Making Liquid Detergents
Find innovative production technology for making liquid detergents and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Although invented in the early 20th century by Otto Rohm, detergents gained popularity in the 1950s due to the development of modern technology and washing machines which started replacing scrub boards. The liquid detergent manufacturing process involves three key stages: soap premix manufacture, ingredient mixing and enzyme addition.
Select your liquid detergents process
Tell us about your production challenge
The essential steps in the liquid detergent manufacturing process
In addition to liquid laundry and dish-washing liquid detergents, household cleaners such as floor cleaning liquids or glass cleaners are also classified as liquid detergents. All these detergents can be produced in the same plant. Substantially, liquid detergents are powders mixed with water and chemical solutions called solubilizers, making detergents dissolvable in water. The first stage of the liquid detergent manufacturing process consists of neutralizing fatty acids with either caustic soda or potassium hydroxide.
After the chemical reaction and the premix step, ingredients such as thickeners and pH adjusters are added to a homogeneous mixer. These balancing ingredients are essential to achieve desirable viscosity, stability, and pH value. In the enzyme addition stage, powdered enzymes are added to the cooled mixture due to their delicate nature.
Their role is to break down tough stains and soils. Enzymes like lipase are good for removing grease and oil while amylase, for instance, can remove starch-based or carbohydrate soils. Lastly, liquidized detergents are pumped into bottles by a filling system, weighted on weighing devices and sealed by a capping machine.
What’s the difference between liquid dishwashing detergent and liquid laundry detergent?

The formula of the two liquid detergents is almost very similar even though, if you think about it, they are designed for totally different applications.
Since dishwashing detergents are designed for frequent contact with human skin they contain mildness additives and antibacterial agents. Moisturizing agents, oils and protein compounds are added to protect the skin and prevent tears. They also contain chelating agents and preservatives due to oxidation. Furthermore, dishwashing detergents use sodium Laureth sulfate as a surfactant which acts as a foaming agent.

On the contrary, surfactants used in liquid laundry detergents are alkyl or aryl sulphonates, which restrict suds. The use of enzymes in laundry detergents is essential since they exterminate stains that grip the fabric. Moreover, laundry detergents use ingredients specified for protecting fabric and washing machine parts. Builders improve the effectiveness of the surfactant, polymers help capture soils and prevent dye from coming off and transferring to textile, bleach preserves color while softeners reduce fabric friction. Finally, corrosion inhibitors protect the parts of washing machines from corrosion.
The environmental impact of liquid detergents
In recent years, the detergent industry has faced various environmental challenges, since detergents contain several harmful chemicals. Surfactants damage the protective layers of fish, leaving them vulnerable to parasites, bacteria and other pollutants. Another problem caused by a standard surfactant was foam creation in the nation’s waterways. It was discovered that the problem was caused by ABS (alkyl-benzene sulfonate). Nowadays, manufacturers replaced ABS with LAS (linear alkylate sulfonate), which biodegrades faster than ABS.

Although phosphates were banned for causing eutrophication by inducing algae population explosions, environmental damage is still driven by its alternatives. Chemicals such as nonylphenol ethoxylated, acetaldehyde and benzene further contribute to water and air pollution.
Additionally, liquid detergents are sold in plastic bottles, which end up in oceans, waterways and landfills. However, manufacturers of liquid detergents are looking for solutions to avoid harming the marine environment. Eco-friendly solutions are being developed such as detergents made with plant-based ingredients and biodegradable packaging.
Processing steps involved in liquid detergents making
Which liquid detergents technology do you need?
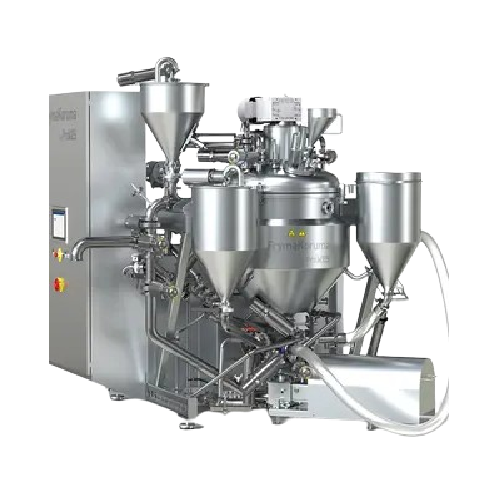

Vacuum deaeration system for mustard and liquid detergents
Ensure optimal product quality by effectively removing air fr...
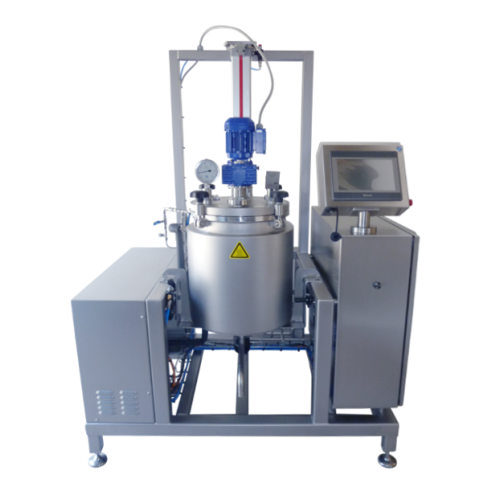

Batch food processing cookers
Achieve precise temperature and pressure control for small-scale food production with modular ...
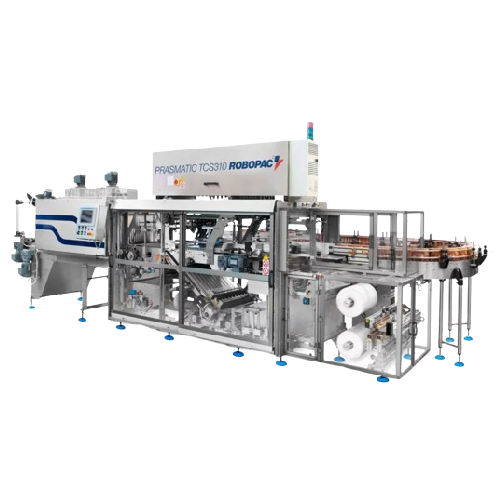

Medium-speed automatic shrink wrapping systems for food and dairy
Optimize your packaging line with this flexible shrin...
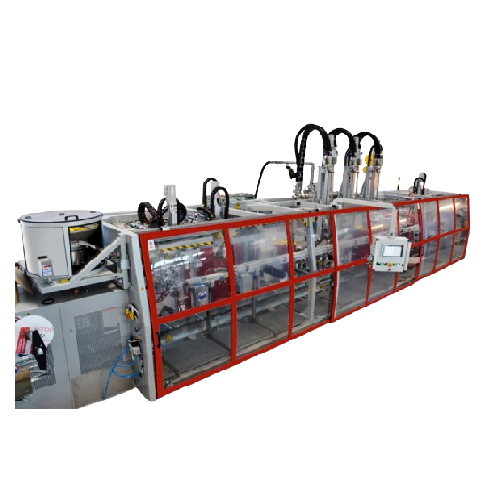

In-line weight filler for drums and kegs
Achieve precise and efficient weight-based filling for large liquid containers, en...
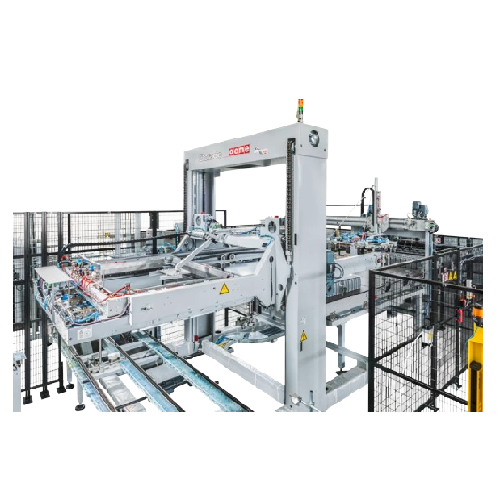

Depalletiser for bulk products
Efficient and precise, this depalletiser streamlines your bulk product handling by seamlessly...
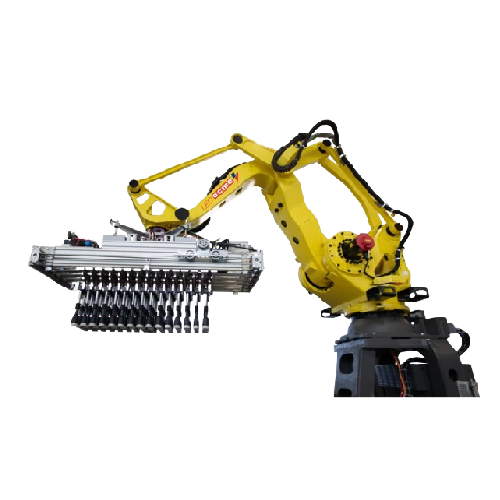

Robotic crating and decrating solution for returnable glass bottles
Streamline your bottling line by efficiently handli...
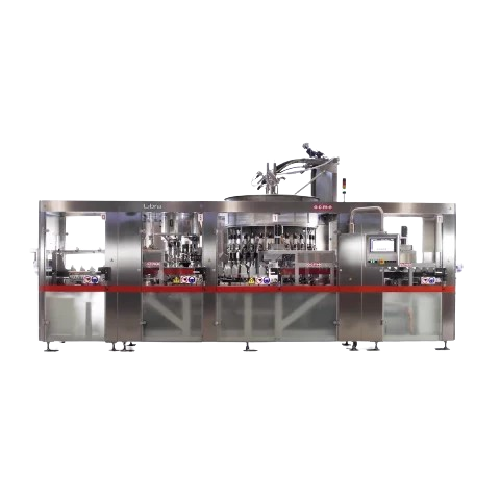

Rotary weight filler for Pet and Hdpe bottles
Enhance your production line with precise weight-based filling, ensuring rap...
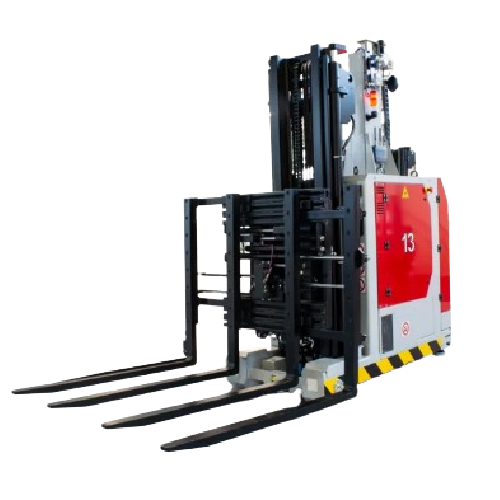

Laser guided vehicle for pallet handling
Efficiently streamline your internal logistics with cutting-edge laser guidance, e...
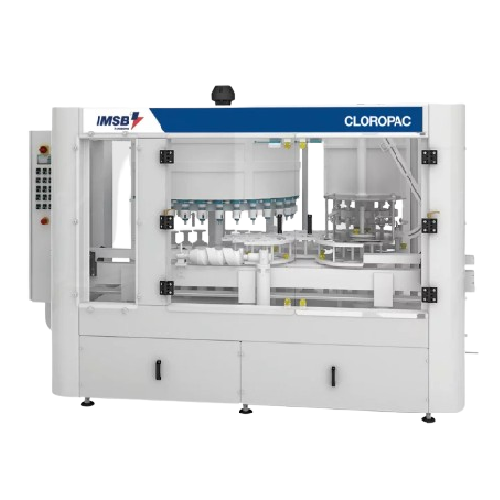

Gravimetric filling and capping system for chlorine solutions
Optimize your filling and capping processes for chlorinate...
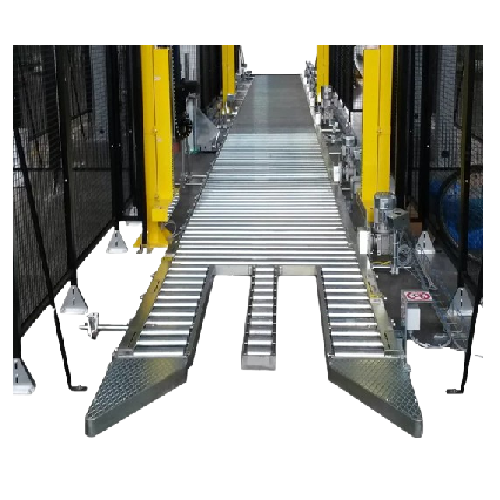

Pallet handling system
Streamline your production line with advanced pallet handling solutions that efficiently automate conv...
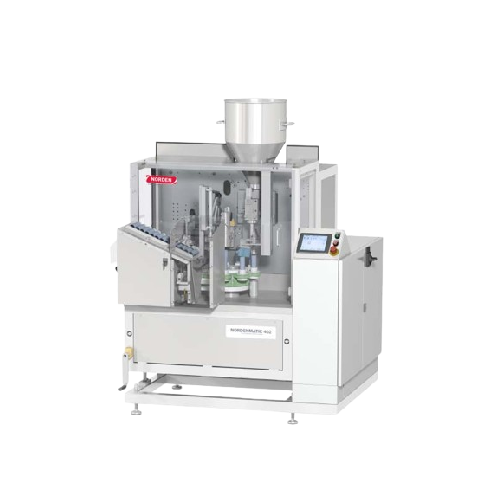

Tube filling solution for plastic and laminate tubes
Ensure precise tube filling and sealing with quick changeovers, enha...
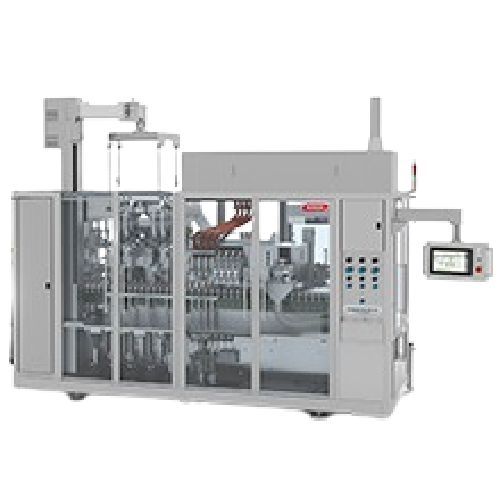

Tube filling station for plastic, laminate, and aluminum tubes
Efficiently seal and fill various tube materials, ensurin...
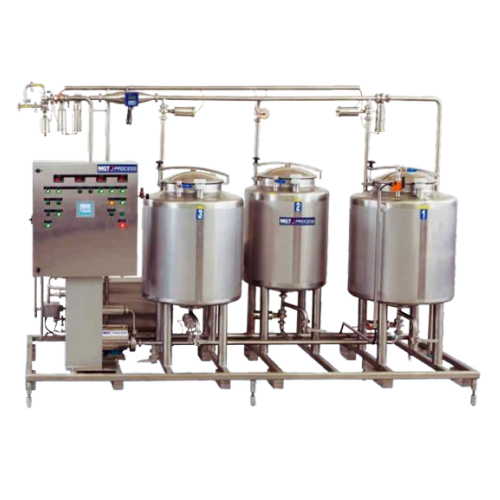

Cleaning-in-place (cip) systems for hygienic processing
Elevate hygiene standards in your liquid processing line with an ...
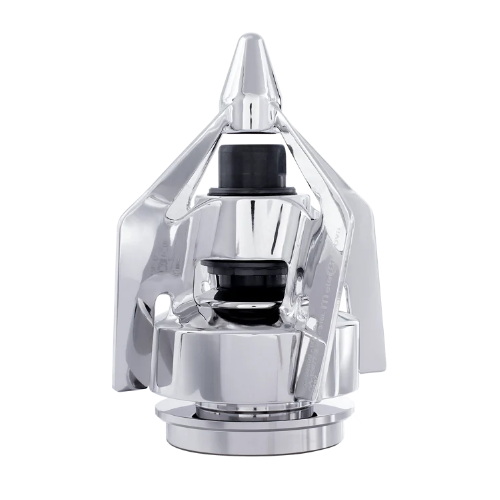

Versatile magnetic mixer for pharmaceutical and biotechnology applications
Optimize your biopharmaceutical mixing proc...
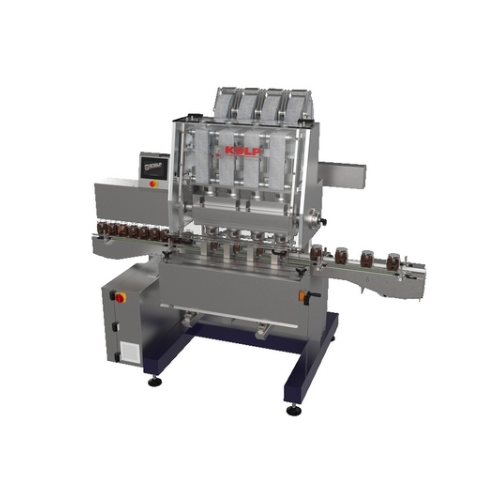

4 head sealing system for plastic and glass jars
Achieve precision sealing for jars of various materials with this high-sp...
Volumetric filling and capping solution for liquids and viscous products
Effortlessly integrate high-precision filling ...
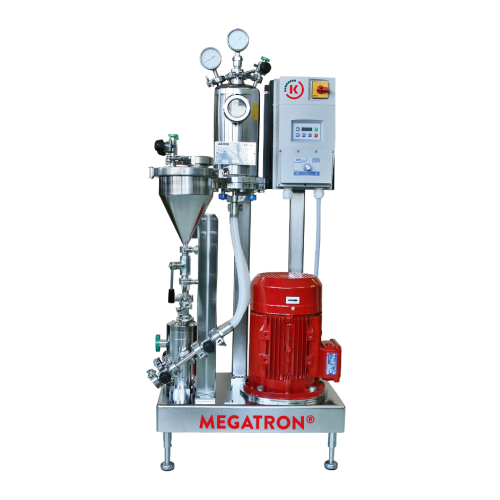

Powder induction system for high solid concentrations
Optimize your production line with this advanced system designed to...
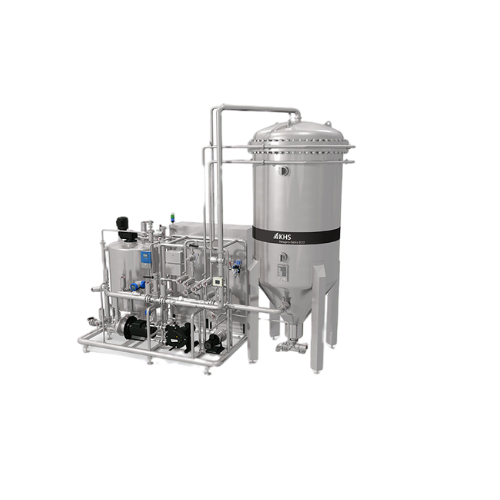

Filter system for beverage stabilization and clarification
Ensure your beverages are crystal clear and stable with a ver...
Energy-efficient hot filling system for beverages
Optimize your beverage filling processes with a system that ensures pre...
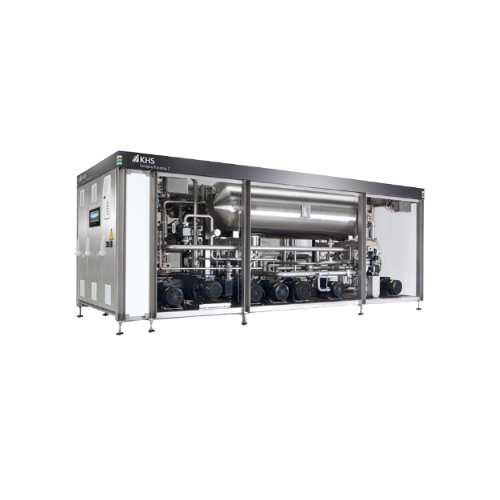

Blending system for deaeration and carbonation of beverages
Achieve precise blending, efficient deaeration, and accurate...
Aseptic linear filler for sensitive beverages
Experience unparalleled versatility and efficient aseptic filling with advan...

