Making Almond Milk
Find innovative production technology for making almond milk and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Although the first association with almond milk might be the modern plant-based lifestyle trend, it is dated even back to the Middle Ages when it was used as an alternative to cow milk during Catholic fasting. Once harvested, almonds undergo a series of treatments in almond milk manufacturing equipment, such as bleaching, peeling, and grinding, to get the delicious final product for breakfast and desserts.
Top picks for making almond milk
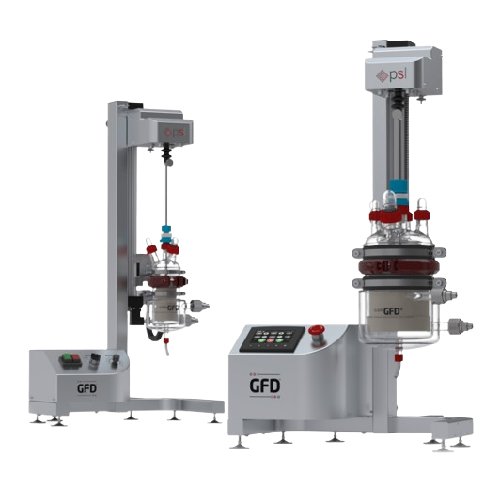
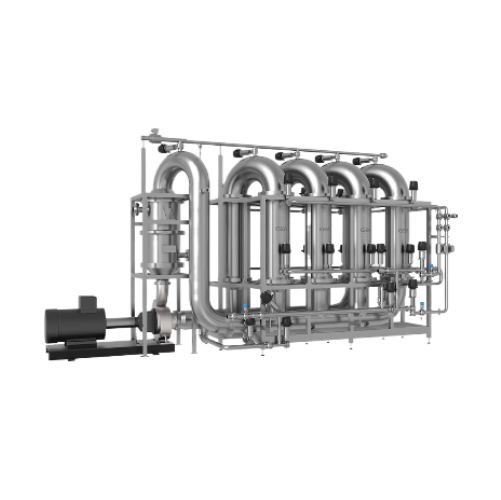
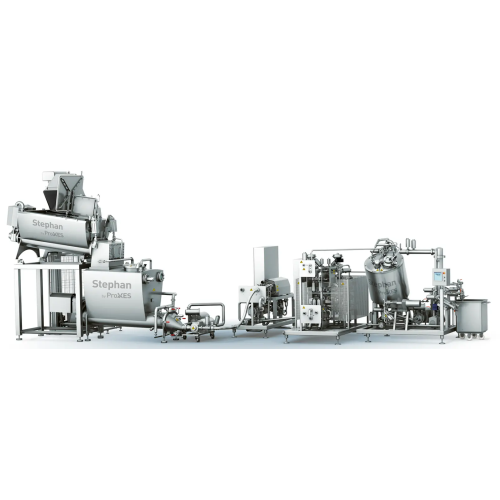
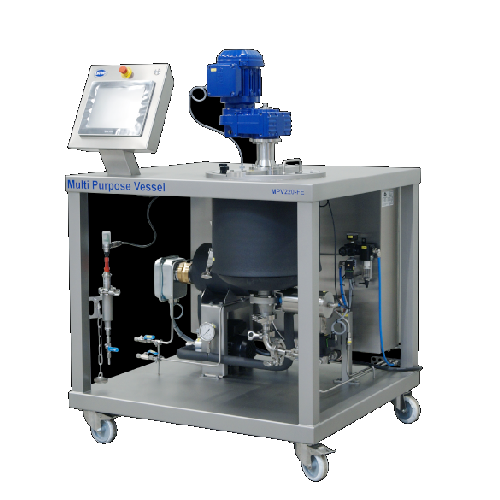
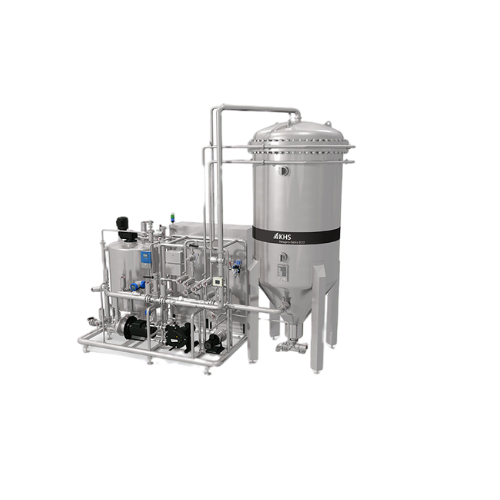
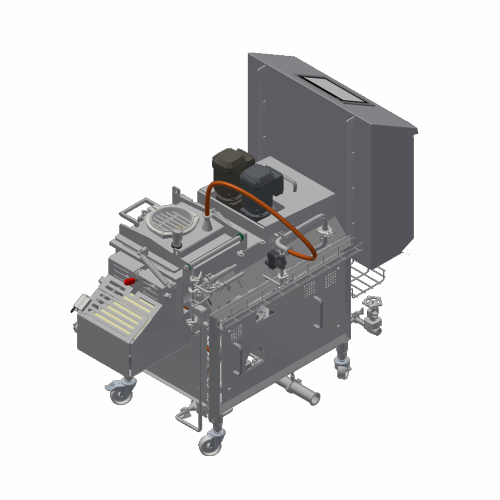
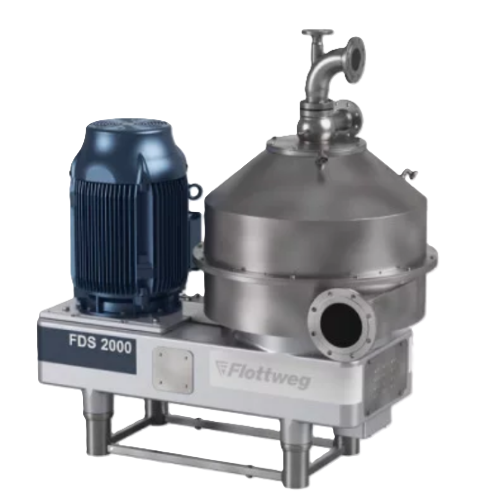
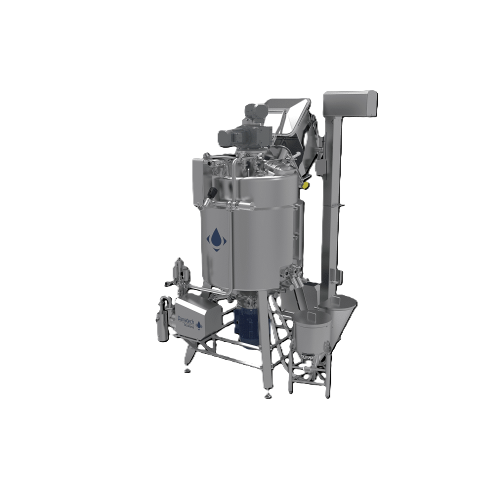
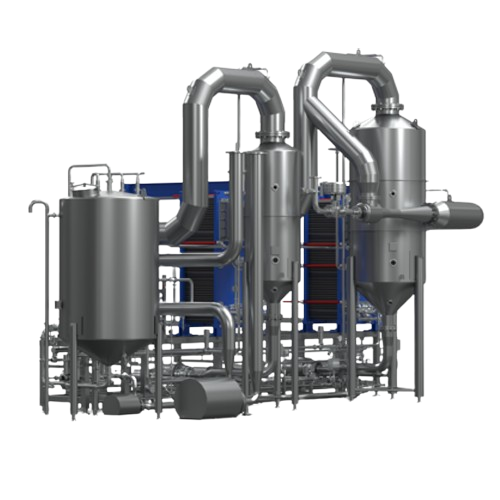
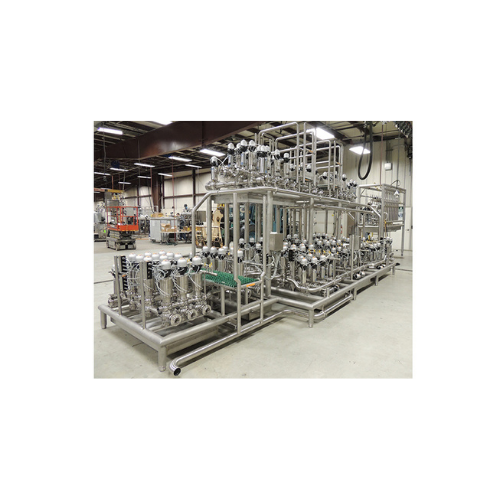
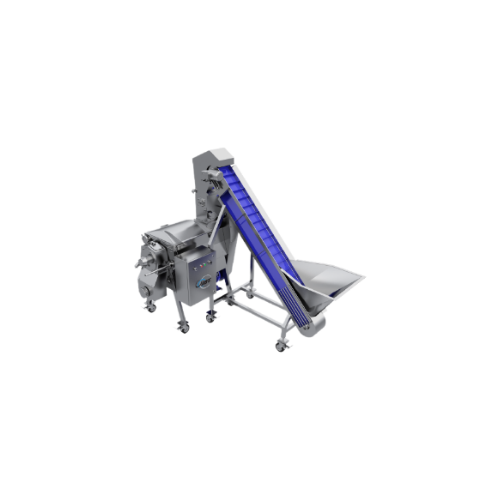
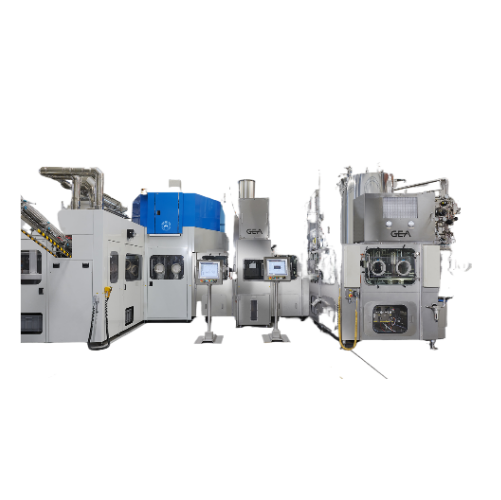
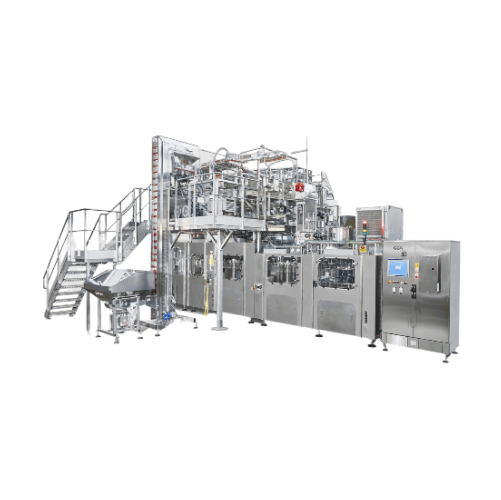
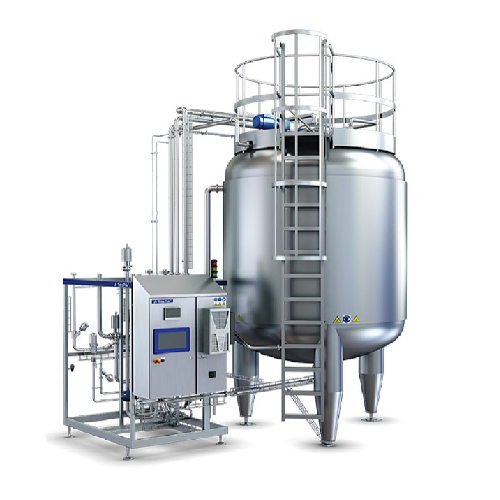
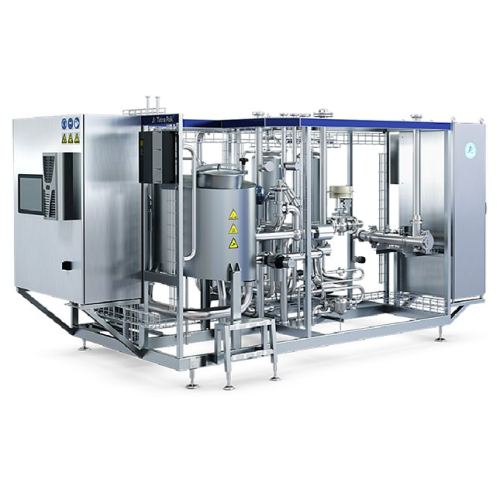
Almond milk production system
Streamline your plant-based beverage production with a comprehensive system designed to finely...
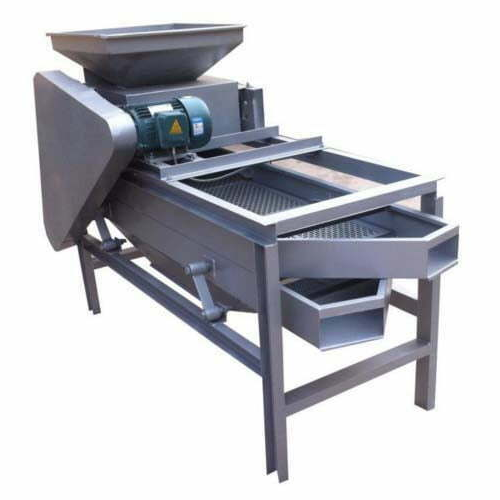

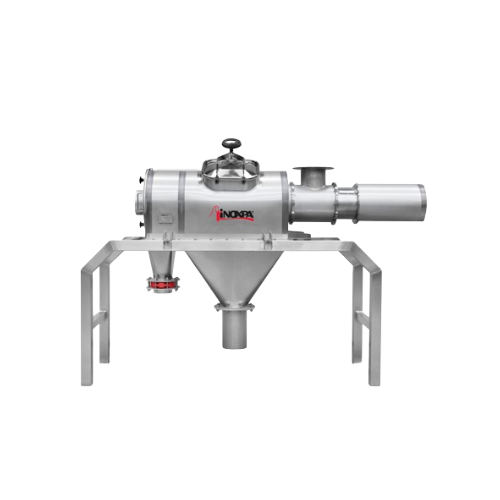
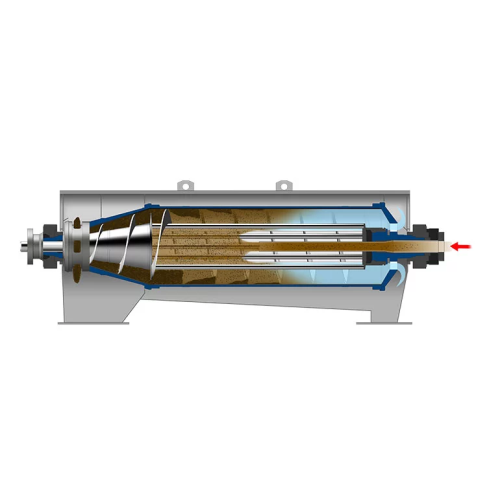
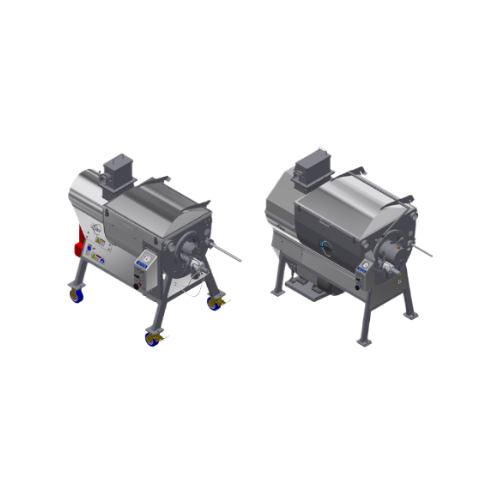
Almond sheller
Streamline your nut processing operations with a high-efficiency shelling machine designed for precision cracki...
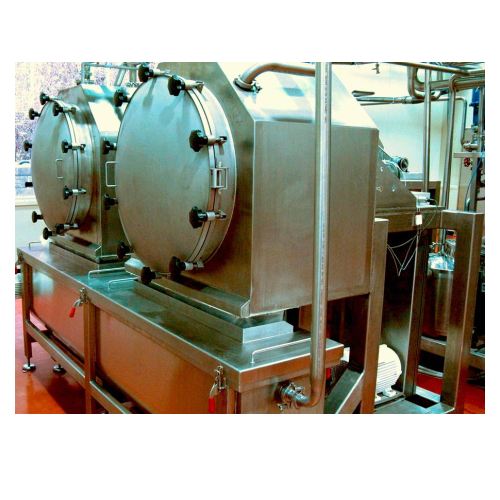
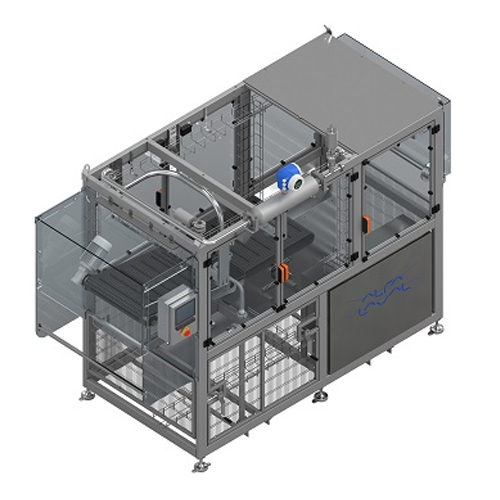
Almond hulling system for soft and semi-hard shells
Efficiently hull almonds with soft or semi-hard shells to streamline ...
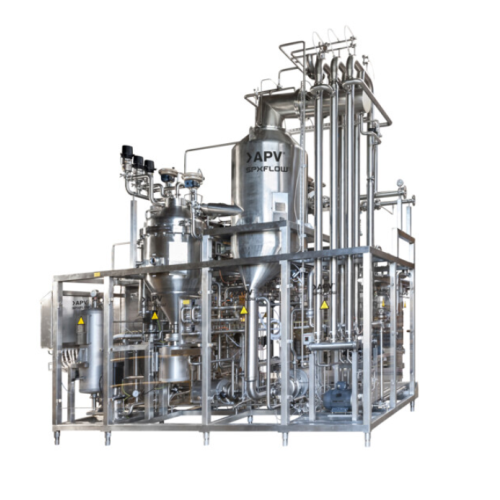

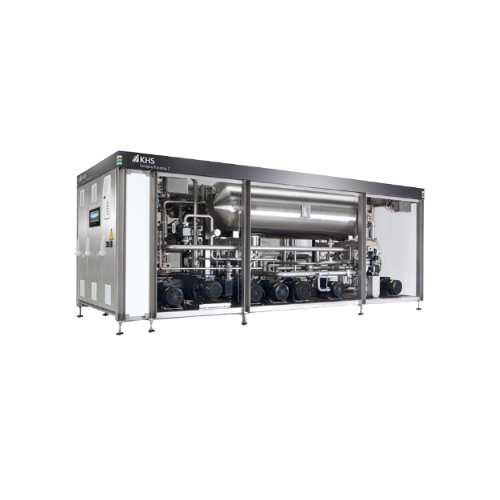
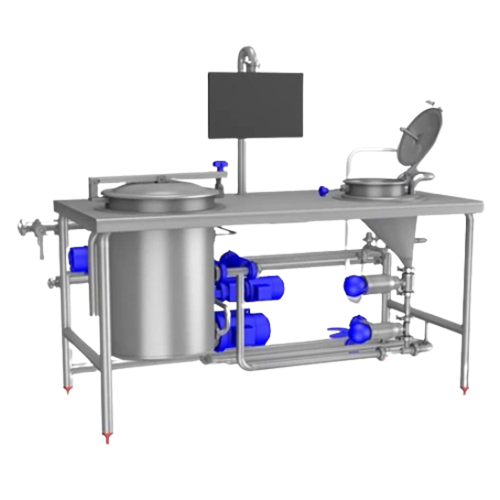
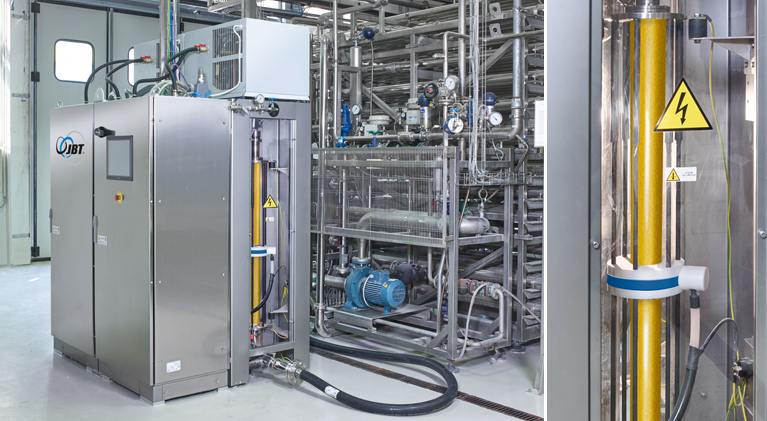
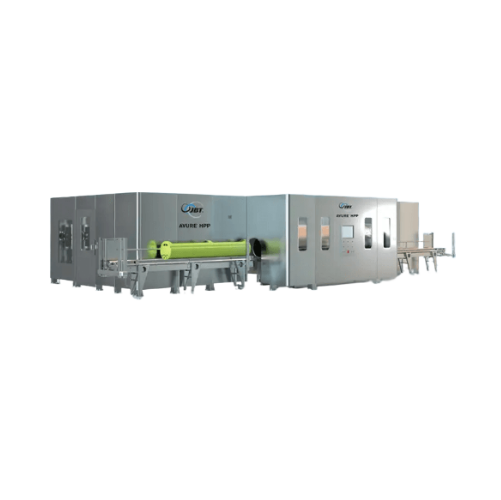
Infusion Uht system for dairy and plant-based beverages
Efficiently extend the shelf life of dairy and plant-based bevera...
Tell us about your production challenge
Picking the perfect almonds for the perfect almond milk
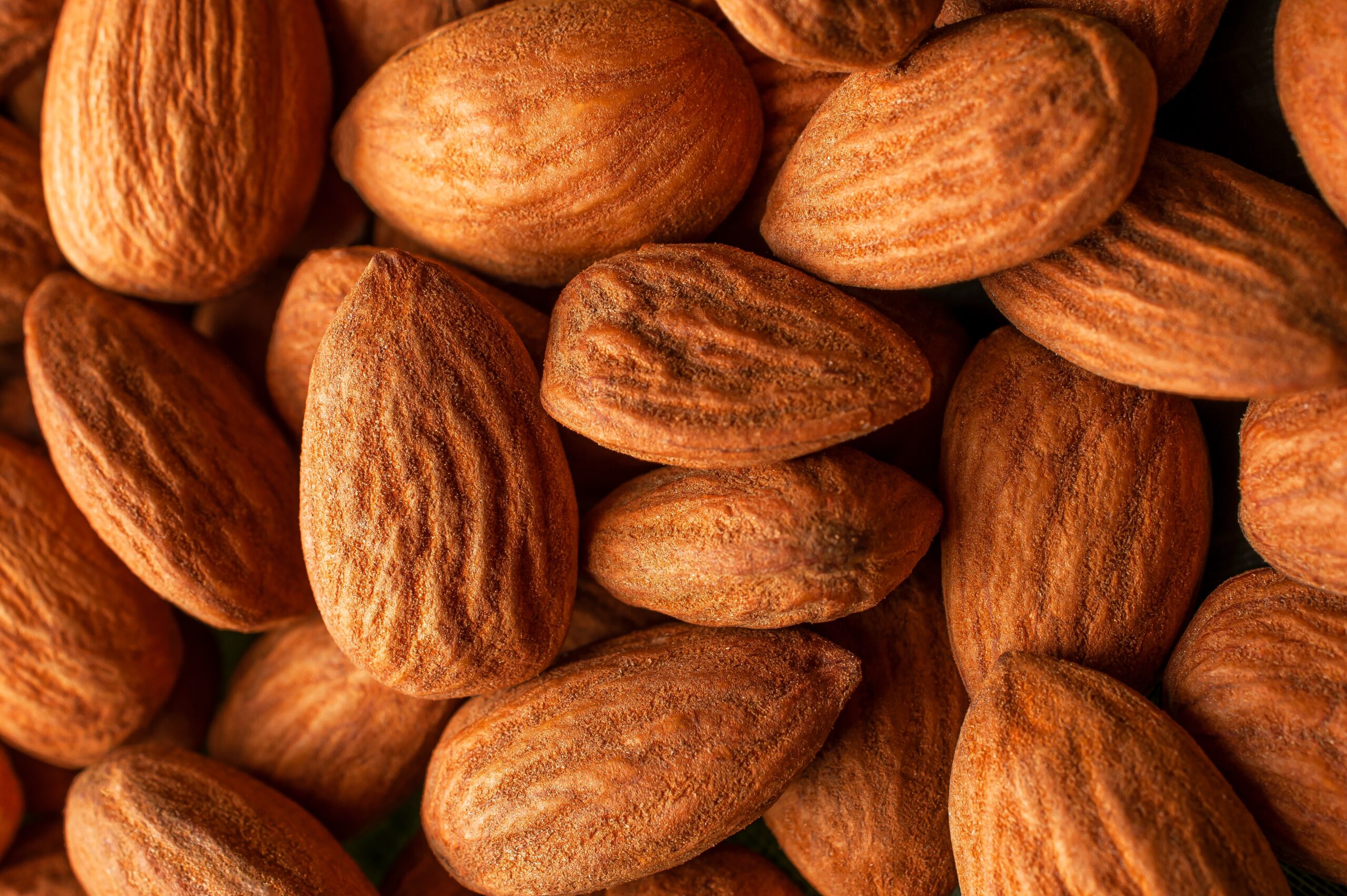

Like any other plant-based milk, nuts, in this case almonds, together with water, are the main ingredients when making almond milk. Interestingly, almond trees bear fruit classified as drupes, and the edible nut is part of its seed. Drupes grow during spring and then split open during summer to allow the almond to dry.
Ideally, almonds for almond milk production should meet the following standards: less than 6.5% of moisture, intact, well developed – more than 75% of the nut must be usable -free from blemishes and discolorated as well as pests. The production starts with the harvest assisted by a harvesting machine called almond shaker that shakes almonds off a tree.
Once harvested, almonds are passed through huller and sheller machines. In order to preserve flavor, it is crucial to store almonds properly. They can be stored in bins, silos, or bulk containers isolated from foreign smells as they absorb odors easily. Furthermore, almonds should be kept at temperatures lower than 10°C and relative humidity under 65%.
Milking almonds: key processes and almond milk manufacturing equipment
Before starting the production process, almonds should be soaked for 6 to 20 hours. Once soaked, almonds are bleached in almost boiling (90°C) water for 2.5 minutes, followed by going through the rubber rollers to remove the skin, preventing potential microbiological hazards. Almonds, water and emulsifiers, mainly soy lecithin, are added to a grinder to achieve emulsion. Soy lecithin decreases the tension between oils and water and stabilizes the emulsion.
The emulsified mixture is then filtered to remove solids which can reduce the mass by 25%. The next piece of almond milk manufacturing equipment in the production process is the blending tank in which the almond paste, syrup, emulsifier and other flavors are added to create the final product.
The type of agitator, temperature and blending play a crucial role in the beverage’s viscosity, texture and flavor. Almond milk is finally pasteurized at 90°C and maintained for 90 seconds to eliminate bacteria and achieve food safety standards. After that, the temperature is brought down to 4°C.
High-Pressure Process as an alternative food safety method
Although pasteurization is the most traditional and widely used method to achieve satisfactory food safety standards, one of the newly designed propositions is a so-called High-Pressure Process. The process is non-thermal, which means it does not use heat but relies on elevating pressure to eliminate hazardous microorganisms from sustenance. This process maintains all qualities of almond milk while, at the same time, damaging membranes of microorganisms, denaturing their proteins and disturbing their cell PH balance which inactivates them. It is achieved by placing the product in a pressure vessel, filling it with water and adding pressure up to 600MPa with a pump. The product is then unloaded and its original temperature is restored.
Do judge almond milk by its cover: different packages and what they mean
Almond milk comes in various packaging, but the difference is more than just aesthetic. For instance, almond milk that comes in glass bottles or tin cans is pre-pasteurized and secondary sterilized once in the packaging. If almond milk is sold in aseptic brick cartons, the product undergoes an ultra-pasteurization process, which is pasteurization at a higher temperature point.
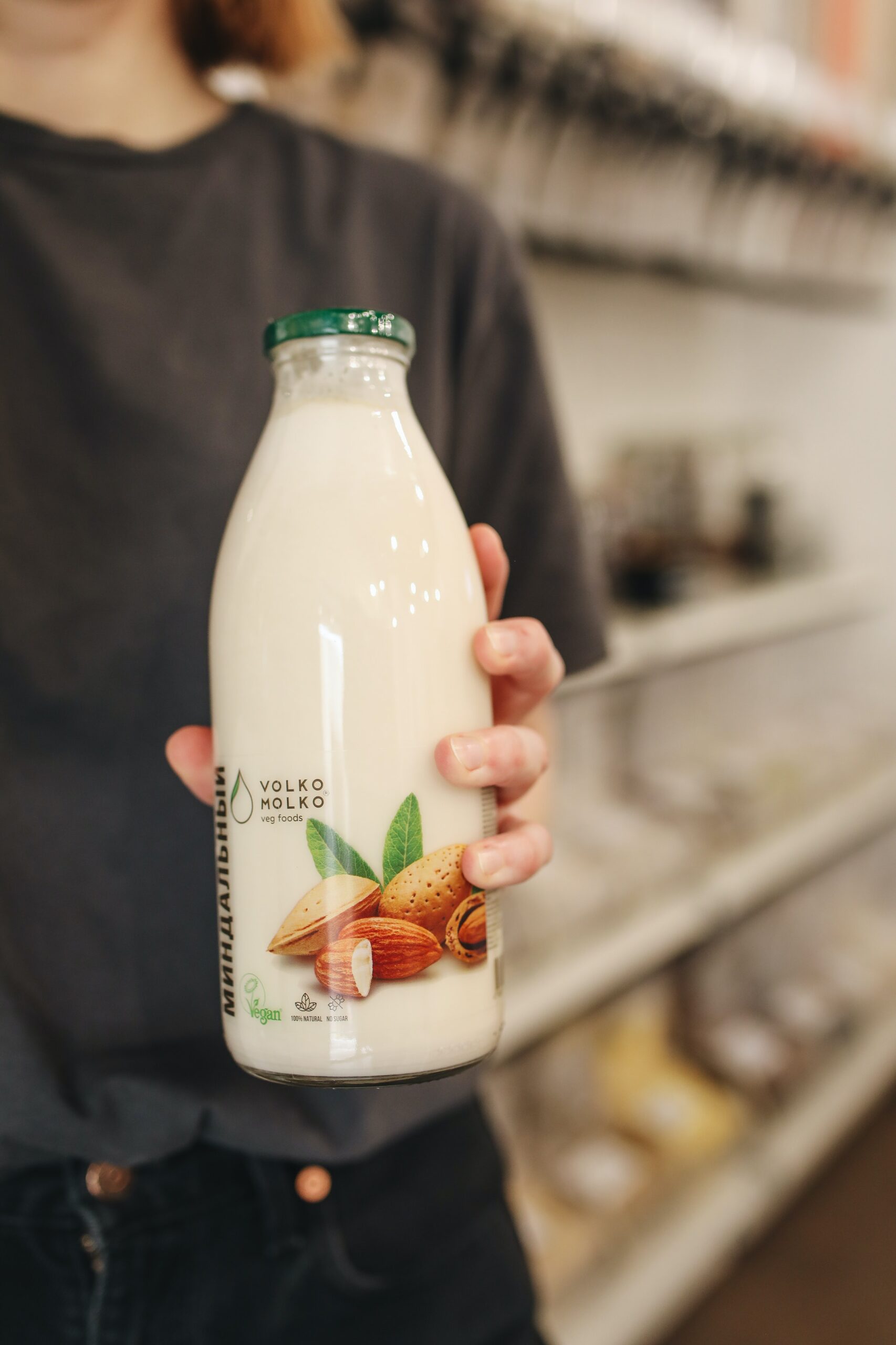

This type of almond milk does not require the addition of antioxidants and has a shelf life of up to a year. Finally, HTST pasteurization was used for almond milk in a gable top carton. This high-temperature short-time process takes place in stainless steel heat exchange plates where the liquid temperature is raised to a minimum of 72°C for at least 15 seconds before being rapidly cooled. It has the shortest shelf life, about one week, and must be kept at low temperatures.
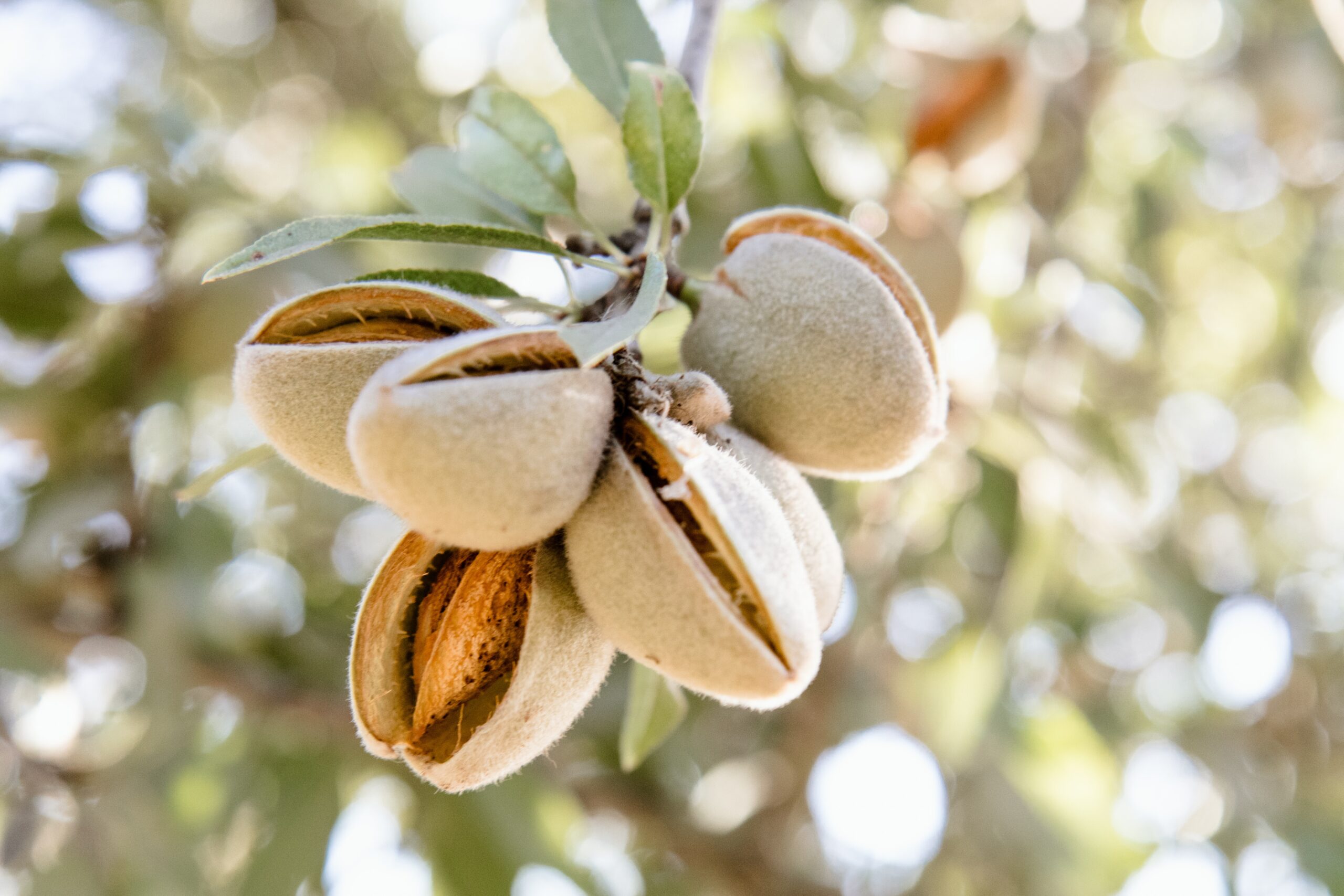

The big question: eco-friendliness and sustainability
When it comes to sustainability and almond milk, there are many questions. Namely, the main issue arising is the relatively large amounts of water, precisely 74 liters, required to produce a glass of almond milk compared to other plant-based alternatives, such as soy and oat milk that need less than 10 and 20 liters, respectively. However, it is still a lesser amount required to produce a glass of cow’s milk – roughly 120 liters.
Nevertheless, almond milk compromises it with a brilliant carbon dioxide emission record: less than 0.2 kg is emitted to produce 200 ml of a beverage, which is the least of all milk alternatives, and considerably less than more than 0.6 kg emitted during the production of the same amount of dairy milk. In addition, dairy milk production emissions are believed to be even 30 times higher than estimated. Therefore, the positive impact on the environment achieved by switching to plant-based alternatives is often underestimated.
Processing steps involved in almond milk making
Which almond milk technology do you need?

