Making Emulsions
Find innovative production technology for making emulsions and connect directly with world-leading specialists
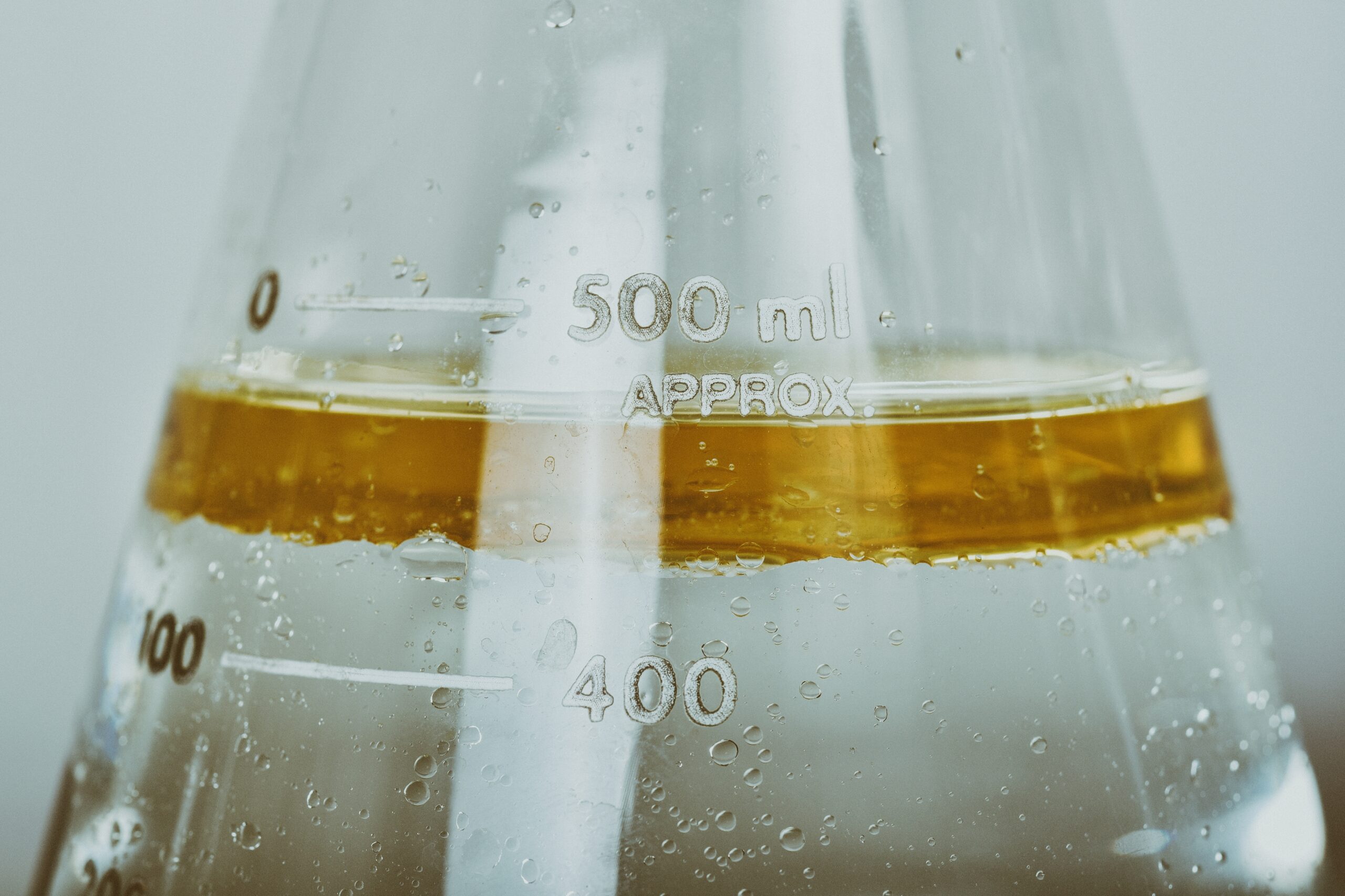
You can make emulsions by combining two immiscible liquids (oil and water, for example) in a suspension through the use of force. The use of emulsifiers is necessary to keep this mixture stable and permanent.
Stories about emulsions
Tell us about your production challenge

Emulsifying equipment and manufacturing processes to know about
To mix two immiscible substances, you first need to break down one of them into millions of tiny droplets. You can then suspend these droplets in the other substance by blending both with an industrial blender. The droplets become known as the dispersed phase, while the other liquid becomes the continuous phase.
Emulsions can be either oil-in-water (O/W) and water-in-oil (W/O). To form oil-in-water emulsions, the dispersed phase must be oil and the continuous phase, water. For water-in-oil emulsions, the phases are the opposite. However, these substances will not stay mixed for long on their own, and this is where the use of emulsifiers becomes necessary. Emulsifying equipment such as shear mixers and high-speed agitators are essential to prevent separation.

Emulsions for cosmetic, food, and pharmaceutical purposes
Some of the most common food items and sauces such as Hollandaise, mayonnaise, and salad dressings are emulsions. Cosmetic products such as shampoos, creams, conditioners, and lotions are also emulsions. Similarly, in healthcare circles, emulsions deliver vitamins, supplements, and other bioactive compounds.
Oil-in-water emulsions are more suitable for products meant for internal use. This is why food sauces and drug supplements are mostly oil-in-water emulsions. On the flip side, products meant for external use, such as creams and lotions, work better with water-in-oil emulsions.
What are the regulations for different emulsions?
The Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) from the World Health Organization (WHO) guide the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical emulsions production. While the institution encourages these regulations, they are not enforceable.
In the US, the FDA regulates pharmaceutical emulsions, and products that don’t meet these regulations are marked adulterated. In Europe, it’s the decentralized European Medicines Agency (EMA) that enforces EudraLex, in collaboration with regional regulatory agencies in the European Union. EudraLex is the collection of rules and regulations governing medicinal products in the EU. In the ASEAN region, marketing authorizations for drugs are country-specific, although pharmaceuticals production regulations are largely based along PIC/S recommendations.

A few words about filling and packaging of emulsions
For starters, packaging laws in several countries oblige you to clearly state whether products are suitable for internal or external use on their labels. You should also use wide-mouthed bottles for viscous emulsions and state clearly on the label that the product should be shaken thoroughly before use. Finally, low temperatures can contribute to the demulsification of emulsions, so you should avoid refrigerating them.
Processing steps involved in emulsions making
Which emulsions technology do you need?

Solid-wall bowl separator for chemical products
Optimize your separation and clarification processes with this high-speed,...

Chub packing system for chemical emulsions
Effectively pack and fill chemical emulsions with precision to enhance the safe...

Industrial cutting system for fine emulsions
Optimize your production line with precision cutting and emulsifying, ensurin...
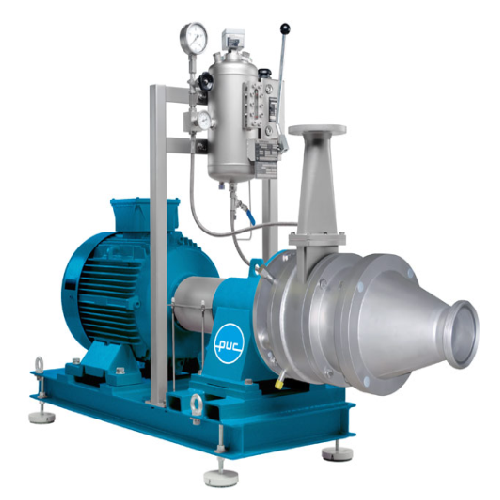

Perforated disc mill for food and chemical processing
Streamline your processing workflow with a versatile solution that ...
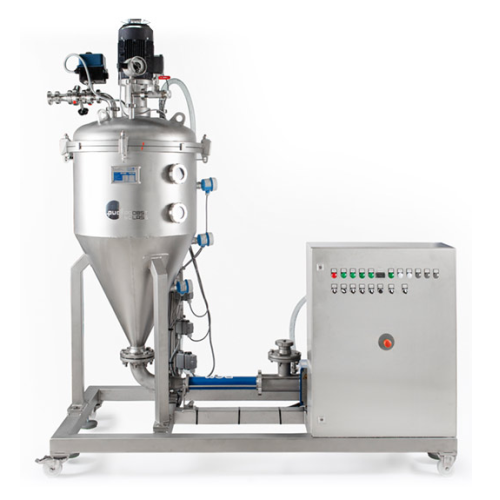

Vacuum de-aeration unit for liquid to pasty products
Optimize your product consistency and stability with continuous de-a...
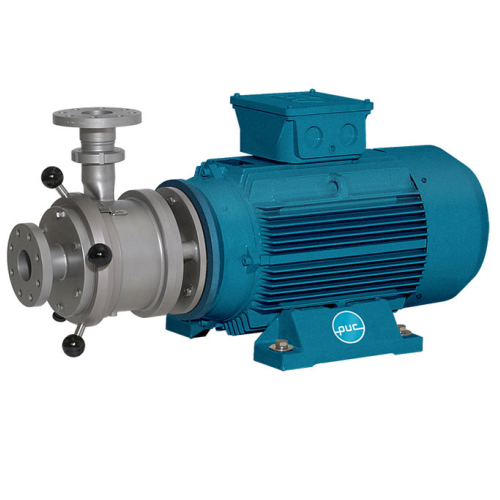

Colloid mill for emulsifying and wet milling applications
Achieve precise mixing and grinding with our colloid mill, des...
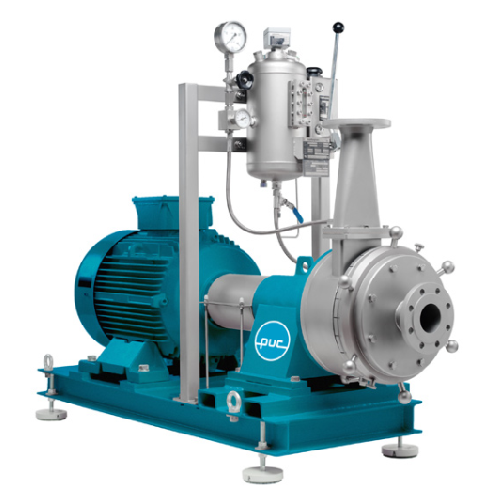

Horizontal colloid mill for precise grinding
Achieve precise particle size reduction and reproducible results with our adv...
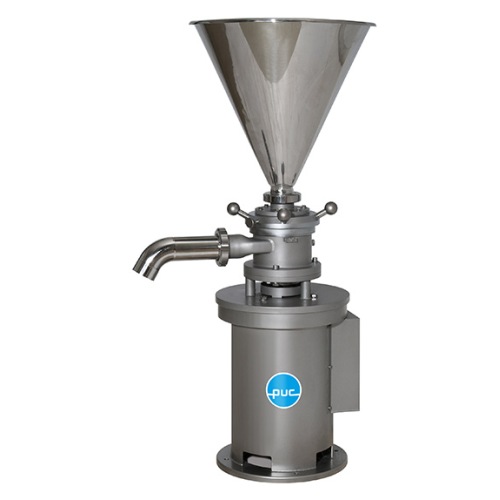

Vertical colloid mill for emulsifying and homogenizing
Optimize your production line with precise particle size reduction...
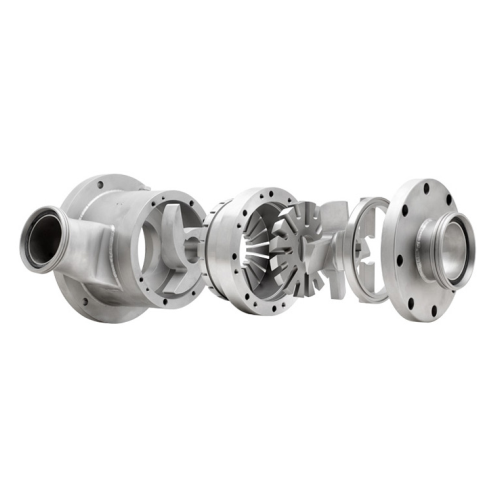

Multistage mixer for emulsions and dispersions
Enhance your production with a versatile multistage mixer that ensures opti...
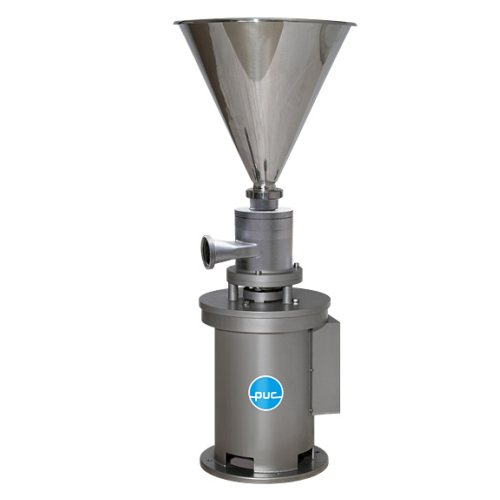

Multistage mixers for emulsions and dispersions
Experience efficient emulsification and dispersion processes with this ver...
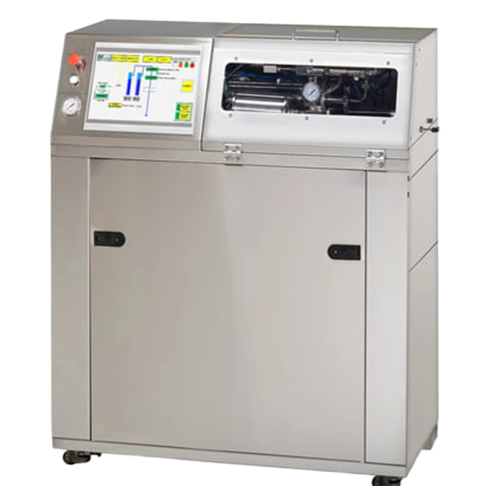

High pressure homogenizer for cell disruption and nanoemulsions
Achieve precise particle size reduction and enhanced bio...
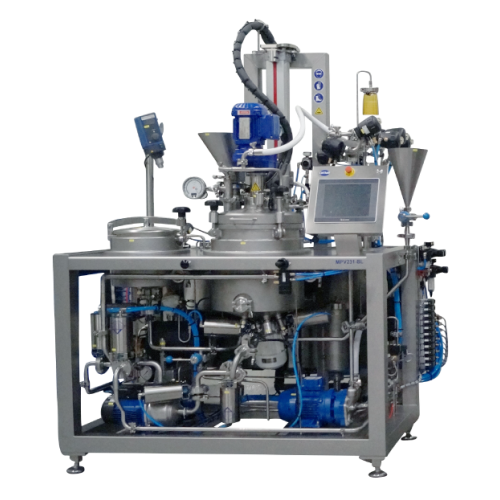

In-line production of fine emulsions
Achieve homogenous emulsions with precise control, reducing the risk of lump formation...
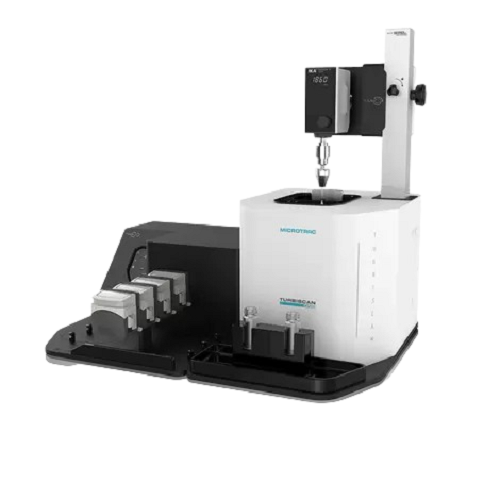

Stability analyzer for emulsions, suspensions, and foams
Accurately detect and quantify changes in dispersibility and sta...
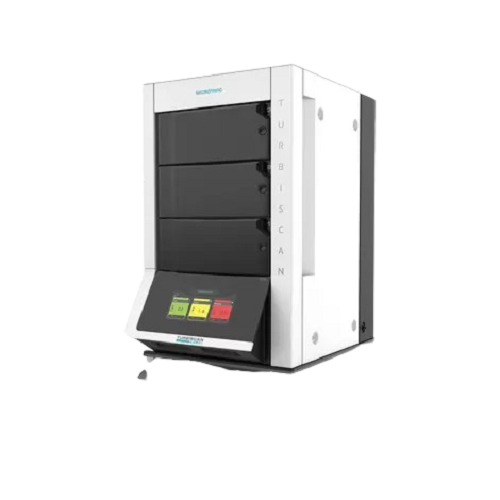

Multi-sample stability analyzer for emulsions and suspensions
Achieve precise, non-destructive stability analysis of emu...
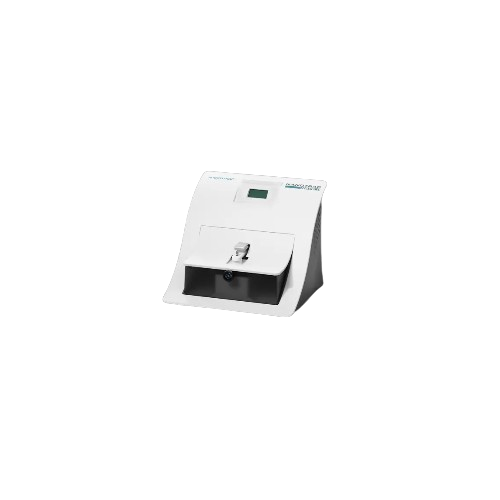

Nanoparticle size analyzer
Master precise nanoparticle and zeta potential analysis with dynamic light scattering technology,...
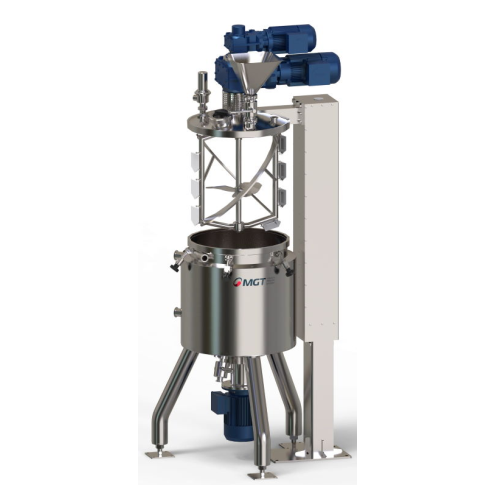

Vacuum mixing system for emulsion and homogenization
Achieve seamless emulsion and homogenization with precision: this sy...
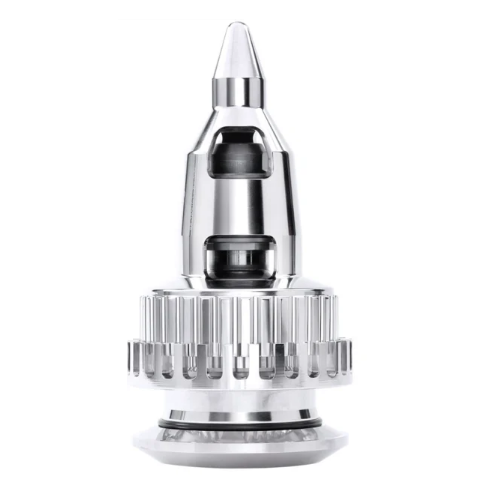

High shear mixer for emulsification
Achieve precise emulsification and dispersions with magnetic high shear technology, ens...
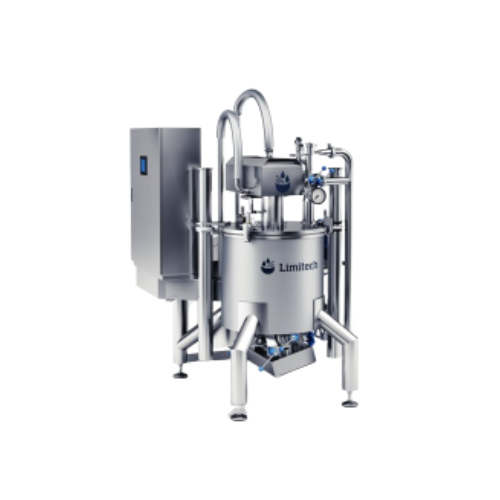

Multifunctional mixer for high volume batches
Efficiently handle complex mixing, emulsifying, and homogenizing tasks with ...

