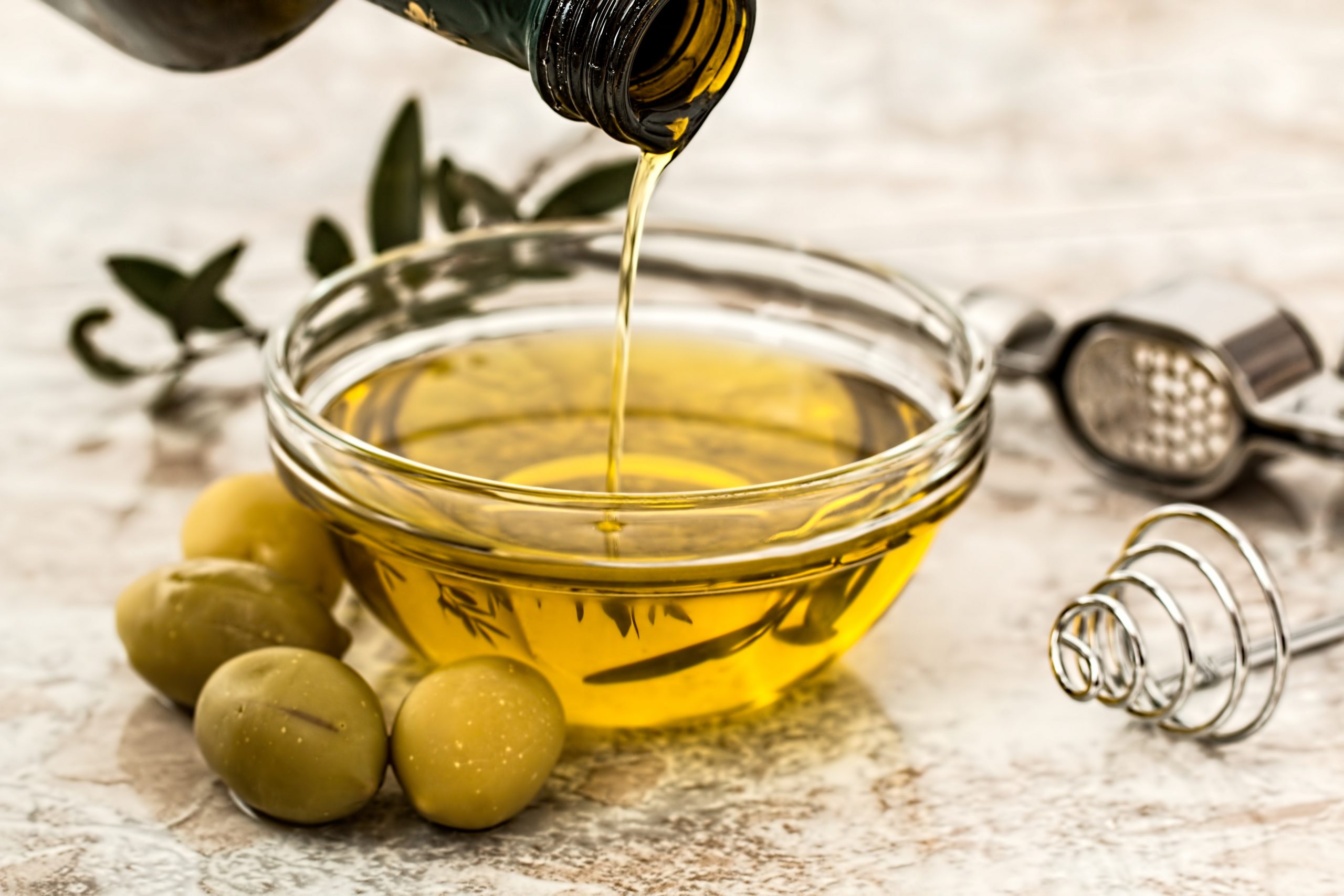
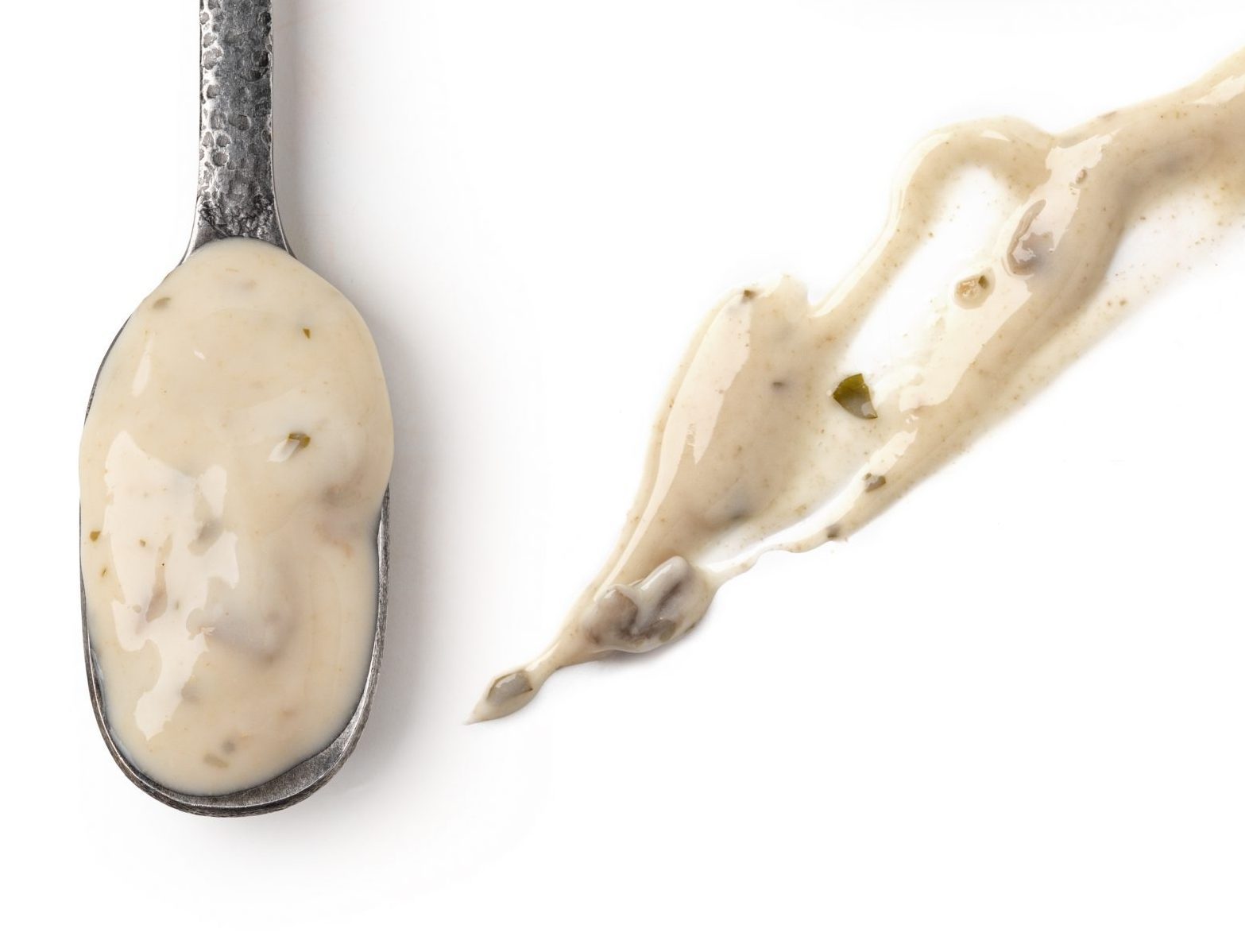
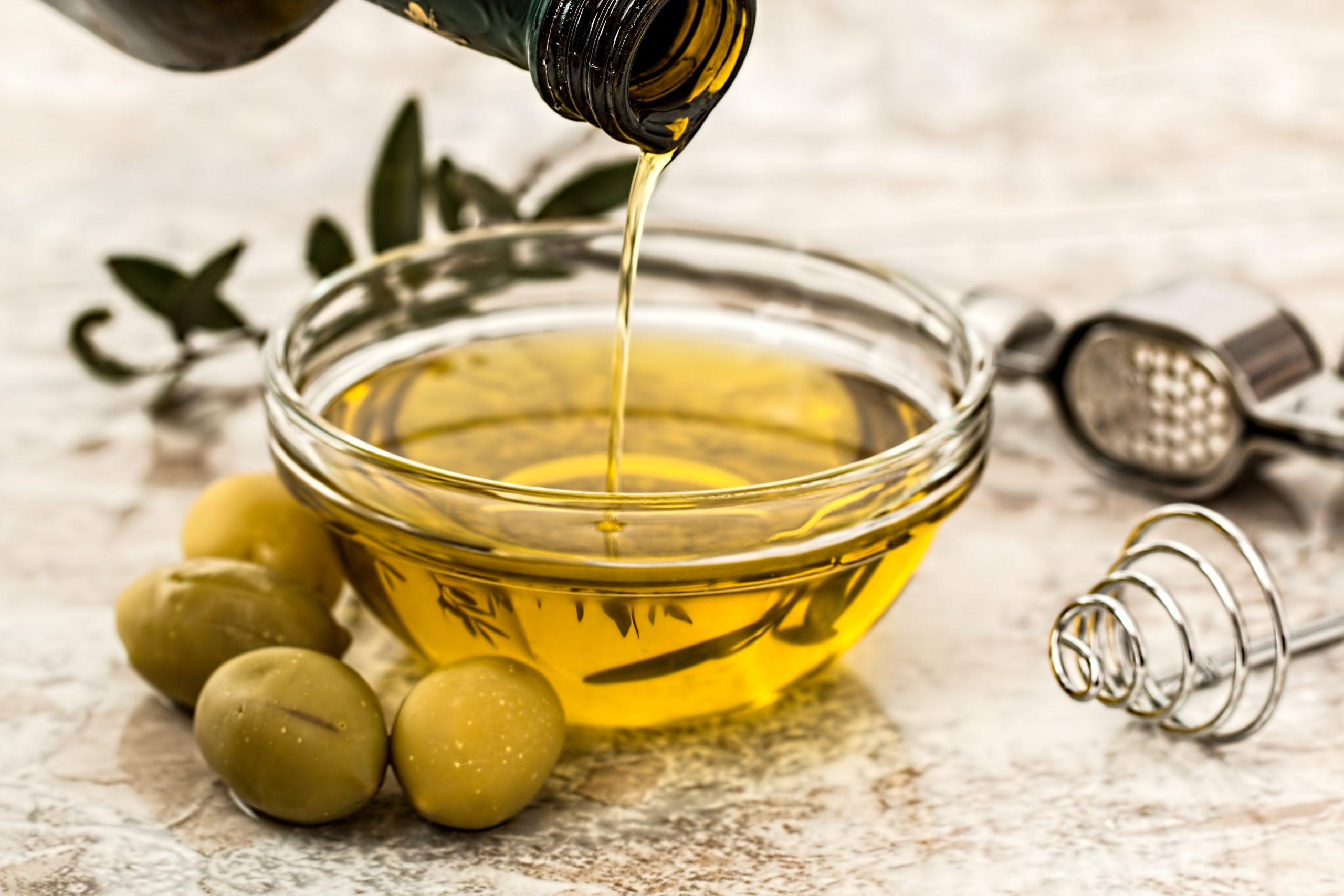
Making Salad Dressing
Find innovative production technology for making salad dressing and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Salad dressing has found its way onto dinner plates for millennia as a quick way to liven up leafy dishes. Experimentation with oil, vinegar, wine, salt, and other ingredients developed into the broad selection of dressings we enjoy today. Through a process of emulsifying the basic formula, adding additional elements, and then bottling and labeling the final mixture, consumers have easy access to reliable tastes on demand.
Select your salad dressing process
Tell us about your production challenge

Unveiling the elements of salad dressing
Oil is the main ingredient in salad dressing. To this, you may add many modifiers for taste, texture, viscosity, and appearance, among others. These include food ingredients such as vegetables and various spices, eggs or mayonnaise as emulsifiers, thickening agents such as corn starch, and stabilizers such as lecithin. Sometimes these mixtures only form partial emulsions in which the oil separates after bottling, so most vinaigrettes must be shaken before use. Others may be fully emulsified for the duration of their shelf-life, which is the case for most creamy dressings.
Mixing and mixing – all the salad dressing equipment you need
All the salad dressing equipment you need involves a range of pre-mixers and mixers. In the first stage of salad dressing production, you create a paste in a pre-emulsifier mixer from water, starch, vinegar, and salt at around 90°C. This mixture is cooled, and you may then pump in the remaining ingredients. Once this preliminary paste is uniform, you slowly incorporate the oil and pump the mixture into a colloid mill or emulsifier until you reach the desired consistency. The dressing is then ready for bottling and labeling.

A question of temperature - heat treatment for food preservation
An essential consideration in the production of salad dressing is the relative inclination for spoilage. The acidity of vinaigrettes helps ward off spoilage naturally by creating an unfavorable environment for microbes. Creamy dressings aren’t quite as acidic due to the addition of milk products and are quite sensitive to spoilage by contrast. By adding preservatives such as sodium benzoate you can help further maintain the freshness of dressings, and prevent microbial growth. Heat treatment provides an additional measure of safety over natural acidity and preservatives to help ensure safety. Temperatures from 63°C to 85°C can be used in this treatment process through direct or indirect heating systems.
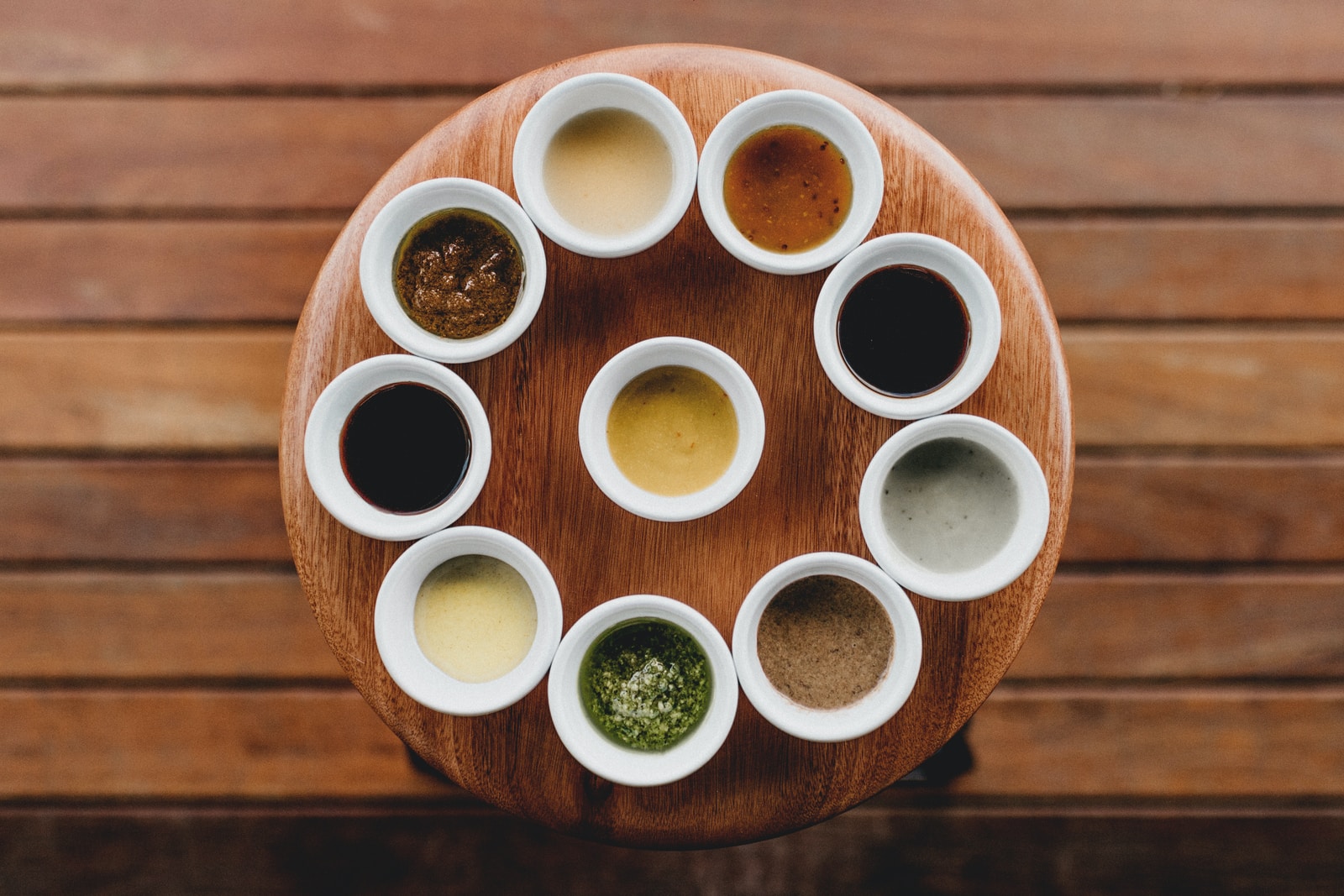

The many roads of dressing formulation
Your two fundamental types of salad dressing are creamy and vinaigrette. Both mix oil and vinegar with a host of other ingredients, but creamy dressings additionally include eggs, milk products, or both. Ranch is a buttermilk-based dressing incorporating mustard and mayonnaise. Italian dressing is traditionally a vinaigrette containing lemon juice and bell peppers for its signature taste but becomes a creamy favorite with the addition of milk products. The greater viscosity of creamy dressings can also lead to difficulties in homogenization, so you may require high-shear agitators to prevent the formation of partially-hydrated agglomerates of ingredients on machine surfaces.
Food regulations for your salad dressing production
Regulation surrounding the production of salad dressing centers around food safety. Ingredients must be inspected upon arrival and intermittently during storage to ensure freshness. Regular sampling must be performed for dressing in production and after dispensing into sterilized bottles. Testing at each production stage helps maintain food safety standards throughout the process and allows for rapid identification of problems when and where they occur.
Ingredients and relative quantities are also regulated, such that in the U.S. salad dressings are required to contain at least 30 percent oil and 4 percent yolk ingredients by weight. In addition, an atmosphere of carbon dioxide or nitrogen should be employed in the mixing and packaging stages. Finally, all batches must pass metal detection before being cleared for consumption.
Processing steps involved in salad dressing making

Bag inspection technology
Bottle filling equipment

Bottling

Conveying
Conveyor belts

Cooking

Cooling

Empty bottle inspection

Filling

Form fill sealing equipment

Heating

Industrial autoclaves
Industrial stretch wrappers
Industrial vacuum mixers

Inspection

Loading

Milling

Mixing

Packing

Palletizing

Pouch packing equipment

Shrink wrappers

Sterilization
Stickpack machines
Vacuum cookers

Wrapping
Which salad dressing technology do you need?
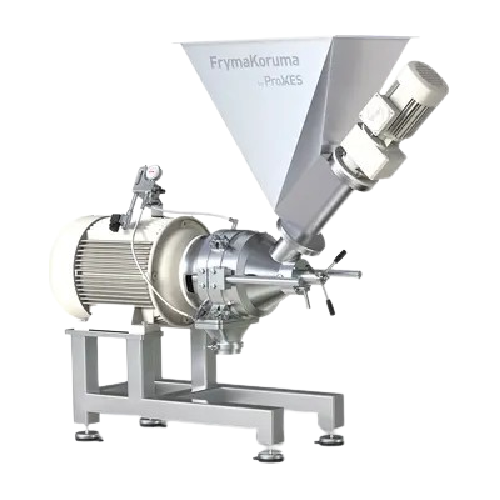

High shear emulsifier for food and pharmaceutical products
Optimize your production line with precise emulsification, ho...

Multistage mixer for emulsions and dispersions
Enhance your production with a versatile multistage mixer that ensures opti...

Industrial premixing system for batch and inline processing
Streamline your production with advanced premixing systems d...

Automatic filtration system for beverage industry
Enhance your beverage production with a multi-stage filtration system t...

Semi-liquid weigh filler for edible oils & fats
Achieve precise weigh filling of semi-liquids while minimizing product was...
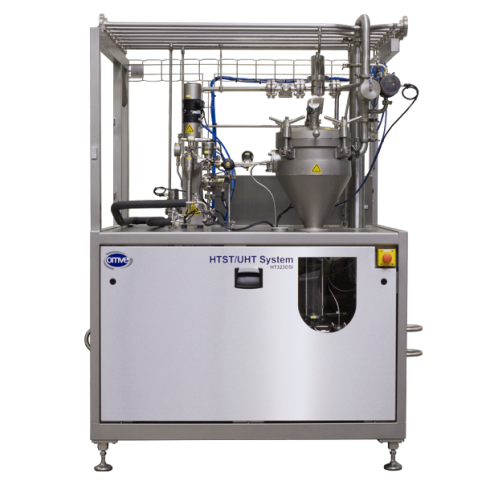

Laboratory in-line sterilization system
Ensure precise temperature control and rapid cooling for diverse liquid application...
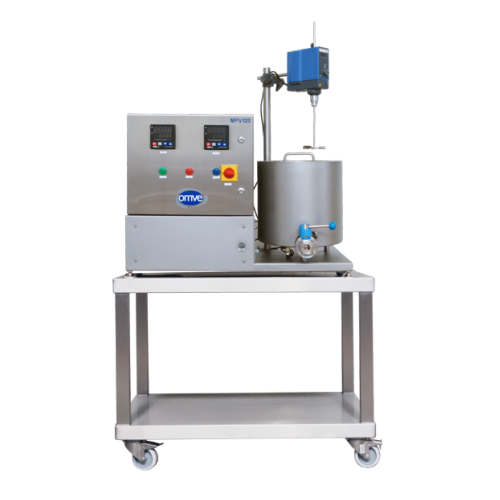

Bench-top blending vessel for small batch preparation
For small-batch liquid products, achieve precise mixing, heating, a...
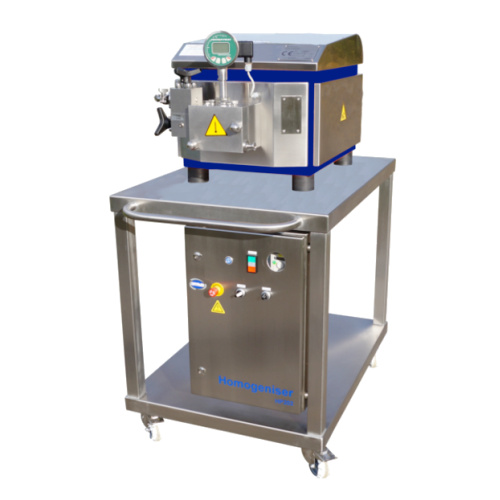

Lab-scale high-pressure homogenization solution
Optimize your lab-scale production with precision homogenization, ensuring...
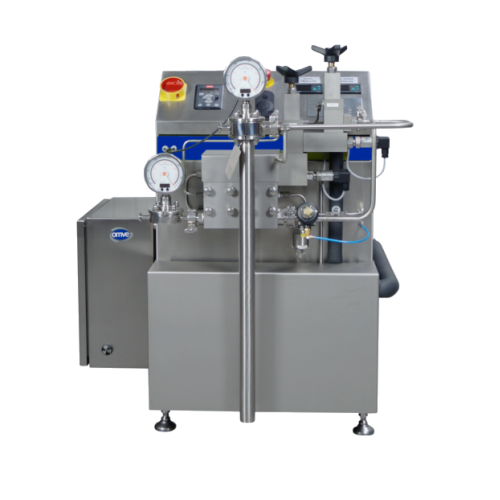

Pilot homogenizer for high-pressure inline homogenization
Achieve precise homogenization and emulsification across vario...