Centrifugal separator for chemicals and minerals
Achieve precise separation of liquids and slurries with this high-speed c...

Sanitary cover for visual inspection
Ensure optimal hygiene and easy access in your production line with a transparent cove...

Pasteurizer for extended shelf-life (esl) milk
Extend the shelf life of milk while maintaining its taste and nutritional i...
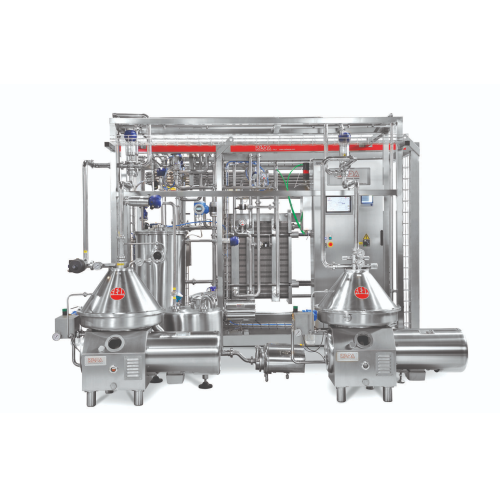
Milk pasteurizer for whey and cream
Ensure optimal product safety and quality with advanced heat exchange technology, reduc...

Milk skimming separators for dairy applications
Enhance dairy production with high-efficiency skimming separators that opt...

Milk standardization system
Achieve precise milk and cream fat standardization with this advanced inline system, optimizing ...
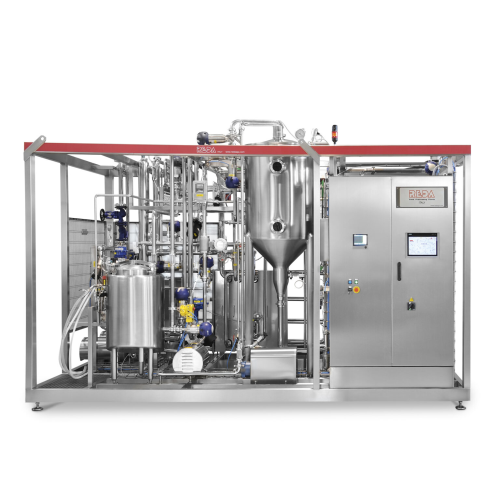

Pasteurizer for fresh milk
Ensure your dairy and beverage lines achieve optimal product safety and quality by leveraging adv...
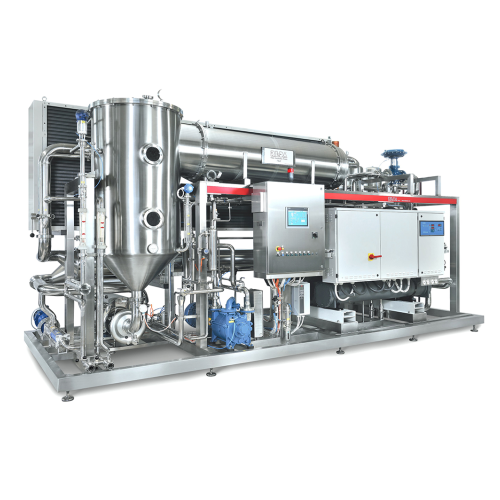

Grape must concentration solution
Optimize the alcohol content and flavor profile of your wines by efficiently concentratin...
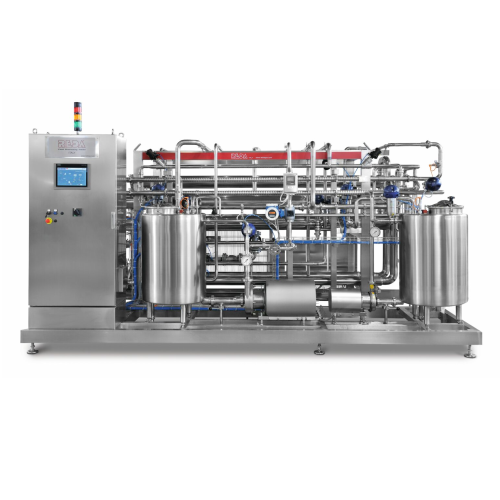

Membrane filtration for whey concentration
Enhance your liquid processing with advanced membrane filtration designed to im...
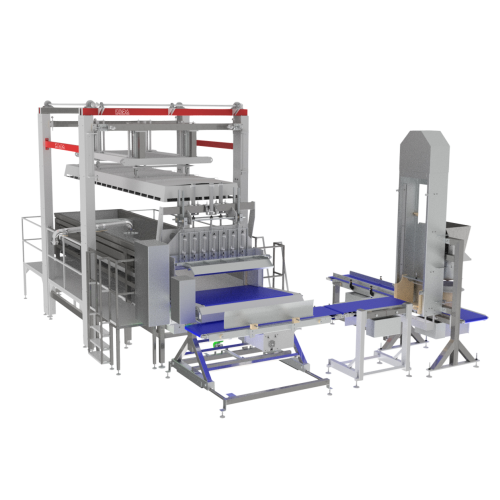

Cheese forming units for hard and semi-hard cheeses
Optimize your cheese production process with advanced moulding and pr...
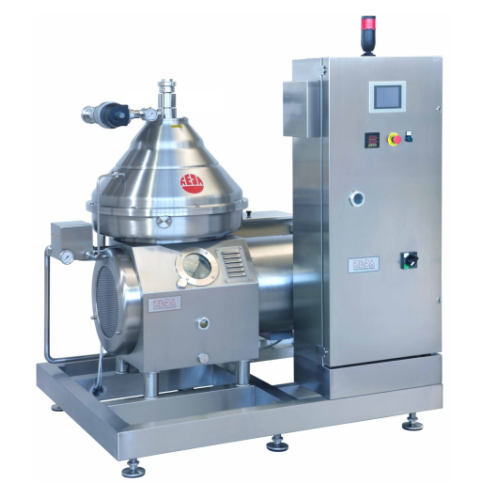

Clarifier for milk and whey
Optimize dairy and beverage production by efficiently removing fine curd residuals, ensuring hig...

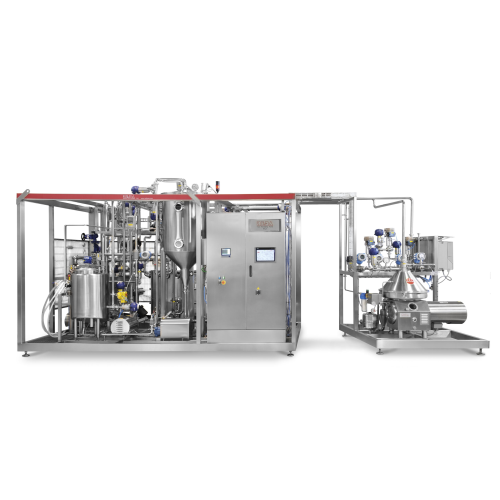
Uht sterilization for milk
Enhance your production line with advanced UHT sterilization, ensuring extended shelf-life and un...

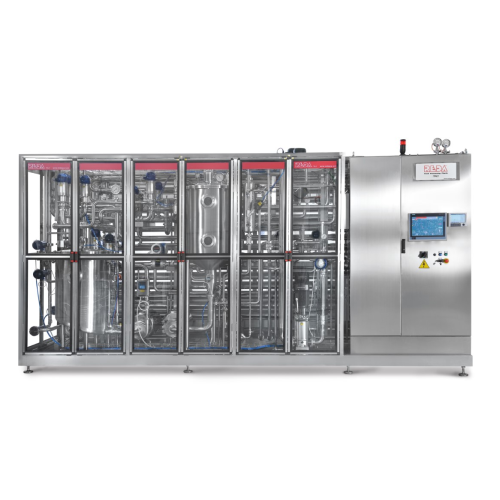
Complete milk processing lines
Optimize liquid product quality with a comprehensive processing line that integrates pasteuri...
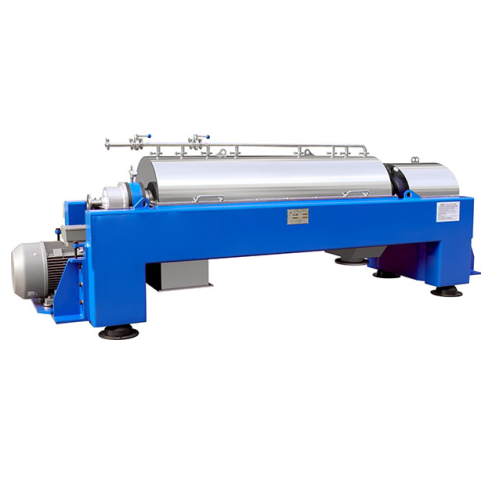

High-performance decanter centrifuge for dewatering
Achieve efficient and reliable dewatering by integrating a decanter c...
Continuous caramel process line
Optimize your continuous food processing with an engineered-to-order line tailored for preci...

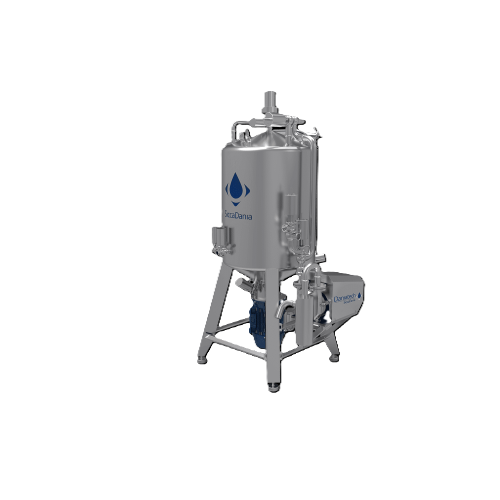
Almond milk production system
Streamline your plant-based beverage production with a comprehensive system designed to finely...
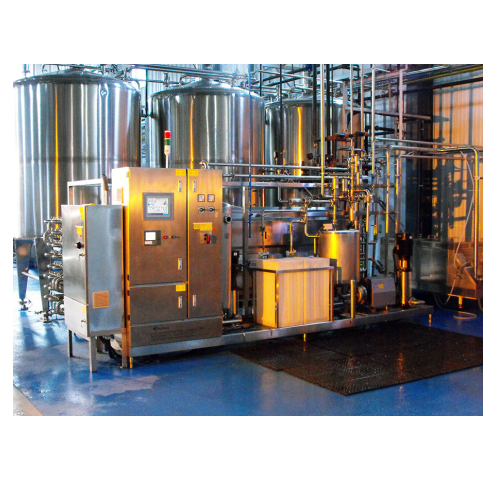

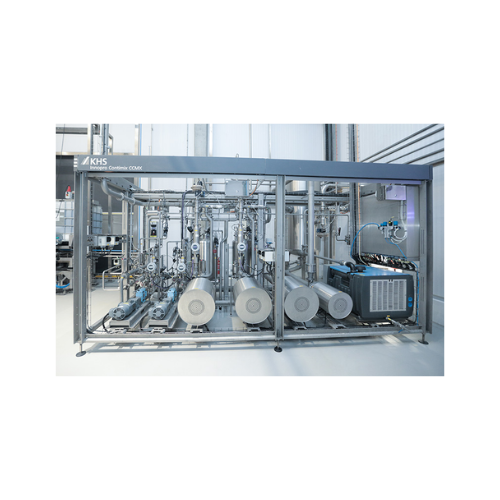
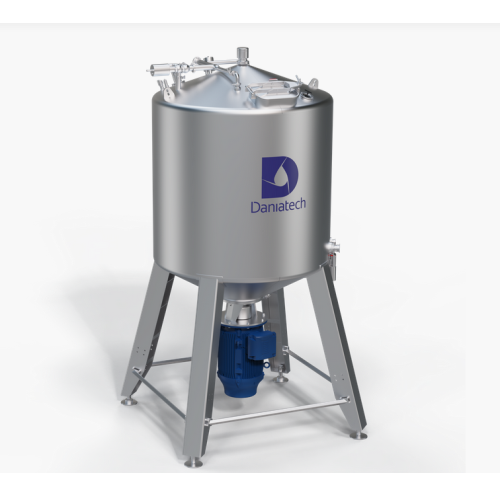
Dairy alternative production technology
Transform your production line with efficient dairy-alternative technology, enablin...
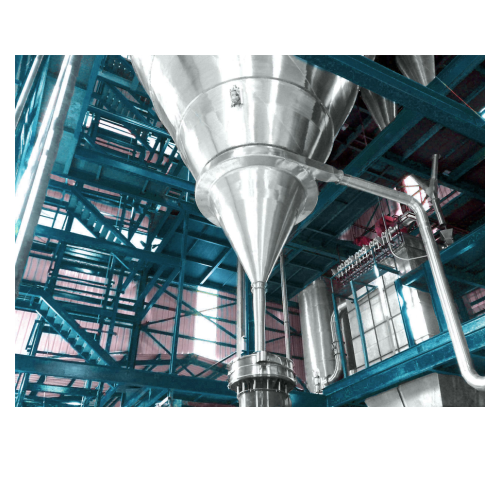

Milk powder processing plant
Achieve precise powder formulations with our state-of-the-art milk powder processing plant, ide...
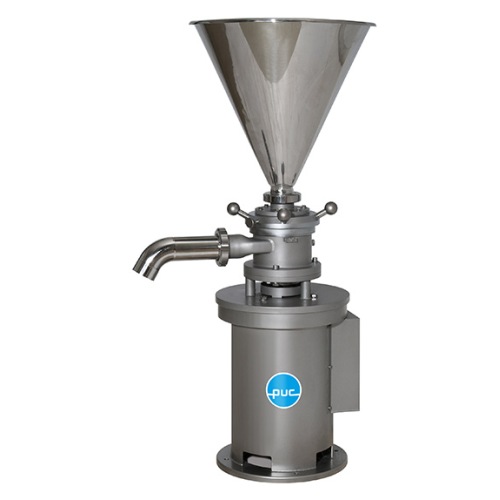

Vertical colloid mill for emulsifying and homogenizing
Optimize your production line with precise particle size reduction...
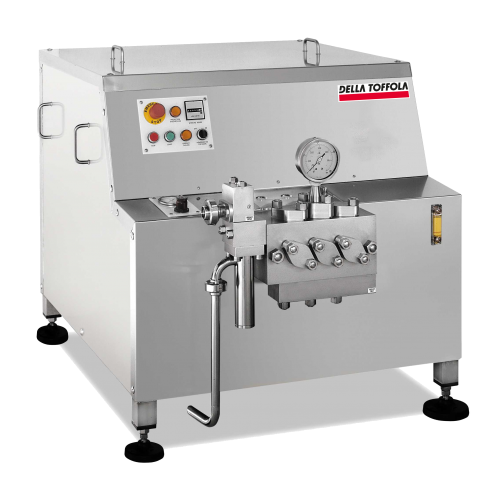

Industrial homogenizers for dairy products
Maximize consistency and quality in your production of milk products and bevera...
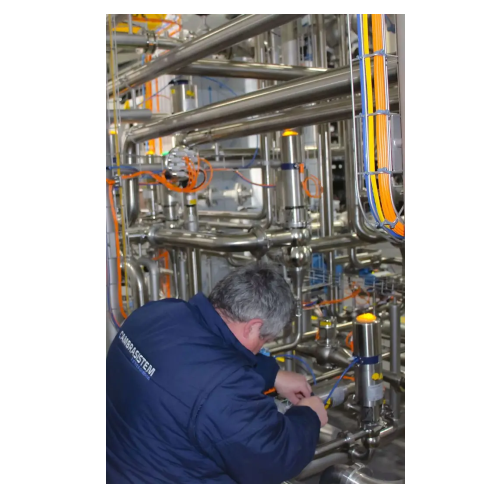

Automation for food processing
Optimize your food production with cutting-edge automation, enhancing efficiency and precisio...
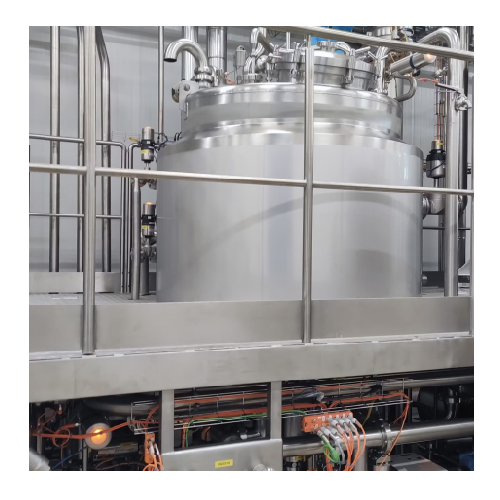

Batch processing systems for industrial applications
Optimize batch production with versatile systems that enhance energy...
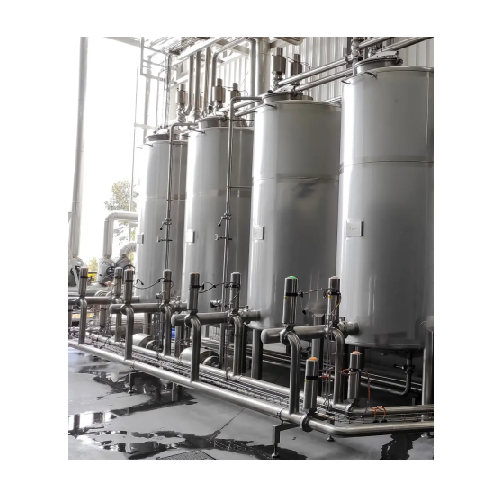

Cip cleaning systems for food and beverage industry
Optimize your cleaning operations with seamless Clean-in-Place and St...
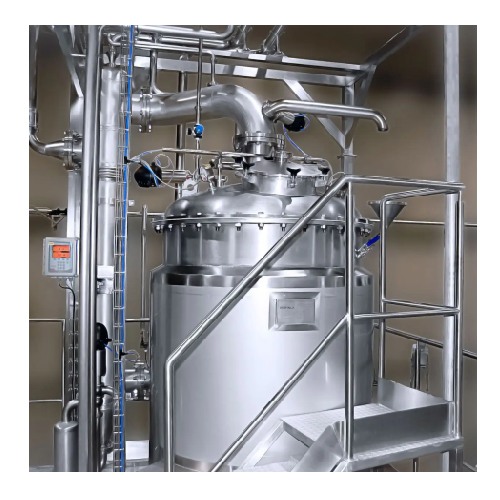

Inline processing system for food and beverage production
Optimize your production line with a versatile inline processi...
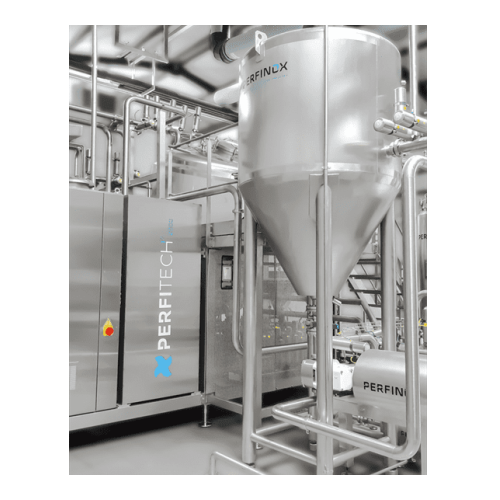

Industrial premixing system for batch and inline processing
Streamline your production with advanced premixing systems d...
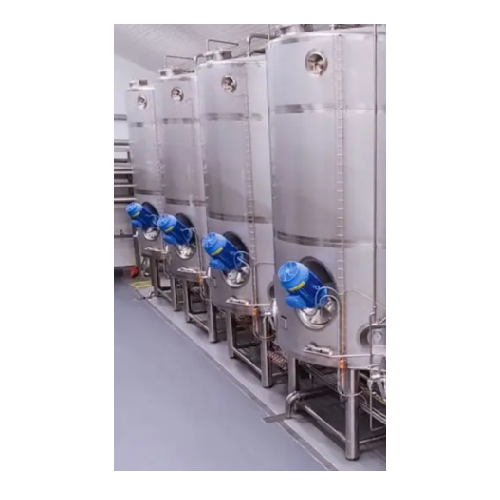

Turnkey food and beverage processing solutions
Optimize your production line with integrated processing systems designed t...
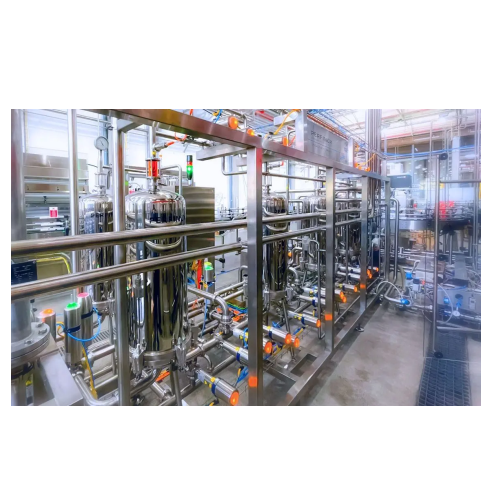

Automatic filtration system for beverage industry
Enhance your beverage production with a multi-stage filtration system t...
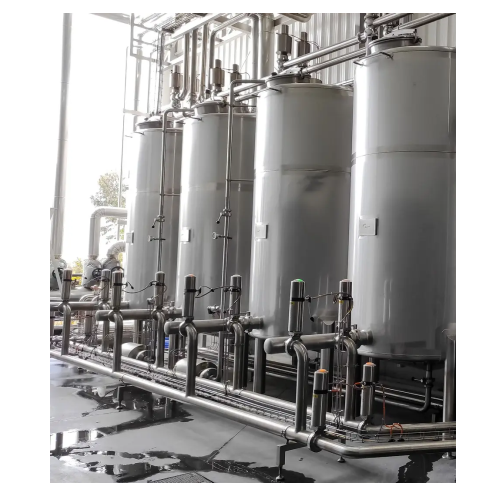

Clean-in-place system for industrial cleaning needs
Optimize your production efficiency with a system that seamlessly int...
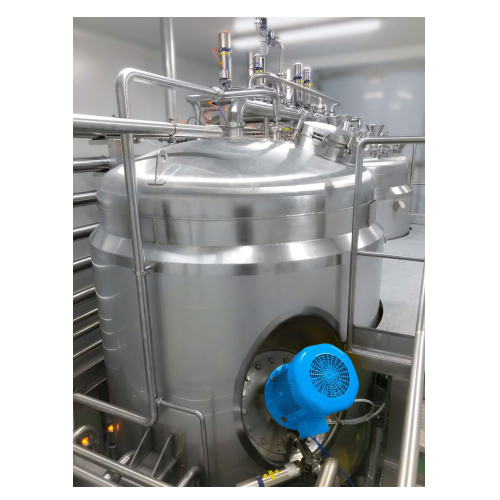

Industrial cooling vessel for ready meal components
Enhance your production with precise cooling and gentle handling of t...
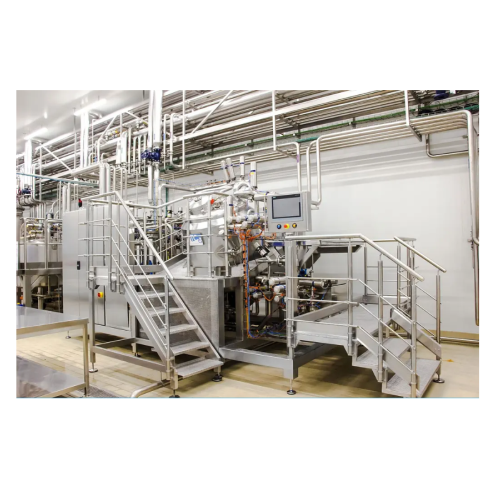

Mayonnaise production system
Ensure precise emulsification for low to full-fat mayonnaise and similar cold emulsions with a ...

Aseptic storage tanks for high efficiency applications
Ensure consistent aseptic storage and efficient handling of variou...
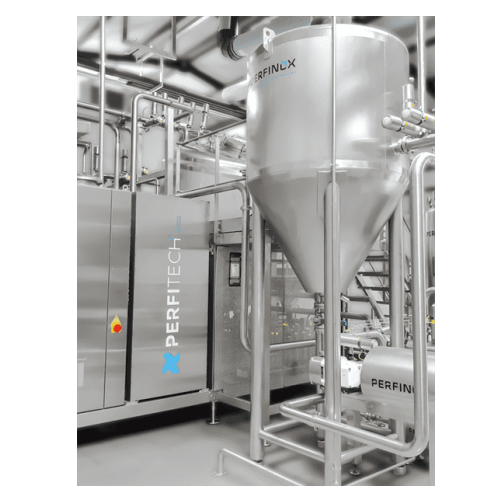

Compact production unit for liquid food products with varied viscosities
Streamline your batch production with this ver...
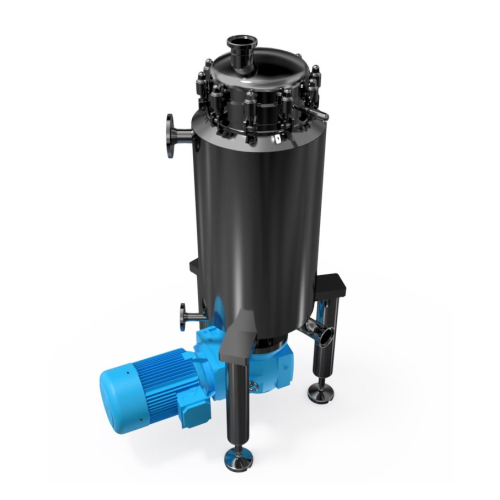

Scraped surface heat exchanger for food processing
Efficiently handle temperature-sensitive food products with a compact ...
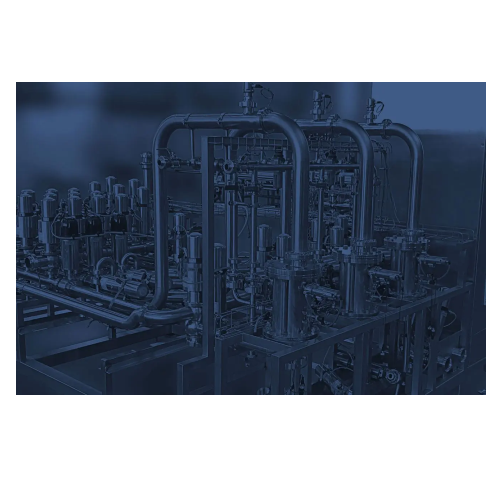

Pig systems for product recovery in food and beverage industry
Maximize yield and minimize waste with advanced PIG syste...
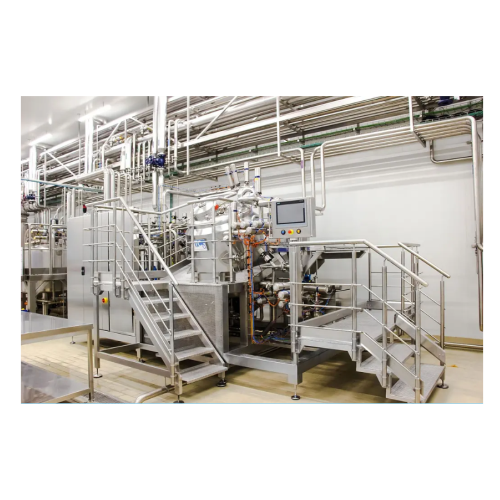

Hygienic fluid storage tanks for food industry
Ensure impeccable hygiene in fluid storage with our customizable tanks, des...
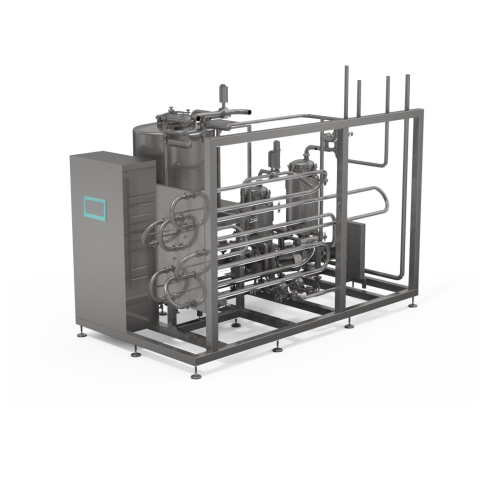

Aseptic thermal processor for high viscosity products
Optimize your processing of high viscosity products with precise te...
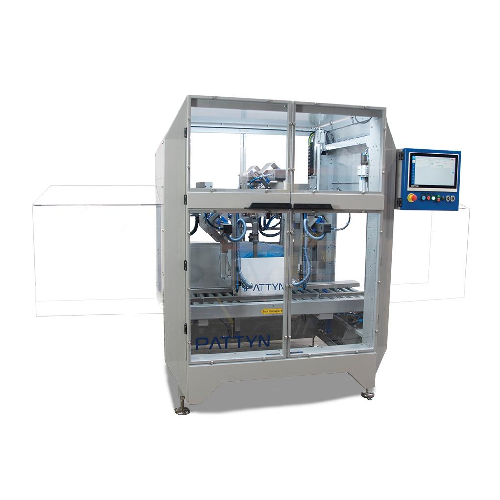

Automatic bag folding solution for bulk packaging
Enhance your production line efficiency and product protection by integ...
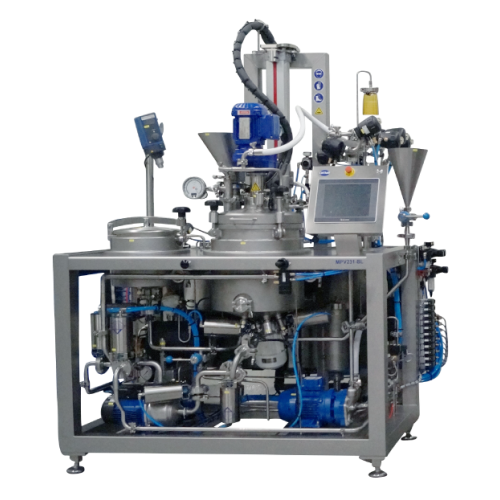

In-line production of fine emulsions
Achieve homogenous emulsions with precise control, reducing the risk of lump formation...
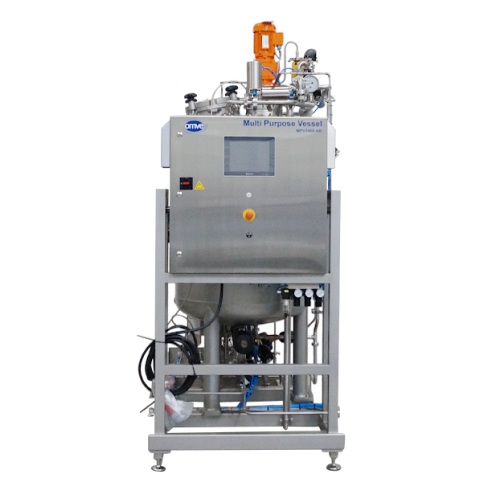

Aseptic buffer tanks for pilot scale process lines
Ensure seamless production flow and quality control in sterile environ...
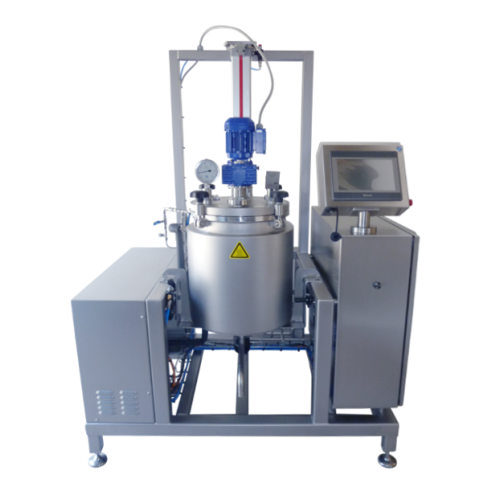

Batch food processing cookers
Achieve precise temperature and pressure control for small-scale food production with modular ...
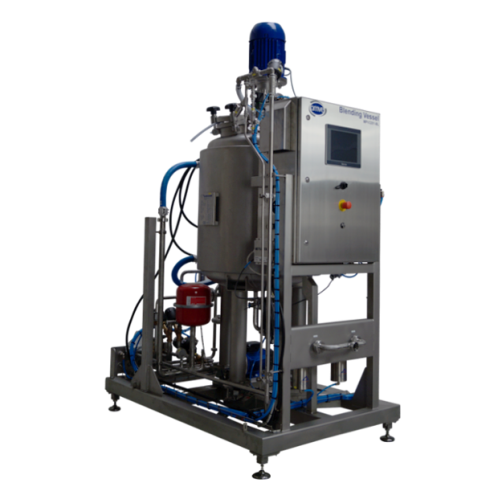

Advanced closed blending vessels for liquid food products
Enhance your production line with advanced closed blending ves...
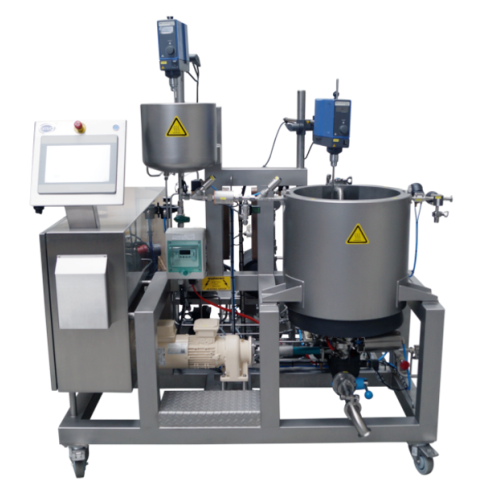

Atmospheric blending vessel for r&d activities
Optimize your liquid blending processes with this versatile vessel, designe...