Large insulated oil storage tank
Ensure optimal temperature control for sensitive liquids like oils, sauces, and creams with...
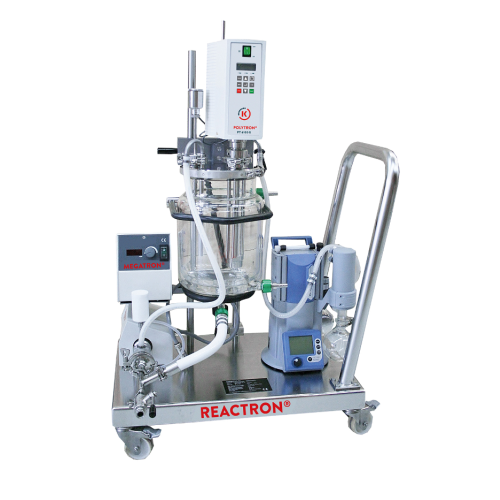

Highly scalable reactors for chemical synthesis
Optimize your production line with versatile reactors designed for seamles...
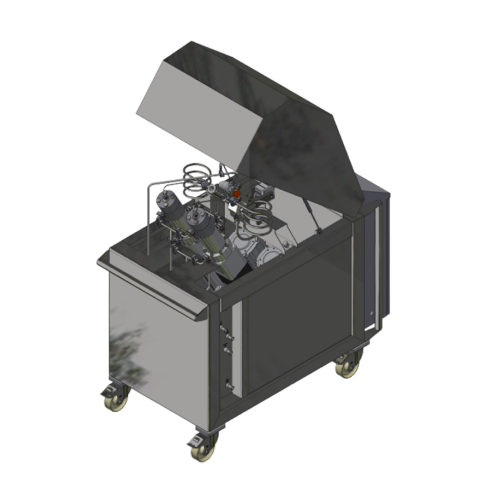
High pressure homogenizer for pharma applications
Achieve precise particle size reduction and stability in liquid formula...
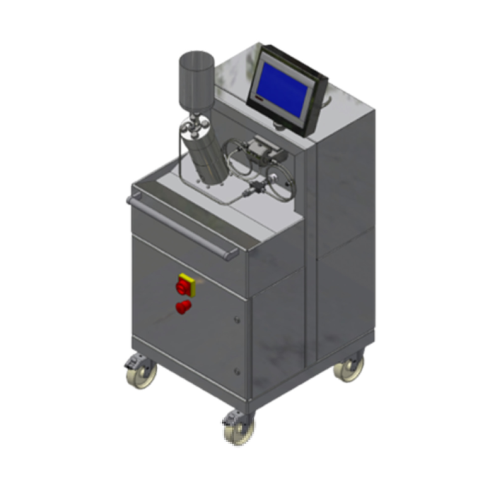

High pressure homogenizer for lab applications
Achieve precise control over droplet size and consistency in high-viscosity...
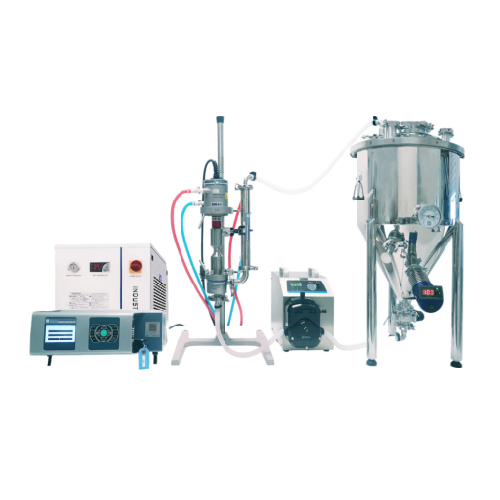

Industrial ultrasonic liquid processor for high volume applications
For large-scale liquid formulations, achieving cons...
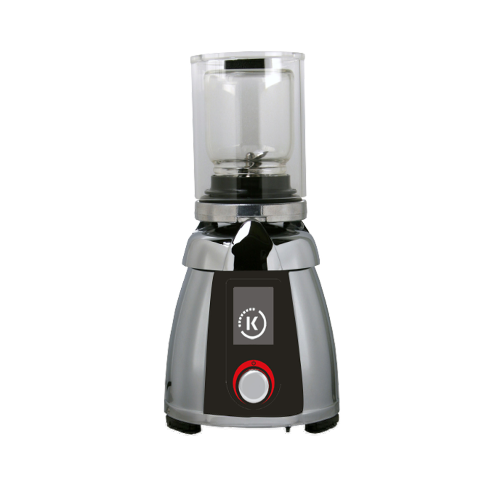

Laboratory mixer for intensive sample preparation
For precise and efficient preparation of both liquid and dry formulatio...
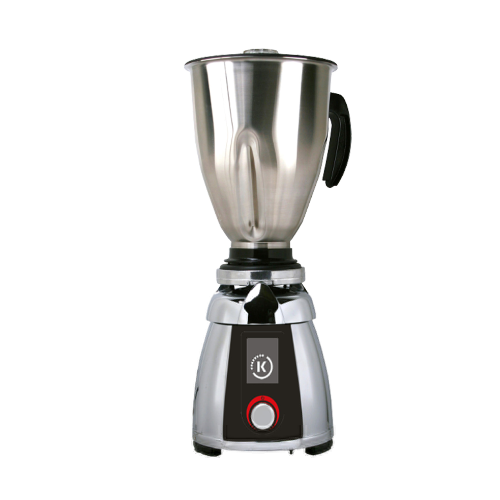

Laboratory mixer for homogenizing and mixing samples
Achieve precise sample preparation and efficient mixing with this ve...
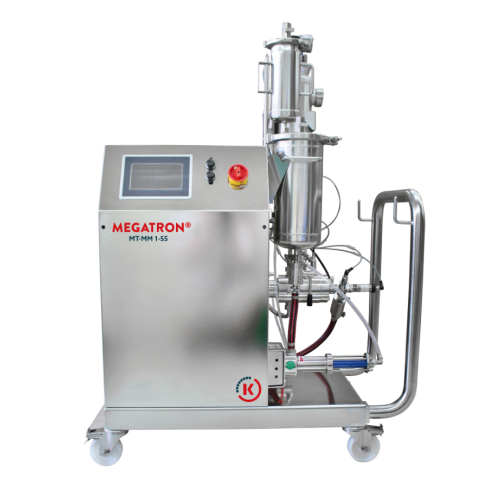

Membrane emulsifying system for double emulsions
Achieve precise control over emulsion droplet sizes and distributions, en...
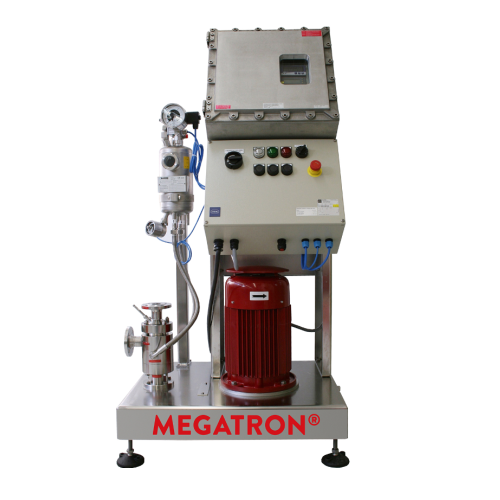

In-line disperser for high-volume liquid processing
Streamline your emulsification process with powerful rotor-stator hom...
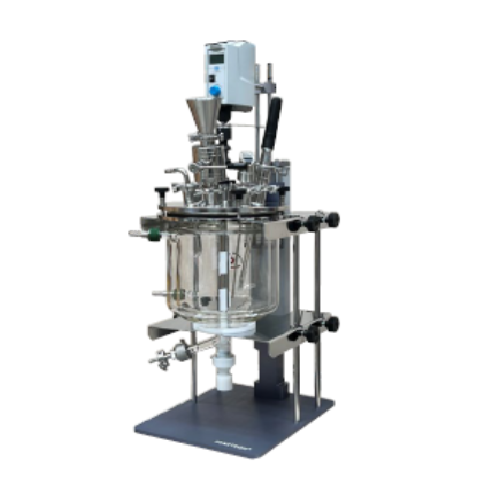

Laboratory dispersion reactor for 10l batch processes
Enhance precision and efficiency in lab-scale liquid formulations w...
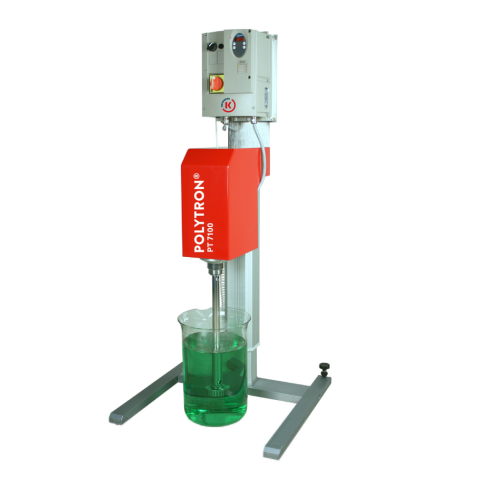

Stand dispersing unit for pilot plant applications
Achieve precise particle size reduction and efficient mixing with this...
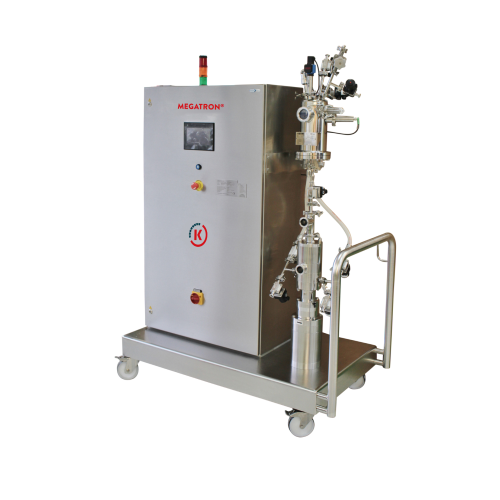

Sterile inline dispersers for pharmaceutical production
Optimize sterile production environments with precision-engineere...
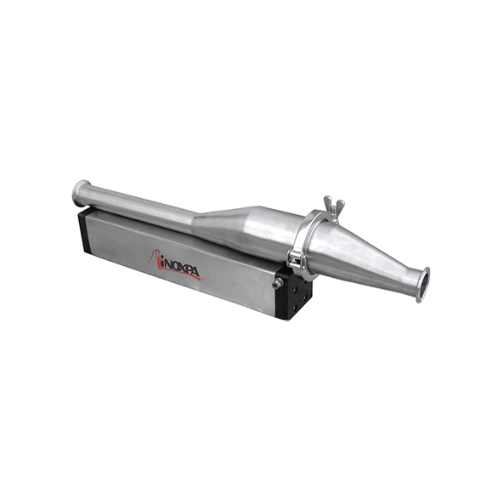

Hygienic pipeline product recovery system
Efficiently recover valuable residuals from pipelines while streamlining your cl...
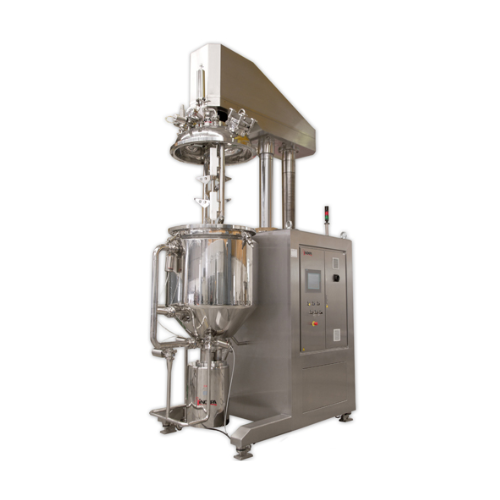

Counter-rotating blender for cosmetic and pharmaceutical mixing
Achieve precise mixing and homogenizing of complex formu...
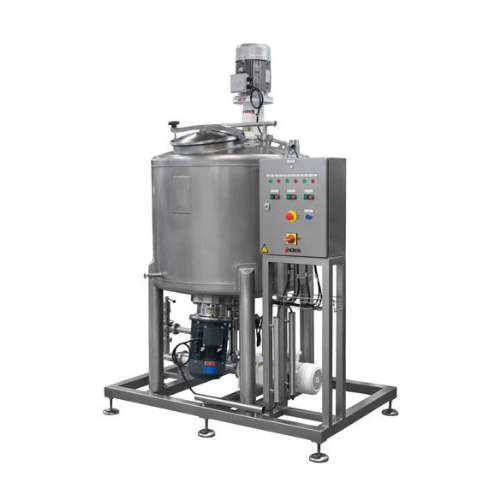

Hydroalcoholic gel mixing system
Ensure seamless production of hydroalcoholic gels with an advanced mixing system designed f...

In-line high shear mixing solution
Achieve precise emulsification and particle size reduction with high shear capabilities,...

High shear vertical mixer for dispersion and emulsification
Achieve seamless emulsification and homogenization in divers...

High-pressure homogenizers for liquid products
Achieve consistent emulsions and stable dispersions with high-pressure homo...

Homogenizers for high-pressure applications
Achieve unparalleled product consistency and stability with precision-engineer...
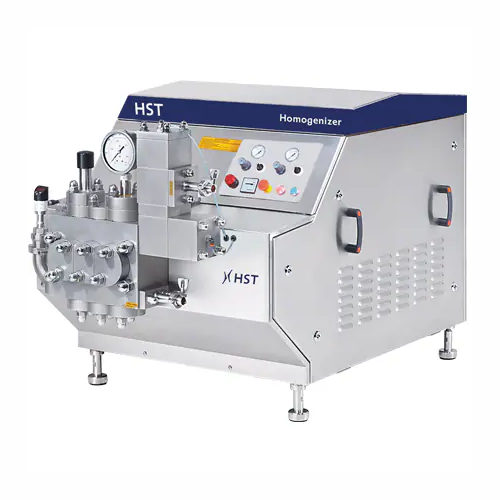

Industrial homogenizer for food and pharmaceutical applications
Ensure product consistency and stability with high-press...
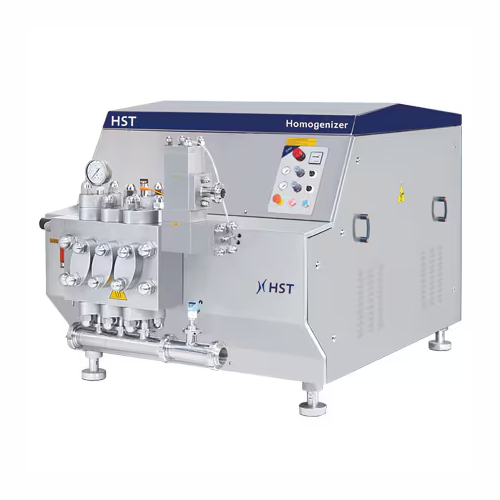

High-pressure homogenizers for dairy and beverage industries
Achieve precise emulsion stability and consistent particle ...
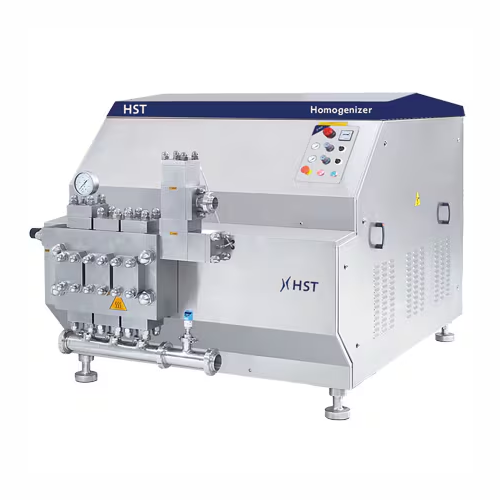

High-pressure homogenizers for dairy and juice processing
Ensure superior texture and stability in your liquid formulati...
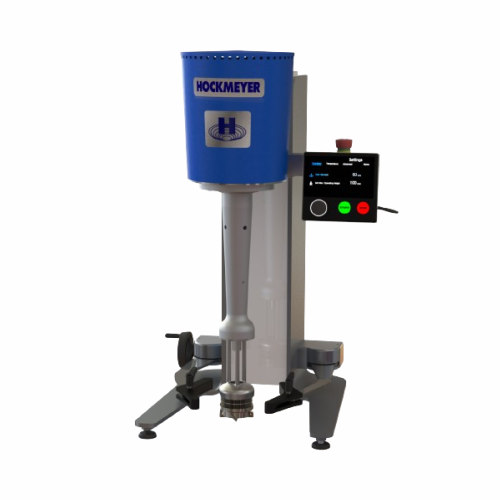

Lab-scale disperser and immersion mill
Achieve precise dispersing and milling with rapid changeover capabilities, ideal for...
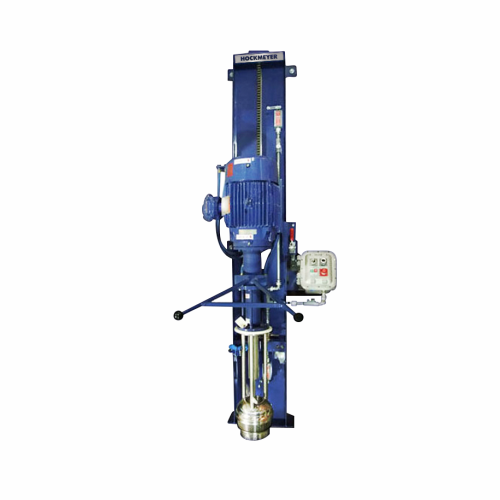

Immersion mill for pail and drum-sized batches
Streamline your production with a versatile solution that efficiently handl...
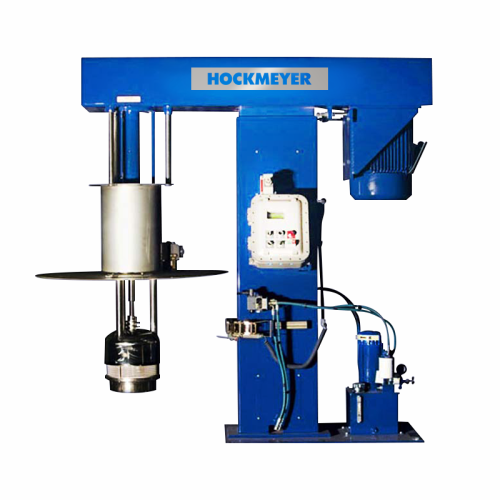

Immersion mill for particle reduction
Achieve streamlined particle size reduction and enhanced mixture homogeneity with imm...
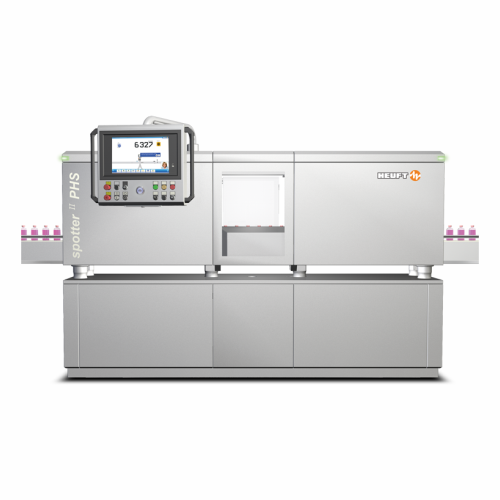

Vial inspection system for pharmaceutical products
Ensure the integrity and safety of parenteral drugs with advanced imag...
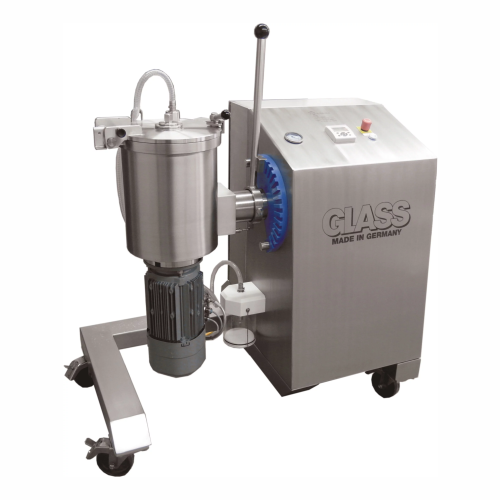

Emulsifying plant for pasty and liquid products
Optimize your production line with seamless emulsification processes, desi...
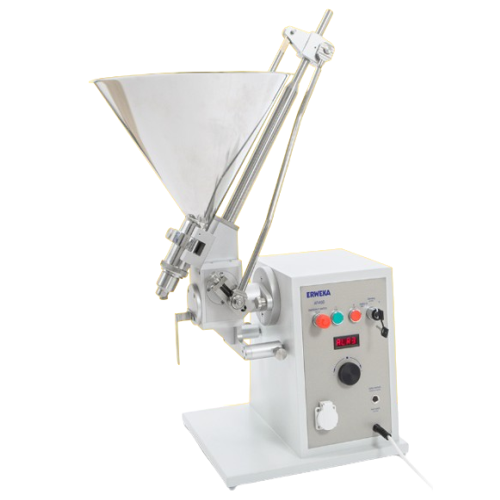

Precision ointment filling and dosing system
Achieve precise filling of liquid formulations with a versatile system capabl...
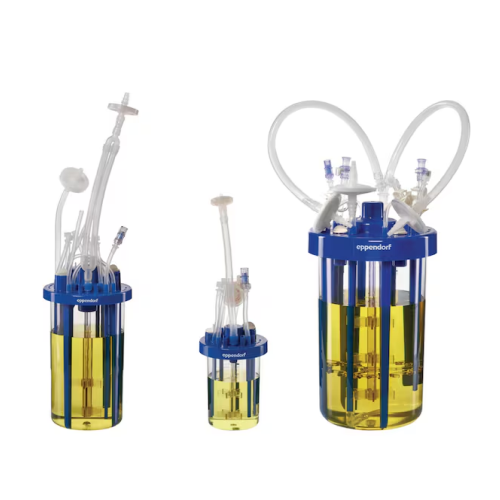
Single-use bioreactors for microbial fermentation
Optimize high-density fermentation with advanced single-use bioreactor ...
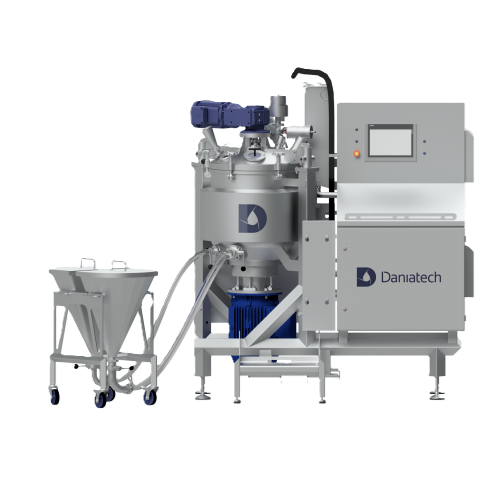

Lab-scale high-shear mixer for recipe development
Optimize your recipe development process with precise mixing, homogeniz...

Inline high shear mixing unit for low to medium viscosity products
Achieve precise emulsification and size-reduction wi...
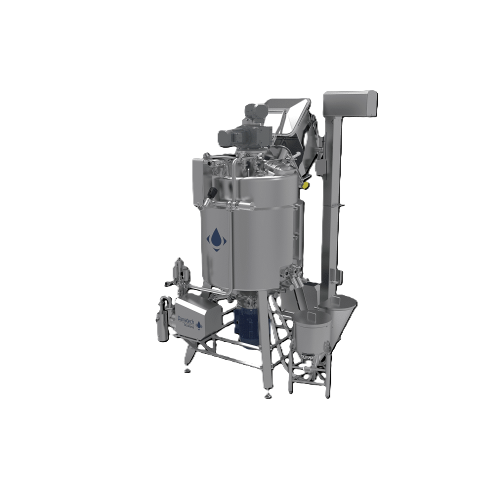

High-shear mixer for high viscosity products
Achieve consistent, homogeneous mixtures of high-viscosity products with a ve...
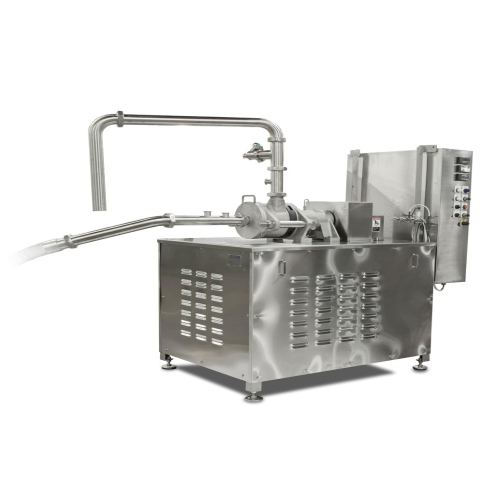

Emulsion and reduction system for meat processing
Achieve precise particle consistency and texture control in food proces...
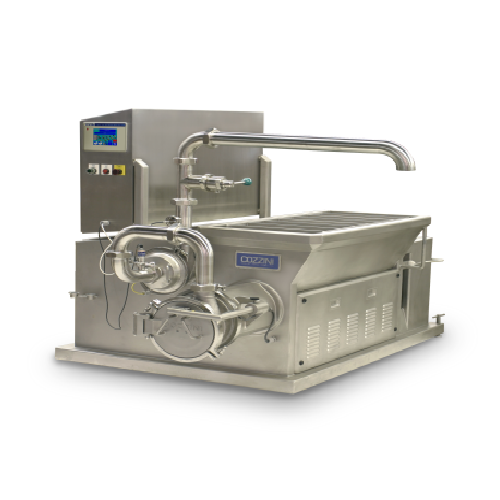

Compact food emulsion and reduction system
Achieve precise control over product texture and temperature with a compact sol...
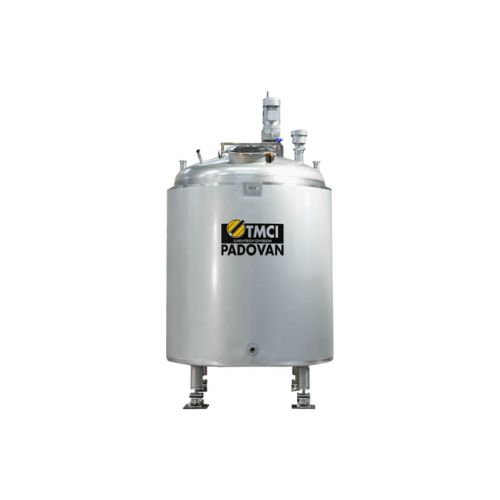