Lab-scale carbonation system for beverage filling
Streamline your beverage development with precision carbonation and ver...

Rotary weight filler for edible oil
Optimize your liquid product filling with precise weight control, ensuring high accurac...

Medium-speed automatic shrink wrapping systems for food and dairy
Optimize your packaging line with this flexible shrin...

Oil and fat filling system for industrial use
Optimize your production line with this precise filling solution, designed t...

Professional dosing system for creams and sauces
Streamline your production with precise dosing of creams and sauces, tail...

Vacuum mixing system for emulsion and homogenization
Achieve seamless emulsion and homogenization with precision: this sy...

Wet mixer for viscous and paste-like products
Achieve high-quality mixing of medium to highly viscous products with precis...

Cryogenic food freezer
Achieve rapid and precise freezing for diverse food products, ensuring optimal texture and moisture re...
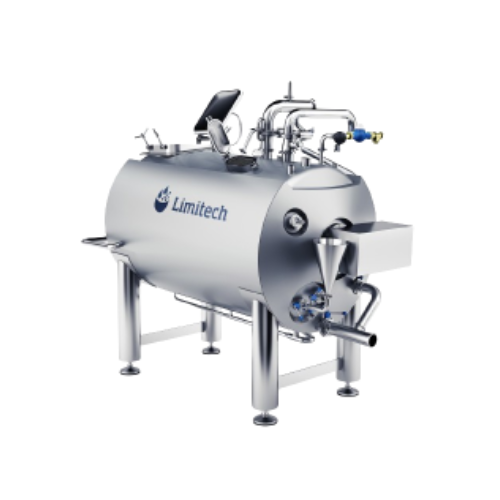

Emulsifying and blending system for liquid and semi-liquid food products
Efficiently emulsify and blend liquid and semi...
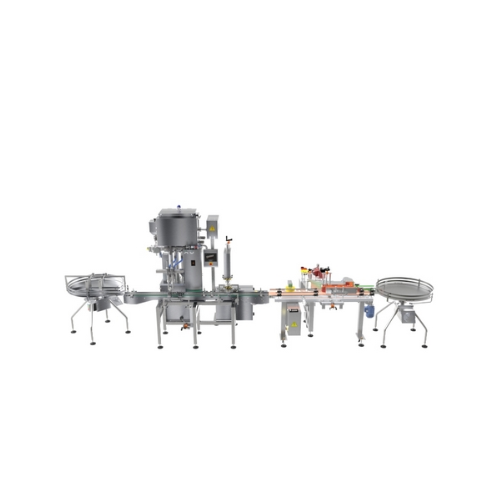

Medium capacity filling line for food and cosmetics
Streamline your production with a versatile filling line that seamles...
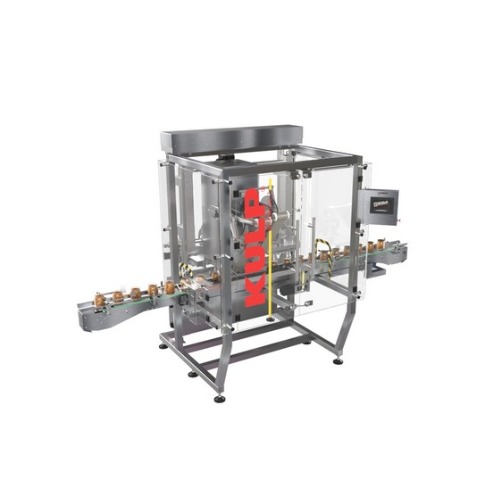

Jar sealing system for plastic and glass containers
Achieve precise and efficient sealing of plastic and glass jars with ...
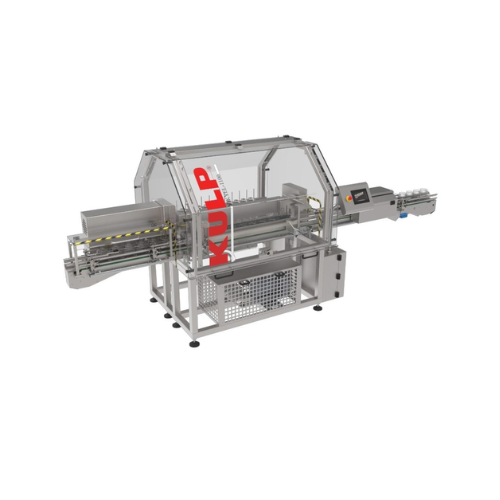

Jars and bottles rinsing solution
Ensure impeccable hygiene and particle-free cleanliness for your jars and bottles by inte...
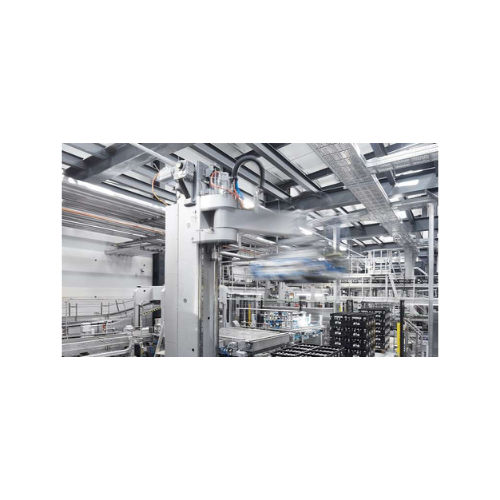

180° palletizing robot for automated palletizing and depalletizing
Optimize your production line with a versatile solut...
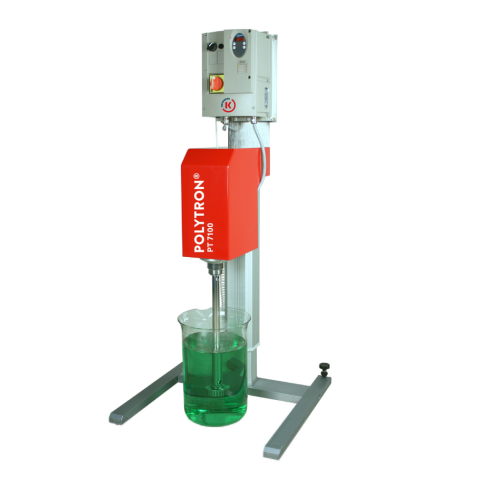

Stand dispersing unit for pilot plant applications
Achieve precise particle size reduction and efficient mixing with this...

Industrial magnetic agitator for homogenizing pharmaceutical products
Achieve precise dispersion and homogenization in ...
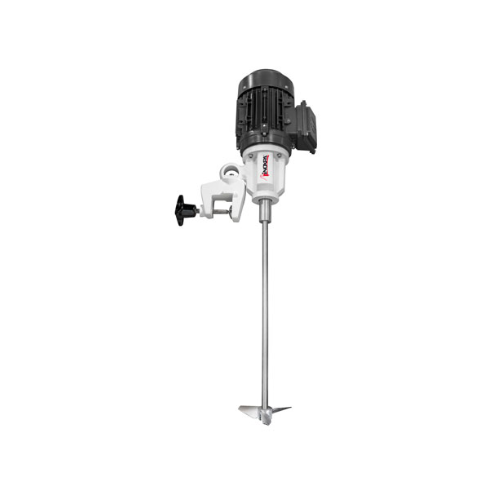

Portable agitator for high-speed mixing
Enhance your liquid formulation processes with an efficient solution for rapid mixi...
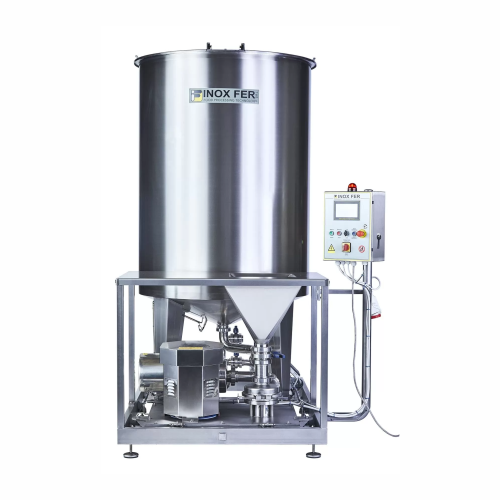

Standard batch mixer for salt and citric acid mixing
Achieve perfectly homogeneous blends of salts, sugars, and challengi...

Tank bottom mixer for high viscosity applications
Achieve seamless emulsification and homogenization of high-viscosity pr...

In-line high shear mixing solution
Achieve precise emulsification and particle size reduction with high shear capabilities,...

High shear vertical mixer for dispersion and emulsification
Achieve seamless emulsification and homogenization in divers...

Steam jacketed kettle for cooking sauces and dressings
Enhance your sauce production with a steam jacketed kettle that en...
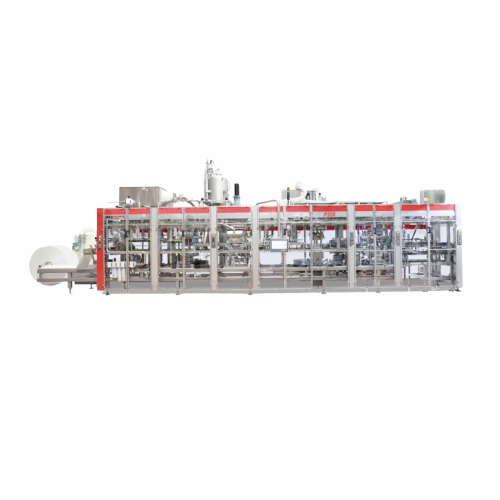

Form fill and seal solution for dairy portion packs
Optimize your production with precision portion packing, reducing mat...
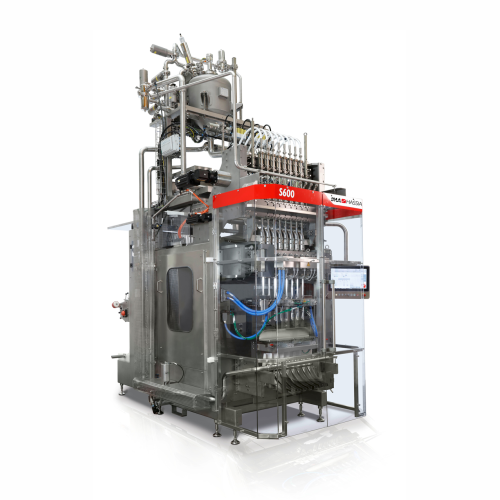

Stick pack forming, filling, and sealing solution
Enhance packaging efficiency with a high-speed solution designed for pr...
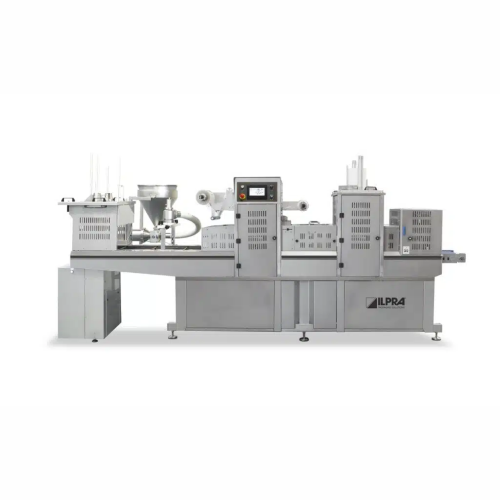

Tray sealing machine for buckets
Ensure efficient sealing and preservation with high-speed tray sealing for various food pro...
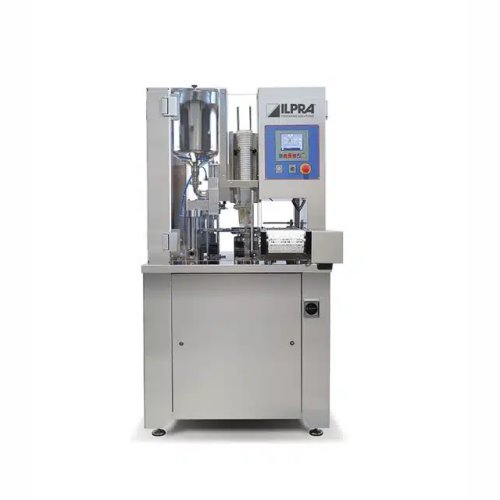

Rotary filler and sealer for dairy products
Optimize your filling and sealing needs with a compact solution designed for c...

Automatic filling and sealing solution for medium to large production
Streamline your high-capacity filling and sealing...

High-speed continuous rotating packaging solution
Transform your packaging efficiency with versatile operations, accommod...

Homogenizer for high-pressure homogenization
Optimize your production with high-pressure homogenization, essential for ach...

High-pressure homogenizer for food and pharmaceuticals
Achieve unparalleled consistency and stability in emulsions and di...

Industrial homogenizer for food and pharmaceutical applications
Ensure product consistency and stability with high-press...

High-pressure homogenizers for dairy and juice processing
Ensure superior texture and stability in your liquid formulati...

Mid-shear mixer for powders and bulk solids
Achieve ultra-short mixing cycles and superior homogeneity without the need fo...

Cheese ribbon cutting solution
Achieve precise and efficient cheese ribbon cutting with high-speed operations, ensuring perf...
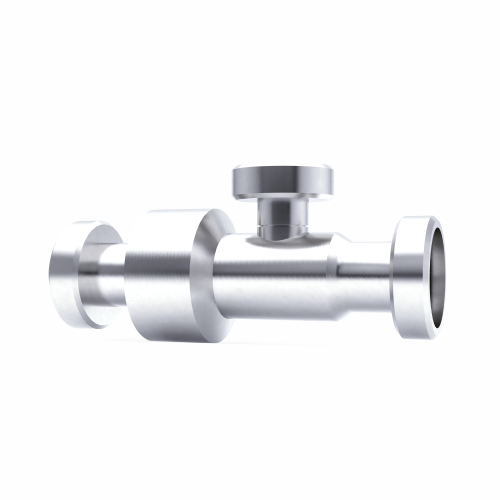

Magnet for emulsion technology for lump-free blends
Achieve perfectly smooth and stable emulsions in a single pass with a...
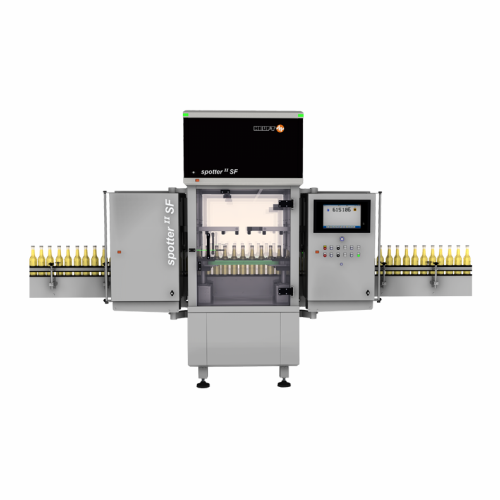

Full container inspection for glass and Pet bottles
Ensure the highest product quality by detecting foreign objects and m...
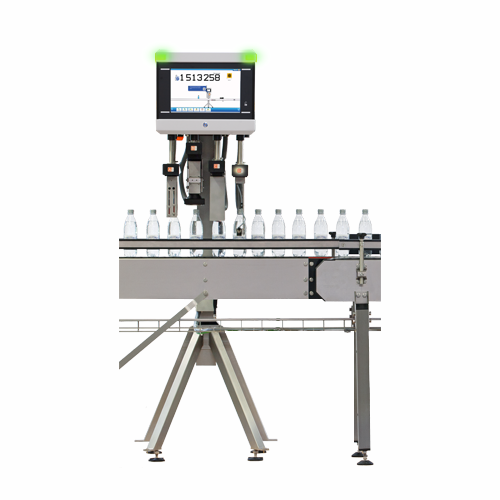

Fill level and closure inspection system
Ensure precise fill levels and secure closures in high-speed liquid packaging envi...
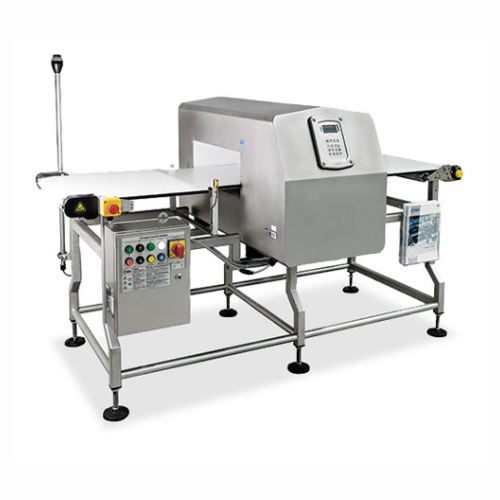

Conveyor belt metal detection system for food processing
Enhance product safety and ensure compliance with the most strin...

Ultraclean aseptic storage tanks for hygienic liquid food
Ensure your liquid products remain uncontaminated and maintain...

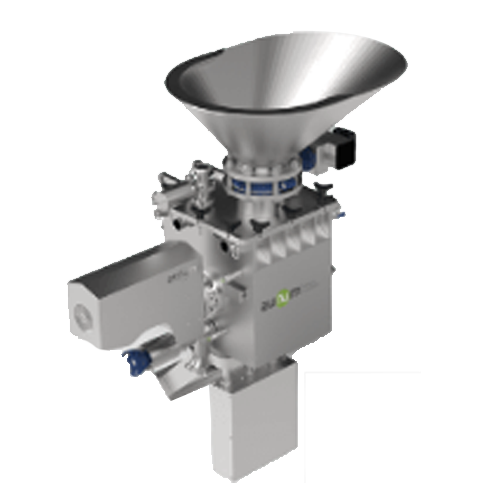
Pneumatic dosers for variable density products
Achieve precise dosing for liquid to dense products with versatile pneumati...

High-capacity inline mixer for dairy and beverages production
Achieve a rapid and homogeneous mix in high-capacity produ...

Lab-scale high-shear mixer for recipe development
Optimize your recipe development process with precise mixing, homogeniz...

High-capacity manual mixer for industrial applications
Optimize your mixing process with a highly efficient, manually ope...

Oilseed cooker/conditioner for optimal seed preparation
Achieve consistent oil extraction and enhanced product quality wi...

Vacuum mixer/blender for food processing
Achieve precise mixing and blending with air removal for consistent quality across...

Robotic handling systems for beverage containers and bins
Streamline your container handling with precision-engineered r...
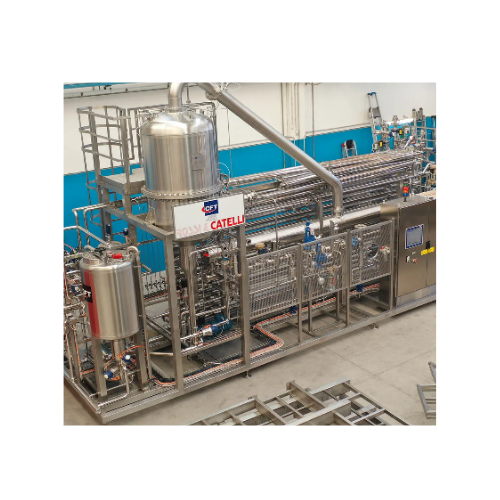

Sterilizers and pasteurizers for industrial food processing
Optimize thermal processing for viscous foods and beverages ...
Aseptic fillers for liquid and viscous products
Ensure sterile and precise filling of liquid and viscous foods with adapta...
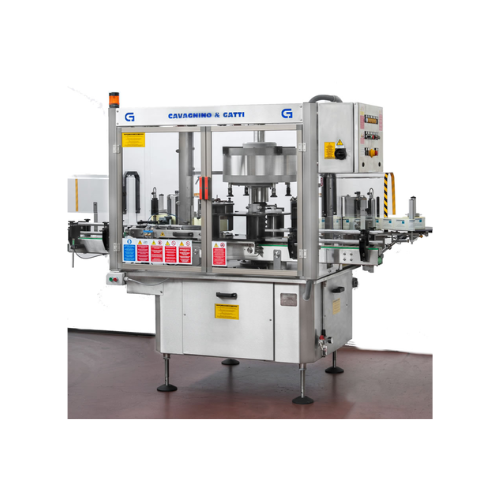

Self-adhesive labeling system for bottles
Streamline your bottling operations with high-precision labeling that enhances p...

Semi-automatic filler for bag-in-box packaging
Streamline your liquid packaging process with a versatile filler that integ...