Hygienic buffer tanks for process optimization
Enhance your production flow with hygienic buffer tanks that ensure consist...
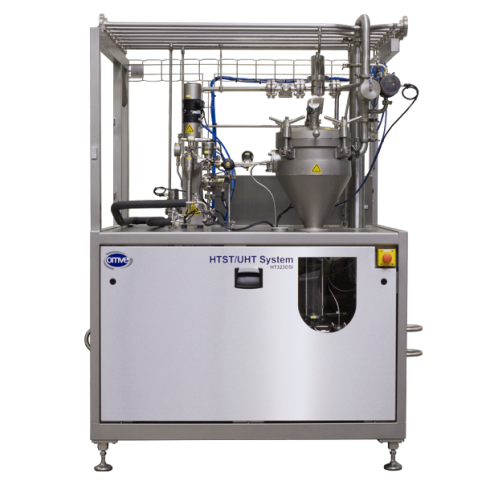

Laboratory in-line sterilization system
Ensure precise temperature control and rapid cooling for diverse liquid application...
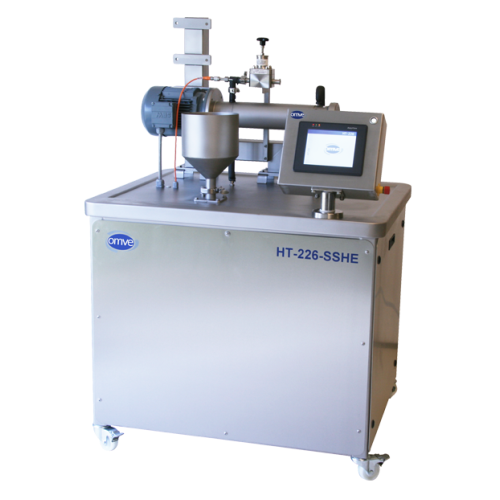

Small-scale scraped surface heat exchanger for high-viscosity products
For R&D teams tackling complex formulations...
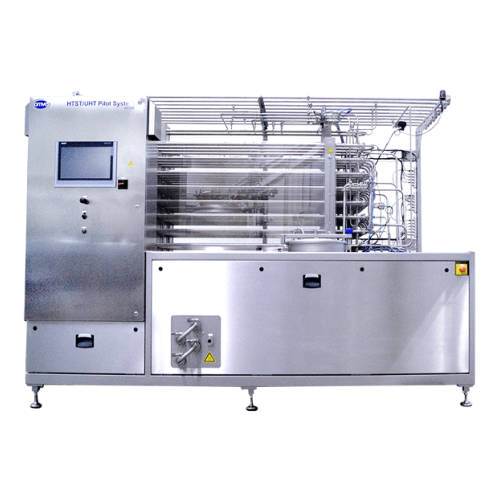

Uht/htst aseptic processor for pilot plants
Achieve precise heat treatment and aseptic processing with flexible pilot syst...
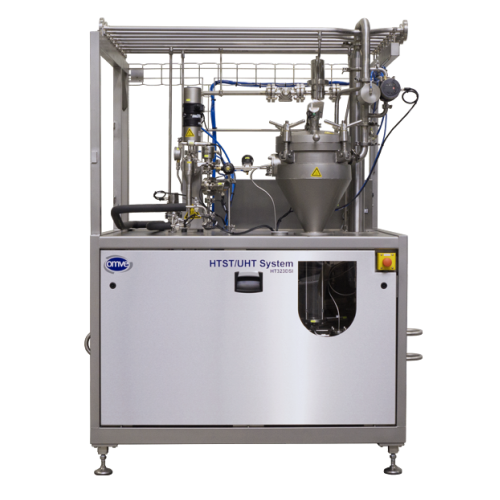

Direct steam injection Uht pilot system
Elevate your production capabilities with a sanitary UHT pilot system designed for ...
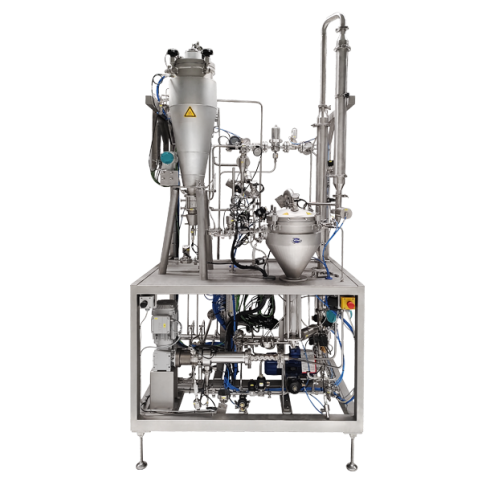
Direct steam infusion for high spore kill rate in sensitive food products
Achieve rapid, efficient sterilization and m...
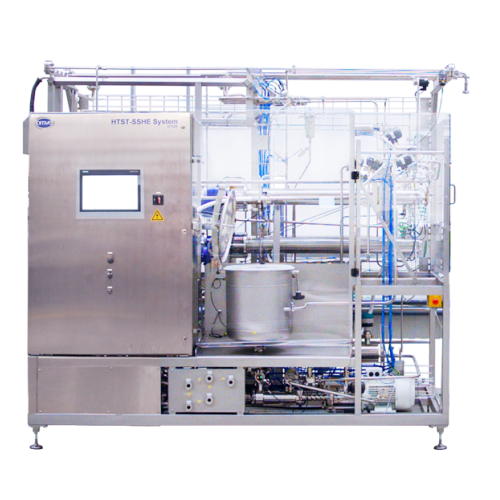

Pilot system for high-viscosity product processing
Efficiently handle high-viscosity or large particle products with this...
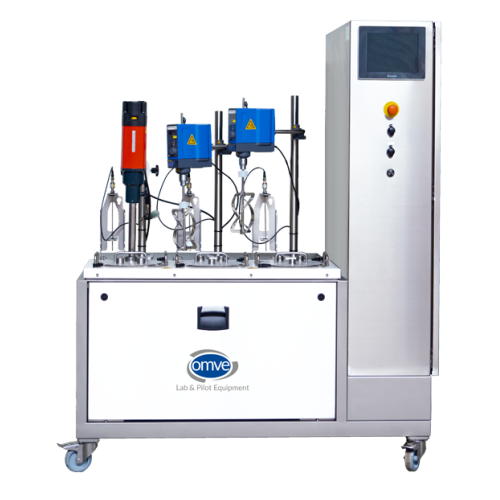

Lab-scale water bath blending vessel for product preparation
Ensure consistent flavor and quality across diverse small-s...
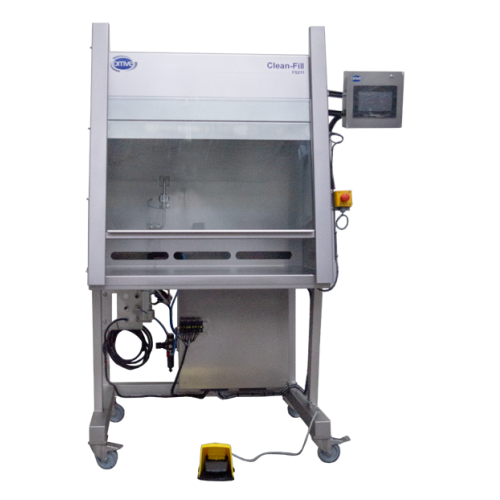

Sterile filling and closing bench for bottles and cups
Ensure precise and sterile filling for liquid products with a hygi...
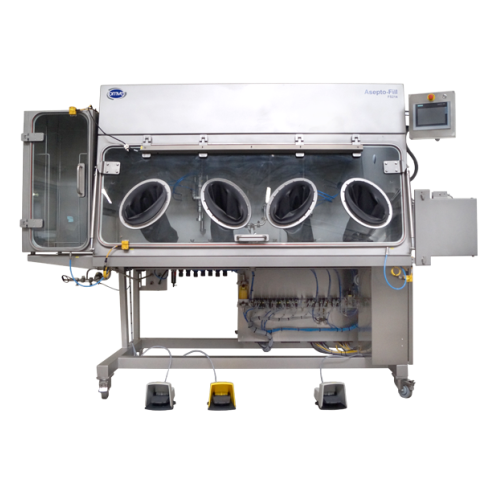

Aseptic filler for nutraceuticals
Ensure the sterility of your liquid nutraceuticals and beverages with a versatile solutio...
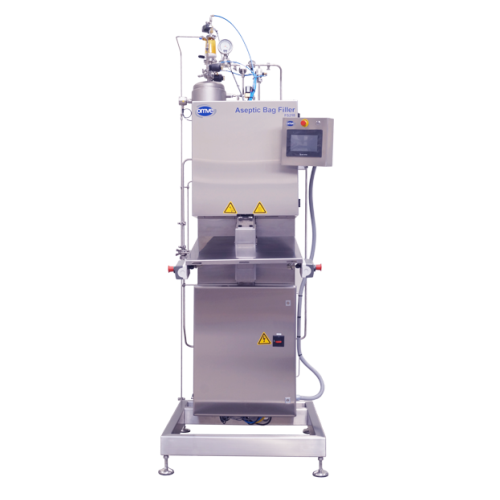

Aseptic bag-in-box filler for laboratory use
Achieve aseptic filling precision on a lab-scale with a compact solution that...
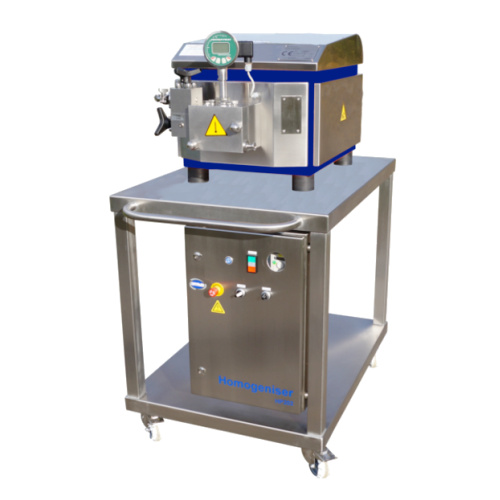

Lab-scale high-pressure homogenization solution
Optimize your lab-scale production with precision homogenization, ensuring...
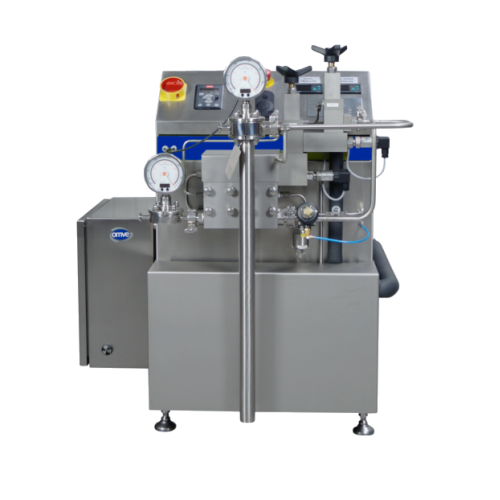

Pilot homogenizer for high-pressure inline homogenization
Achieve precise homogenization and emulsification across vario...
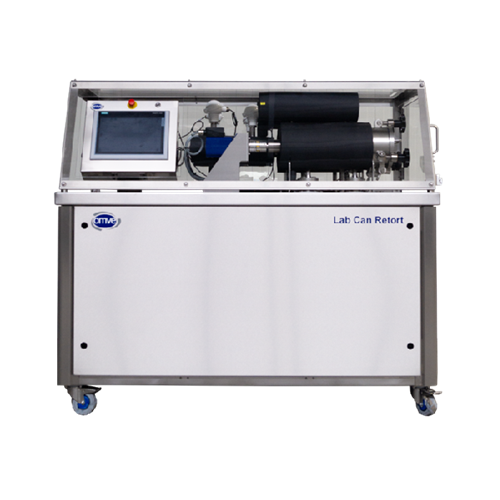

Lab can retort for precise temperature and pressure control
Achieve precision in recipe validation and packaging testing...
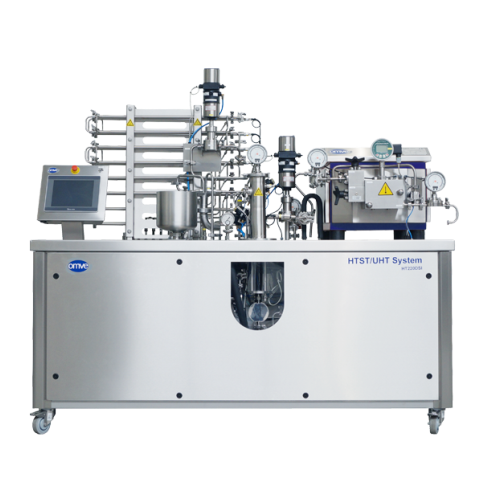

Direct steam injection system for heat treatment
Achieve precise thermal processing and enhance product quality for comple...
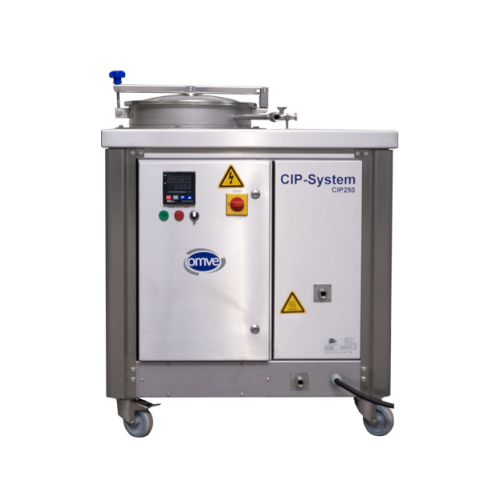

Manual Cip unit for lab and pilot plant cleaning
Need thorough cleaning without disassembling your pilot plant? This compa...
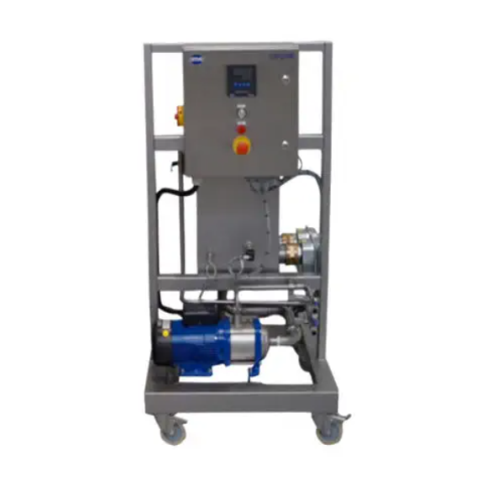

Cleaning in place unit for lab and pilot equipment
Streamline your lab and pilot-scale cleaning processes with a mobile, ...
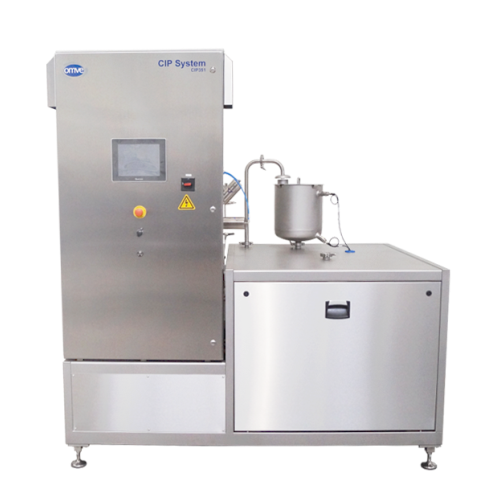

Fully automated cleaning in place unit for food processing plants
Enhance food safety and streamline operations with a ...
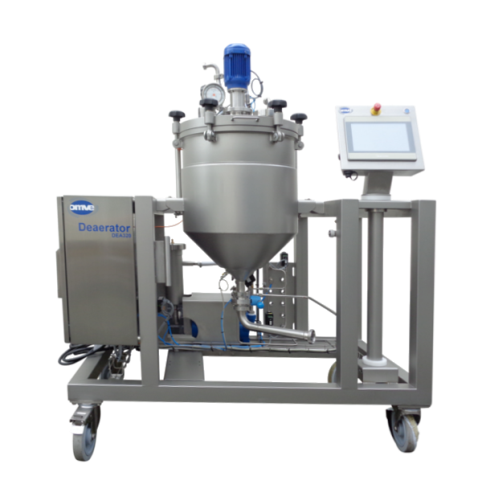

Batch deaerator for reduced oxidation in liquid processing
Optimize product shelf life and quality by efficiently removi...
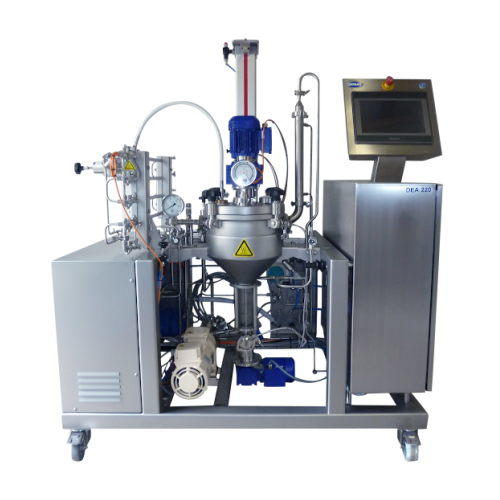

Continuous deaeration solution for laboratory and pilot systems
Achieve superior product stability and minimize foaming ...
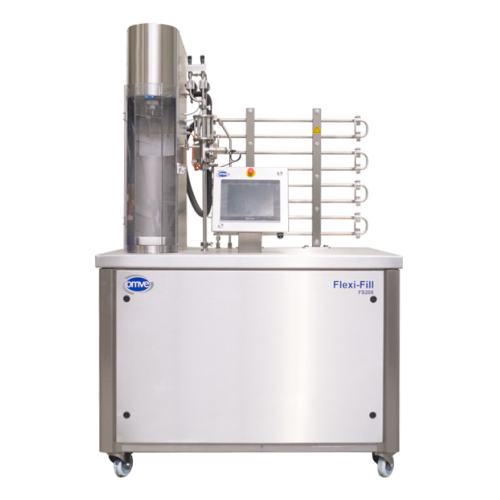

Counter-pressure filler for carbonated drinks
Enhance your carbonated beverage production with advanced counter-pressure f...
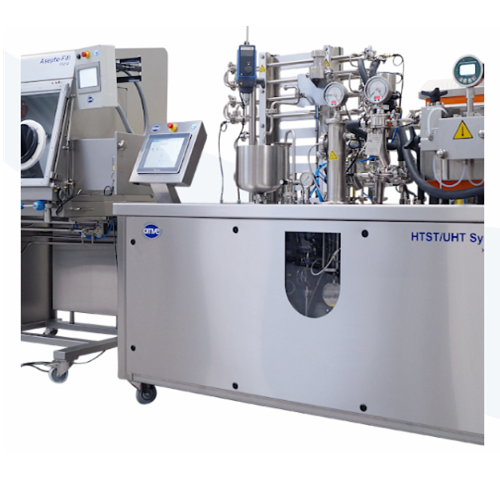

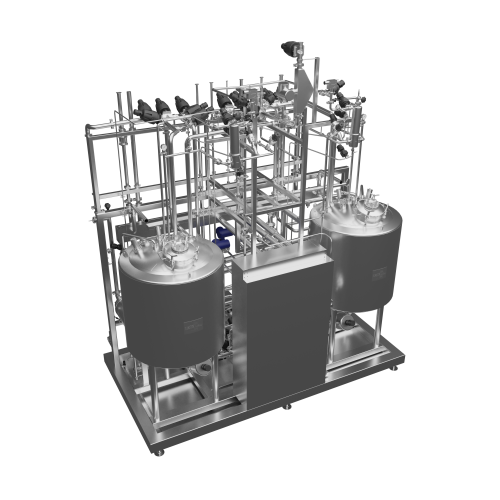
Customized process plants for plant-based beverages
Efficiently scale your production of plant-based beverages with modul...
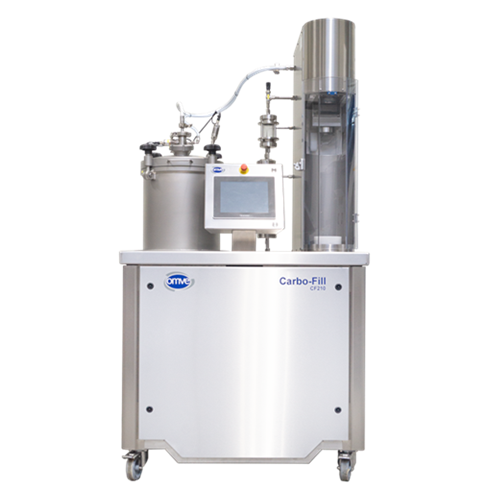

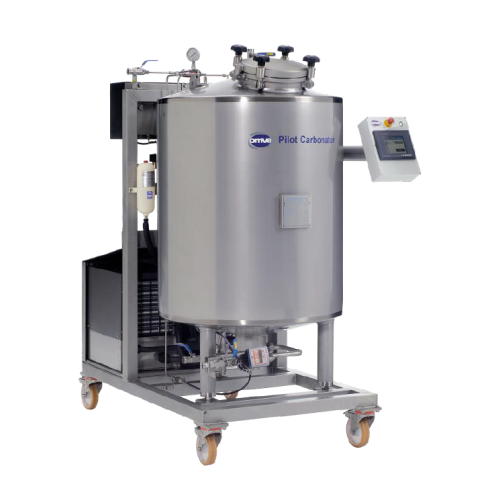
Lab-scale carbonation system for beverage filling
Streamline your beverage development with precision carbonation and ver...
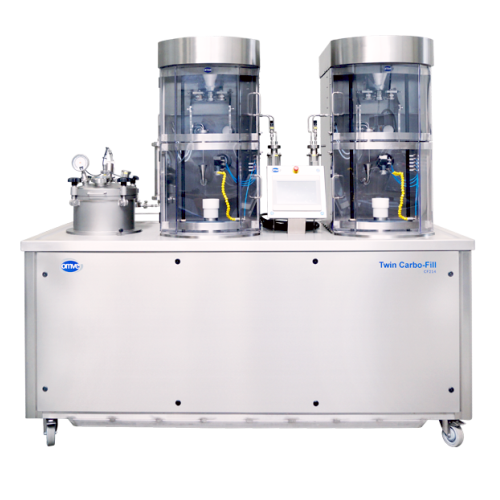

Carbonation and can seaming solution for beverages
Optimize your beverage production with a seamless integration that sim...

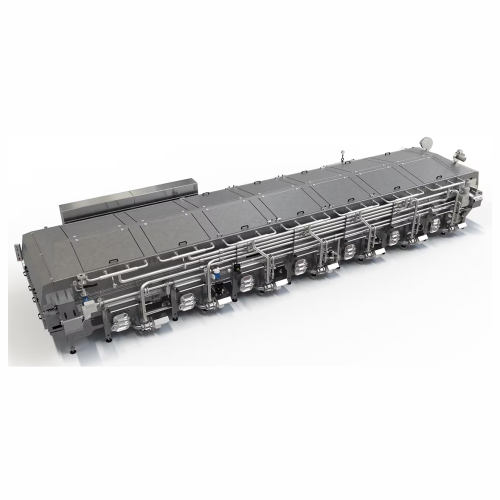
Atmospheric fermenter for lab and pilot scale projects
Streamline your fermentation process with precise control over tem...

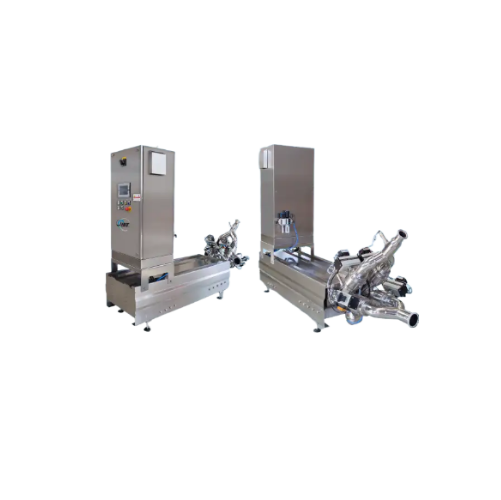
Almond hulling system for soft and semi-hard shells
Efficiently hull almonds with soft or semi-hard shells to streamline ...

Compact tunnel pasteuriser for beverages
Ensure beverage safety with precise pasteurisation in a compact design that integr...

Ultrahygienic block for aseptic filling
When handling sensitive beverages, ensuring microbiological safety and quick produc...
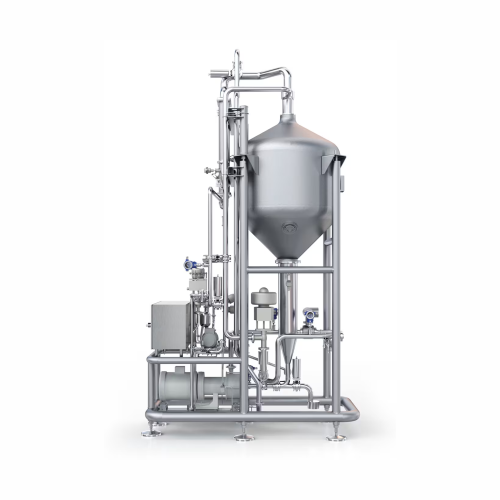

Juice product deaerator
Ensure high-quality filling without foam formation through efficient deaeration, perfect for manufact...
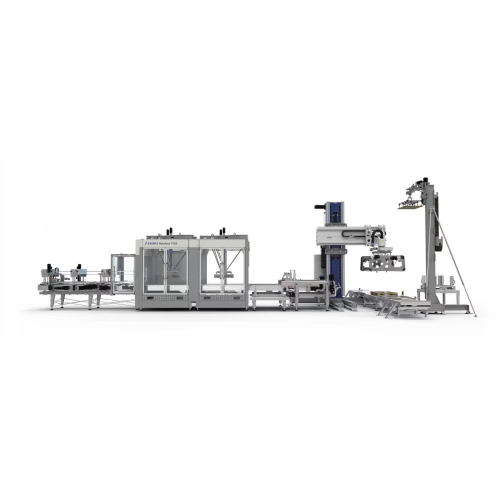

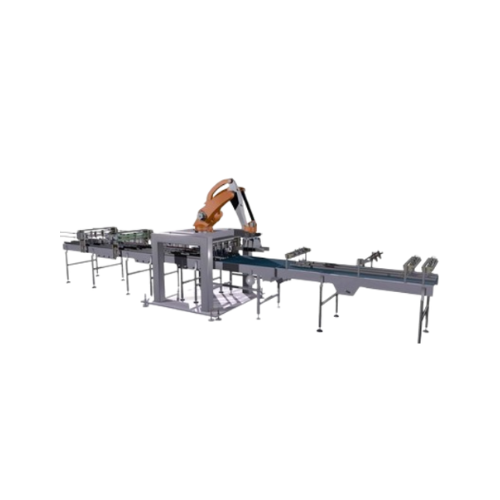
Palletizing grouping system for non-returnable packs
For beverage and packaging lines, precise and rapid palletizing of n...
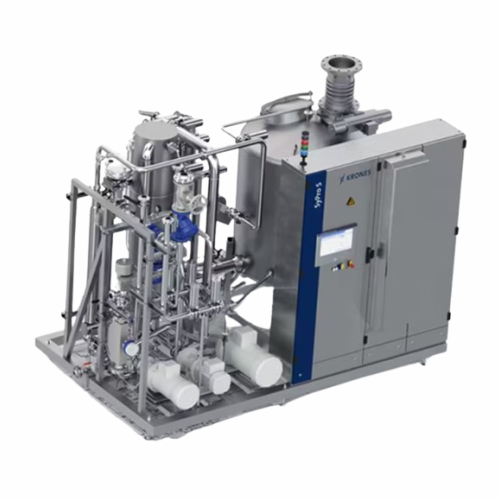

Syrup room for customized beverage ingredient preparation
Achieve unparalleled flexibility in beverage production with a...
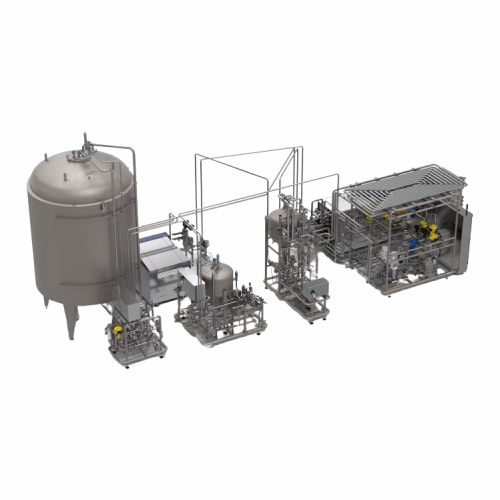

Uht system for milk products
Achieve optimal product safety and quality for dairy and plant-based beverages with precise UHT...
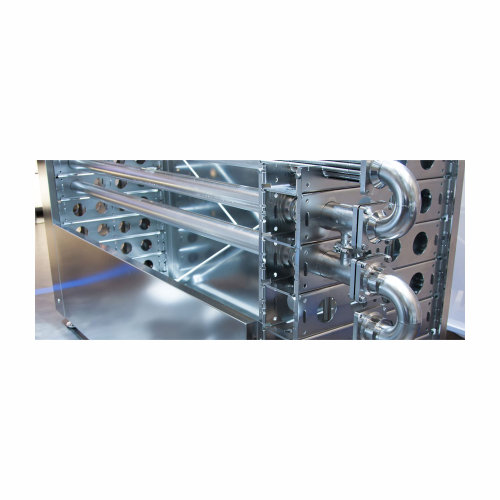
Heat exchanger for beverage production
Ensure your beverages maintain their quality and safety with a versatile heat exchan...
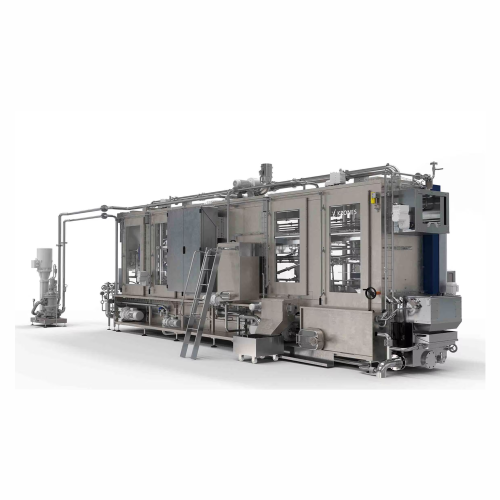

Crate washer for beverage manufacturers
Ensure thorough cleaning of beverage crates with an advanced washing system featuri...
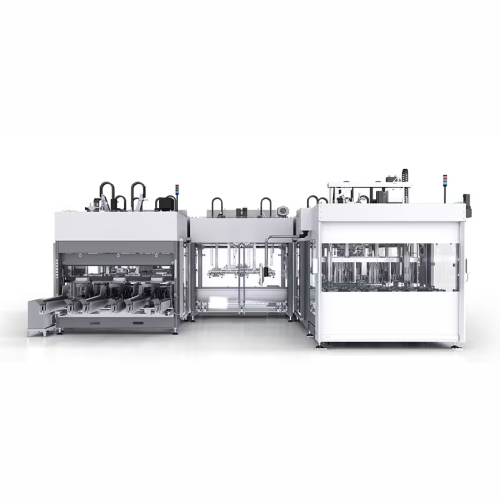

Flexible packaging line for beverage production
Streamline your beverage production with a flexible system capable of hand...
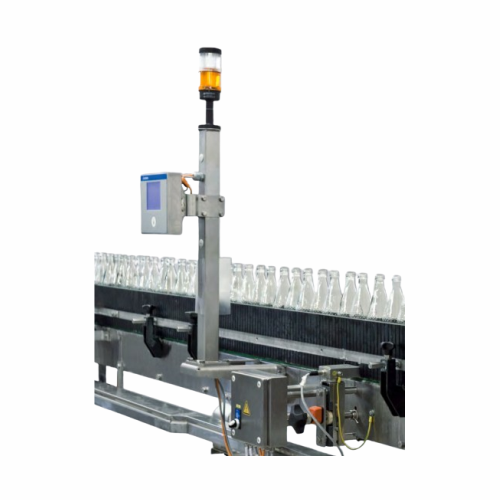

Caustic residue detection for bottle washing
Ensure product purity by detecting and eliminating residual caustic in return...
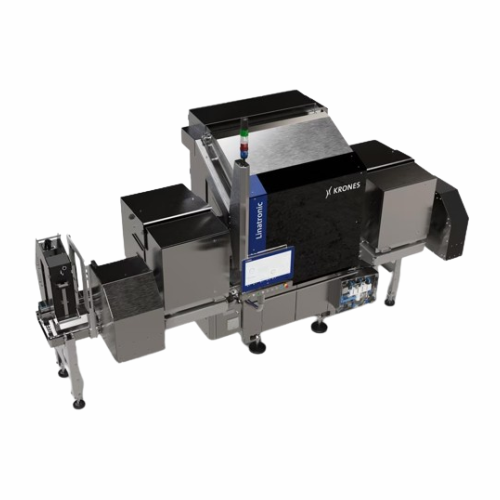

Bottle inspection system for foreign particles detection
Ensure your beverage products remain uncontaminated with high-pr...
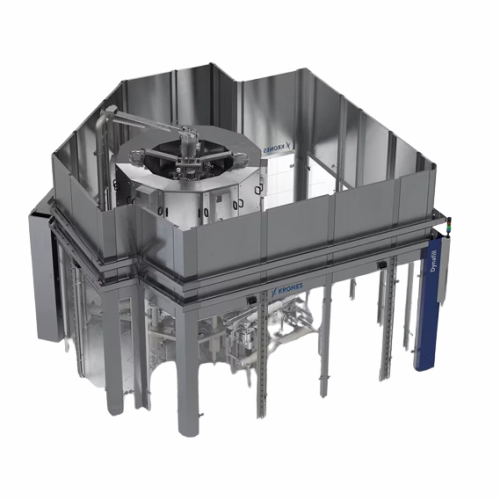
Innovative beer filling and capping technology
Revolutionize your filling process with an integrated system that combines ...
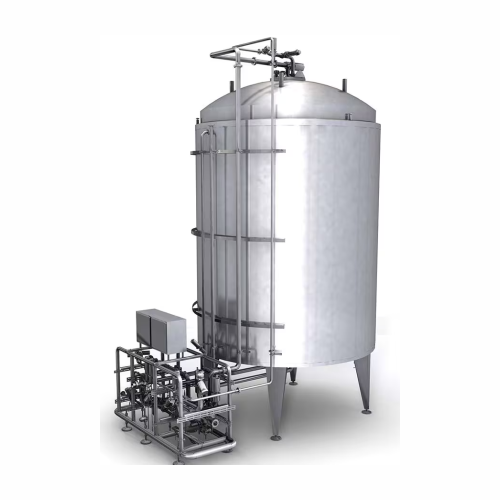

Sterile tank system for aseptic processing
Optimize your production with aseptic tank systems that ensure sterile storage ...

Aseptic bottle sterilisation system for Pet containers
Ensure aseptic integrity and high-speed efficiency in beverage pro...

Automated product change-over system
Maximize your production line efficiency by reducing downtime during product changeove...

Mixer for carbonated and non-alcoholic drink production
Efficiently mix and carbonate a variety of beverages while optimi...

Aseptic filling system for Pet containers
Ensure your beverage products maintain sterility and longevity with a high-speed...

Filter system for beverage stabilization and clarification
Ensure your beverages are crystal clear and stable with a ver...

Blending system for fine adjustment of original gravity in beer
Ensure precise control over your beer’s original gravity...

Blending system for deaeration and carbonation of beverages
Achieve precise blending, efficient deaeration, and accurate...

Pet bottle stretch blow molding with coating and filling
Extend the shelf life of your beverages and liquid products with...

Dosing and blending system for beverage production
Enhance your beverage production with a flexible system capable of pre...

High-performance distribution and combining system
Streamline your packaging operations with a versatile system designed ...

