Making Softgel Capsules
Find innovative production technology for making softgel capsules and connect directly with world-leading specialists
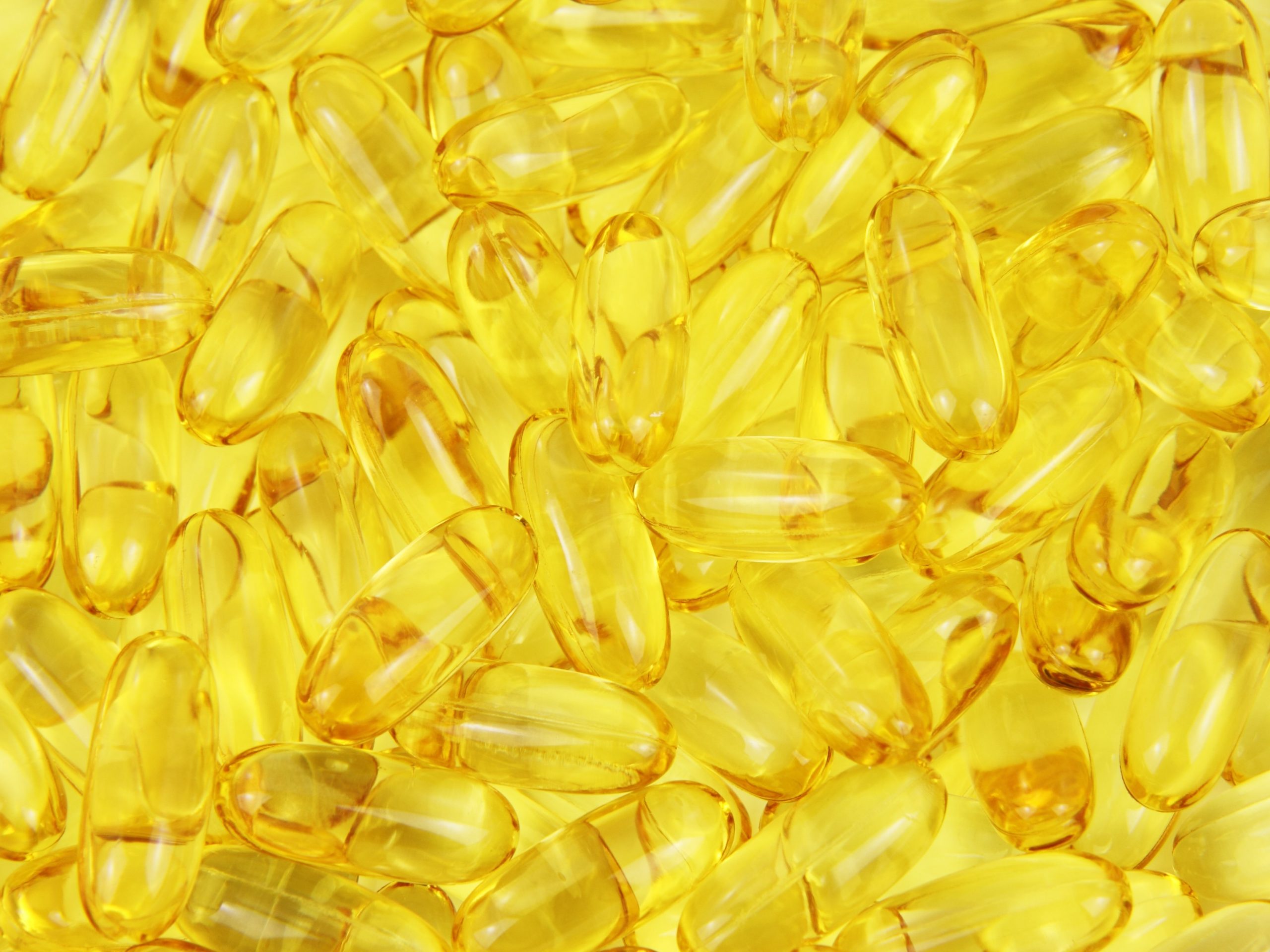
Softgel capsules fast-track the delivery of medication to the bloodstream. Unlike solid pills, they do not need to be broken down by the body before the drugs can be absorbed. Moreover, they are optimal vehicles for oils and fat-soluble formulations that cannot be compressed into tablets.
Select your softgel capsules process
Tell us about your production challenge
Primary ingredients to manufacture a softgel capsule
The essential ingredients of a softgel capsule are gelatin, water, and a plasticizer such as glycerin or sorbitol. The presence of water means that the API formula must not be hydrophilic because it would deteriorate the shell over time.
The capsule is typically transparent, so adding opacifiers protects your fill matrix from sunlight. Preservatives, meanwhile, ensure that your capsules remain free from bacteria. Finally, you may also incorporate colorants and flavorings to make the final product more palatable.

Preparing the gelatin base for softgels
The propensity of gelatin to melt in warm environments and form a gel while it is cooling down makes it an ideal substance for the administration of medication in a liquid or semisolid state.
Gelatin is an effective combining agent that holds the structure of the capsule together. Granulated gelatin is added to a blend of water and plasticizing substance, and the mixture is heated to around 60 °C until the particles are fully dissolved.

Inspect the capsules for air bubbles
Air pockets pose a risk to the production of softgel capsules. Bubbles weaken the structure of the shell and may lead to leakage of the drug.
This manufacturing defect typically occurs when your blending process is not conducted at the right temperature or for a suitable duration. The air inside the base components naturally rises to the surface and escapes the mixture, but inadequate heating leads to trapped bubbles.
Using vegan materials for softgels
You can substitute the gelatin to produce a vegetable-based softgel capsule. Derived from animal bone or connective tissue, gelatin makes traditional formulations incompatible with vegan requirements.
Hypromellose (HMPC) and Tapioca starch present viable alternatives made from vegetable cellulose. Besides using non-animal materials, vegan softgel capsules offer a higher bioavailability rate compared with gelatin options. Their low-moisture content also makes them less brittle in reduced humidity.
Processing steps involved in softgel capsules making
Which softgel capsules technology do you need?

High shear emulsifier for mayonnaise production
Streamline your production of high-quality emulsions with this high-capaci...
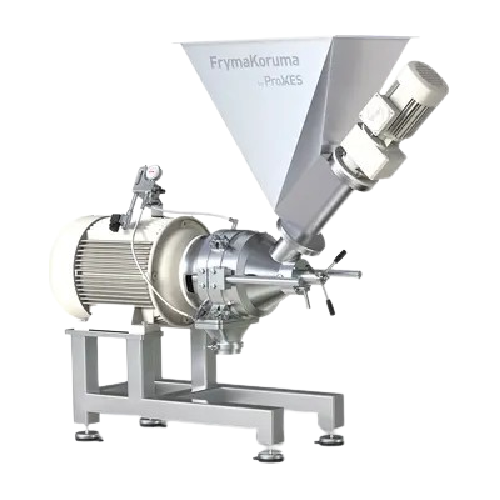

High shear emulsifier for food and pharmaceutical products
Optimize your production line with precise emulsification, ho...
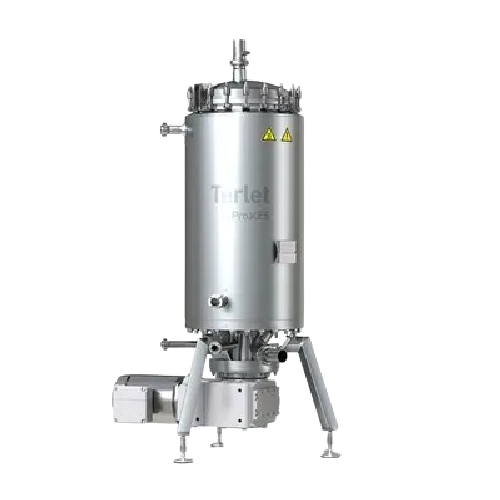

Heat exchangers for efficient heat transfer in industry
Achieve precise temperature control across diverse viscosities wi...
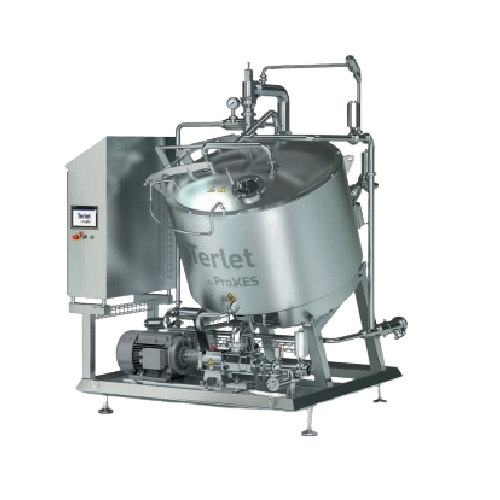

Precise liquid cooling solution for food processing
Ensure high-quality preservation of flavors and textures in liquid fo...
Continuous nut paste production line
Elevate your production efficiency with a versatile preparation line designed to seaml...

Continuous mustard production line
Optimize your condiment production with precision-engineered systems capable of transfor...
Cheese blending and heating line for processed cheese
Optimize your processed cheese production with a solution that seam...
Continuous caramel production line
Optimize your caramel production with seamless integration, achieving precise fat meltin...
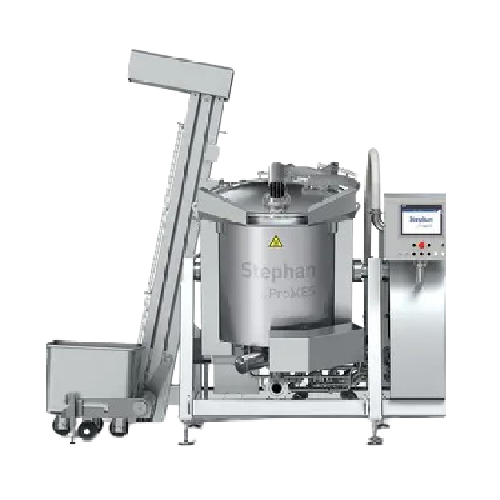

Industrial cooker for sauces and stews
When producing diverse culinary delights such as sauces and stews, achieving even he...
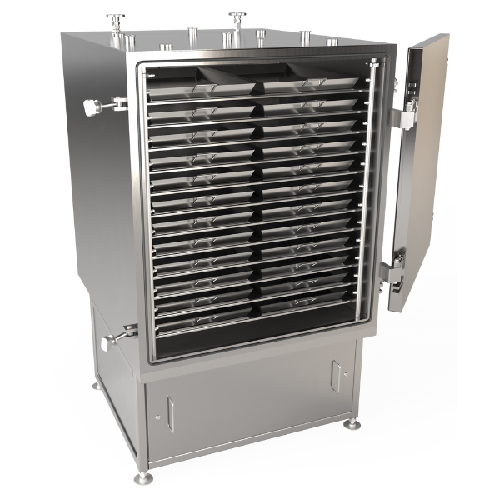

Continuous heat exchanger for soups and sauces
Optimize your soup and sauce production with a continuous heat exchanger th...
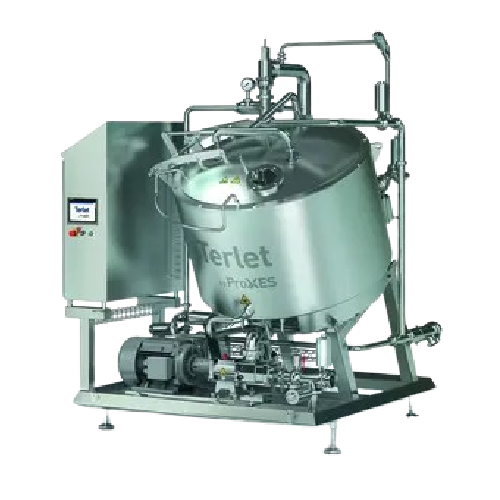

Efficient cooling and cooking systems for food processing
Streamline your production with integrated cooling and cooking...
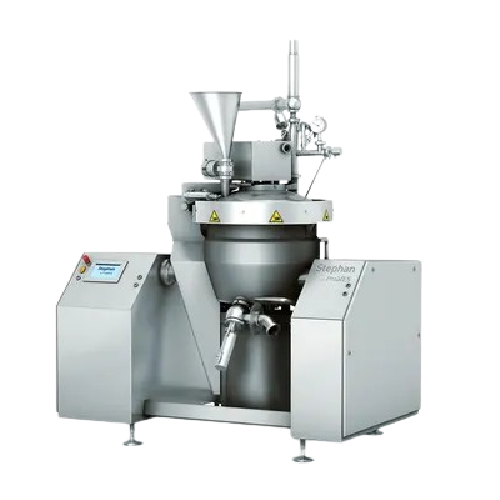