Manual filling system for bag-in-box packaging
Streamline your liquid filling process with a manual system designed for pr...
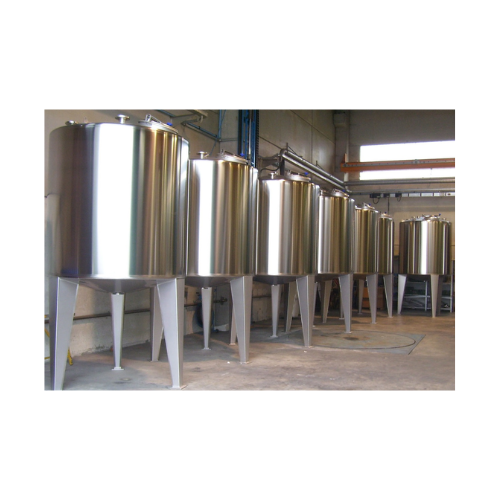

Storage tank for dairy products and juices
Designed for optimal preservation and hygiene, these storage tanks prevent sedi...
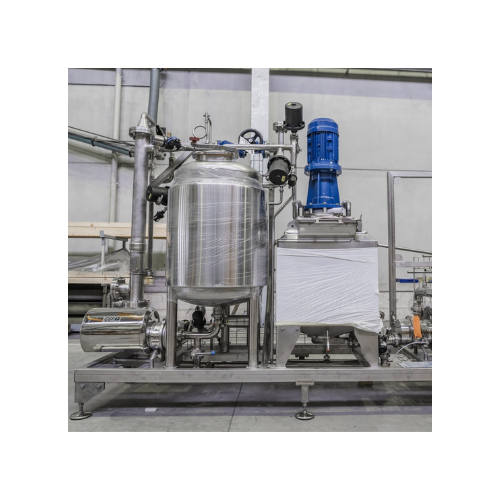

Turbo mixer for homogeneous solutions in food and pharmaceutical industries
Effortlessly achieve uniform suspensions a...
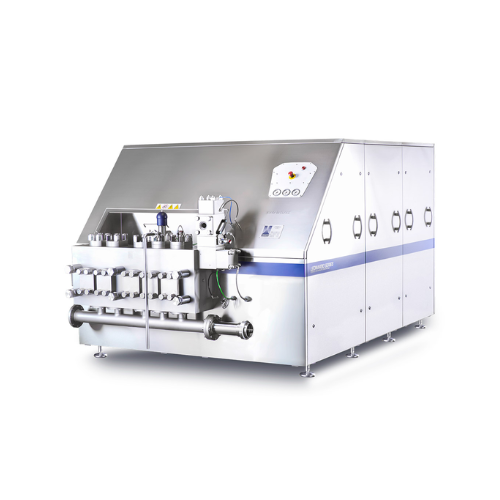

High-pressure homogenizer for dairy and food production
Optimize your product consistency and stability with a high-press...
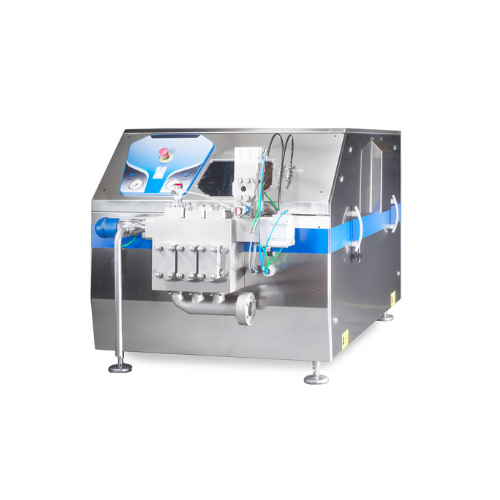

Industrial homogenizers for high-pressure applications
Optimize homogenization with high-pressure solutions designed for ...
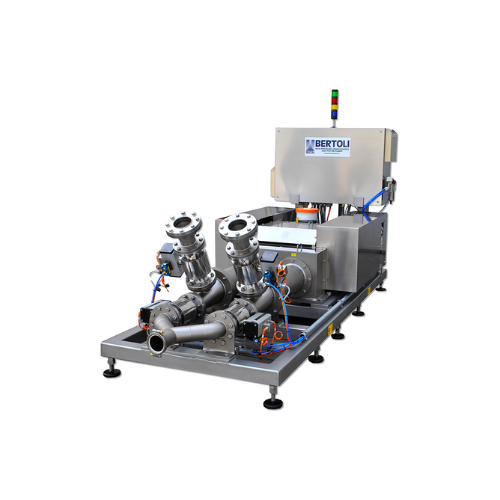

Industrial homogenizer for food and beverage applications
For manufacturers seeking consistent quality, this homogenizer...
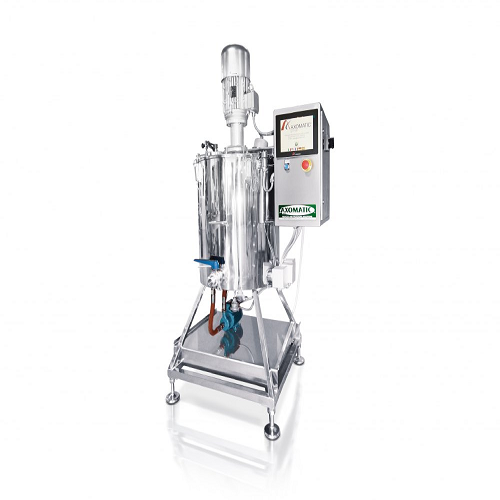

Melter for vacuum turboemulsifiers
Achieve optimal mixing, dispersion, and temperature control with precision-engineered me...

Pneumatic dosing system for dense and semi-dense products
Easily handle dense and semi-dense products with precision dos...

Alternate movement bottle filling and capping system
Enhance your production line with a versatile filling and capping so...

Automatic bottles and jars filling and capping line
Streamline your liquid product packaging with this high-speed solutio...

High-efficiency high-capacity reactor for industrial processing
Enhance production efficiency with a reactor system desi...
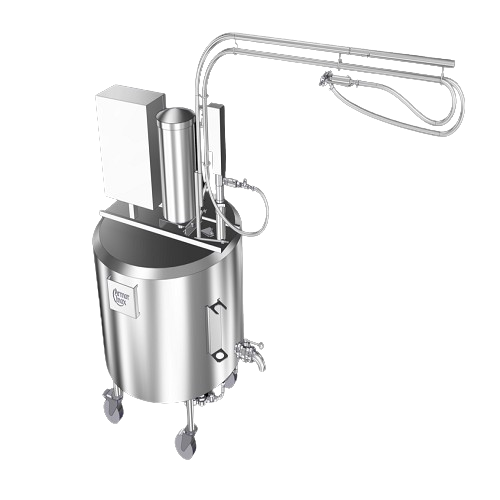

Tank for jelly and liquid preparations
Optimize your food processing line with a versatile solution that efficiently blends...
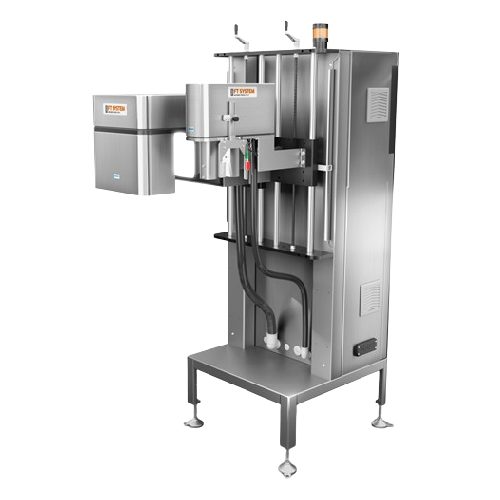

Cap and fill level inspection system for bottles
Ensure precise cap placement and accurate fill levels in your bottling li...
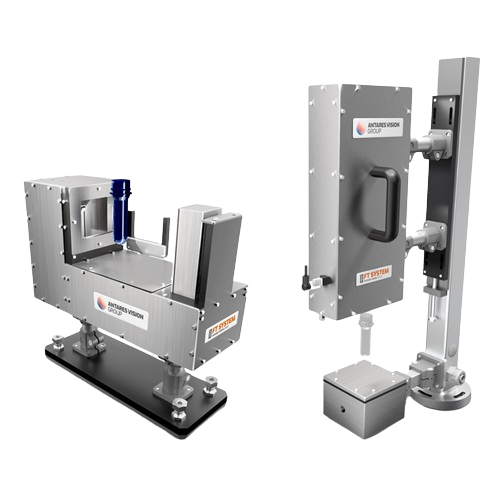

Preform inspection system for blown containers
Ensure defect-free blown containers and minimize line jams with a robust pr...
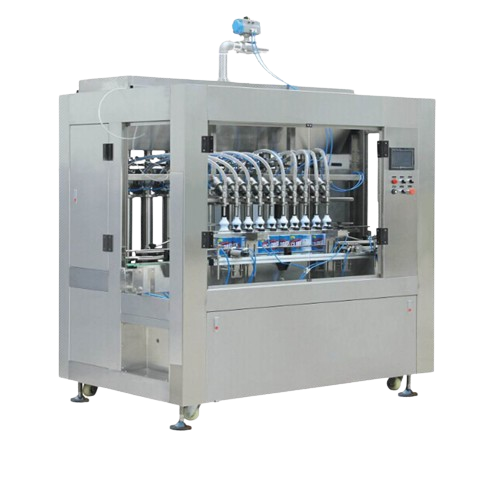

Automatic detergent shampoo filling solution
Streamline your filling process with precise volume control, achieving consis...

Vegetable oil separator for high-quality oil processing
Achieve optimal separation of oils and fats with advanced centrif...

Plate heat exchanger sterilizer for food products
Ensure consistent product quality and microbiological stability in your...
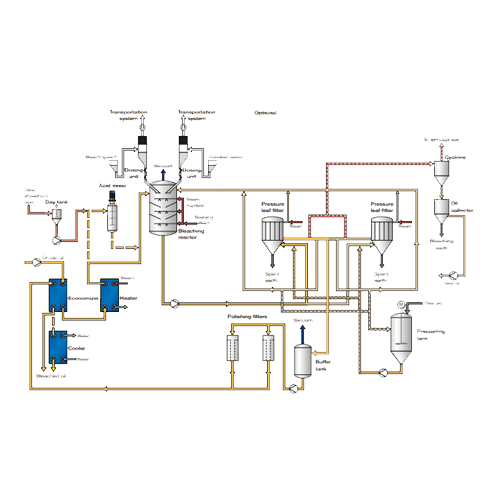
Bleaching systems for edible oil refining
Achieve clarity and stability in your edible oils with cutting-edge bleaching sy...

Double-wall scraped surface heat exchanger
Achieve high-capacity processing with gentle handling for shear-sensitive produ...

Scraped surface heat exchanger for viscous products
Efficiently handle challenging viscosities and heat-sensitive product...

Scraped surface evaporator for high-viscosity materials
Efficiently concentrate high-viscosity and hard-to-handle materia...

Gasketed plate heat exchangers for hygienic applications
Ensure optimal hygiene and thermal efficiency in your processing...

Scraped surface heat exchanger for high-pressure applications
Handle high-viscosity and particulate-rich products with p...

Air-operated single-seat valves for food and beverage industries
Achieve precise flow control and elimination of downtim...
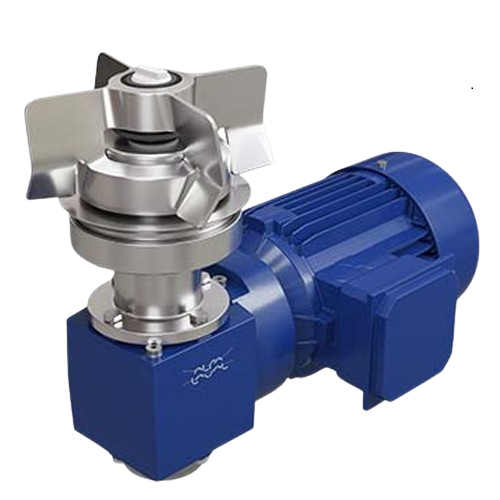

Aseptic magnetic mixer for hygienic production
Experience seamless mixing to the last drop with advanced levitating impell...
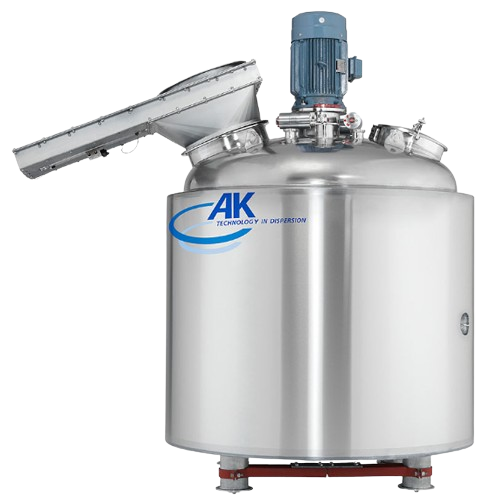

Emulsion processing system for homogenizing solids into liquids
Achieve precision in emulsifying and homogenizing proces...
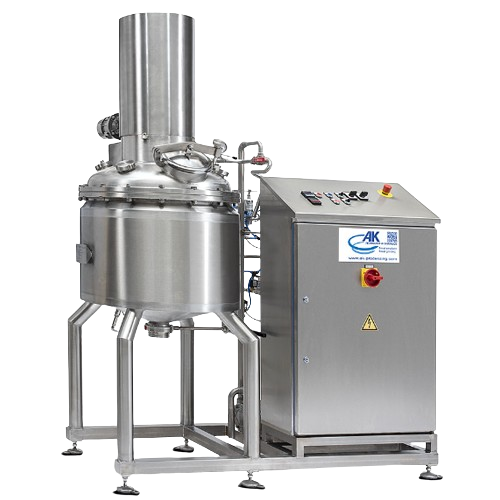

Hydro grind reactor for meat, vegetable, and vegan product processing
Achieve precision grinding and emulsification of ...
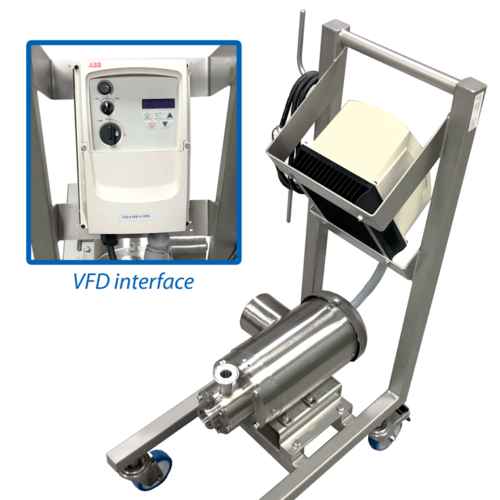

Inline continuous mixer for dairy and beverage processing
Achieve precise emulsification and particle size reduction for...
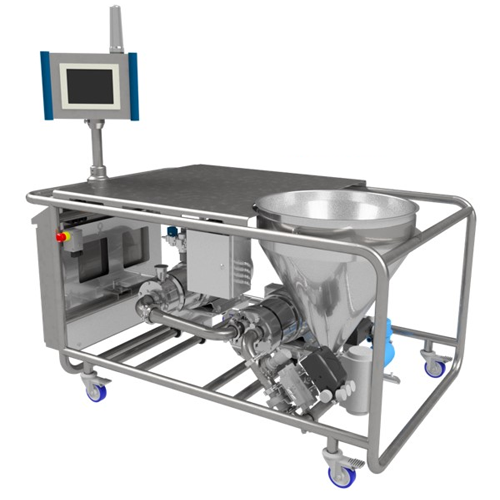

Automated powder induction and dispersion system for industrial mixing
Achieve rapid and efficient incorporation of pow...
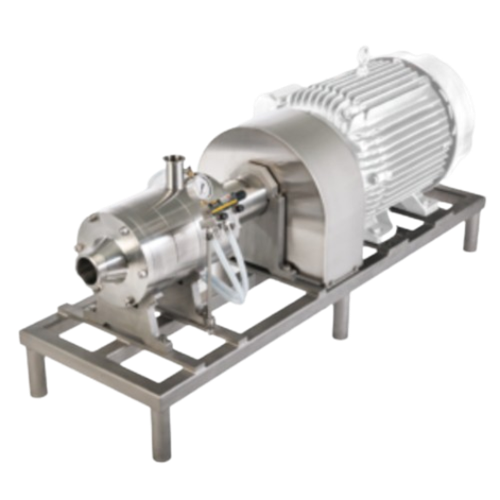

Inline wet mill for mayonnaise emulsions
Eliminate the challenges of achieving stable, uniform emulsions in your sauces and...
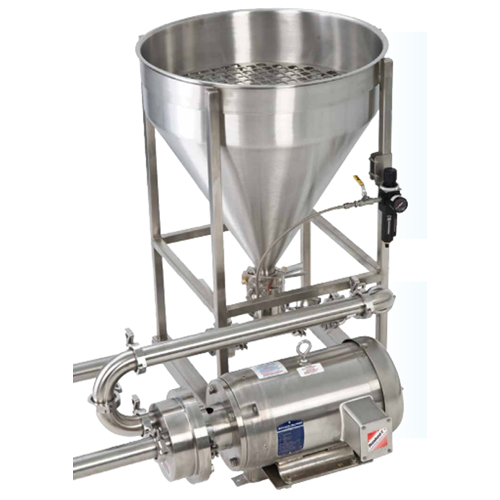

Atmospheric powder induction system
Enhance your mixing efficiency with a system designed for rapid powder induction and th...
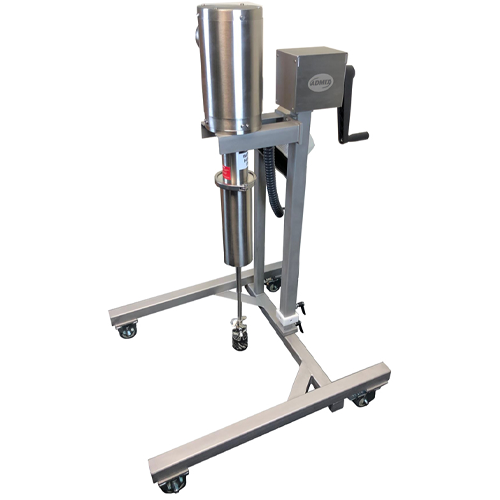

Pilot scale mixers for product development and small production runs
Optimize your mixing processes with precision cont...
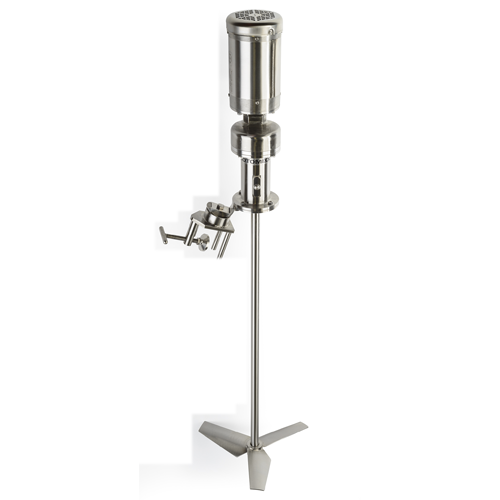

Low-shear portable mixer
For processes demanding strict hygiene, this mixer eliminates rust and chipped coatings by offering ...
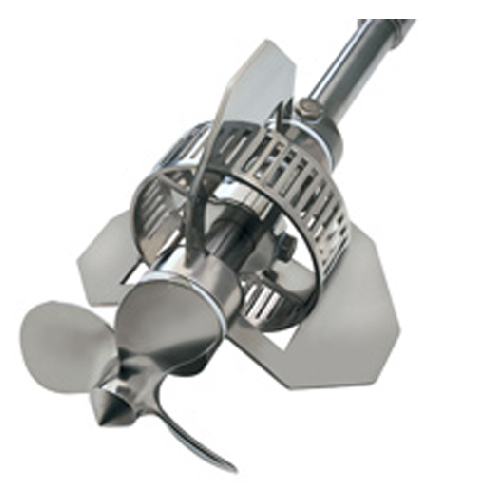

High shear emulsifier for hygienic applications
Achieve precise emulsification and consistent mixture quality with enhance...
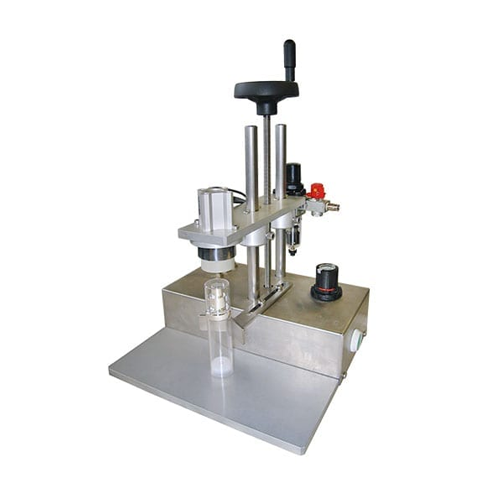

Pneumatic cap press for bottles and jars
Streamline your packaging process with a pneumatic solution designed for precision...
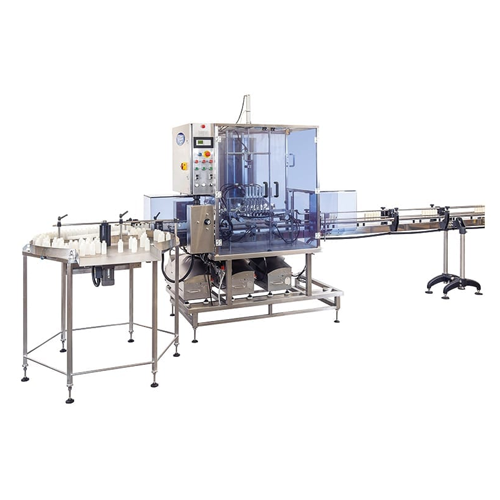

Automated bottle and jar filling solution
Streamline your production and minimize waste with a versatile filling solution,...

Bag and pouch filling solution for liquid products
Efficiently package diverse liquid products with precision and speed, ...

Filler and capper for bottles and jars
Optimize your production with a compact filling and capping solution that delivers f...

Compact filler and closer for vial processing
Efficiently streamline your vial filling and closing processes with a compac...