Modular labeling system for beverage containers
Easily adapt to evolving labeling needs with this flexible system, designe...
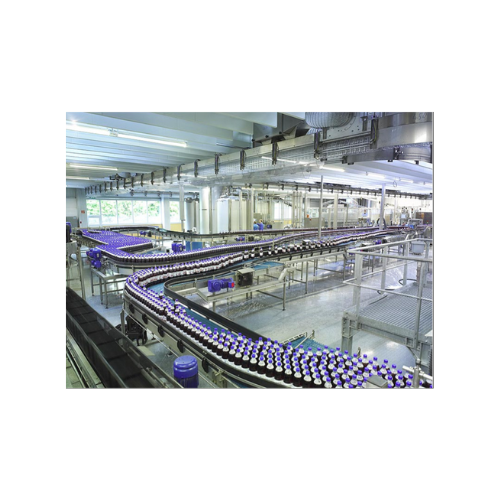

Gentle container conveyor for bottles and cans
Achieve seamless container flow with minimal noise and enhanced precision, ...
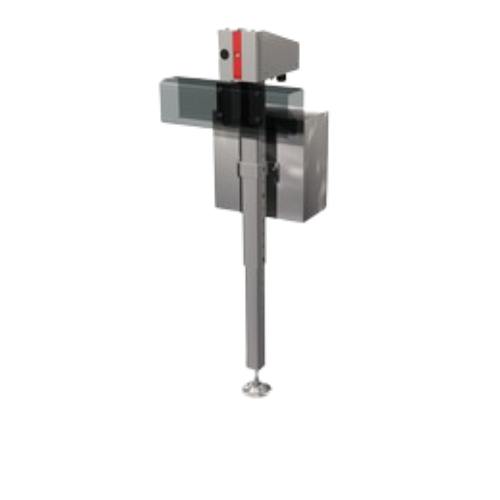

Container rejection system for high-speed operations
Ensure product safety by swiftly removing defective containers at hi...
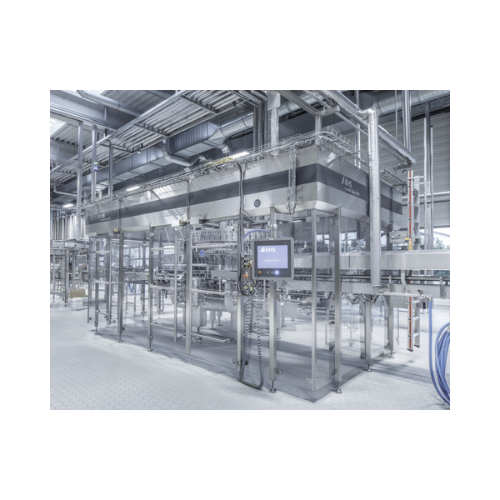

Bottle filler for beer and soft drinks in glass bottles
Achieve precision in bottling with reduced CO2 emissions and low ...
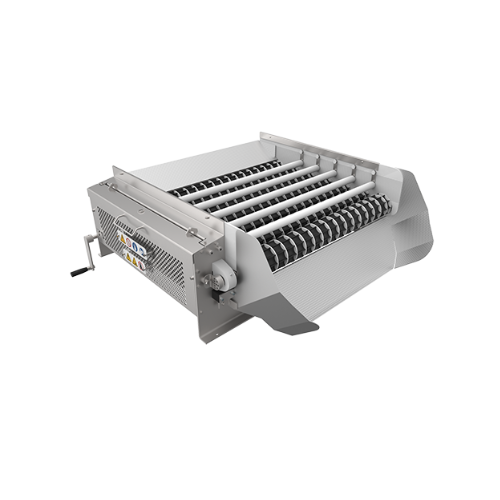

Rotary size grader for food processing
Enhance your production line by efficiently sorting and classifying produce to ensur...

Inspection systems for poultry and seafood processing
Enhance the quality control of your food production with cutting-ed...

Industrial air cleaner for food processors
Optimize your production line with high-speed air separation, effectively remov...

Htst pasteurization system for liquid foods
Ensure your liquid products are safe and long-lasting with high-temperature-sh...

Centrifugal separators for dairy products
Enhance your liquid food product quality with centrifugal separators designed fo...

Industrial homogenizer for food and pharmaceutical applications
Ensure product consistency and stability with high-press...
Multifunctional batch processing system for processed cheese
Enhance your production line with a sophisticated batch pro...

Hydrogen compression solution for refueling stations
For operations demanding efficient hydrogen compression, this modula...

High pressure processing for bulk liquid beverages
Streamline your liquid processing with high-pressure in-bulk technolog...

Hpp system for small-scale food production
Enhance food safety and prolong shelf life with this compact high pressure proc...
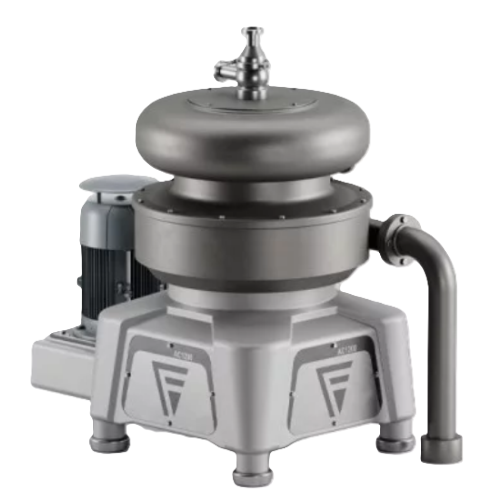

3-phase liquid separation solution
Achieve precise separation of liquids and solids to enhance product quality and streamli...
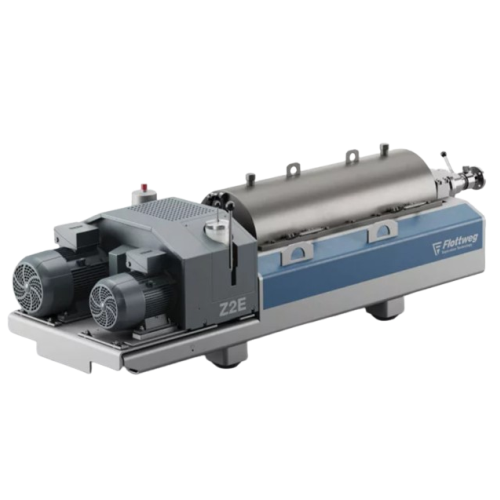

3 phase decanter centrifuge for industrial separation
Optimize your production line with efficient three-phase separation...
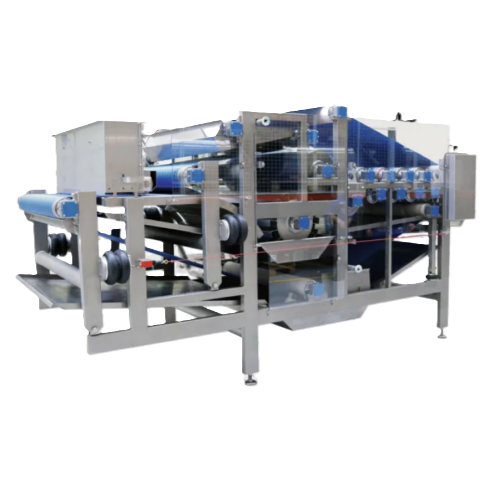

Industrial belt press for fruit and vegetable processing
Optimize your juice yield and reduce drying costs in starch and ...
Advanced sludge dewatering for sewage treatment plants
Optimize sludge dewatering with a centrifuge that enhances separat...
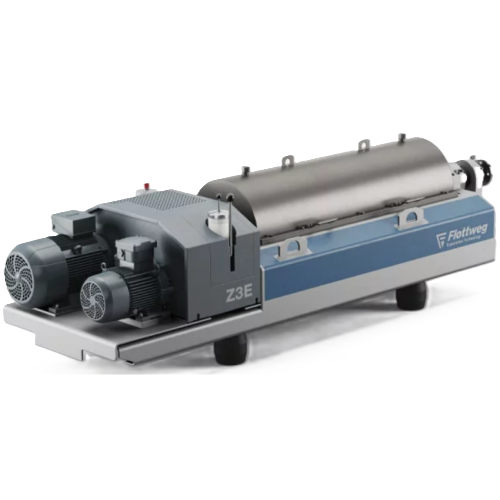

High-performance decanter centrifuge for industrial separation
Optimize your production with a centrifuge solution that ...

Industrial nozzle separator for high solids concentration
Optimize your production with high-performance nozzle separato...

Electronic filling system for non-carbonated beverages
Optimize your bottling process with precision filling technology t...

Inline high-shear mixer for powders and liquids
Achieve efficient mixing and homogenization in your production line with a...

High-capacity inline mixer for dairy and beverages production
Achieve a rapid and homogeneous mix in high-capacity produ...

High-shear mixer for high viscosity products
Achieve consistent, homogeneous mixtures of high-viscosity products with a ve...

Ultra-high shear mixer for emulsification and homogenization
Optimize your production with ultra-high shear mixing, acce...

Vacuum high shear mixer for medium to high viscosity products
Achieve flawless blending and air-free consistency in visc...

High-capacity manual mixer for industrial applications
Optimize your mixing process with a highly efficient, manually ope...
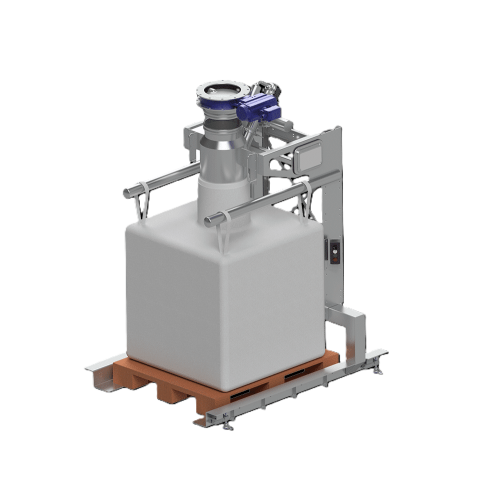

Bigbag filling system for powder and bulk materials
Ensure precise and dust-free bigbag filling with this versatile syste...
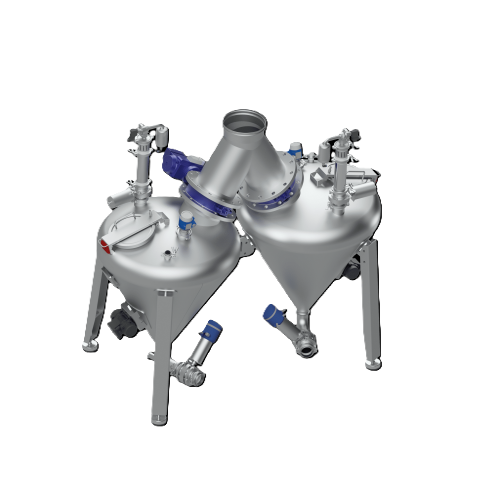

Dense-phase powder conveying system
Optimize your powder processing with a system designed to handle abrasive and fragile m...
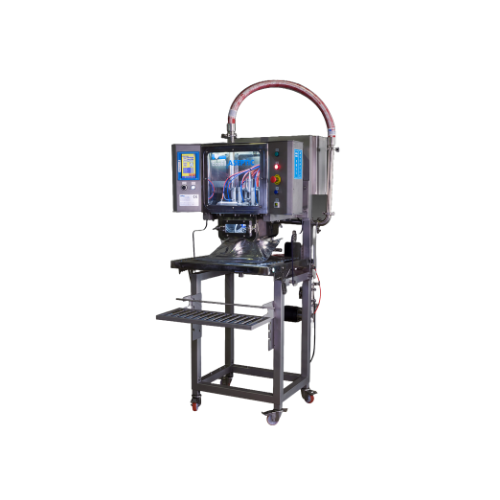

Semi-automatic aseptic filler for single bags
Ensure aseptic integrity and flexibility for your liquid and semi-liquid pro...
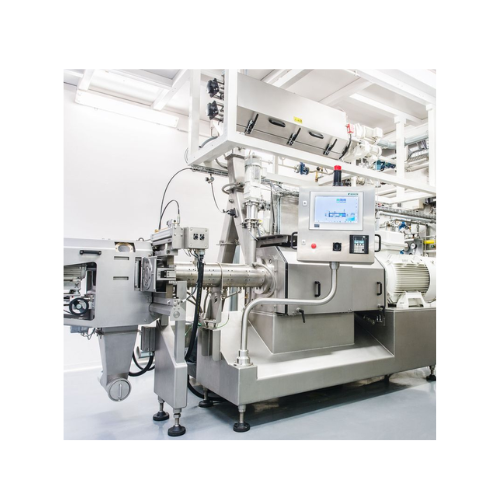

Twin-screw extruder for breakfast cereals production
Enhance your product range with flexible twin-screw extrusion techno...
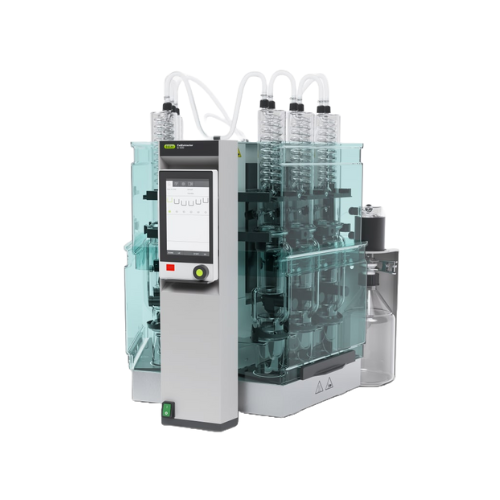

Industrial fat extraction system for food and feed analysis
Optimize your laboratory workflow with a versatile fat extra...
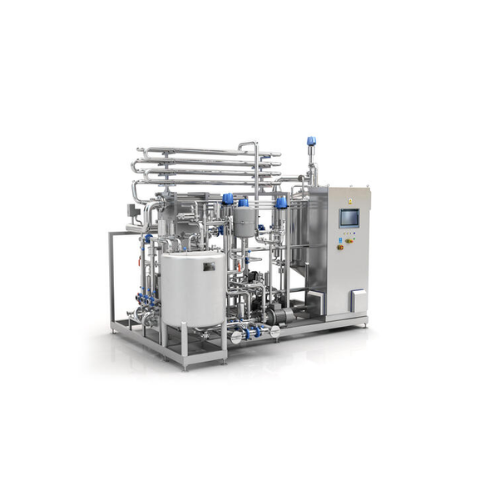

Industrial pasteurizer for juice, dairy, and vegetable purees
Ensure product safety and extend shelf life with this comp...
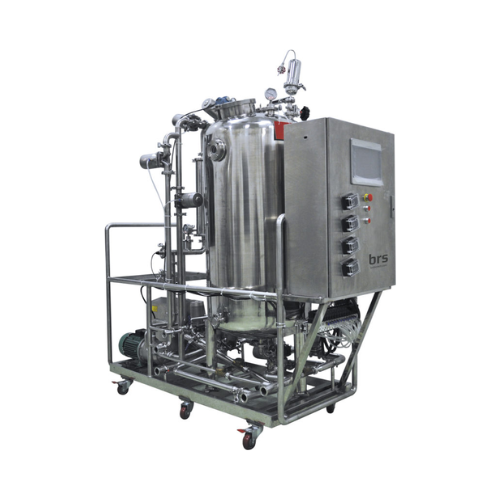

Clean-in-place systems for biotechnology and pharma
Ensure seamless transitions between production batches with efficient...
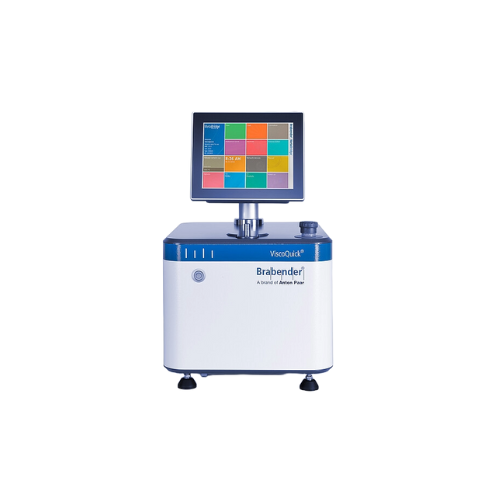

Digital torque viscometer for starch analysis
Experience rapid and precise starch gelatinization analysis with a compact, ...
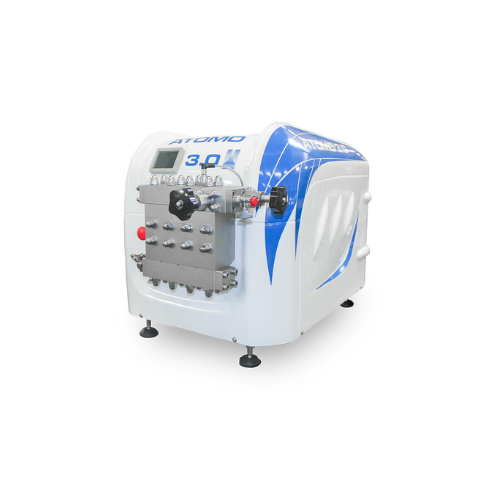

Laboratory homogenizer for dairy and biotech applications
Ensure precise particle size reduction and consistent texture ...

Combi x-ray and checkweigher for vertical products
Ensure precise weight control and contamination detection for vertical...

Plant-based protein extraction technology
Achieve optimal purity in plant-based milk, yogurt, and cheese production with c...

Multipurpose membrane filtration system for pilot testing
Optimize your pilot-scale processes with a versatile filtratio...
Bag-in-box filling solution for non-aseptic products
Maximize your production line’s efficiency with a high-speed f...

Foodec decanter centrifuge for food processing
Achieve high yields and clear liquid separation in your food processing lin...

Rising film evaporator for concentration of viscous liquids
Effortlessly concentrate low-to-medium fouling and highly vi...
Water remineralization system for mineral and flavored water production
Achieve precision in mineral content with a sys...
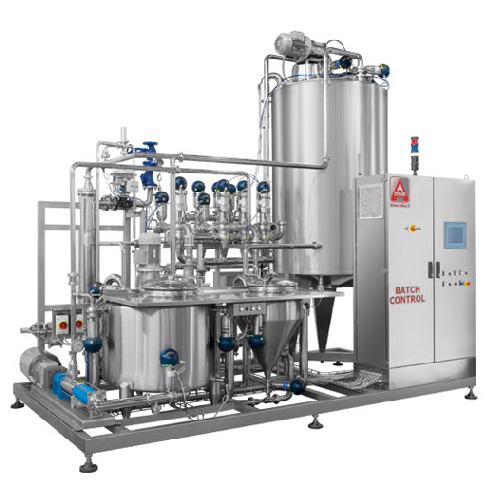

Ingredient management system for beverage production
Efficiently manage a diverse range of solid and liquid ingredients t...

Stabilizer dissolving systems for beverage production
Efficiently dissolve and disperse stabilizers in complex beverage f...

Continuous sugar dissolving system for beverages
Optimize your beverage production with an efficient sugar dissolving solu...

Versatile industrial water disinfection system
Ensuring optimal water disinfection is crucial for beverage manufacturers s...

Aseptic storage tank for beverage industry
Ensure product sterility with advanced aseptic storage that compensates for fil...

Cleaning in place system for beverage production
Ensure maximum hygiene and efficiency in beverage production with a modul...

Bi-directional frame scale for industrial weighing
Achieve precise product accumulation and streamlined batch processing ...

Flat belt product transfer conveyor for food processing
Efficiently streamline your production line with a hygienically d...

Twin lane separator for automated tray sealing
Optimize your production line with this conveyor system designed to effortl...

Semi-automatic tray sealing for ready meals
Achieve versatile packaging with a semi-automatic tray sealing solution design...

Automatic tray sealer for high-speed food packaging
Optimize your production line with a high-capacity tray sealing solut...

High-speed tray sealer for food packaging
Streamline your packaging process with high-speed tray sealing, reducing labor c...

Automatic tray sealing system for high-speed packaging
Experience seamless high-speed packaging with this versatile tray ...

Automatic tray sealer for high-speed production
Ensure your product packaging stays fresh and secure with this high-capaci...

Industrial case packing solution for high-speed operations
Optimize your production line with a compact, efficient case ...
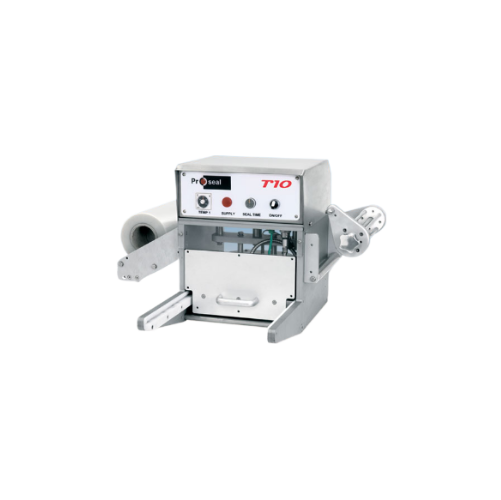

Bench mounted tray sealer for small-scale production
Perfect for pilot runs and small batches, this compact tray sealer e...
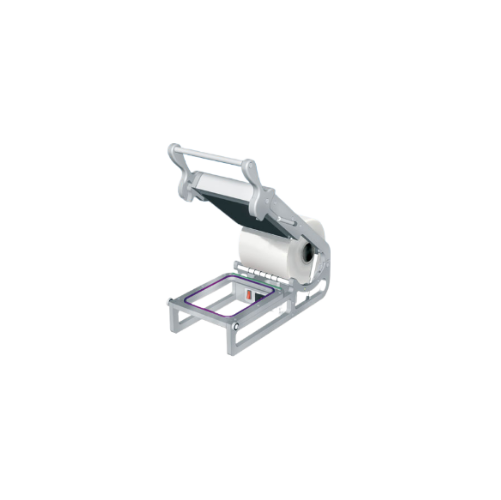

Hand operated tray sealer for small-scale food production
Optimize your packaging process with this compact tray sealing...
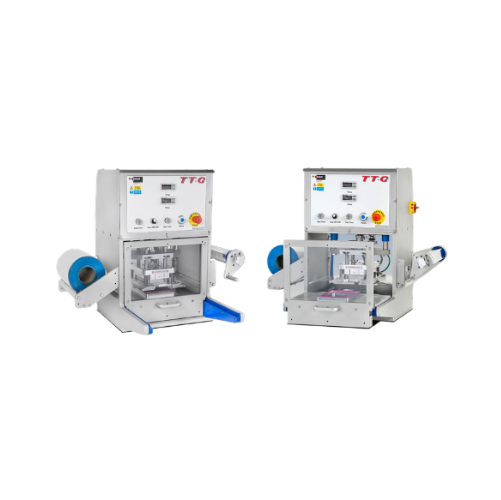

Bench mounted tray sealer with gas flush
Optimize your production line with a compact tray-sealing machine designed for pre...
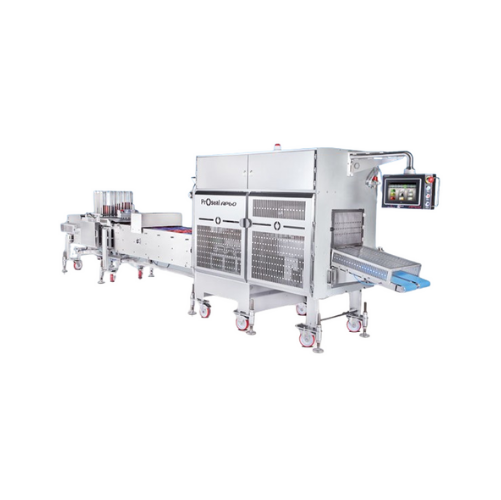

Linear conveyor tray sealing
Experience unparalleled flexibility and efficiency in tray sealing with high-speed integration,...

High throughput tray conveyor system
Looking to streamline your tray sealing process? This modular conveyor system integrat...

High-speed tray sealer for food
Enhance your packaging line’s efficiency with a high-speed, in-line tray sealer design...

Industrial high speed tray sealer
Enhance your production line efficiency with precision sealing capabilities, accommodatin...

Automatic tray sealer
Maximize throughput and shelf life with our high-speed inline tray sealing solution, ideal for diverse ...

In-line tray sealer for high-speed packaging
Optimize your packaging line with a high-speed solution that accommodates mul...

High-capacity tray sealer for vacuum gas packaging
Enhance your production efficiency with a versatile twin-lane tray sea...

In-line tray sealing system
Streamline your packaging line by implementing a high-speed, in-line tray sealing system designe...

High-capacity tray sealer for poultry, meat & seafood
Optimize your high-speed packaging line with this large-capacity tr...

Automatic tray sealer for high-speed packaging
Streamline your packaging line with an in-line tray sealer that adapts to t...

Large-capacity automatic tray sealer
Optimize your production line with this tray sealer, designed for high-speed sealing a...

R&d vessels for research and development centers
Optimize your R&D operations with versatile vessels designed to hand...

Mixing tank for soups, sauces, and dressings
Streamline your soup and sauce production with advanced mixing technology des...

Aseptic storage tank for sterile liquid products
Ensure the sterile safety of your liquid products with a reliable storage...
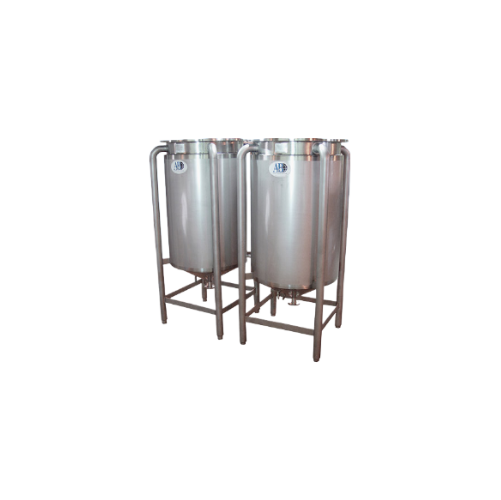

Customizable storage tanks for industrial use
Optimize your production with versatile storage tanks designed for precise c...

Automatic tray sealing system
Optimize your packaging line with versatile tray sealing technology that accommodates various ...
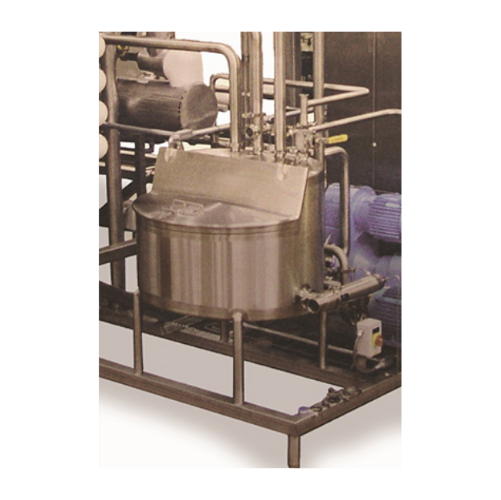

Balance tank for pasteurization systems
Ensure consistent product quality with precise liquid holding and heating capabilit...
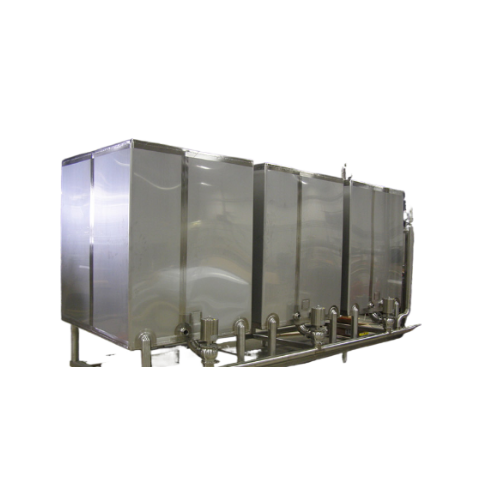

Clean-in-place tanks for industrial sanitation
Optimize your sanitation processes with clean-in-place tanks, designed to r...
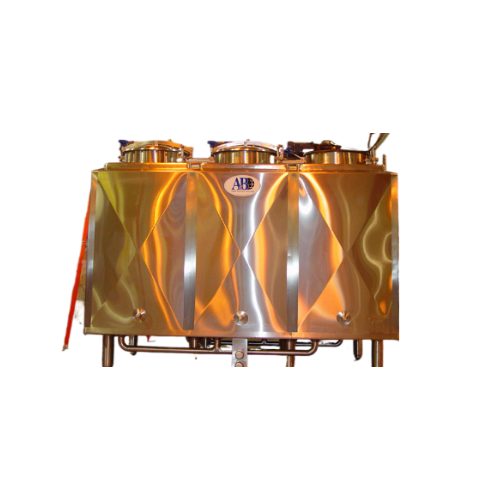

Flavor vats for ice cream and food production
Maximize your product line versatility with customizable flavor vats, design...
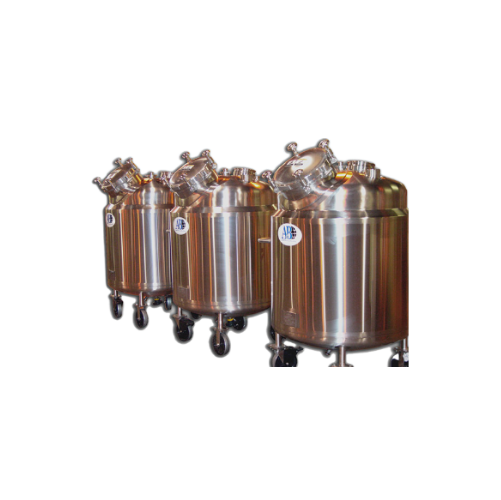

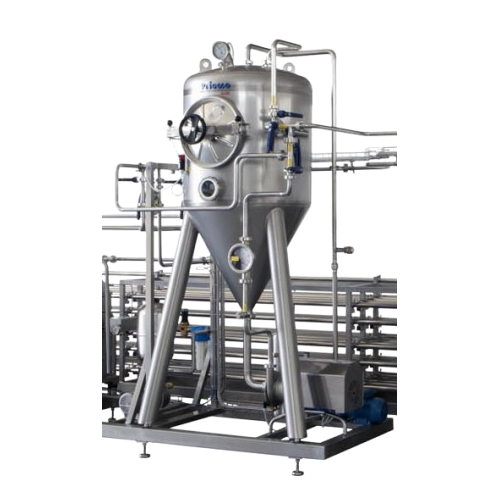
Industrial pressure vessels
Ensure product integrity and regulatory compliance with engineered-to-order pressure vessels, de...
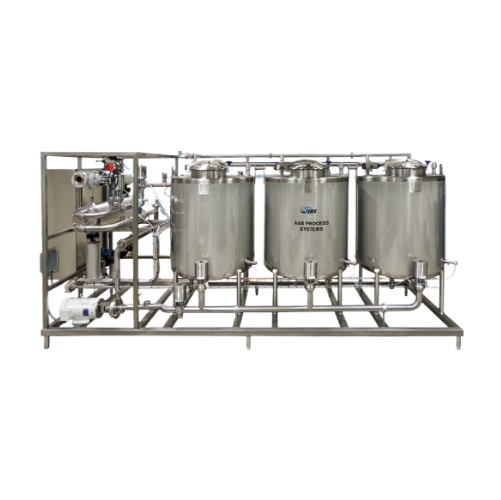

Clean-in-place system for diverse processing needs
Ensure the precision and consistency of your cleaning cycles with a ro...
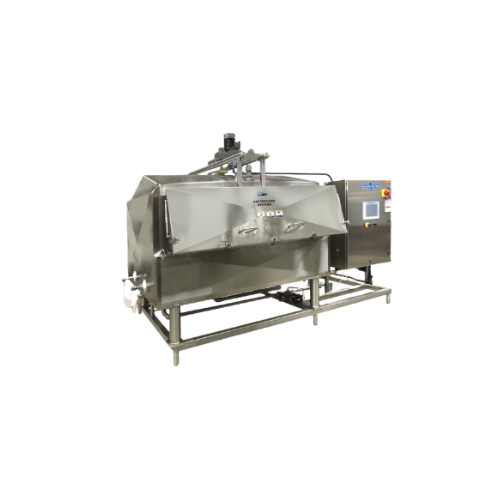

Industrial block melt system for butter and chocolate
Efficiently transition solid blocks of butter, chocolate, or waxes ...
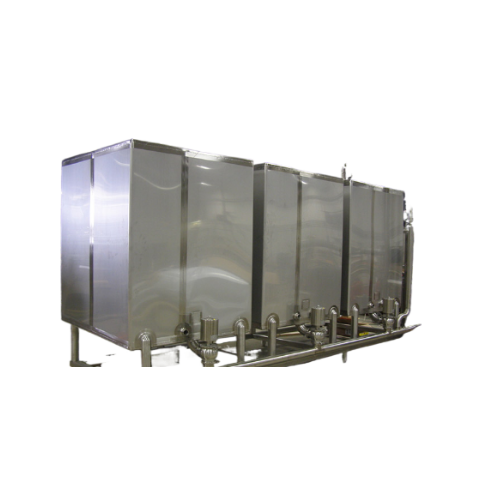

Industrial clean-in-place (cip) system
Ensure seamless cleaning and sanitation in your production line with innovative CIP ...

Industrial hot water heating system
Optimize your production line’s efficiency with precise water temperature control...

Automated valve manifolds for clean-in-place solutions
Optimize your production efficiency with automated valve manifolds...

Pump for products with large particulates
When handling products with large particulates, maintaining integrity is paramou...

Ohmic heat exchanger for high viscosity foods
Optimize the thermal processing of heat-sensitive foods with precise ohmic h...
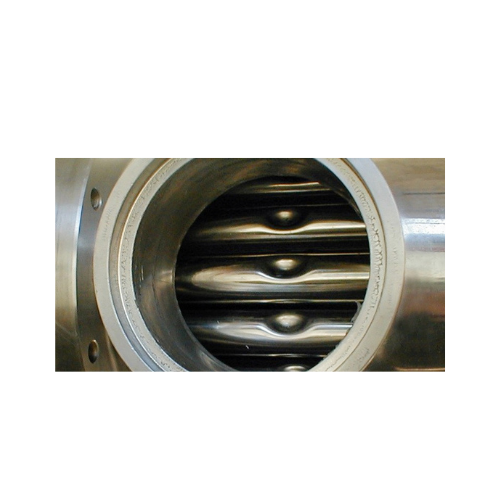

Tube-in-shell heat exchanger for low viscosity products
Enhance your beverage and food processing efficiency with a cutti...
Poultry processing efficiency monitoring system
Maximize production efficiency with real-time monitoring and precise track...