Industrial cutting system for fine emulsions
Optimize your production line with precision cutting and emulsifying, ensurin...
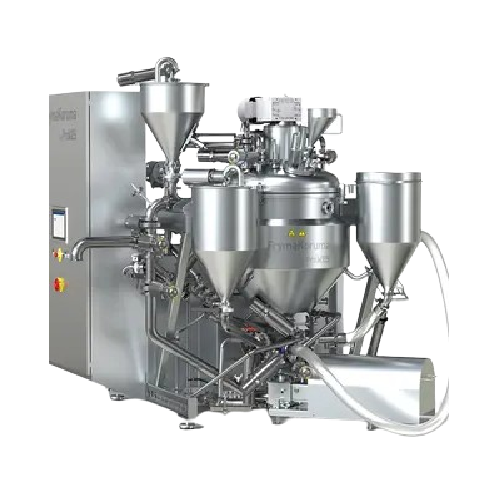

Vacuum deaeration system for mustard and liquid detergents
Ensure optimal product quality by effectively removing air fr...
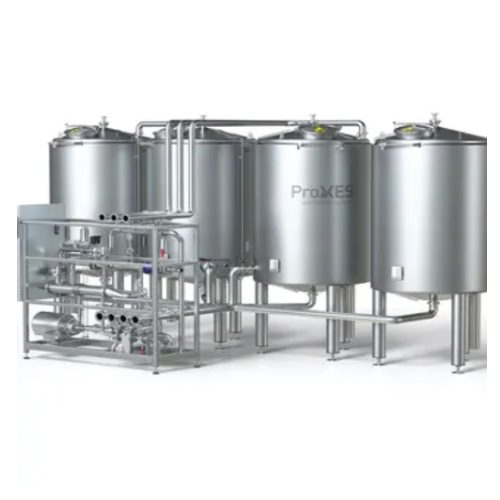

Cleaning systems for food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics
Ensure optimal hygiene and safety with advanced cleaning syste...
Continuous caramel process line
Optimize your continuous food processing with an engineered-to-order line tailored for preci...
Continuous cheese line
Achieve precise temperature control and seamless product transitions with this equipment, ideal for en...
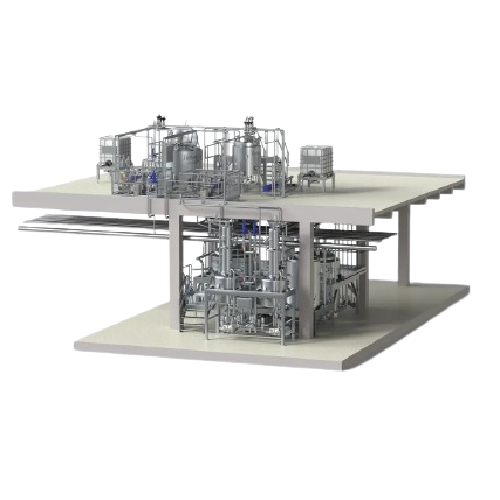

Continuous mustard line
Streamline mustard production with high-capacity continuous processing that reduces air pockets and e...
Continuous tahina production line
Streamline your tahina production with precise grinding and controlled cooling, ensuring ...
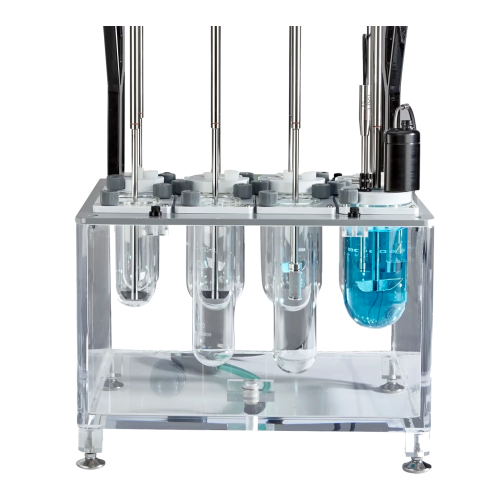

In vitro dissolution and flux measurement platform
Optimize drug formulation by accurately assessing dissolution, solubil...
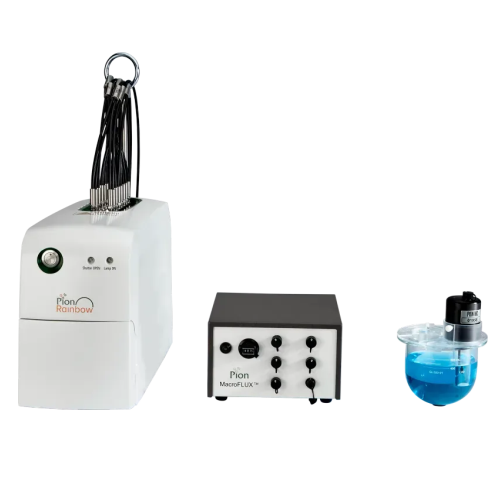

Dissolution-absorption study system for drug formulations
Optimize drug formulations with precise in-situ dissolved subs...
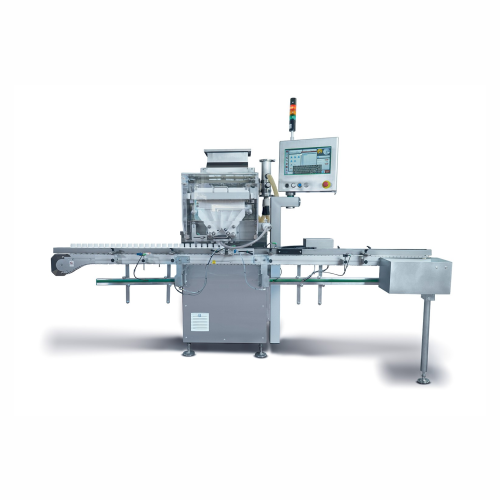

Tablet and capsule counting system
Need precise counting and filling of solid doses like tablets and capsules in your produ...
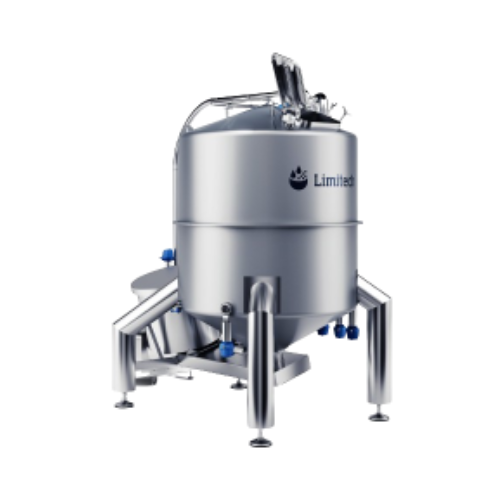

High shear mixer for viscous powder dissolution
Need consistent, homogeneous blending of high-viscosity liquids and powder...
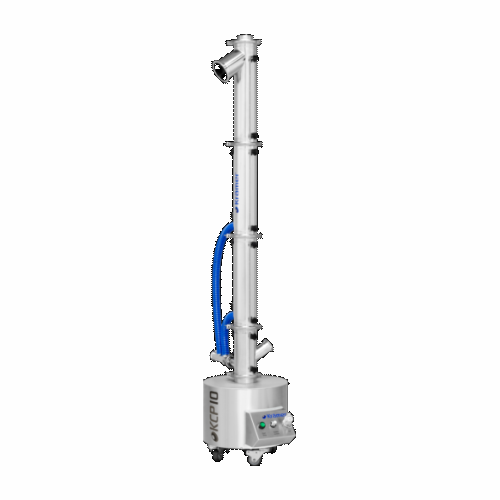

Capsule polisher for pharmaceutical production
Enhance capsule quality and safety by effectively polishing, dedusting, and...
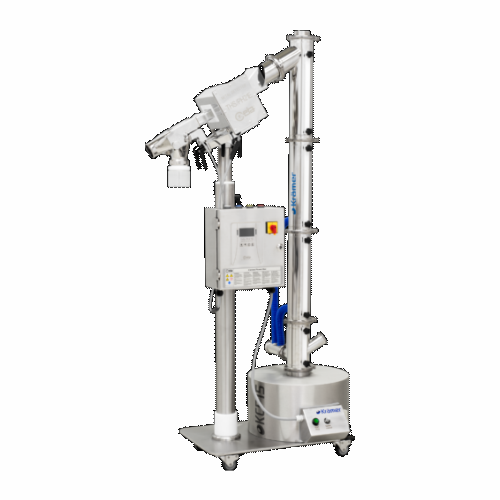

Capsule polisher for pharmaceutical capsules
Ensure your capsules are free from dust and perfectly polished with a solutio...

Electronic tablet counter for tablets and capsules
Optimize your production line with precise counting solutions for a wi...

High-speed blister packaging with integrated cartoner
Optimize your blister packaging process with a solution that seamle...

Pharmaceutical metal detectors
Ensure product purity by detecting and eliminating metal contaminants in pharmaceuticals, enh...

In-process weighing system for capsules and tablets
Ensure precise dosing and consistent quality with a format-free syste...

High-containment capsule dosing and filling system
Achieve precise dosing and optimal containment for pharmaceutical prod...
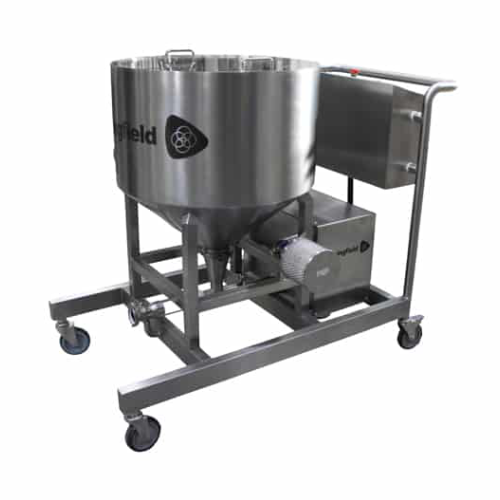

Empty capsule transfer system
Ensure seamless capsule filling operations by eliminating manual handling and preventing produ...
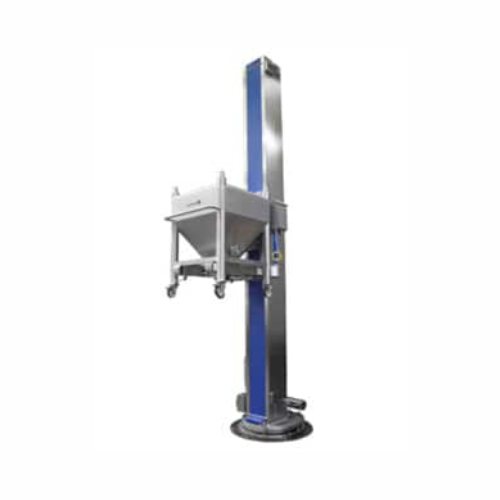

Industrial container lifting system
Optimize your production line with a versatile lifting solution designed to safely hand...
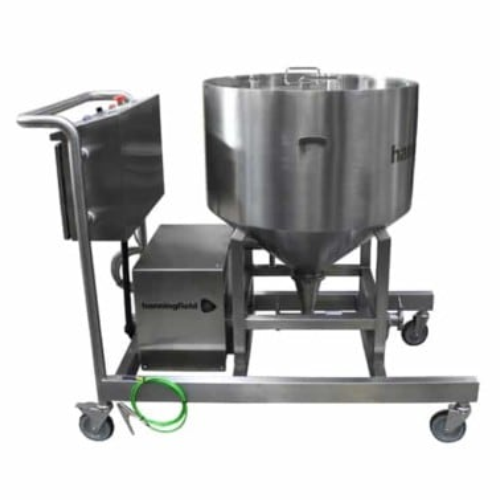

Capsule conveyors for gentle capsule transfer
Streamline your capsule production line with a system designed for high-spee...
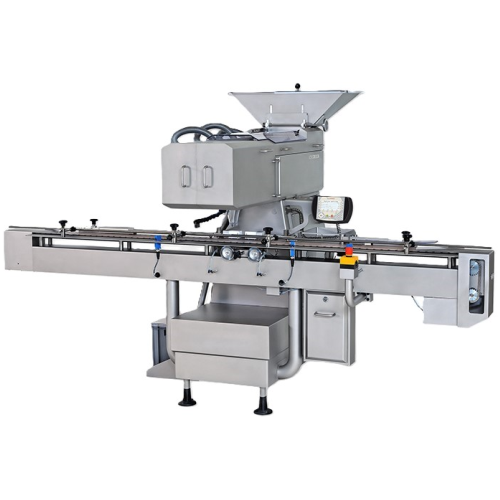

Linear tablet and capsule counter
Ensure precise and efficient bottle filling with a cutting-edge counting system that guar...

High containment powder transfer valve for bulk material
Ensure operator safety and prevent cross-contamination with robu...

High speed blister packaging for pharmaceuticals
Need efficient packaging with quick format changeovers for various capsul...

High-speed continuous motion horizontal cartoner
Achieve seamless high-speed cartoning with precision cartoner systems des...