Automatic volumetric filler for liquid products
Optimize your production with this high-precision volumetric filler, desig...
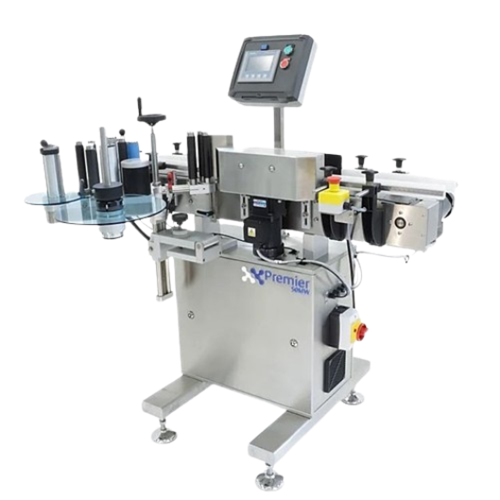

Compact wraparound labelling system for bottles
Streamline your packaging process with a fast and reliable wraparound labe...
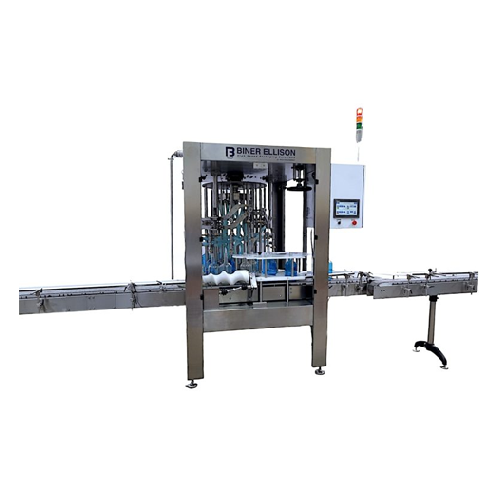

Rotary overflow filler for non-carbonated liquids
Achieve precise fill levels effortlessly with a high-speed rotary overf...
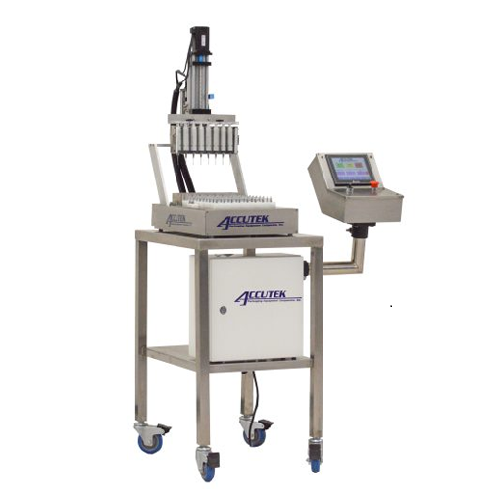

High precision automatic mini dose filler
Achieve unparalleled precision when filling small volumes, from 0.1 ML to 200 ML...
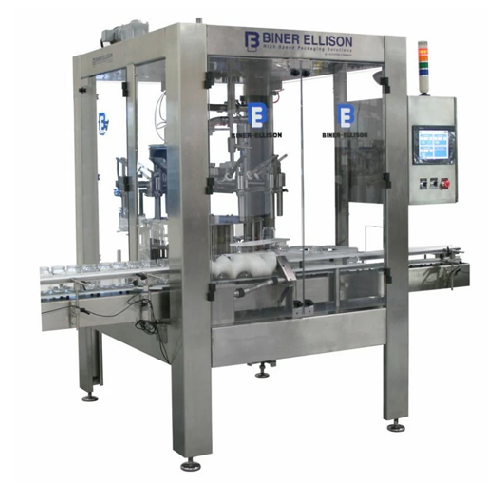

Rotary volumetric filling solution for viscous products
Achieve precision in volumetric filling with a machine designed f...
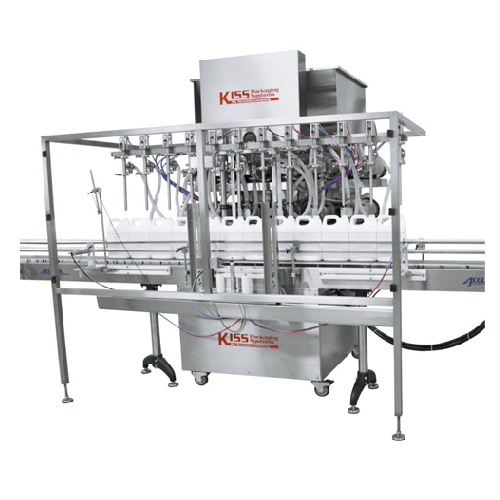

Automatic positive displacement filler for various liquids
Achieve precision and versatility in liquid filling operation...
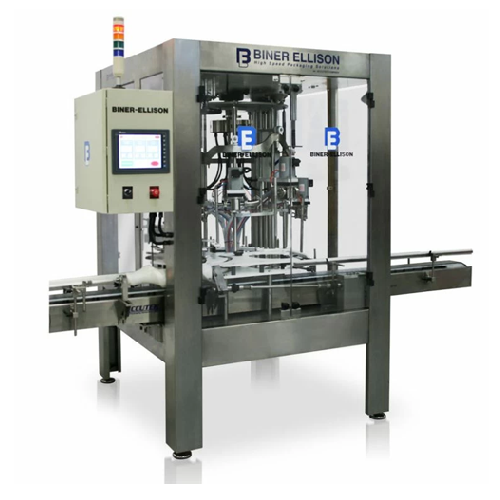

Automatic positive displacement bottle filler
Streamline your liquid filling operations with precision and flexibility, id...
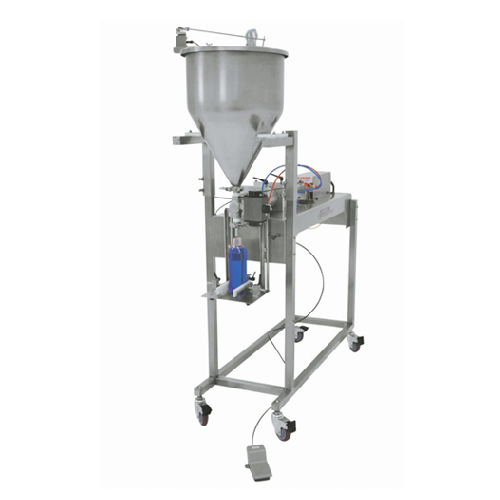

Semi-automatic volumetric piston filler
Achieve precise filling of diverse liquids and viscous products while minimizing wa...
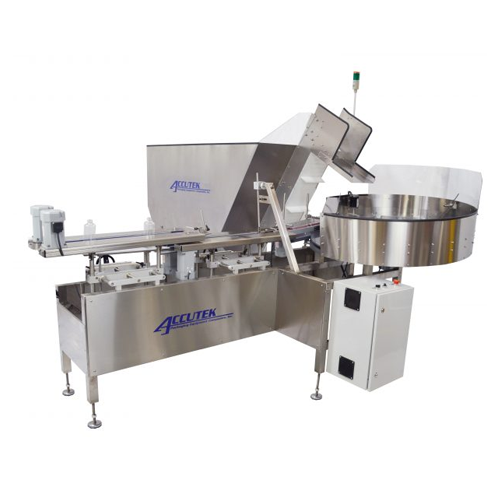

Bottle unscrambler for plastic containers
Efficiently organize and streamline your production line by ensuring plastic con...
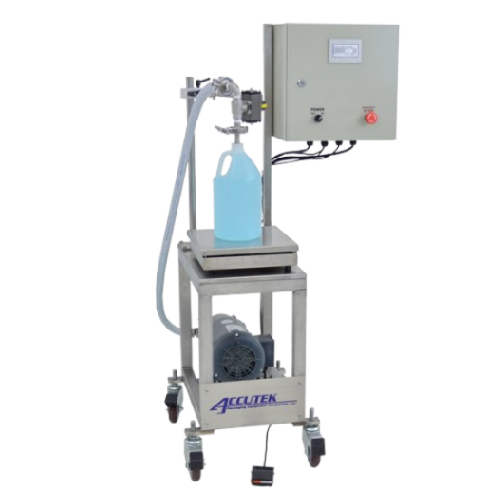

Accurate net weight filling for liquid and semi-liquid products
Ensure precise filling of diverse viscosities, from thin...
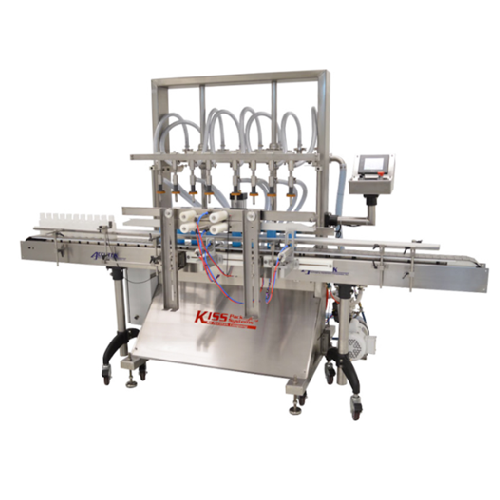

Automatic pressure overflow filler for low to medium viscosity liquids
Ensure consistent fill levels for low to medium ...
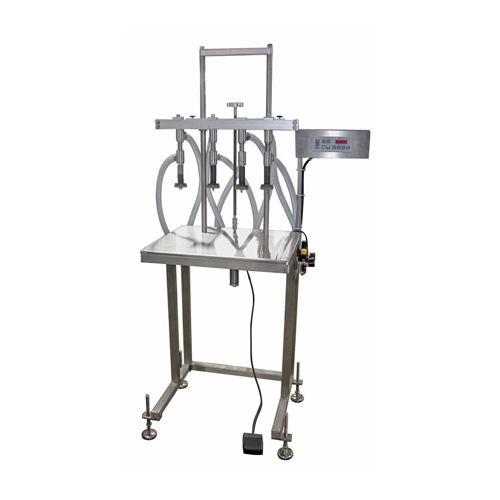

Semi-automatic overflow liquid filler
Optimize your production line with a reliable filling solution for low to medium visc...
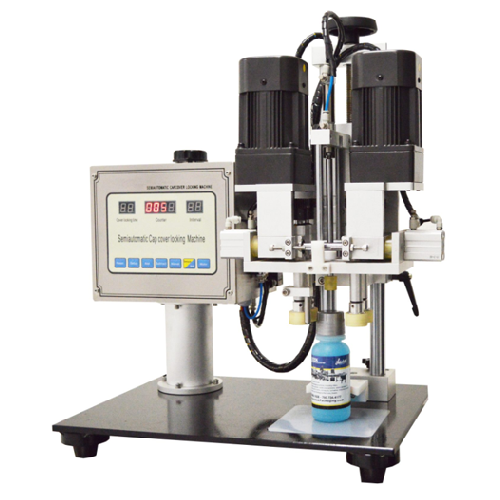

Tabletop spindle tightener for screw caps
Eliminate inconsistencies and errors in cap tightening with this tabletop spindl...
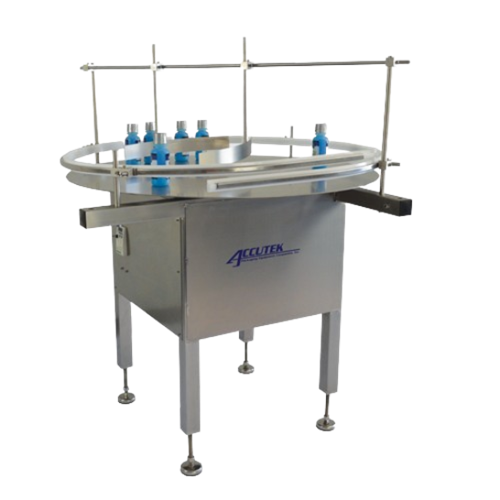

Container unscrambler for filling lines
Streamline and automate the loading of containers onto your production line with th...
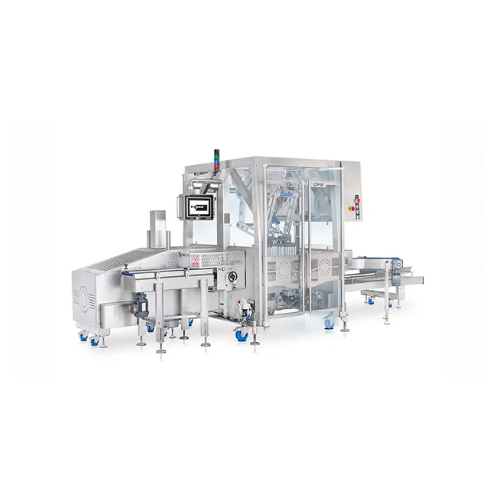

Industrial case packing solution for high-speed operations
Optimize your production line with a compact, efficient case ...
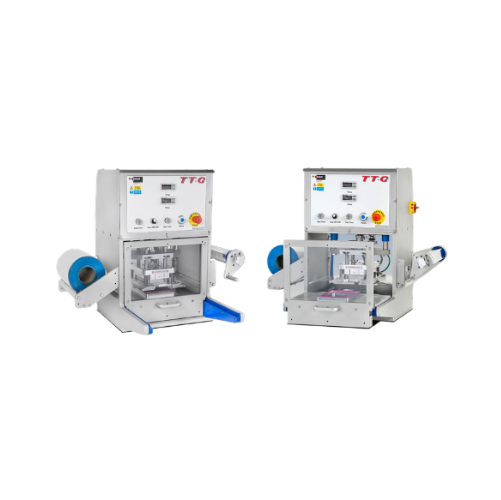

Bench mounted tray sealer with gas flush
Optimize your production line with a compact tray-sealing machine designed for pre...
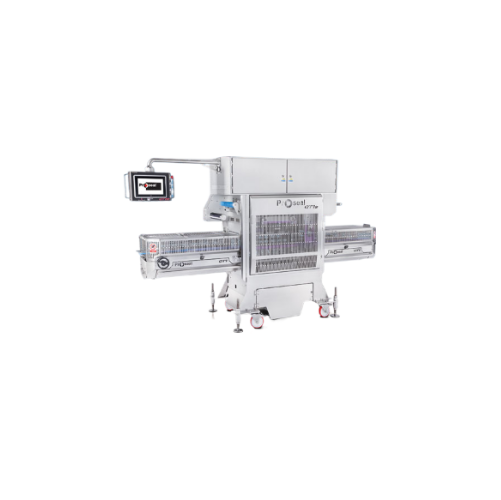

Automatic tray sealer
Maximize throughput and shelf life with our high-speed inline tray sealing solution, ideal for diverse ...
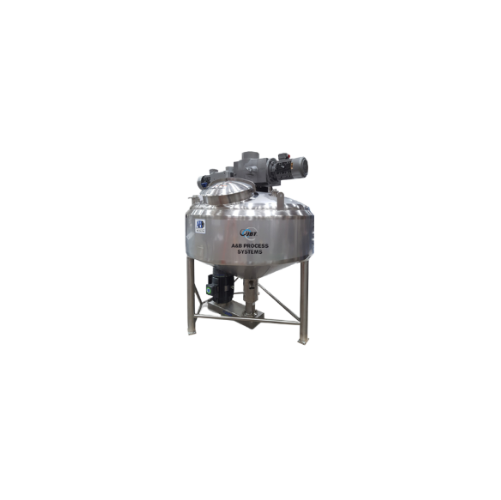

Mixing tank for soups, sauces, and dressings
Streamline your soup and sauce production with advanced mixing technology des...
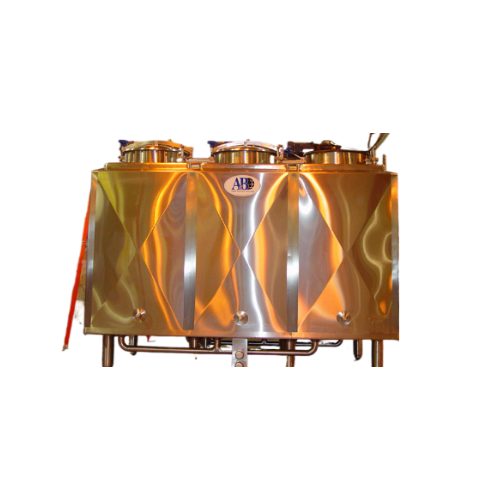

Flavor vats for ice cream and food production
Maximize your product line versatility with customizable flavor vats, design...
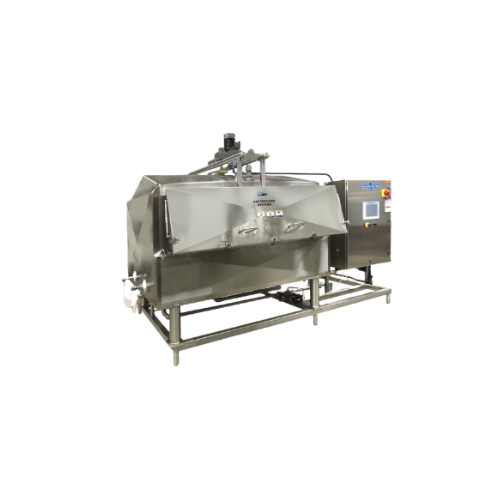

Industrial block melt system for butter and chocolate
Efficiently transition solid blocks of butter, chocolate, or waxes ...
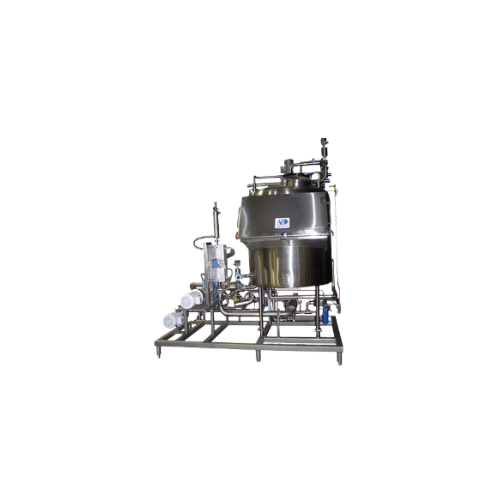

Ergonomic melt systems for solid food and personal care products
Eliminate manual lifting and enhance safety by integrat...
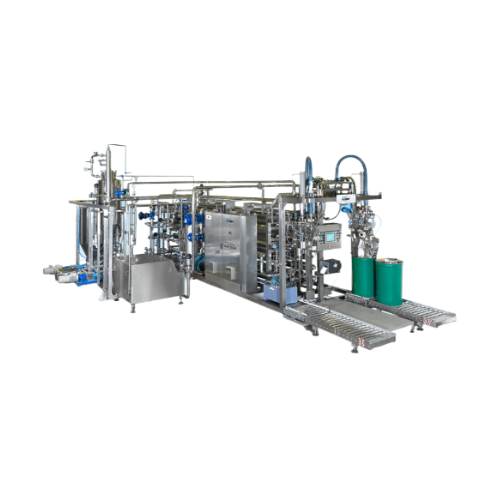
Aseptic processing system for food products
Streamline your food processing line with an efficient aseptic processing syst...
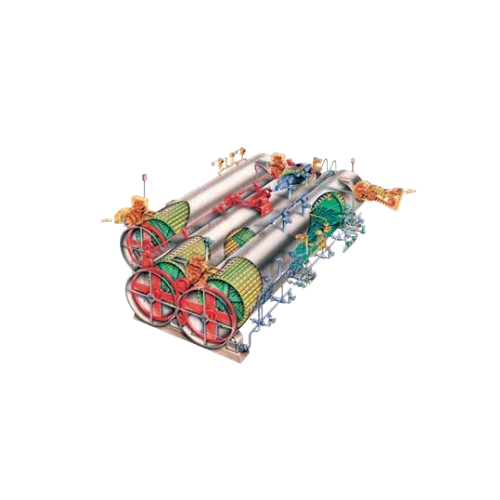
Gentle can handling ejector for rotary cooker
Achieve seamless can transfer and sterilization with reduced damage during h...
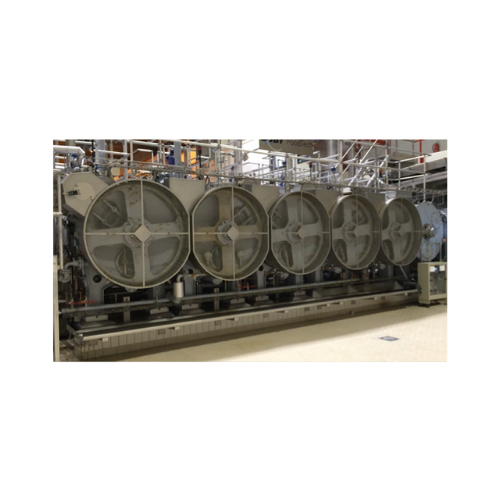

Rotary pressure sterilizer for canned food products
Streamline your canning operations with continuous high-speed sterili...
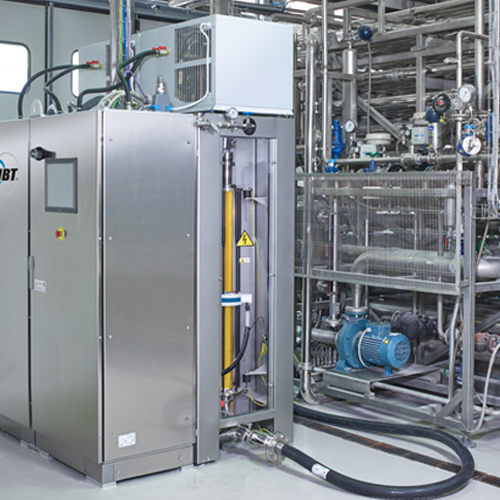

Heat exchanger for liquid and semi-liquid foods
Optimize your heating and cooling processes with superior heat transfer ef...
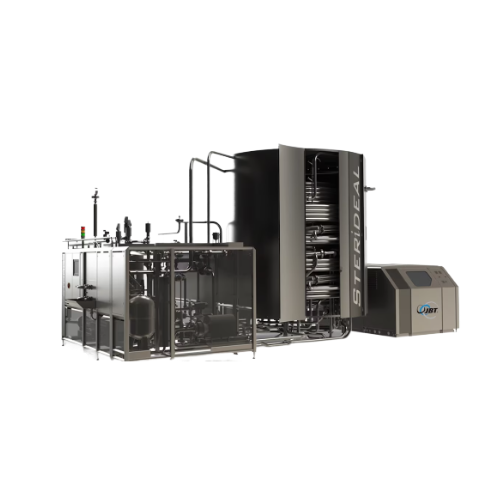

Coil heat exchanger for dairy and beverage processing
Quickly sterilize and retain product quality with this coil heat ex...
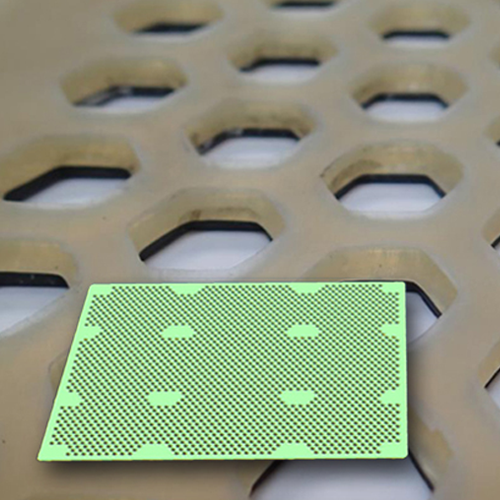
Layer pad for agitating retorts in food processing
Efficiently secure and process irregularly shaped containers in retort...
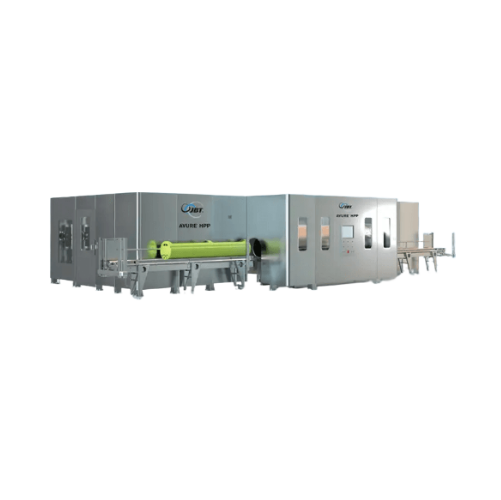

Expandable high pressure processing system
Optimize your production line with an expandable high-pressure processing syste...

High pressure food processing solution for medium-scale producers
Achieve reduced operational costs with high-pressure ...

Fruit and vegetable shelf life extender
Extend the freshness and appeal of your produce with our innovative dipping solutio...

Rotary level filler for low to high viscosity liquid products
Ensure precise fill levels and enhance production efficien...

Rotary can filler and closer for metal cans
Achieve seamless integration in your production line with a solution that sinc...

Volumetric filler for various food products
Achieve high precision and flexibility in your filling processes with a volume...

Granular filler for wide mouth containers
Ensure precise filling and minimize product loss with this granular filler, expe...