Process tanks for oils and fats
Optimize your oil and fat processing with versatile tanks designed for precise emulsificatio...
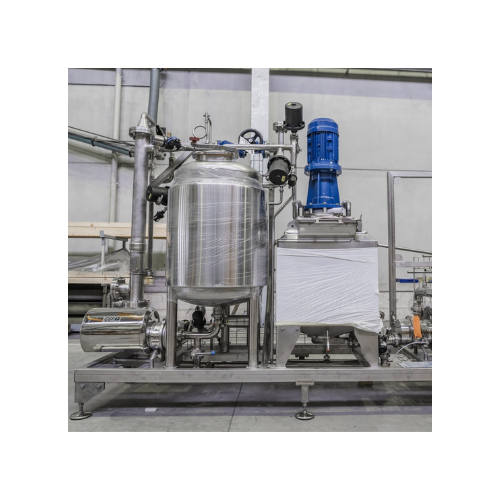

Turbo mixer for homogeneous solutions in food and pharmaceutical industries
Effortlessly achieve uniform suspensions a...
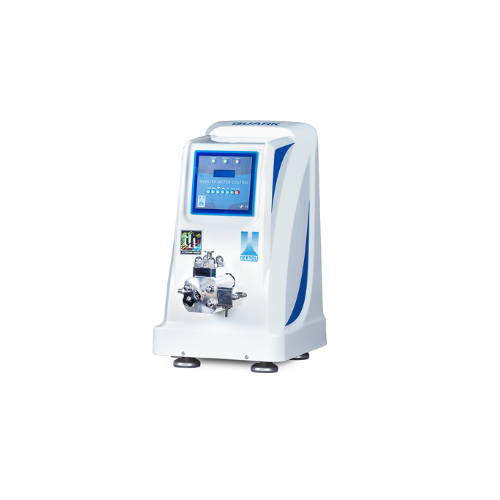
Laboratory homogenizer for pharmaceutical and biotech applications
Achieve precise homogenization for your laboratory n...
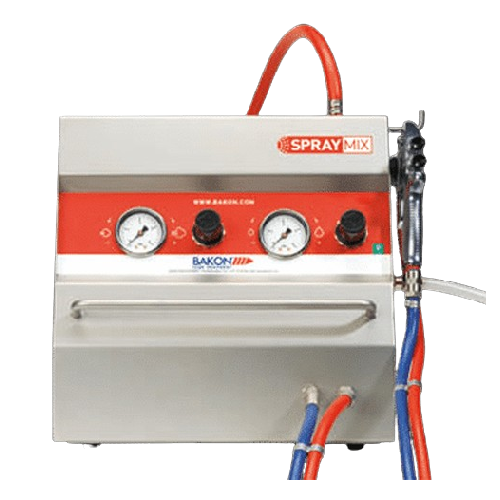

Bakery spraying system for accurate liquid application
Achieve precise and consistent liquid application across diverse c...
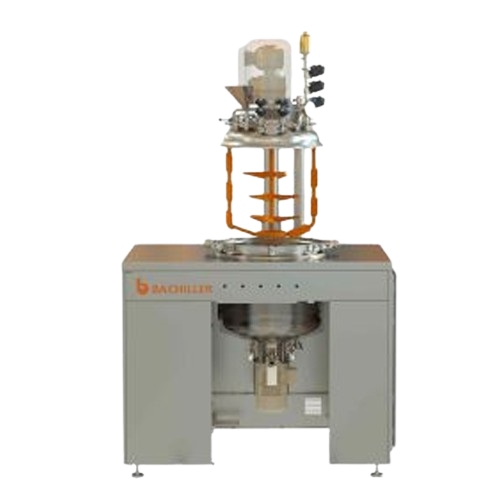

Laboratory vacuum mixer reactor for liquids and semi-solids
Achieve precise emulsification and mixing for high-viscosity...
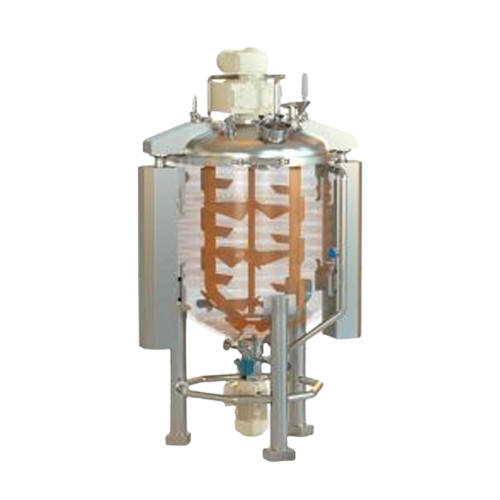

Industrial mixer for liquid and viscous products
Achieve precise mixing and homogenization of high-viscosity liquids and s...
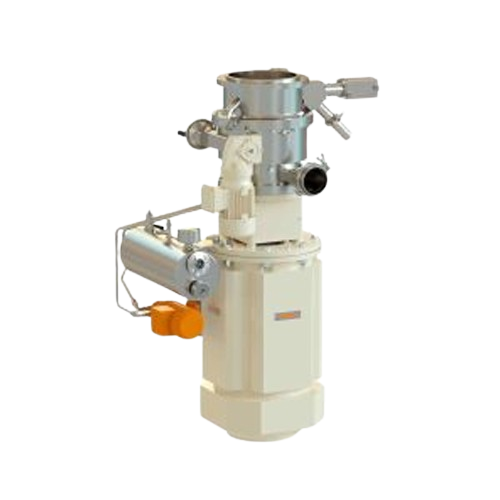

Homogenizer for high viscosity emulsion and dispersion
Achieve unparalleled dispersion and emulsification with a system d...
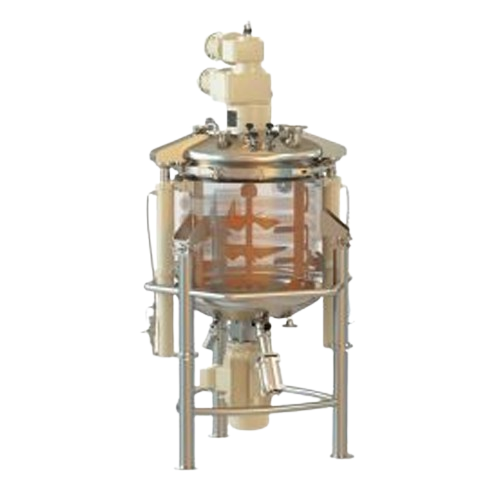

Industrial vacuum mixer and reactor for liquids
For manufacturers needing precise blending and stability, this advanced va...
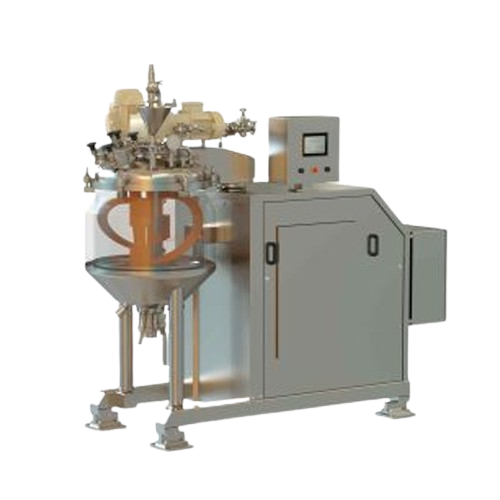

Vacuum mixer for liquids and semi-solids
Achieve precise mixing and homogenization of liquid and semi-solid formulations wi...
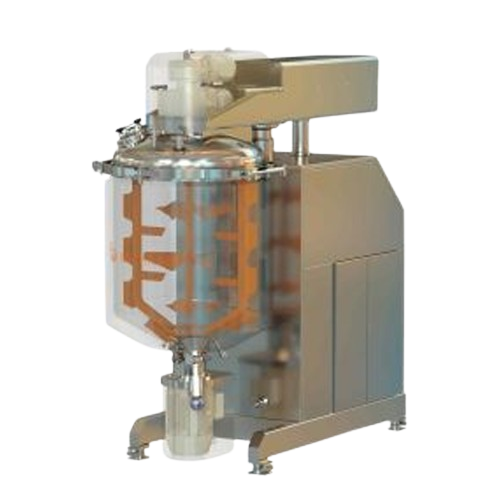

Vacuum mixer reactor for liquids and semi-solids
Achieve precise mixing and emulsification of complex liquid formulations ...
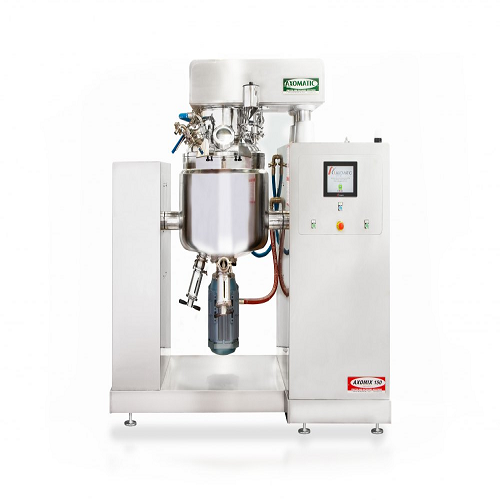

Vacuum homogenizer for high-quality mixing and emulsification
Achieve optimal consistency and enhanced product stability...
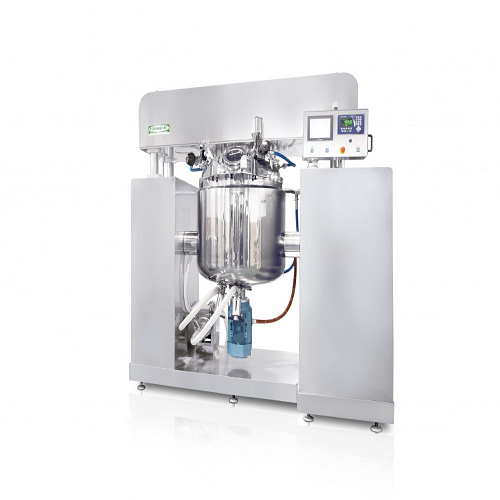

Industrial under vacuum homogenizer
Optimize your batch production with an under-vacuum homogenizer that ensures precise mi...
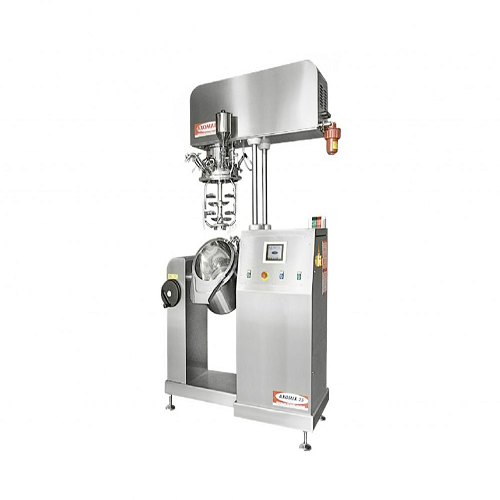

Industrial under vacuum homogenizer
Optimize the consistency and texture of creams and lotions with precision-controlled mi...
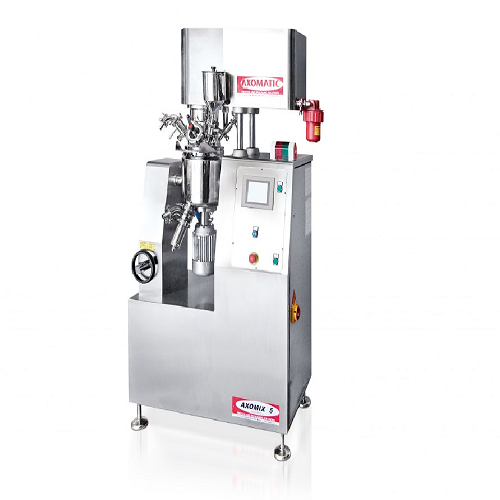

Vacuum homogenizer for creams and ointments
Streamline your production with cutting-edge vacuum homogenization, perfect fo...
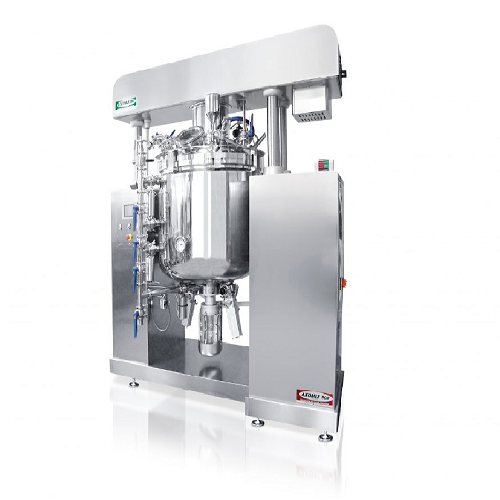

Undervacuum homogenizer for cosmetic and pharmaceutical creams
Optimizing the production of creams and lotions, this und...
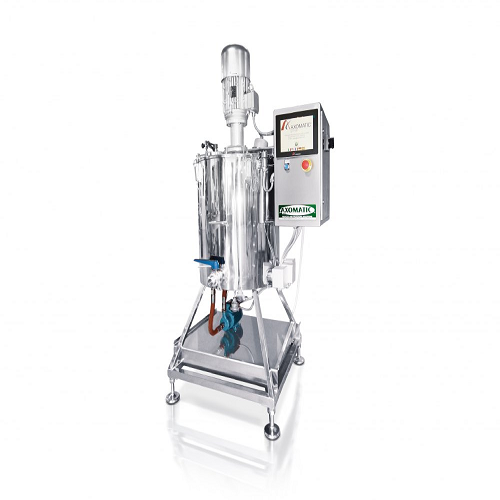

Melter for vacuum turboemulsifiers
Achieve optimal mixing, dispersion, and temperature control with precision-engineered me...
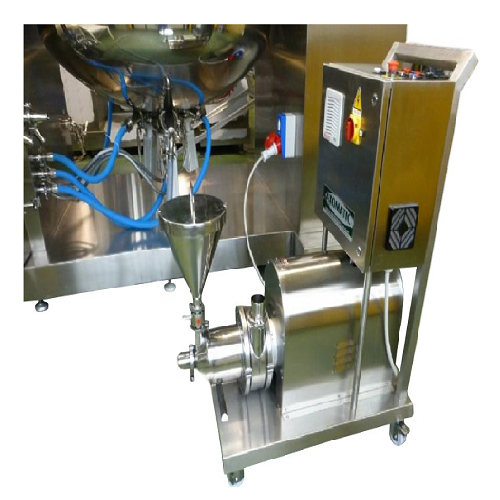

In-line external homogenizer for industrial fluid processing
Maximize fluid consistency and ensure efficient material di...
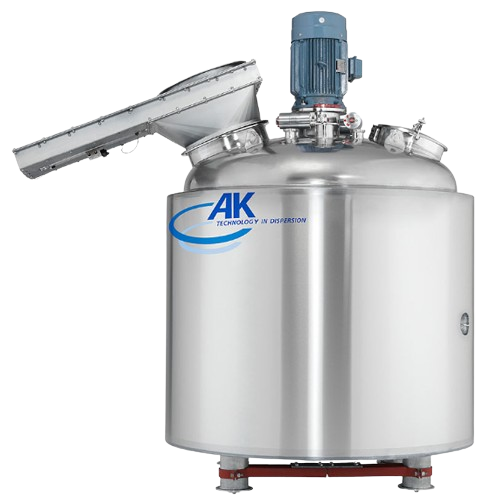

Emulsion processing system for homogenizing solids into liquids
Achieve precision in emulsifying and homogenizing proces...
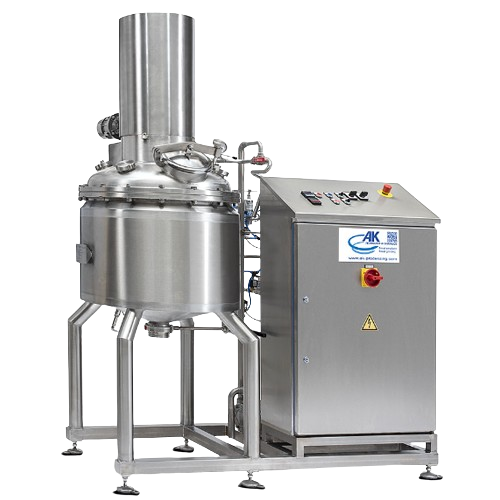

Hydro grind reactor for meat, vegetable, and vegan product processing
Achieve precision grinding and emulsification of ...
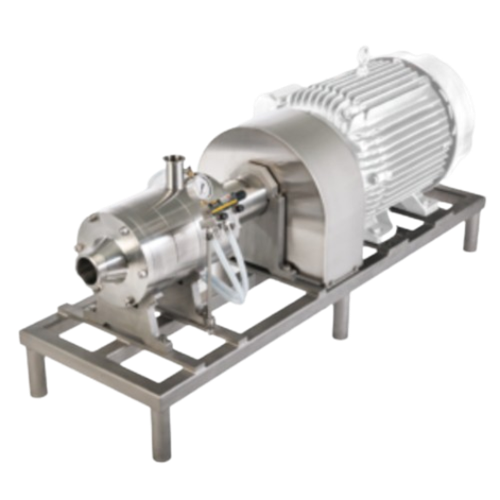

Inline wet mill for mayonnaise emulsions
Eliminate the challenges of achieving stable, uniform emulsions in your sauces and...
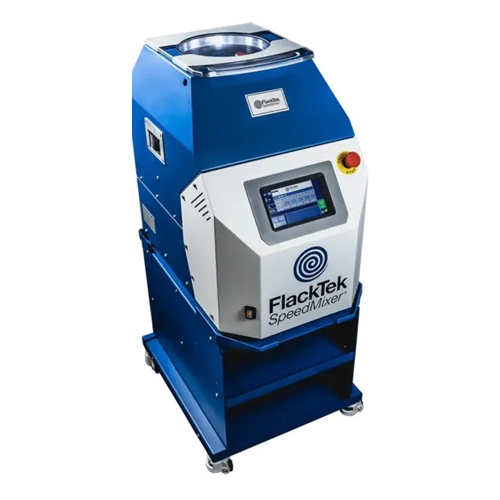

Dual asymmetric centrifugal mixer for epoxy and slurry mixing
Achieve precise mixing and consistency in your formulation...
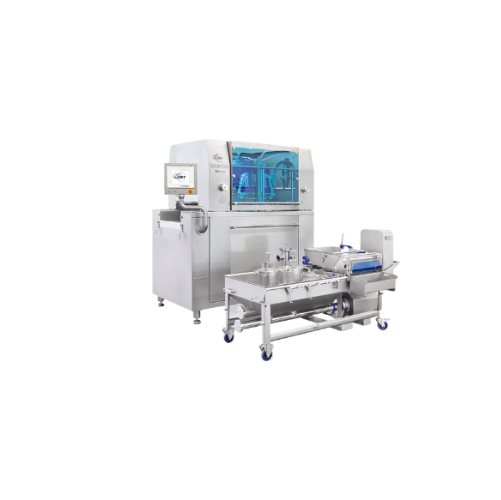

Highline injector for brine and emulsion injection
Achieve consistent brine distribution and flavor enhancement in meat, ...
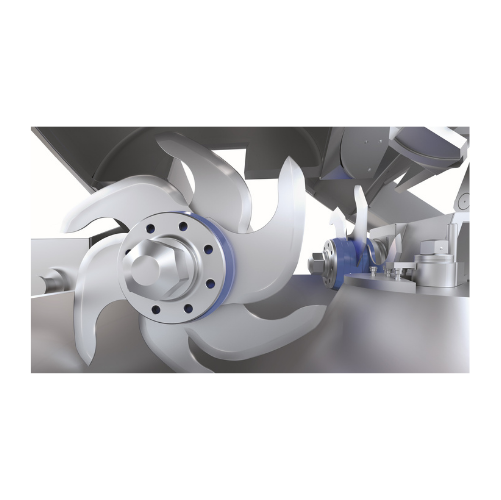
Bowl cutter for dry fermented sausages
Enhance your production efficiency with this powerful bowl cutter, designed to rapid...
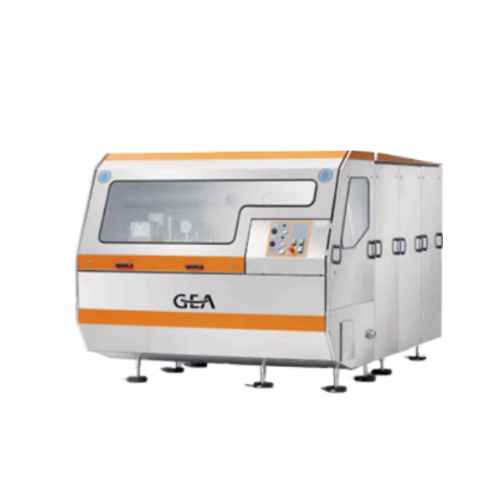

Industrial homogenizer for dairy, beverage, and pharmaceutical applications
Enhance your production efficiency with a ...