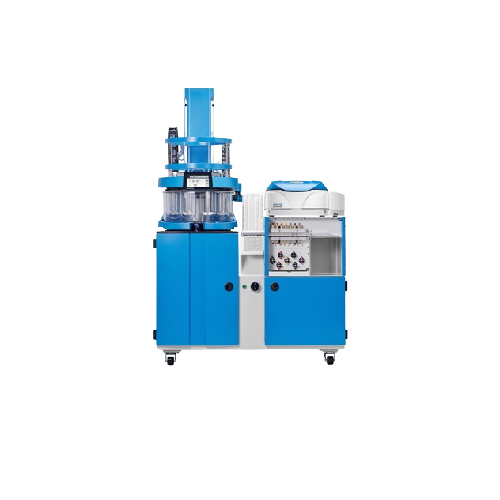
Soft gel encapsulation system
Efficiently produce high-quality soft gel capsules with precision encapsulation, rapid drying,...
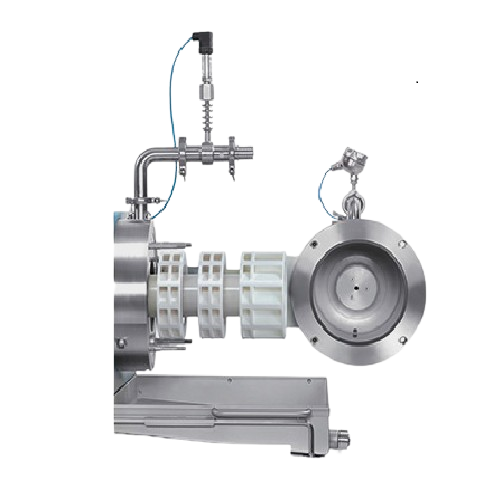

Bead mill for nano-preparation grinding
Achieve precise nano-processing and efficient wet grinding for pharmaceuticals and ...
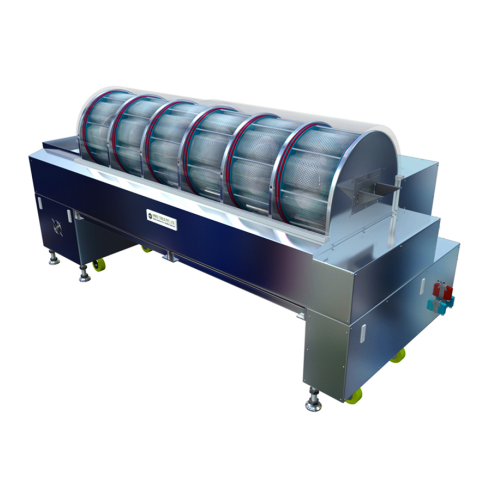

Softgel pre-dryer tumbler system
Ensure optimal shape and seam formation of softgel capsules with efficient oil removal, pav...
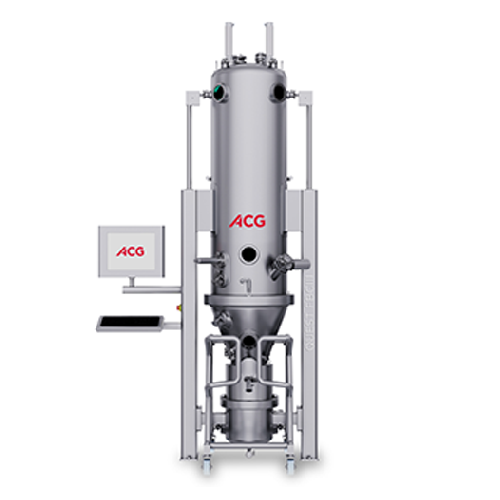

Intermediate-scale fluid bed system for drying and granulation
Achieve precise drying and granulation with this versatil...
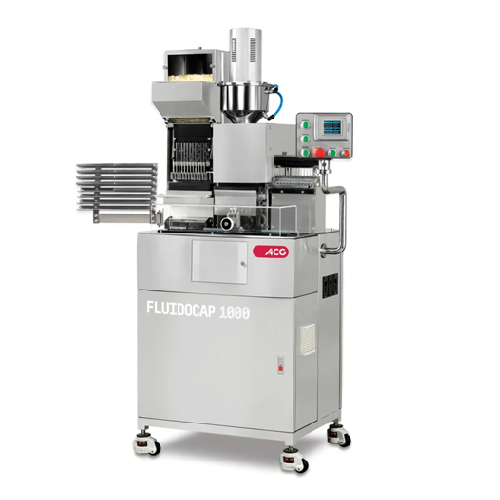

Liquid capsule filling for r&d and pilot-scale production
Optimize liquid capsule production with a compact machine that...
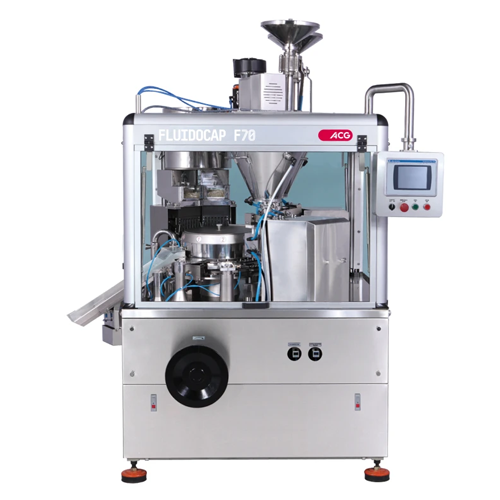

Liquid filling system for hard capsules
Easily fill two-piece hard capsules with liquids, pastes, and suspensions with prec...
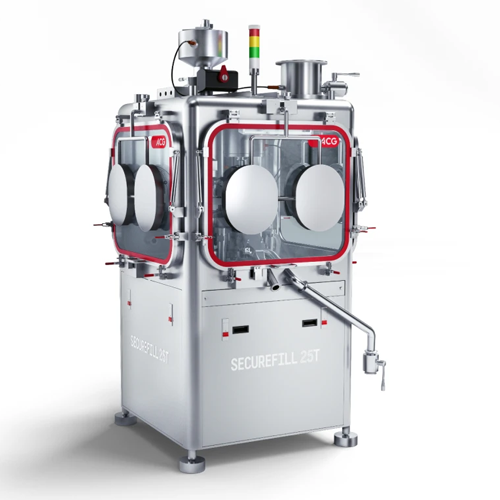

Containment capsule filler for highly potent drugs
Achieve complete operator safety while encapsulating potent pharmaceut...
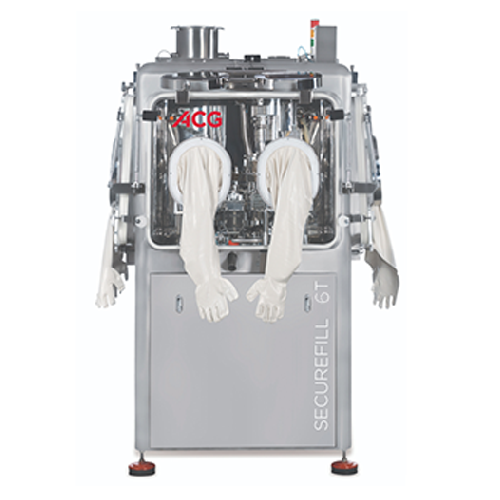

Containment capsule filling system for highly potent drugs
Ensure operator safety while filling capsules with high-poten...
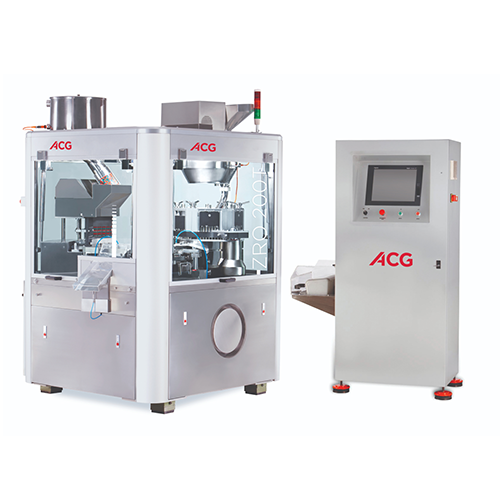

High-speed capsule filler for large batch production
Achieve higher yields and reduce powder waste with a capsule filling...
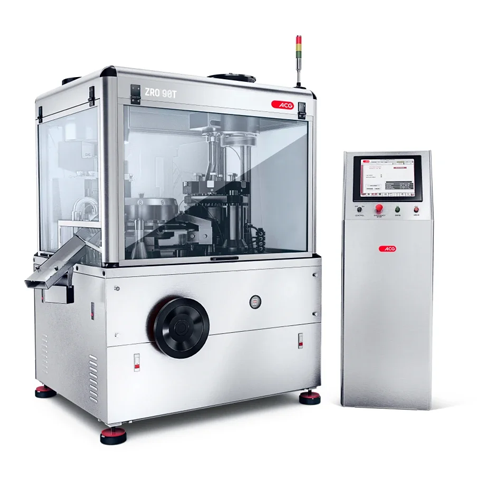

Capsule filler for high-speed, dust-free capsule production
Enhance your production efficiency with a solution designed ...
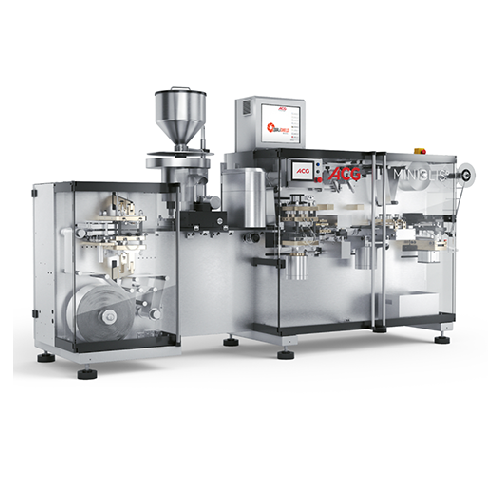

Flat-forming blister packager for small production batches
Ideal for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical firms seeking effi...
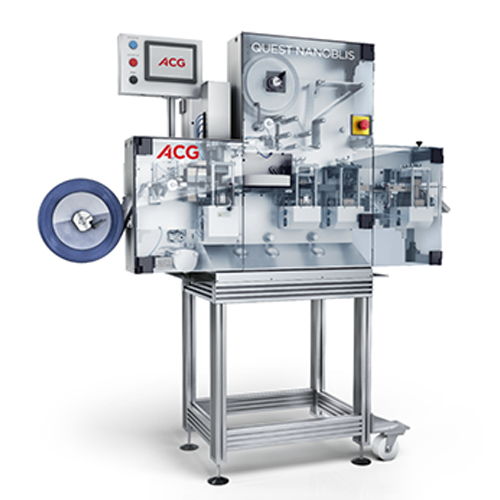

Tabletop blister packaging for clinical trials
For R&D facilities conducting clinical trials or feasibility studies, ...

Containment blister packaging for highly potent Apis
Ensure operator safety during the blister packaging of highly potent...
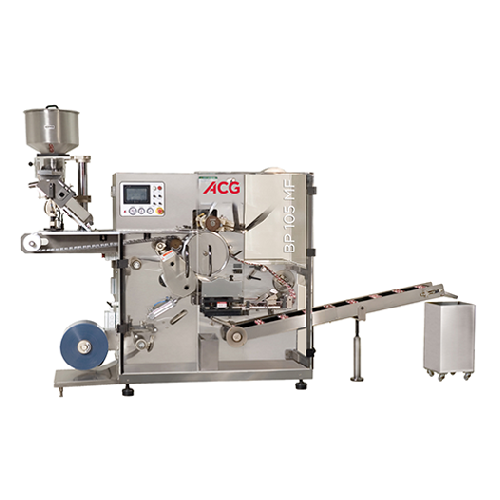

Rotary blister packaging for tablets and capsules
Optimize your blister packaging with high-performance rotary forming an...
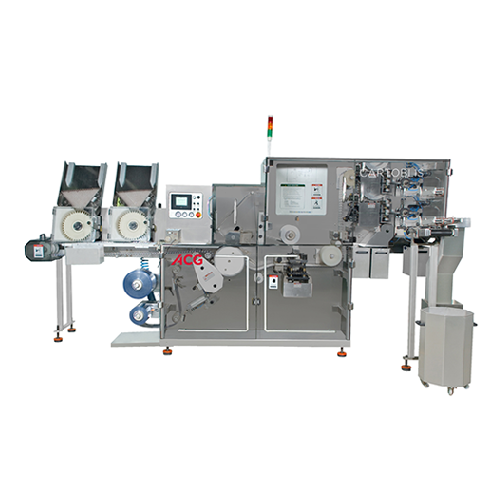

Blister packaging for solid dosage forms
Optimize your packaging line with high-speed, continuous blister packaging that en...
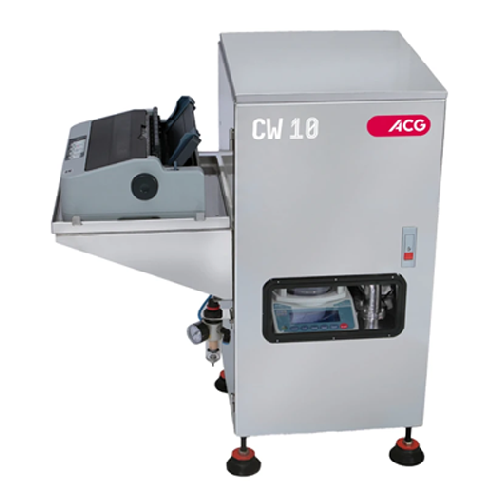