Hydrostatic sterilizer for continuous food processing
Maximize your production line’s efficiency with a continuous ...
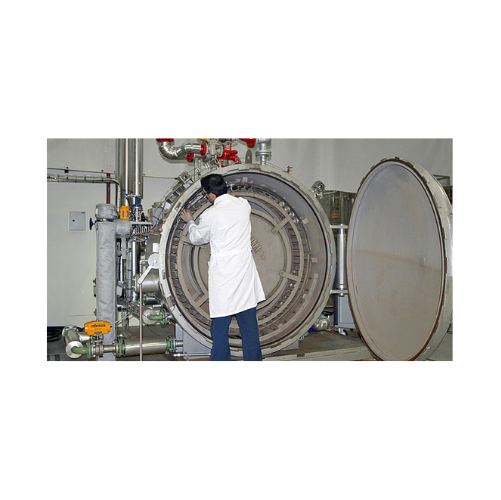

Pilot rotary retorts for laboratory sterilization
Optimize your prototype testing with precision thermal simulations to p...
Aseptic processing system for food products
Streamline your food processing line with an efficient aseptic processing syst...
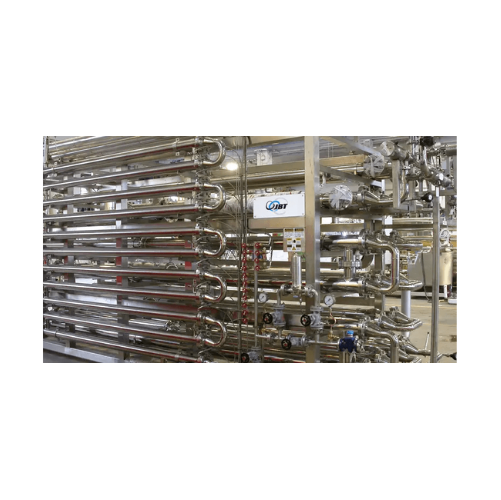

Heat exchanger for dairy and beverage applications
Optimize your liquid product thermal processing by directly regenerati...
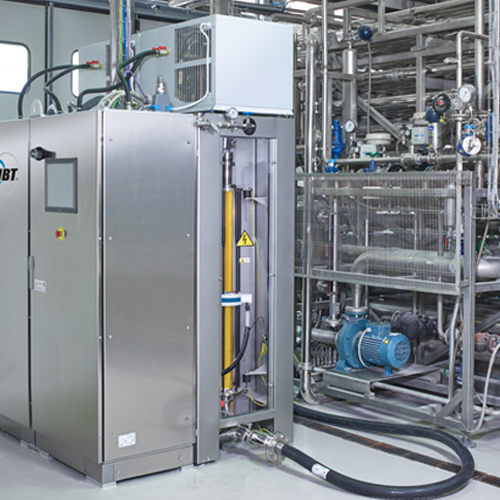

Heat exchanger for liquid and semi-liquid foods
Optimize your heating and cooling processes with superior heat transfer ef...

Low energy suction system for food processing retorts
Optimize your sterilization process with innovative suction technol...
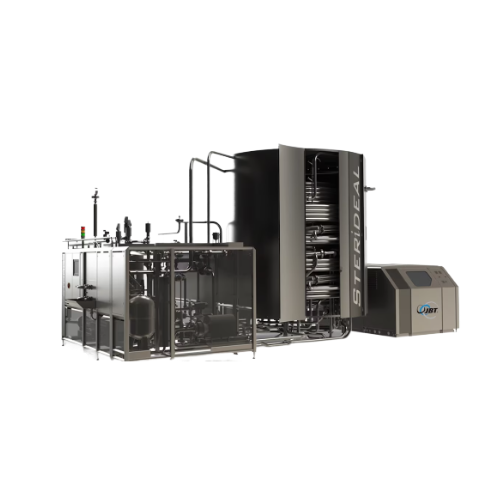

Coil heat exchanger for dairy and beverage processing
Quickly sterilize and retain product quality with this coil heat ex...
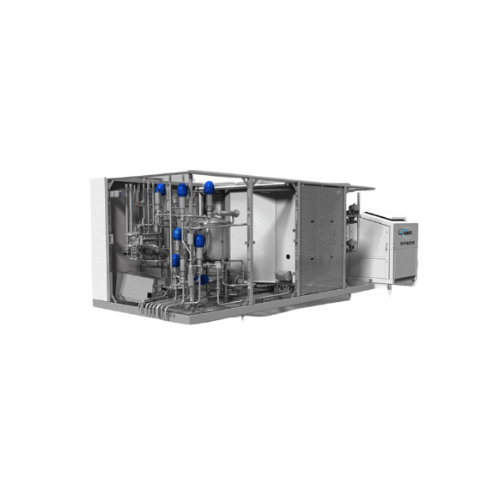

Uht sterilizer for dairy and high-viscosity products
Optimize your production of dairy alternatives and fruit-based drink...

Dual heating coil for dairy and beverage processing
Achieve precise temperature control for your liquid products with a s...
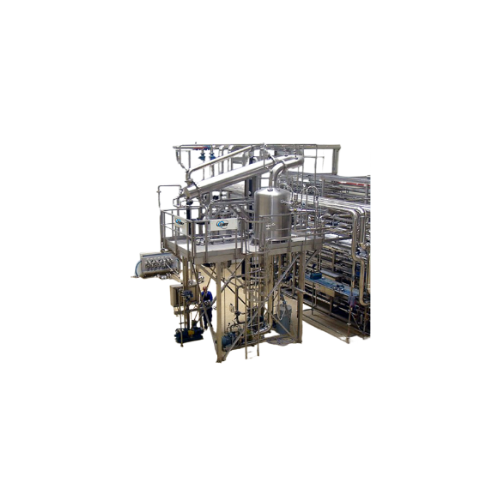

Deaerator for juices and dairy processing
Ensure the quality and shelf-life of liquid foods by effectively removing entrap...
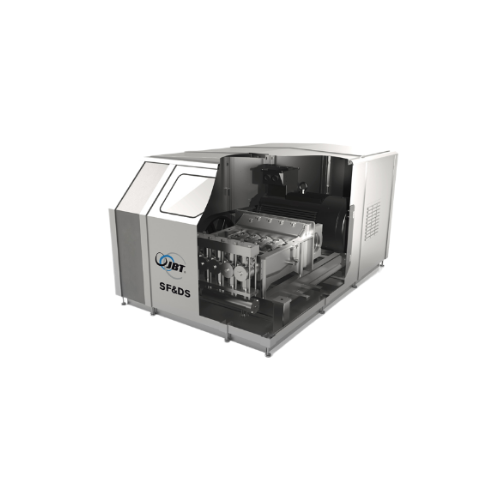

Industrial homogenizer for Uht sterilization systems
Achieve smoother product consistency with high-pressure homogenizati...
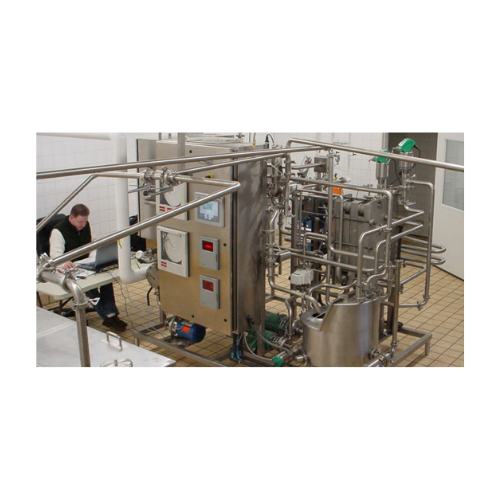

High temperature short time (HTST) dairy pasteurization system
Ensure precise pasteurization with advanced heat transfer...
Efficient agitation system for retort packages
Enhance product quality and reduce processing time with this advanced agita...
Layer pad for agitating retorts in food processing
Efficiently secure and process irregularly shaped containers in retort...

High speed fruit and vegetable juicer
Optimize your production with a high-capacity juicer designed to efficiently process ...

Screw finishers for citrus processing
Optimize your production line with screw finishers designed to efficiently separate l...

Citrus juice finisher
Optimize your juice and essential oil production with precision separation and finishing technology, en...

Expandable high pressure processing system
Optimize your production line with an expandable high-pressure processing syste...
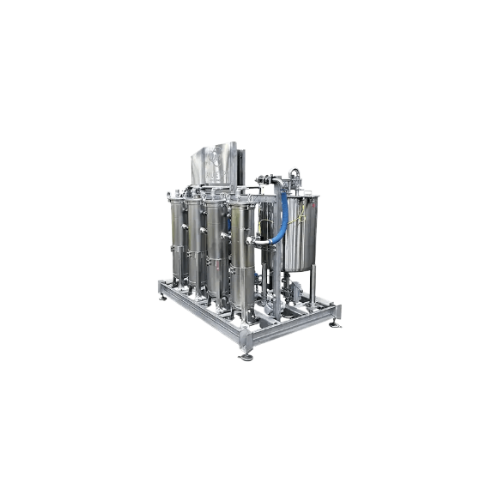

High pressure processing water filtration system
Ensure super clear water after high pressure processing to protect your s...
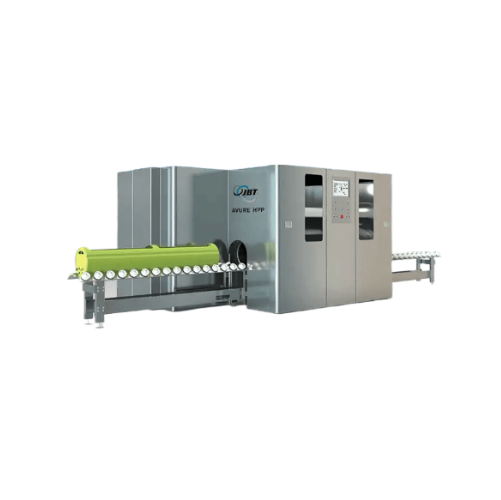

High pressure food processing solution for medium-scale producers
Achieve reduced operational costs with high-pressure ...

High pressure processing for diverse food products
Maximize production versatility and ensure product safety with a high-...

Self-stacking belt for industrial freezers
Enhance your production line with advanced self-stacking belt technology, desig...
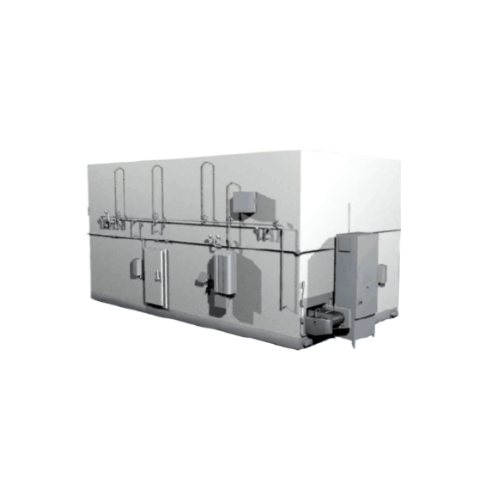

Industrial spiral freezer for high-volume food processing
Optimize your production line with a modular spiral freezer th...
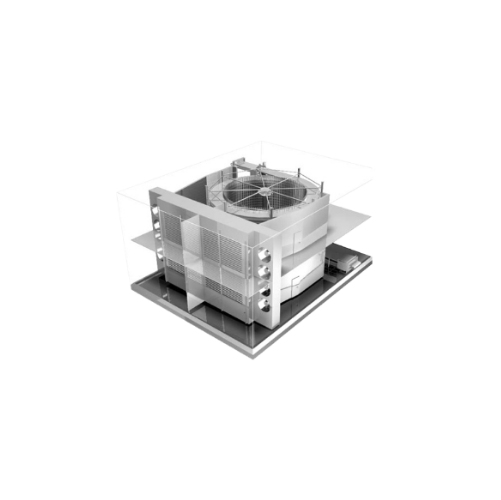
Industrial spiral freezer for high-volume processing
Optimize your high-volume food production with a robust spiral freez...
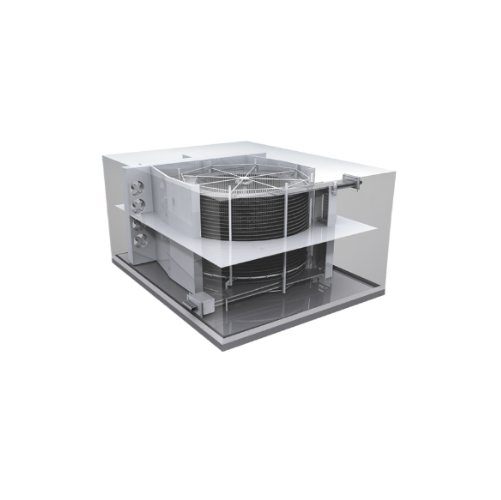

Structure supported spiral freezer for food products
Optimize your high-speed production with a versatile spiral freezer ...
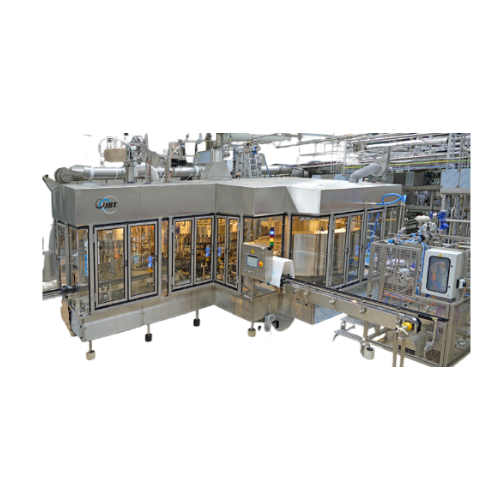

Rotary level filler for low to high viscosity liquid products
Ensure precise fill levels and enhance production efficien...
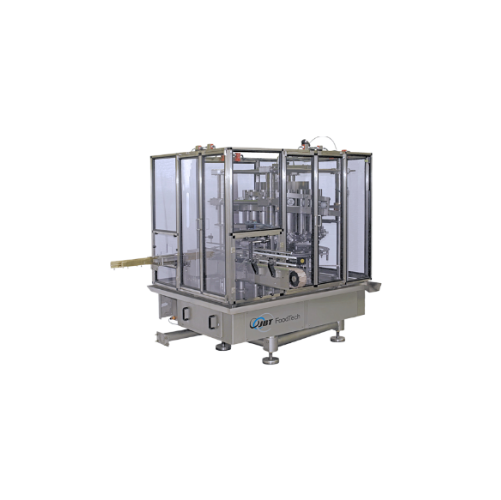

Volumetric piston filler for liquid and viscous products
Achieve precise volume control and enhance product integrity wit...

Rotary can filler and closer for metal cans
Achieve seamless integration in your production line with a solution that sinc...

Volumetric filler for various food products
Achieve high precision and flexibility in your filling processes with a volume...

Industrial weight filler for bottles and jars
Achieve precise product filling with our weight filler system, expertly desi...

Aseptic filler for packaged dairy and beverages
Ensure product sterility and extend shelf life efficiently with high-speed...
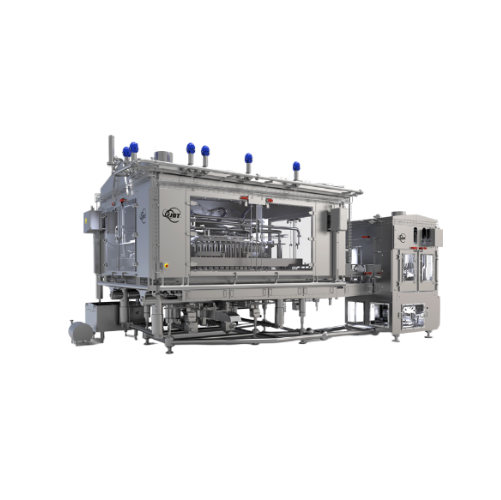

High capacity volumetric filler for pumpable products
When you need high-speed, precise filling for diverse liquid and sl...
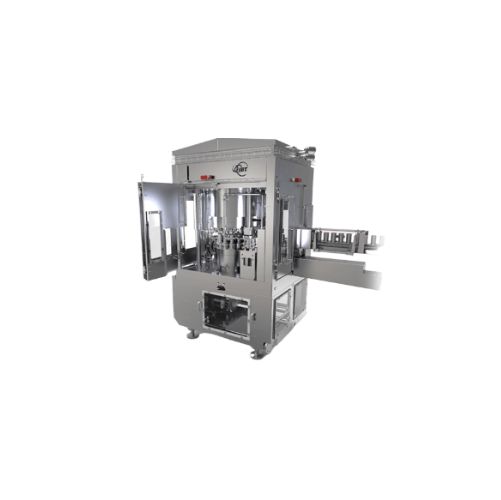

Can seamer for high-speed liquid applications
Ensure consistent seal integrity and maximize throughput with this advanced ...
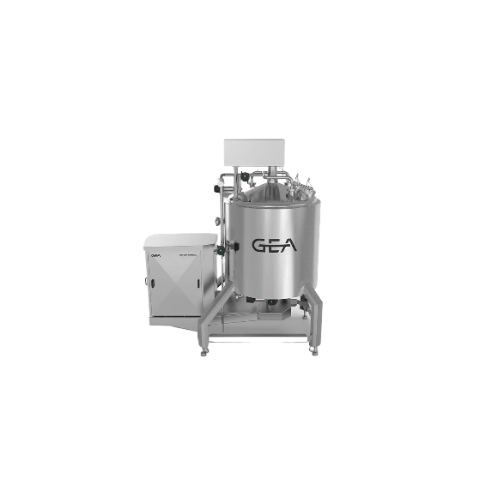

High shear mixer for dairy and personal care products
Achieve consistent emulsification and stable homogeneity with high ...

High shear mixer for low viscosity products
Achieve precise mixing and dispersion for diverse liquid applications with a h...

High shear test mixers for developing new products
Streamline product development with high shear test mixers, allowing y...
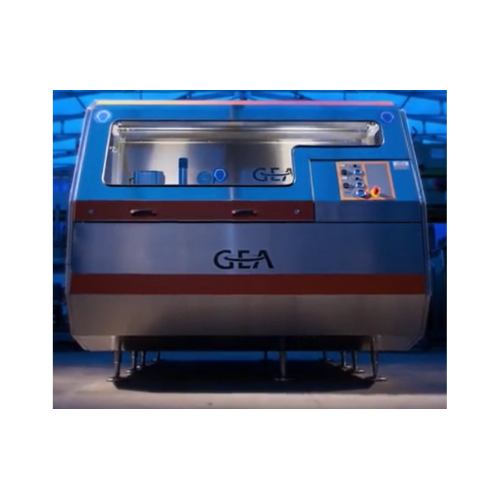

Industrial high-pressure homogenizer
Achieve precise homogenization with superior flow rates and efficiency, ensuring optim...

Hygienic filling system for short shelf life milk
Optimize your cold-chain distribution with a filling system engineered ...

Reverse osmosis dealcoholization technology
Elevate your beverage production capabilities with advanced dealcoholization t...

Reverse osmosis dealcoholization technology for beer
Achieve consistent flavor profiles in your non-alcoholic beer produc...

Reverse osmosis beer dealcoholization technology
Achieve precise alcohol removal from beer while preserving flavor integri...

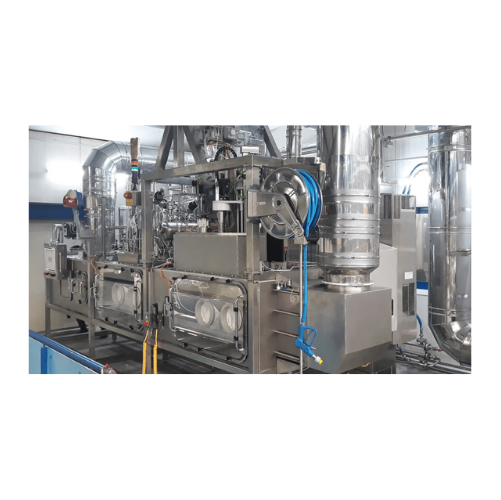
Aseptic blow fill system for beverage bottling
Designed for high-speed aseptic bottling, this system ensures sterility thr...

Aseptic filling system for sensitive beverages
Optimize your beverage production with an aseptic filling system that ensur...
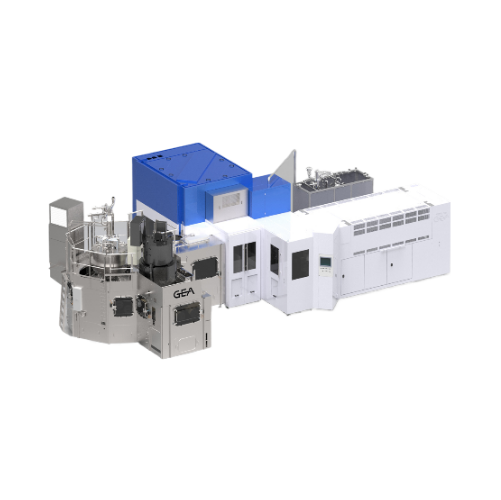
Decontamination blow fill system for beverages
Optimize your beverage production with a technology that integrates preform...
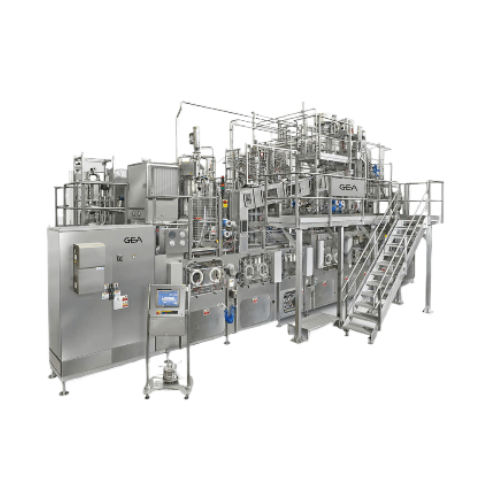
Aseptic filling for high and low acid beverages
Ensure aseptic integrity while maximizing operational efficiency with a co...

Aseptic filling system for milk-based drinks
Ensure sterile bottling of milk-based and sensitive beverages with this syste...

High-yield fermentation system for raw material processing
Achieve precise control in fermentation with advanced systems...
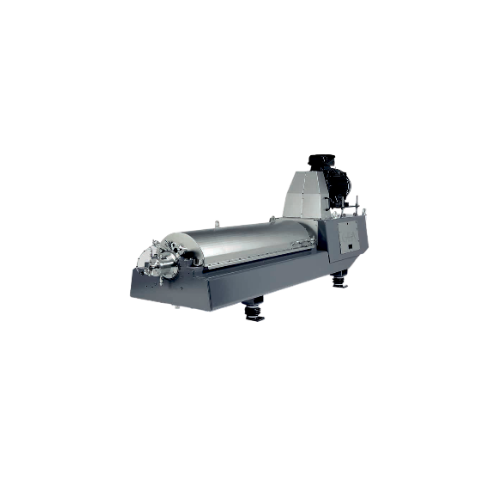

Decanter for plant-based beverage extraction
Ensure high-yield extraction and optimal purity from plant-based ingredients ...
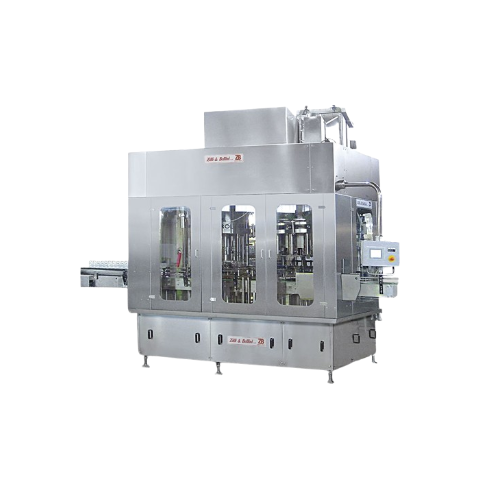

Ultraclean filling monoblocks for food industry
Enhance product safety and quality with monoblocks designed for ultraclean...
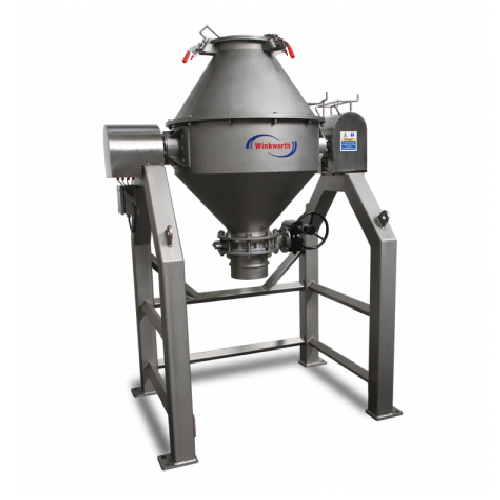

Double cone mixer for free-flowing material blending
Optimize your production with precision blending and gentle drying o...
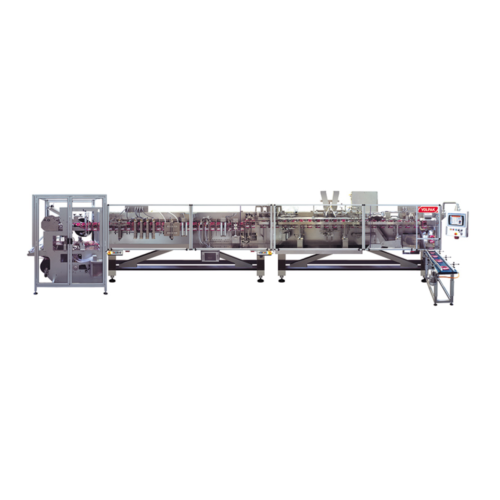

Stand-up pouch filling and sealing system
For packaging lines that demand quick, efficient, and flexible pouching, this hi...
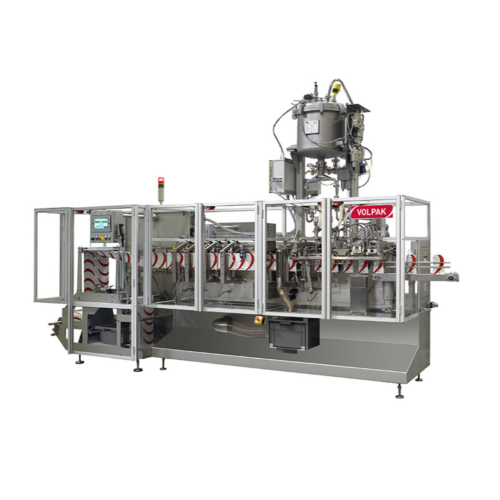

Stand-up pouch packaging for various products
For manufacturers seeking versatile packaging solutions, this machine delive...
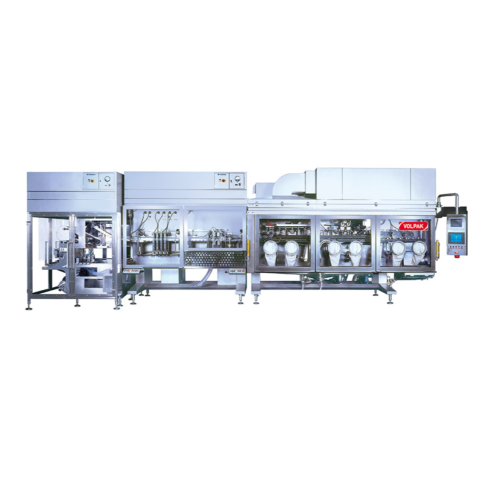

Horizontal stand-up pouching for beverages, dairy, and pet care
Optimize your liquid product packaging with rapid, high-...
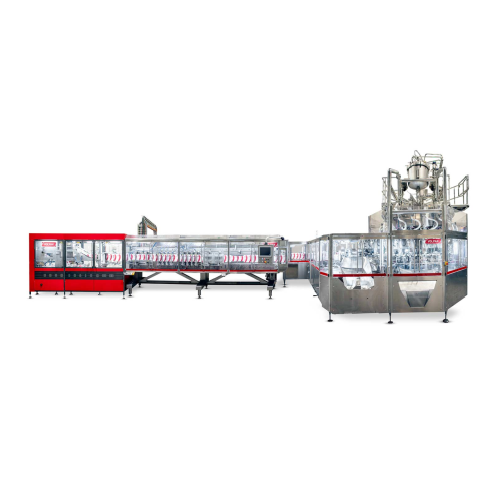
Continuous stand-up pouching solution for up to 1000ml
Maximize efficiency in high-speed production lines with precise st...
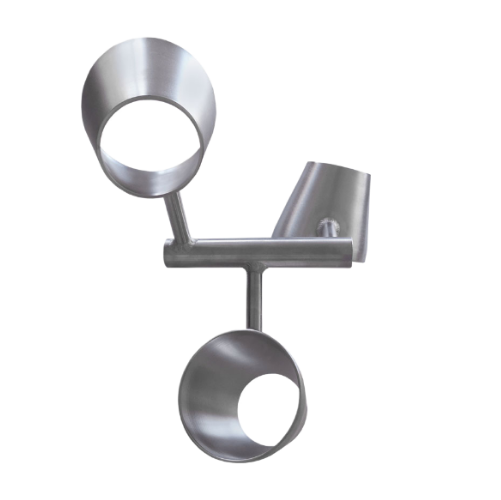

Side-mount agitator for large tank mixing
Achieve efficient mixing in large tanks with reduced energy consumption by lever...
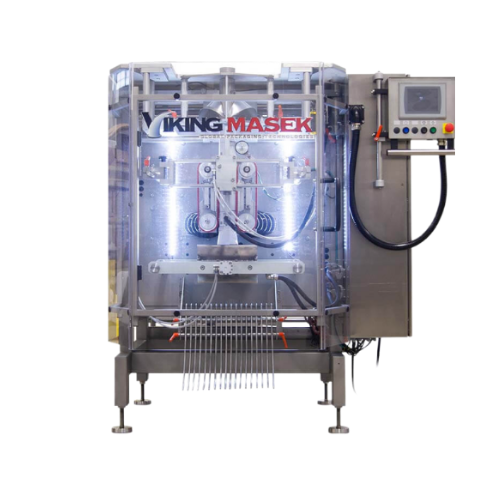

Vertical form fill seal for dusty and liquid products
Optimize your packaging line with a versatile solution designed to ...

Automated infeed and outfeed systems for packaging lines
Streamline your production line by integrating reliable infeed a...
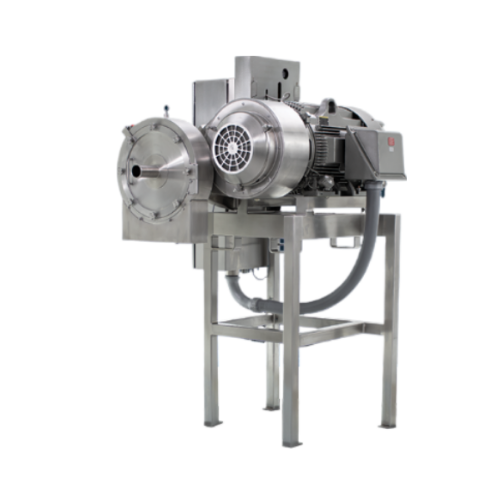

Industrial particle size reduction processor
Optimize your production line with high-capacity, continuous particle size re...
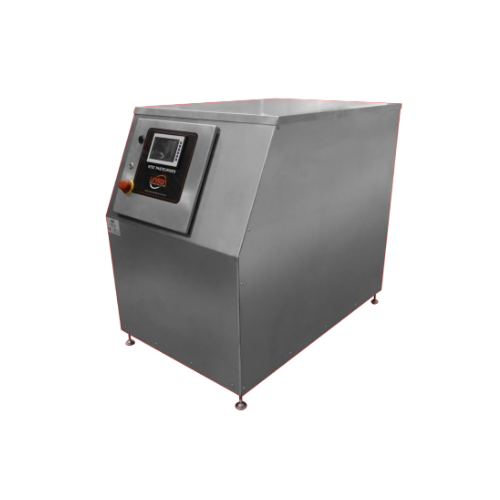

High performance industrial pasteurizers
Enhance your liquid processing with fully autonomous pasteurizers that ensure opti...
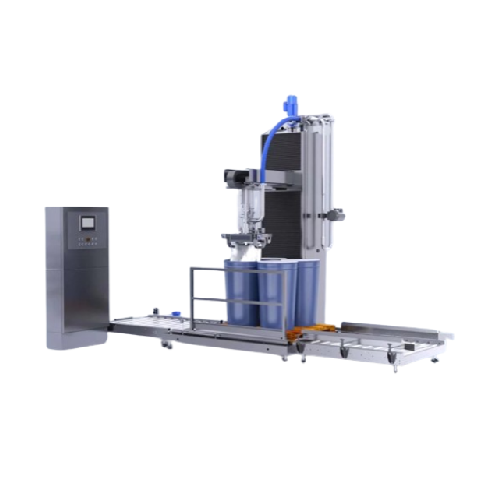

Aseptic filler for various liquid and semi-liquid food products
For manufacturers focused on quality, this aseptic filli...
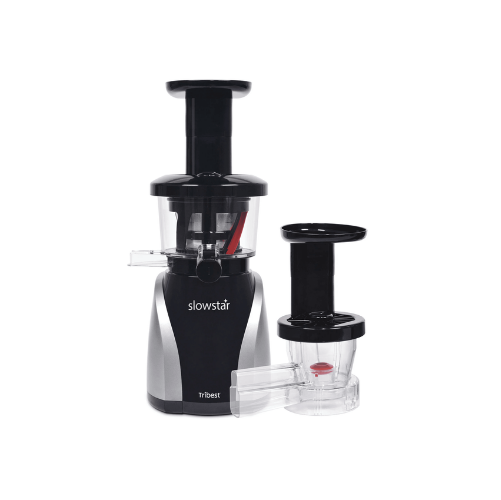

Vertical slow juicer for producing cold pressed juice
Achieve optimal juice quality and versatility with low-speed crushi...

High-speed vacuum blender for commercial use
Achieve optimal blending with cutting-edge vacuum technology, ensuring vibran...

High-speed blender for commercial use
Designed for high-performance blending tasks, this solution integrates vacuum technol...