Blending silo for free-flowing and poorly flowing bulk materials
Achieve precise blending and mixing of diverse bulk mat...
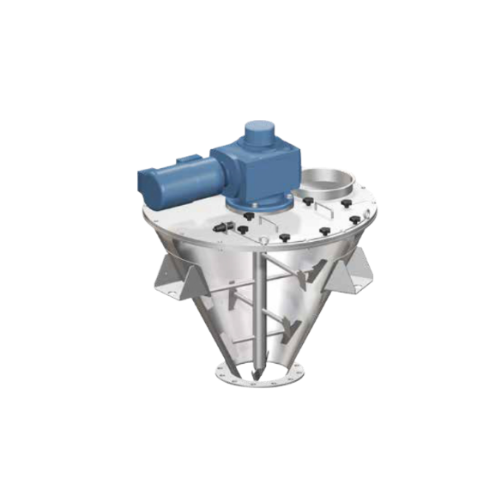

High-speed paddle mixer for food industry blends
Achieve rapid, high-energy blending of varied particulate materials with ...
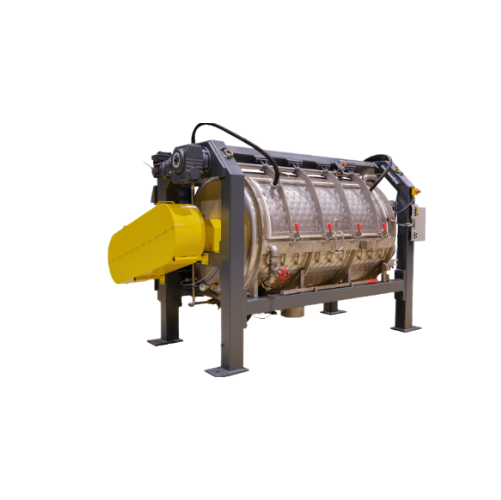

Horizontal cooling mixer for industrial applications
Efficient cooling in your production line enhances material quality ...
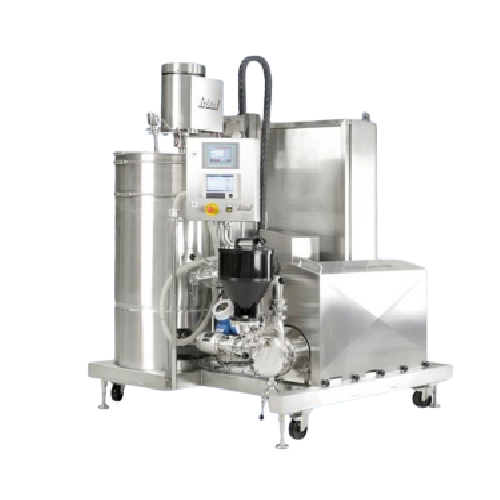

Inline disperser for food production
Quickly achieve stable, agglomerate-free dispersions and emulsions with minimal manual...
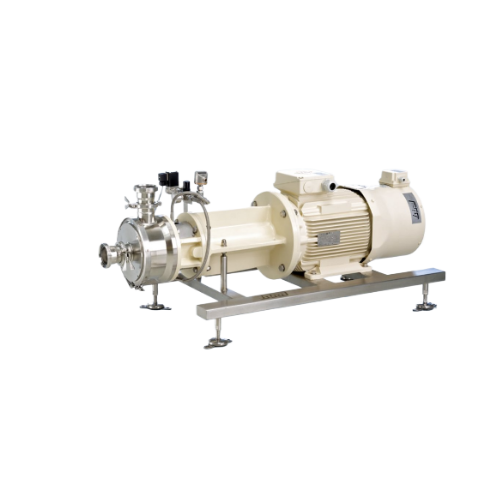

Inline disperser for homogeneous emulsions and suspensions
Achieve precise control over particle size and distribution w...
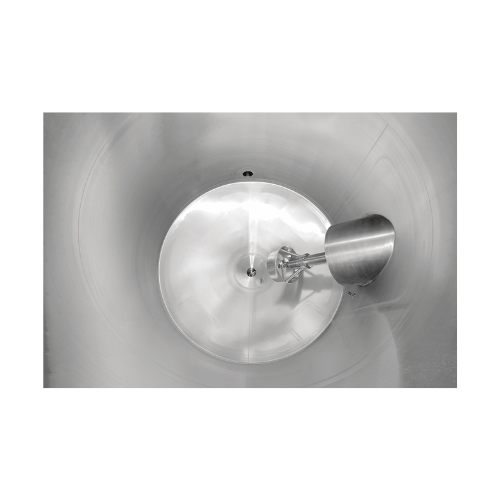

Industrial jetstream mixer for homogeneous mixing
Achieve consistent product quality with precise micro and macro mixing ...
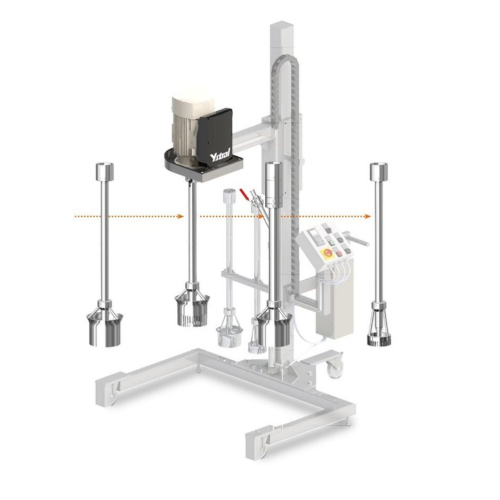

Multipurpose mixing equipment for chemical and pharmaceutical production
Achieve unparalleled flexibility with modular,...
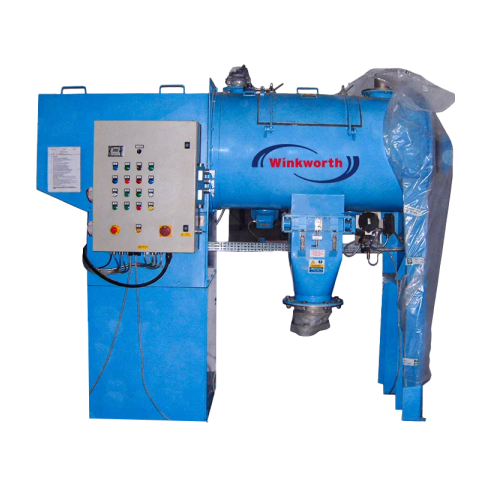

High-speed mixer for homogenous mixing of powders and pastes
Achieve rapid and precise mixing with high-speed dispersion...
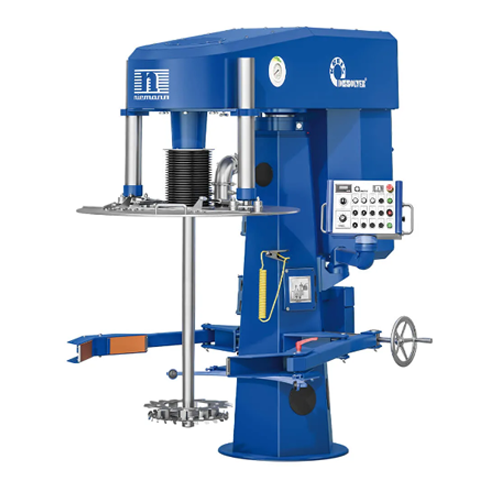

High-efficiency disperser for viscous products
Achieve precise control over the mixing and dispersing of high-viscosity ma...
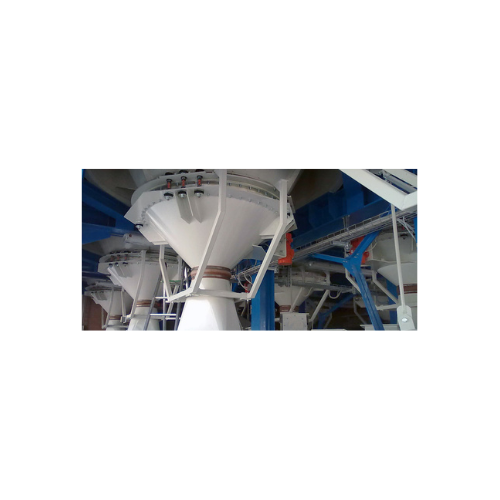

Bulk solids discharging and loading solution
Optimize your bulk material handling with equipment that ensures efficient an...
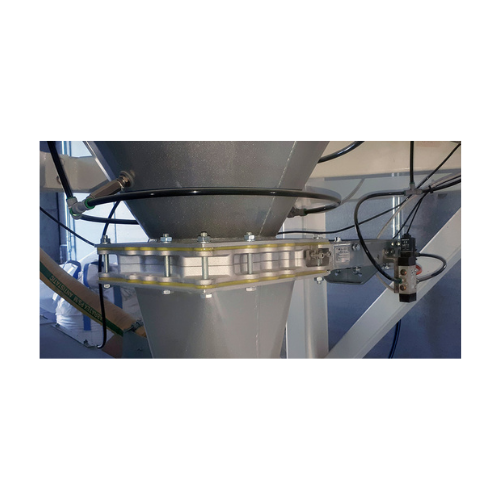

Slide valves for flow interception in powder and granular materials
Effectively manage the flow of powdery and granular...
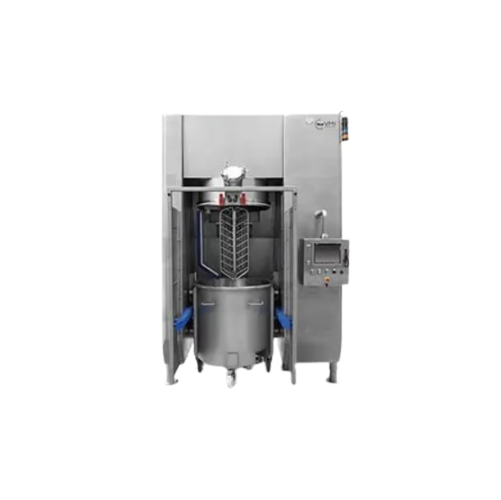

Planetary mixers for baking and food industries
Achieve precise mixing and consistency across a range of products with adv...
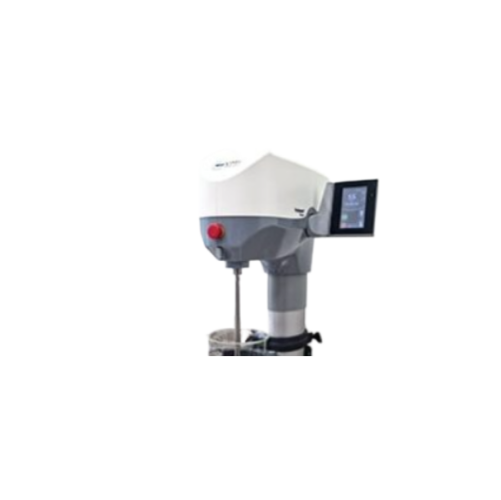

Vacuum homogenizers for cosmeto-pharma and fine chemistry
Bring precision and efficiency to your formulation processes w...
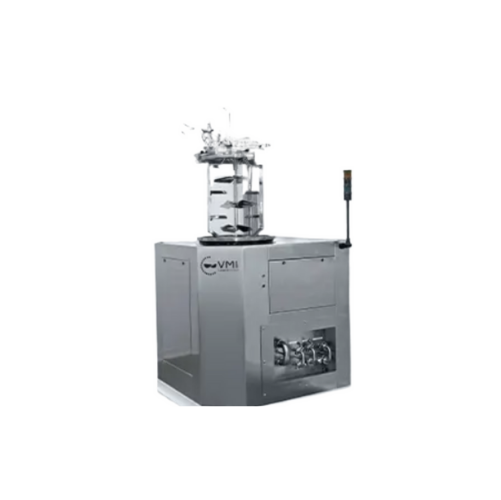

Vacuum homogenizer for cosmetics and pharmaceuticals
Optimize your production with precision mixing and homogenizing, ess...
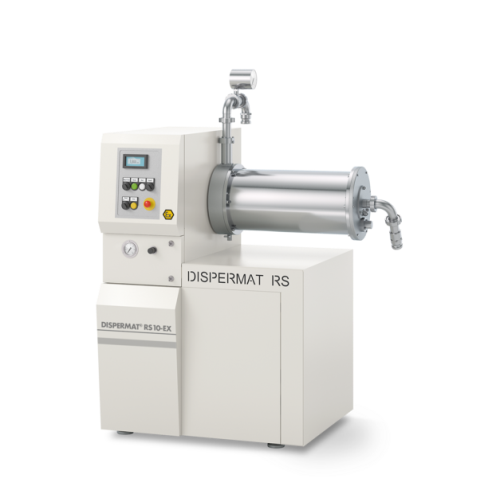

Explosion-proof bead mill for industrial grinding applications
For manufacturers seeking precise particle size control, ...
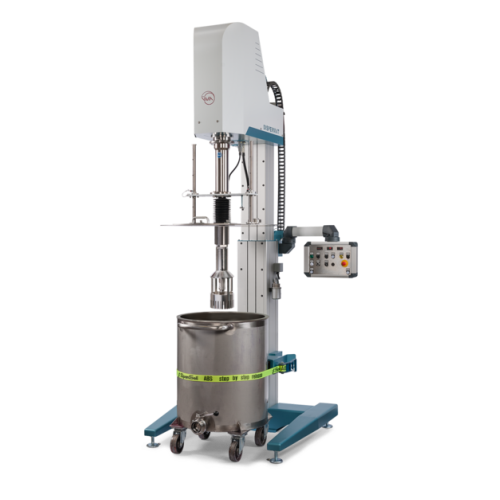

High shear batch process homogenizer for production
Achieve efficient emulsifying, homogenizing, and dispersing with prec...
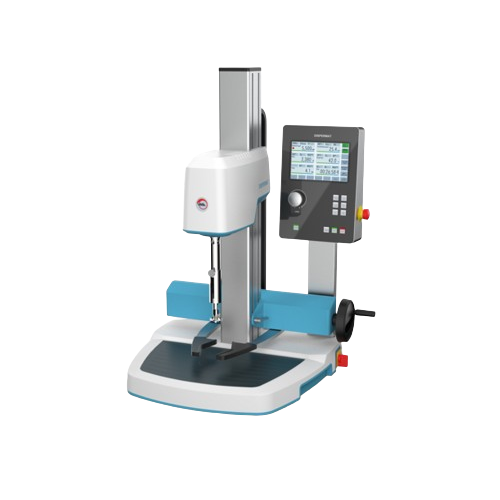

Laboratory dissolver for multiple applications
Efficiently streamline your laboratory processes with this versatile dissol...

Rotary homogenizer for laboratory and pilot plant
For achieving optimal dispersion in complex formulations, this solution...
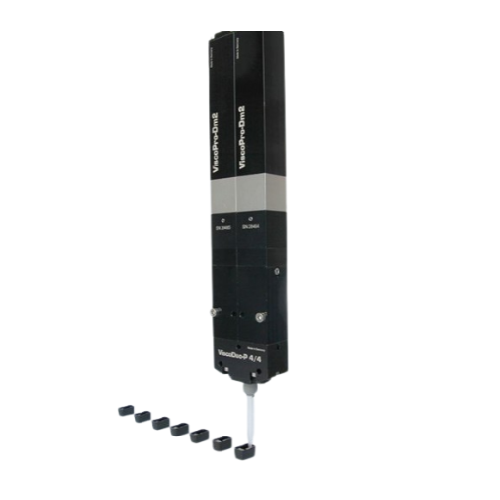

Precision 2k dispenser for automated systems
Achieve precise mixing and dispensing of two-component materials with minimal...
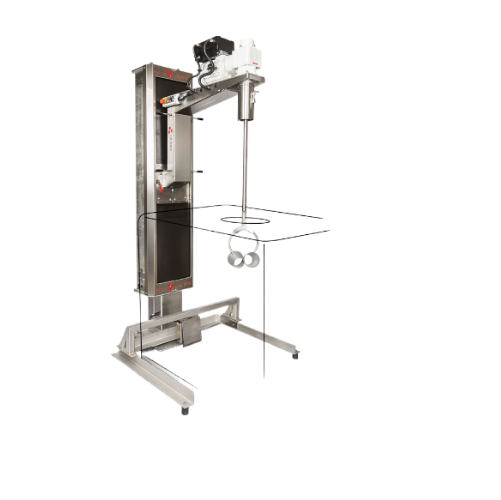

Adjustable integral stand mixer for transport containers
Achieve optimal mixing and stirring in diverse transport contain...
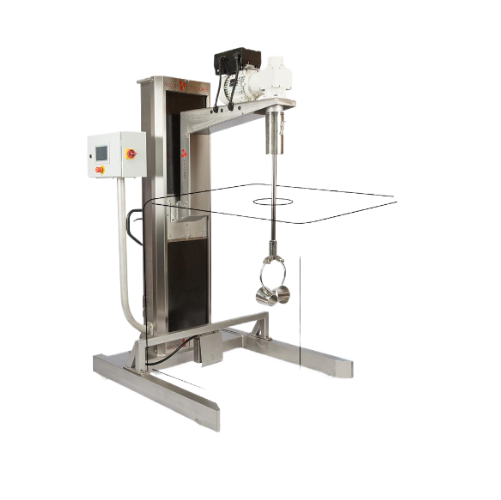

Industrial stativ mixer with adjustable height
Achieve precise mixing and stirring across diverse batches with a mobile, a...
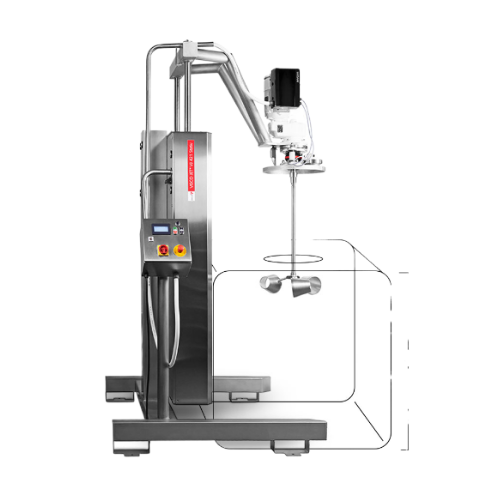

Industrial mixer for product-critical processes
When dealing with high-hygiene requirements and complex mixing tasks acros...
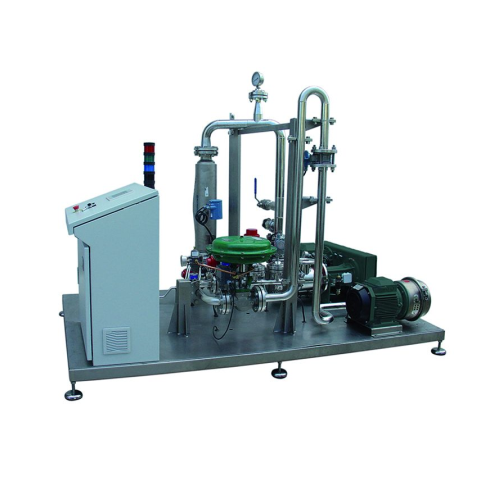

Complete mixing systems for industrial applications
Optimize your production efficiency and product consistency with adva...
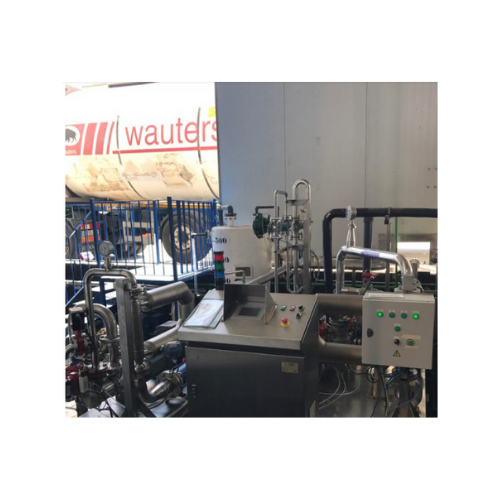

Complete mixing solutions for food, chemical, and cosmetic industries
Enhance your production line with precision mixin...
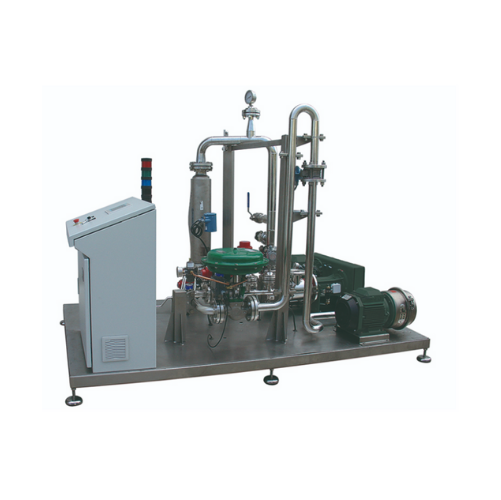

Complete mixing solution for food, cosmetics, and chemical industries
Optimize your production line with a system that ...

Mechanical homogenizer for fine cutting and emulsifying
Achieve precise particle size control and consistent texture in y...
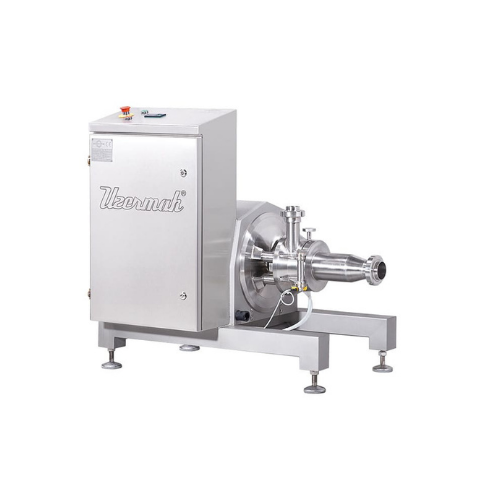

Inline mechanical homogenizer for food processing
Achieve precise particle size and uniform texture in your emulsions and...

Versatile size reduction processor for food applications
Enhance your food production line with a processor that excels i...
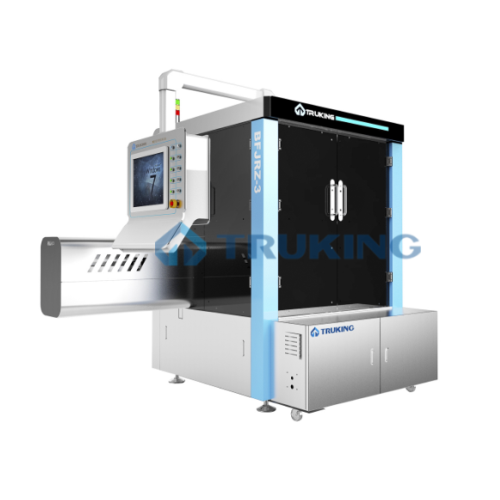

X-ray inspection for pharmaceutical vials
Ensure product purity by detecting contaminants in pharmaceutical vials with adv...
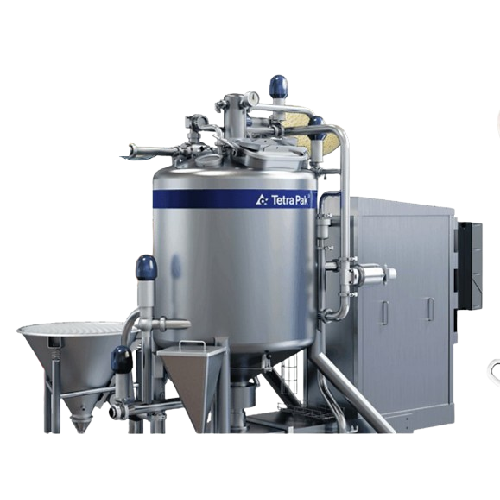

High shear mixer for emulsions and dispersions
Achieve precise emulsification and dispersion with advanced high-speed mixi...