Automatic capsule checkweigher for statistical weight control
Ensure precise weight control of capsules with automatic s...
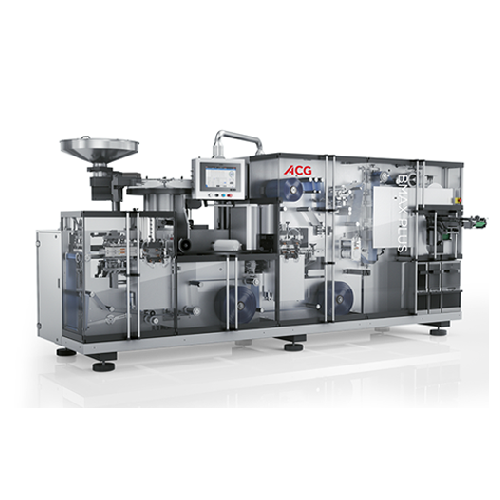

Flat forming and sealing blister packaging solution
Enhance your blister packaging process with a solution that ensures p...
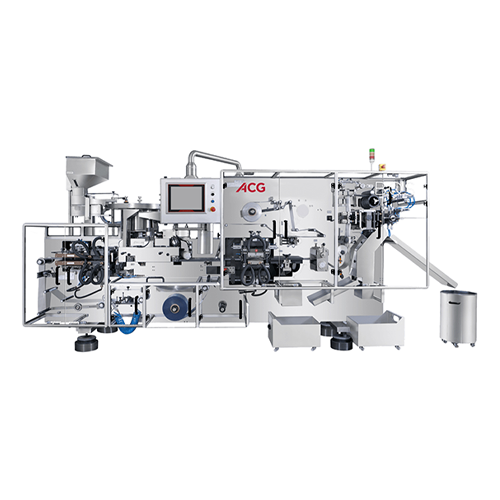

Flat-sealing continuous-motion blister packaging solution
Enhance your blister packaging with precise, high-speed sealin...
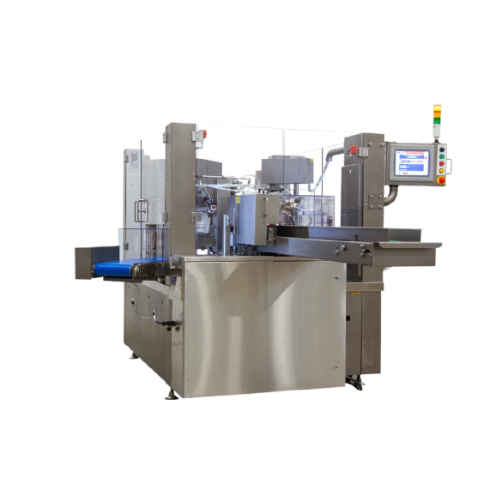

Automatic rotary premade pouch filler for food products
Enhance your packaging line with a high-speed solution designed t...
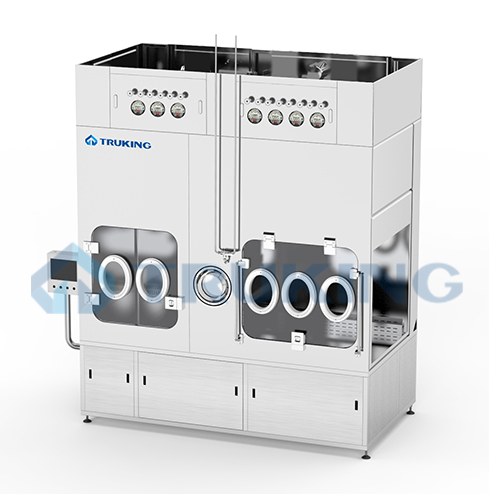

Autoclave unloading isolator for sterile assembly
Ensure aseptic conditions and prevent microbial contamination during th...
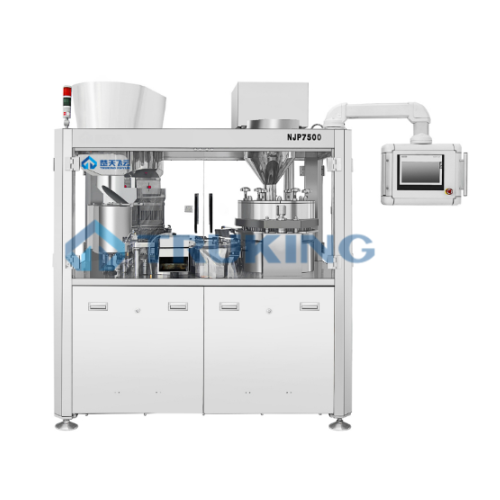

Fully automatic hard capsule filling machine
Enhance pharmaceutical production with precise capsule filling, ensuring opti...
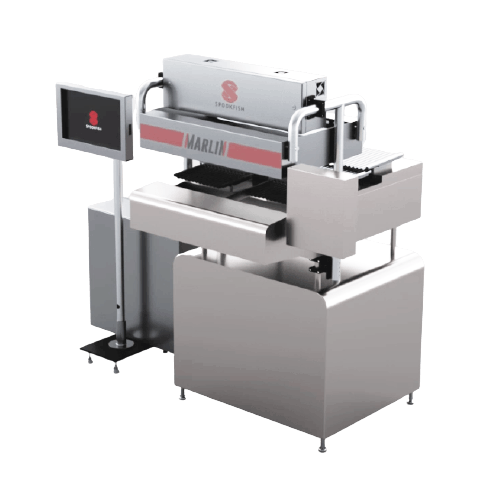

Online tablet counter inspection system
Ensure product integrity by precisely inspecting and rejecting defective tablets an...

Semi-automatic tablet hardness tester
Optimize your tablet production with precise and reliable testing of hardness, dimens...

Tapped density tester for pharmaceutical powders
Ensure precise quality control in pharmaceuticals by accurately measuring...

Automated weighing system for tablets
Ensure precision in pharmaceutical manufacturing by seamlessly integrating advanced w...

Automated sample preparation workstation for lab efficiency
Streamline laboratory operations by automating sample prepar...

Automated sample preparation workstation for content uniformity testing
Streamline your laboratory workflows with autom...
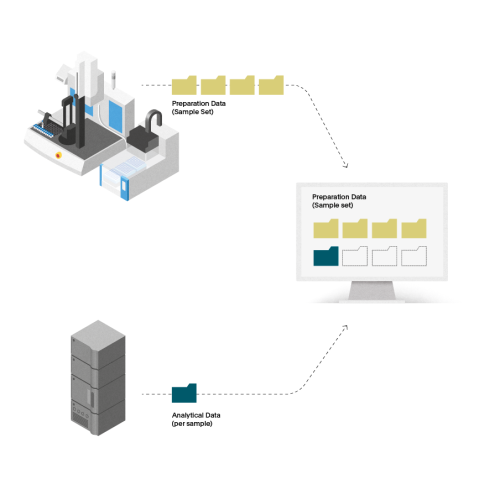
Automated sample preparation software for pharmaceutical testing
Streamline your laboratory’s sample preparation w...

Dissolution medium preparation system
Streamline your laboratory workflows with a system that prepares and manages dissolut...
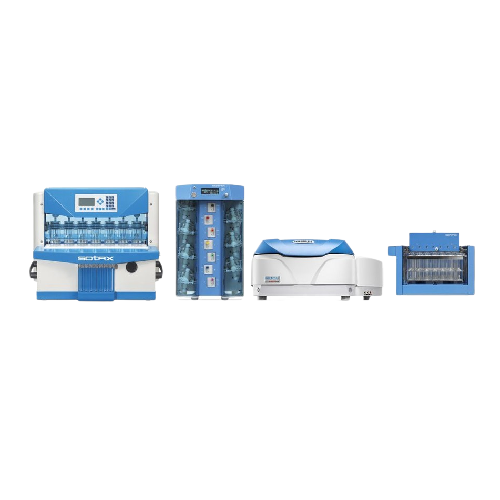

Automated flow-through cell dissolution testing system
Enhance precision in dissolution testing with real-time UV-Vis ana...
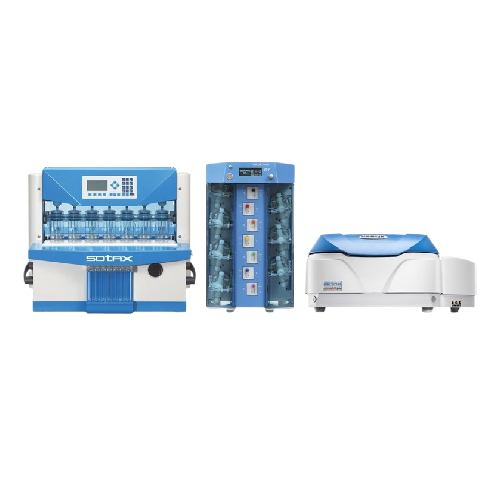

Flow-through cell dissolution testing with Uv analysis
Effortlessly monitor real-time dissolution with flow-through cell ...
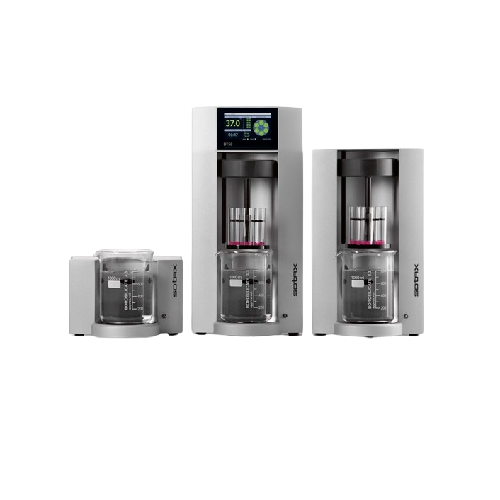

Bathless disintegration apparatus for tablet and capsule testing
Achieve rapid and precise disintegration testing of tab...
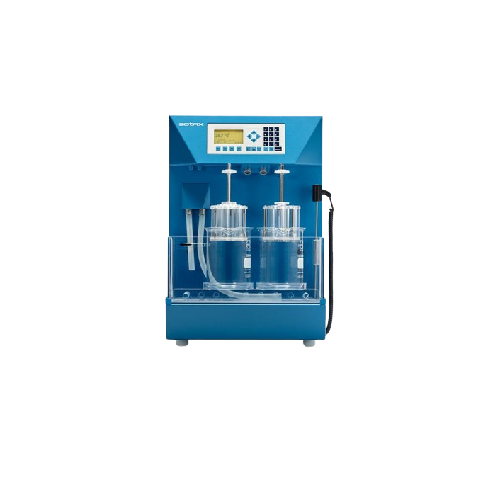

Manual tablet disintegration tester
Ensure precise and reliable disintegration testing of pharmaceutical tablets, capsules,...
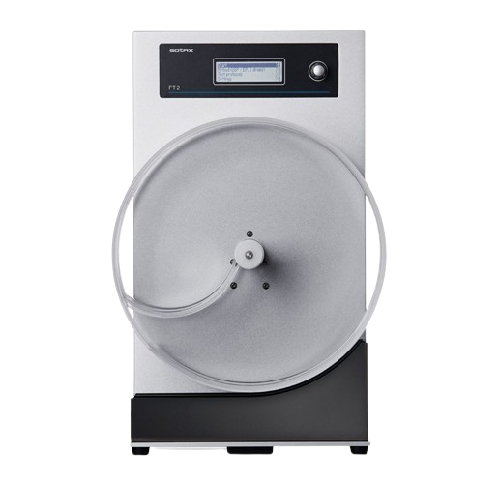

Tablet friability tester
Ensure your tablets meet rigorous quality standards by accurately measuring friability and abrasion,...

Powder flow tester for pharmaceutical powder flowability
Quickly assess powder flow characteristics to ensure consistent ...

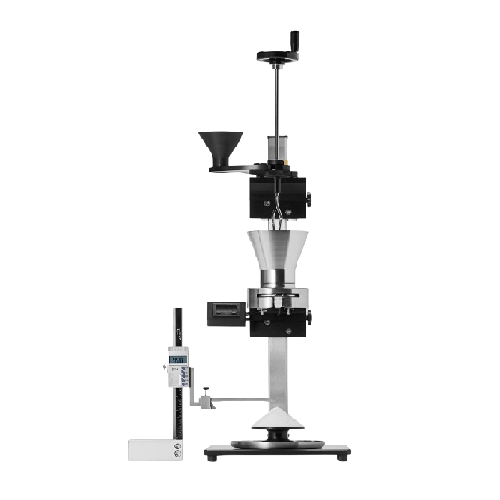
Multi-parameter tablet hardness tester for laboratories
Optimize your tablet production line with a versatile tester that...