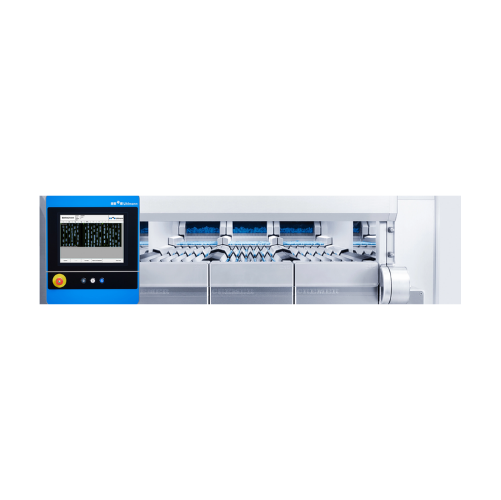
Aseptic rotary cup filling and closing solution
Maximize your production capacity with this cutting-edge aseptic solution,...
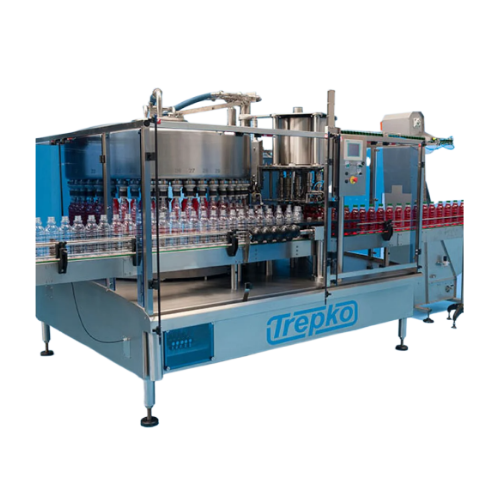

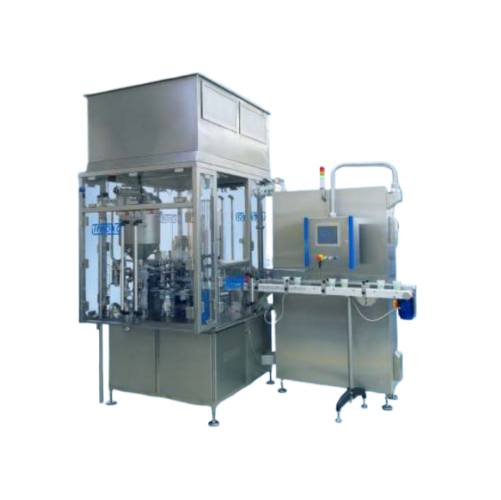
Bottle filling system for diverse specifications
Optimize your bottle-filling operations with a modular system that seamle...
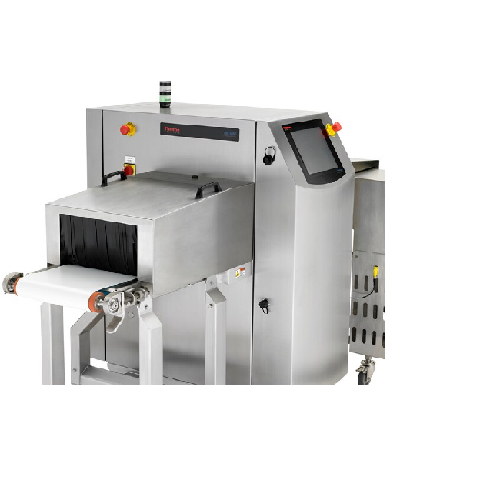

X-ray detection for food inspection
Ensure product integrity in high-speed packaging lines by detecting metallic and non-me...
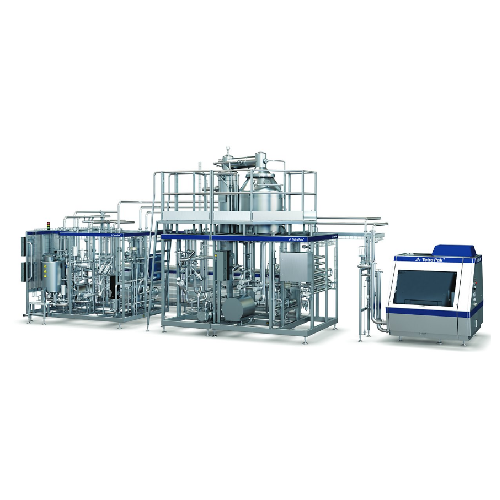

Direct Uht treatment for liquid foods
Optimize aseptic production with advanced UHT technology to preserve nutritional valu...
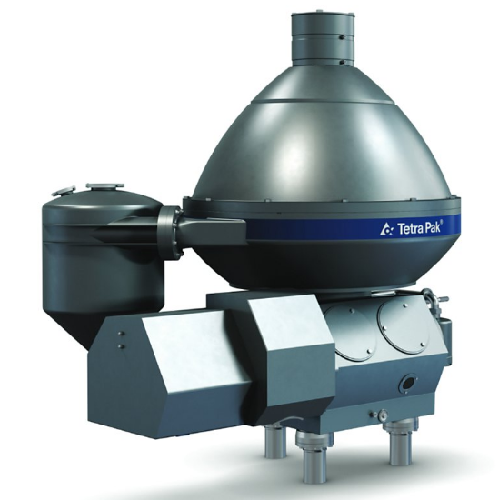

Milk skimming separator
Achieve superior separation efficiency and reduced energy consumption in dairy processing with seamle...
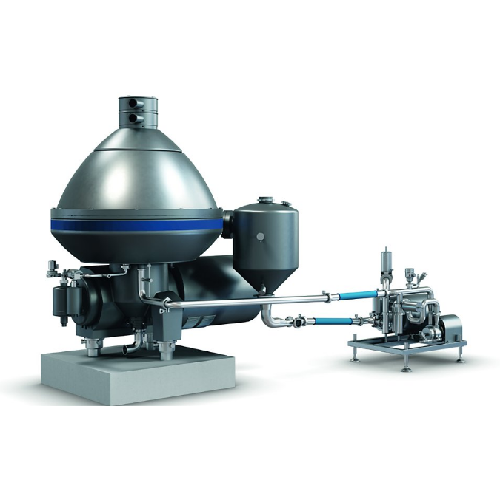

Efficient dairy product separator
Achieve precise fat separation and enhance product quality while reducing energy consumpt...
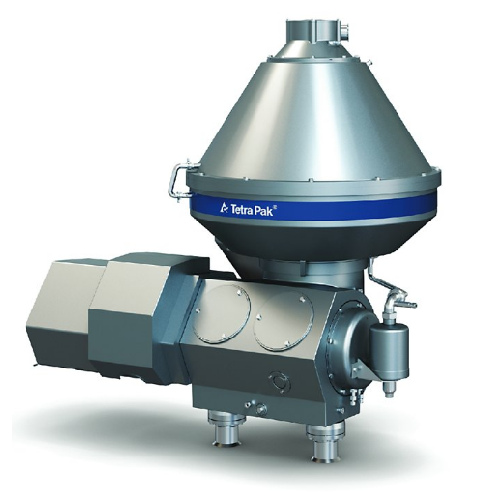

Industrial clarifier for dairy and plant-based products
Optimize your production line with cutting-edge clarification tec...
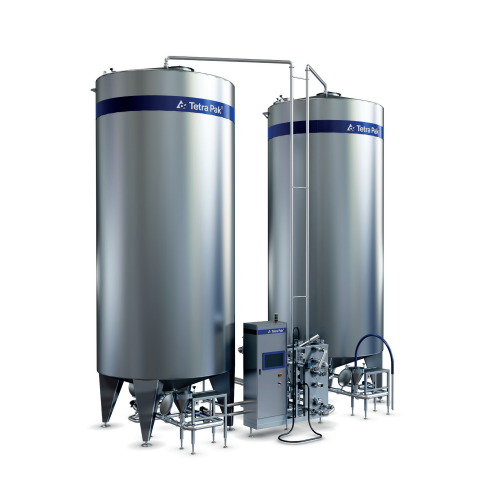

Beverage preparation system for large-scale production
Ideal for producers looking to scale up, this versatile system eff...
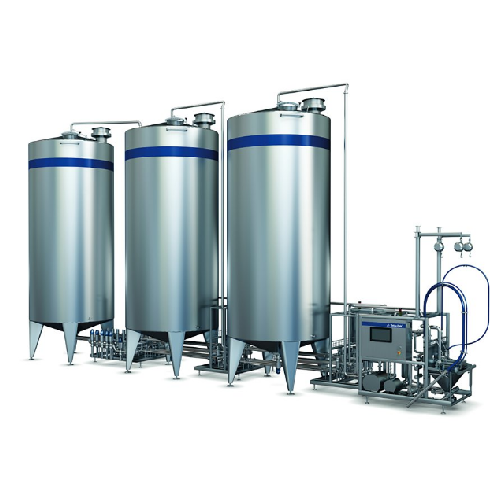

Syrup and beverage preparation system
Enhance your beverage production with a versatile solution that optimizes mixing, hyd...
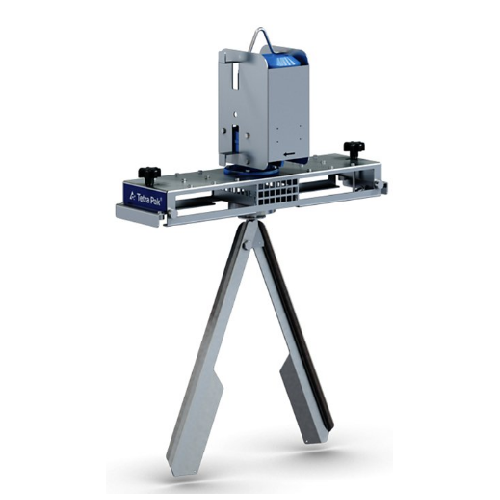

Agitator for Ibc containers
Achieve consistent and efficient mixing of various liquid products with this agitator, ensuring ...
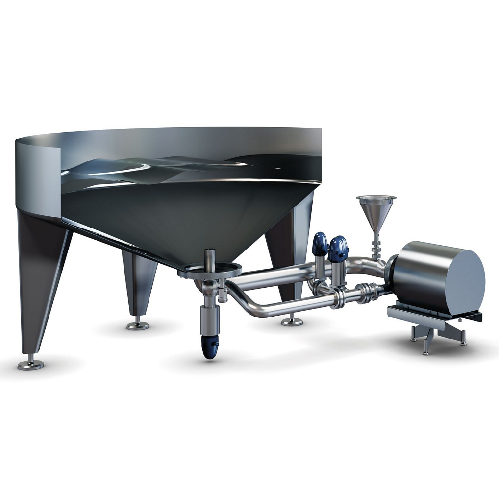

High-speed liquid mixing solution
Optimize your beverage mixing operations with a system that ensures even ingredient distr...
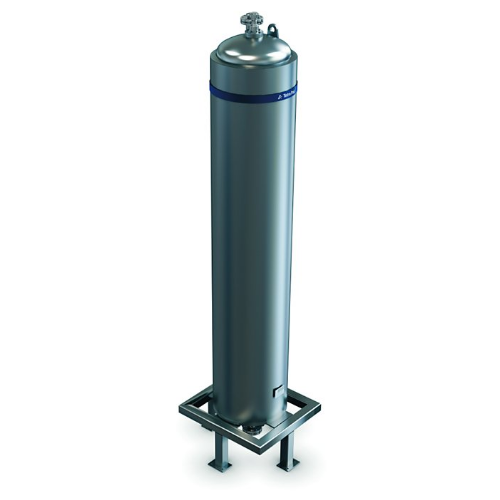

Coiled heat exchanger for high viscosity products
Efficiently handle high-pressure, viscous product heating and cooling w...
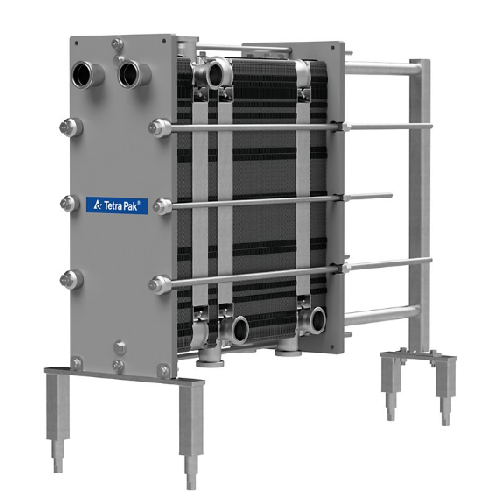

Plate heat exchanger for food products
Achieve precise temperature control in your processing line with this plate heat exc...
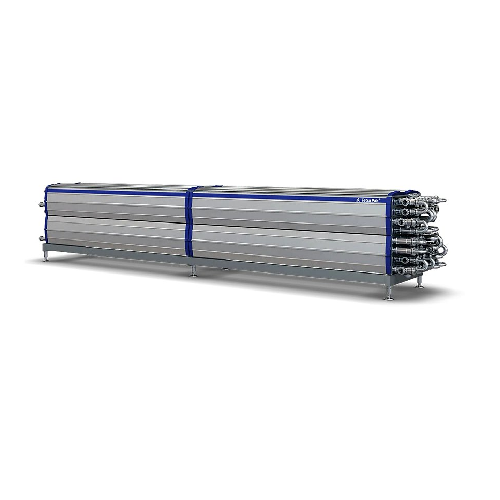

Tubular heat exchanger for food processing
Optimize energy consumption and ensure unparalleled food safety during heat tre...
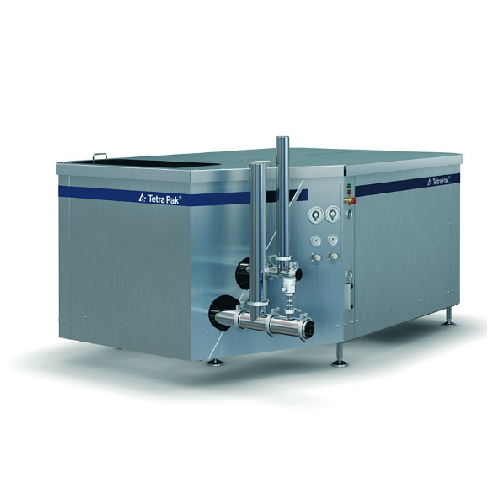

Industrial homogenizer for liquid food applications
Achieve unparalleled product consistency and quality with high-speed ...
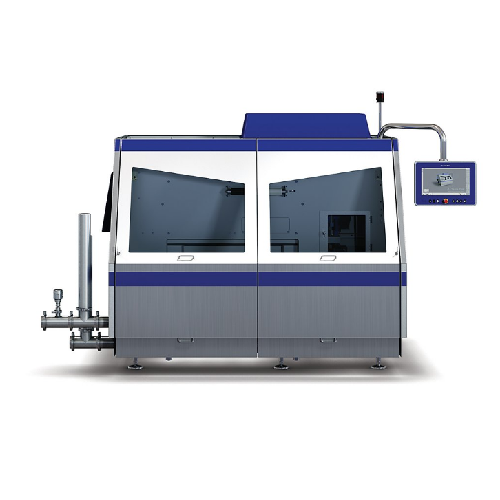

Homogenizer for high-capacity food processing
Achieve superior emulsification and suspension handling with this high-press...
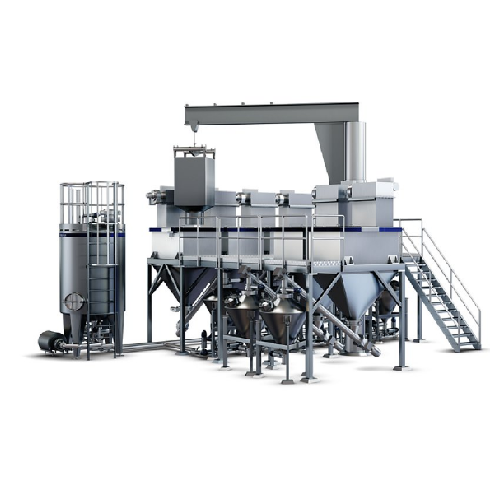

Autonomous ingredient dissolver for high-volume dry ingredient mixing
Efficiently mix multiple high volumes of dry ingr...
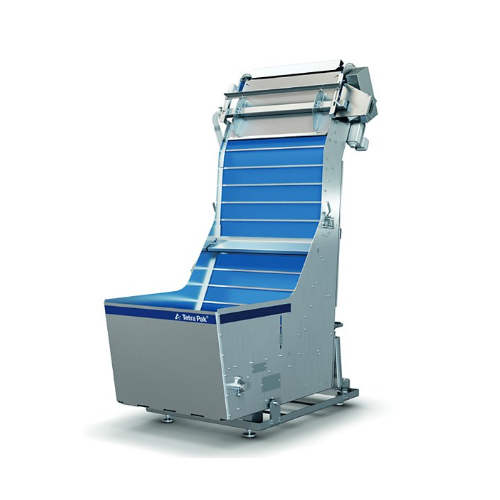

Lid unscrambler for unstackable lids in round containers
Streamline your packaging process with this lid unscrambler, eff...
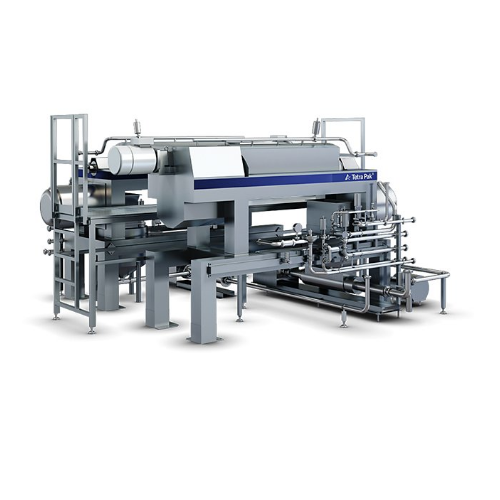

Double decanter for plant-based beverages
Optimize your plant-based beverage production by achieving high protein yield an...
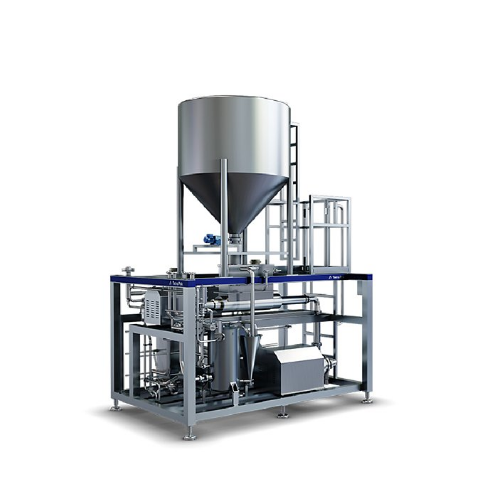

Industrial grinder for plant-based beverages production
Achieve optimal particle size for seamless integration with your ...
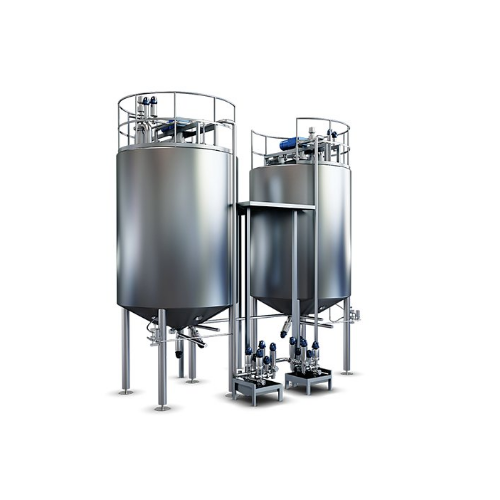

Hydrolysation tank for plant-based beverage production
Ensure optimal hydrolysis conditions for plant-based beverages wit...
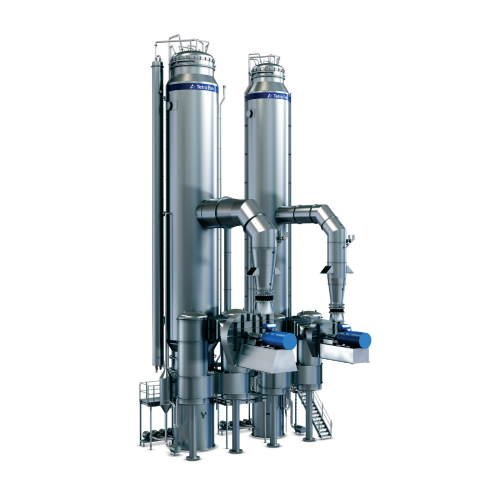

Continuous evaporator for dairy products
Enhance your production efficiency with a fully automatic evaporator designed to m...
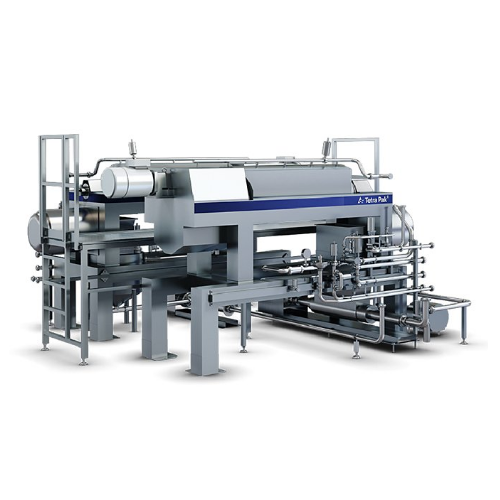

High-precision decanter for plant-based beverages
Enhance your plant-based beverage production with a decanter engineered...

Aseptic tank with blending function for liquid food storage
Achieve seamless integration of aseptic buffering and in-lin...
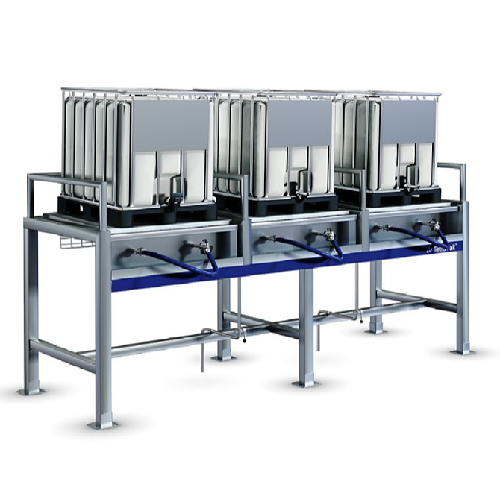

Ibc rack for storing and discharging intermediate bulk containers
Optimize liquid handling in your production line with...
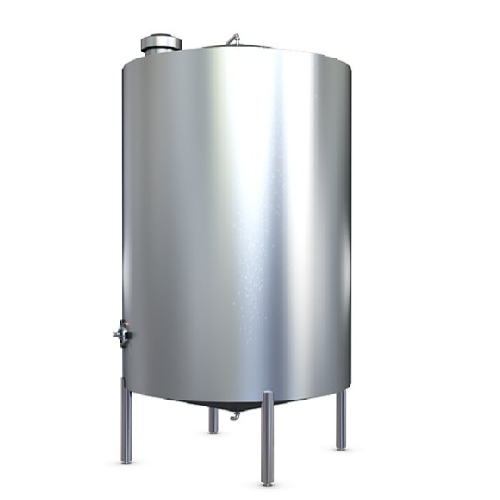

Liquid ingredient reception tank
Optimize your liquid processing with versatile tanks designed for efficient storage and han...
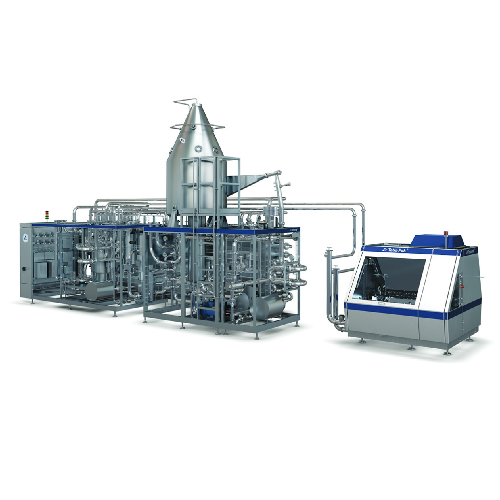

Direct Uht processing system for dairy and plant-based beverages
Achieve ultra-high temperature treatment with minimal i...
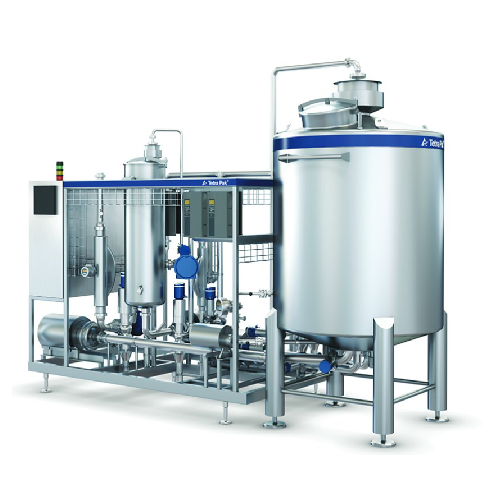

In-line blender for beverage production
Enhance beverage production with a versatile solution that offers precise blending,...
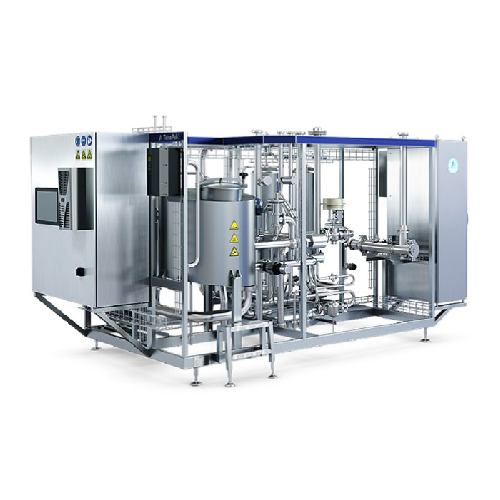

Water treatment system for aseptic blending in Jnsd production
Ensure a reliable aseptic blending process for your bever...
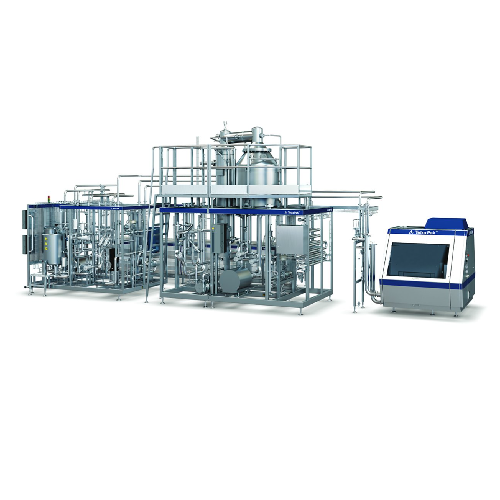

Ultra-high temperature processor for premium liquid foods
Achieve superior product quality and flexibility with advanced...
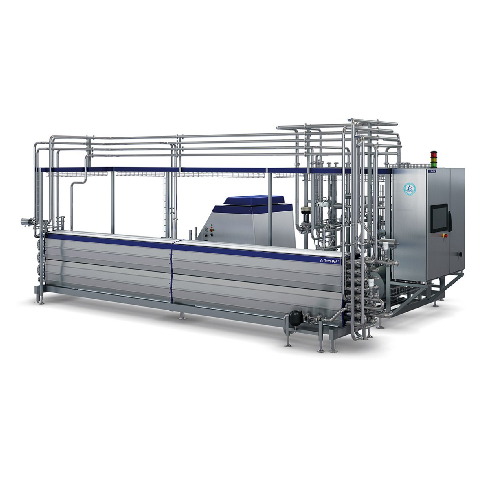

Uht processing unit for dairy products
Optimize your liquid food production with continuous, high-capacity UHT treatment th...

High capacity milk separator with polynode technology
Achieve unprecedented milk skimming efficiency and reduced environm...

Spore removal unit for dairy processing
Optimize your dairy production by efficiently removing spores and bacteria, ensurin...

Energy-efficient dairy product separator
Achieve up to 40% energy savings in your dairy and beverage processing operations ...

High shear mixer for emulsification and powder dissolving
Achieve seamless mixing and emulsification for high and low vi...
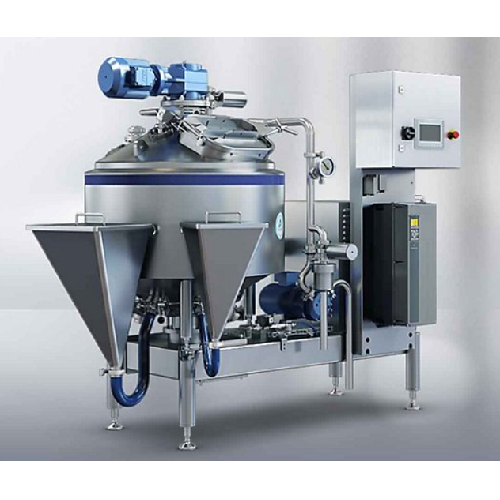

High shear mixer for smooth or particulate food products
Achieve consistent quality in diverse food products with precise...
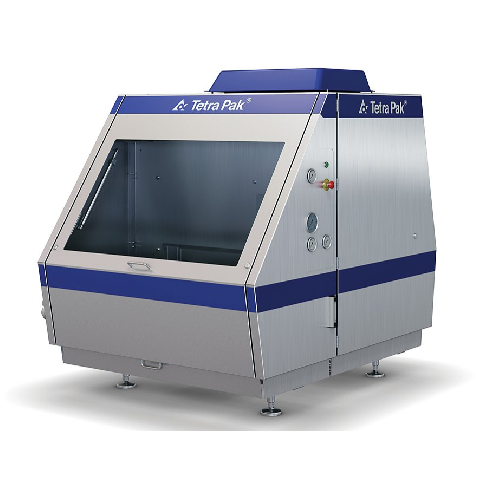

Mid-range capacity homogenizer for dairy and beverage
For operations demanding consistent product quality and high uptime...
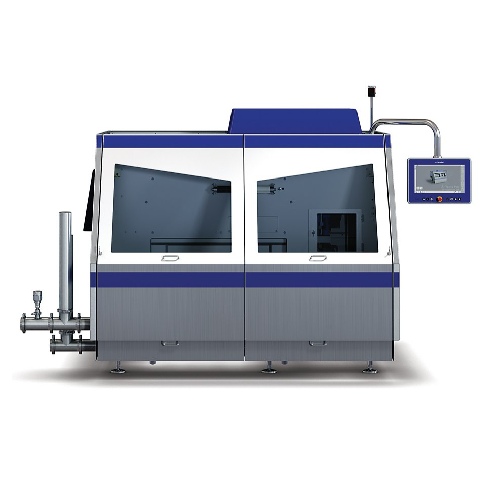

High-pressure homogenizer for dairy and beverage products
Achieve optimal product consistency and extend shelf life with...
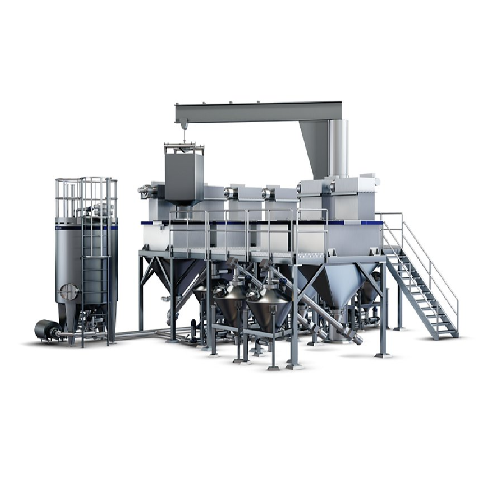

Autonomous ingredient dissolver for high volume dry ingredient mixing
Streamline your production by seamlessly mixing d...

Ingredient dissolver for small batches
Efficiently dissolve water-soluble powders and concentrates up to 200 cP with precis...

Final syrup and beverage preparation system
Optimize your beverage production with a modular system designed for flexibili...

Preparation system for syrup and beverages
Streamline syrup and beverage preparation with a versatile system designed to r...

Double decanter for plant-based beverage extraction
Maximize protein yield and enhance extraction efficiency in your plan...
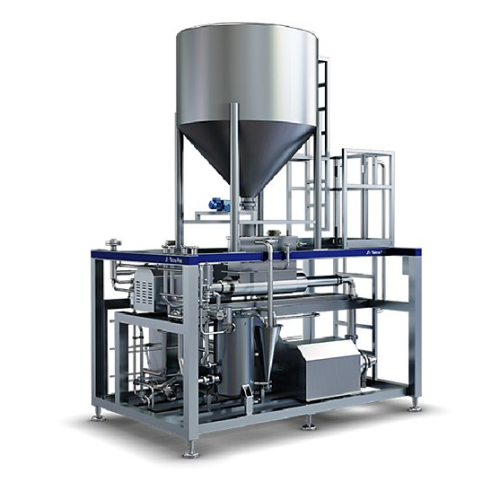

Industrial grinder for plant-based beverages
Ensure optimal particle size for hydrolysis in plant-based beverage productio...
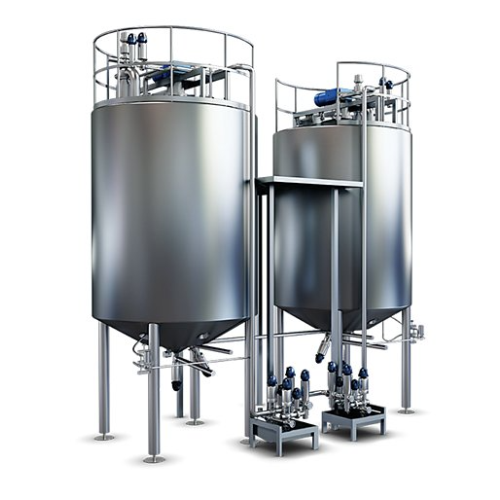

Hydrolysation tank for plant-based beverages
Optimize your plant-based beverage production with a hydrolysation tank that ...
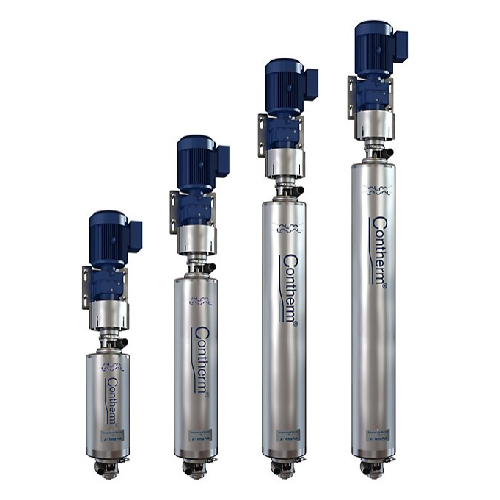

Contherm scraped-surface heat exchanger for viscous food products
Optimize your heating and cooling processes for stick...
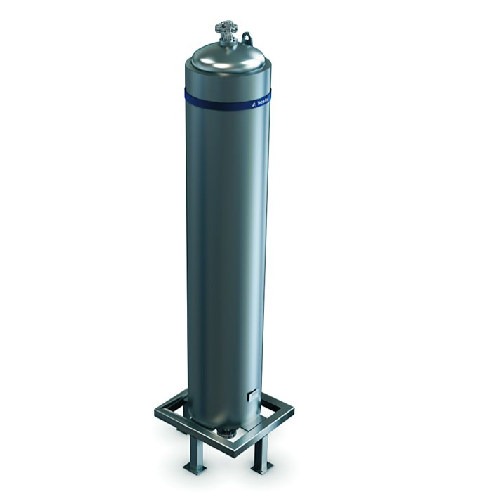

Coiled heat exchanger for viscous and particulate products
Optimize heat treatment of viscous and particulate foods with...
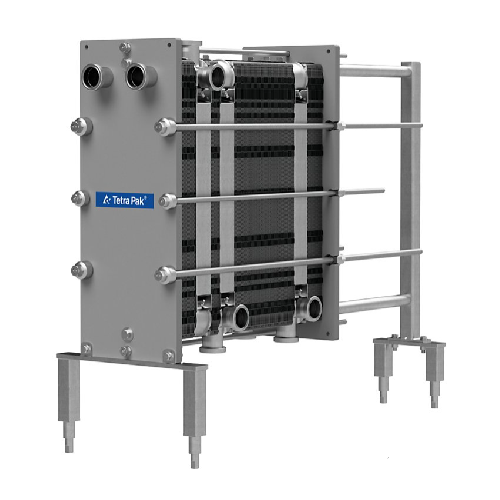

Industrial plate heat exchanger for food processing
Ensure consistent product quality with precise temperature control an...
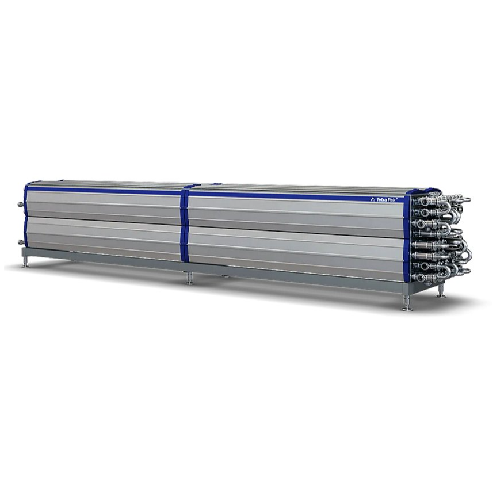

Tubular heat exchanger for food products
Achieve precise temperature control and energy efficiency with this innovative tub...
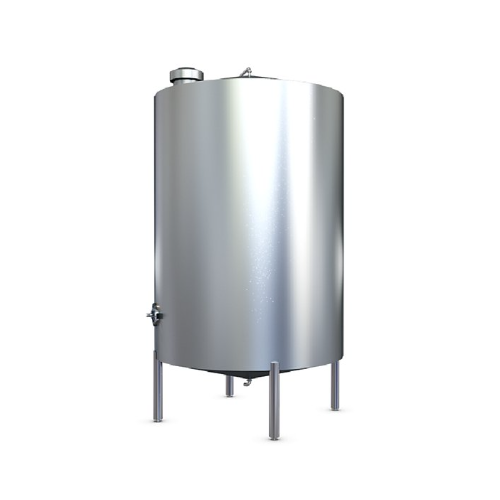

Storage tank for food liquid storage
Ensure seamless liquid product handling with precision-engineered storage tanks design...
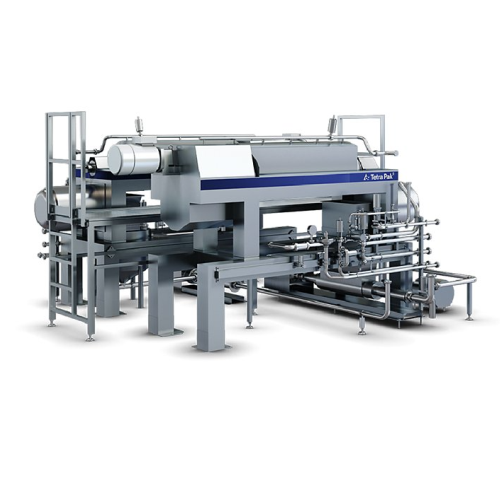

Plant-based beverage extraction system
Maximize yield and product quality in plant-based and dairy beverages with high-effi...