Automated clipped netting system for meat packaging
Enhance your packaging line with a system designed for rapid and prec...

High shear mixer for dairy and personal care products
Achieve consistent emulsification and stable homogeneity with high ...
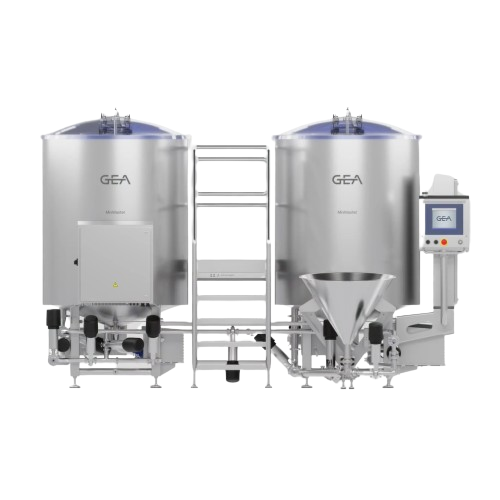

Brine preparation system for marination processes
Ensure consistent and high-quality brine and marinade mixtures with a s...
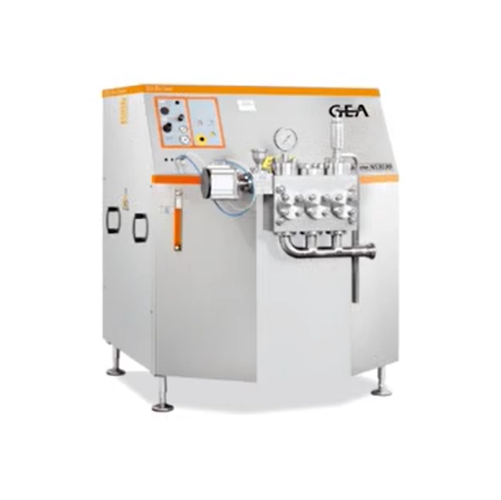

High pressure industrial homogenizer
Enhance liquid formulations with precision and efficiency—our high-pressure homogenize...
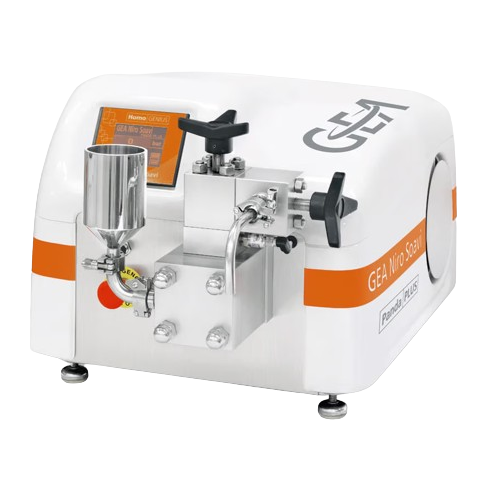

Laboratory homogenizers for nanoparticles and emulsions
Tackle the challenge of achieving consistent nano-scale dispersio...
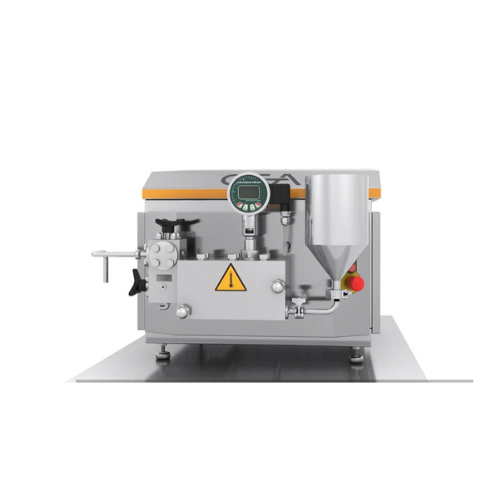

Laboratory homogenizer for small production processes
Optimize your production of nanoemulsions, vitamin suspensions, and...
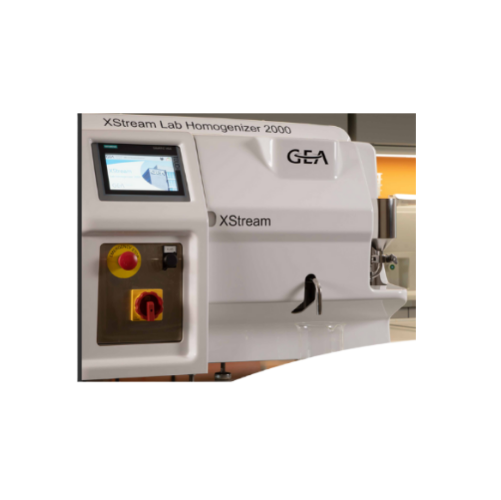

Laboratory homogenizer for scaling nisox-valve benefits
Achieve reliable scaling from lab to production with this precise...
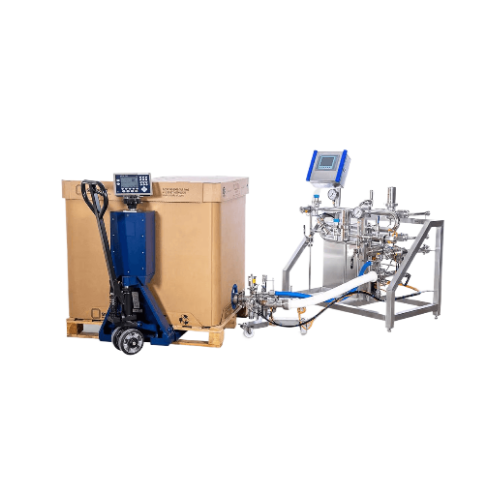

Aseptic filling system for bag-in-box containers
Ensure sterility and precision in filling aseptic liquid products, with s...
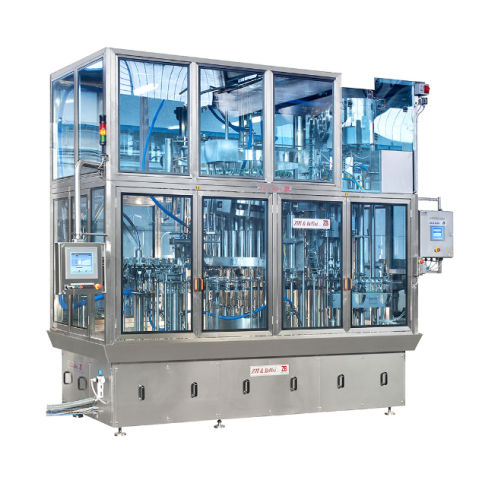

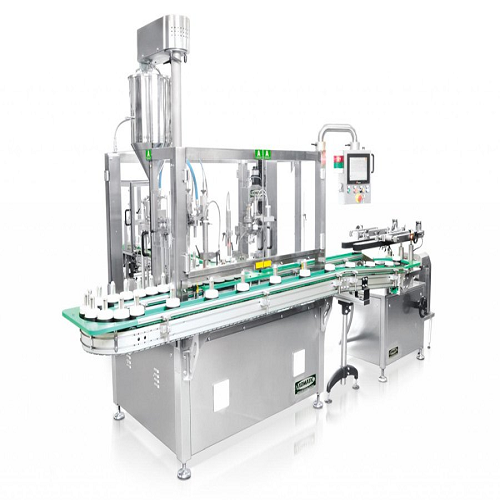
Integrated filling and capping system for food and soft drinks
Streamline your bottling operations with an integrated sy...
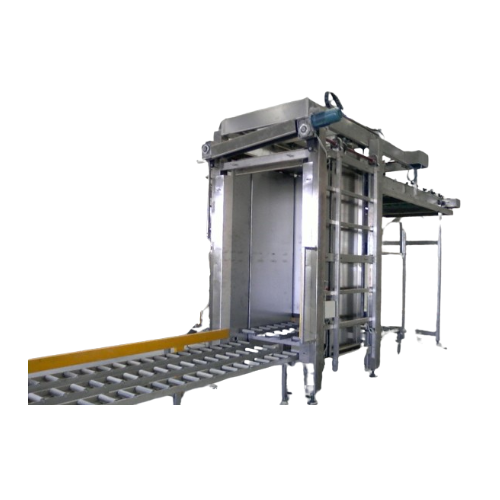

Complete filling and closing line for food containers
Optimize your production line with a versatile solution that ensure...
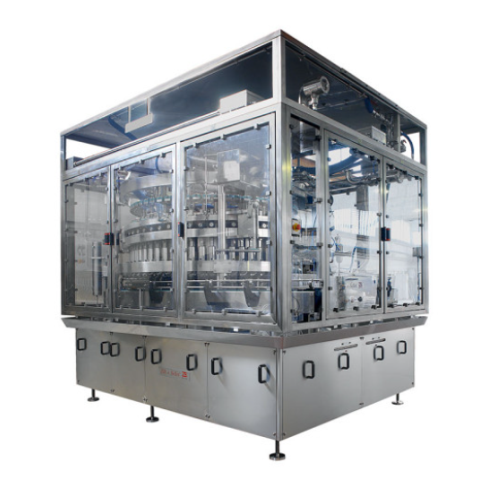

Rotary piston fillers for pumpable products
Optimize high-speed production lines with precision filling for diverse liquid...
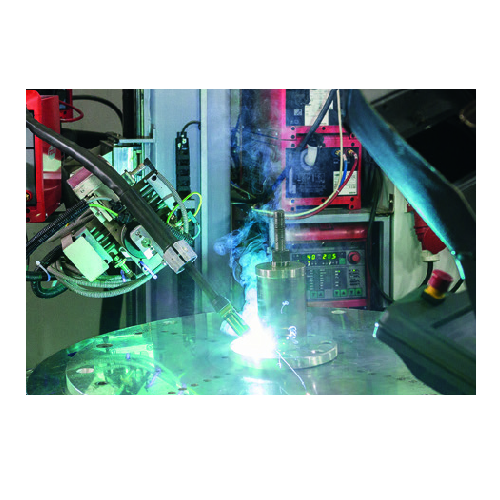

Traditionally welded silos for constrained installation sites
Ideal for facilities with limited space, these traditional...
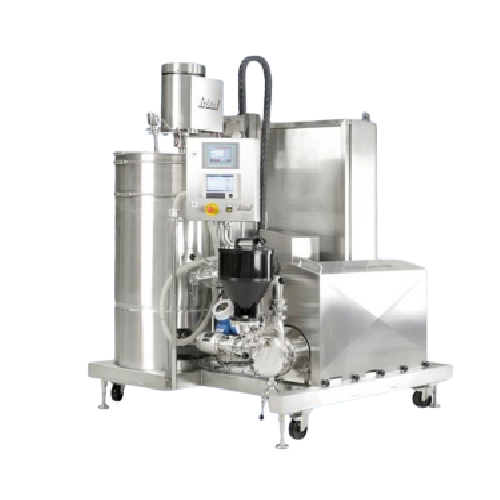

Inline disperser for food production
Quickly achieve stable, agglomerate-free dispersions and emulsions with minimal manual...
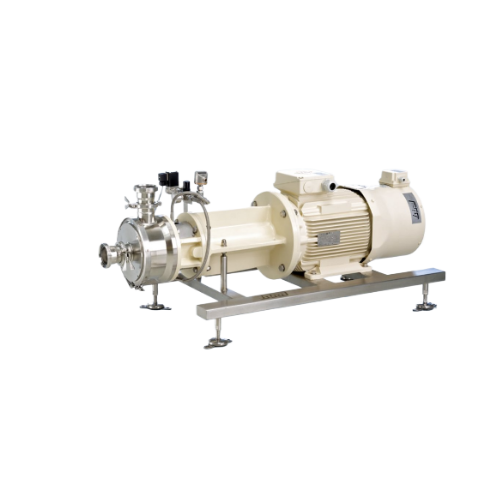

Inline disperser for homogeneous emulsions and suspensions
Achieve precise control over particle size and distribution w...
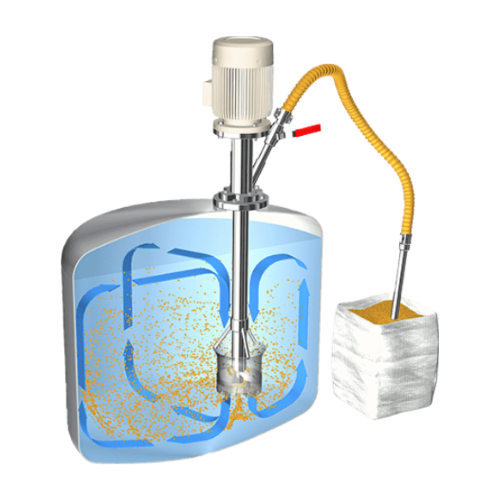

Low-dust powder induction mixer for liquids
Achieve dust-free induction and homogenization of powders in liquids with prec...
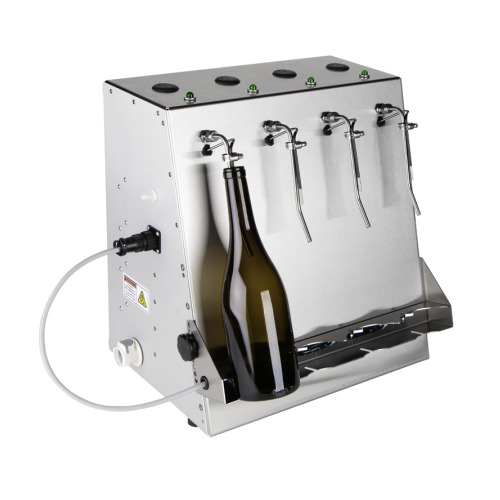

Hot fill bottling unit for juices and isotonic beverages
Ideal for producers handling delicate or specialty liquids, this...
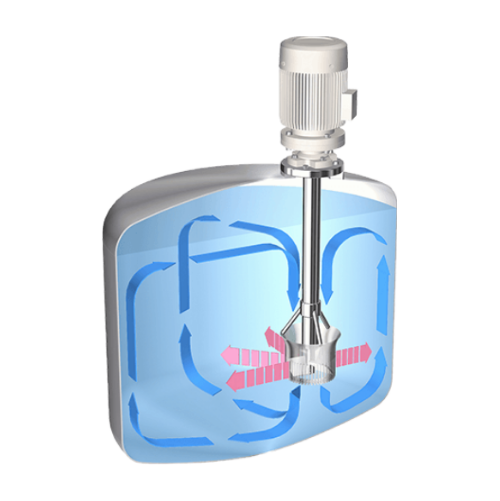

High-performance dispersing and mixing solutions
Enhance your mixing and dispersing processes with advanced fluid stream t...
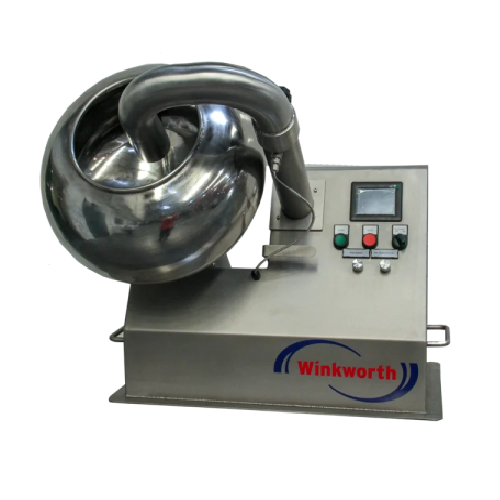

Industrial coating pan for food and pharmaceutical products
Optimize your production with precision mixing and coating, ...
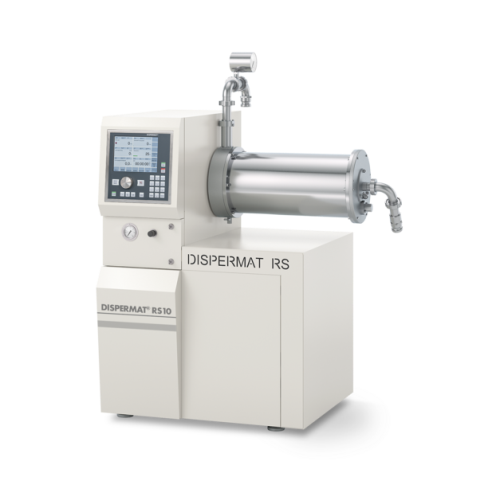

Horizontal bead mill for industrial production
Ensure ultra-fine particle size reduction in high-demand processes with thi...
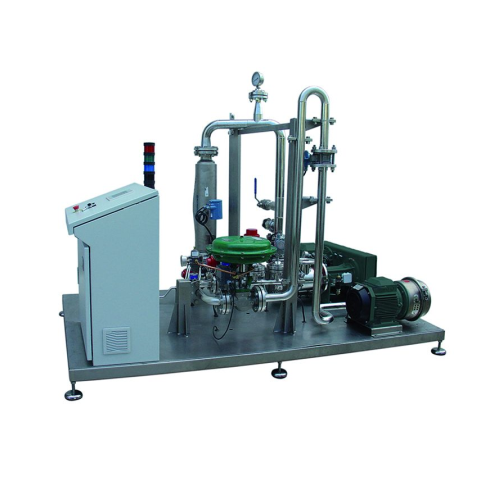

Complete mixing systems for industrial applications
Optimize your production efficiency and product consistency with adva...
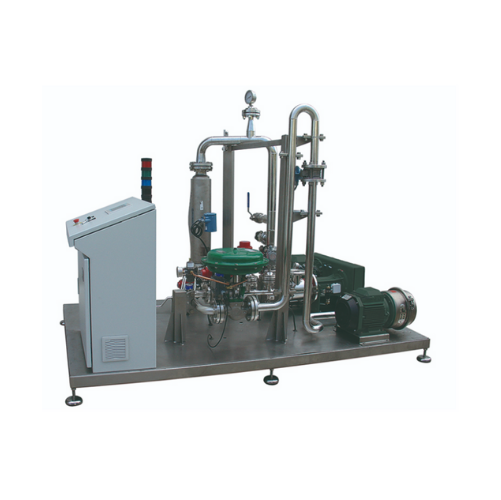

Complete mixing solution for food, cosmetics, and chemical industries
Optimize your production line with a system that ...

Mechanical homogenizer for fine cutting and emulsifying
Achieve precise particle size control and consistent texture in y...
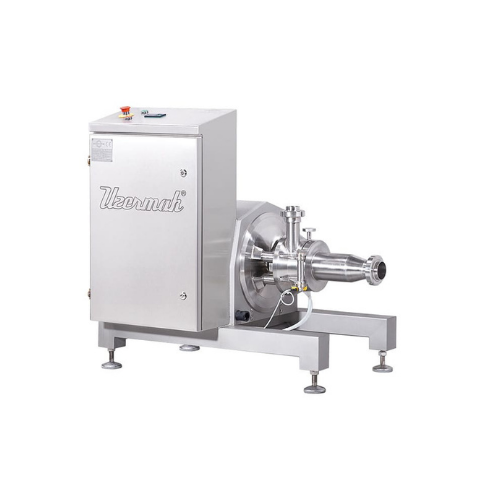

Inline mechanical homogenizer for food processing
Achieve precise particle size and uniform texture in your emulsions and...
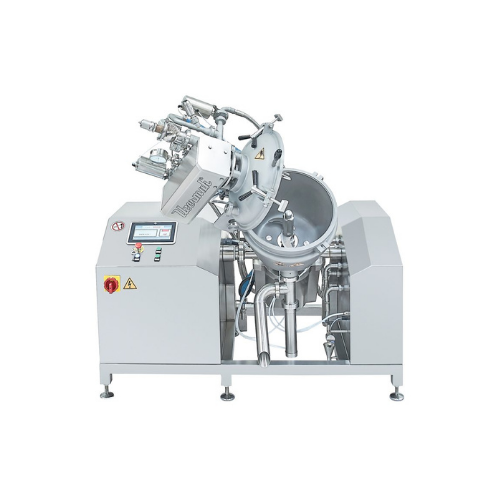

Multifunctional cheese and sauce processor
Optimize your production of sauces, dressings, and confectionery fillings with ...
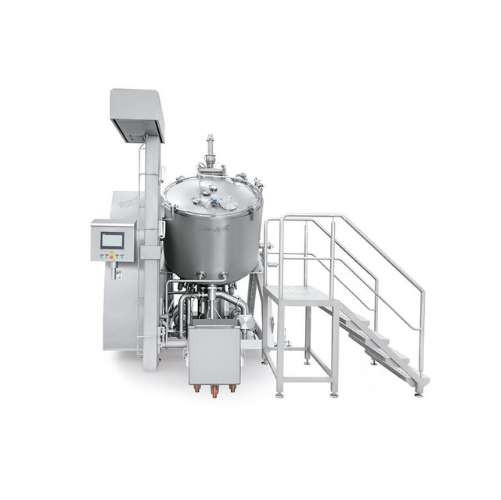

Multifunctional industrial mixer for processed cheese and sauces
Optimize your batch production with a versatile solutio...
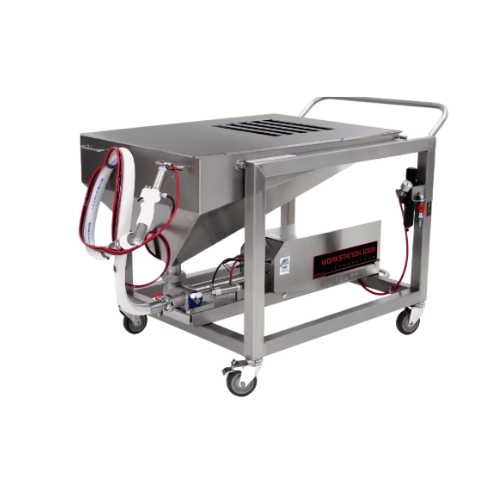

Industrial food depositor for large volume applications
Efficiently handle diverse food textures with precise portion con...
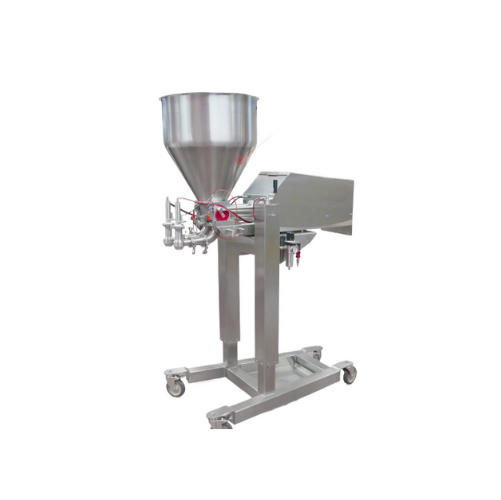