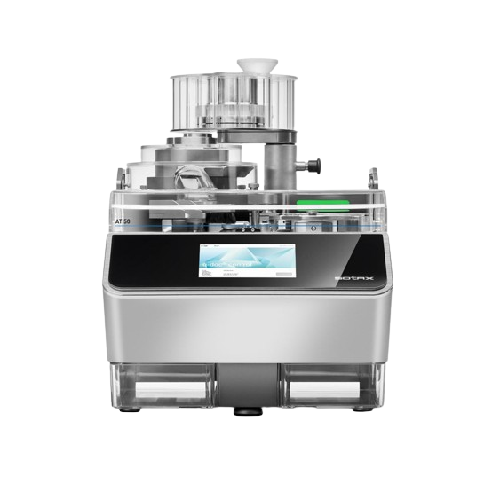
Advanced dissolution tester for pharmaceutical laboratories
Achieve consistent and reproducible dissolution results with...
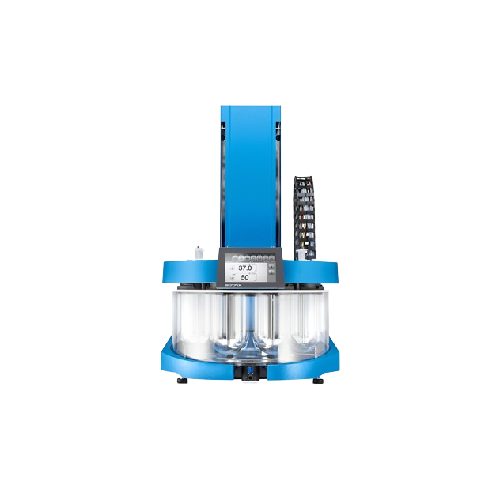

Manual dissolution tester for pharmaceutical applications
Achieve precise and repeatable sampling in pharmaceutical test...
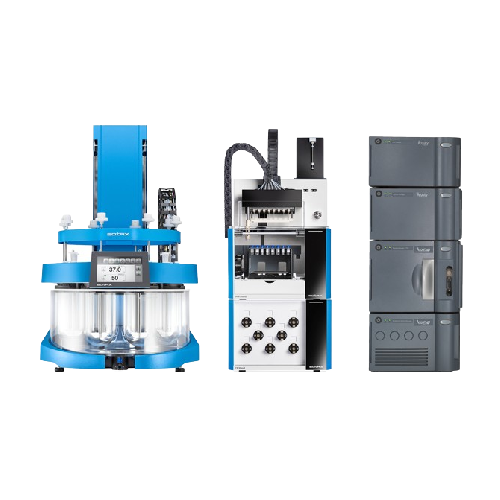

Automated dissolution testing with direct Hplc injection
Streamline your lab operations with precise and efficient direct...
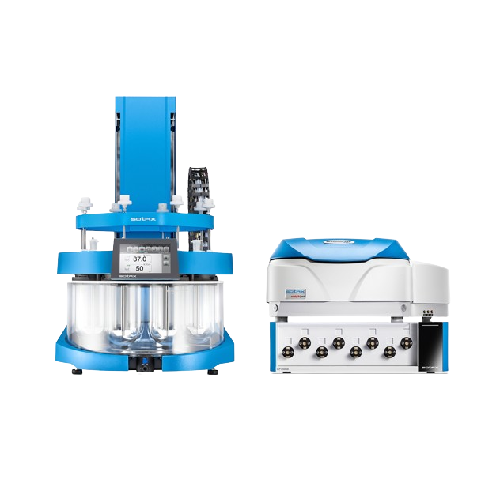

Integrated Uv-vis spectrophotometer for dissolution testing
Streamline your dissolution testing with real-time UV-Vis an...
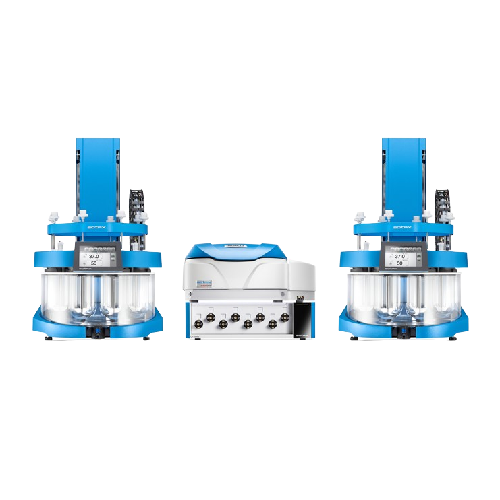

Real-time Uv-vis analysis for dissolution testing
Efficiently perform dual dissolution tests simultaneously, seamlessly i...
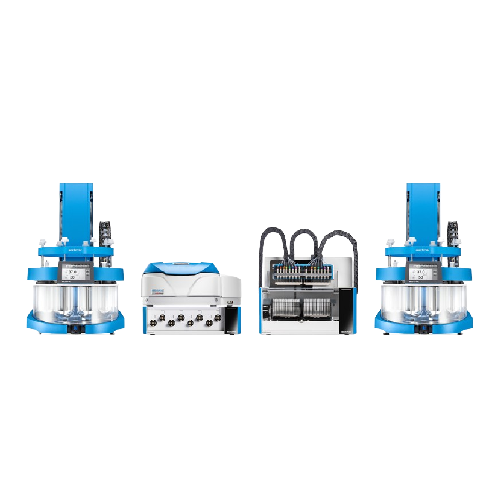

Automated dissolution testing system for 16 vessels
Maximize your laboratory throughput by conducting parallel dissolutio...

Dissolution testing software for automated analysis
Streamline your laboratory testing with seamless data capture and in-...

Dissolution testing software for pharmaceutical industry
Optimize dissolution testing with advanced software that manages...
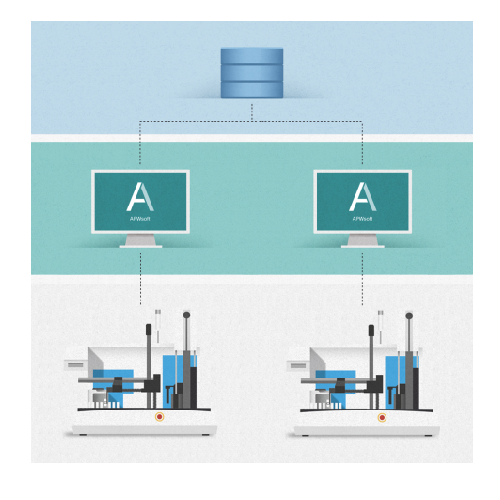
Automated sample preparation software
Enhance your laboratory’s efficiency with a software solution that automates sa...
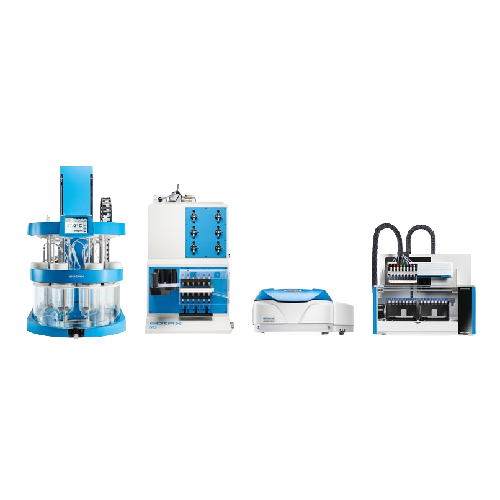

Benchtop dissolution tester for multiple test runs
Streamline your laboratory’s workflow with a fully automated ben...
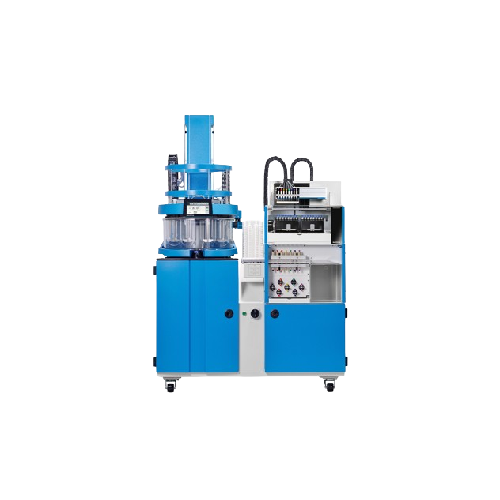

Self-cleaning dissolution tester for automated series testing
Achieve unparalleled precision in dissolution testing with...
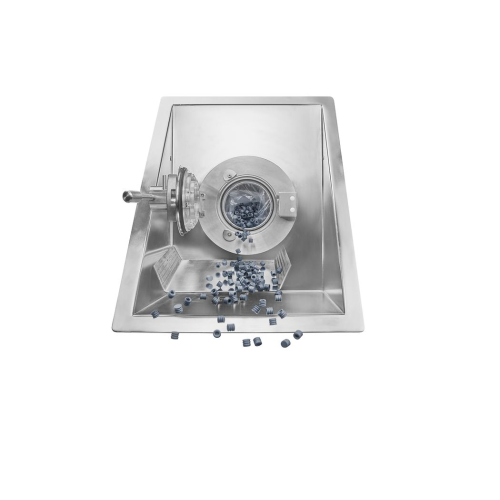
Single-use transfer and filling solutions in barrier isolated filling lines
Ensure sterile, high-volume liquid transfe...

Dual laser capsule marking system
Ensure precise and rapid laser marking of tablets and capsules with a dual-laser system, ...
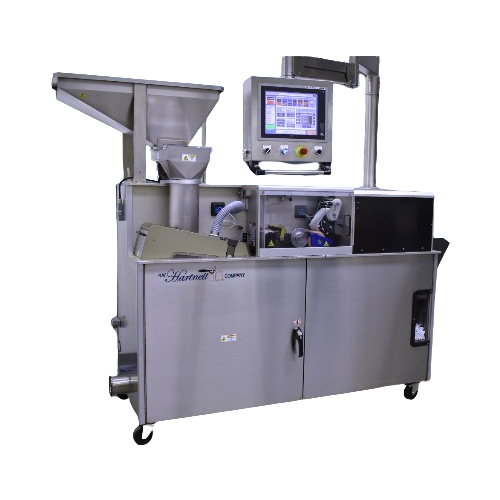

H-track ink printing solution for tablets and capsules
Ensure precise ink printing on tablets and capsules with high-spee...
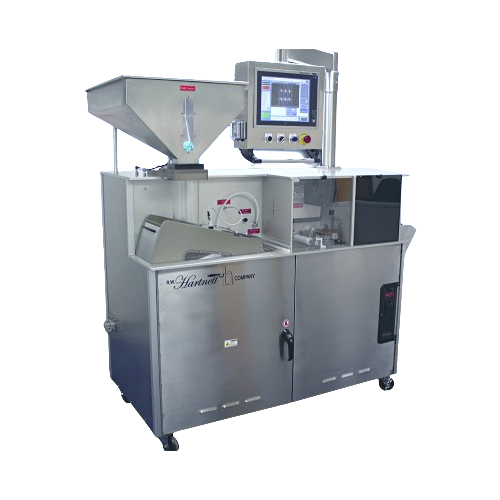

Uv laser writer for tablets and capsules
Achieve precise laser marking on tablets and capsules with high-speed production, ...
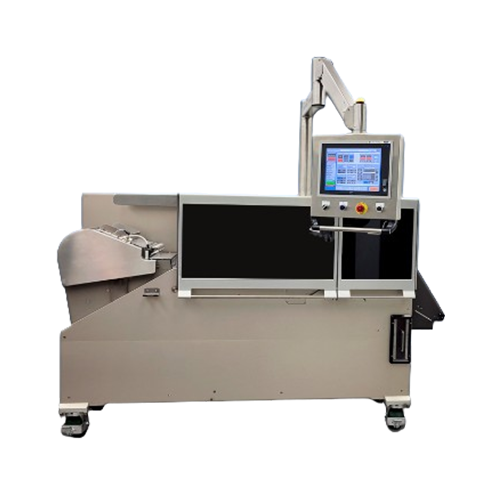

High-speed laser writer for soft gelatin capsules and caplets
Achieve precise laser marking on up to 300,000 tablets or ...
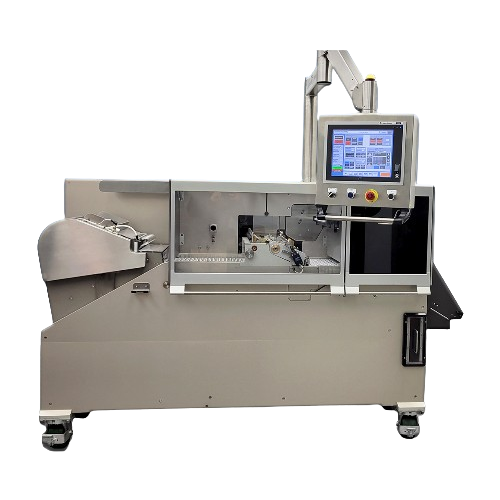