Water treatment unit for aseptic blending in Jnsd production
Ensure aseptic quality and consistent flavor in beverages b...
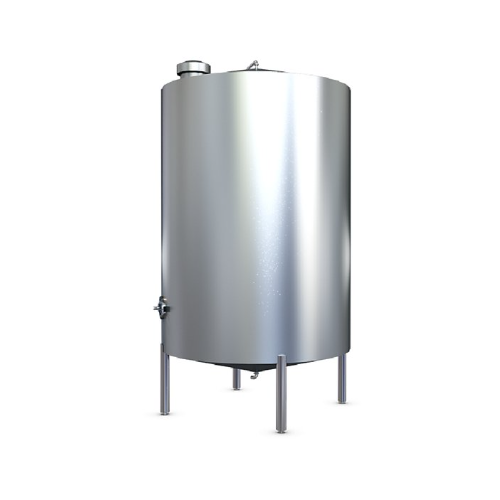

Liquid sugar storage tank
Ensure seamless liquid sugar management in your production line with advanced storage solutions de...
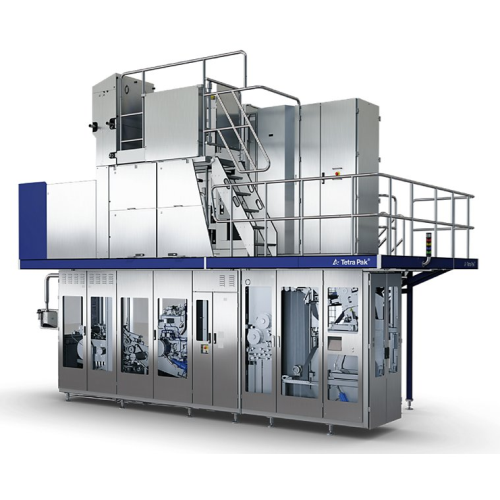

High-speed aseptic carton filling solution
Maximize production efficiency and meet growing demand with this high-output fi...
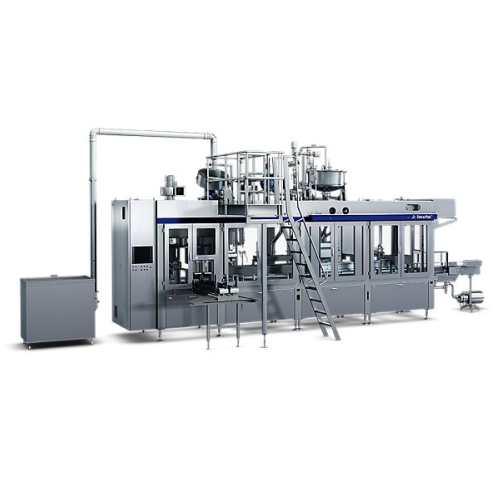

Filling system for gable top packages
Achieve precise, cost-effective filling with reduced energy consumption for chilled l...
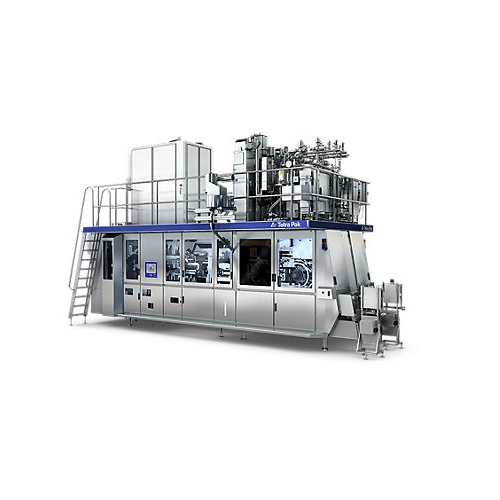

Filling solution for water packaging
Achieve efficient packaging for a variety of beverages with this high-speed filling so...
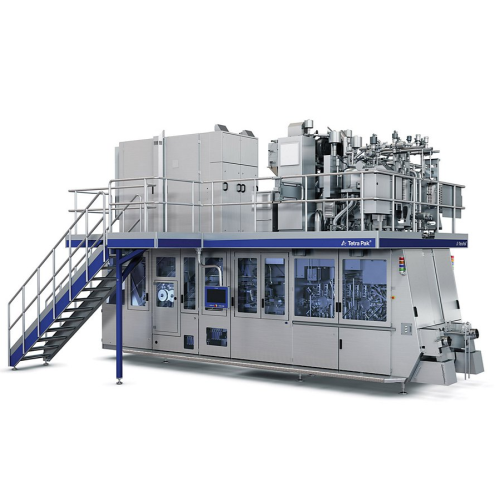

Dual-line filler for tetra top packages
Maximize your production flexibility with a high-speed, dual-line filling solution ...
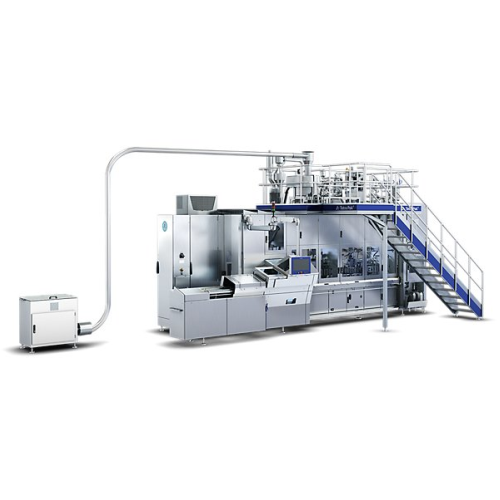

Filling machine for tetra rex® gable top cartons
Maximize efficiency and food safety in high-speed liquid filling with pre...
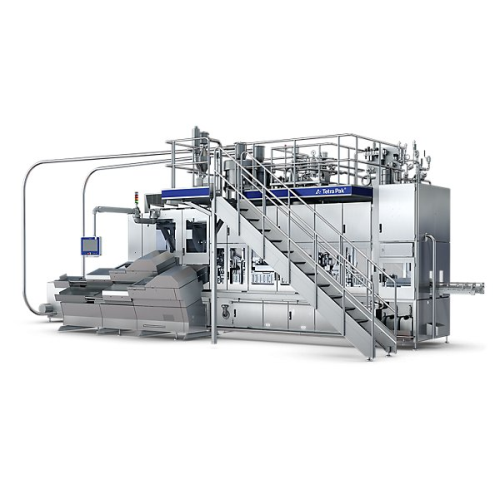

Filling system for gable top cartons chilled products
Achieve precise filling and reliable sealing for chilled beverages ...
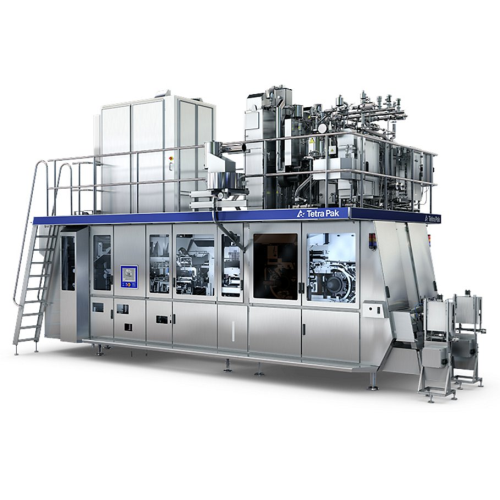

Dual filling solution for tetra top packages
Boost production flexibility by simultaneously filling different liquid produ...
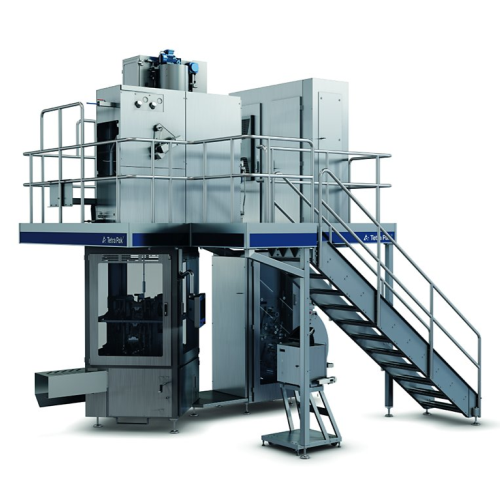

Aseptic filling solution for tetra classic packaging
Experience efficient aseptic packaging with high-speed operation, of...
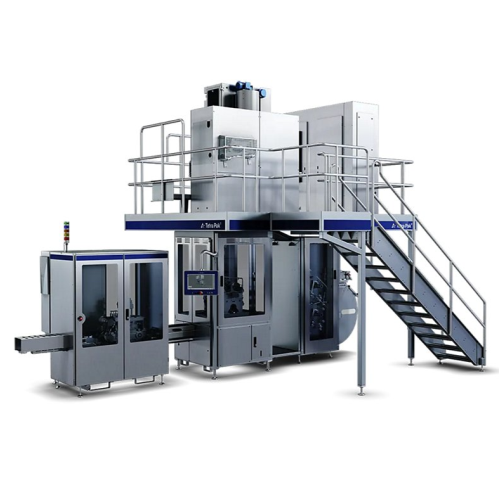

Filling system for tetra brik 100 slim packages
Optimize your chilled product packaging with a high-speed filling system d...
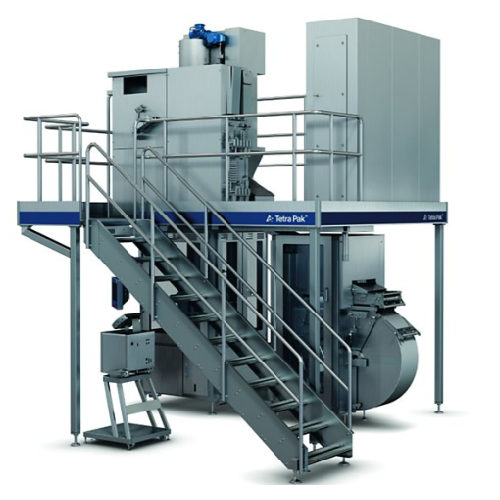

Aseptic carton filling system for tetra fino packaging
Elevate your production efficiency with a high-speed aseptic filli...

Filling system for tetra wedge aseptic packages
Optimize your production line with a reliable filling system designed to e...

Compact aseptic filling solution for versatile production
Maximize production line efficiency with a compact filling sys...

Versatile filling system for aseptic packaging
Achieve seamless integration in high-speed aseptic packaging with this flex...

High-speed carton filler for aseptic packaging
Maximize production efficiency with this high-speed filling solution that e...

Filling solution for tetra brik® packages
Optimize your filling and packaging process with a system that seamlessly switch...
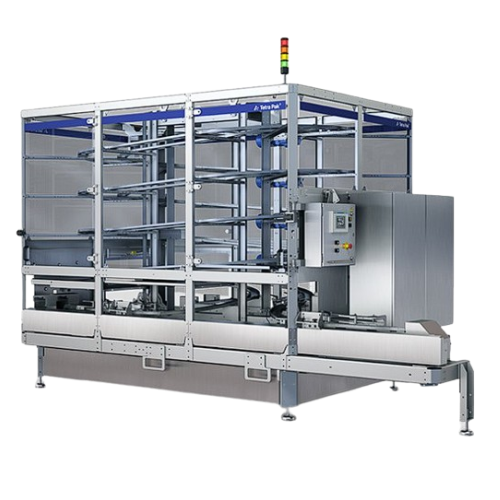

Vertical package accumulator for food and beverage production
Ensure seamless flow and precise order tracking of package...
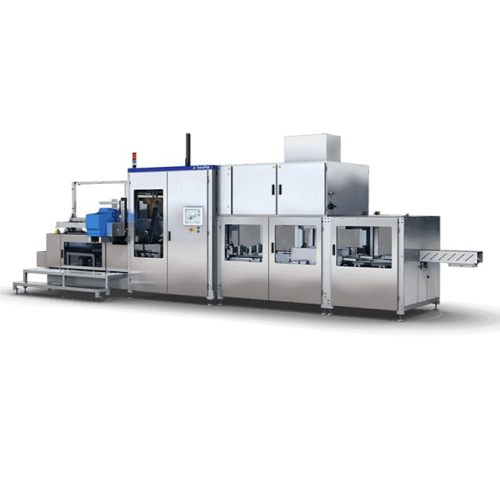

Cardboard packer for secondary packaging
Streamline your packaging process with a high-speed, automated cardboard packer th...
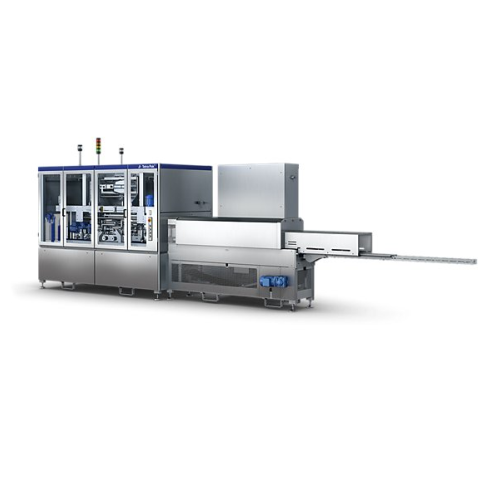

Shrink wrapping system for flex portion packages
Optimize your packaging line with a high-speed shrink wrapping system des...

Industrial tray shrink wrapper
Optimize your packaging line with rapid, resource-efficient shrink wrapping, accommodating di...
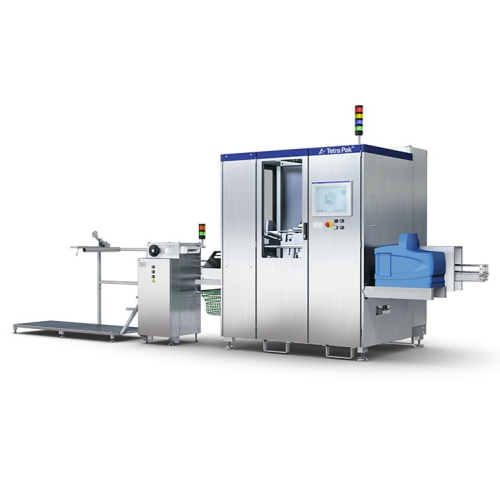

Straw applicator for tetra pak cartons
Ensure precise straw attachment and minimize production interruptions with a high-sp...
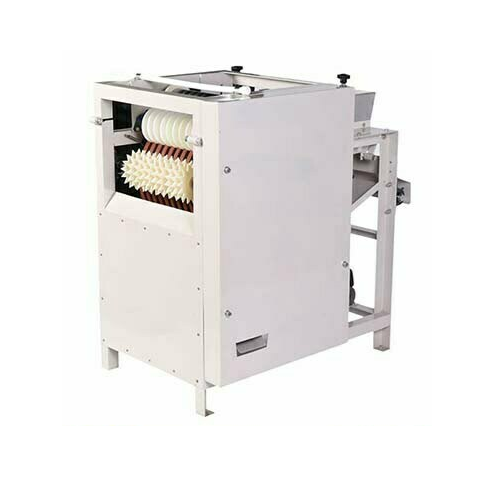

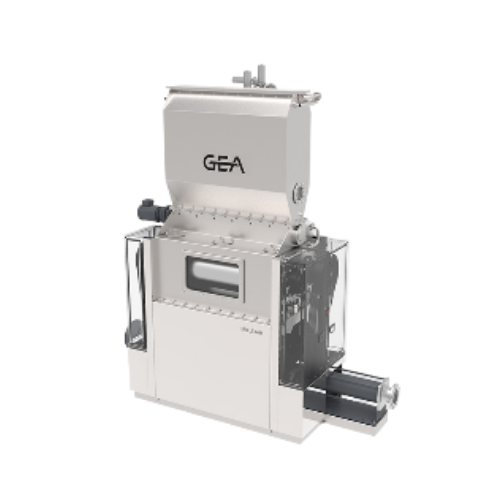
Wet almond peeling machine for nut processing
Enhance your nut processing efficiency by achieving up to 98% peeling rate w...

Paper forming technology for sustainable packaging
Elevate your product’s sustainability with advanced paper formin...
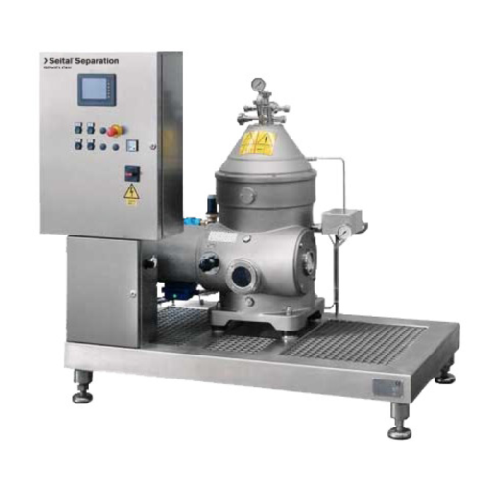

Self-cleaning separator for industrial liquid/solid separation
Optimize your production line with self-cleaning separato...
Tubular juice pasteurizer
Ensure optimal safety and quality of liquid products with precise temperature control and high hea...
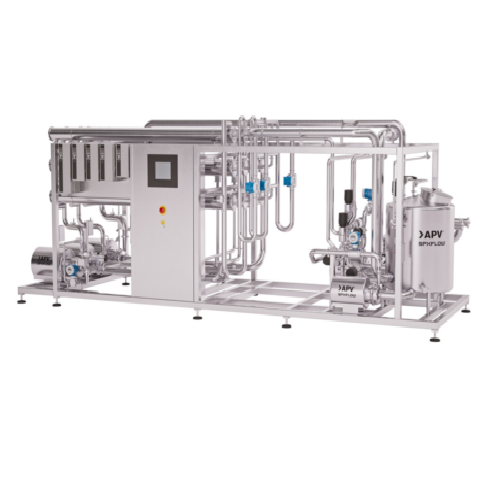

Ultrafiltration for dairy and plant-based protein concentration
Optimize your production capacity and increase yield wit...
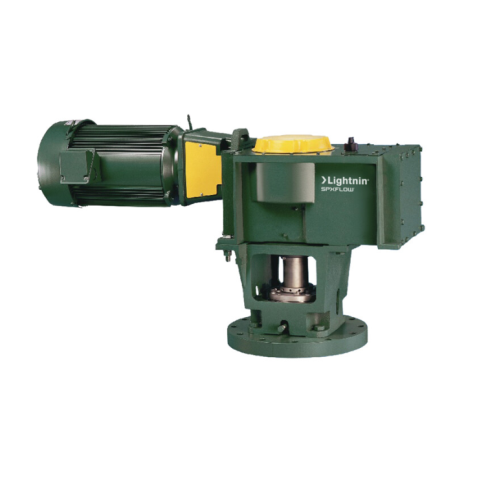

Medium torque top entering mixer for complex mixing tasks
Optimize your production line with a versatile mixing solution...
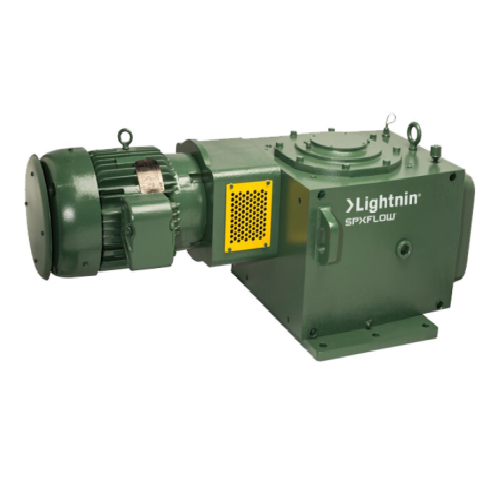

Medium torque top entering mixer for industrial applications
Optimize your mixing and blending operations with precise t...
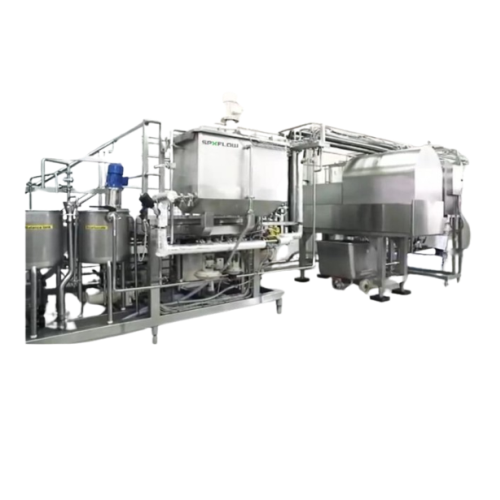

Soymilk processing plant
Enhance your plant-based production with our tailored soymilk processing plants, designed to efficie...
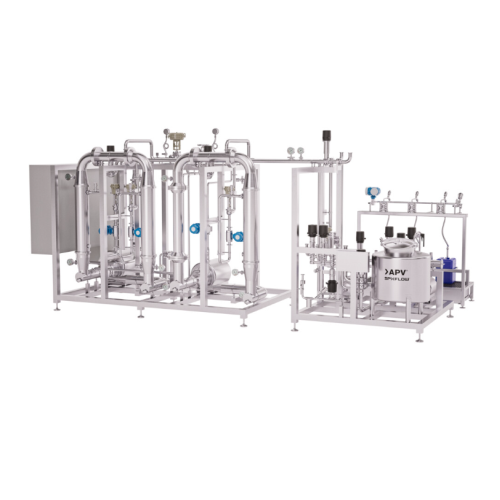

Microfiltration system for dairy and plant-based applications
Enhance your production capacity and reduce waste with adv...
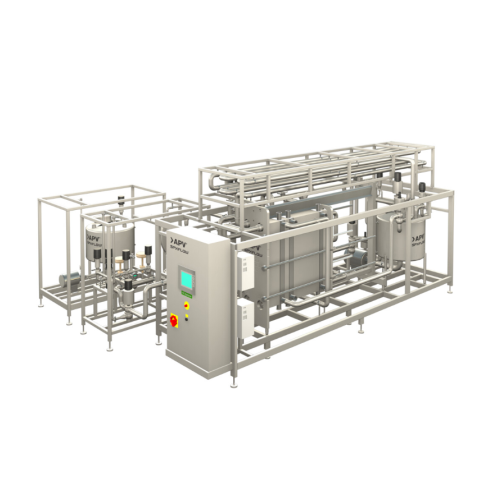

Milk pasteurizer system
Ensure your dairy and plant-based beverages achieve optimal safety and quality with precise temperatu...
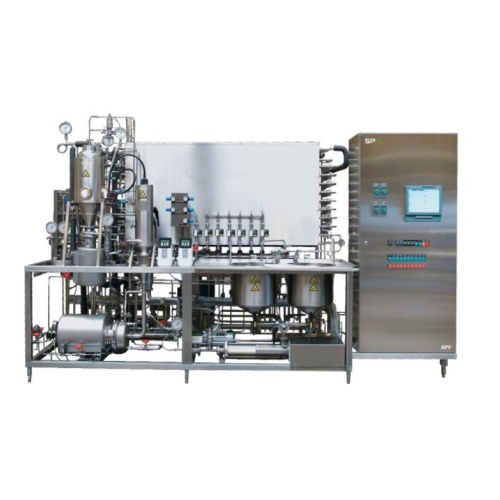

Multipurpose ultra high temperature (uht) pilot plants
Optimize liquid food production with a versatile pilot unit design...
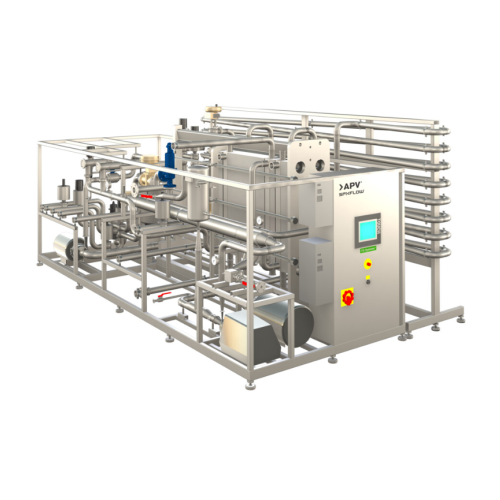

Plate juice pasteurizer system
Ensure optimal pasteurization with precise temperature control and high heat recovery, reduci...
High pressure homogenizer for food and beverage processing
Optimize your production line with a versatile high-pressure ...
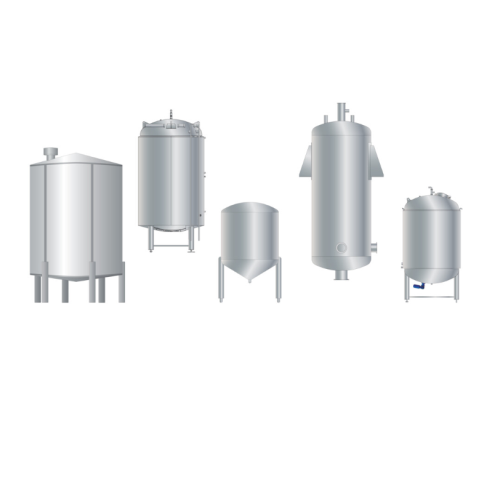

Hygienic tanks for various processing needs
Achieve optimal processing and storage with customizable hygienic tanks, desig...

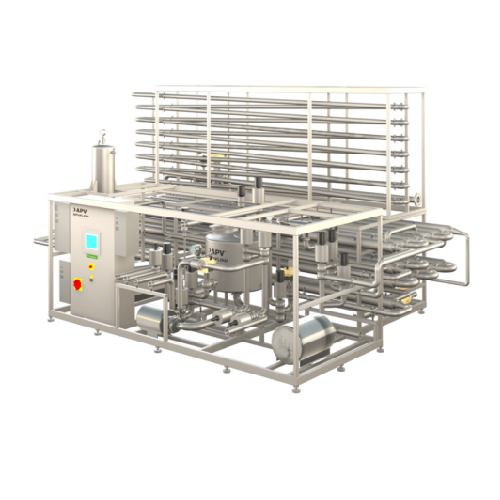
Infusion Uht system for dairy and plant-based beverages
Efficiently extend the shelf life of dairy and plant-based bevera...
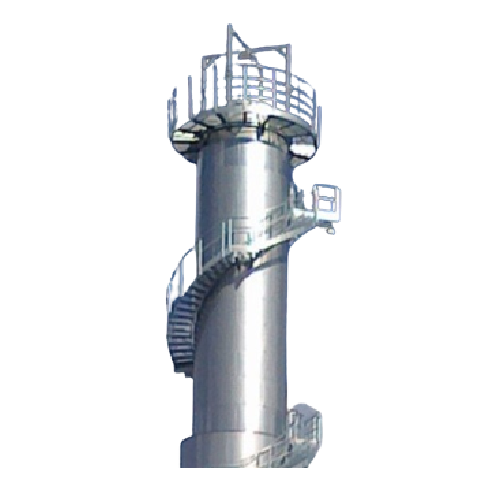

Mechanical vapor recompression evaporator for pre-concentration in food industry
Achieve efficient energy use by utili...
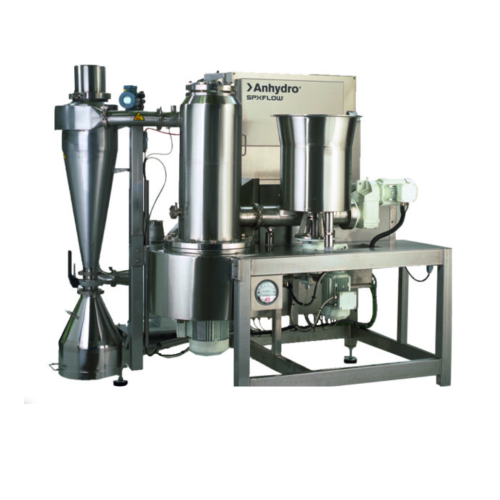

Small scale spin flash dryers for high-viscosity liquids
Optimize moisture control with cutting-edge spin flash dryers de...
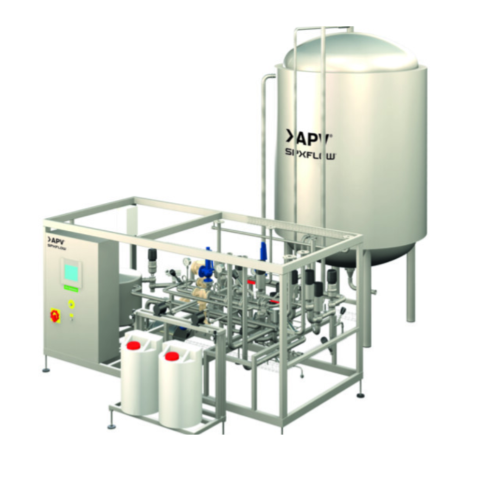

Aseptic storage tank for aseptic products
Ensure uninterrupted aseptic product storage with this advanced tank system, des...
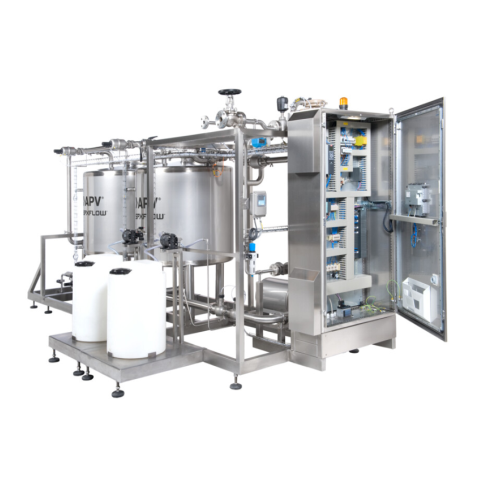

Clean in place (cip) system for industrial cleaning
Ensure optimal hygiene and production efficiency with a system that s...
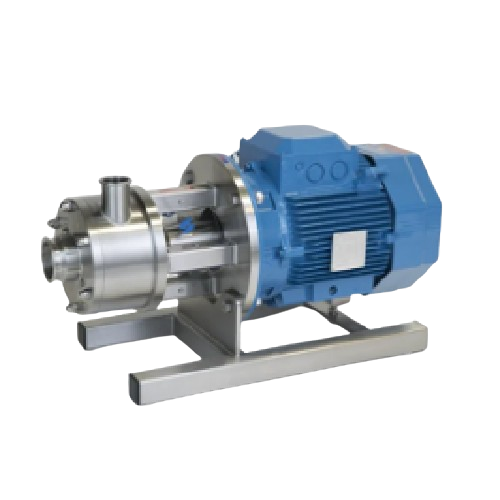

High shear mixer for efficient particle size reduction
Achieve rapid and precise blending and particle reduction in your ...

Chilled water milk can cooler for small farms
Ensure milk quality and safety with rapid cooling from 35°C to 8°C in under ...

Uht sterilization solution for liquid food products
Enhance your liquid food processing with reliable UHT sterilization, ...

Energy efficient grinder for plant-based milk
Buying pre-processed materials, such as flour, and handling and dispersing t...

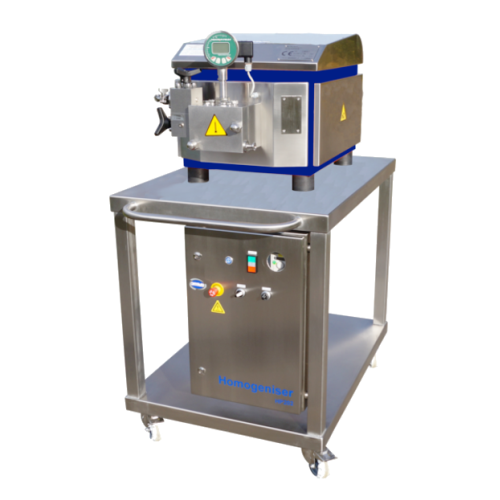
Pilot plant homogeniser
From food to pharma, homogenization is an essential step in the production process that provides unif...

Pasteurization Machine for Milk
Manual processing of dairy products can cause inconsistent quality between batches due to po...
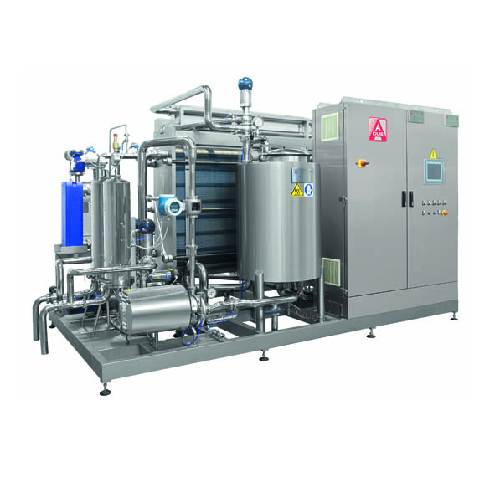

Pasteurizer machine for sensitive beverages
When you want to expand your beverage production line, following a new global ...
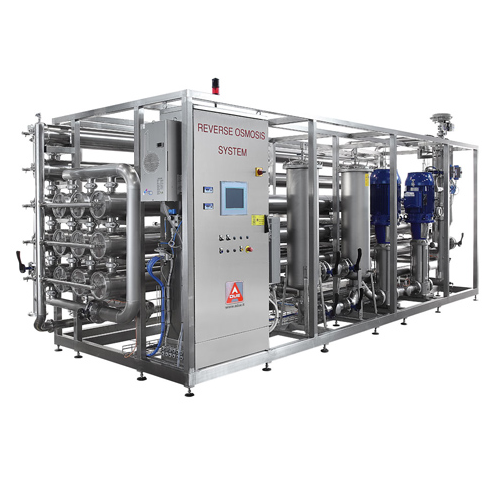

Water treatment for beverage preparation
Water is one of the main ingredients in producing juices and other beverages. If i...
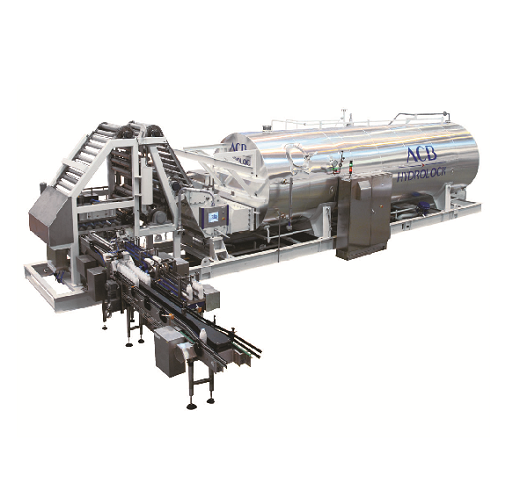

Continuous sterilizer for milk beverages
An important goal of heat processing in the manufacturing of milk beverages is to ...
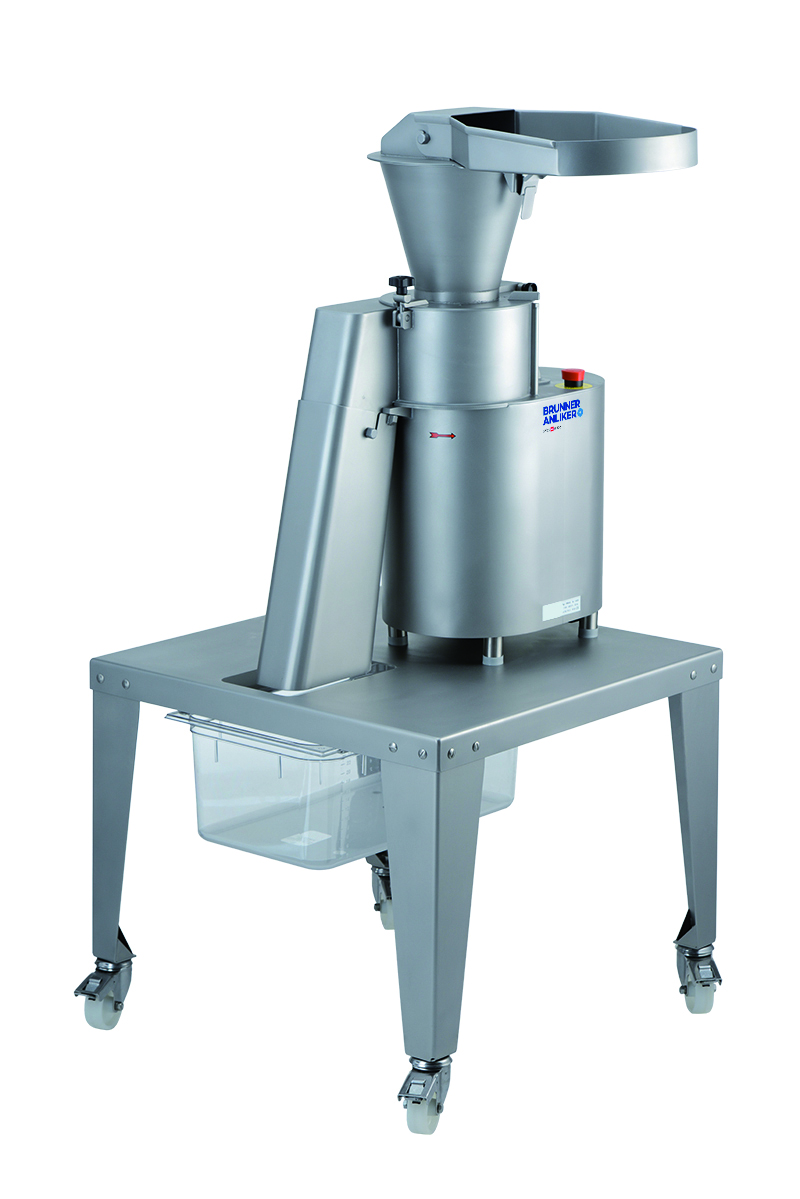

Nut and cheese grater
Smearing, clumping and crumbling are common problems when cheese and other soft textured foodstuffs are...