High shear mixer for dairy and beverage industry
Achieve consistent product quality with a high shear mixer, enabling seam...
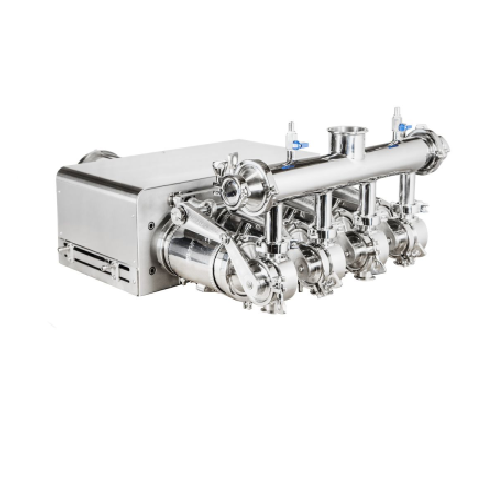

Pneumatic syringe dosing system
Streamline your liquid dosing process with precision and efficiency, ensuring each applicati...
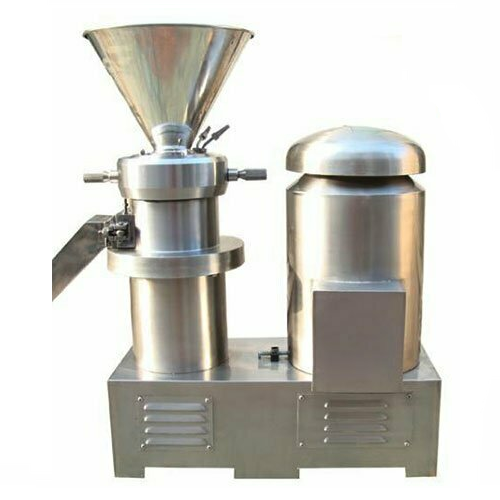

Stainless steel peanut butter grinder
Optimize your production line with high-speed emulsification and grinding, achieving ...
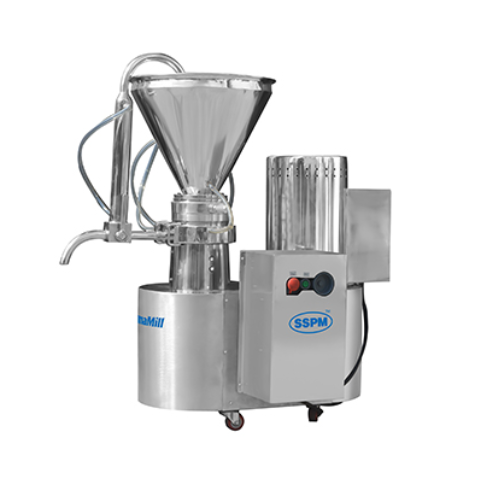

Colloid mill for particle size reduction and emulsification
Achieve precise particle size reduction and stable emulsions...
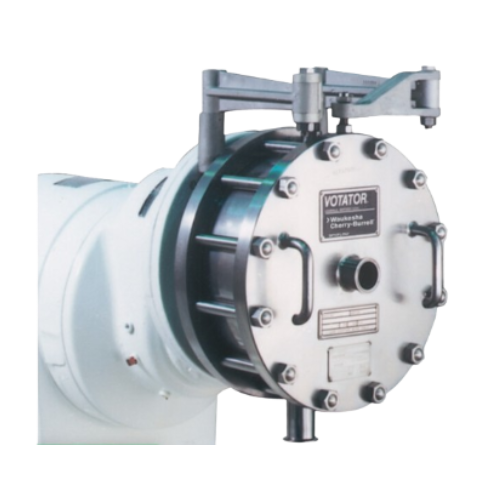

High-shear mixer for emulsions, dispersions, and foams
Achieve precise emulsions and dispersions effortlessly with high-s...
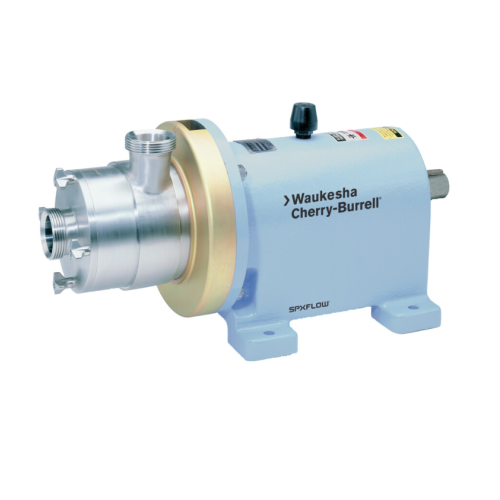

Shear pumps for continuous on-line dispersion
Effortlessly achieve consistent shearing and mixing with versatile shear pum...
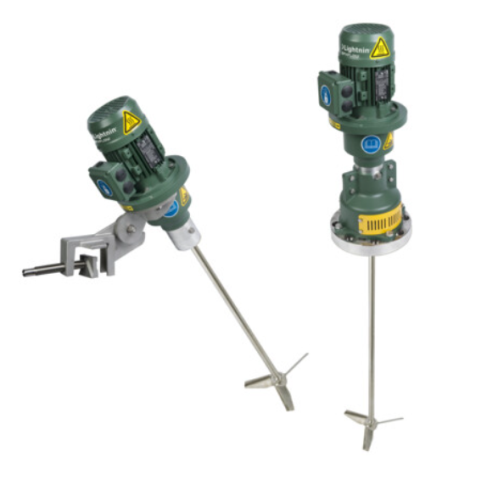

Portable and fixed mount mixing system
Optimize your mixing operations with a versatile system that adapts seamlessly betwe...
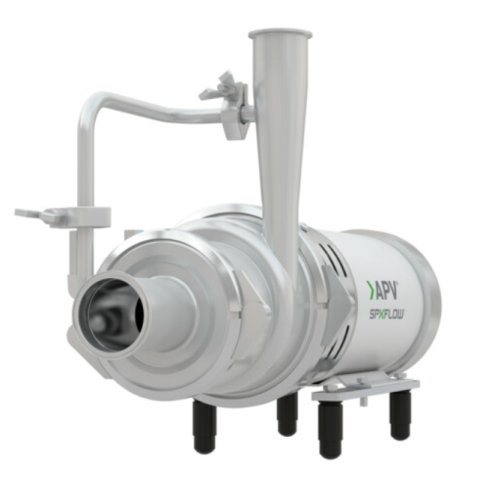

Self-priming centrifugal pump for entrained air handling
Effortlessly manage entrained air and foam in fluid processing w...
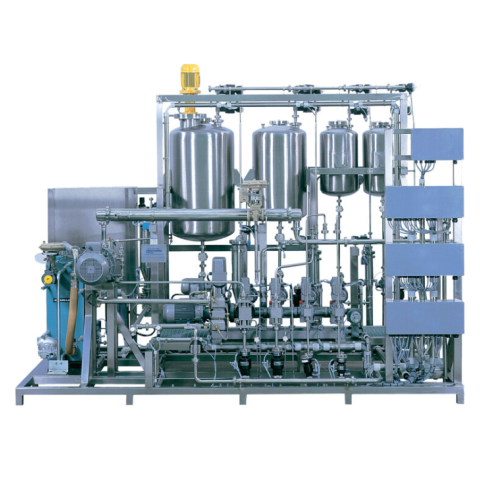

Automated body lotion blending system
Streamline your personal care product manufacturing with a seamless blending and emul...
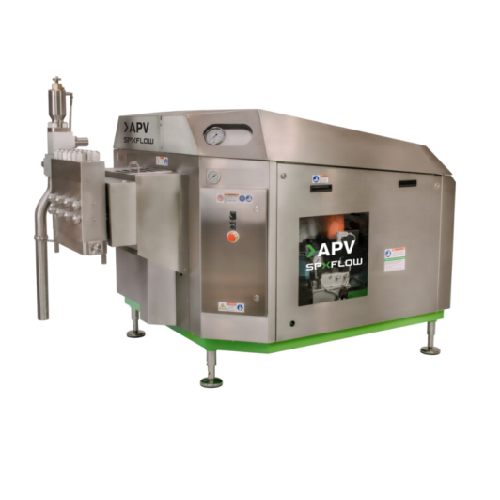

High pressure homogenizer for dairy and pharmaceutical industries
When uniform texture and stable emulsions are critica...
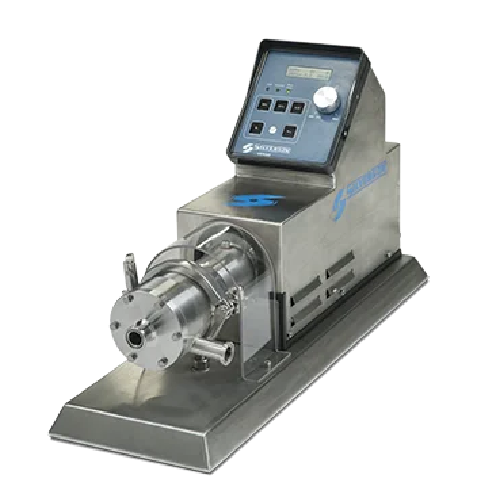

Laboratory in-line mixer for precise mixing and reproducibility
Achieve precise laboratory-scale mixing with rapid proce...
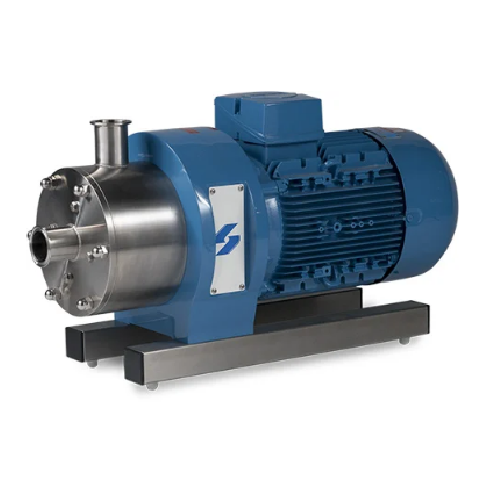

High shear inline mixer for continuous processing
Effortlessly streamline your mixing process with this solution capable ...
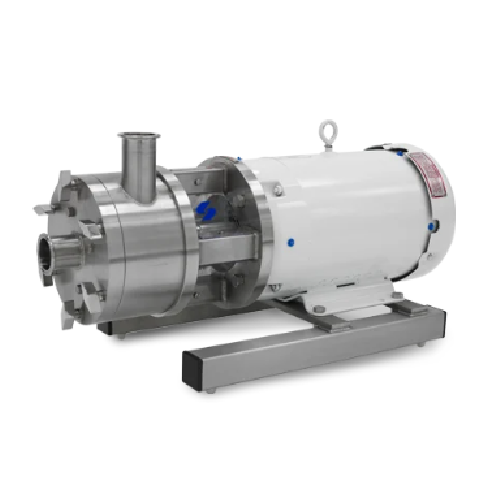

In-line ultra sanitary mixer for pharmaceutical and food applications
Enhance your liquid formulations with precision m...
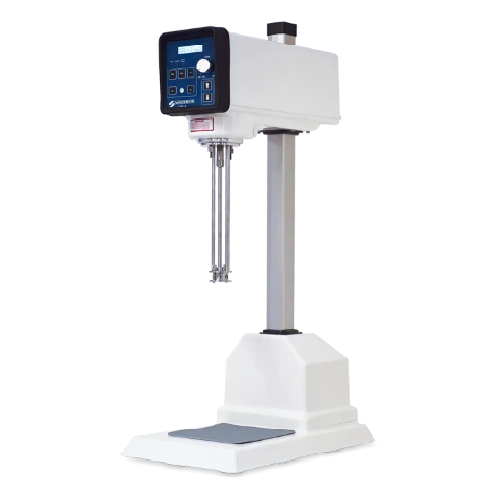

High shear lab mixer for laboratory work and r&d
Achieve unparalleled precision and consistency in laboratory and pilot-sc...
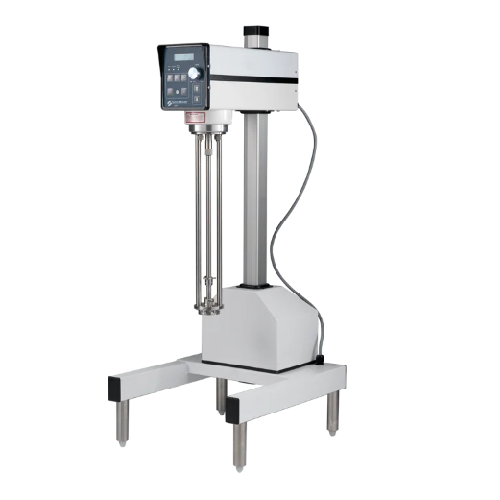

Pilot scale batch mixer for small scale production
Achieve precise control and consistency in small-scale production with...
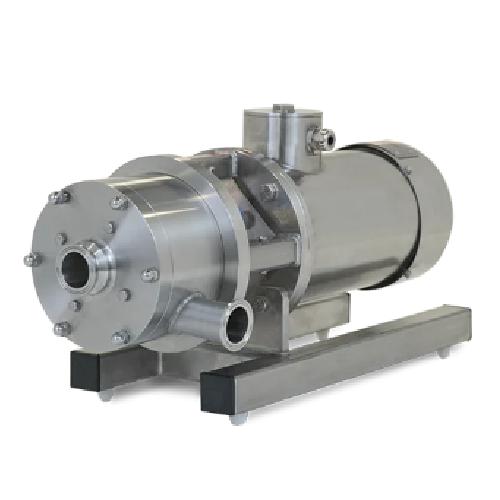

Sanitary high shear mixers for pharmaceutical production
Achieve unparalleled hygiene and efficiency in your mixing proce...
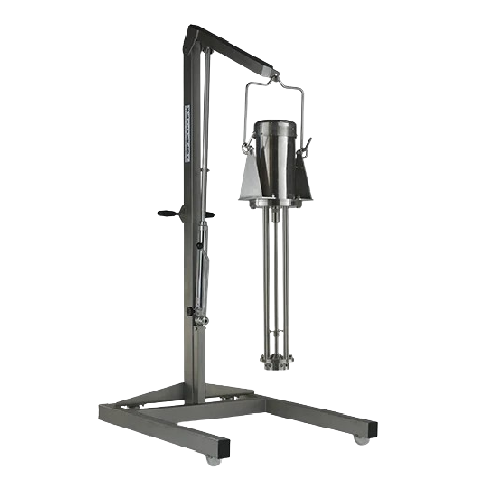

High shear batch mixer for industrial mixing
Optimize your production cycle with this high shear batch mixer, designed to ...
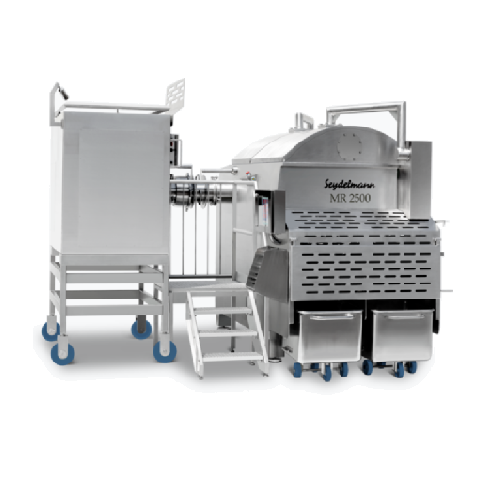

Automated production line for ground meat products
Enhance your meat processing efficiency by seamlessly integrating grin...
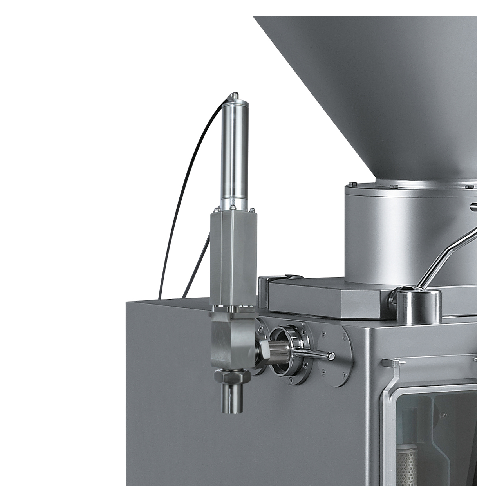

Vertical dosing valve for accurate food portioning
Ensure precision in portioning liquid and semi-liquid food products wi...
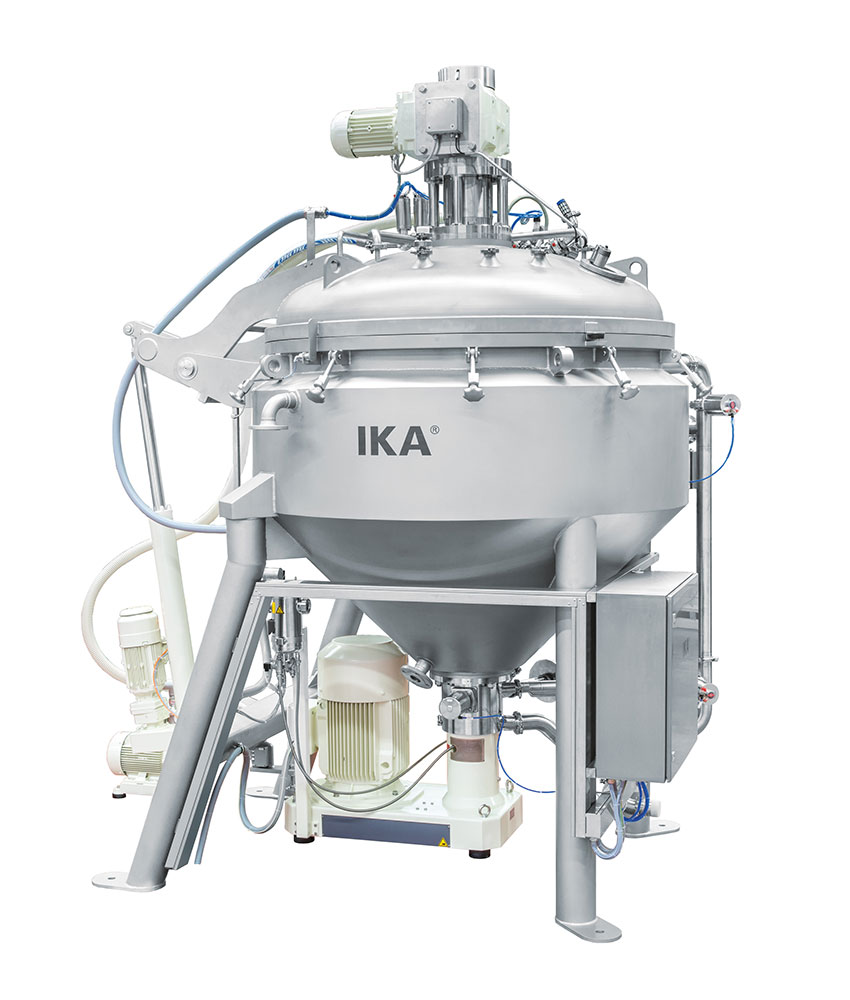

Industrial Sauce Homogenization and Emulsifying System
Texture and consistency are critical to foods with delicate compos...

Self-adhesive linear labeling machine for bottles
It is vital to have precise and long-lasting labels on bottles to avoid...

Cosmetic cream filler
From thin liquid baby oils and perfumes to thicker lotions and creams for hair and skincare, cosmetic p...

High pressure electric laboratory homogenizer
It’s vital that small units for experimentation can scale up with 100% accur...
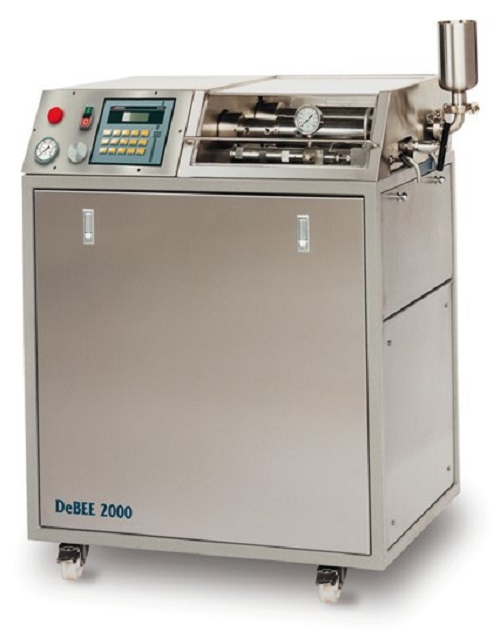

High pressure pilot homogenizer
Biotech and pharmaceutical development programs often require a mixing method that achieves ...
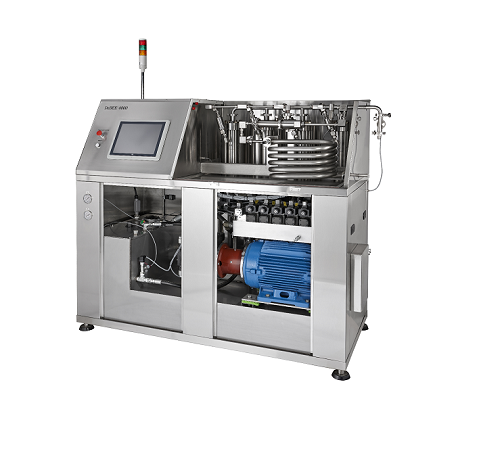

High pressure industrial homogenizer
For any industrial pharmaceutical process that relies on high pressure homogenization ...
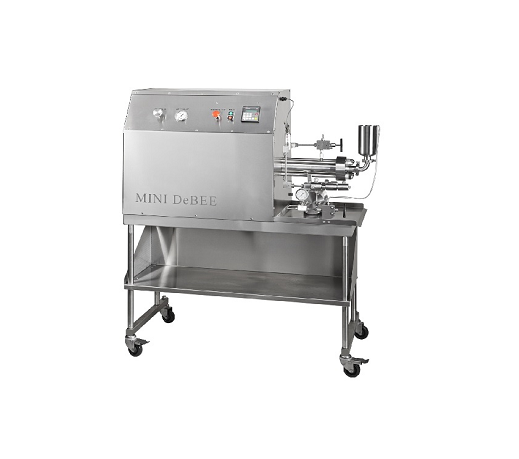

Pilot high pressure homogenizer
For maximum value, a high-pressure homogenizer that’s suitable for both laboratory and pilot...
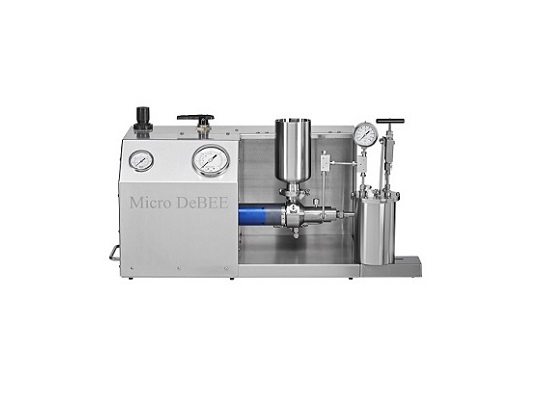

High pressure air powered laboratory homogenizer
Offering lab-scale to small pharmaceutical production scale output for in...
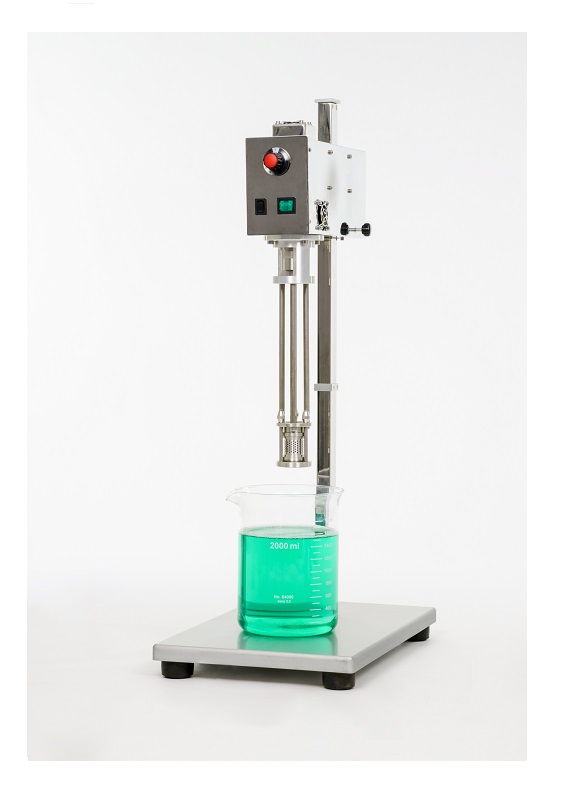

High shear lab mixer for creams
Lab-scale mixers are vital in the design or small-batch production of a range of pharmaceuti...
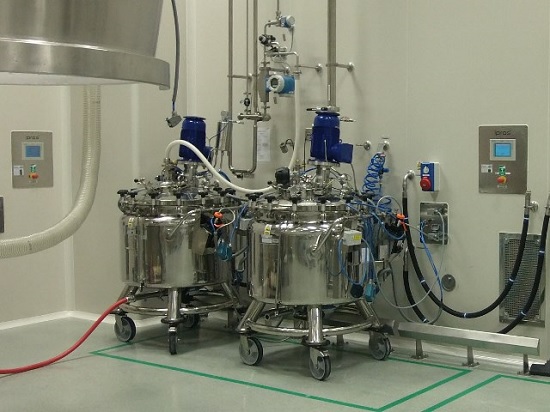