High-speed tablet ink printer
Achieve precise and high-speed printing on tablets and capsules for streamlined production and...
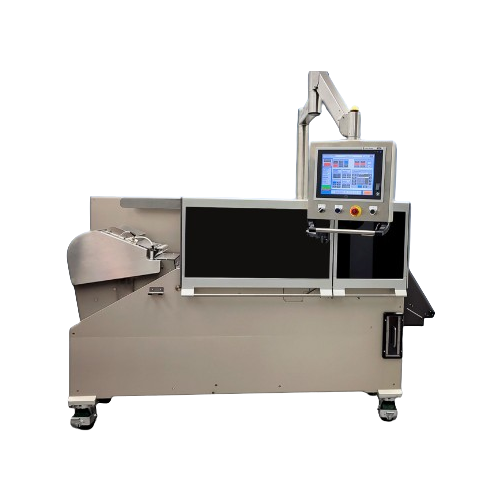

Uv laser writer for high-speed tablet marking
Achieve precise and rapid marking of pharmaceutical and nutraceutical tablet...
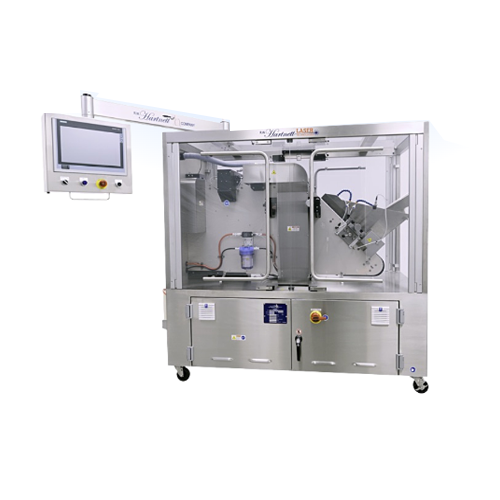

Co2 laser writer for soft gelatin capsules
Achieve precise and efficient laser marking on soft gelatin capsules and caplet...
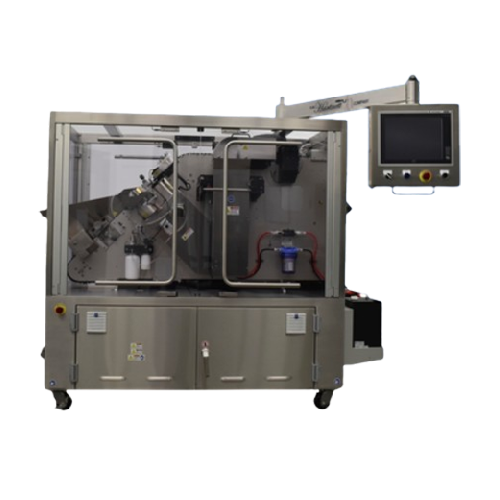

Tablet and capsule ink print and laser marking system
Streamline tablet and capsule identification with a high-speed syst...
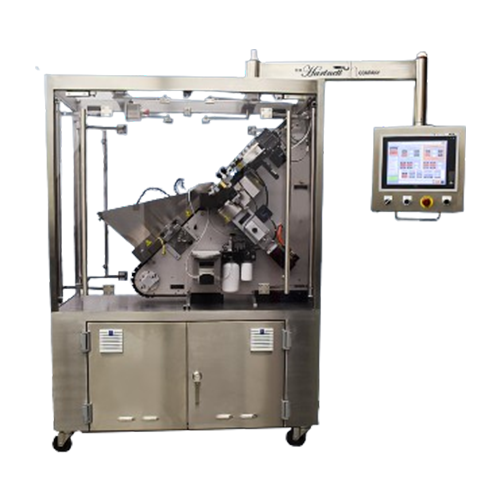

Tablet and capsule ink printer
Achieve precise and high-speed printing on tablets and capsules, ensuring clear product ident...
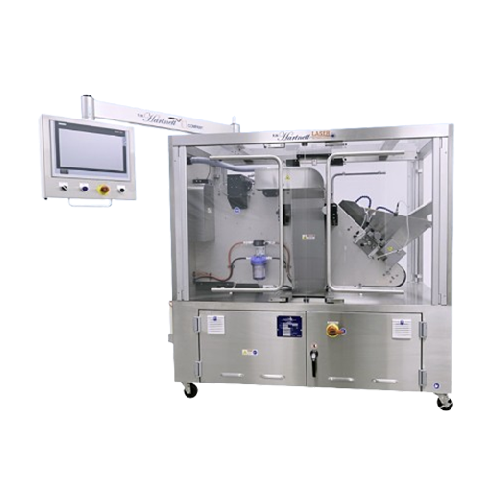

Uv laser marker for tablets and capsules
Achieve precise laser marking on tablets and capsules at high speeds while maintai...
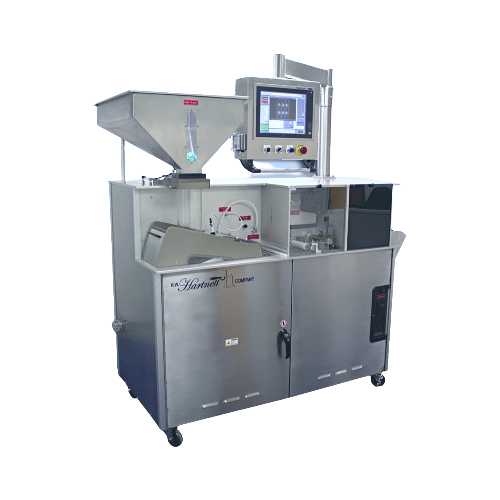

Co2 laser writer for gelatin capsules
Achieve high-speed laser marking on gelatin capsules and caplets with precision, ensu...
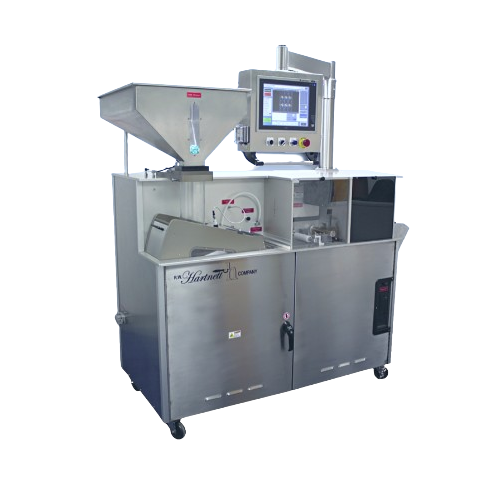

Tablet and capsule ink printing and laser writing solution
Maximize efficiency in marking and coding with a high-speed s...
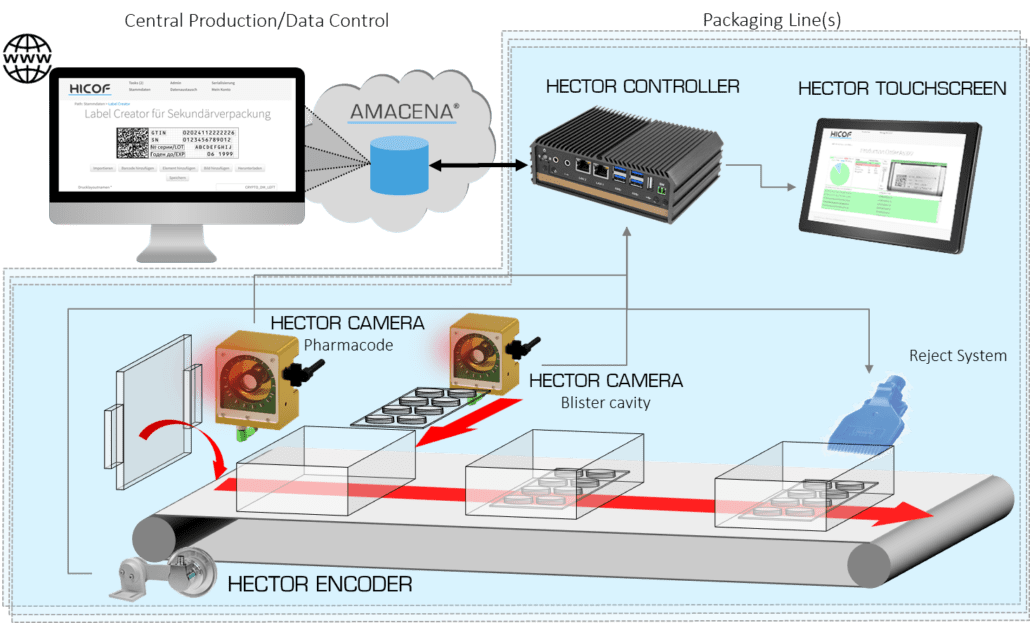
Serialization and aggregation inspection system
Including serialization and aggregation inspection systems to packaging li...

Automatic medical forming and sealing blister machine for packing capsules and tablets
Product safety is very importa...

High speed bottle filler with inspection
Medicines in tablet, capsule, or soft gel forms undergo various processes before r...
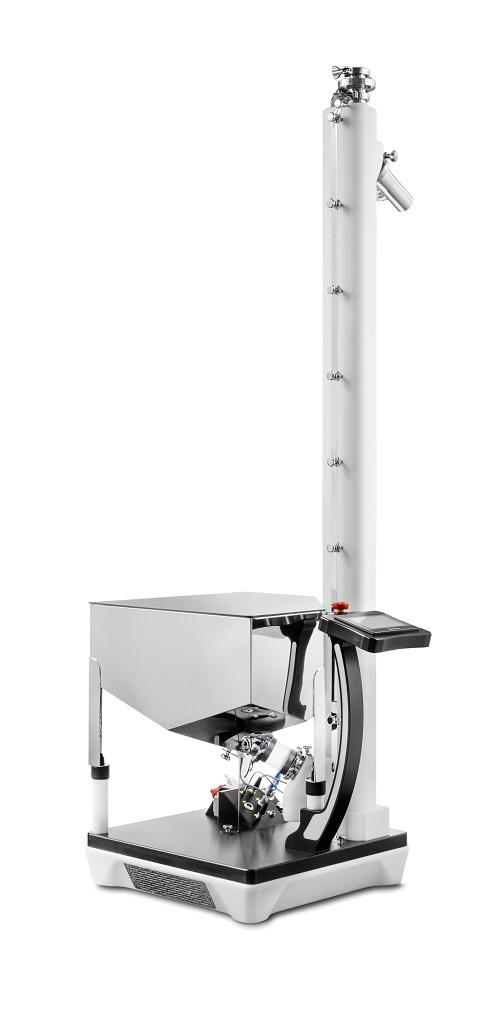

Lifter and De-duster for Tablets
The use of several different tools for lifting, de-dusting, and polishing in the pharmaceut...

High Speed Visual Inspection System for Tablets
In order to ensure quality and standard specifications of tablets, capsule...

Pharmaceutical bottle unscrambler
Pharmaceutical packaging industry requires the ability to quickly manage the process yet ...

Dessicant inserting machine
Desiccant canisters play an important role in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. T...
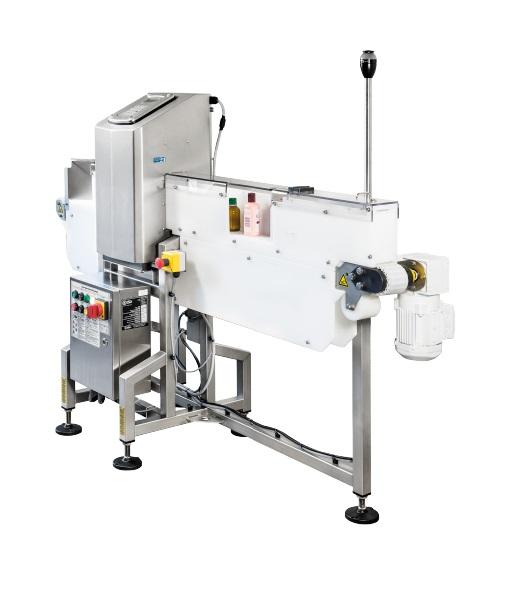

Metal detector for bottles
For metal contamination detection in finished products that are bottled, traditional solutions re...
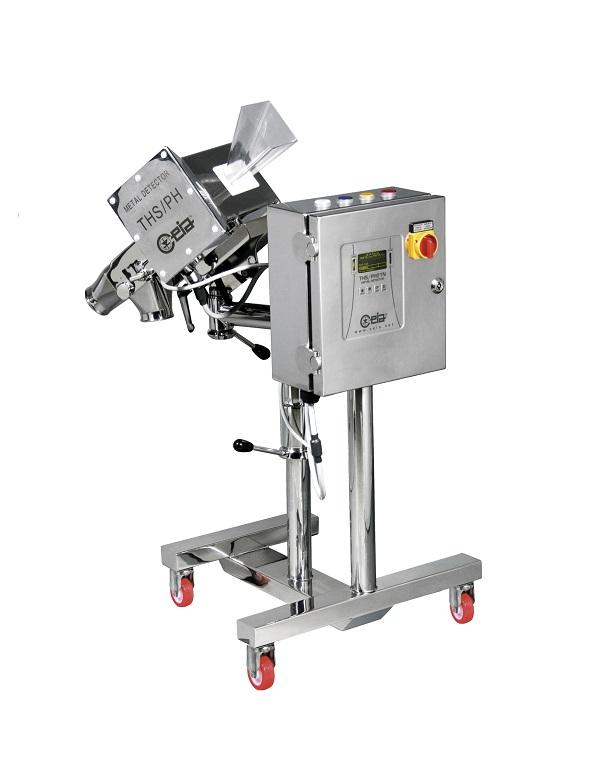