Pet bottle stretch blow molding with coating and filling
Extend the shelf life of your beverages and liquid products with...

Transparent glass barrier coating for Pet bottles
Ensure the longevity of sensitive beverages and liquid foods with glass...
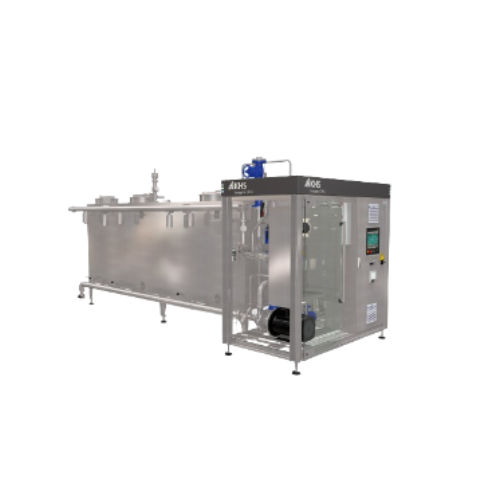

Compact cleaning system in container format
Optimize your production lines with a space-saving cleaning system capable of ...

Twin-column palletizer for beverage and food packaging
Achieve seamless operation with a flexible twin-column design that...
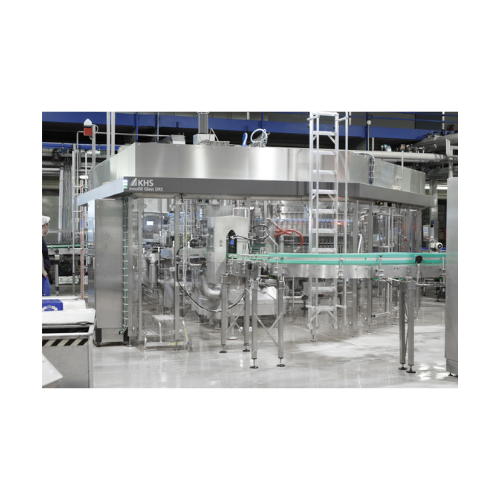

Glass bottle filler for beer and soft drinks
Optimize your beverage production with a high-speed filling solution that red...

Modular labeling system for beverage containers
Easily adapt to evolving labeling needs with this flexible system, designe...

Industrial code verification system for product packaging
Ensure flawless packaging integrity with high-speed code verif...

Horizontal element kieselgur filters
Enhance your production with a filtration system that ensures effective separation of ...

Portable agitator for high-speed mixing
Enhance your liquid formulation processes with an efficient solution for rapid mixi...

In-line high shear mixing solution
Achieve precise emulsification and particle size reduction with high shear capabilities,...
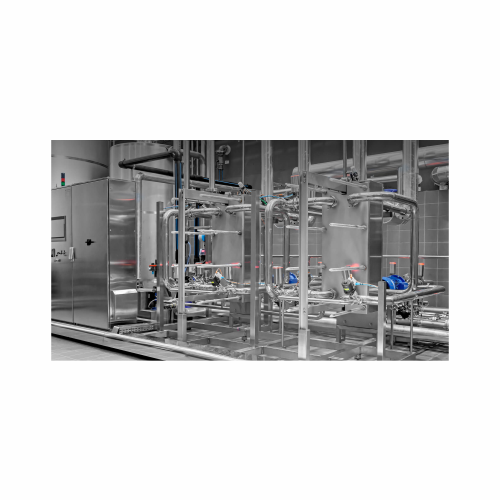

Automated system for cleaning in place (cip)
Ensure thorough, efficient cleaning of your production equipment with a syste...
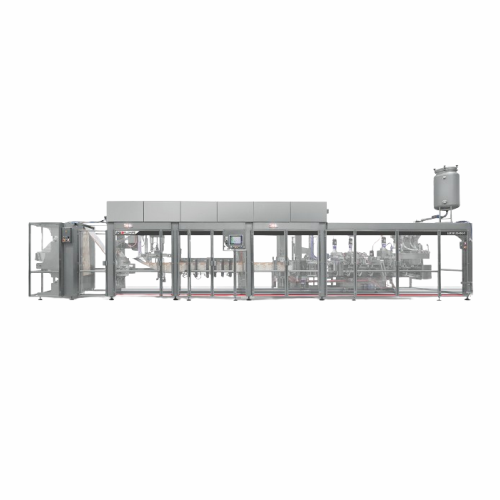

High-speed drift-dwell motion doypack forming system
Optimize your liquid packaging efficiency with a dual-motion system ...
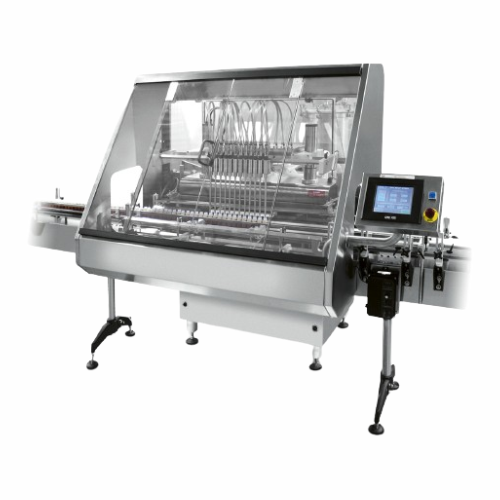

Positive displacement gear pump liquid filler
Optimize your liquid filling operations with precision gear pump technology,...
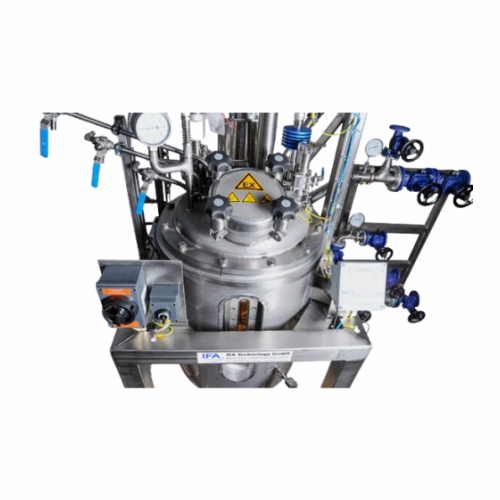

Wastewater treatment system for industrial applications
Optimize resource management and environmental impact by integrat...
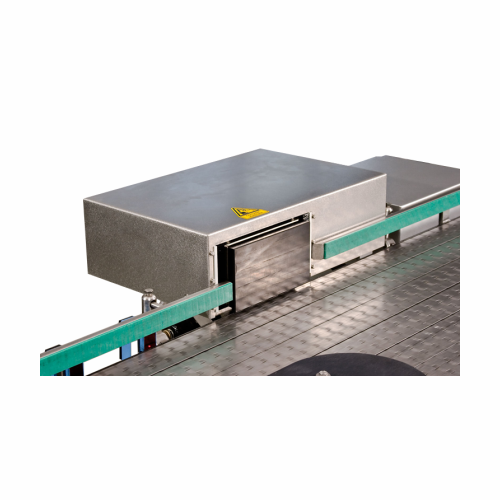

Precision case rejector for faulty packaging
Ensure seamless production flow by reliably removing defective packaging with...
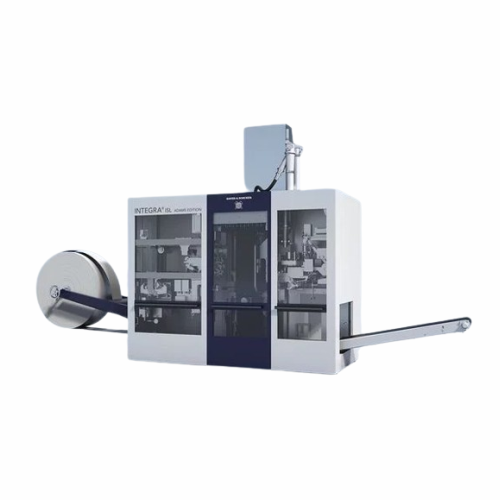

Integrated packaging system for cement and building materials
Streamline your packing operations with a fully enclosed s...
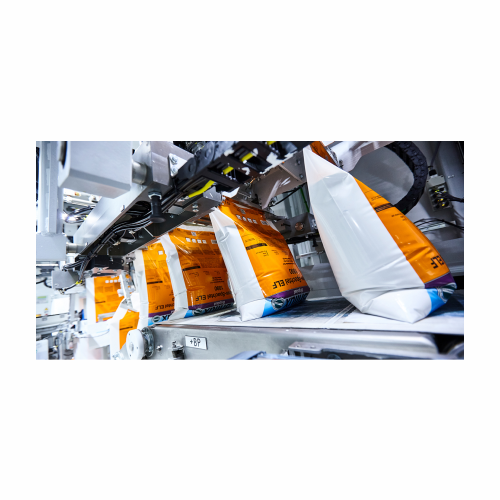

Integrated packaging system for valve and tubular film bags
Achieve precision and efficiency in your packaging line with...
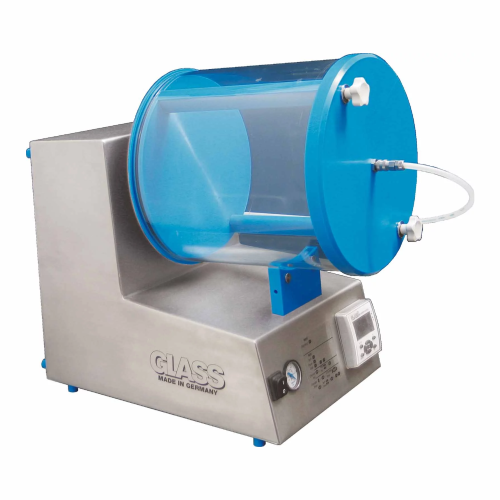

Small batch free fall mixer for food industry applications
Efficiently handle diverse ingredient integration for plant-b...
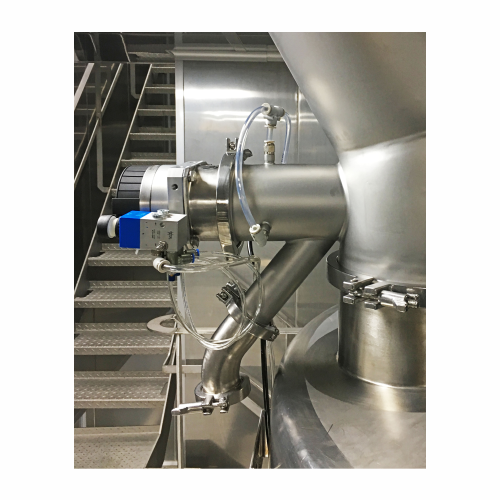

Sampling valve for secure sample extraction
Ensure product quality by safely extracting representative samples without hal...
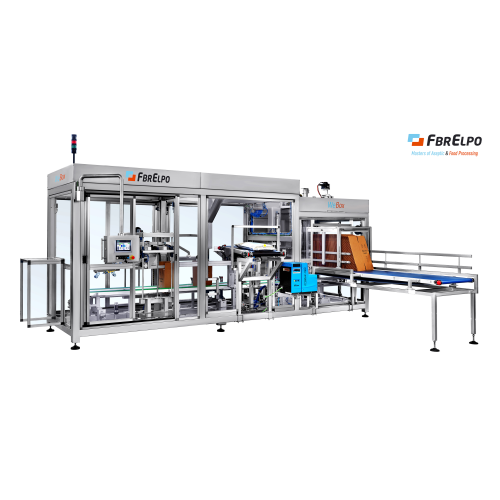

Automatic cartoning solution for 3-20l aseptic bags
Streamline your aseptic packaging with an integrated cartoning soluti...
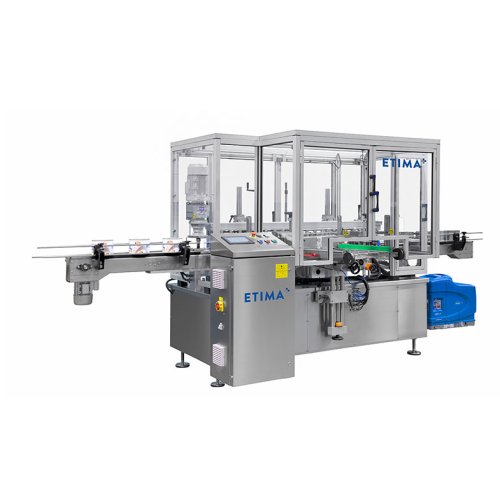

High speed wraparound label applicator for cylindrical containers
Experience efficient high-speed labelling for cylindr...
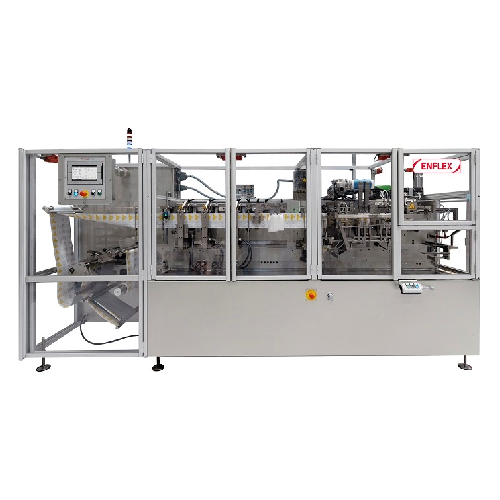

Horizontal flat pouching system for liquid soaps
Optimize your liquid packaging with high-speed, continuous operations tha...
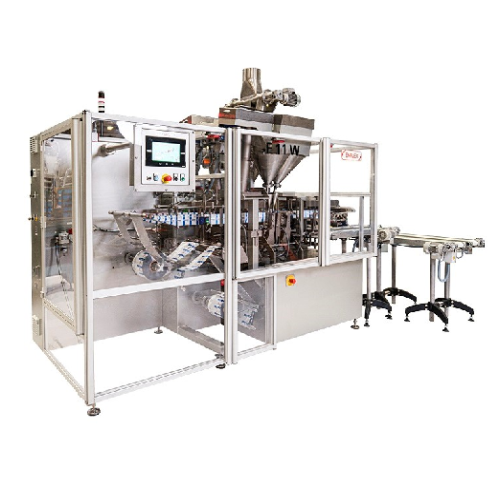

Horizontal flat pouching line for liquid soaps
Streamline your liquid product packaging with a dual-lane flat pouching lin...
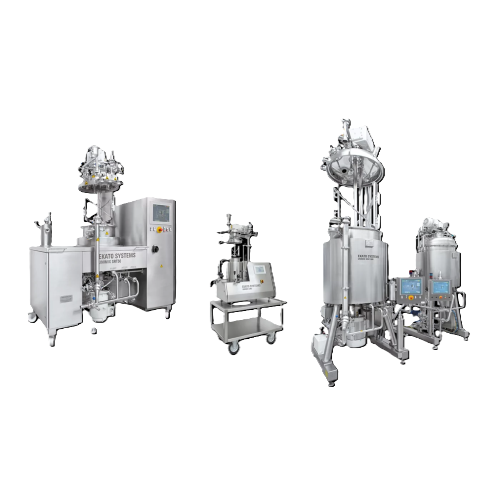

Vacuum processing units for high-viscosity products
For manufacturers seeking to streamline production of high-viscosity ...
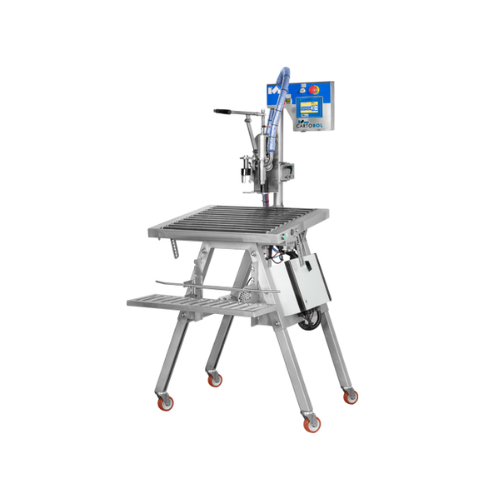

Manual bag-in-box filling solution
Streamline your liquid packaging with a compact, easy-to-operate filling system that sim...
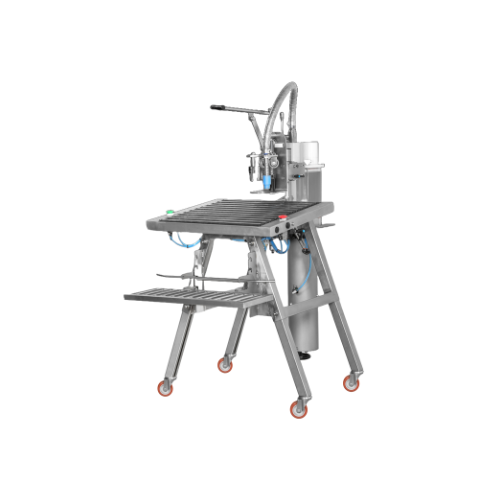