Vacuum mixer for suspensions
The production of high quality pharmaceuticals often requires mixing of suspensions and similar...
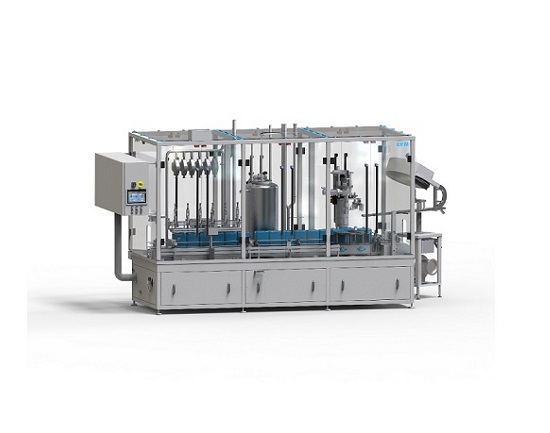

In-line monoblock linear filler & capper
In many food, chemicals and cosmetic industry processes it is vital to have a...
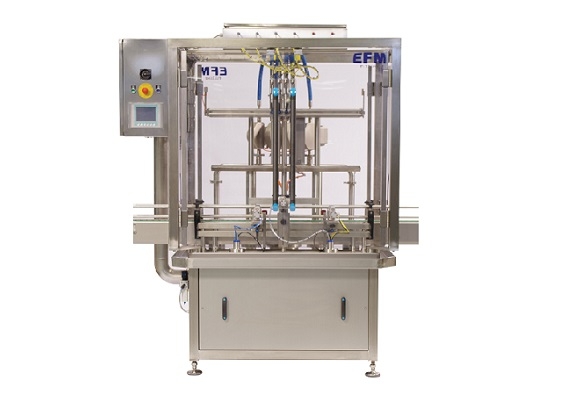

Flowmeter filler
For larger production runs of food, non-food and cosmetics industries, where accuracy and volume of filling i...
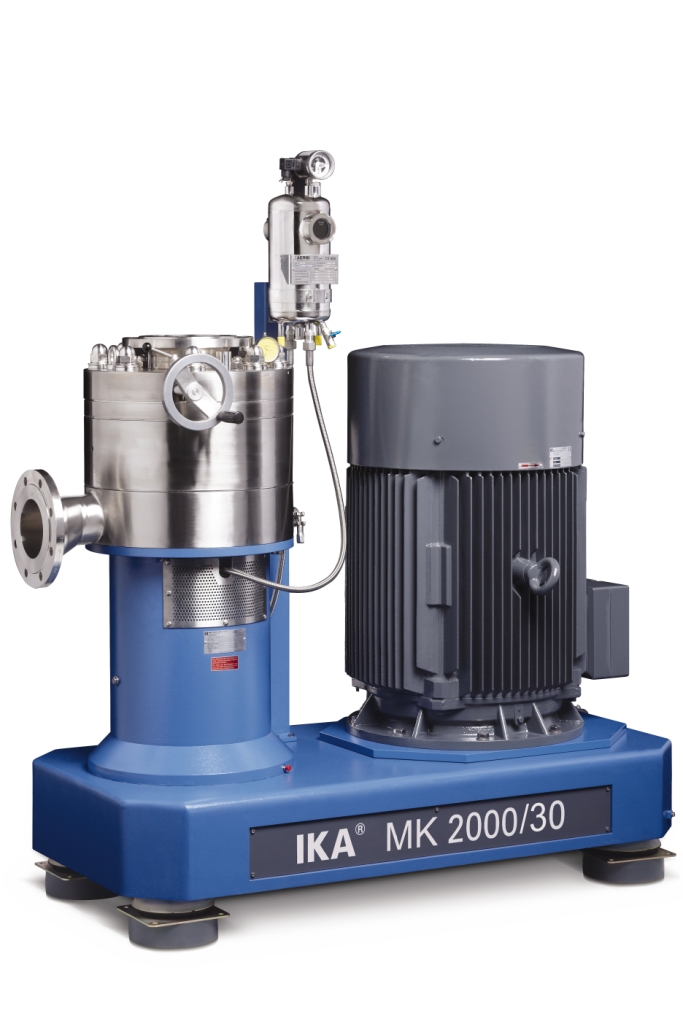

Colloid mill
For creating extremely fine emulsions and high quality dispersions a high pressure homogenizer is often chosen. ...
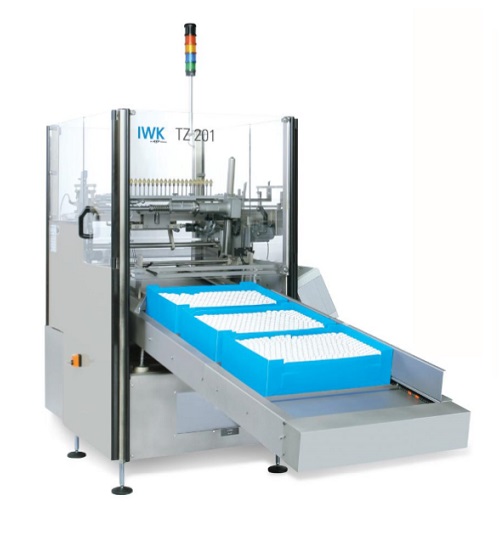

Tube unloader and feeder
The pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries utilise high speed tube fillers on large-scale production...
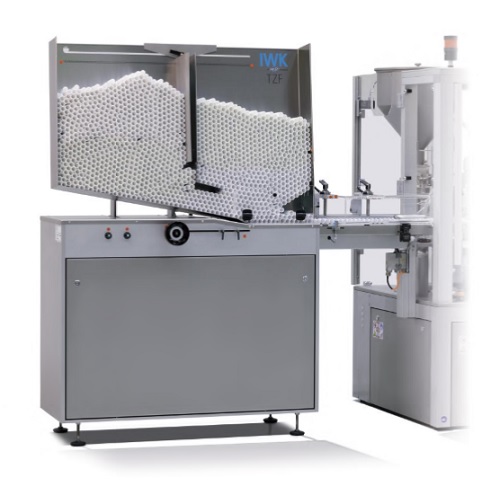

Tube feeding unit for high volume and high speed tube filler
High performance tube-filling machines are used for large s...
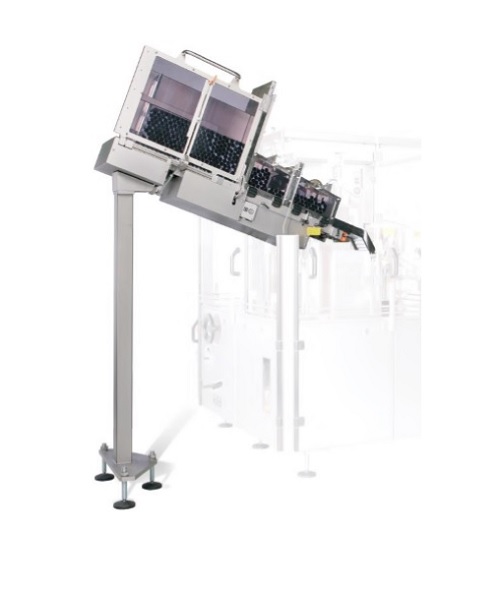

Loading cassette for a tube filler
High performance tube-filling machines are used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic indus...
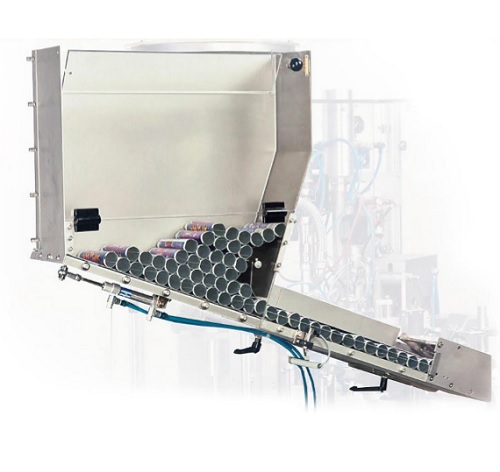

Tube feeder for a small scale production tube filler
Low speed tube-filling machines are used for small scale production ...

High speed automatic tube filler
For high-volume lines filling pharmaceutical, cosmetic or food products into tube container...

High-capacity horizontal cartoner for pharma and cosmetics appliances
Cartoners take carton blanks which are formed and...
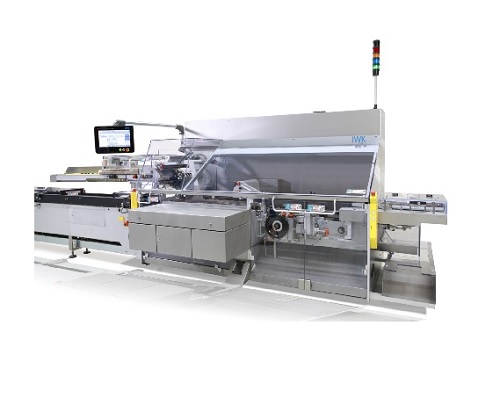

Automatic cartoner for applications in pharma and cosmetics
For high capacity production of cosmetics and pharmaceutical...

Horizontal cartoner for pharma and cosmetics
Most pharmaceutical and cosmetics products are packed in cardboard cartons fo...

Medium speed tube filler and sealer
For scale-up filling of tube packaging for pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and food products...
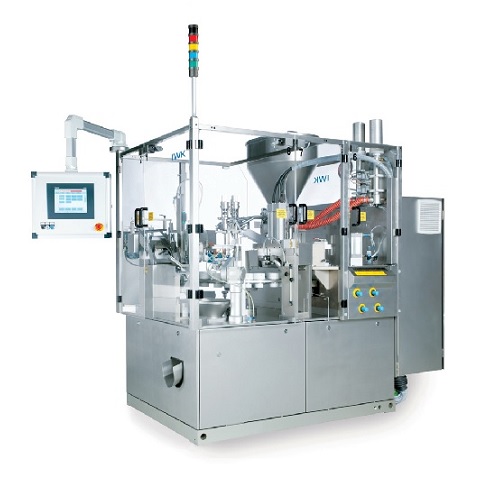

Medium and high speed range automatic tube filler
When scaling up production of pharmaceutical, food or cosmetic products...
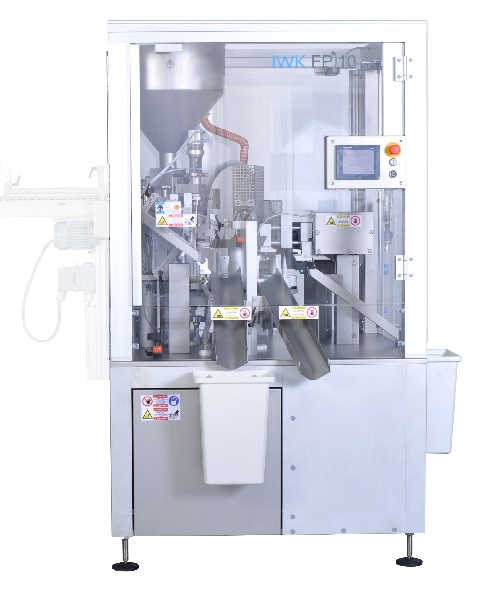

Low speed tube filler
Increasing numbers of products in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries are delivered in fle...
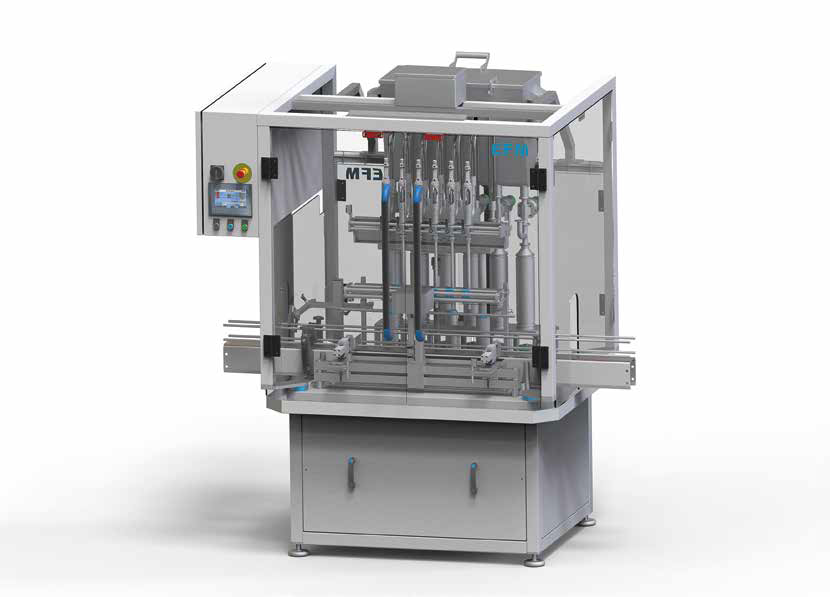

Servo controlled filler
For food and non-food liquid products that are high foam or have a high viscosity a specialist fillin...
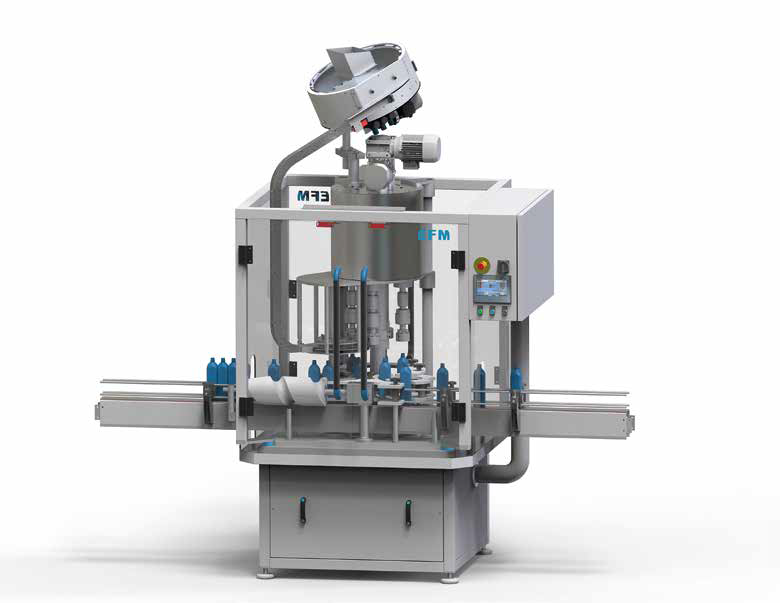

Multi-head capper
For the stand-alone capping of bottles of up to 2.5litre capacity you need a robust and flexible machine wi...
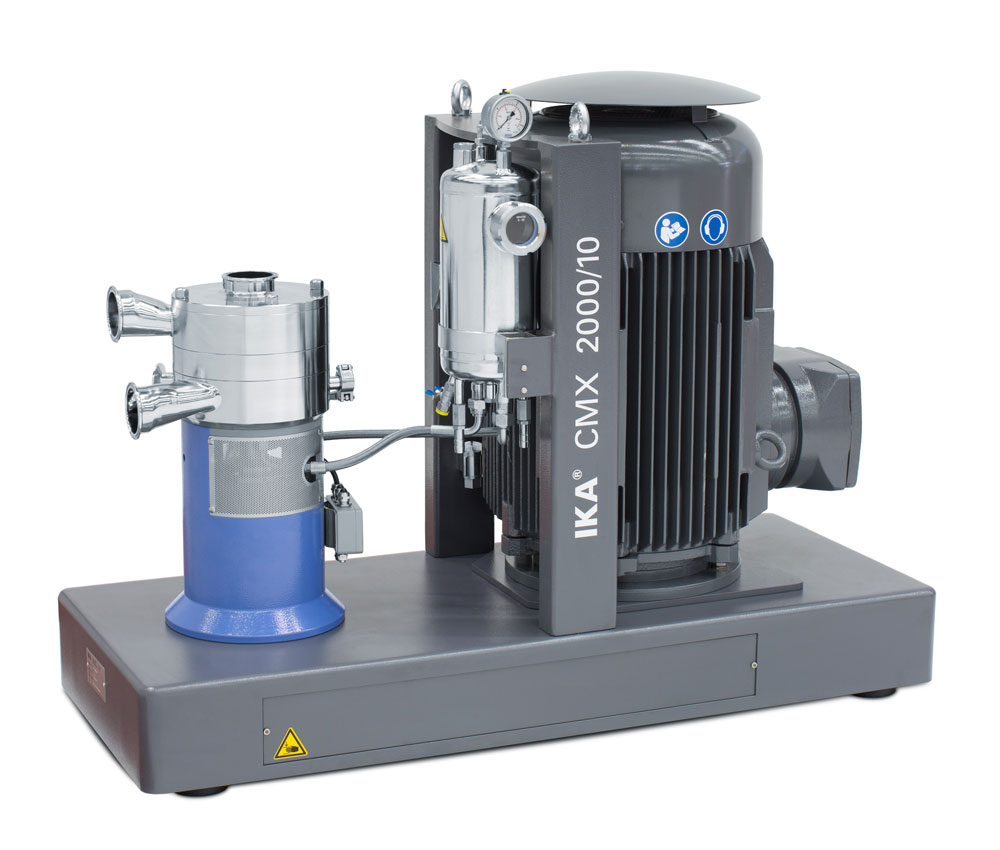

Inline batch mixer for solids and liquids
Several issues often arise when your process requires batch-wise mixing of powde...
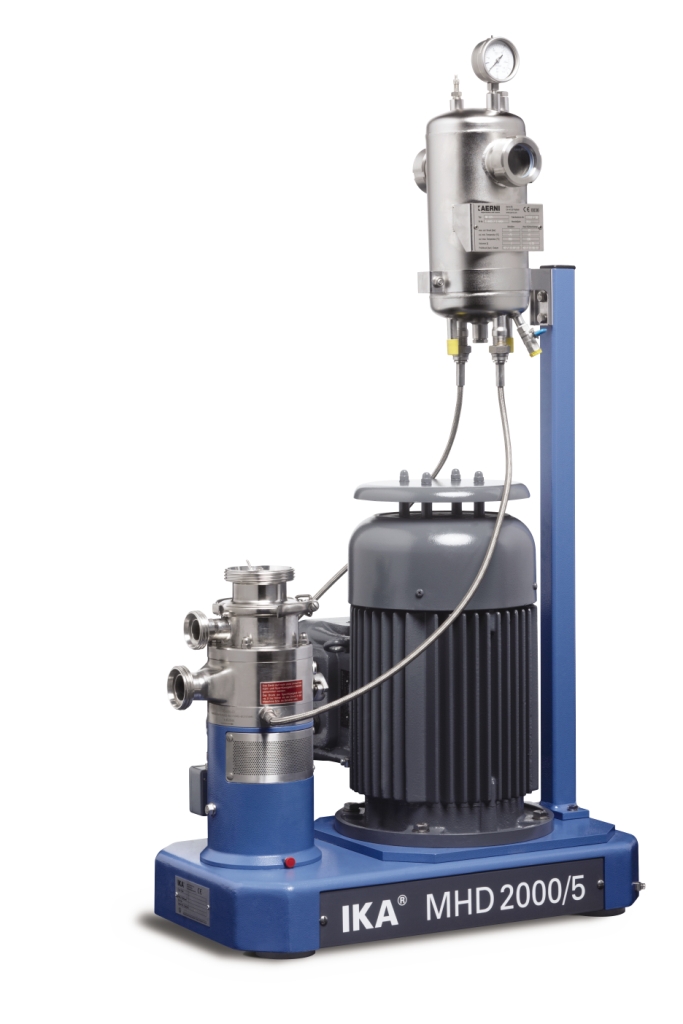

Continuous homogenizing system
Certain mixing tasks present unique challenges and manufacturers need equipment that is speci...
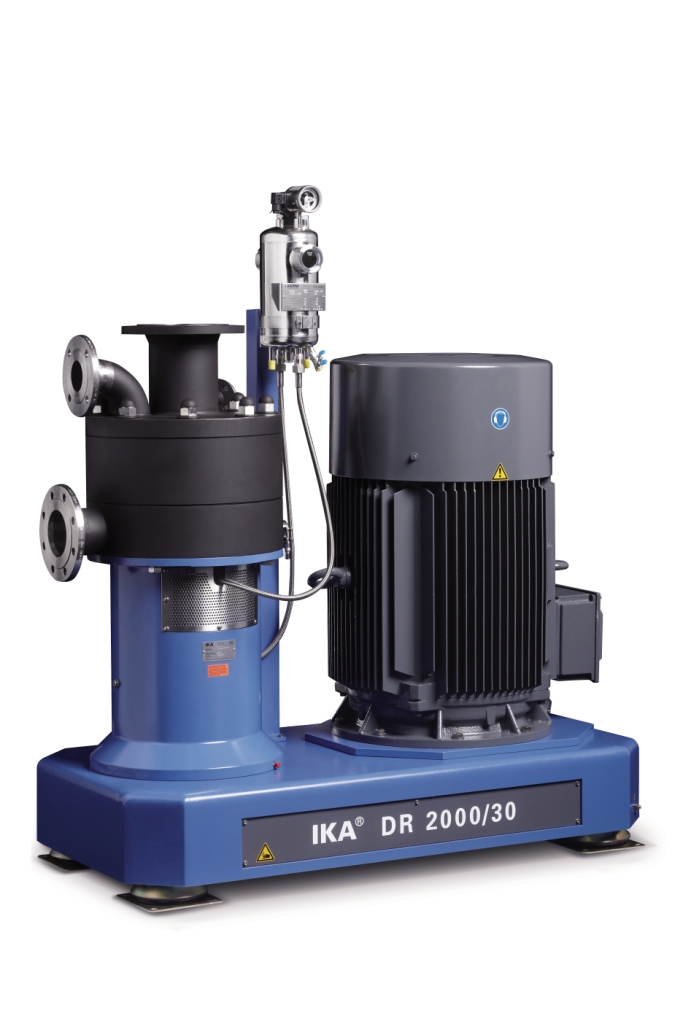

High accuracy homogenizing system
When extremely high accuracy is required in your recipe or formulation traditional mixing...
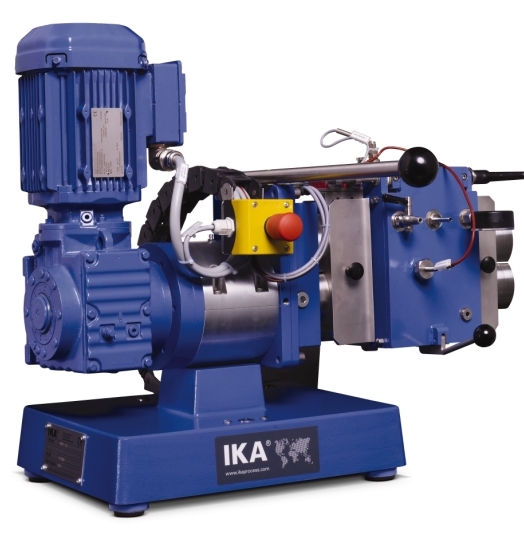