Metal detector for tablets and capsules
Identification of metallic contaminants is a vital part of pharmaceutical quality c...
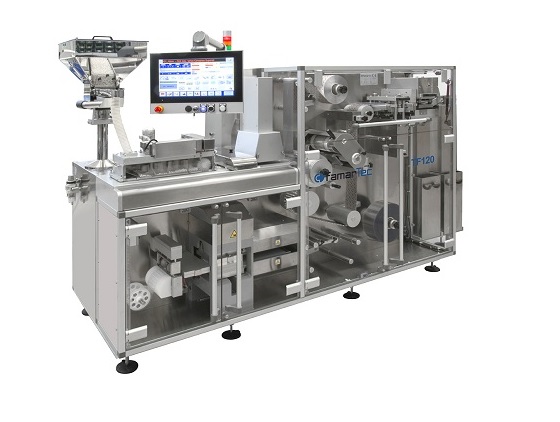

Entry-level blister packaging machine
Blister packaging is a popular packing method in the pharmaceutical industry thanks t...
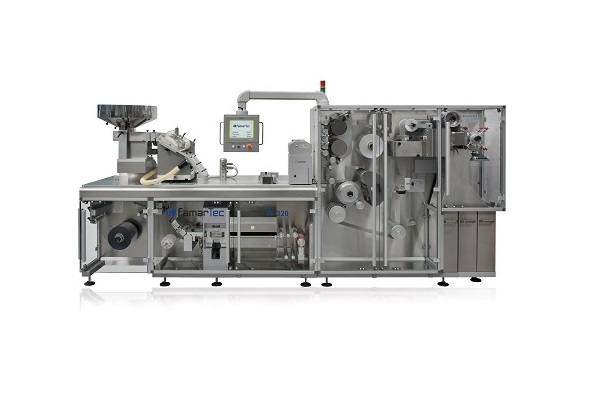

Industrial blister packaging machine
High-volume, fully-automated blister packaging is the perfect choice for large scale p...
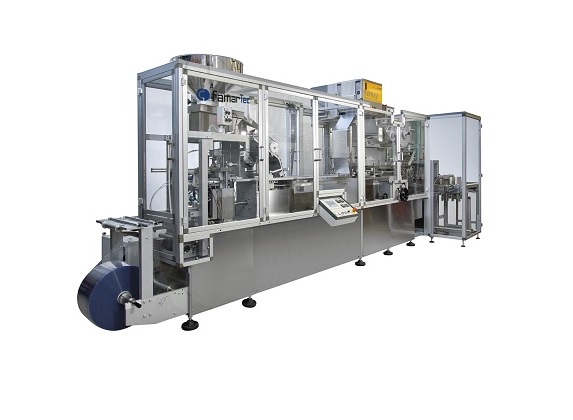

Plate sealing blister machine
Blister packaging is the preferred choice for most large-scale pharmaceutical lines, and a pla...

Automatic blister packaging machine
Automated blister packaging is a popular choice for pharmaceutical production thanks to...
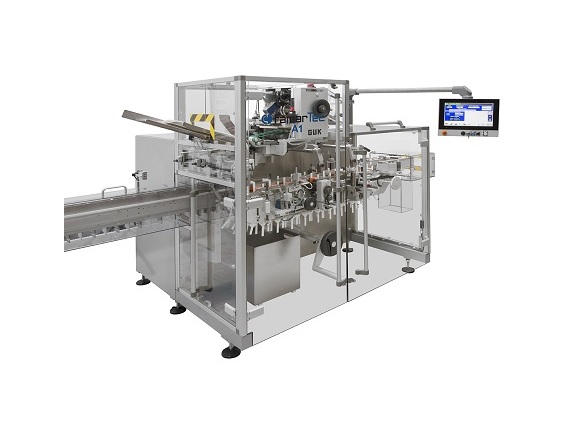

Horizontal cartoner for pharmaceutical applications
Automatic cartoning for cosmetic or pharmaceutical products is a requ...
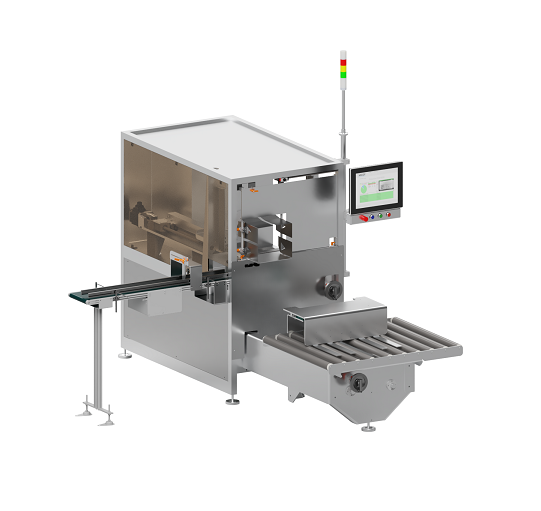

Semi-automatic case packer
Pharmaceutical products require complete traceability throughout the production cycle. For smalle...
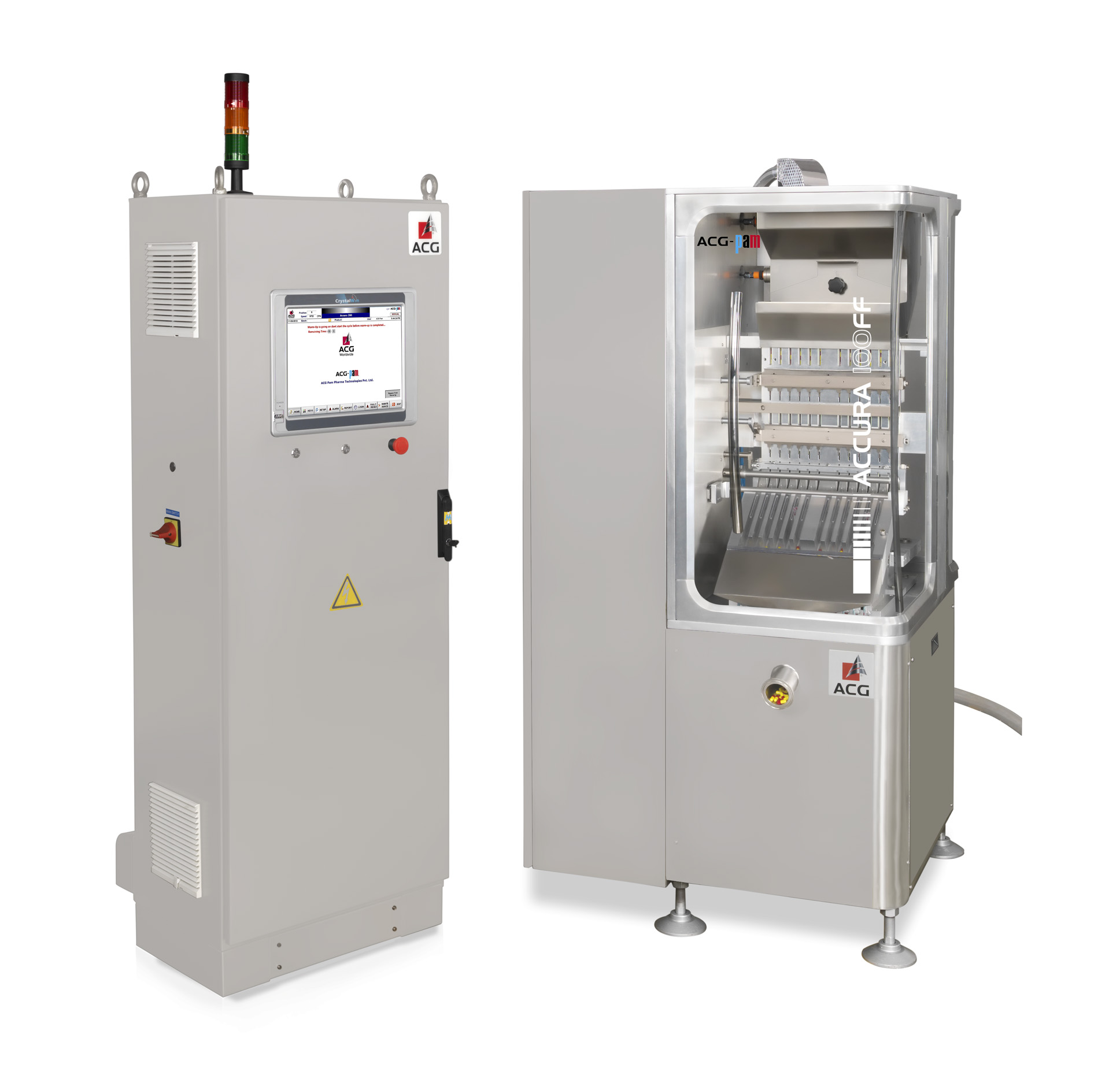

Industrial capsule checkweigher
Pharmaceutical manufacturing demands the highest quality standards and completely consistent...
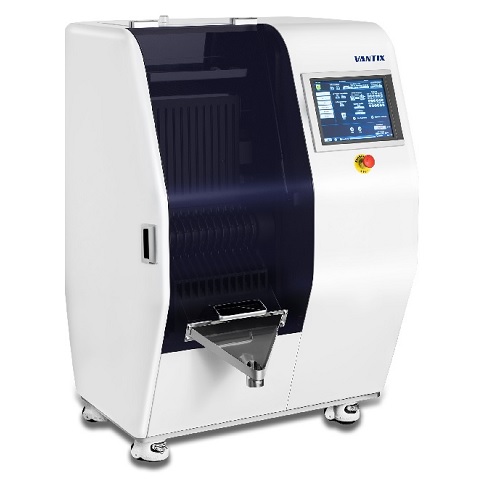

Capsule checkweigher
The production of pharmaceutical capsules requires that individual doses are checked for accuracy. In a ...
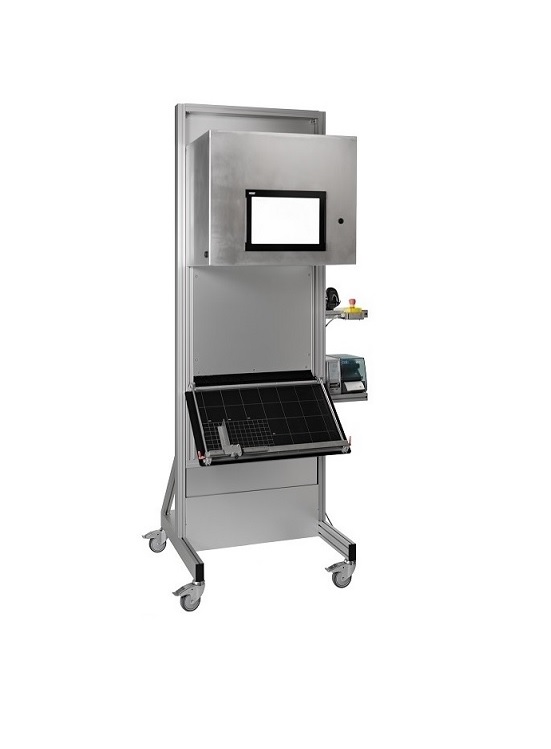

Stand-alone aggregation station
The aggregation of pharmaceutical products for tracking purposes is already compulsory in ma...
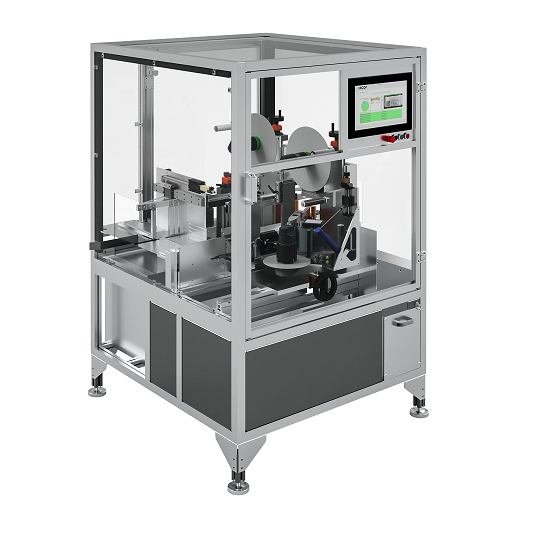

Serialization coding and labeling equipment
In the pharmaceutical industry, product serialization is the cornerstone of al...
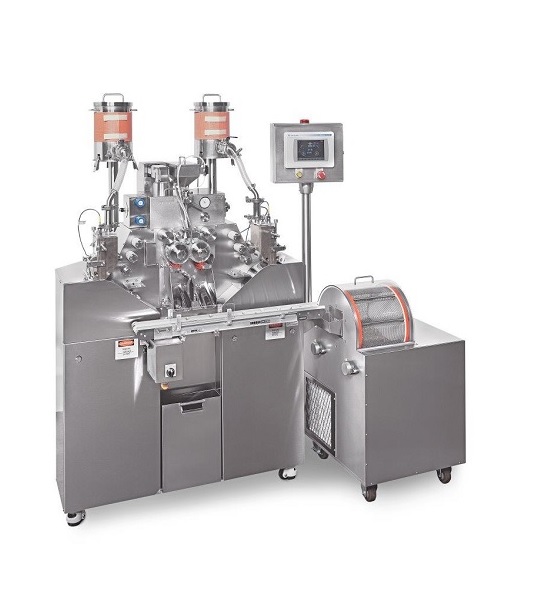