Manual pneumatic filler for bag-in-box
Experience seamless filling for liquid formulations with this pneumatic solution, en...
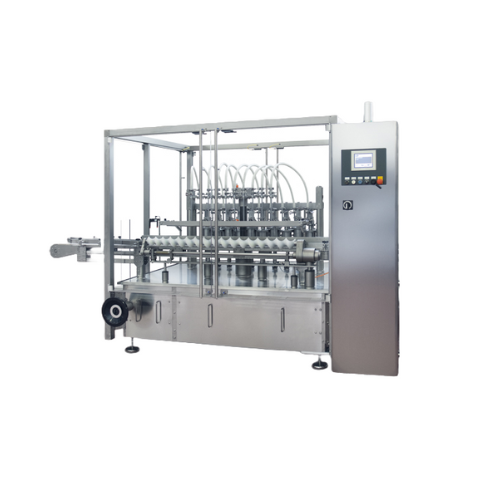

Linear intermittent motion filling system for high-density liquids
Ensure precise dosing of high-density liquids like c...
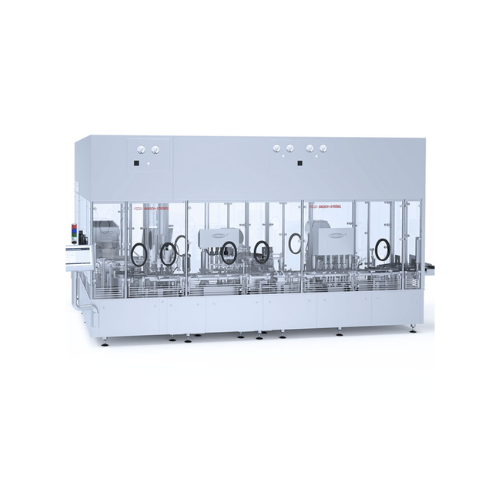

Filling and closing solution for plastic bottles
Efficiently sort, fill, and close a variety of plastic bottles with preci...
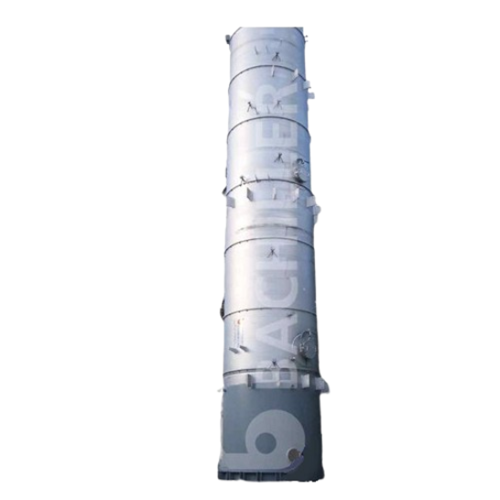

Industrial columns and towers for chemical processing
Optimize your chemical production with robust columns and towers, d...
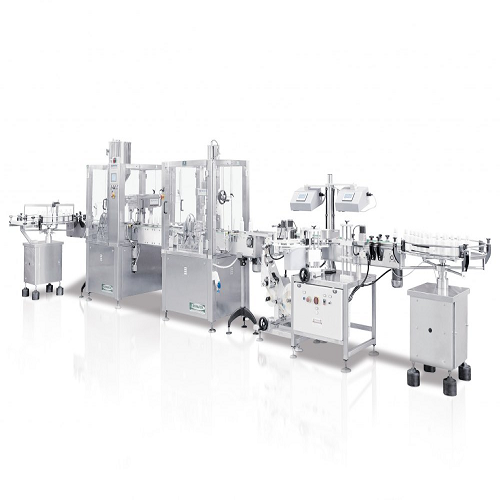

Automatic bottle filling and capping line
Streamline your liquid product packaging with this high-speed solution, integrat...
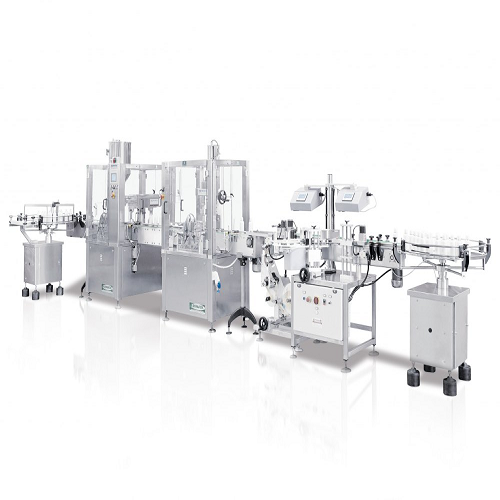

Linear filling and capping for stable bottles
Enhance your production efficiency with a solution designed for precise liqu...
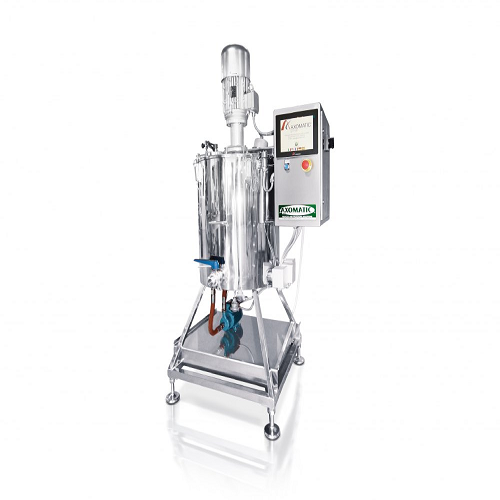

Melter for vacuum turboemulsifiers
Achieve optimal mixing, dispersion, and temperature control with precision-engineered me...
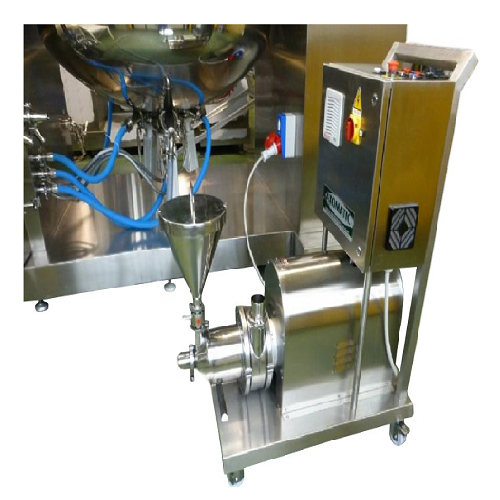

In-line external homogenizer for industrial fluid processing
Maximize fluid consistency and ensure efficient material di...
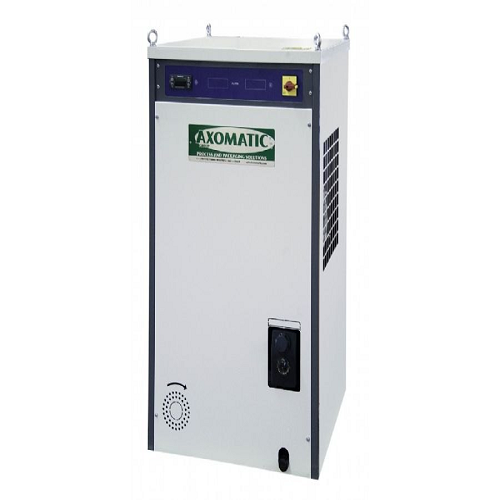

Industrial water chiller for homogenizers and filling machines
Optimize your production line with customizable water chi...
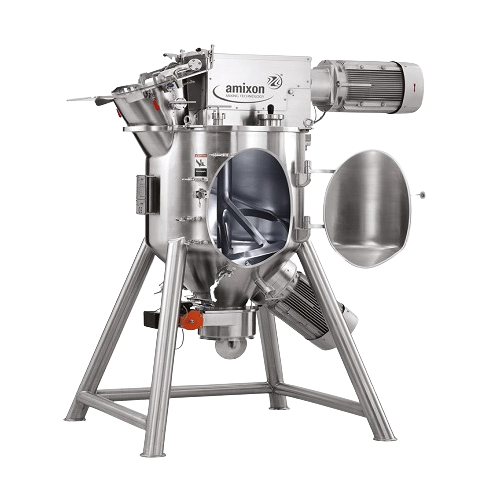

Conical mixer for dry, moist, and viscous materials
Achieve optimal mixing consistency and precision for diverse material...
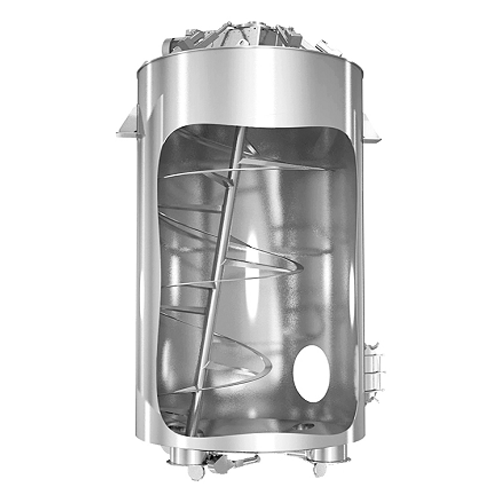

Large batch gyraton® mixer for homogenizing moist and poorly flowing materials
Optimize your production line with this...
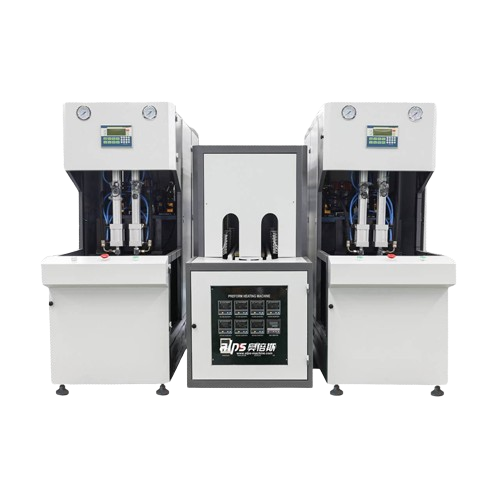

Semi automatic Pet bottle blow molding solution
Streamline your production with a semi-automatic solution designed for eff...
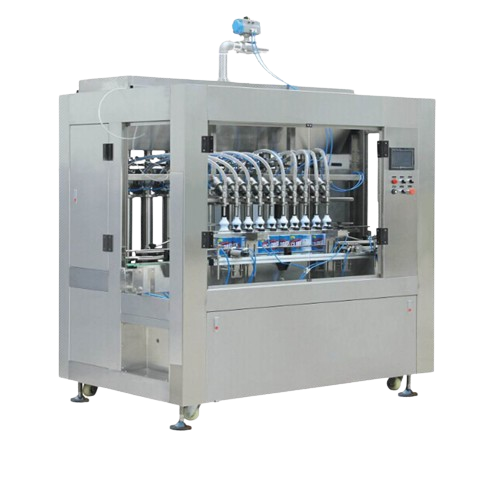

Automatic detergent shampoo filling solution
Streamline your filling process with precise volume control, achieving consis...
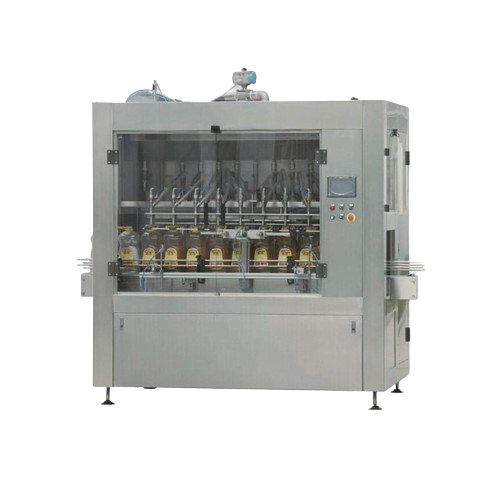

Automatic food cooking oil bottling solution
Ensure precise volumetric filling for a range of liquid products, enhancing y...
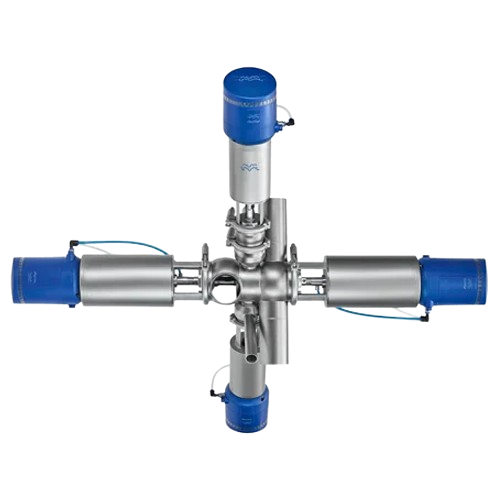

Aseptic mixproof valve for sterile processing
Ensure absolute product safety and optimize cleaning efficiency in sterile p...
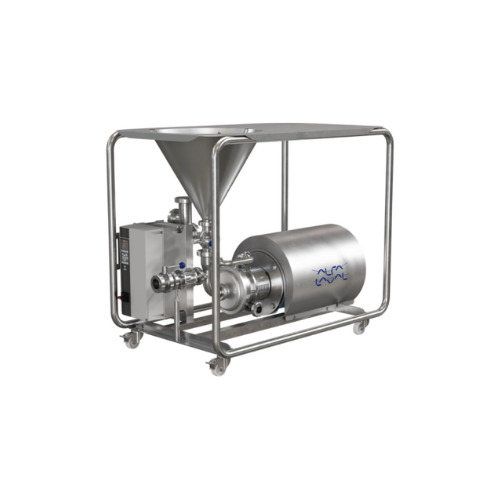

Hybrid powder mixer for powder-liquid blending
Achieve consistent powder-liquid blends with reduced processing times and e...
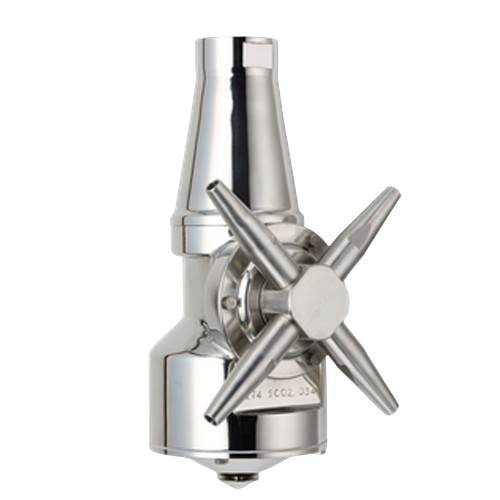

Rotary jet mixer for efficient liquid, gas, and powder mixing
Achieve seamless integration and efficiency in liquid, gas...
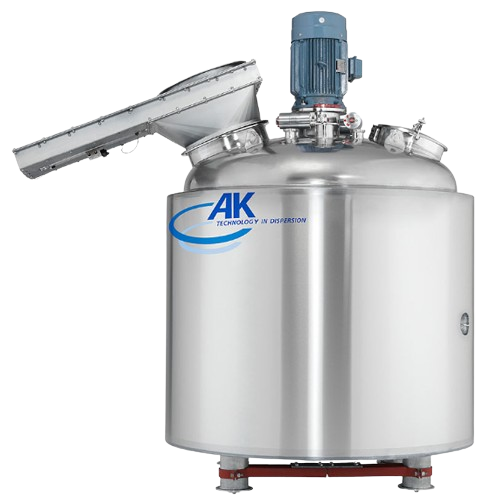

Emulsion processing system for homogenizing solids into liquids
Achieve precision in emulsifying and homogenizing proces...
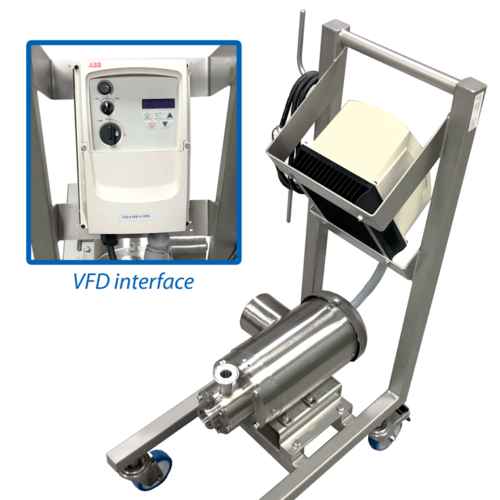

Inline continuous mixer for dairy and beverage processing
Achieve precise emulsification and particle size reduction for...
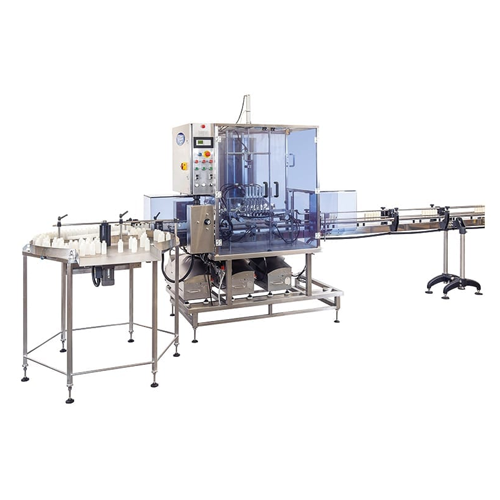

Automated bottle and jar filling solution
Streamline your production and minimize waste with a versatile filling solution,...
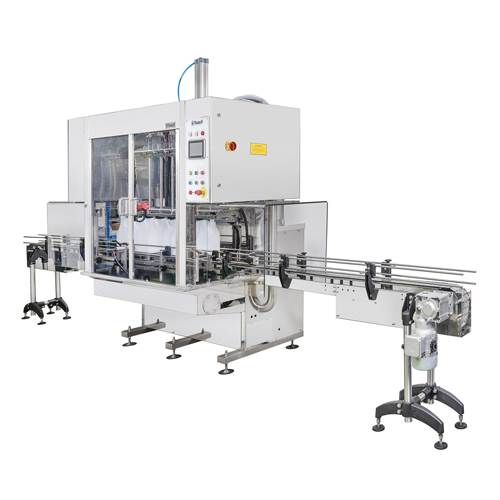