Horizontal kneader
For high viscosity products, better results and reduced process times can be achieved with kneading type r...
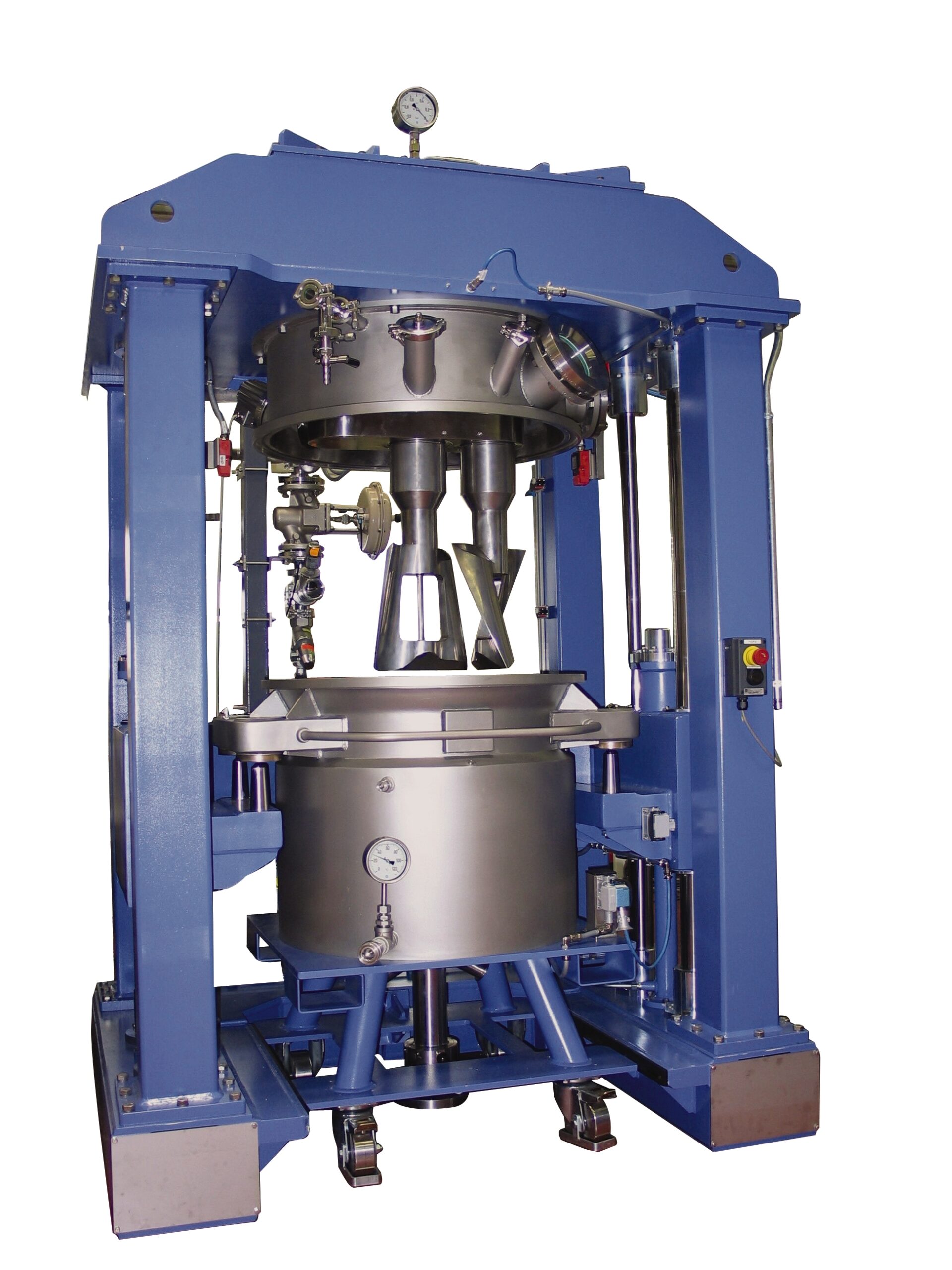

Vertical kneader
Production of highly viscous products with high solid content often benefits from kneading processes rather t...
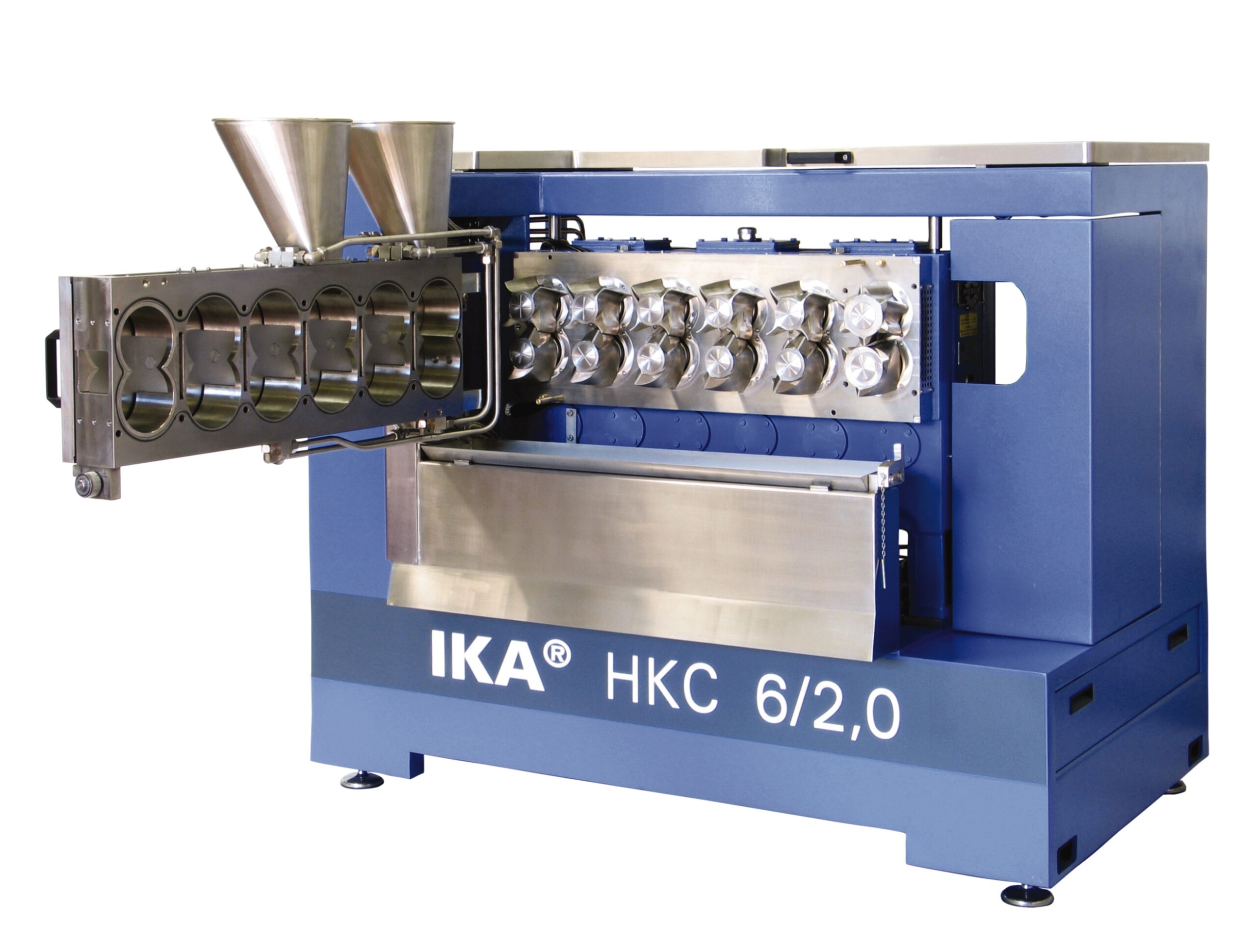

Continuous kneader
Effective mixing of highly viscous products with extremely high solids content can be difficult and the re...
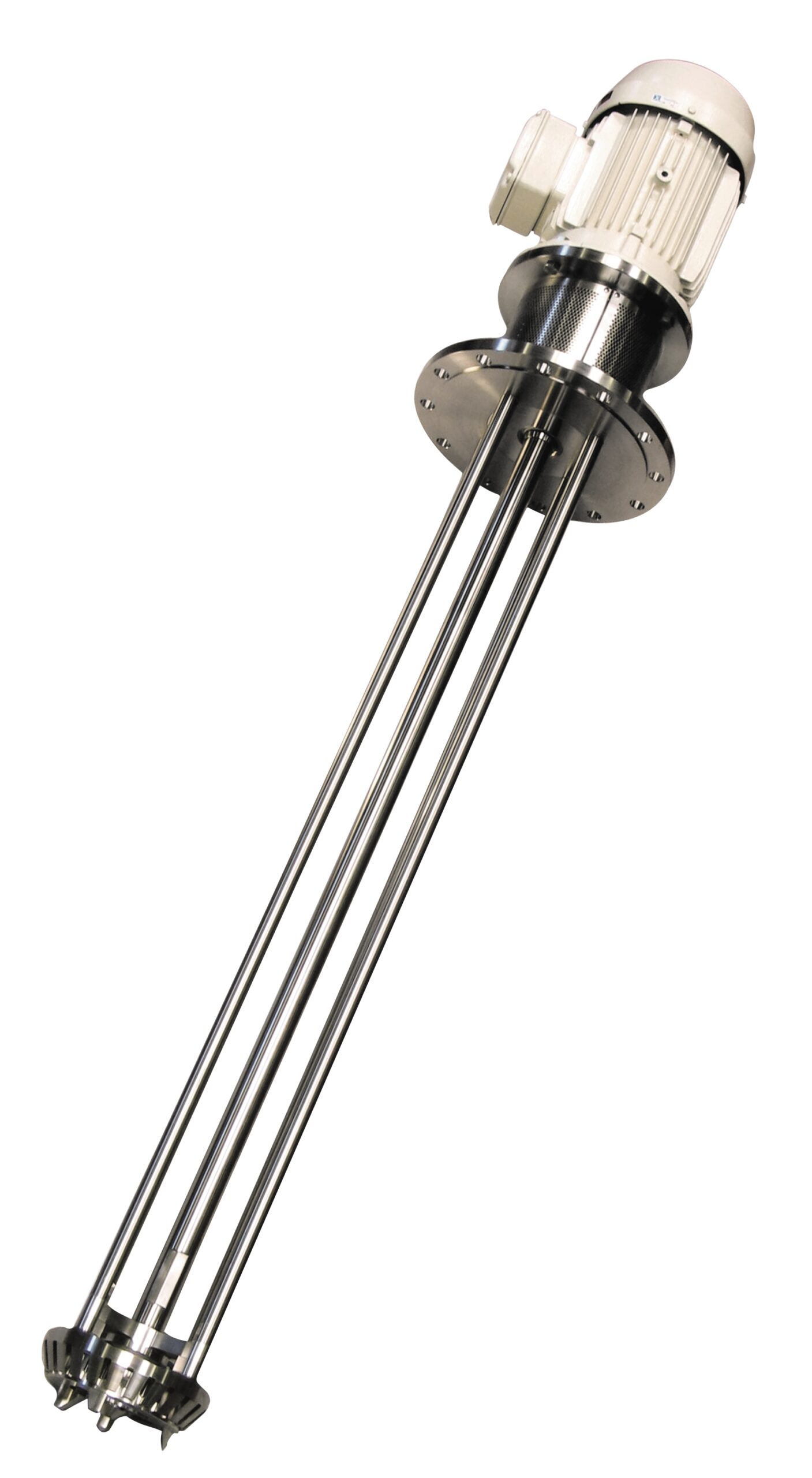

Batch dispersing machine for abrasive products
For mixing and dispersing tasks that cannot be completed by conventional st...
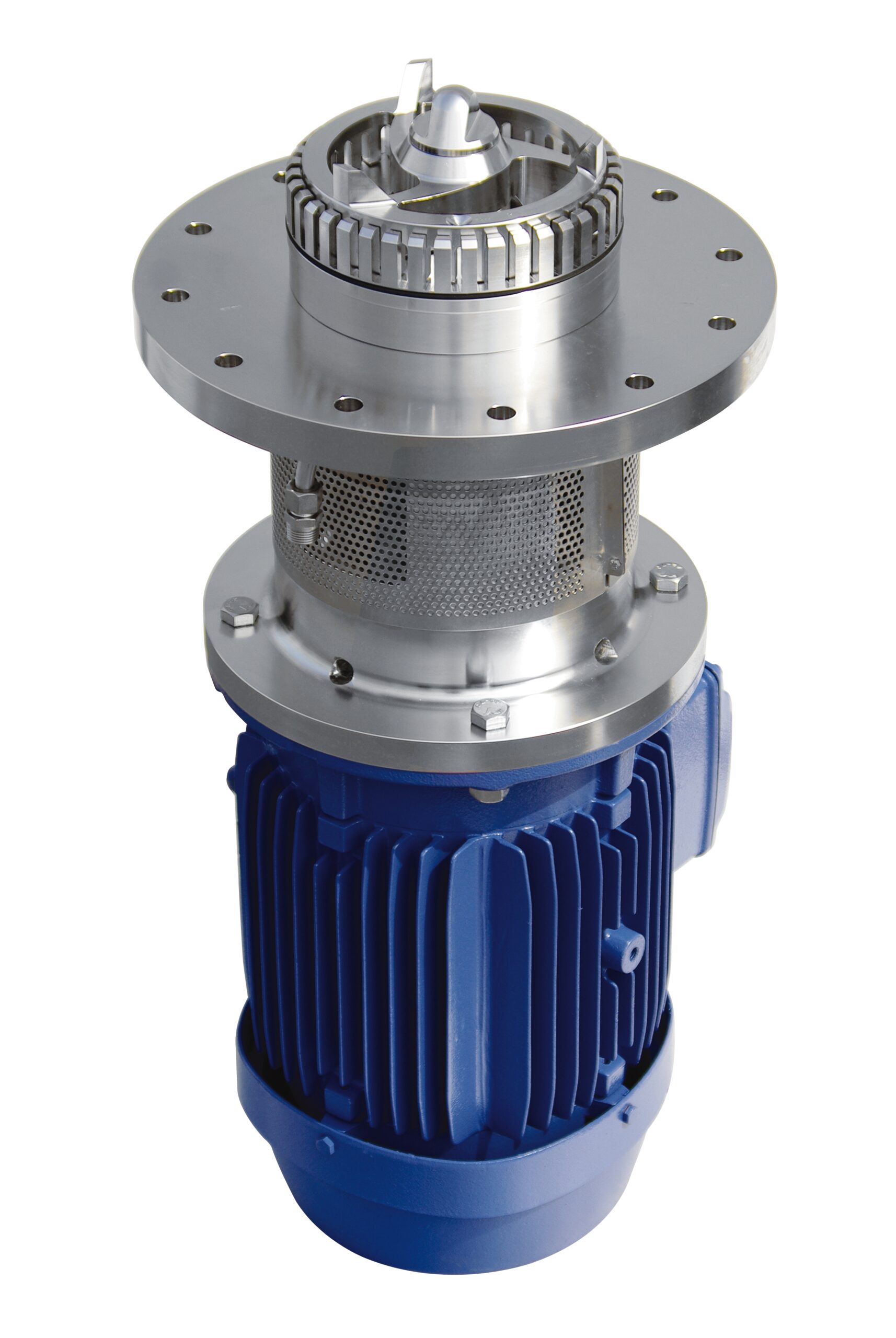

Batch dispersing machine for bottom entry into vessels
When your process requires high performance mixing or dispersion b...
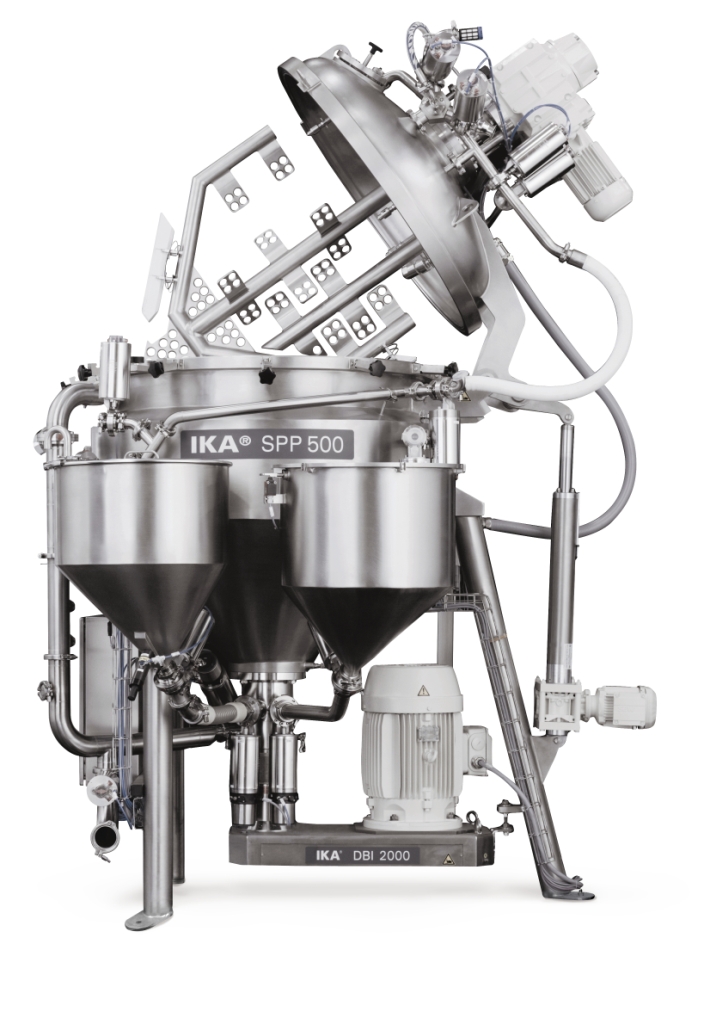

Cost-effective homogenizing and emulsifying system
Manufacturers of cosmetic products need mixing equipment that is capab...
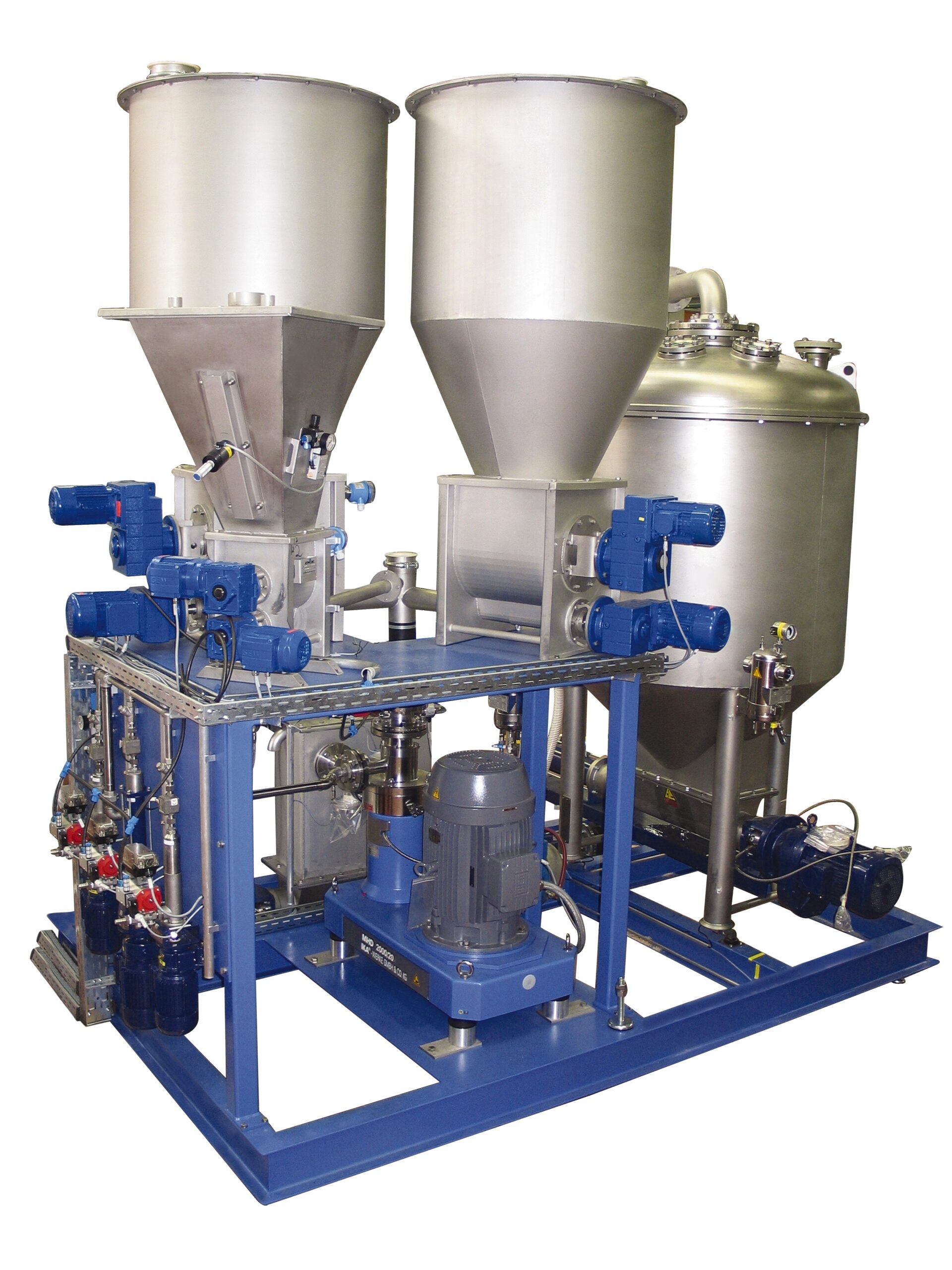

Dust-free continuous homogenizing system
Producers in a wide variety of industries benefit from equipment that can continuo...
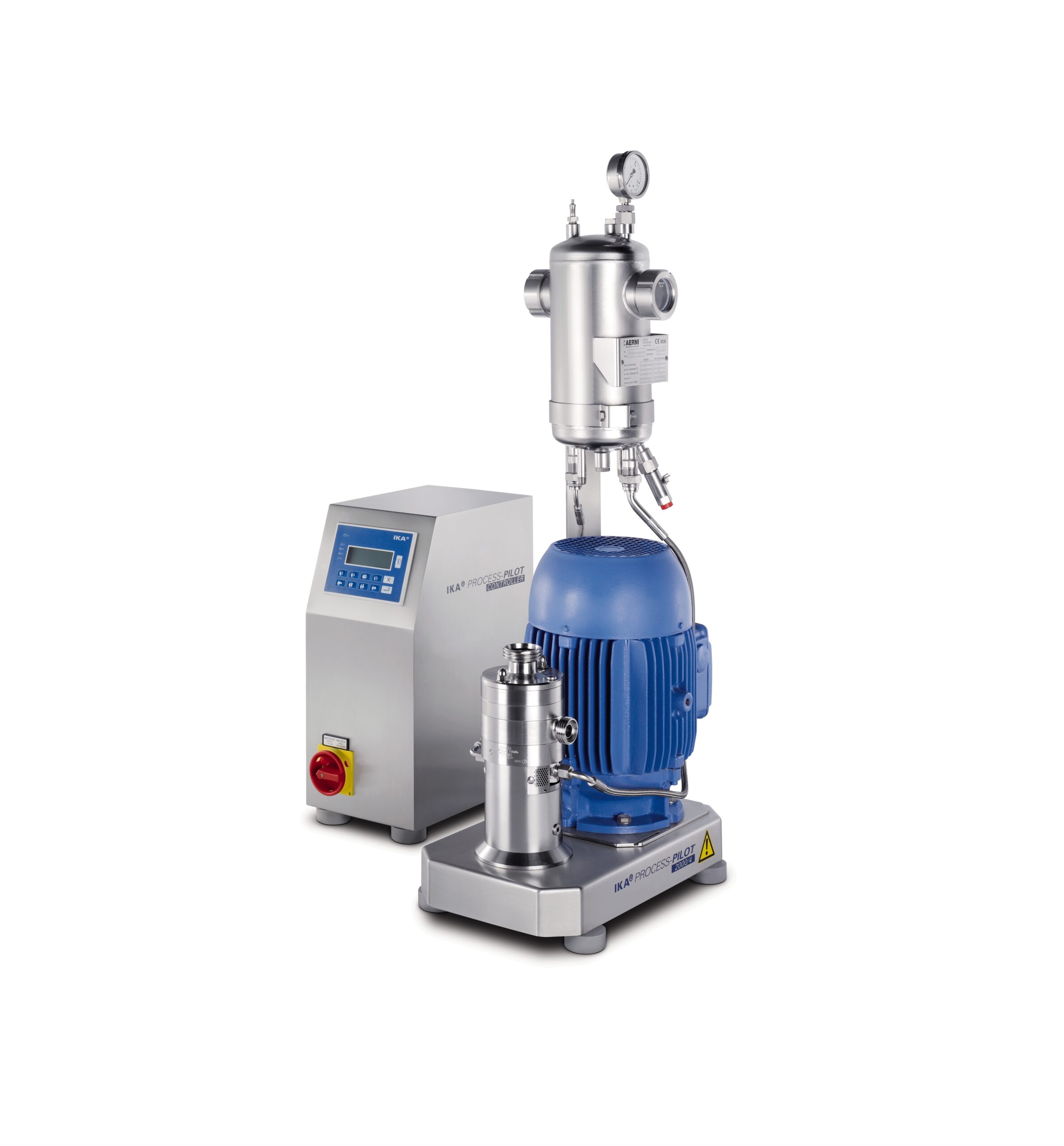

