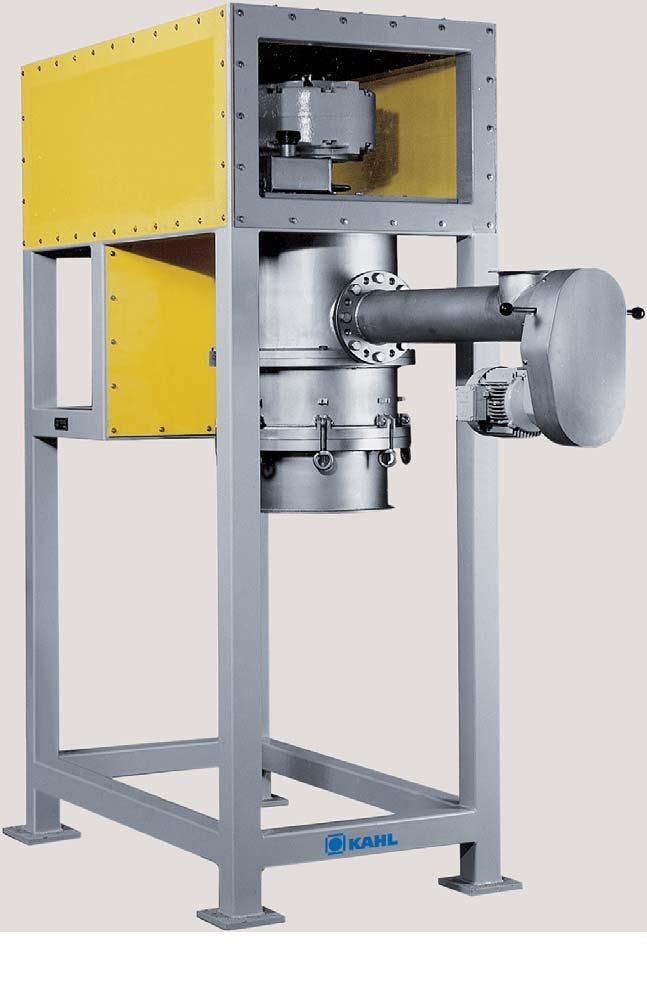

Pelleting press with overhead drive
Production of certain pelletized products requires working with output products of a pa...

Small scale pelleting press
Many industries require reliable pelletizing equipment with smaller scale production capacities....