Automatic volumetric filler for liquid products
Optimize your production with this high-precision volumetric filler, desig...
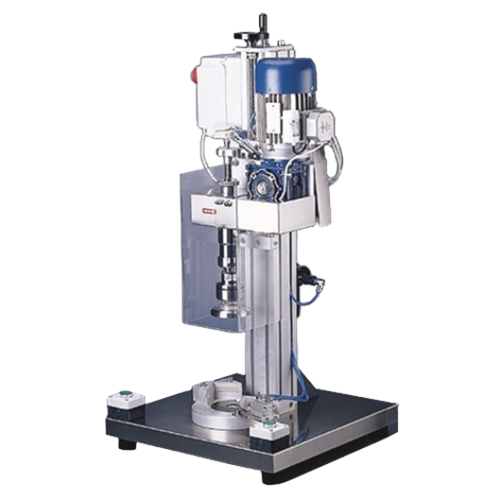

Benchtop screw capper for diverse bottle sizes
Ensure precision and efficiency in your capping process with this adaptable...
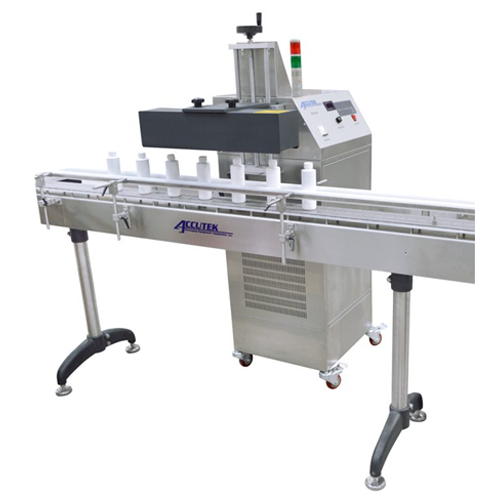

Automatic induction sealer for cap sealing
Achieve precise and reliable cap sealing with our advanced induction technology...
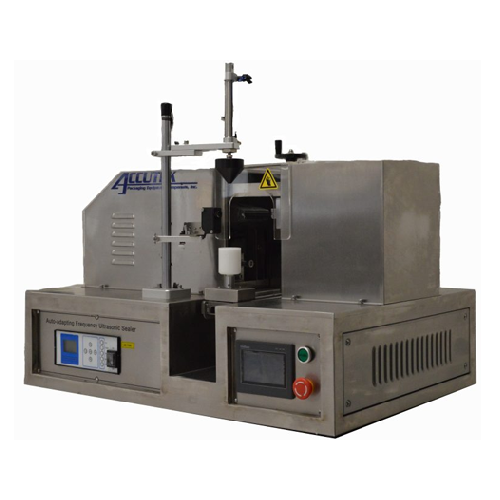

Ultrasonic tube sealer for plastic tubes
Seal plastic tubes with precision and speed using our ultrasonic technology, ensur...
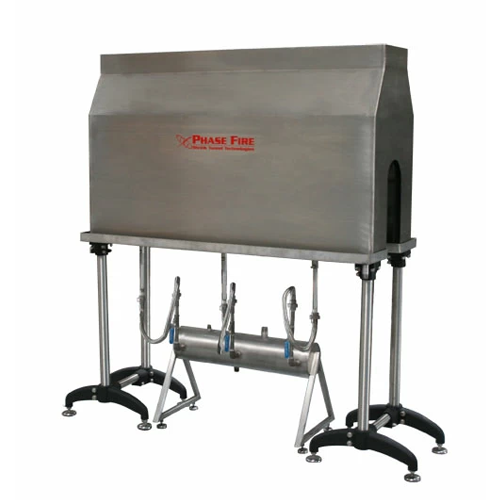

Steam shrink tunnels for versatile packaging
Enhance your packaging efficiency with this adaptable steam shrink tunnel, de...
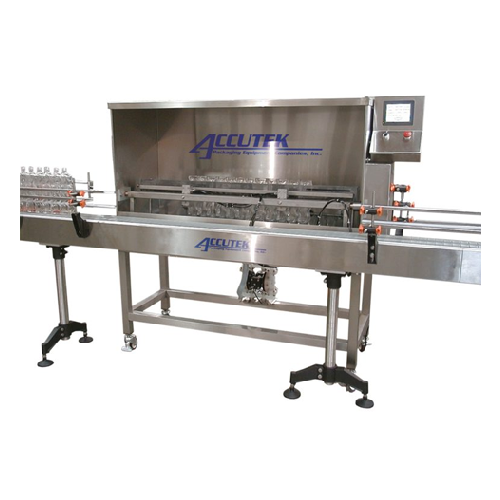

Automatic bottle washer for packaging lines
Ensure your bottles are impeccably clean and ready for filling, as this soluti...
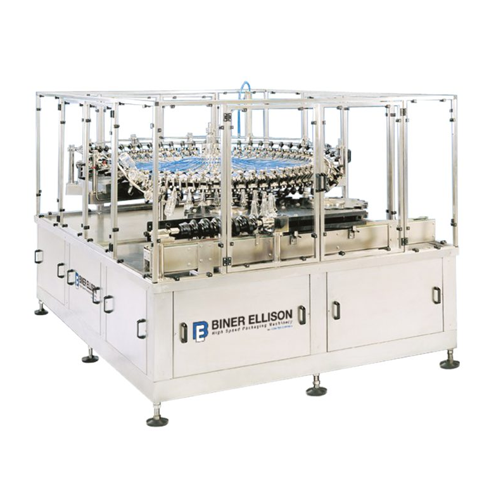

Rotary bottle rinser for high-speed production lines
Ensure thorough cleaning and preparation of containers with a high-s...
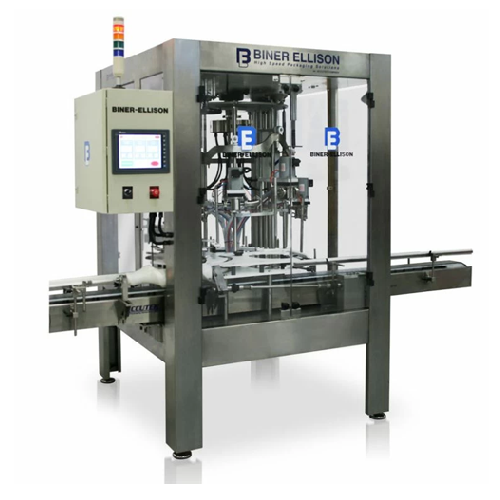

Automatic positive displacement bottle filler
Streamline your liquid filling operations with precision and flexibility, id...
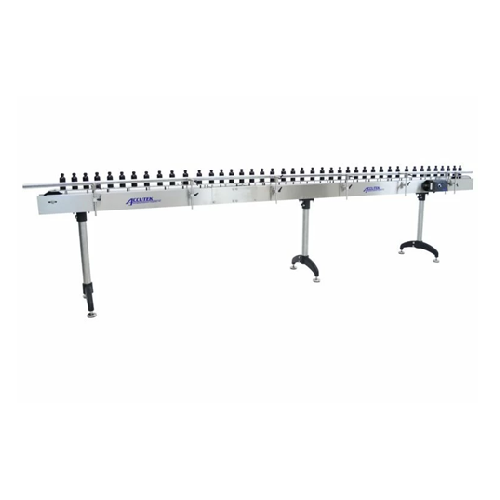

Customizable sanitary conveyor systems
Efficiently transport and handle diverse products with a sanitary conveyor system de...
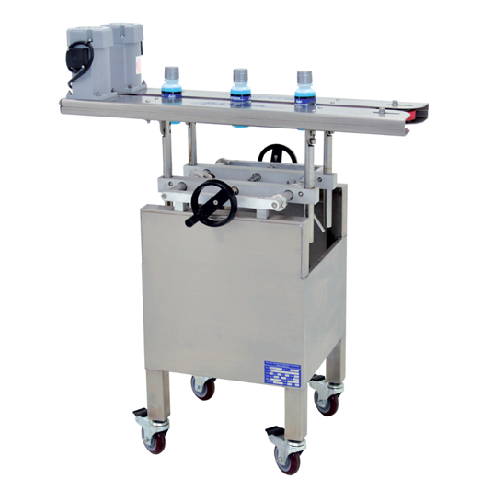

Bottomless conveyor for 90° bottle transfer and coding
Efficiently connect disparate production systems in your bottling ...
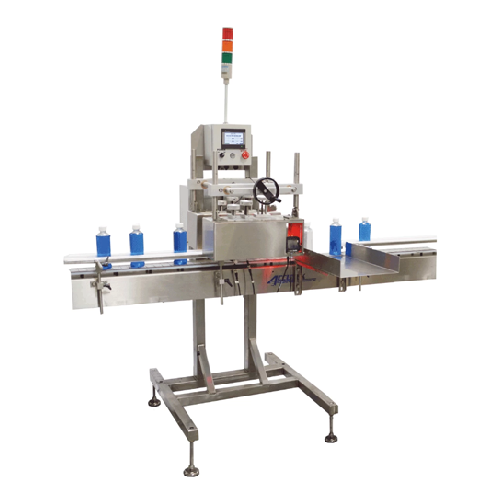

Inspection-rejection station for bottled products
Ensure your bottled and packaged products ship defect-free by automatic...
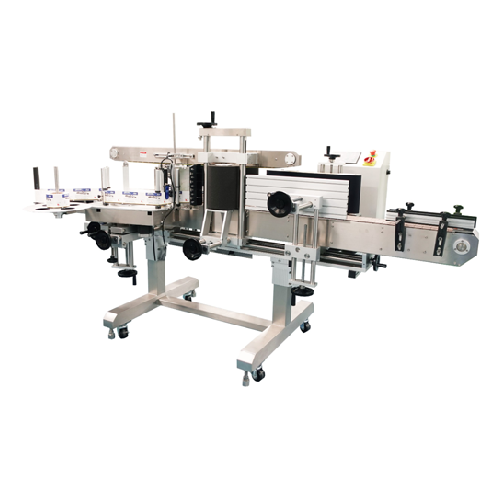

Automatic pressure sensitive labeling system
Enhance your production line’s efficiency with a versatile labeling sys...
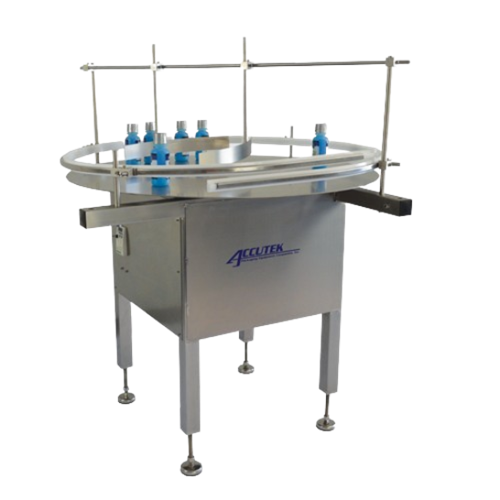

Container unscrambler for filling lines
Streamline and automate the loading of containers onto your production line with th...
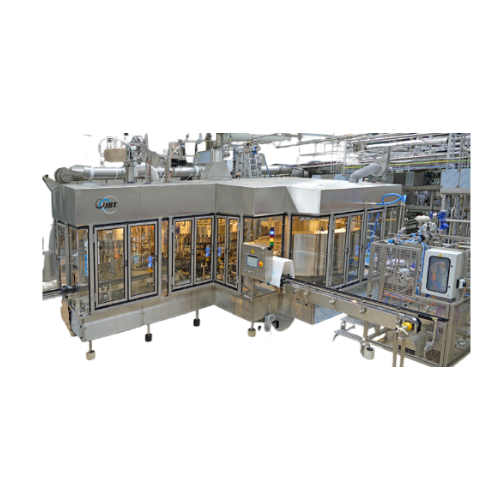

Rotary level filler for low to high viscosity liquid products
Ensure precise fill levels and enhance production efficien...

Industrial ejectors for reliable jet pump applications
Enhance process efficiency and reliability with industrial ejector...
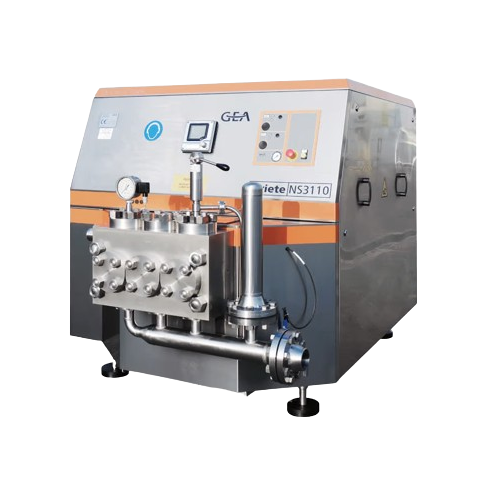

High pressure pumps for viscous fluid transfer
Optimize fluid transfer with high pressure pumps designed to handle viscous...
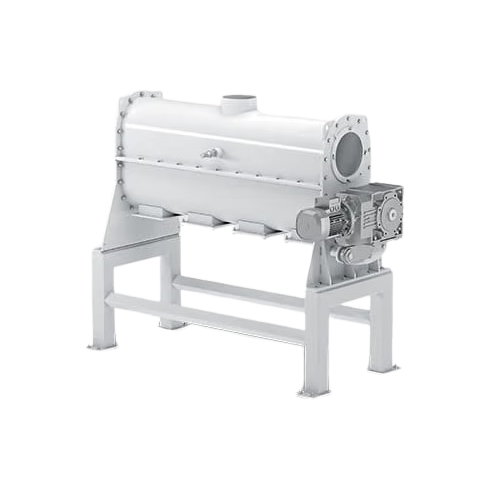

Homogenizing mixer for product distribution
Optimize the flow of your production with a high-speed distributor mixer, ensu...
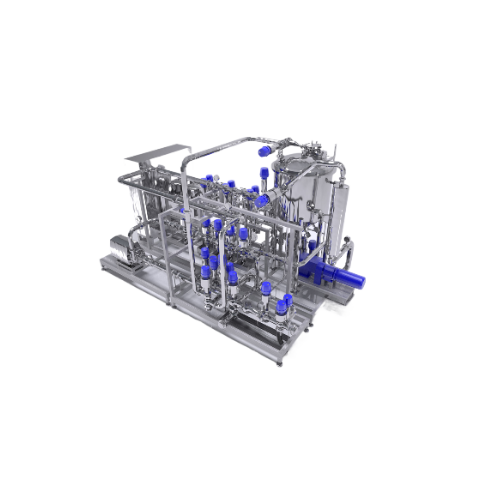
Tailor made mixing systems for personal and home care products
Achieve precise mixing for liquid formulations with conti...
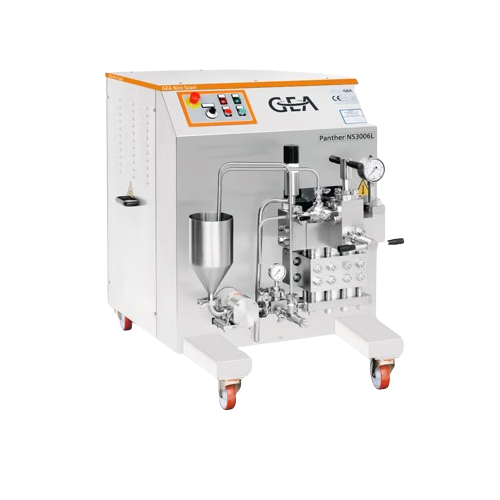

Pilot plant homogenizer for continuous operation
Achieve consistent fluid textures and prolonged shelf life with high-pres...
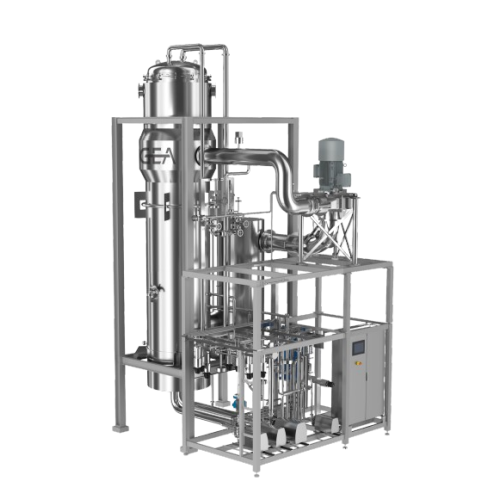

Compact plate evaporator for temperature-sensitive products
Ensure optimal heat transfer and minimal space usage with th...
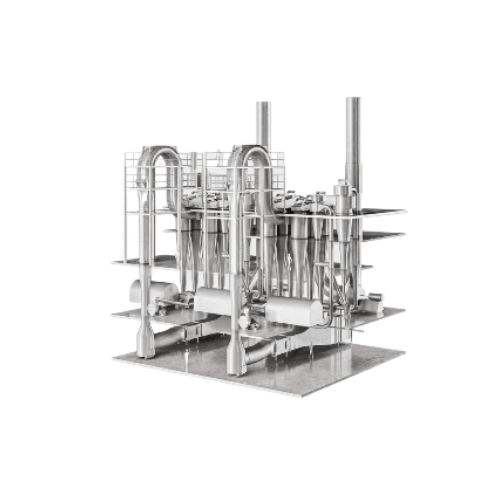
Flash dryer for industrial moisture removal
Optimize your production with rapid moisture removal, efficiently transforming...
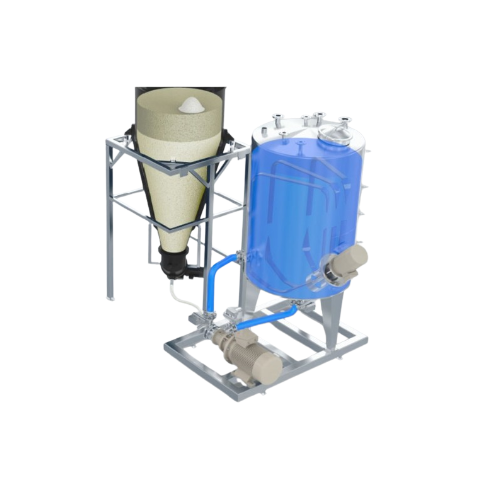