Dual or triple lane food depositor
Enhance your production efficiency with a depositor that seamlessly handles a variety of...
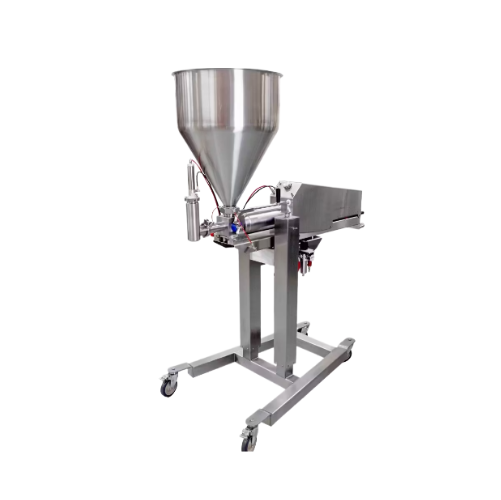

Large portion depositor for food production
Achieve precision and efficiency in depositing large portions with versatile s...
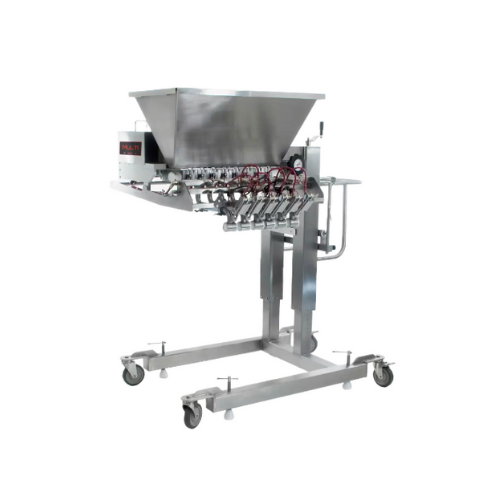

Multi piston food depositor for sauces and dips
Efficiently fill and deposit sauces, dips, and more with precision across ...
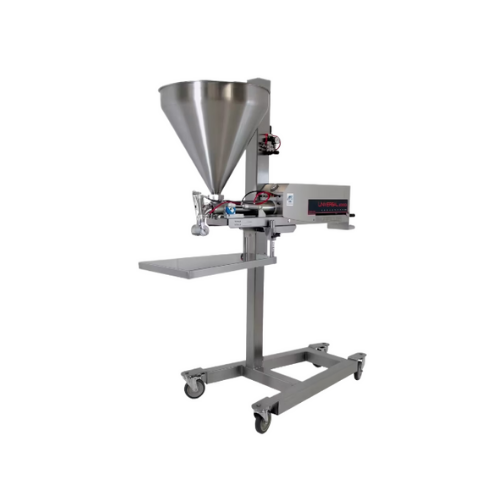

Single piston food depositor
Achieve precise portion control for diverse food products, from soups to chunky fillings, with ...
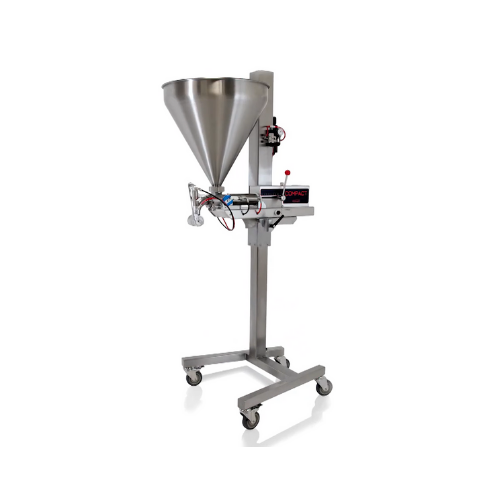

Compact food filling and portioning solution
Ideal for facilities needing precise portioning, this versatile filling machi...

Compact food transfer pump
Effortlessly maintain your production flow with a compact transfer pump designed to handle a wide...

Single-serving blender for home use
Create smooth, nutrient-rich beverages and culinary delights effortlessly, whether you&...

Pre-formed container filling system for multi-layer products
Efficiently handle a diverse range of products with this fl...
Fully automated packaging lines
Streamline your production with versatile packaging lines designed to handle a range of good...

Homogenizer for high-capacity food processing
Achieve superior emulsification and suspension handling with this high-press...

High shear mixer for smooth or particulate food products
Achieve consistent quality in diverse food products with precise...

Batch mixer for soft drinks ingredients
Effectively manage diverse ingredient formats with a high-performance mixing system...

Compact aseptic filling solution for versatile production
Maximize production line efficiency with a compact filling sys...

Cardboard packer for secondary packaging
Streamline your packaging process with a high-speed, automated cardboard packer th...

Industrial tray shrink wrapper
Optimize your packaging line with rapid, resource-efficient shrink wrapping, accommodating di...

Manual dosing and capping for semi-dense products
Enhance your production line efficiency by seamlessly integrating manua...
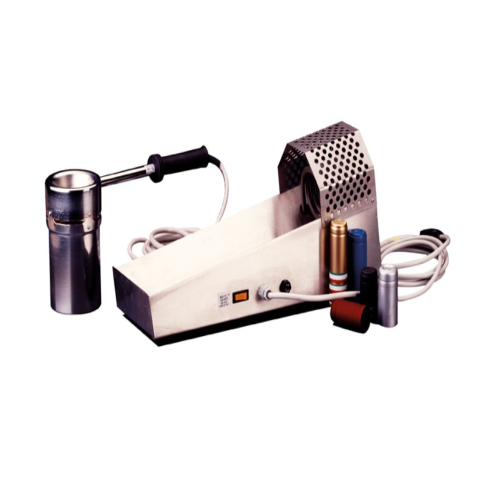

Manual heat shrink capsule applicator
Quickly and precisely apply shrink capsules to bottlenecks, ensuring perfect adherenc...
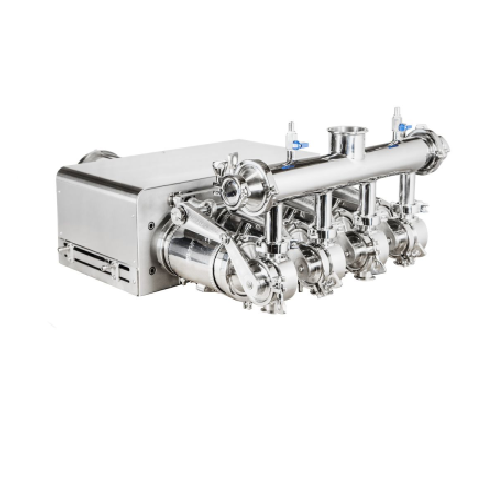

Pneumatic syringe dosing system
Streamline your liquid dosing process with precision and efficiency, ensuring each applicati...
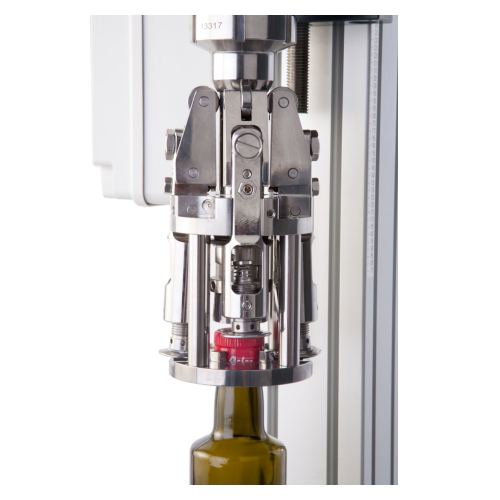

Semi-automatic capping solutions for small to medium production
Streamline your capping process with versatile, customiz...
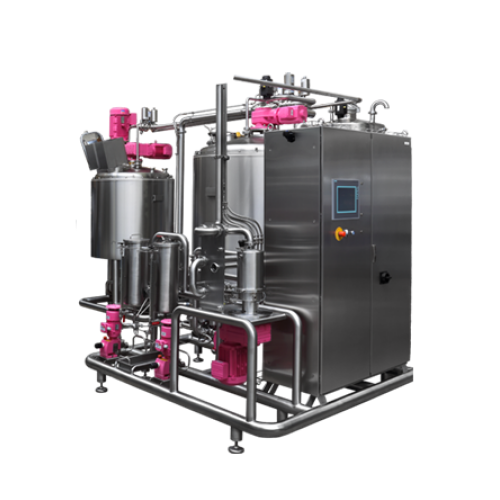

Inline blender for liquid ingredients
Optimize your production line with seamless liquid blending, enhancing flavor consist...
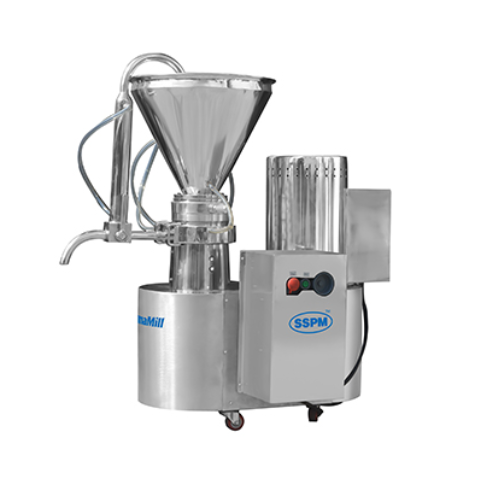

Colloid mill for particle size reduction and emulsification
Achieve precise particle size reduction and stable emulsions...
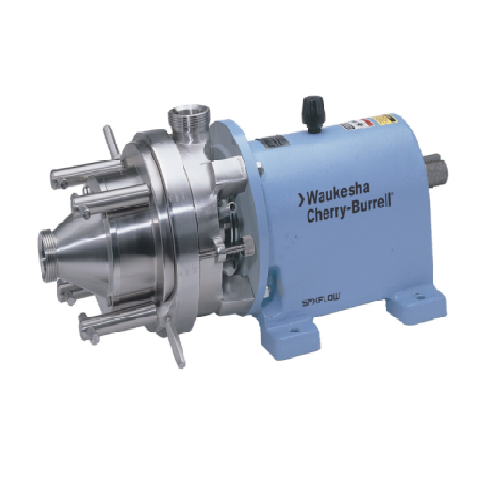

Colloid mills for shearing and mixing in food processing
Optimize your liquid formulations with precise colloid mills, en...
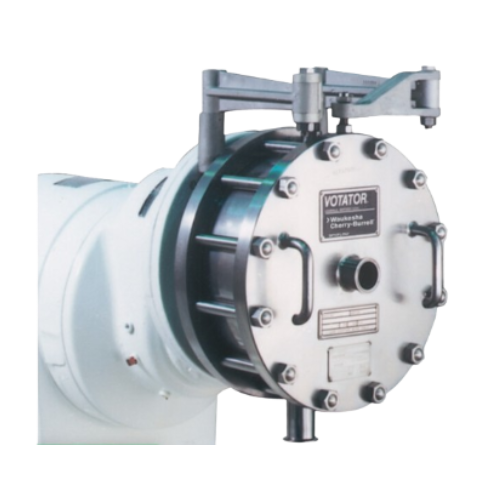

High-shear mixer for emulsions, dispersions, and foams
Achieve precise emulsions and dispersions effortlessly with high-s...
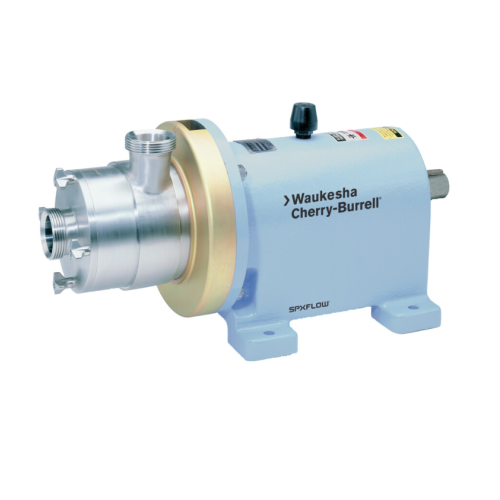

Shear pumps for continuous on-line dispersion
Effortlessly achieve consistent shearing and mixing with versatile shear pum...
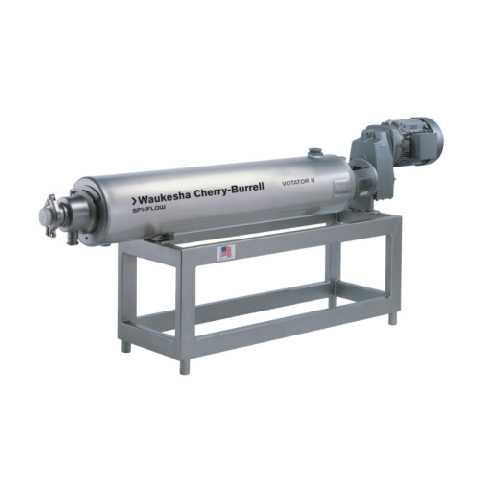

Scraped surface heat exchangers for high viscosity products
Ideal for continuous processing, these heat exchangers effic...

Side entry mixer for industrial tank applications
Ensure optimal mixing and blending of liquids and slurries with high ef...
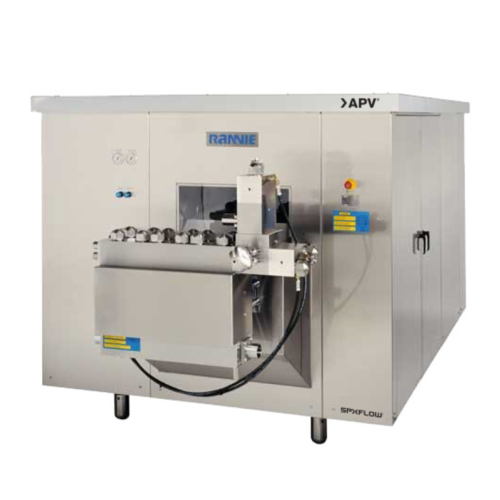

High pressure homogenizer for dairy and food processing
Achieve uniform particle size and enhance product stability with ...
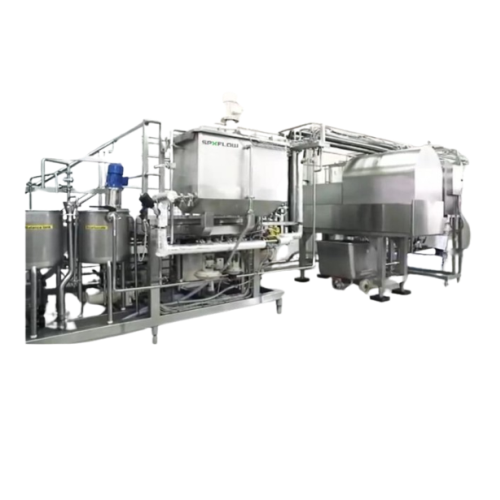

Soymilk processing plant
Enhance your plant-based production with our tailored soymilk processing plants, designed to efficie...
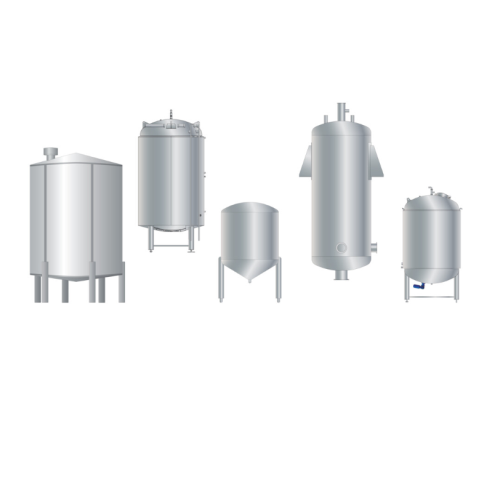

Hygienic tanks for various processing needs
Achieve optimal processing and storage with customizable hygienic tanks, desig...
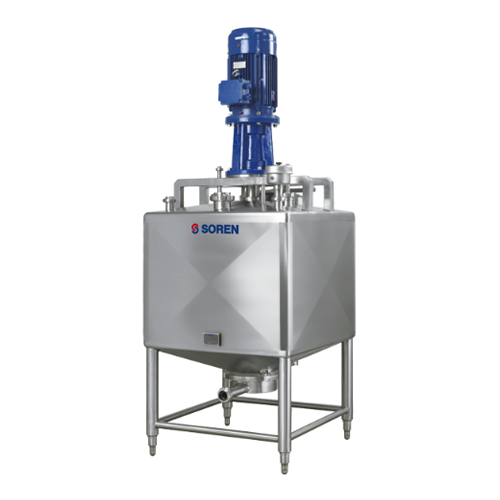

Industrial dissolver for liquid-solid mixing applications
Optimize your production line with an industrial dissolver tha...
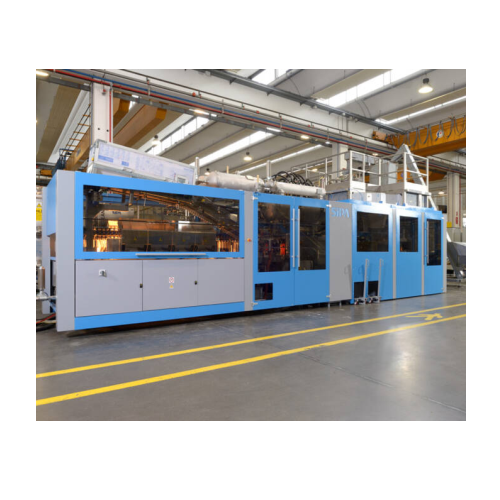

Integrated linear blowing and filling system for Pet containers
Streamline your PET container production with integrated...
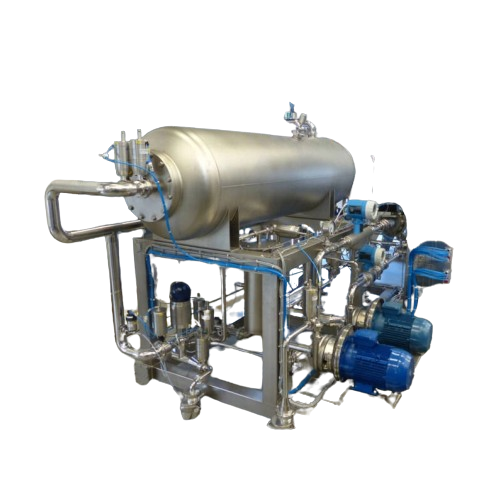

Degassing and mixing unit for beverage production
Ensure precise beverage formulation and maintain high quality standards...
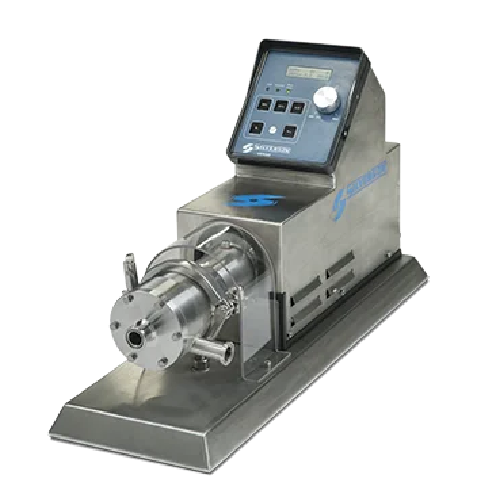

Laboratory in-line mixer for precise mixing and reproducibility
Achieve precise laboratory-scale mixing with rapid proce...
Linear blowing systems for Pet bottle production
Ideal for producers seeking versatile container solutions, this system en...
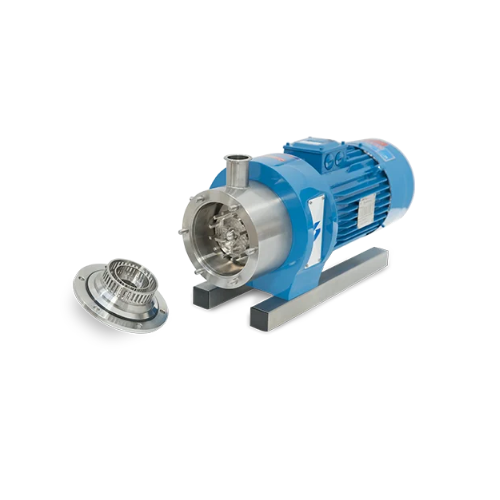

Homogenizers for creams and ointments
Achieve superior consistency and particle size reduction in skincare creams, sauces, ...
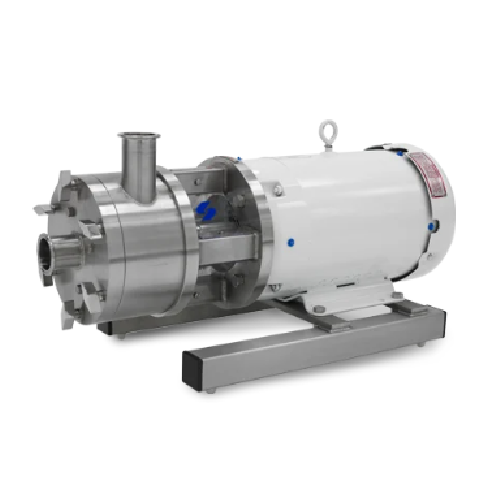

In-line ultra sanitary mixer for pharmaceutical and food applications
Enhance your liquid formulations with precision m...
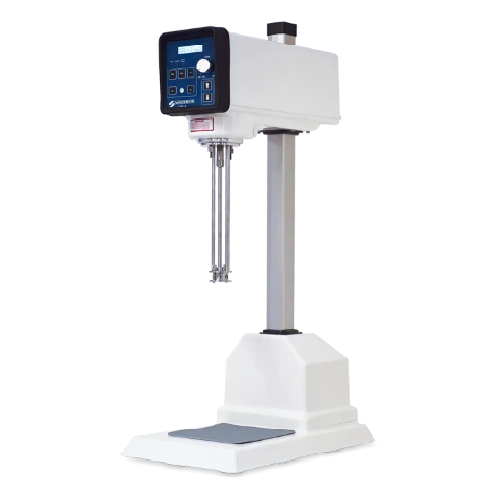

High shear lab mixer for laboratory work and r&d
Achieve unparalleled precision and consistency in laboratory and pilot-sc...
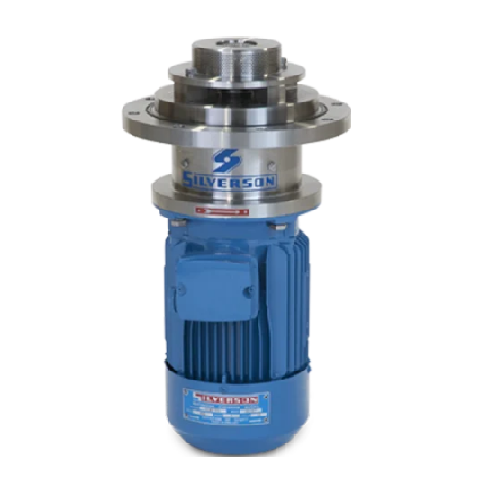