Laboratory scale soft gelatin capsule machine
Softgel (or soft gelatin) capsules are a very popular method for providing o...
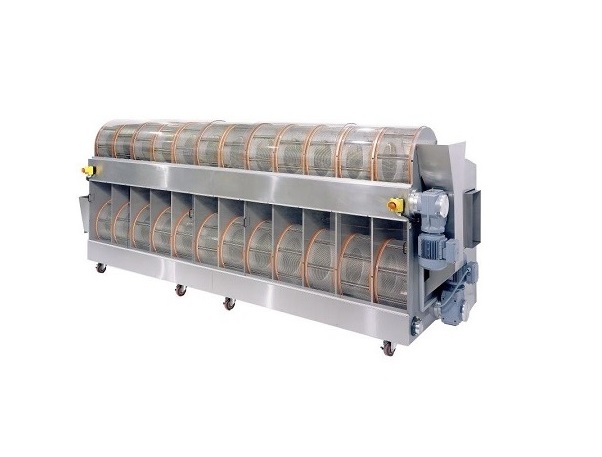

Softgel tumble dryer
Softgel (or soft gelatin) capsules are a very popular means of delivering oral doses in the pharmaceutic...
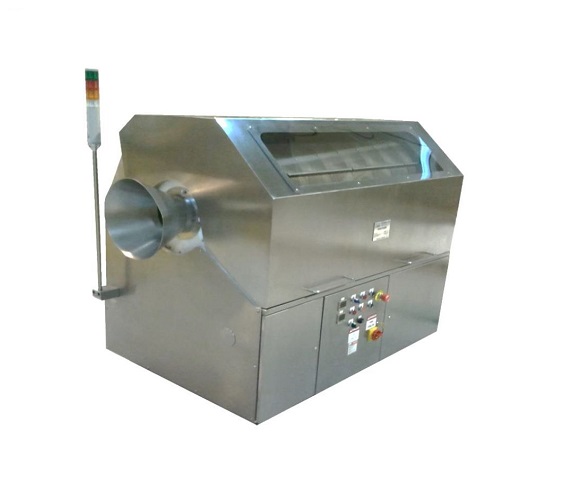

Softgel capsules polisher
The final stage in high quality softgel (or soft gelatin) capsule production is the capsule polish...

Continuous in-line softgel drying system
High output softgel (or soft gelatin) capsule encapsulating machines can operate b...
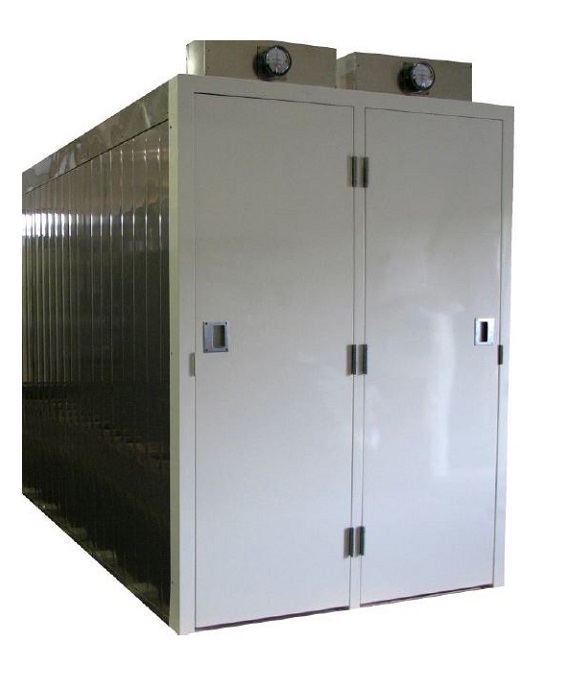

Softgel drying tunnel
Softgel capsules require a controlled secondary drying to reduce water content in the capsule to levels...

Gelatin melters and tanks
When producing high quality softgels its important that the gelatin base is processed and stored c...

Automatic soft gelatin capsule machines
Soft gelatin (or softgel) capsules have become a popular mode of oral liquid dosing...
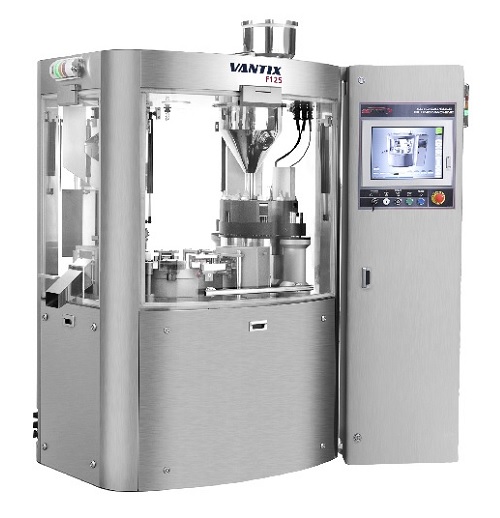

Scale up capsule filler
For higher production volumes of pharmaceutical capsules, speed, accuracy and reliability of producti...

Waste minimization weight sorter for tablets & capsules
For medium scale production, you can improve line efficiency and ...
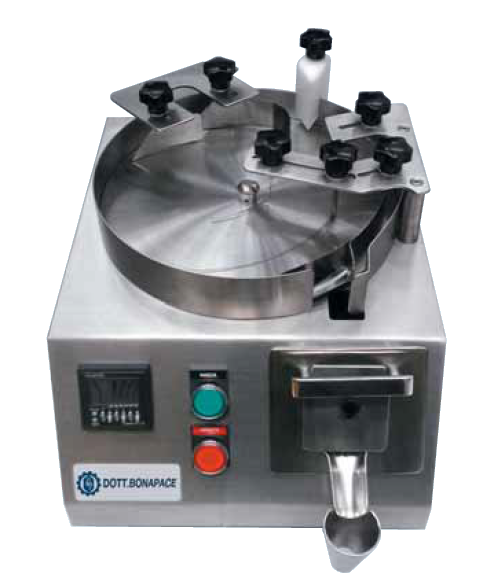

R&D electronic counter for capsules and tablets
This machine has been designed to offer an ever-precise and reliable count...

Compact blister machine
A compact blister machine ideal for packing tablets, capsules, ampoules and syringes and other applic...
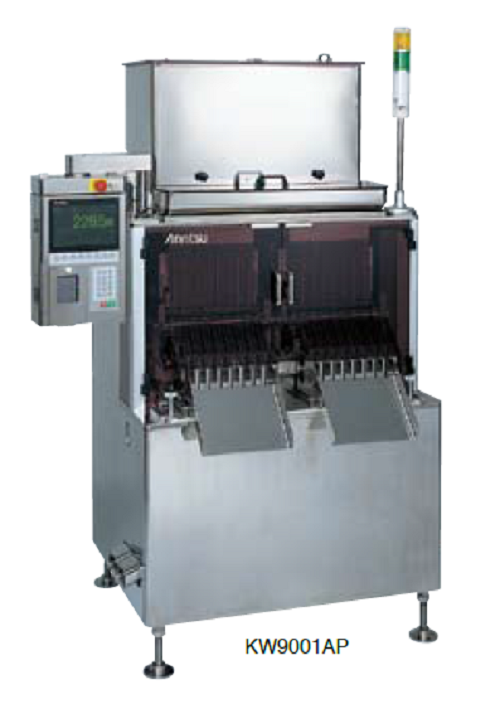

Checkweigher for capsules
The new interactive indicator unit allows for even easier use. High-rigidity weighcells have been ...
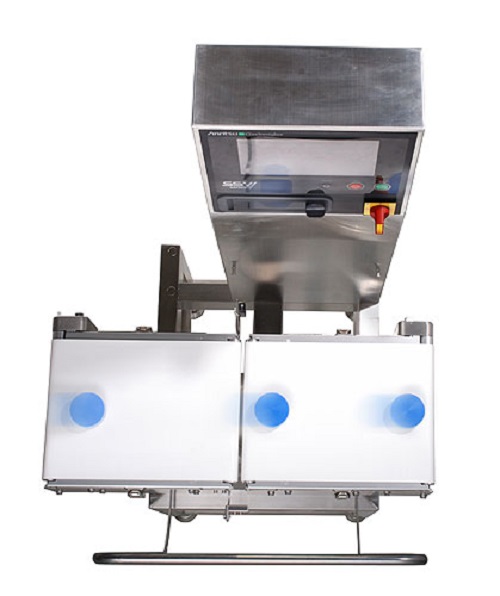

Checkweigher
A check weigher that is equipped with high speed/high accuracy force balance load cell. It meets stringent accura...
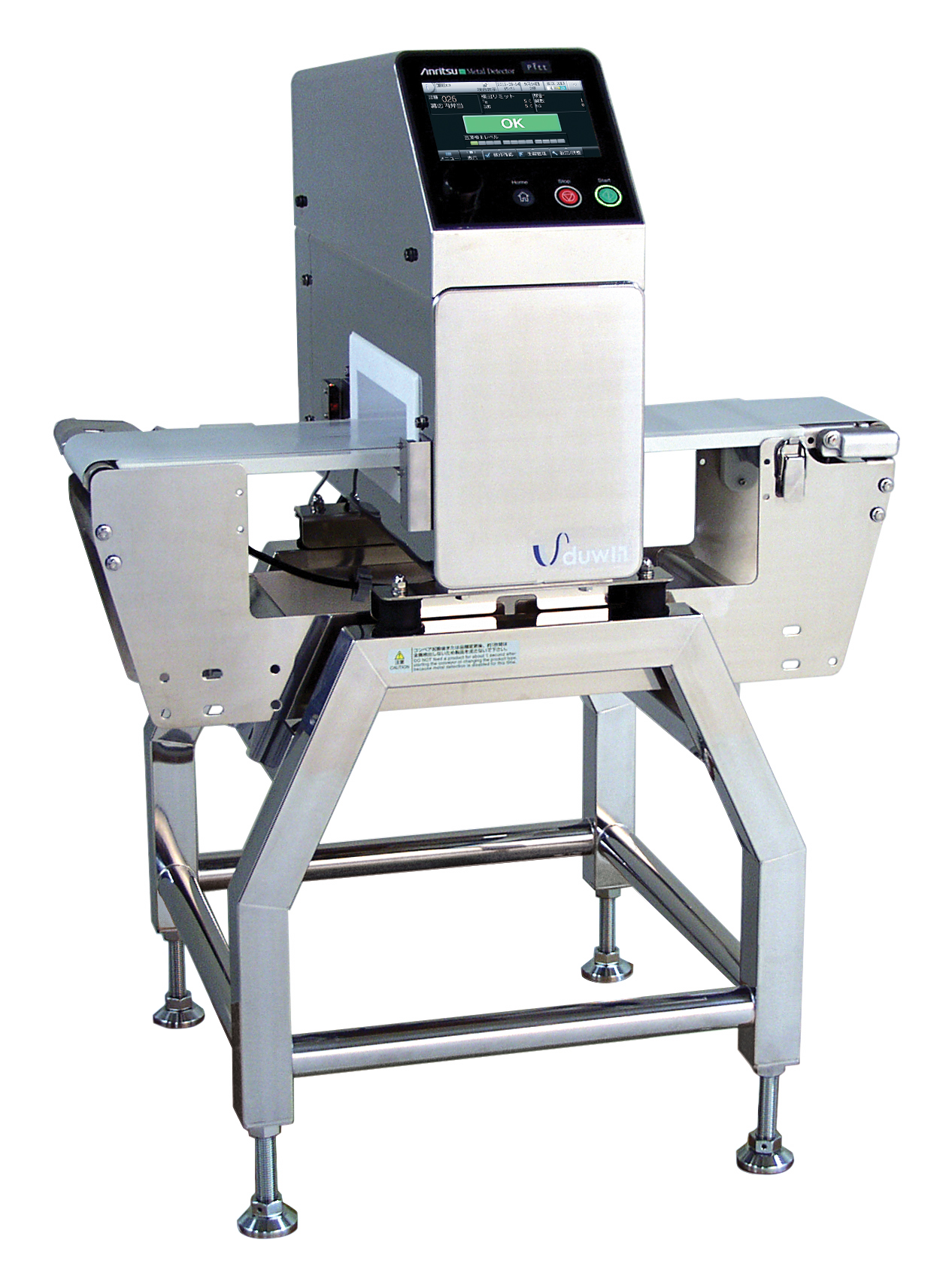

High-sensitivity metal detection system
Highly efficient metal detector with enhanced quality control and reporting capabil...