Powder wetting and dispersion system
Revolutionize your production with a system that seamlessly inducts, wets, and dispers...
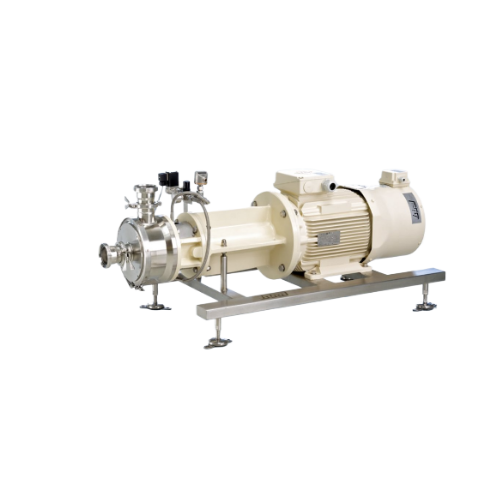

Inline disperser for homogeneous emulsions and suspensions
Achieve precise control over particle size and distribution w...
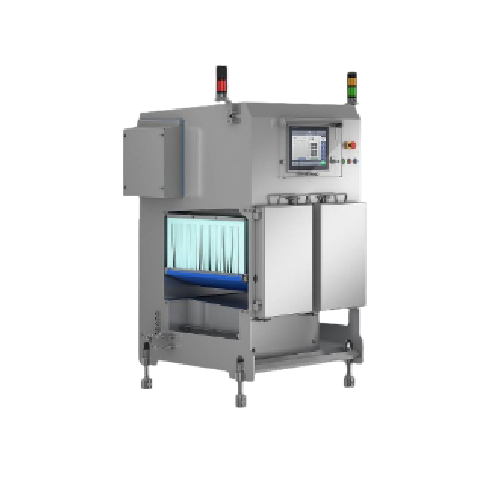

X-ray inspection system for wet environments
Ensure unparalleled product inspection under extreme cleaning conditions with...
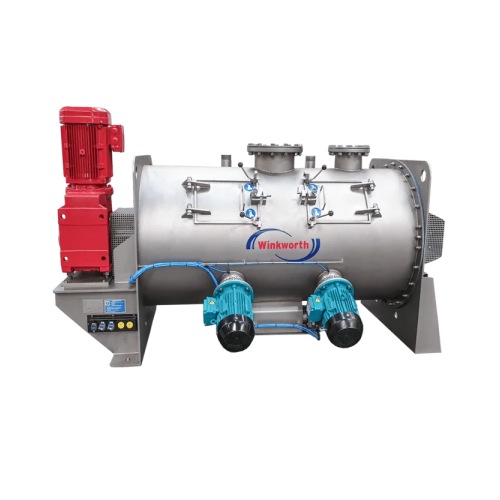

High-speed mixer for industrial mixing applications
Achieve rapid, consistent mixing and dispersion across diverse materi...
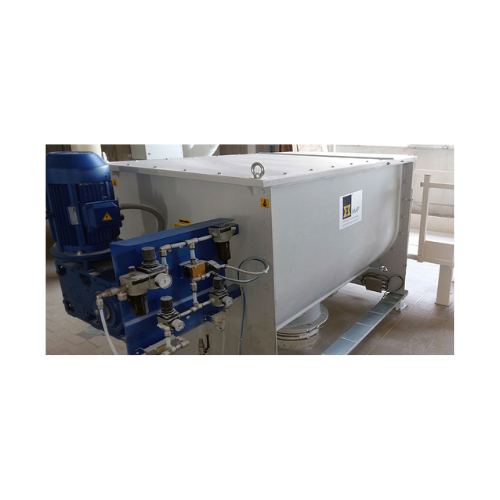

Single-shaft ribbon blender for homogeneous mixing
Achieve high-quality, precise blending of delicate and temperature-sen...
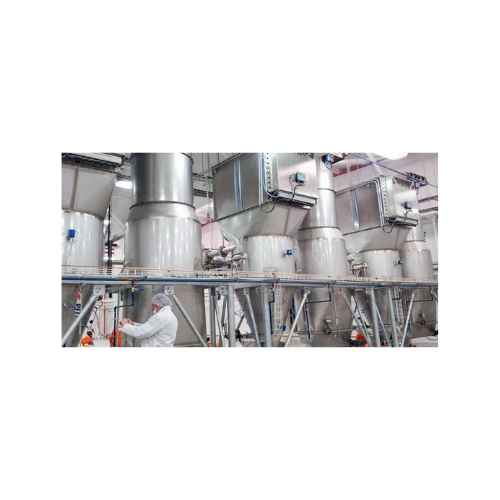

Atex-certified flanged polygonal dust collectors
Ensure dust control and compliance in explosive environments with our com...
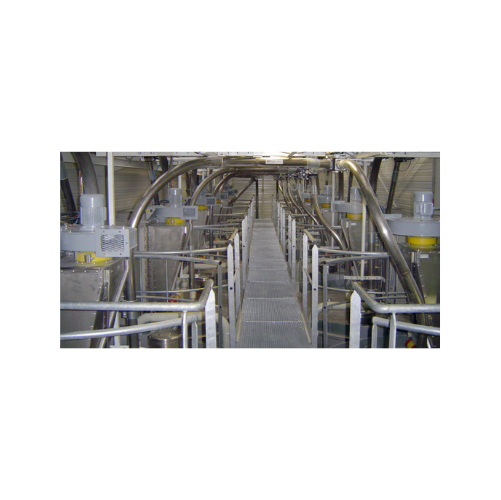

Atex certified flanged round dust collectors
Designed for potentially explosive environments, these flanged round dust col...
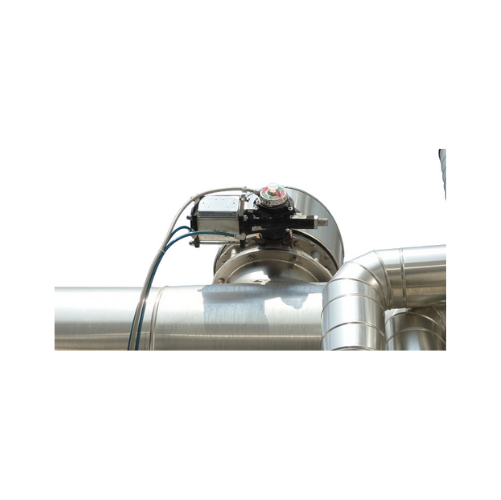

Fit-frame butterfly valves for dry bulk solids
Achieve precise control and minimize contamination in your dry bulk materia...
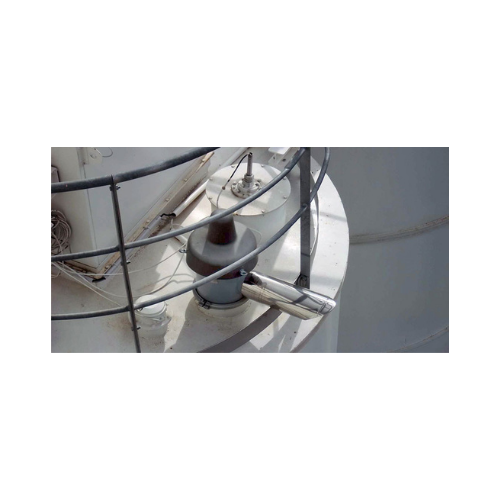

Membrane pressure relief valve for silos and bins
Ensure silo safety with our valve that instantly balances internal pres...
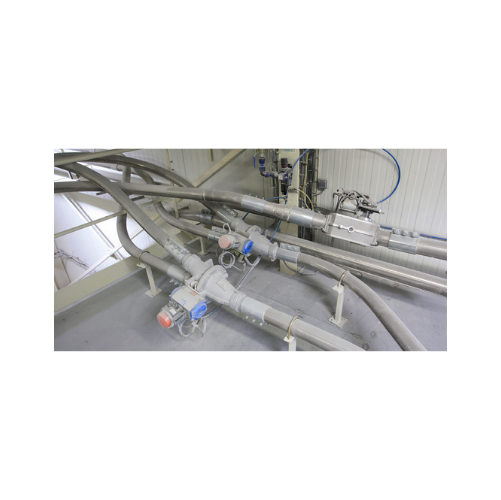

Flap diverter valves for pneumatic conveying
Streamline material flow in your pneumatic conveying system by effortlessly r...

Diverter valves for pneumatic conveying lines
Experience precise flow control in pneumatic conveying with diverter valves ...
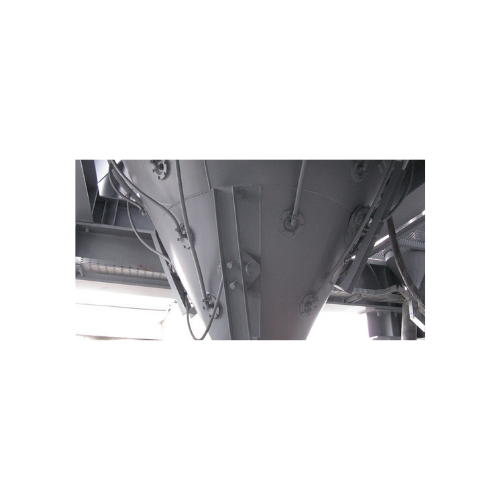

Vibro-aerators for bulk solids discharging
Optimize your powder flow and ensure consistent discharge with this advanced ae...
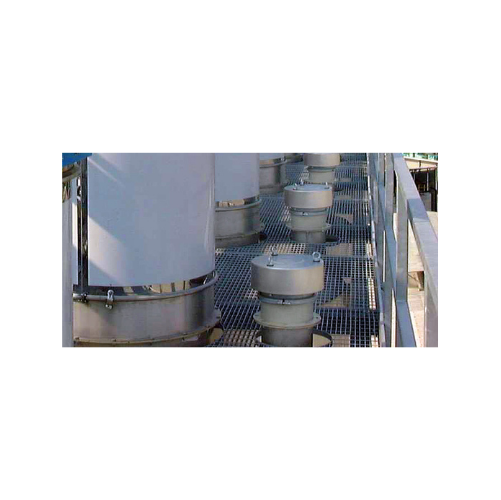

Spring-loaded pressure relief valves for silo overfill protection
Ensure safety and prevent costly overfills with press...
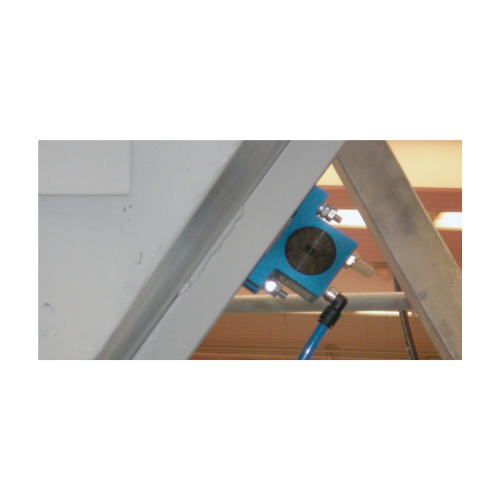

Rotary ball vibrators for fine powders and granular materials
Ideal for preventing material build-up and blockages, thes...
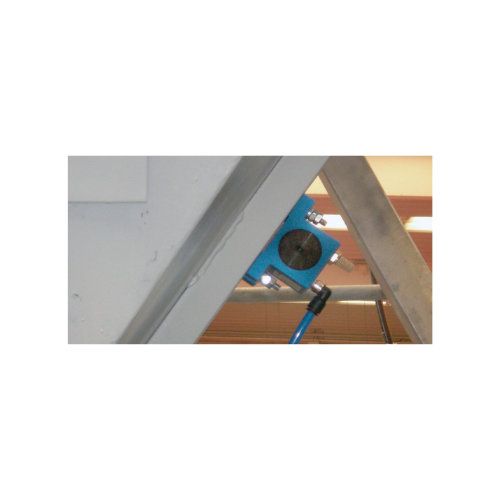

Rotary ball vibrators for bulk solids discharging
Ideal for enhancing material flow, this equipment efficiently handles f...
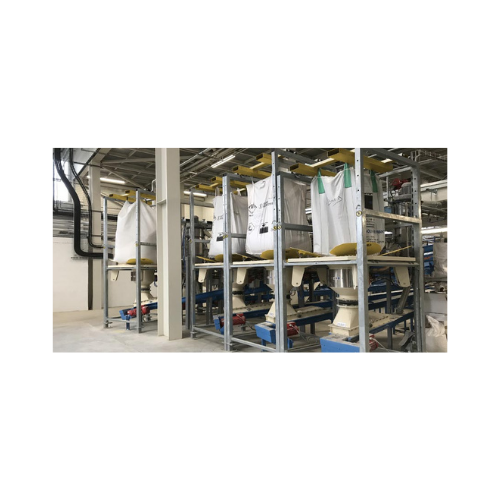

High flow rate Fibc discharger
Optimize your bulk material handling with a system designed for efficient and dust-free FIBC ...

Rotary turbine vibrators for bulk solids discharging
Enhance the efficiency of material handling with high-speed, low-noi...

Continuous impact vibrator for aggregate reclaiming
Tackle material flow challenges head-on by preventing common issues l...

External electric motovibrators for industrial applications
Optimize material movement and improve discharge efficiency ...

External electric motovibrators for bulk solids conveying
Enhance material flow efficiency and solve challenging dischar...
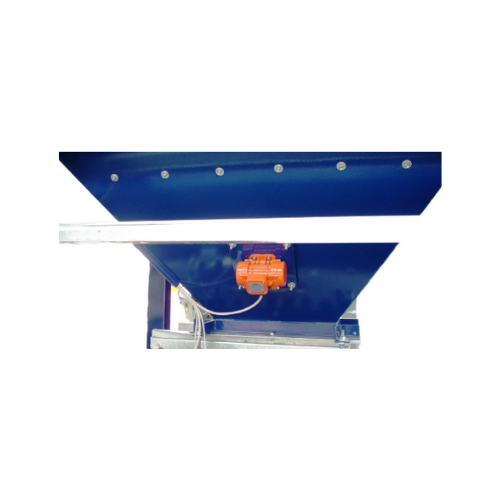

External electric motovibrators for industrial material flow
Experience enhanced material flow and precise material disc...
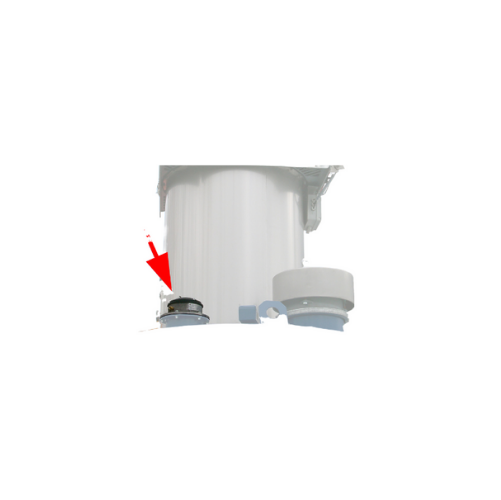

Electronic pressure meter for silo safety
Ensure the safety of your silos by efficiently monitoring internal pressure chan...
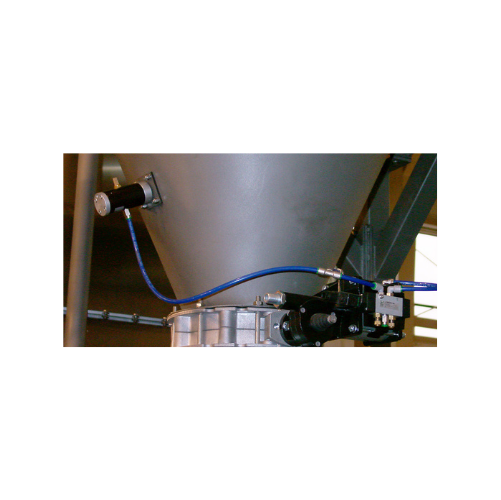

Cushioned pneumatic linear vibrators for bulk solids
Combat material bridging and rat-holing with silent vibratory techno...
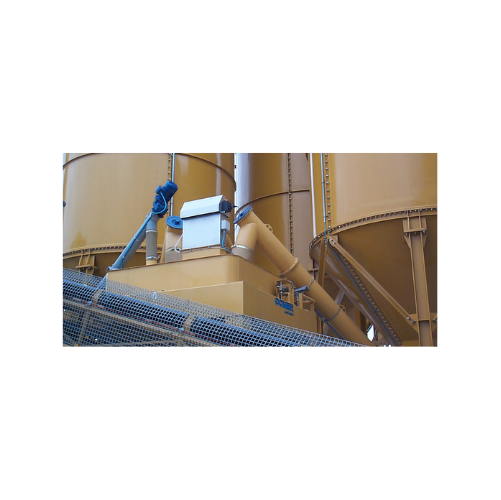

Hopper venting filter for efficient dust filtration
Achieve superior dust control and efficient material handling with a ...
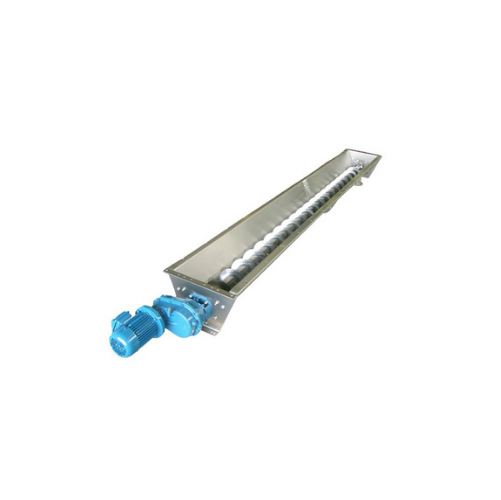

Stainless steel trough screw conveyor
Ideal for precise handling of powdery and granular materials, this solution ensures m...
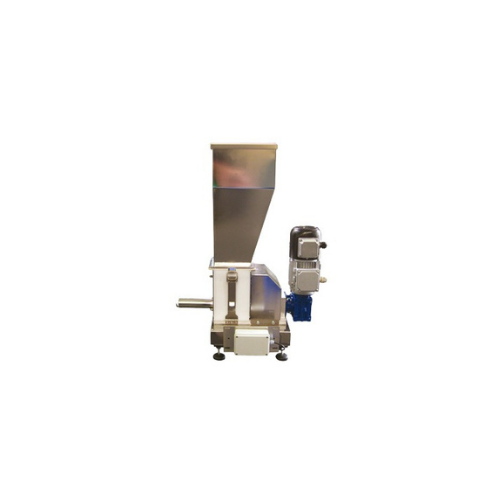