Bottom entry mixers for high viscosity products
Optimize your production line with mixers designed to handle both high and...
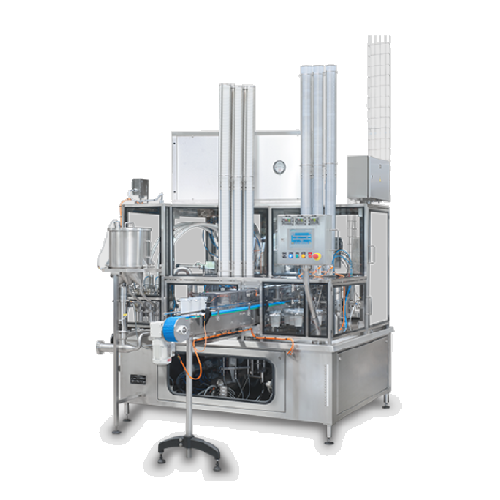

Filler for yoghurt and white cheeses
For manufacturers seeking efficient, versatile filling for products like yoghurt and s...
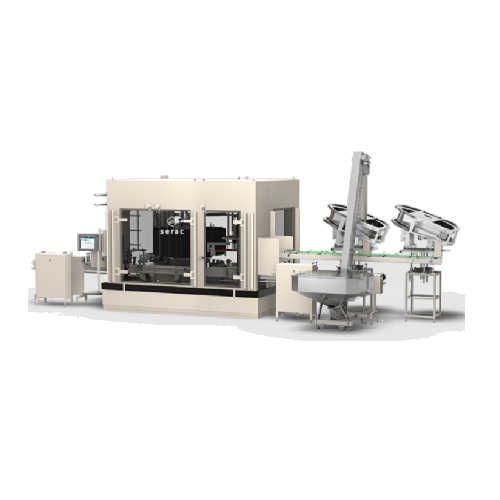

Anti-corrosion filling system for aggressive liquids
When dealing with corrosive liquids, ensure durability and safety wi...
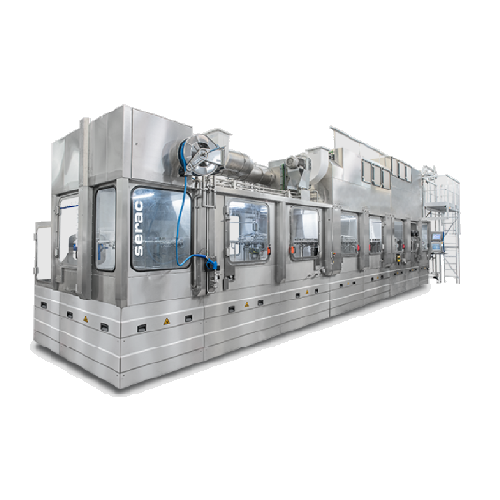

Aseptic filling technology for dairy products
Ensure product integrity and extend shelf life with a high-speed aseptic fil...
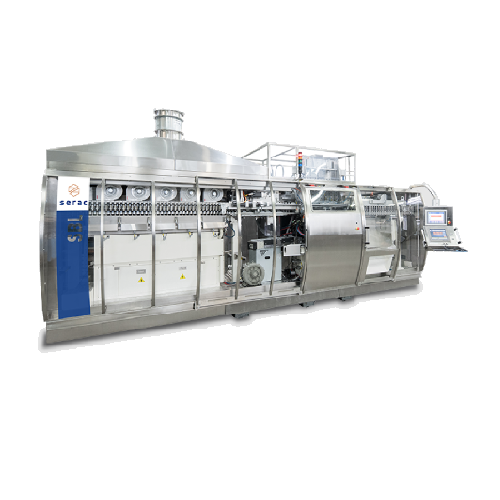

Pet bottle production for small and medium outputs
Optimize your production line by manufacturing PET bottles in-house, r...
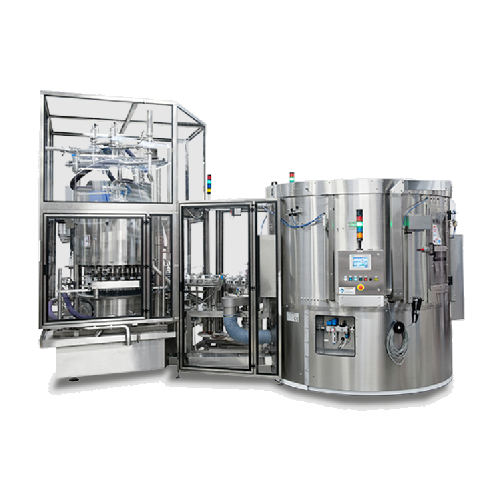

Space-saving packaging solution for high-velocity production
Optimize your manufacturing floor space with a versatile in...
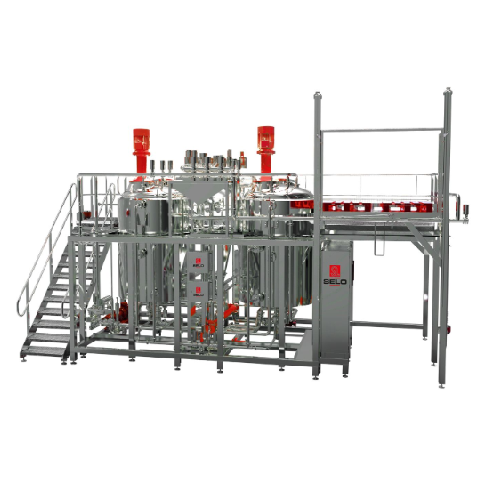

Automated sauce production lines
Streamline your sauce production with flexible lines designed for rapid recipe changeovers,...

Semi-automatic weight filling system for liquid products
Achieve precise and versatile liquid filling performance with th...
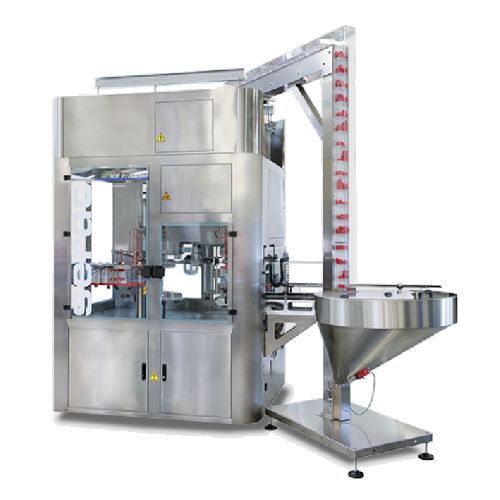

High hygienic filler for chilled beverages
Enhance cold beverage production with a modular, hygienic filler offering chemi...
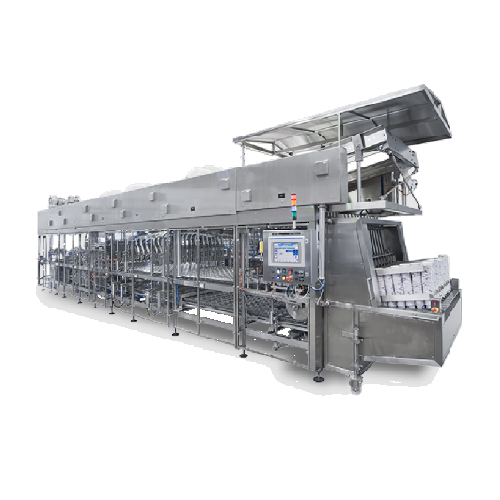

Yoghurt and dairy desserts filling solution
Maximize efficiency in filling and sealing multi-product dairy desserts and be...

Ketchup manufacturing line
Streamline your sauce production with precision-engineered efficiency, allowing for seamless reci...
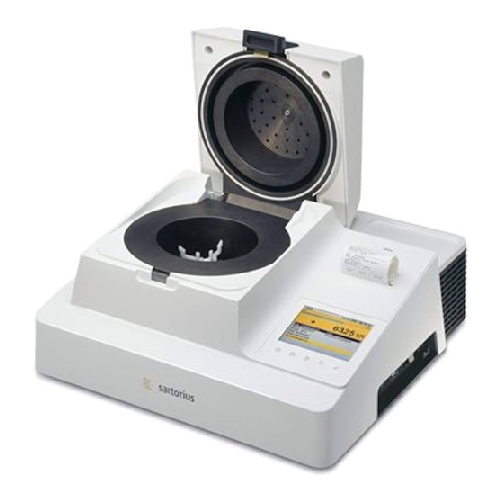

High-speed moisture analyzer for liquid and pasty samples
Ensure precise moisture analysis with rapid microwave drying, ...

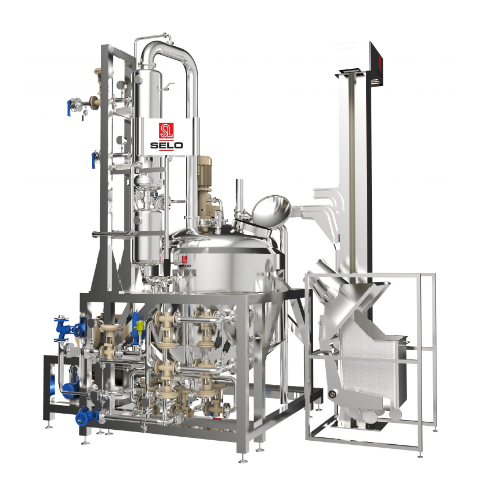
Vacuum process system for food product mixing and emulsifying
Optimize your production of sauces, dressings, and condime...
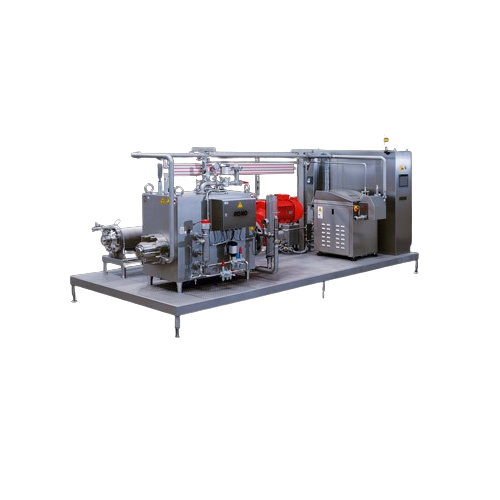

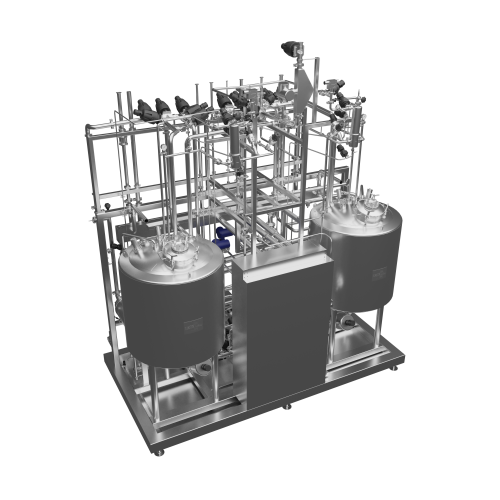
Skid mounted process plant
Simplify your production setup with skid-mounted process plants, designed for quick installation ...
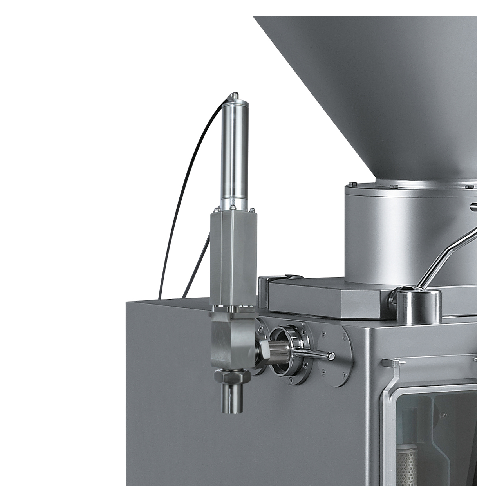

Vertical dosing valve for accurate food portioning
Ensure precision in portioning liquid and semi-liquid food products wi...
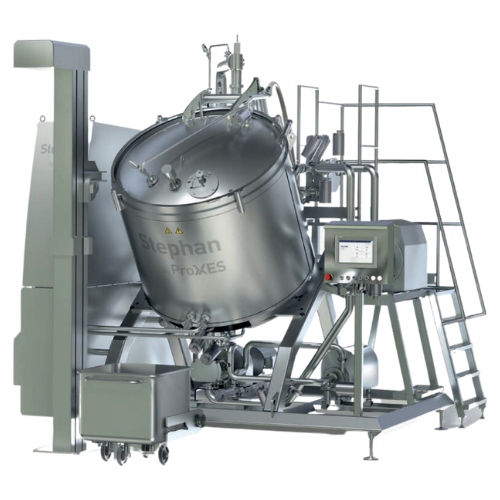

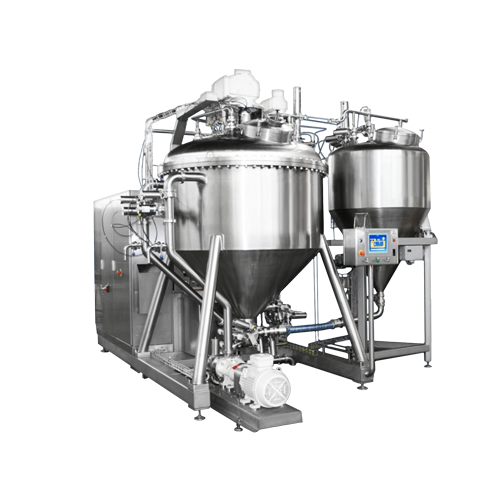
All-in-one system for making emulsions
To make smooth batches of mayonnaise or ketchup you need to use process equipment fo...
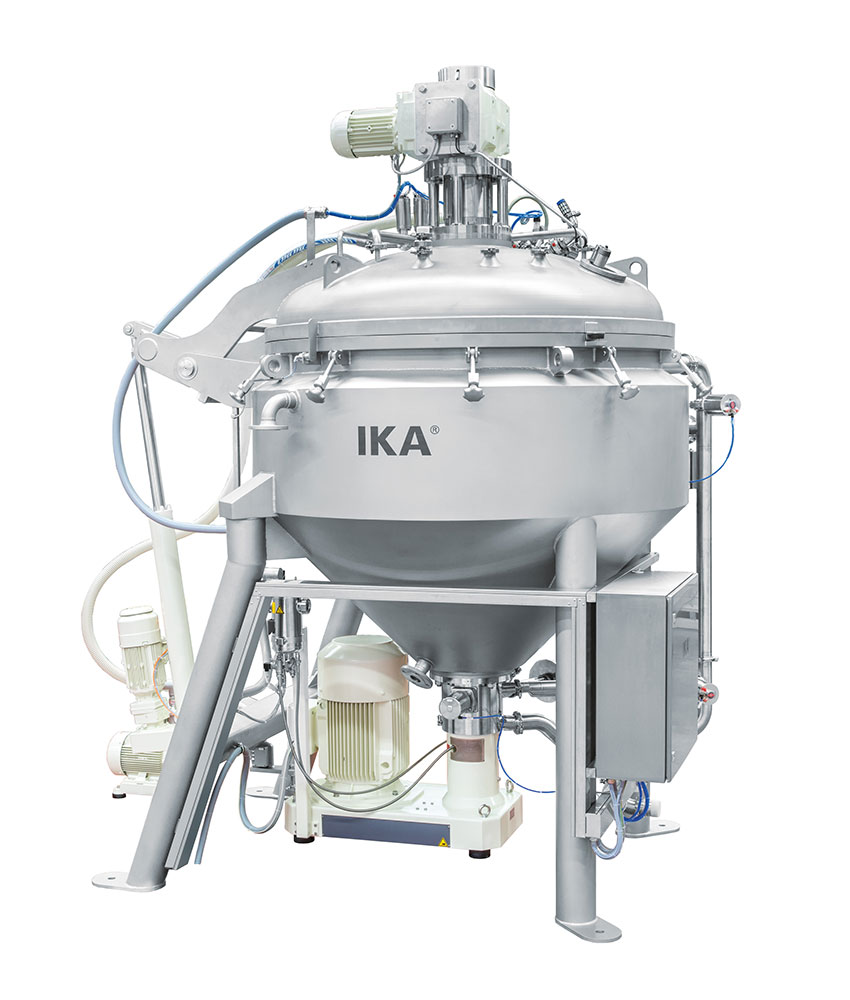

Homogenization and emulsifying system for fine foods
Texture and consistency are critical to foods with delicate composit...
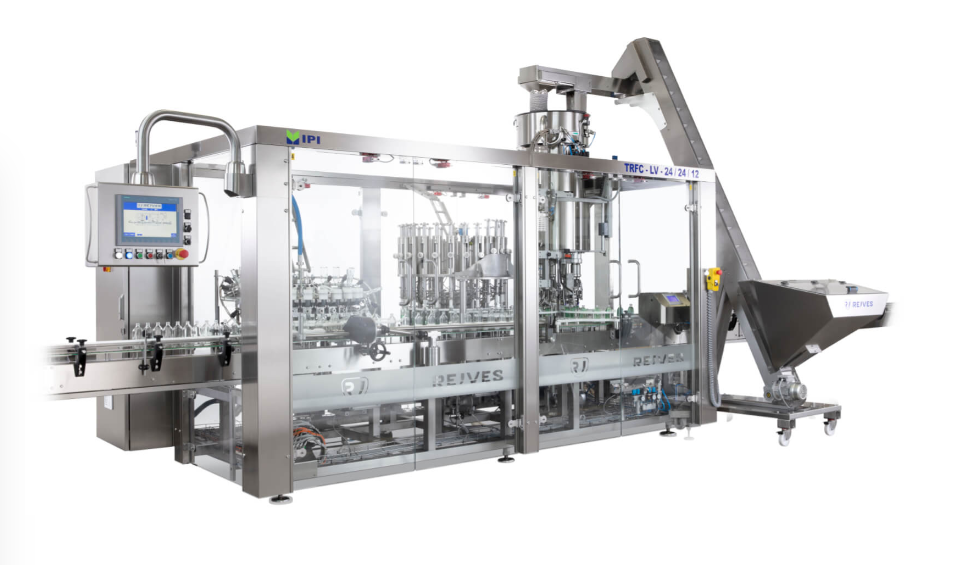

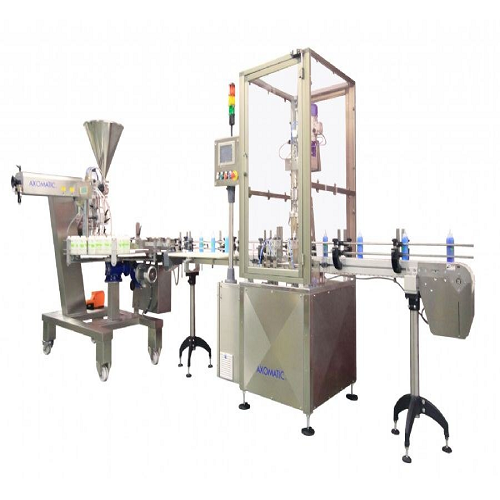
Bottle filling and capping monobloc
Spillage and overfilling are common problems in most production lines for bottled produ...
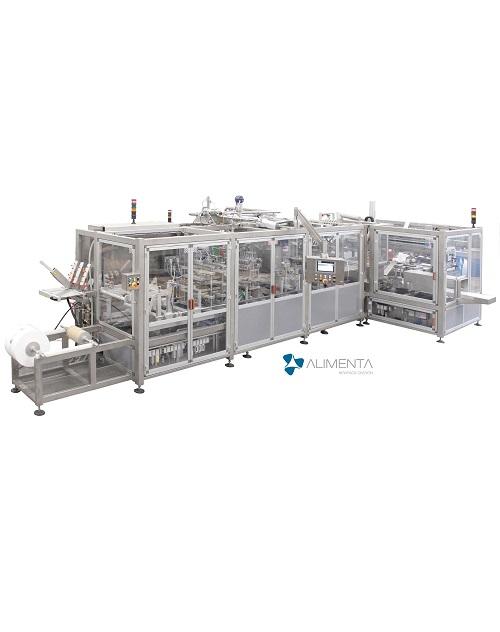

Aseptic FFS machine for UHT products
UHT products (ultra high temperature processing) such as sterilized milk, are products...

Automatic filling machine for sauce
Traditional sauce filling units can struggle to maintain a high quality of output in ca...

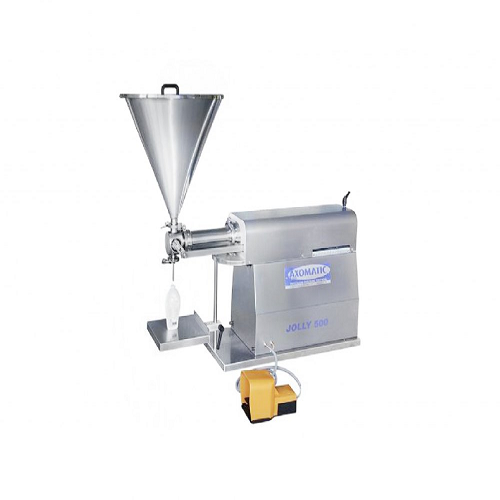
Pre-made cup filler for salad dressings
Pre-made cup fillers are mostly used by food companies to assist in the mass produc...