Dilution system for two or more liquids in one pass
Onsite dilution of liquid process ingredients has historically been a...
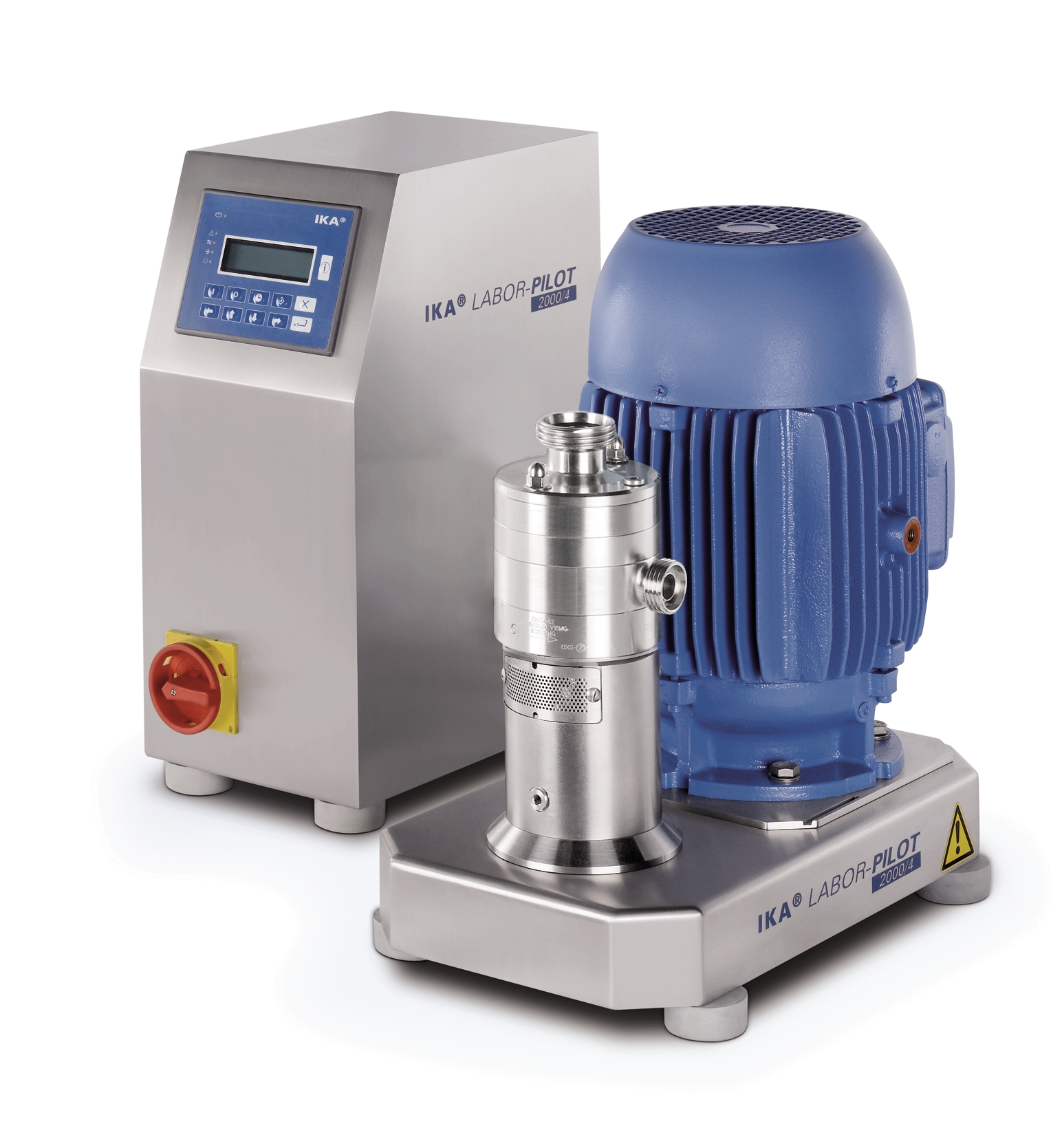

Pilot dispersing machine for testing and scale-up
Innovators in process development need laboratory equipment that helps ...
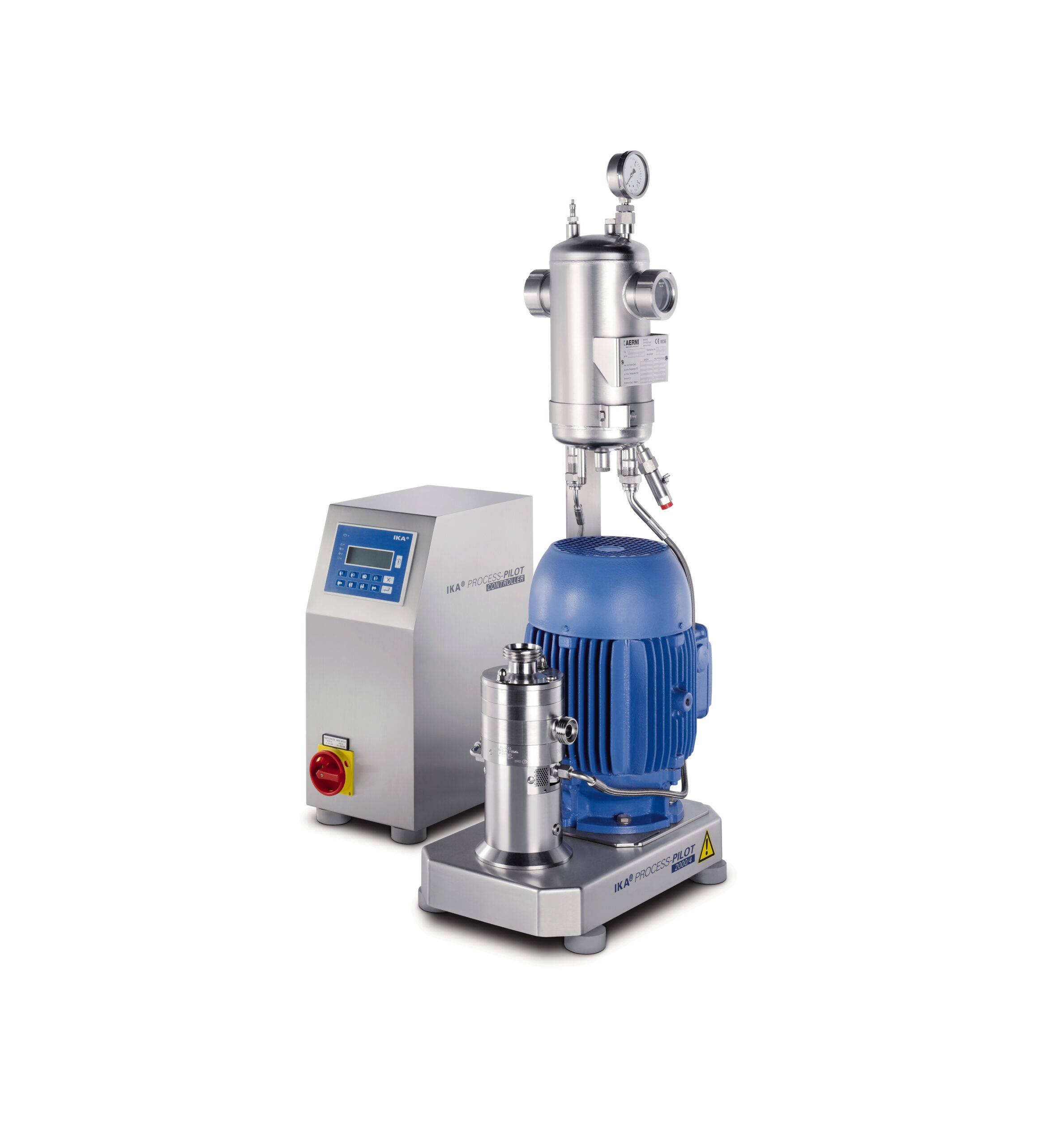

In-line laboratory dispersing machine
Innovators in a wide variety of industries need laboratory equipment on which process...
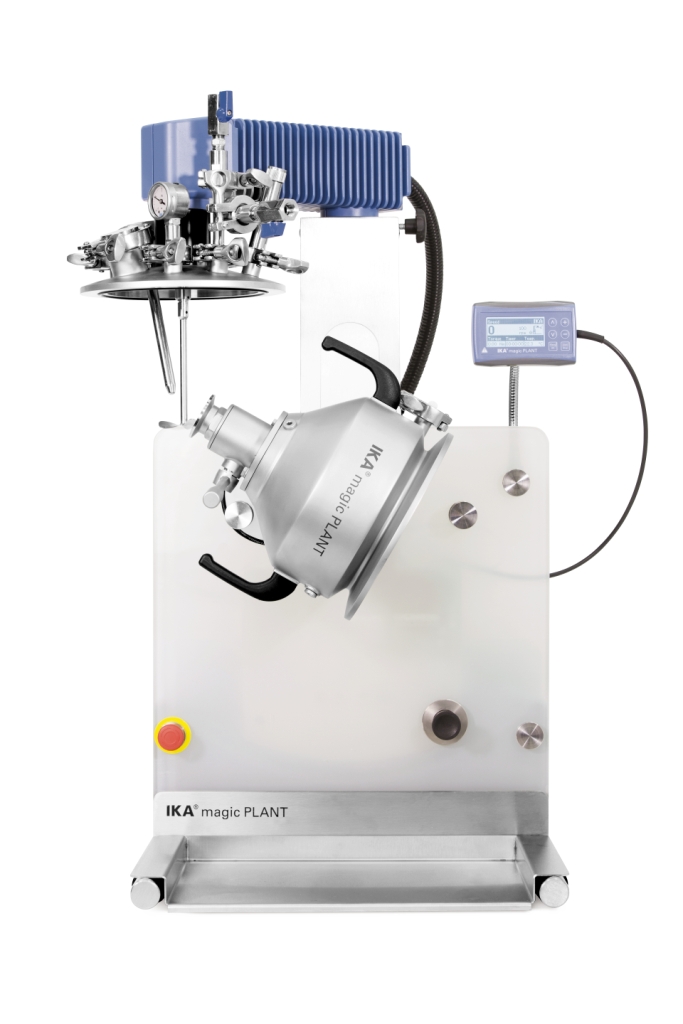

Laboratory dispersing machine for low-viscous masses
Laboratory mixers have not always been easy to work with. Getting a...
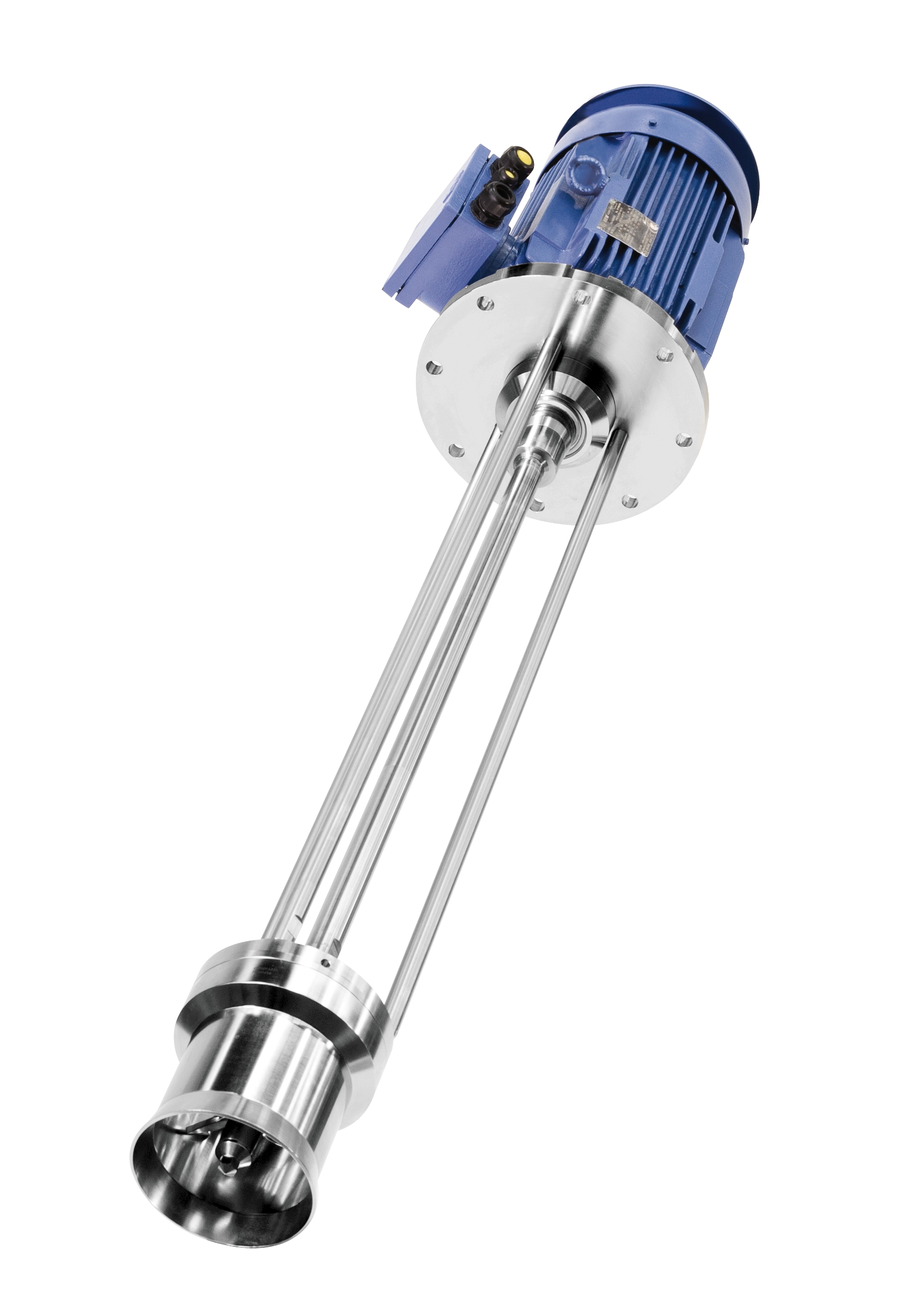

Jet flow agitator for high-viscosity media
Processes including homogenization, dispersing, suspension, emulsification and ...
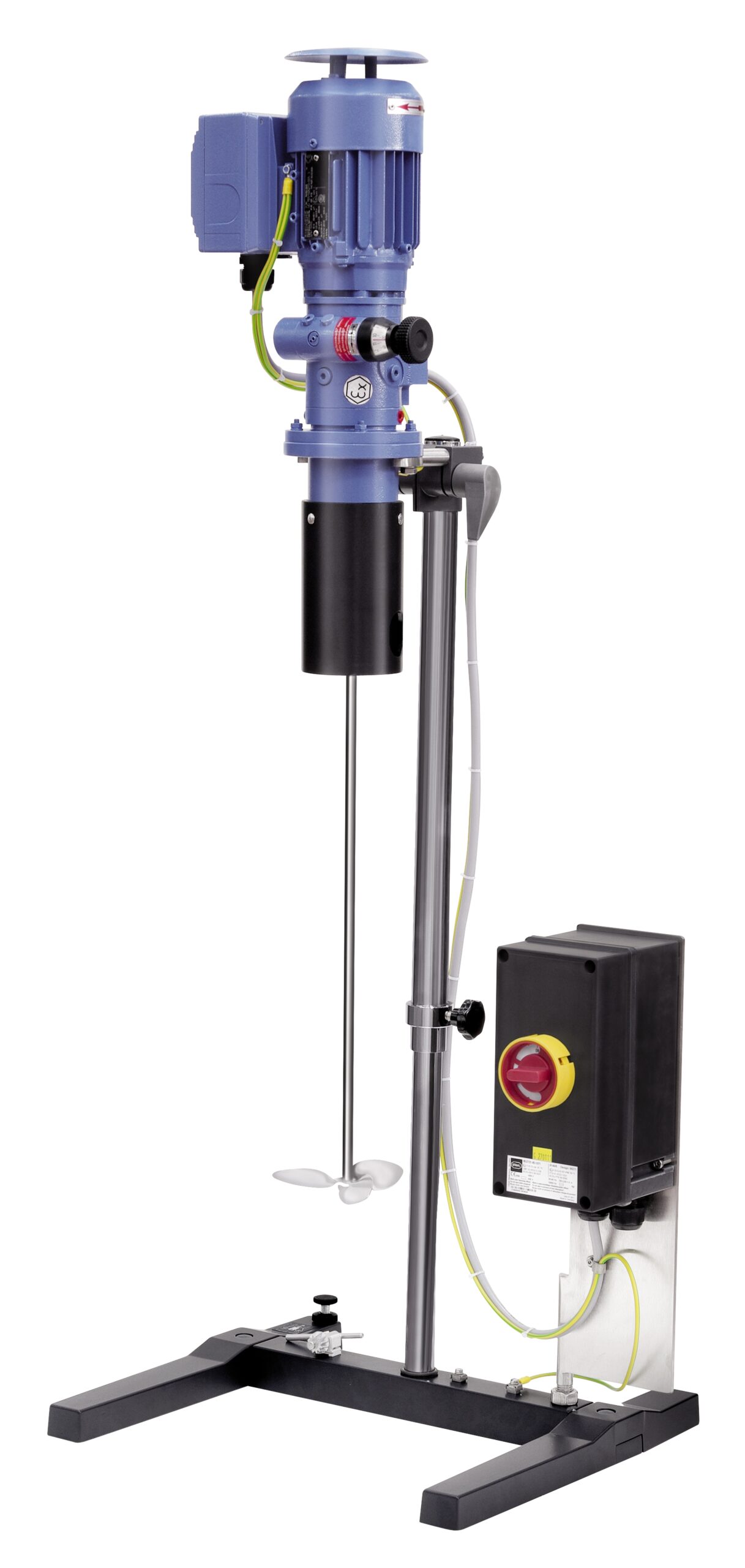

Agitator for medium viscosity media
Mixing fluids of medium viscosity for many production processes requires an agitator wi...
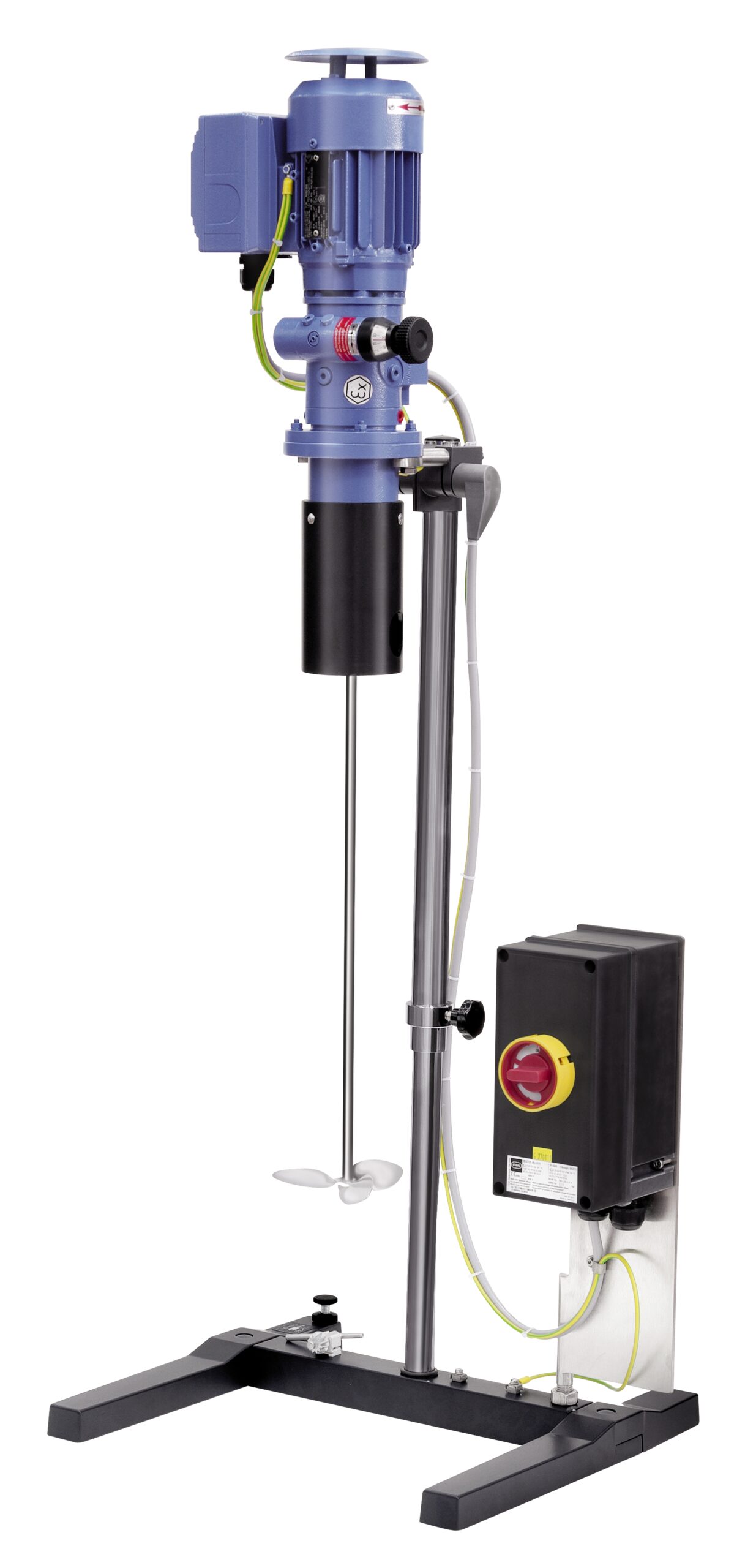

Agitator for low viscosity media
Reliably agitating fluids in open or pressure-less vessels in a laboratory or small scale p...