Loss-in-weight screw feeder for precise powder dosing
Achieve high precision in continuous dosing with this advanced scre...
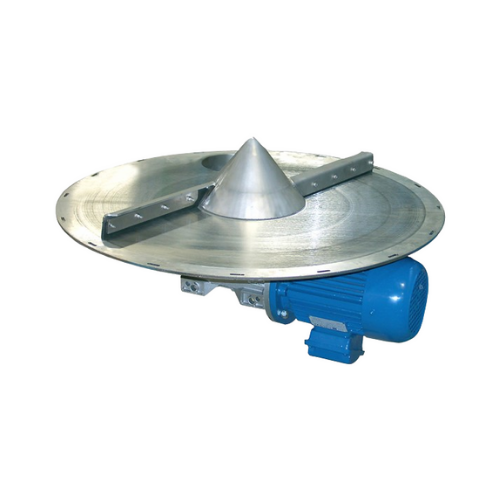

Rotary bin discharger for bulk solids
Efficiently manage bulk solids with a rotary bin discharger that minimizes residue an...
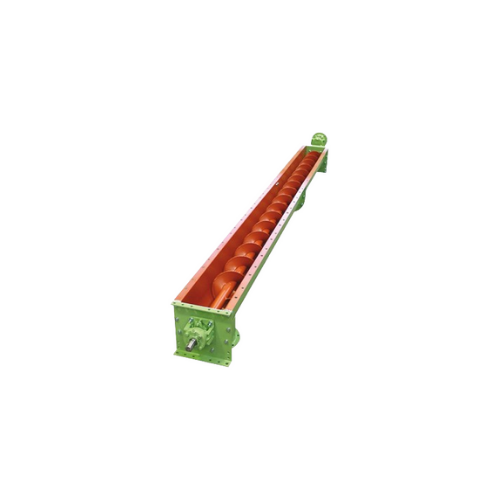

Trough screw conveyors for powdery and granular materials
Optimize your material handling process with a flexible screw ...
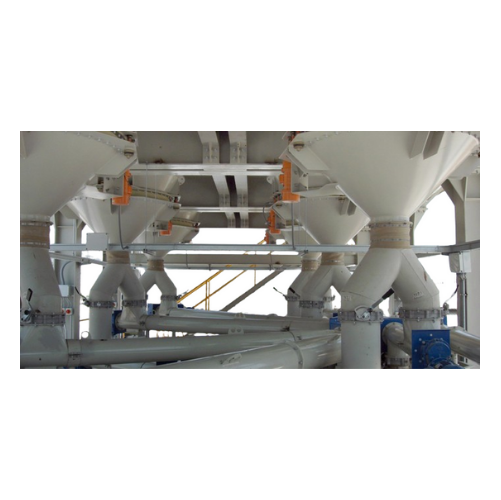

Bin activator for silo and hopper discharge
Ensure optimal material flow and prevent blockages in your storage systems wit...
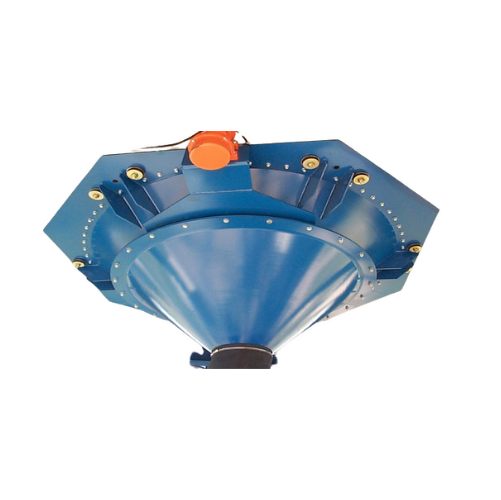

Vibratory outlet hopper for bulk solids discharge
Reduce material handling challenges with highly efficient vibration tec...
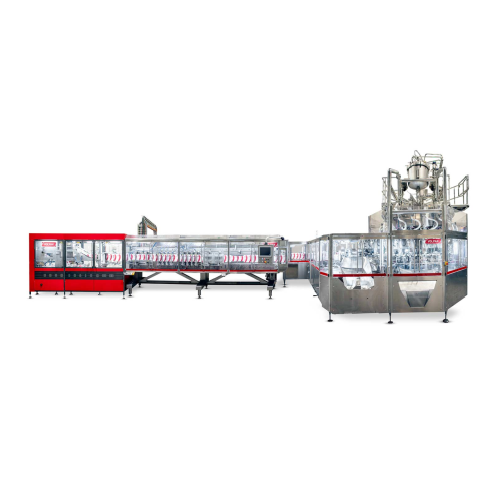
Continuous stand-up pouching solution for up to 1000ml
Maximize efficiency in high-speed production lines with precise st...

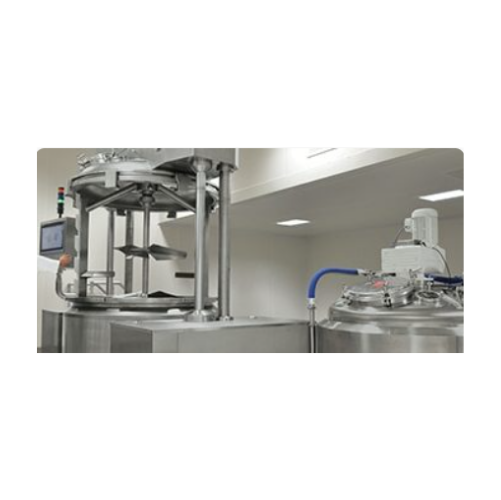
Adjustable industrial mixers for thick product blending
Experience precise blending and control for thick and high-viscos...

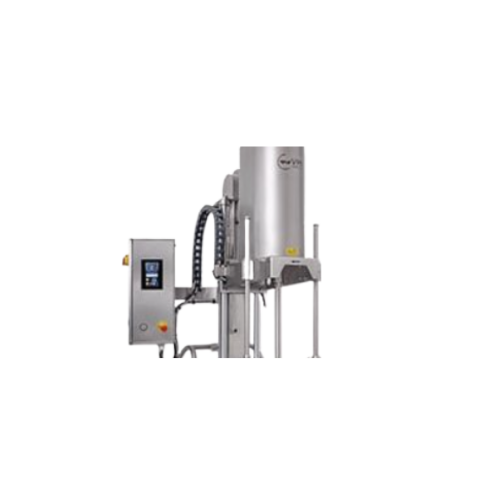
Vacuum homogenizer for cosmeto-pharma applications
Optimize your formulations with our vacuum homogenizers, ensuring prec...
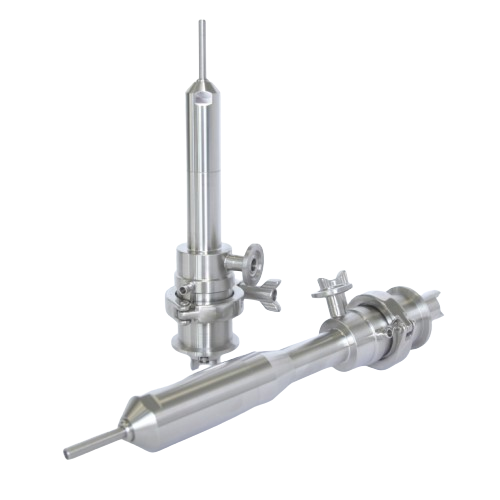

Accurate pharmaceutical dispenser for high-viscosity fluids
Achieve precise liquid dosing with ease, designed to handle ...

Fully automatic filling lines for liquids
Achieve precise dosing and filling of liquids with minimal cycle times using com...

Pressure monitoring solution for dosing processes
Optimize your production line by ensuring precise pressure monitoring, ...
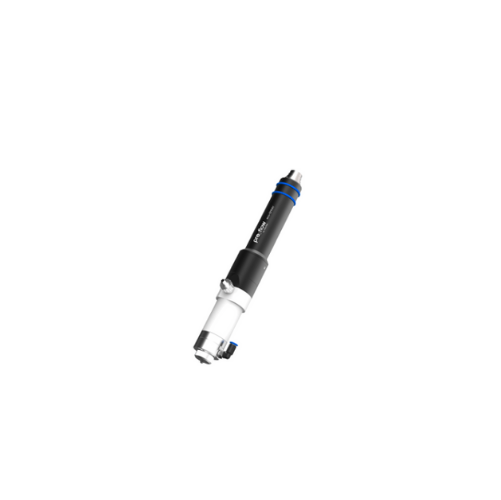

Automated precision spraying dispenser for high viscosity materials
Achieve precise spraying and consistent coating res...
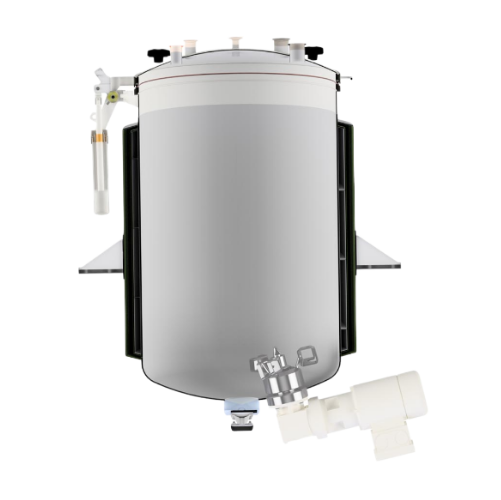

Magnetic coupling agitator for sealed mixing
Achieve leak-free, hermetically sealed mixing for critical and aggressive med...
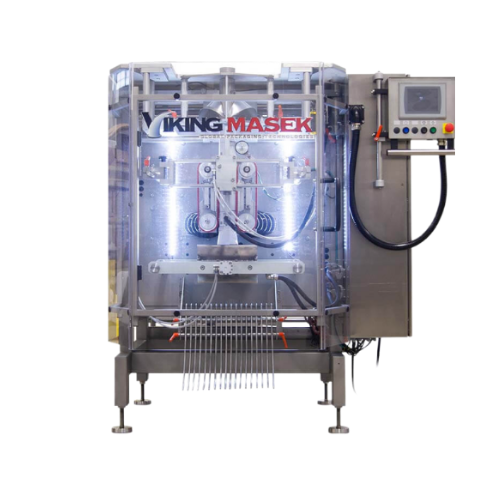

Vertical form fill seal for dusty and liquid products
Optimize your packaging line with a versatile solution designed to ...
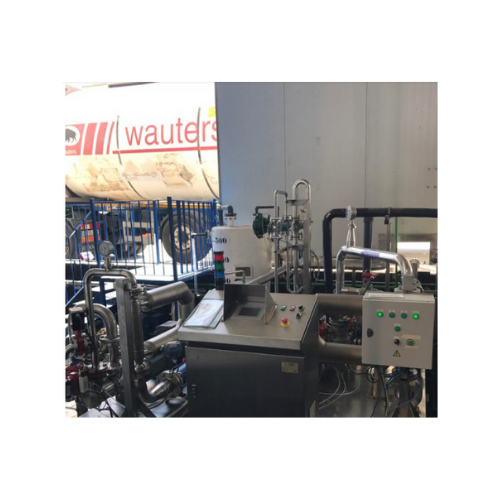

Complete mixing solutions for food, chemical, and cosmetic industries
Enhance your production line with precision mixin...
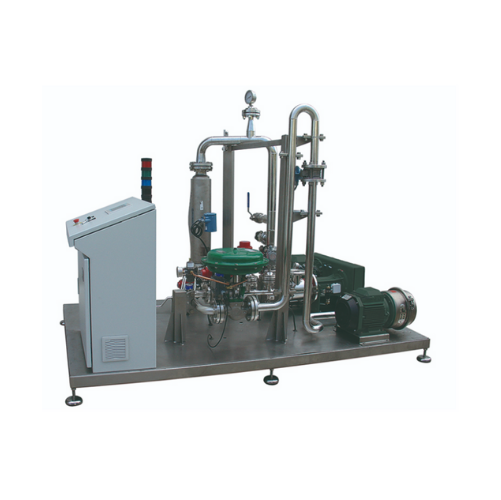

Complete mixing solution for food, cosmetics, and chemical industries
Optimize your production line with a system that ...
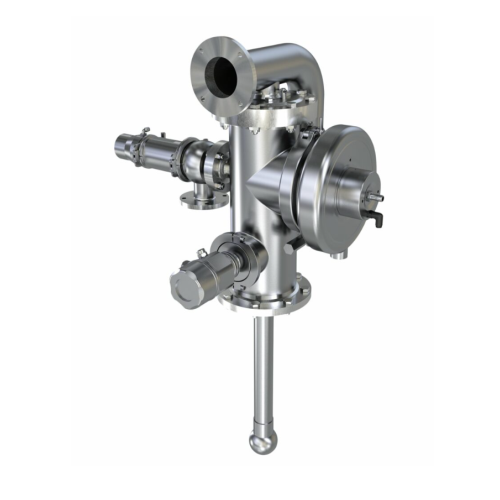

Vessel dome fittings for tank protection
Ensure seamless production by preventing tank damage due to overpressure or vacuum...
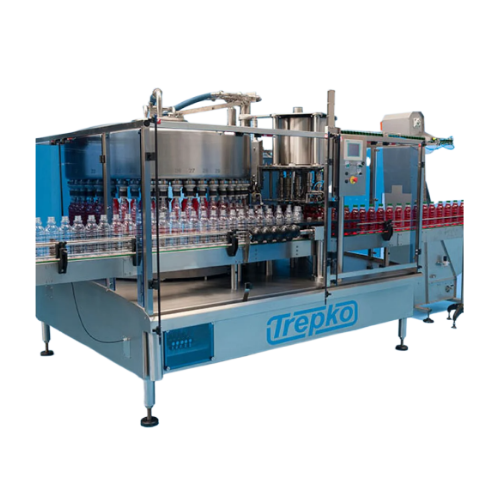

Bottle filling system for diverse specifications
Optimize your bottle-filling operations with a modular system that seamle...
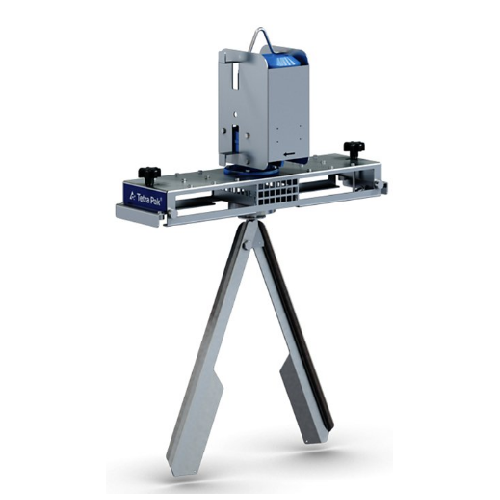

Agitator for Ibc containers
Achieve consistent and efficient mixing of various liquid products with this agitator, ensuring ...
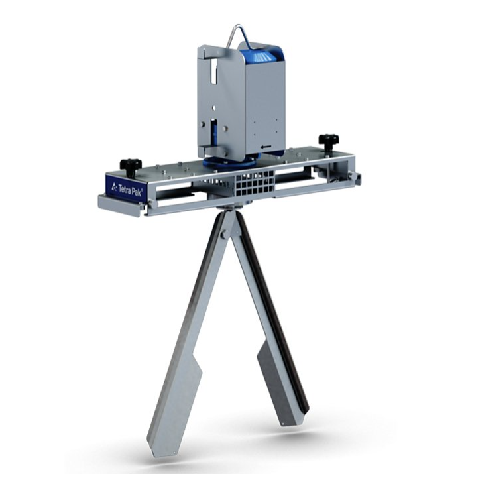

Agitator for bulk containers
Achieve consistent mixing results for low-to-medium viscosity liquids in bulk containers with o...
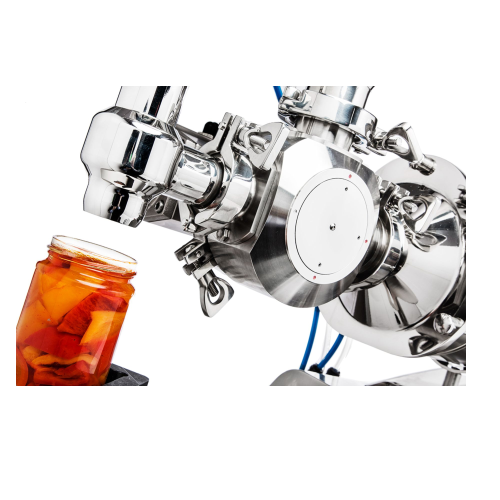

Automatic liquid filling solutions for various containers
Ensure precise liquid packaging for diverse container types, e...
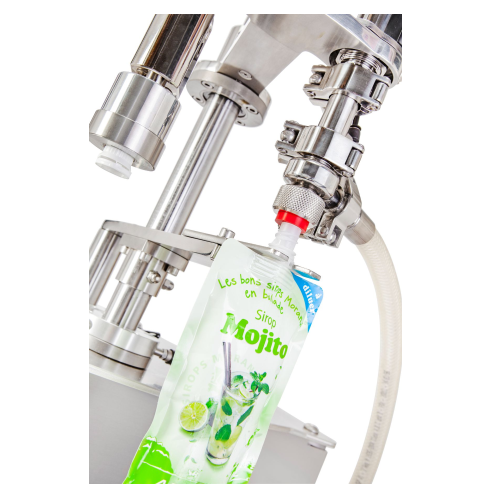

Manual monoblock for filling and capping spouted pouches
For those handling liquid or semi-dense products, this manual mo...
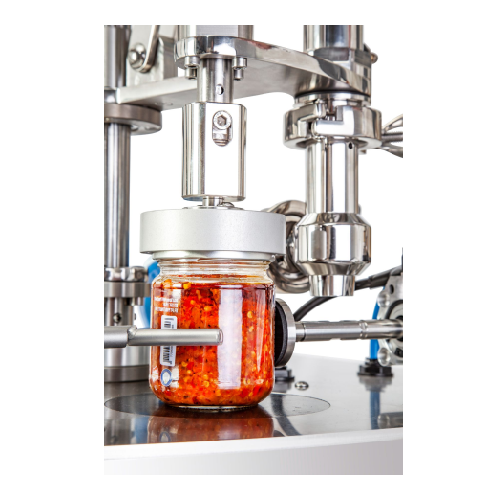