High pressure electric laboratory homogenizer
It’s vital that small units for experimentation can scale up with 100% accur...
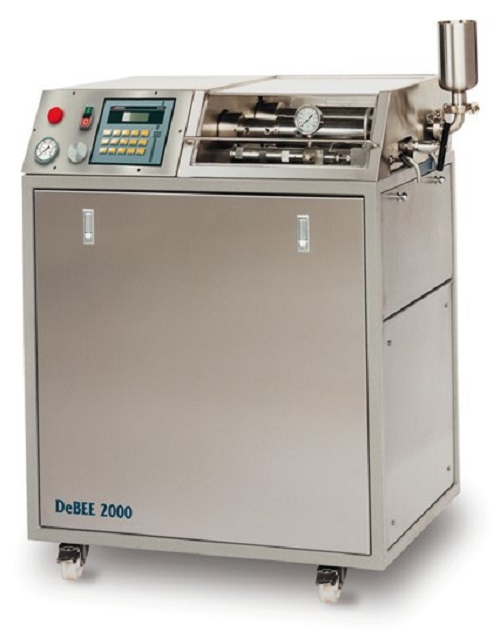

High pressure pilot homogenizer
Biotech and pharmaceutical development programs often require a mixing method that achieves ...
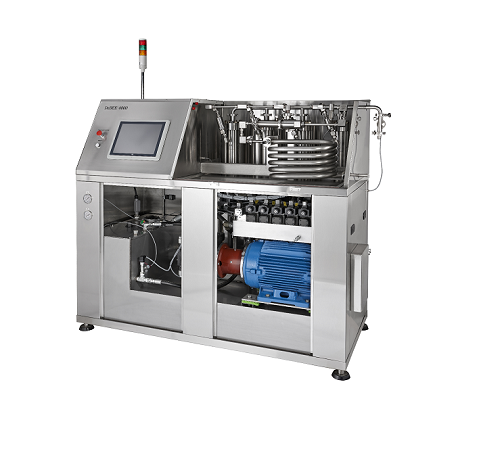

High pressure industrial homogenizer
For any industrial pharmaceutical process that relies on high pressure homogenization ...
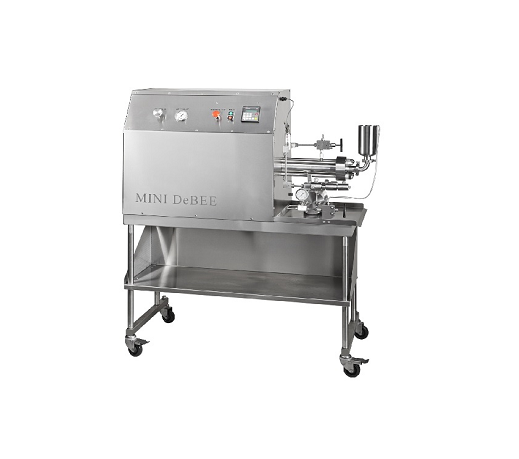

Pilot high pressure homogenizer
For maximum value, a high-pressure homogenizer that’s suitable for both laboratory and pilot...
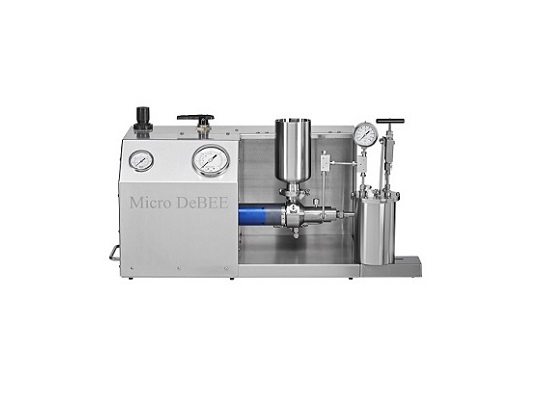

High pressure air powered laboratory homogenizer
Offering lab-scale to small pharmaceutical production scale output for in...
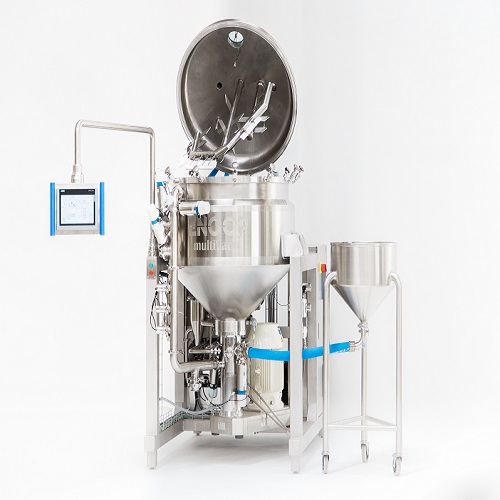

Vacuum based homogenizer
When producing liquid and viscous products such as mayonnaise, sauces, dressings and ketchup it’s vi...

Universal Mixer and Cooker for Sauces
Sauce cookers and mixing machines have traditionally been designed to suit one proces...
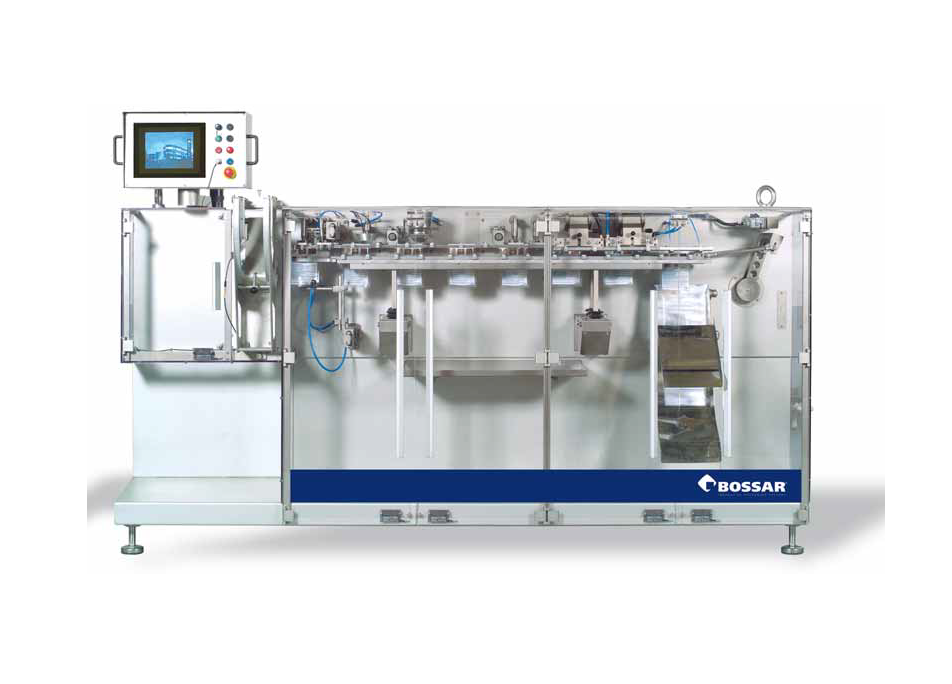

Retort Pouch Packaging Machine
A wide variety of products that were previously canned are now able to be more economically p...
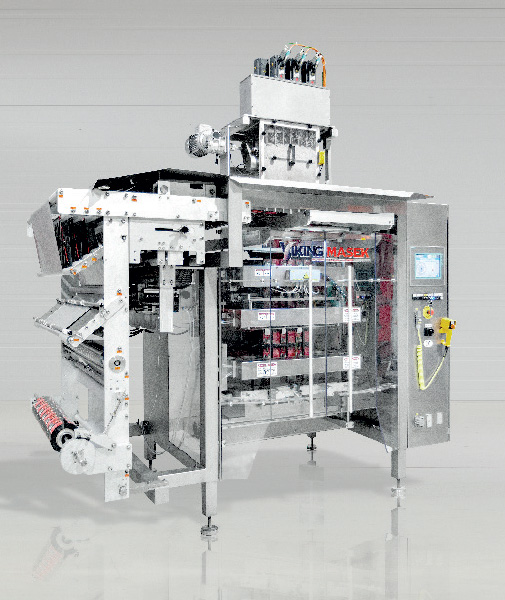

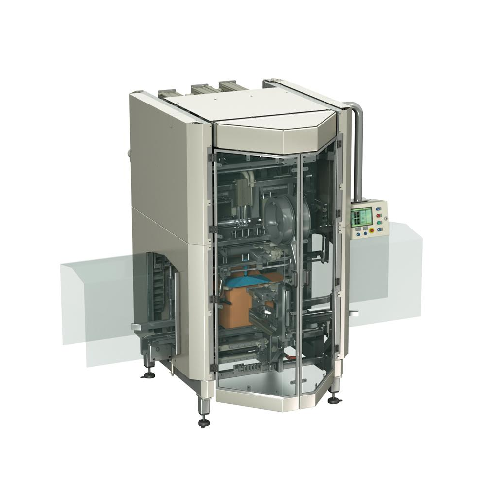
Sachet Machine
If you want to pack into eye-catching 4-side sealed sachets between 40×50 mm and 250×200 mm in size, ...
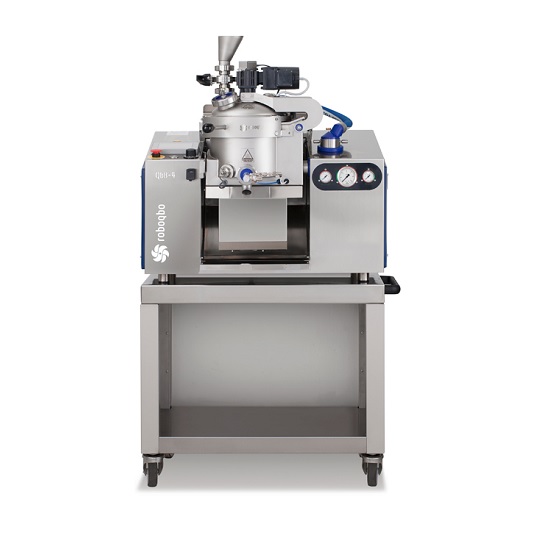

Easy to use food processor for gastronomy sauces and pastes
For the development and production of high quality gastronom...
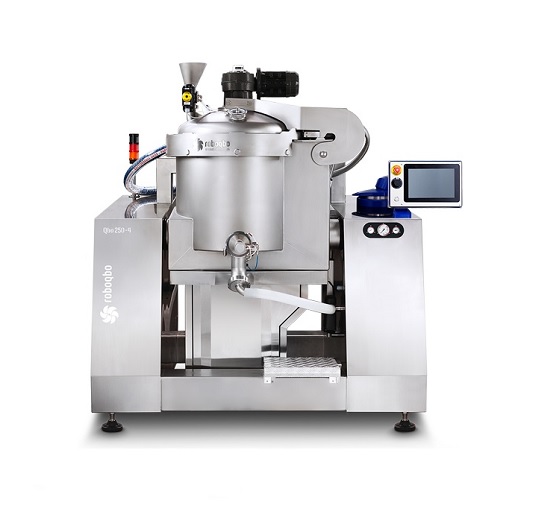

Vacuum cooker for concentrating sauces and purees
When producing high quality prepared food, concentrating products for s...
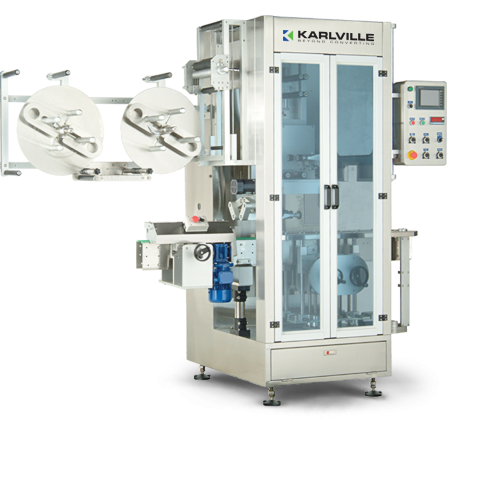

Shrink sleeve applicator - 400 per minute
Flexible medium to high speed application of shrink sleeveing to containers is u...
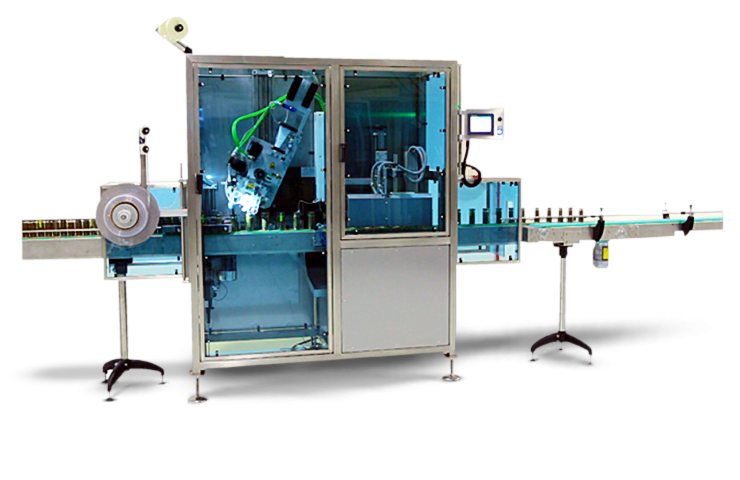

Compact shrink sleeve applicator
Adding tamper prevention to product packaging can be expensive and difficult to set up. Thi...
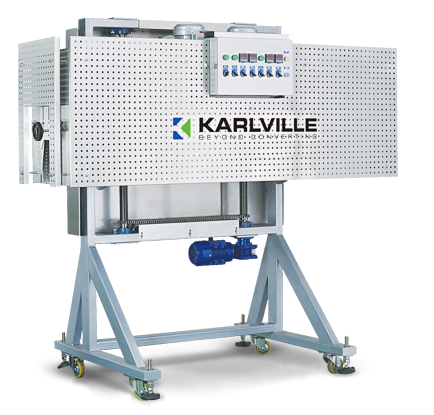

Electric shrink tunnel solution
Adapting shrink sleeve heating tunnels for different applications can be a lengthy and expen...
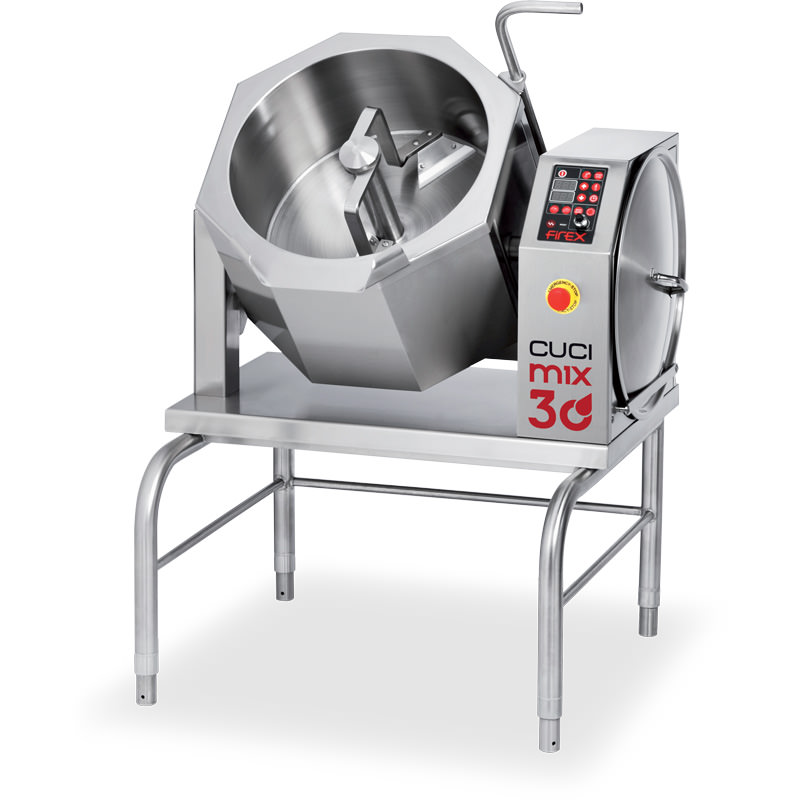

Compact industrial sauce pan
Safe, reliable cookers that operate unobtrusively are required in any kitchen where space and t...
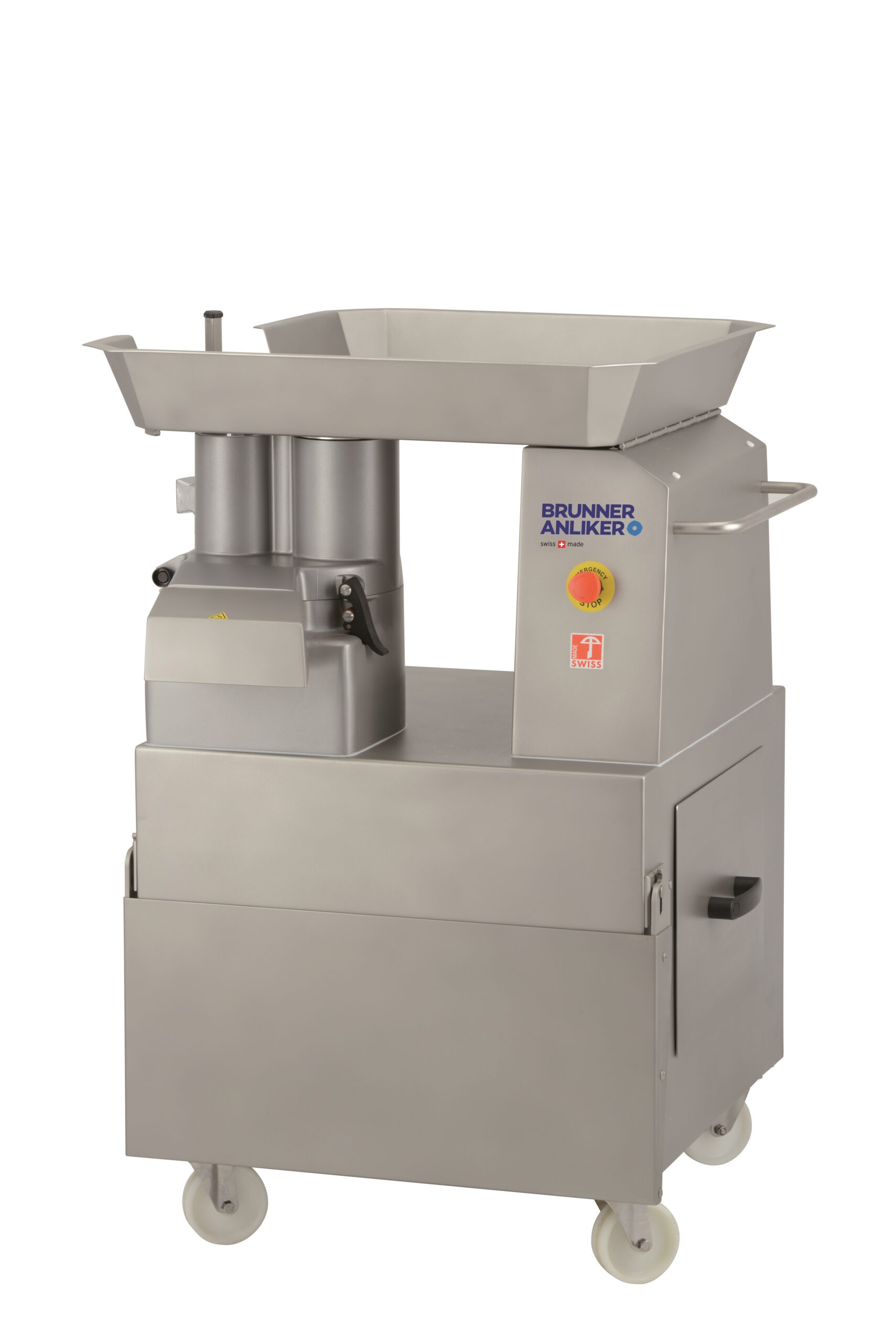

Industrial vegetable cutter
Retaining freshness in cut vegetables, as well as retaining vitamins and nutrients, is a top pri...
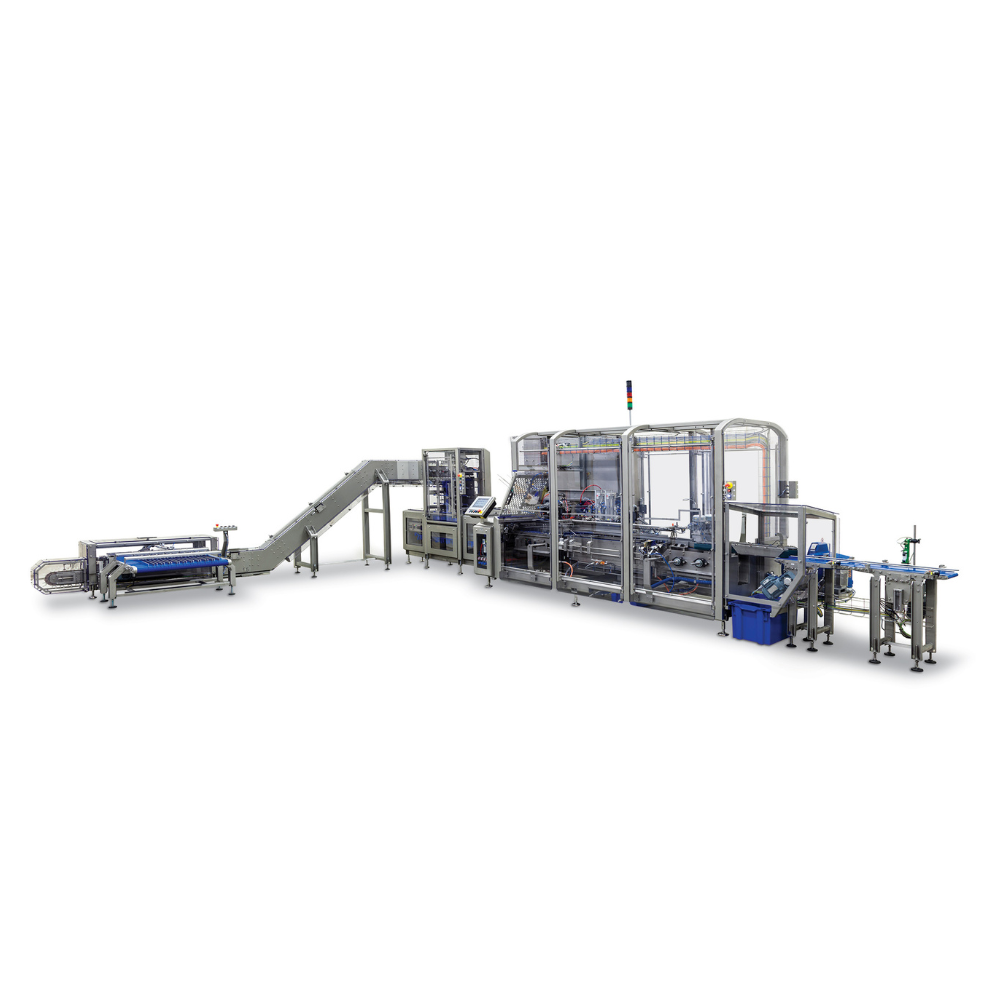

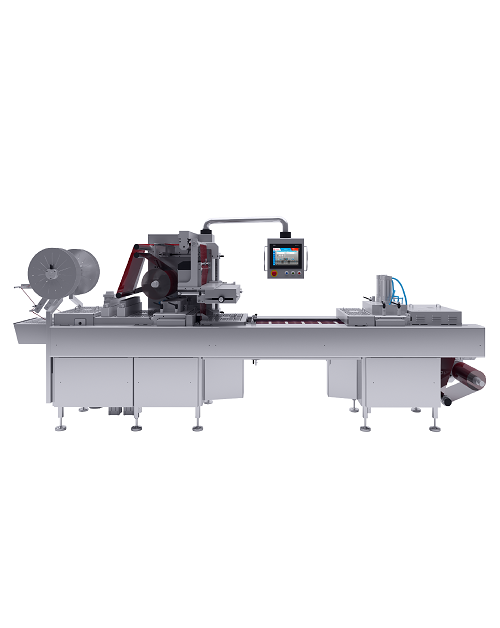
Smart Industrial Sauce Cartoning System
Large volume producers of sauces and ready meals continuously pack different produc...

Batch processing system for emulsions and suspensions
Emulsions enhance foods with a creamy mouthfeel and richer flavors....