Automatic bottling machine for beverage
One of the biggest challenges when bottling beverage drinks is that many of the bot...
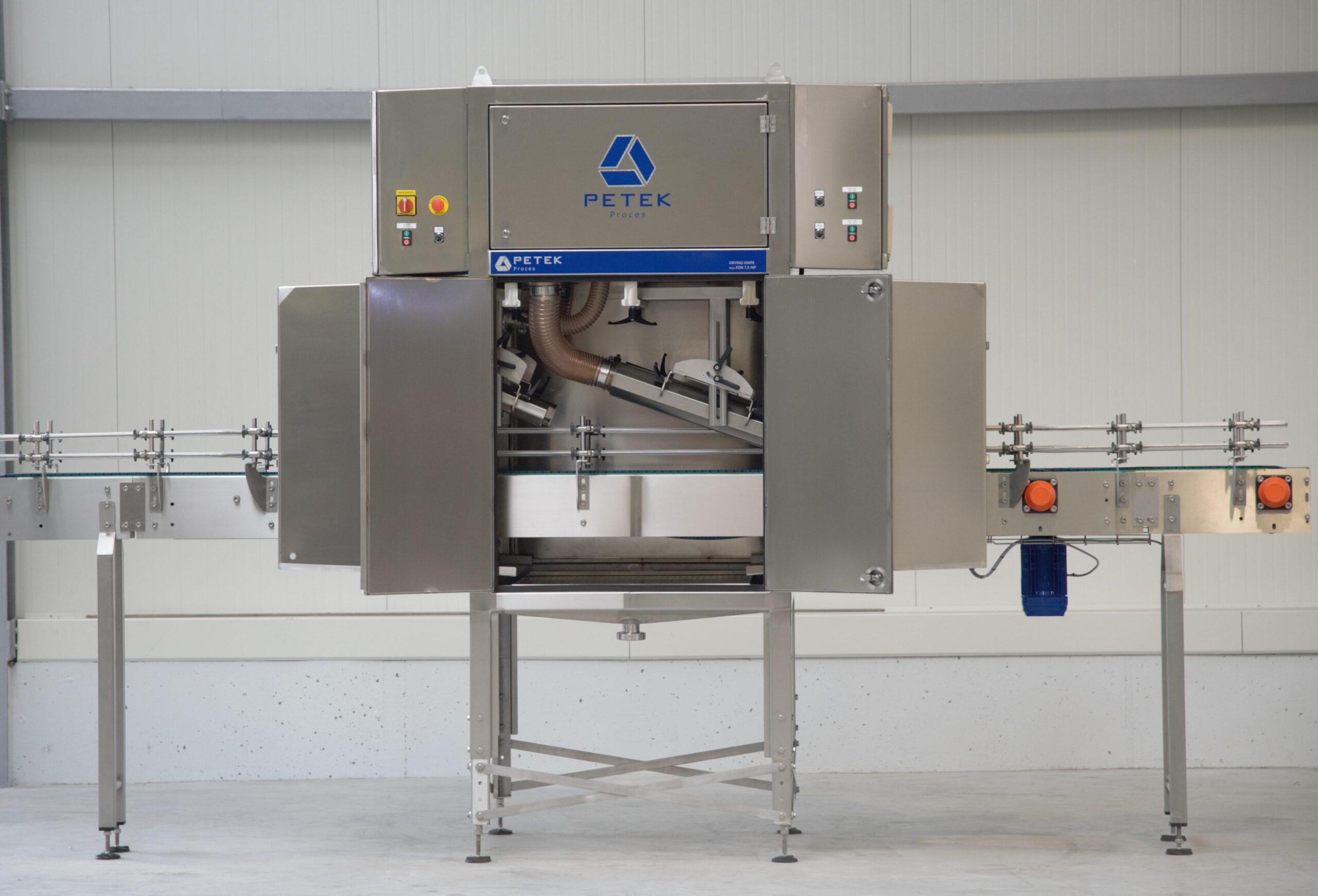

Air knife system for bottling lines
Wet containers are unacceptable and can be problematic in the food and beverage industr...
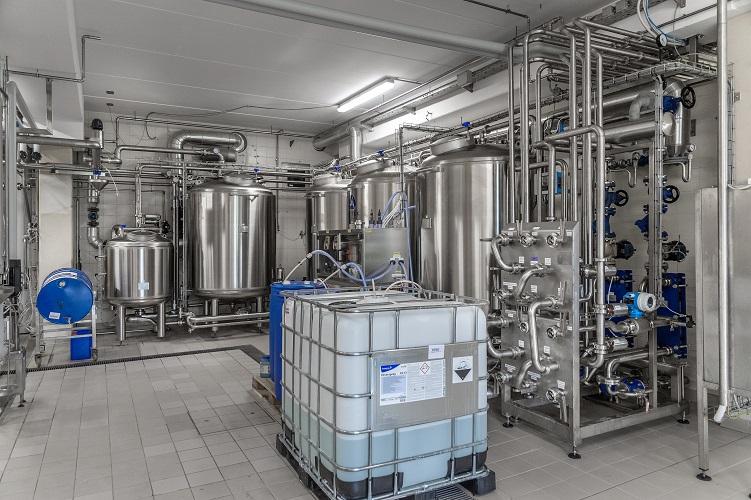

CIP system for beverage
Clean-in-place operations are a mandatory part of food and beverage processing which cannot fail. How...
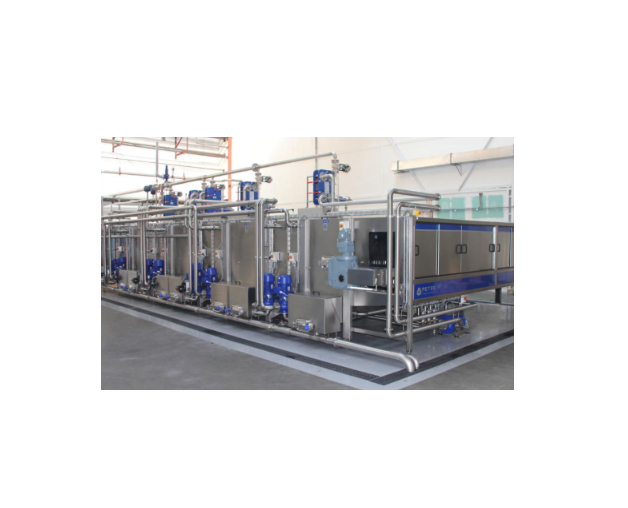

Tunnel pasteurizer for beverage
In the beverage industry, beverages need to be pasteurized in order to destroy pathogens, an...

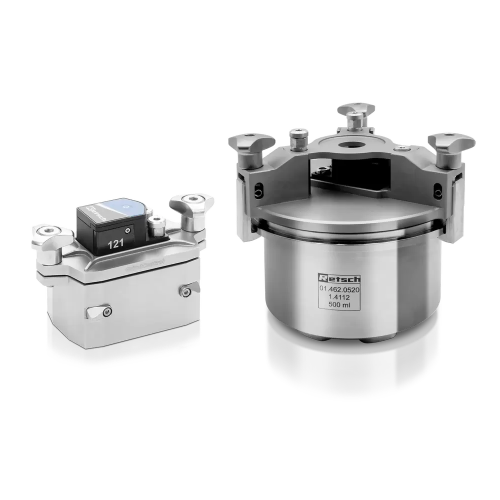
High pressure electric laboratory homogenizer
It’s vital that small units for experimentation can scale up with 100% accur...
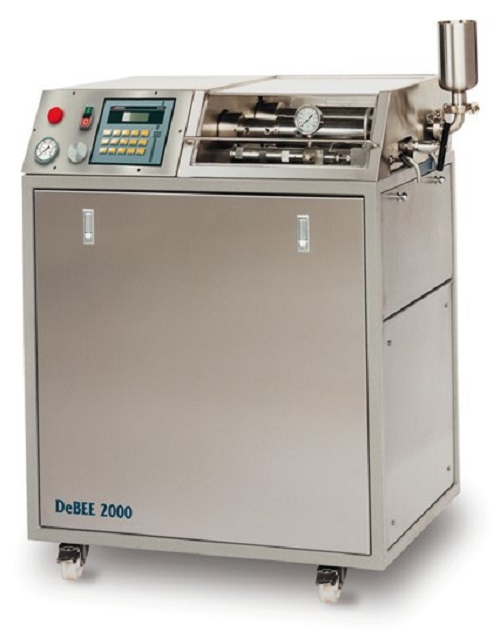

High pressure pilot homogenizer
Biotech and pharmaceutical development programs often require a mixing method that achieves ...
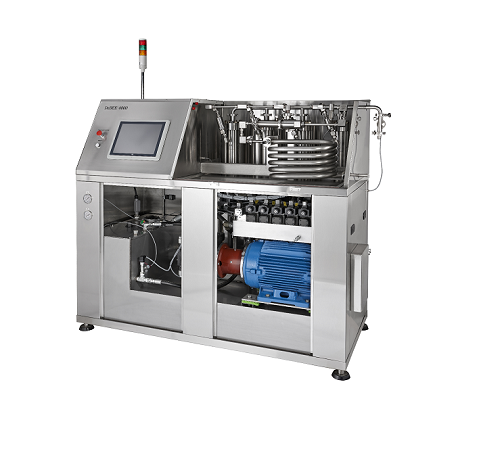

High pressure industrial homogenizer
For any industrial pharmaceutical process that relies on high pressure homogenization ...
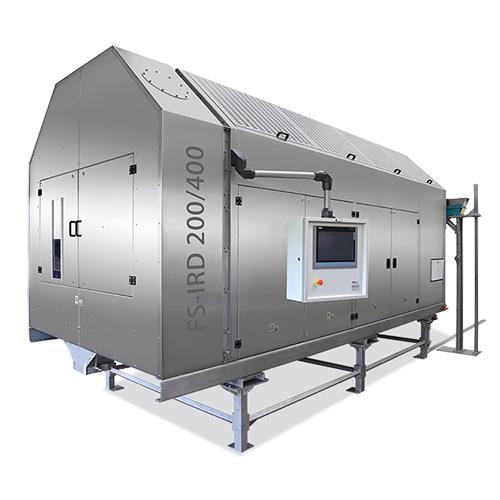

Infrared rotating drum dryer
Traditional drying methods are often slow and can actively damage ingredients, reducing the fin...
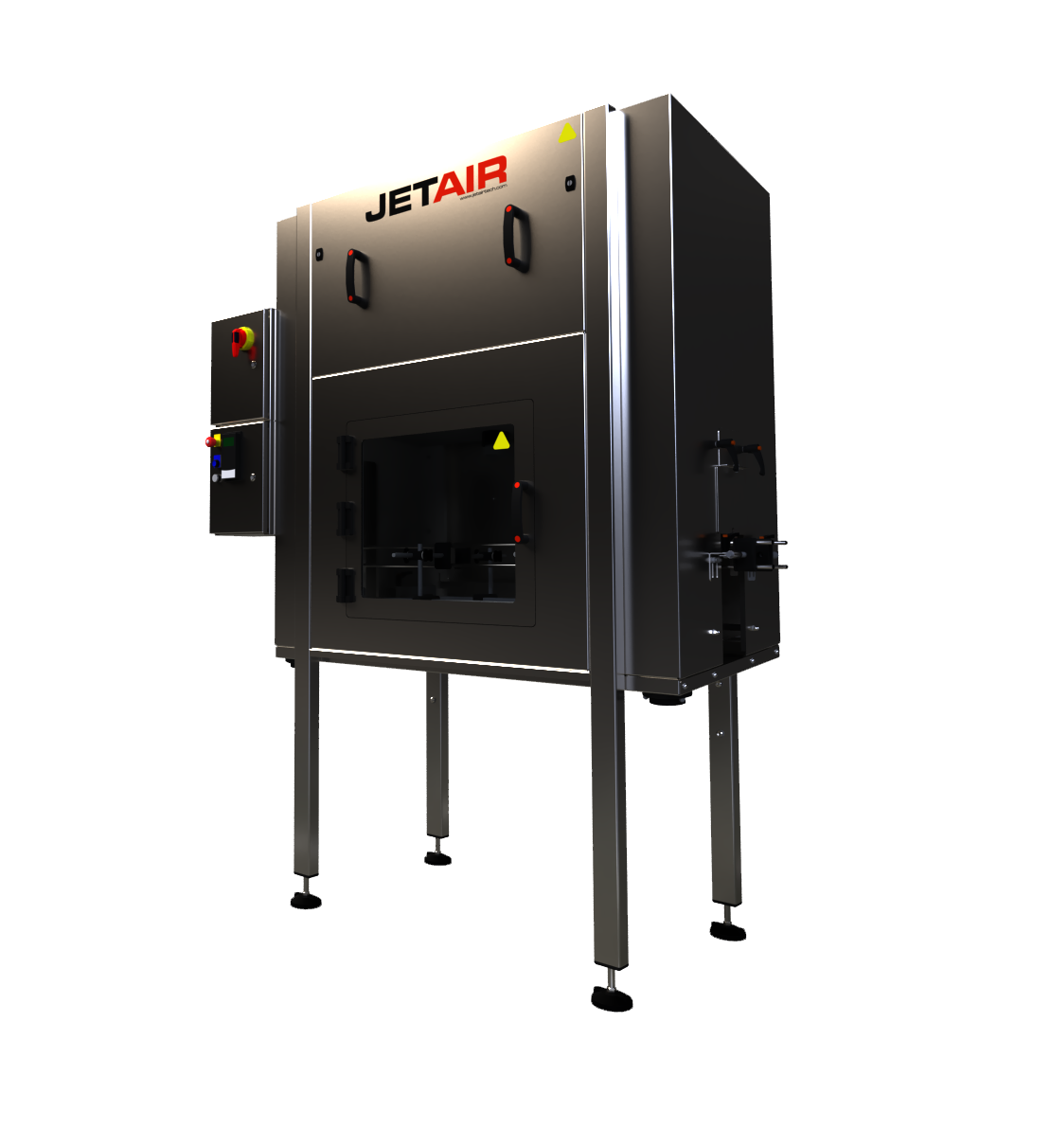

Air knife dryer for bottles
When filling glass bottles during beverage production, the cleaning and filling processes often ...
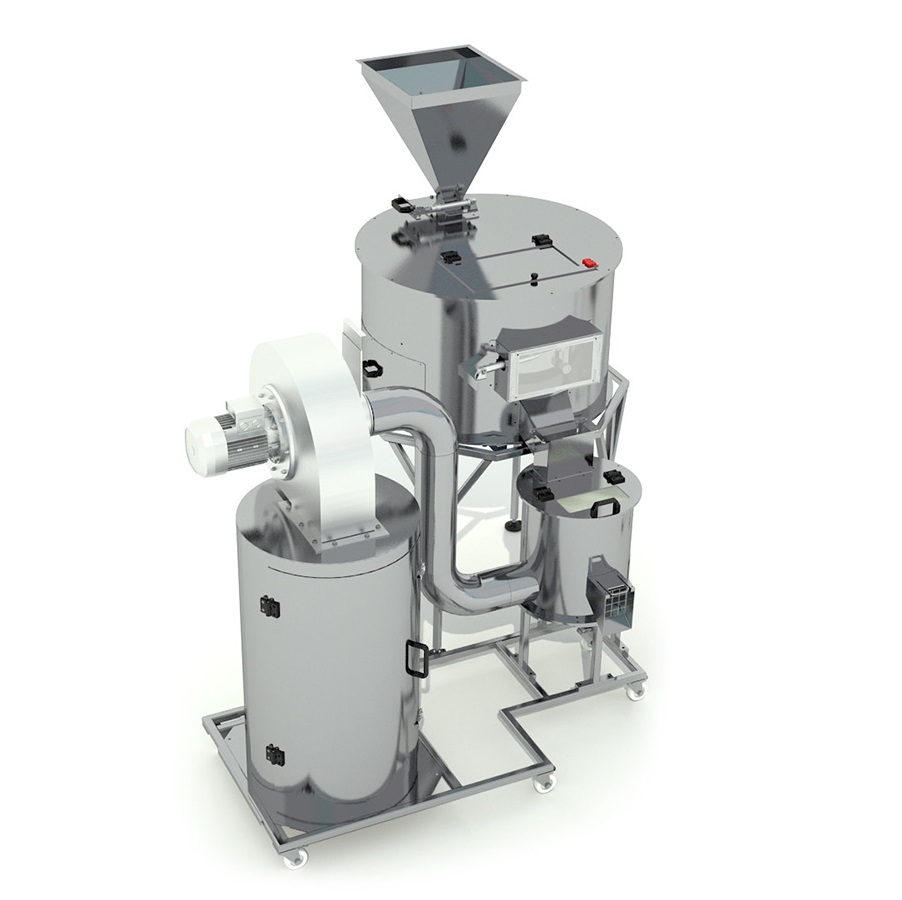

Entry-level infrared nut drying machine
For small scale production of cocoa beans and nuts, the use of traditional toasters...
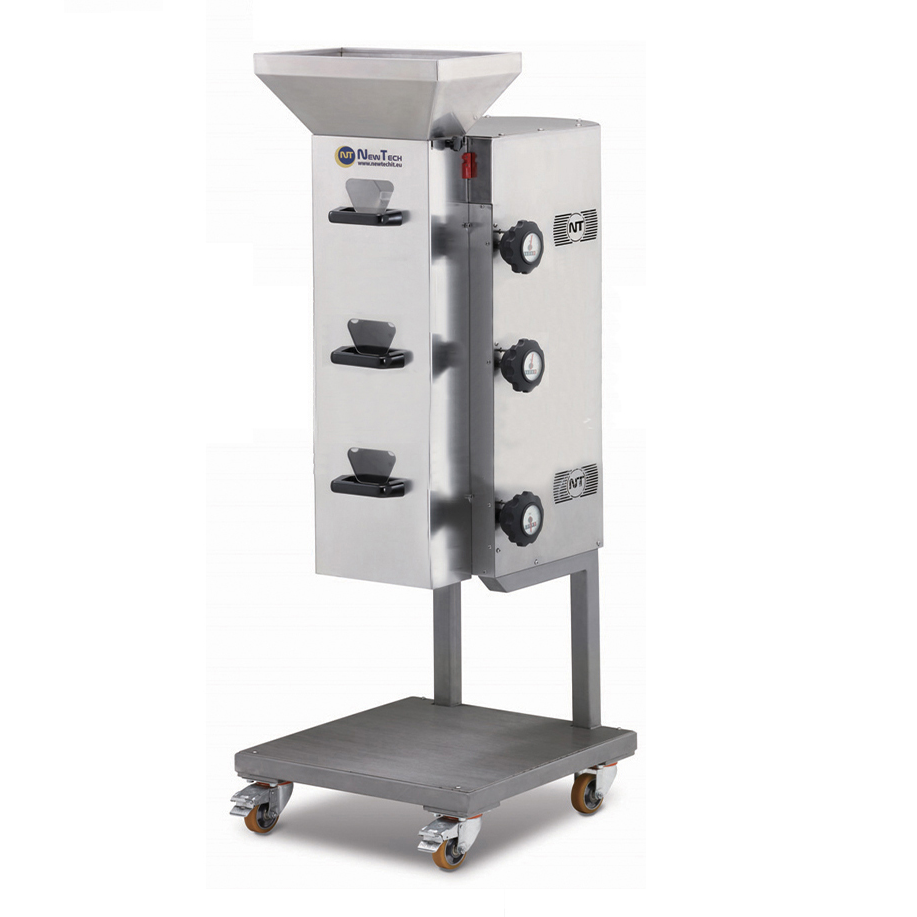

Small scale nut chopping machine
Many confectionery and bakery products use nuts as a key ingredient or decoration. The abil...
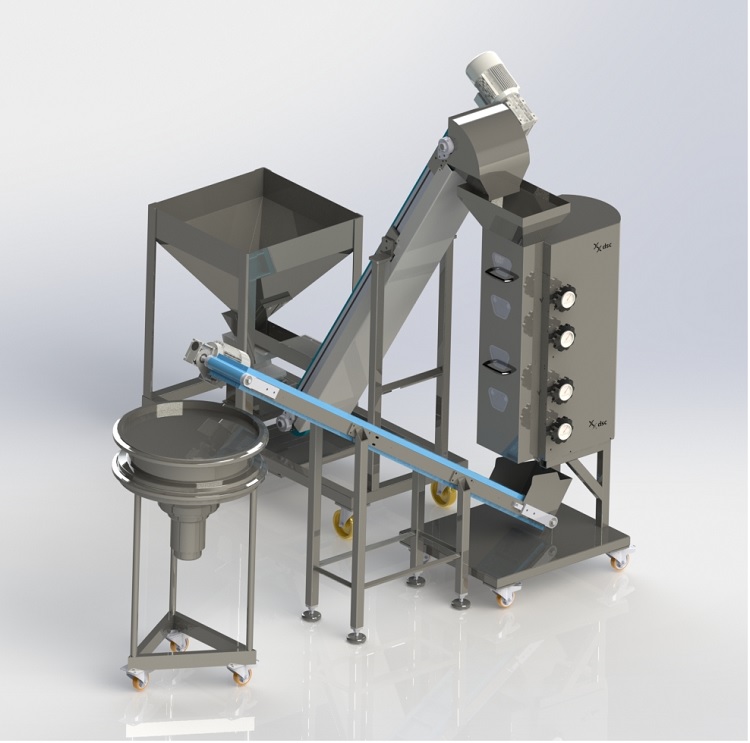

Small scale linear sieve for nuts
Removing dust and grading grains is an important part of producing a high quality chopped...
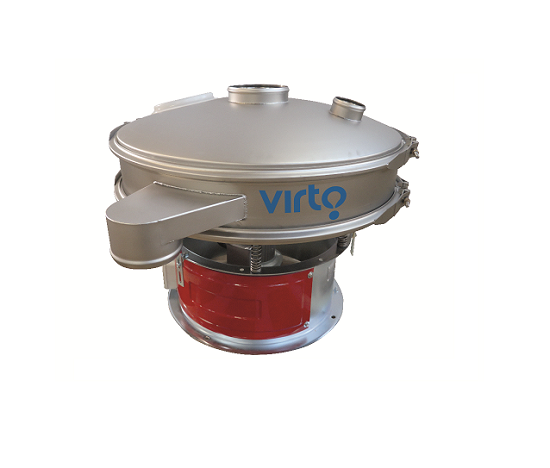

Vibrating sieve for liquid solid separation
Many industrial processes require the efficient separation of solids from a sl...
Versatile bottle sorting system
Quality bottle sorting machine and inspection system which can be put to use not only after ...
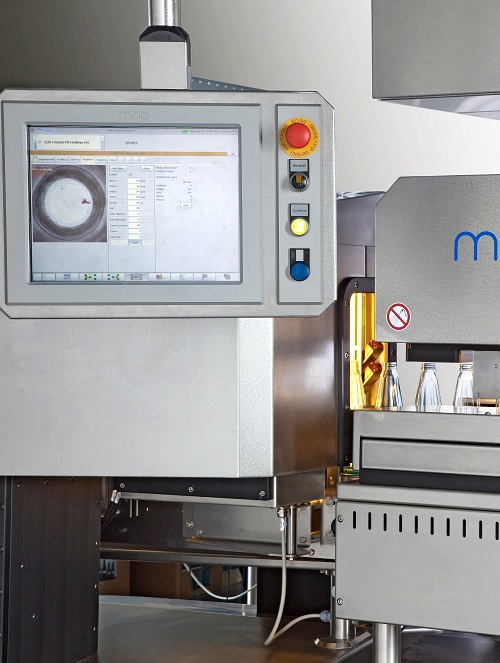

High-end empty bottle inspection system
If you are looking for a system with empty bottle inspection; base, residual liquid...
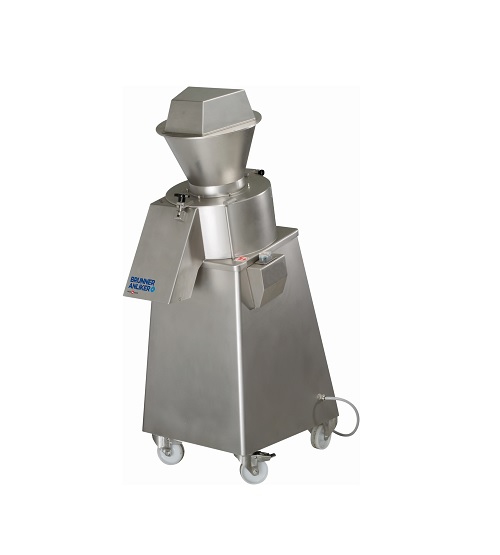

Industrial nut grater
Pressure from the grinding process can cause damage to food products as well as induce unwanted heating...
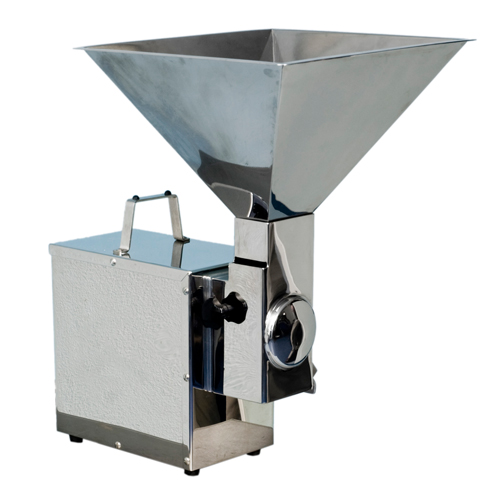

Nut dicer
Dicing nuts can generate a large volume of wasteful and messy powdered nut residue.
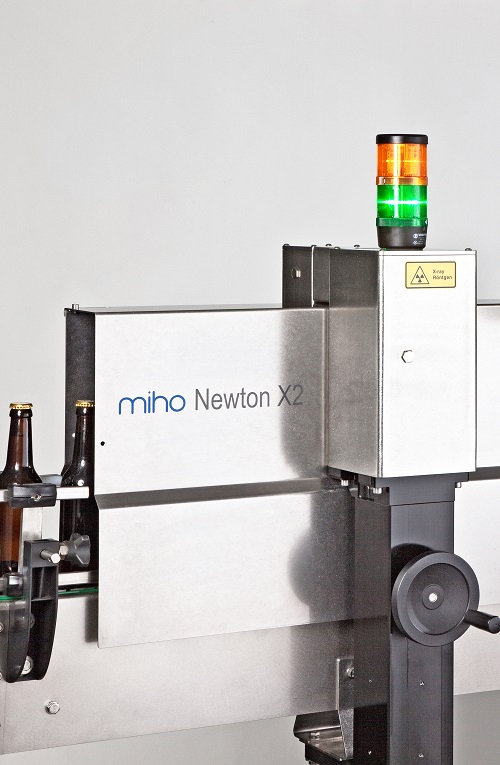

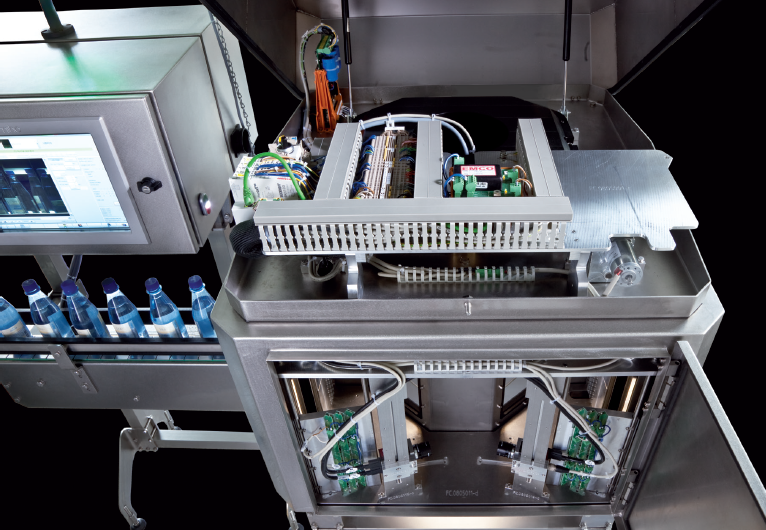
High-precision X-ray fill level controller
High-speed, high precision X-ray system to inspect containers that are difficul...
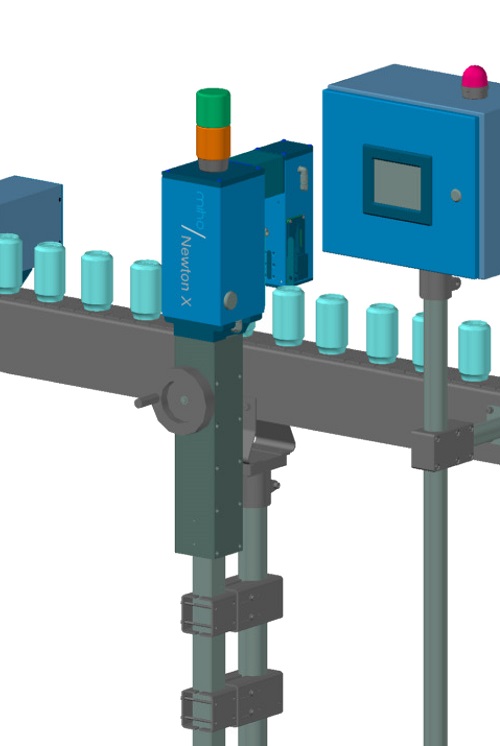
X-ray fill level controller
For containers that are difficult to see through, such as cans or cartons lined with aluminium, ...
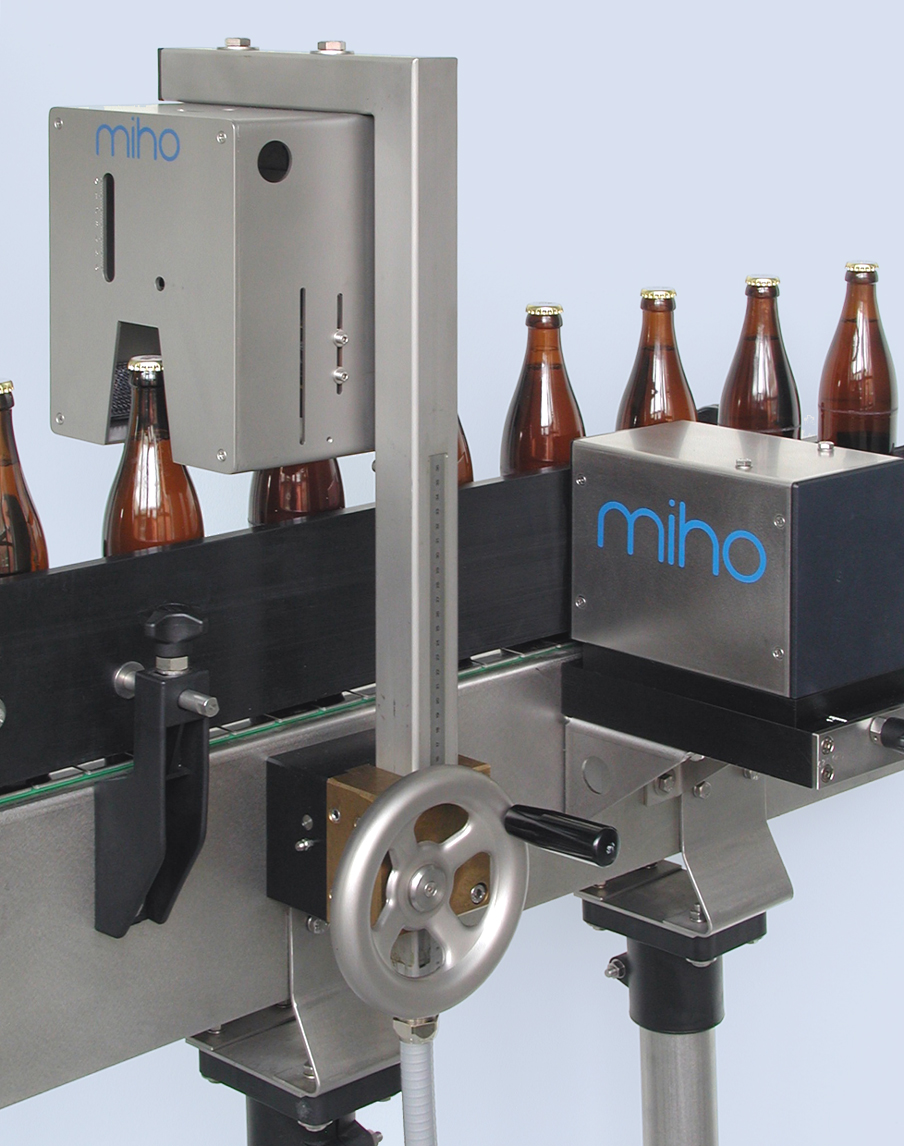

High-frequency fill level controller
In terms of high-frequency technology, the fill level detection is considered a standa...