Manual dosing and capping for semi-dense products
Enhance your production line efficiency by seamlessly integrating manua...
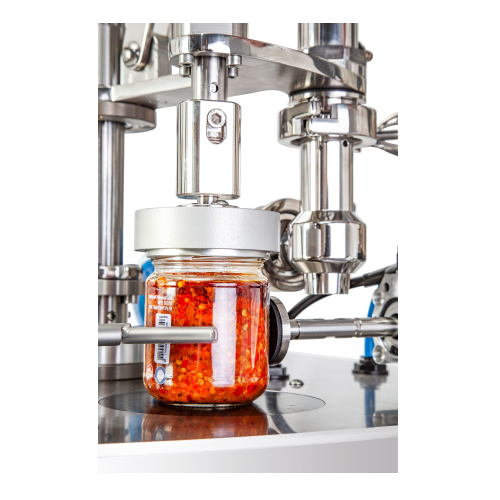

Manual system for filling and capping jars
Ideal for efficiently handling liquid and semi-dense products, this manual syst...
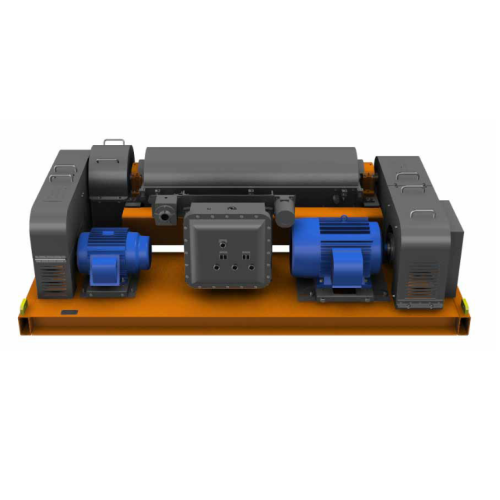
Industrial decanter centrifuge for solids separation
Optimize your production line with high-speed decanter centrifuges t...
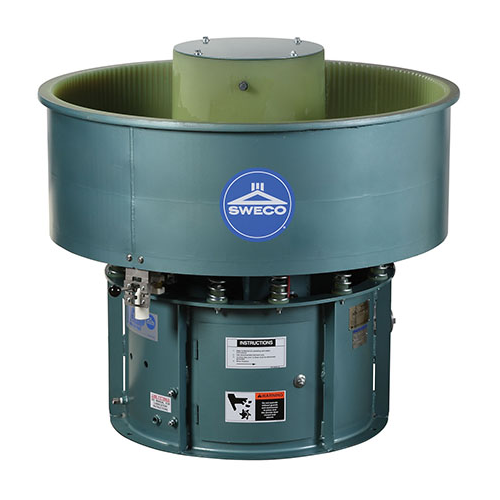

Vibratory finishing and deburring technology
Achieve precise surface finishing and deburring with advanced vibratory motio...
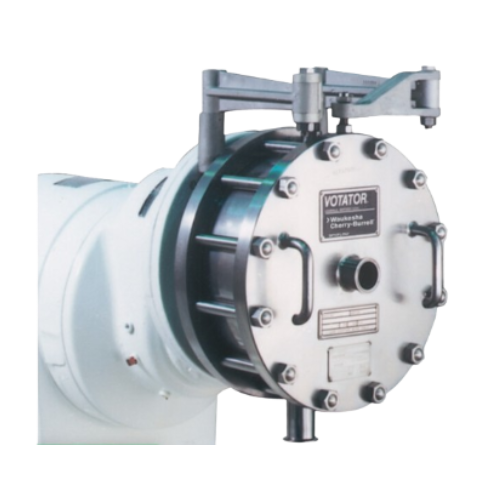

High-shear mixer for emulsions, dispersions, and foams
Achieve precise emulsions and dispersions effortlessly with high-s...

Side entry mixer for industrial tank applications
Ensure optimal mixing and blending of liquids and slurries with high ef...
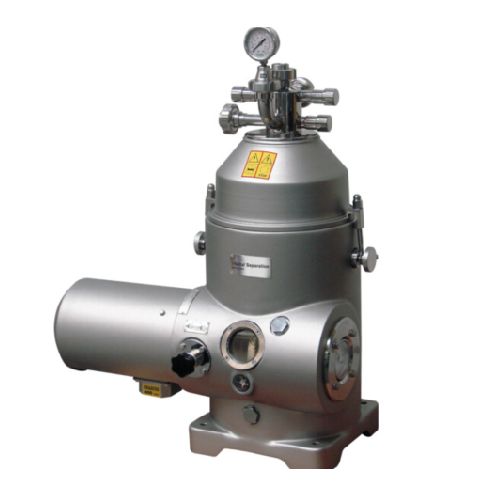

Solids retaining separator for liquid/liquid/solid separation
Achieve precise liquid-liquid-solid separation even with l...
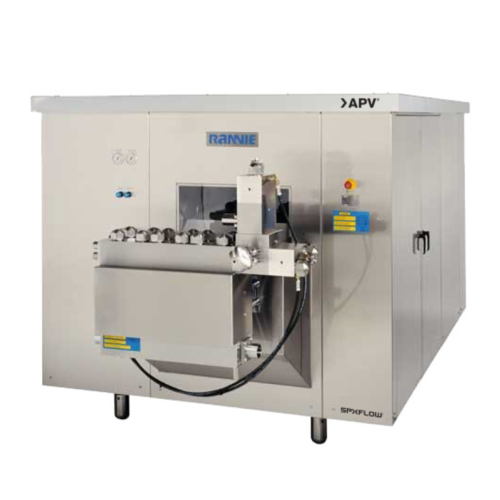

High pressure homogenizer for dairy and food processing
Achieve uniform particle size and enhance product stability with ...
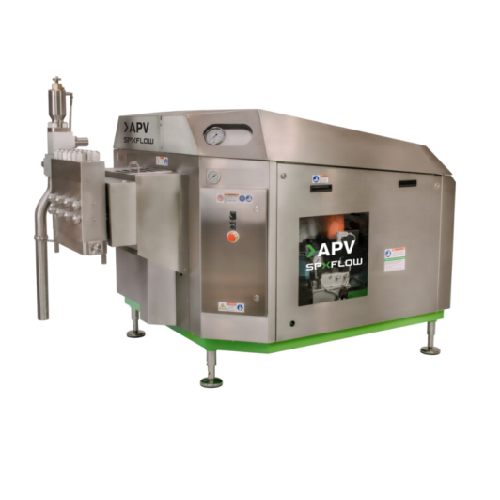

High pressure homogenizer for dairy and pharmaceutical industries
When uniform texture and stable emulsions are critica...
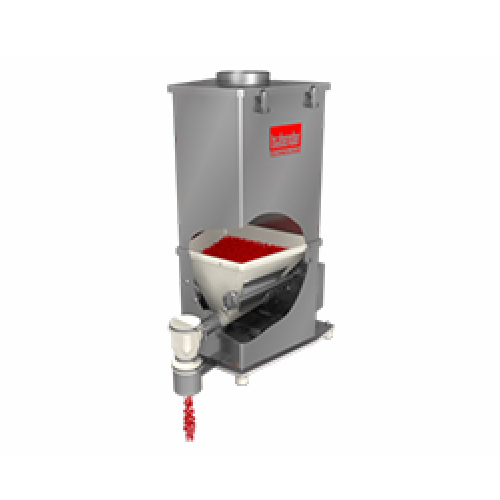

Loss-in-weight feeder for flowable ingredients
Achieve precise ingredient delivery with this feeder, designed to handle a ...
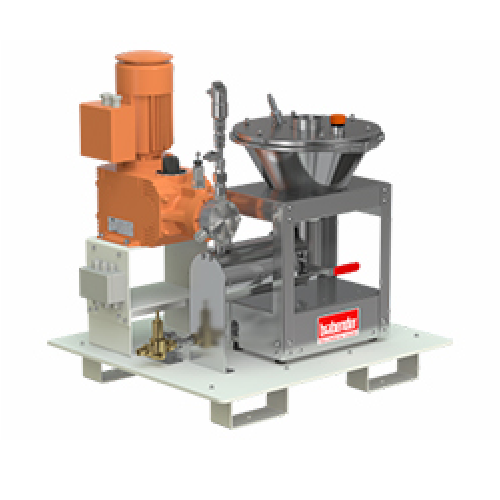

Loss-in-weight feeder for liquids
Achieve precise and continuous liquid dosing with high accuracy, adapting seamlessly to y...
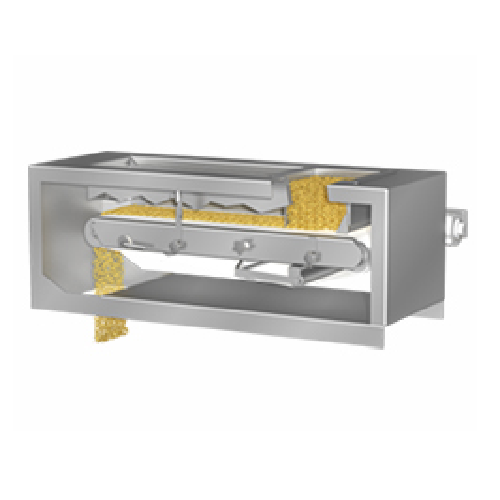

Weigh-belt feeder for industrial processes
Efficiently manage material flow and precision with a dependable weigh-belt fee...

Hopper scale for precision batching
Achieve high batch accuracy with a central weighing hopper engineered for seamless inte...

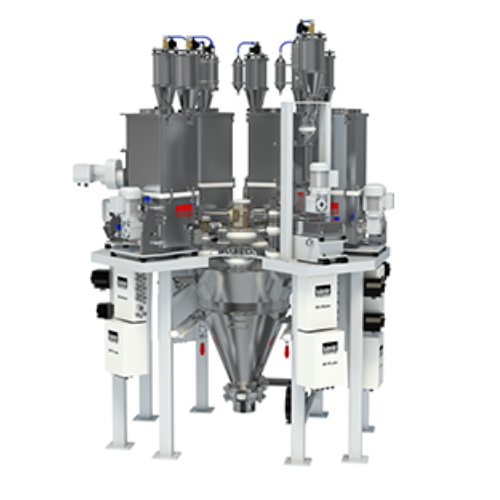
Batch ingredient dosing system for high-accuracy weight control
Achieve precise weight measurement for multi-ingredient ...
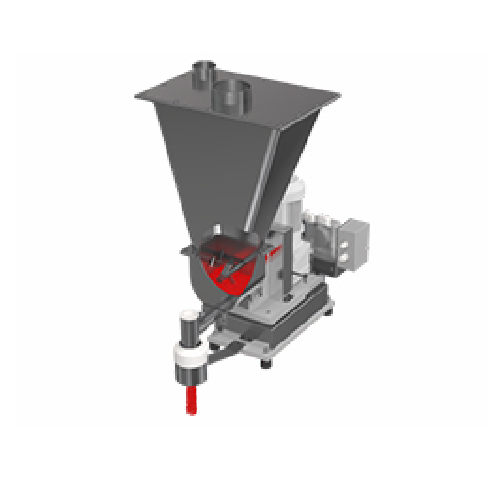

Single screw batch feeder with stirring agitator for powders and pellets
Ensure precise ingredient control and consiste...
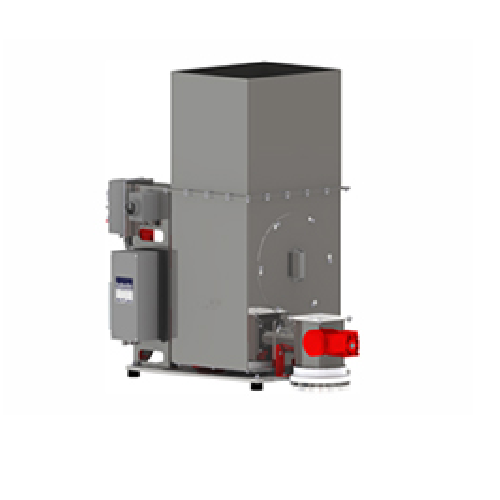

Loss-in-weight feeder for long and uneven fibers
Optimize feeding precision for challenging materials like long and uneven...
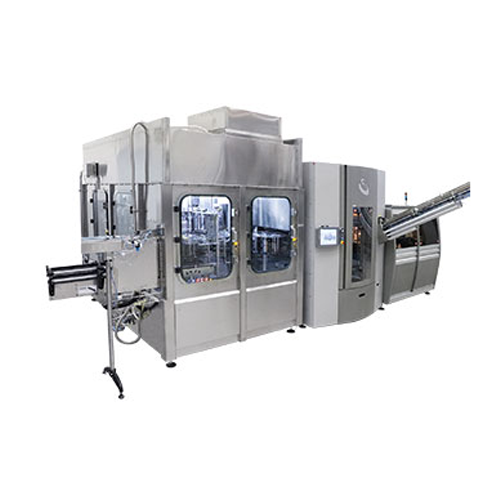

Integrated stretch-blow moulding, filling, and capping system for still liquids
Streamline your bottling process with ...
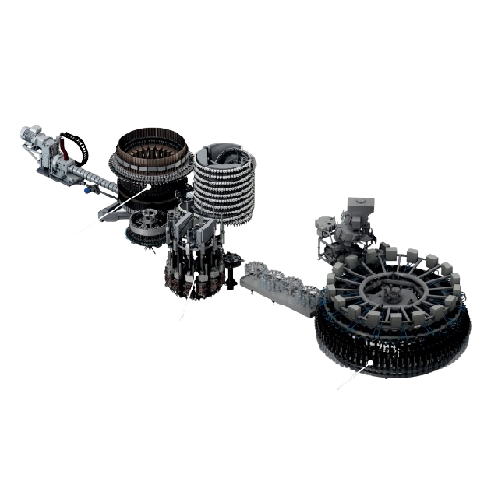

Integrated preform production and bottling system for Pet bottles
Achieve seamless production of PET bottles, from pref...

Volumetric filler for Pet bottle beverages
Experience seamless integration into your bottling line with this advanced volu...
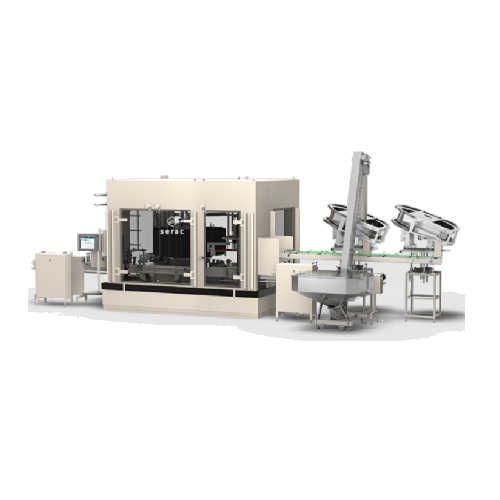

Anti-corrosion filling system for aggressive liquids
When dealing with corrosive liquids, ensure durability and safety wi...
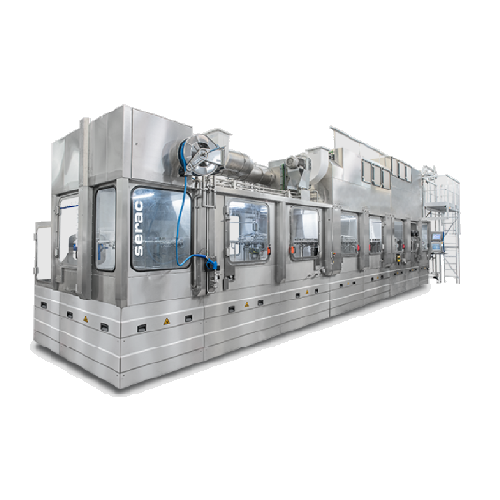

Aseptic filling technology for dairy products
Ensure product integrity and extend shelf life with a high-speed aseptic fil...

Semi-automatic weight filling system for liquid products
Achieve precise and versatile liquid filling performance with th...
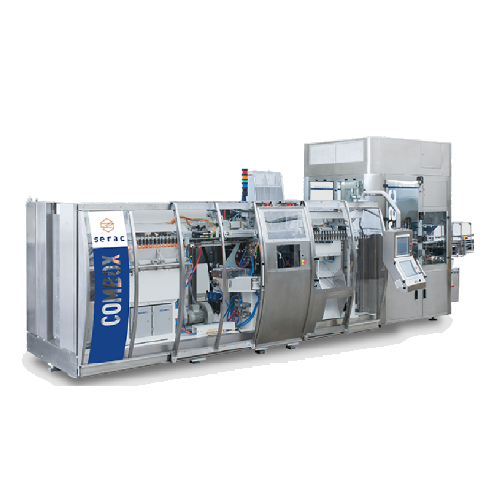

Blow-fill-cap solution for low/medium batch production
Streamline your production line with a compact blow-fill-cap syste...

Industrial grinding mill replacement parts service
Optimize production efficiency with high-precision grinding solutions ...
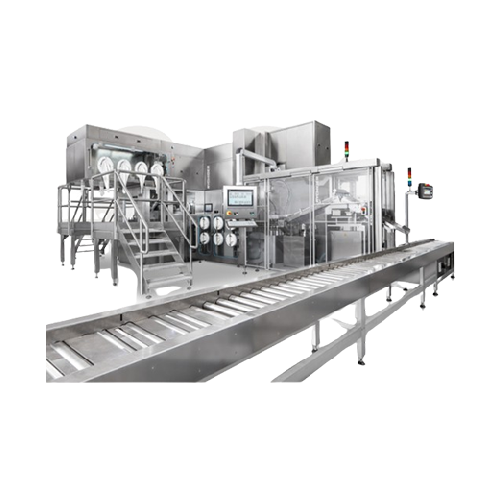

Filling solution for powders and liquids in diagnostics
Simplify precision filling of diverse products, from freeze-dried...
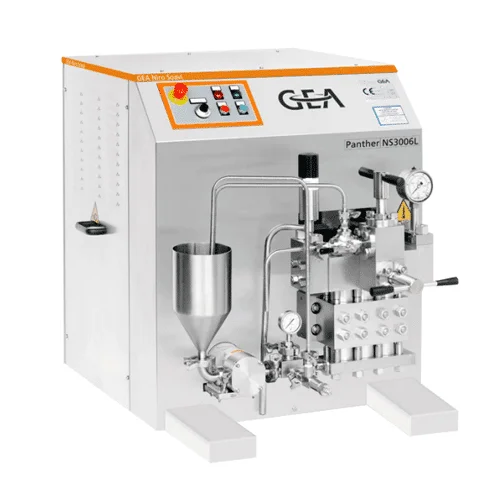

Cannabis nanoemulsification system for high-precision production
Achieve rapid bioavailability and stable formulations i...

Multifunction case packer for bottles and jars
New ways of packaging products are popping up all the time on the market. T...

Shrink wrapping machine for PET bottles
During a shrink-wrapping process, a change of reel can slow down the production cyc...

Wrap-around case packer for cans or bottles
When it comes to beer packaging, most of the manufacturers use plain box carto...

Self-adhesive linear labeling machine for bottles
It is vital to have precise and long-lasting labels on bottles to avoid...
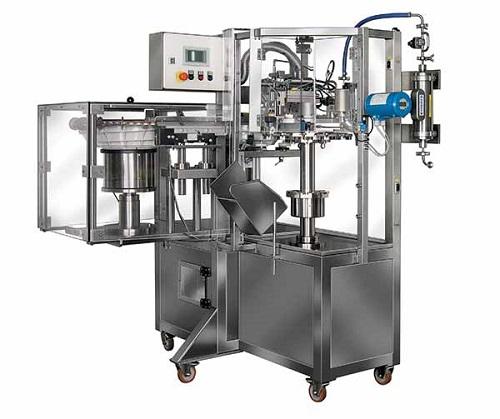

Low speed Filler for large-volume parenterals
Large-volume parenteral bottles are usually manufactured with a resin that c...
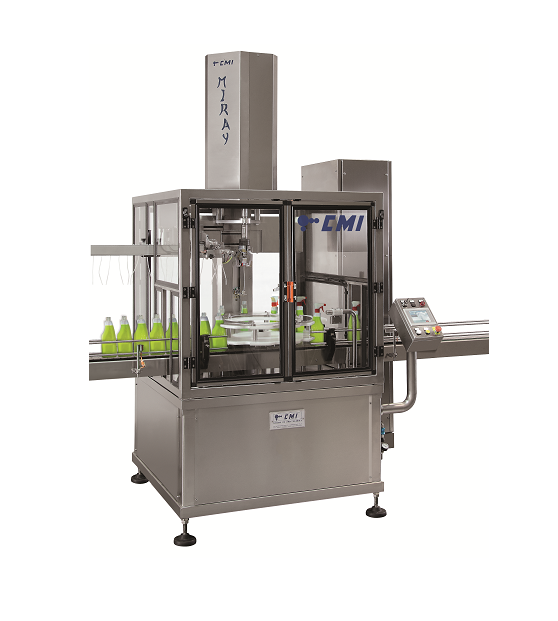

Automatic bottle capping machine
Traditional bottle capping systems are inflexible, limiting the scope of your packaging and...

Acid filling machine
Traditional filling solutions are not appropriate for corrosive substances as they make extensive use of...

Semi-automatic trigger capping machine
Trigger spray bottle are the ideal capping solution for many chemical and household ...

Liquid detergent filling machine
Filling of liquid detergents requires specialised equipment because of the foaming nature o...
Versatile bottle sorting system
Quality bottle sorting machine and inspection system which can be put to use not only after ...
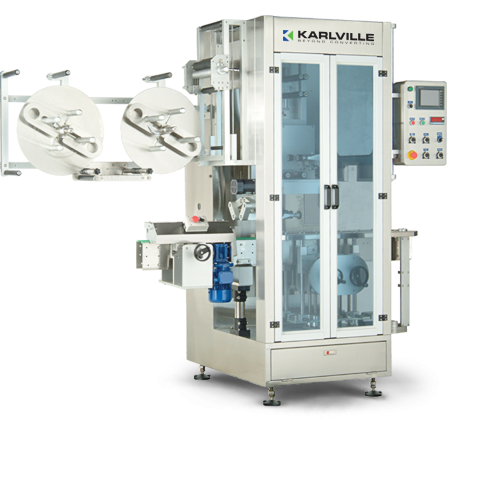

Shrink sleeve applicator - 400 per minute
Flexible medium to high speed application of shrink sleeveing to containers is u...
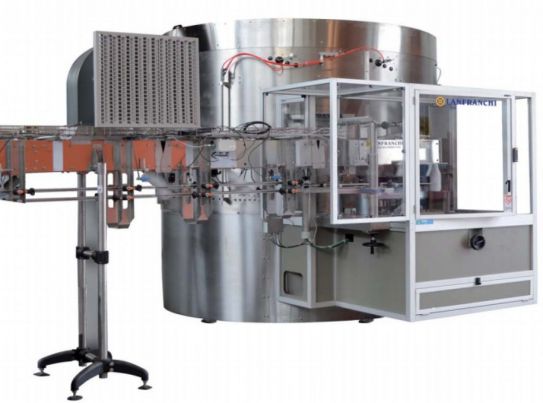

High-speed unscrambler for large bottles
Large volume plastic bottling plants need high-speed unscramblers suitable for lar...
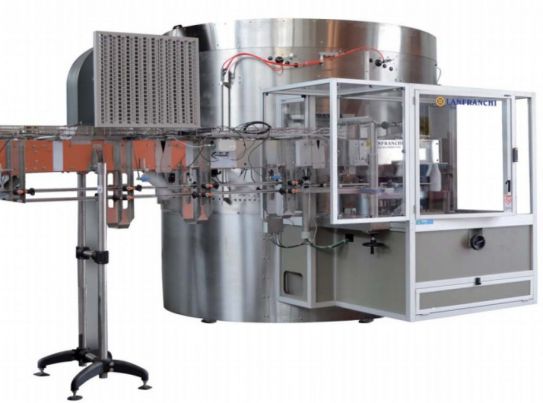

High-speed unscrambler for small bottles
Large-scale production of smaller volume bottled product needs a gentle, accurate ...
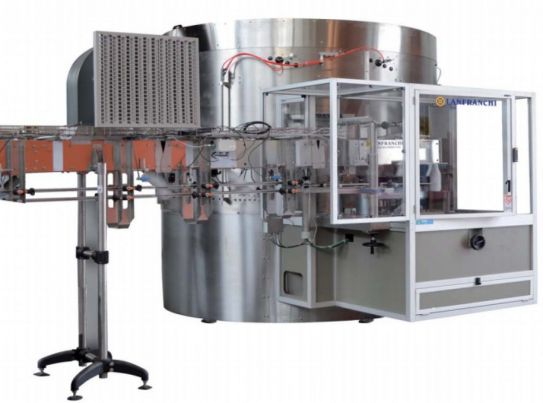

Low-speed unscrambler
Smaller plastic bottling lines need a lower cost, lower volume unscrambling machine that maintains gent...
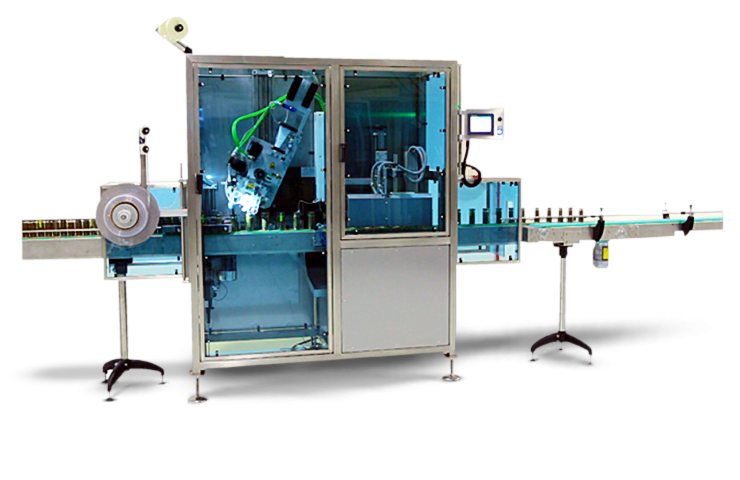

Compact shrink sleeve applicator
Adding tamper prevention to product packaging can be expensive and difficult to set up. Thi...
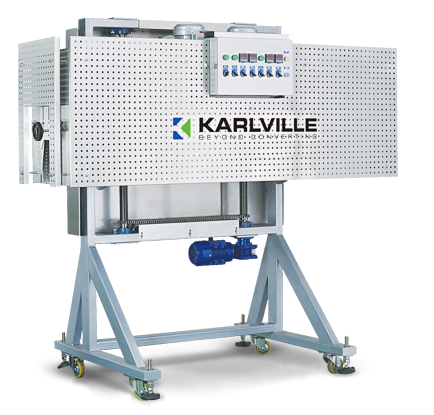

Electric shrink tunnel solution
Adapting shrink sleeve heating tunnels for different applications can be a lengthy and expen...

Low speed can sleeve applicator
Flexible automatic low speed application of shrink sleeving to cans is used in various indus...

Low speed shrink sleeve applicator
A variety of industries require flexible addition of shrink sleeves to containers on the...

Laboratory size auto-steam shrink system
When managing sleeving projects, fast prototyping and testing can gain massive com...
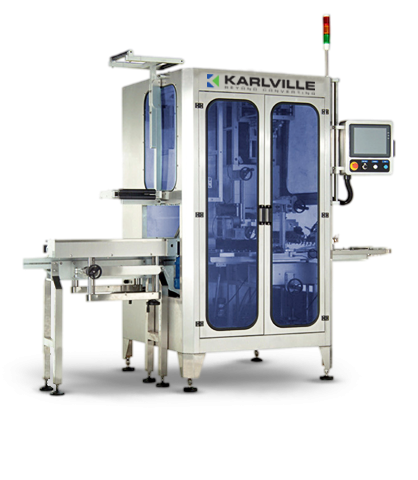

Shrink sleeve applicator - 600 per minute
Several industries require the flexible addition of shrink sleeves to containers...

In-line tamper evident applicator head
Integrating tamper protection equipment into an existing production line means addit...
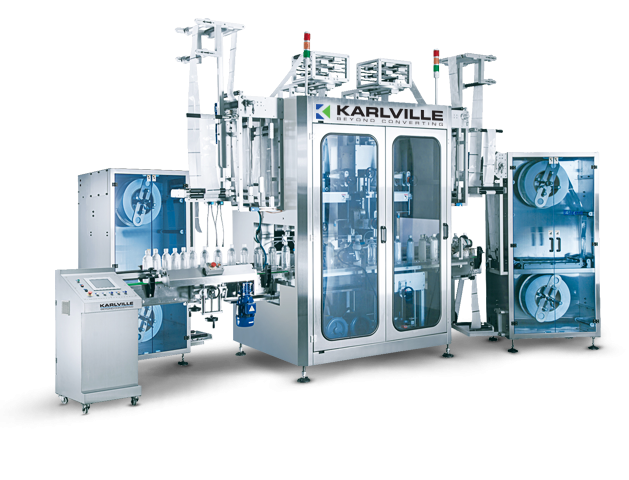

Shrink sleeve applicator - 800 per minute
High speed, in-line shrink sleeving systems require dual head capability with hi...

Advanced auto-steam shrink system
Design and development of shrink sleeves could be made much easier if small batches of sa...

Premium steam tunnel for sleeve application
Maximum flexibility in terms of pressure, temperature and ramp setting and adj...

Tamper-evident sleeve applicator for caps
Reliability, continuity and changeover time are key success factors for tamper-e...

Energy efficient tunnel for sleeve application
Hot air application of shrink sleeves is much more efficient than tradition...
X-ray fill level controller
For containers that are difficult to see through, such as cans or cartons lined with aluminium, ...
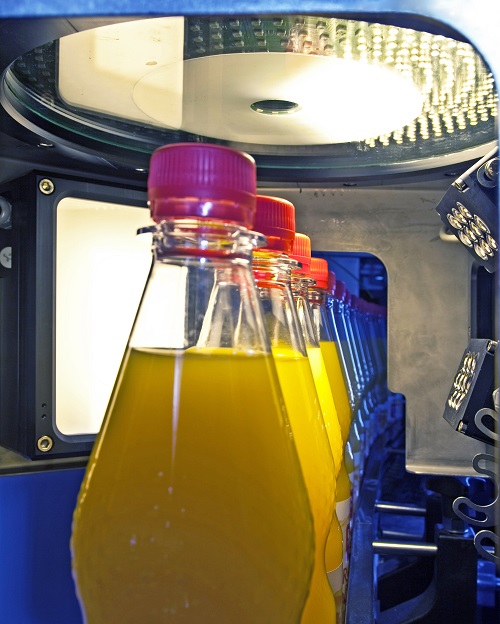

Optical fill level controller
Accurate fill level inspection for transparent, opaque and foaming liquids, that makes sure th...
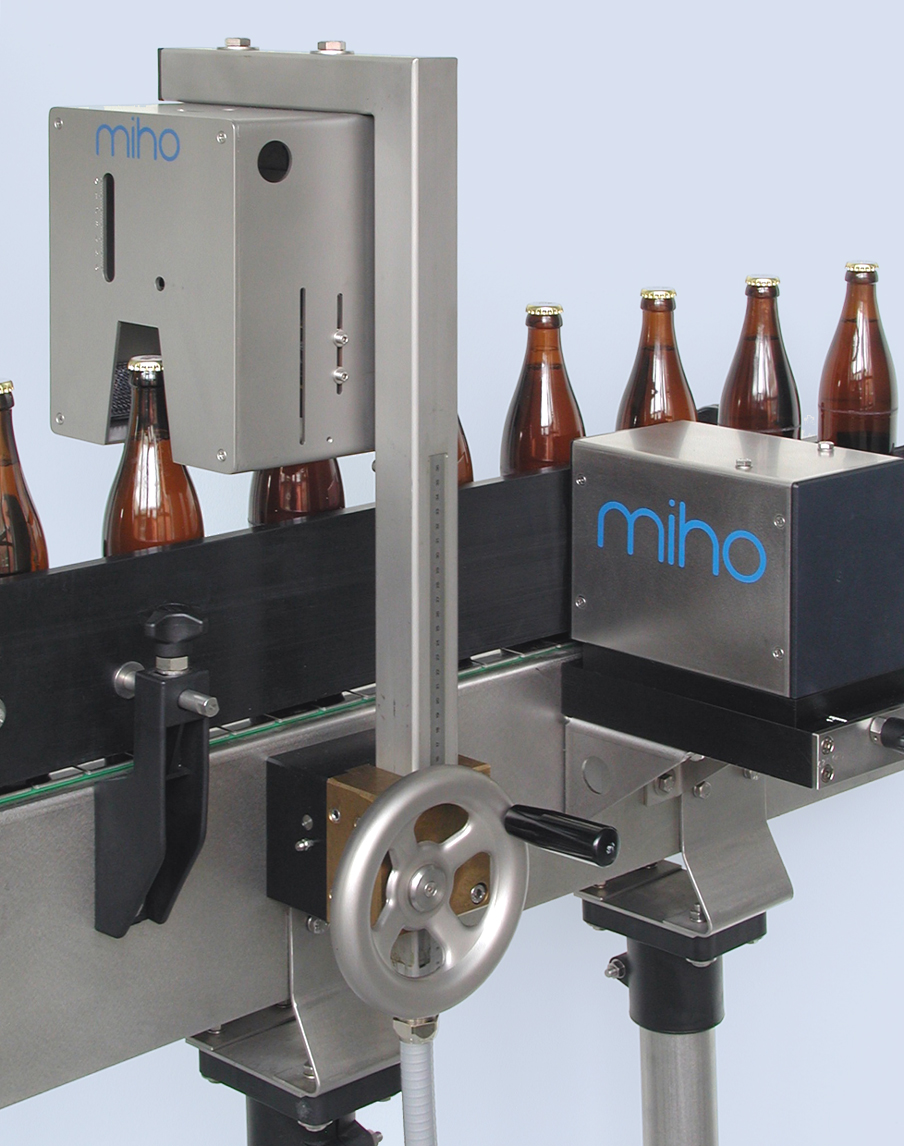

High-frequency fill level controller
In terms of high-frequency technology, the fill level detection is considered a standa...
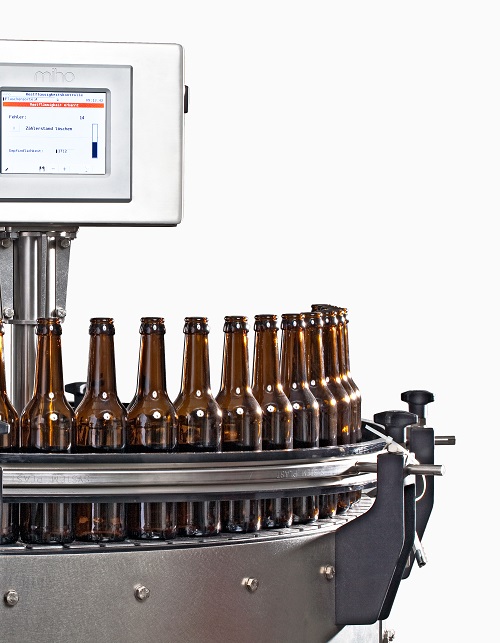

Advanced residual liquid inspection system
Advanced and easy to use inspection system that eliminates the risk of residual...
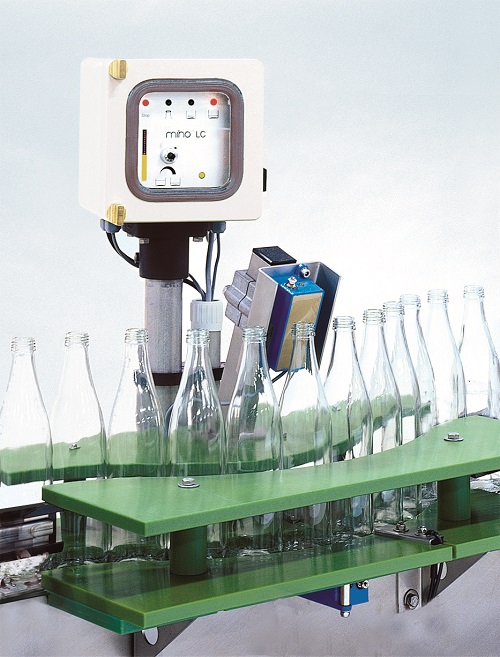

Residual liquid inspection system
Inspection system that eliminates the risk of residual liquid, water or left over drink i...