Making Liquid Dosage Forms
Find innovative liquid dosage forms equipment and connect directly with world-leading technology suppliers
Liquid dosage forms are designed for easy absorption. The body quickly carries the active ingredients through the system and triggers the required response. But the greatest advantage of this medicinal type is its flexibility in formulation and dispensation. From lotions and syrups to drops and sprays, liquid solutions can be adapted to different administration routes including parenteral, topical, and oral. The fundamental liquid dosage manufacturing process involves dissolving or suspending solutes in a fluid. But that is not enough. A precise blend of excipients is needed to make the medicine go down.
Top picks for liquid dosage forms
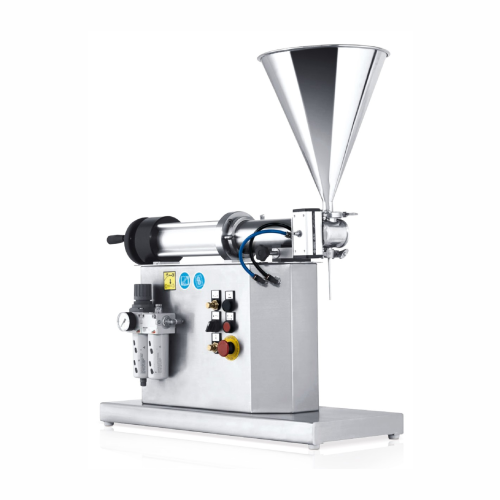

Laboratory filling system for liquid and creamy products
Optimize your laboratory processes by precisely handling liquid,...
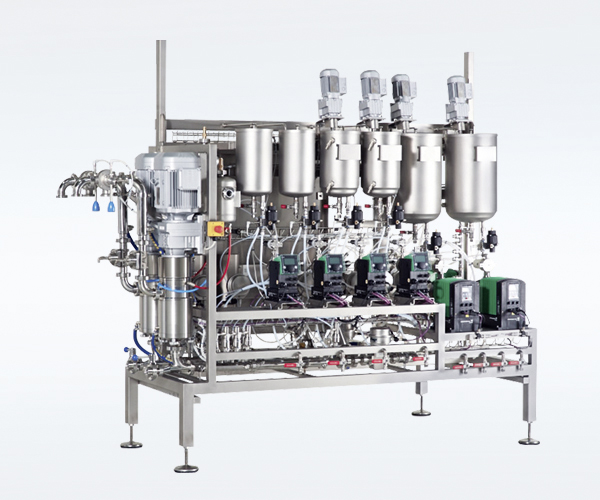

High precision dosing system for liquid media
Producing confectionery and bakery products implies mixing large amounts of ...
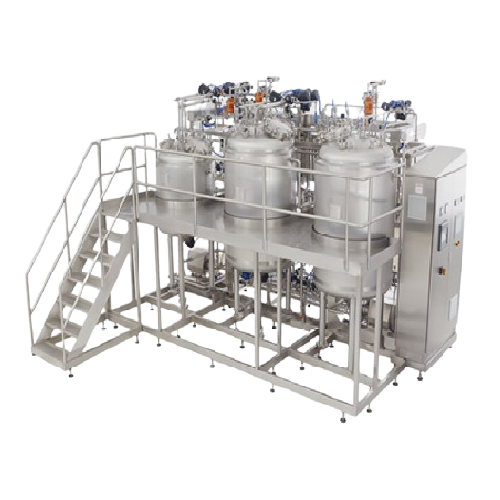

Sterile liquid preparation system for pharmaceutical use
Ensure the sterility and precision of your liquid formulations w...
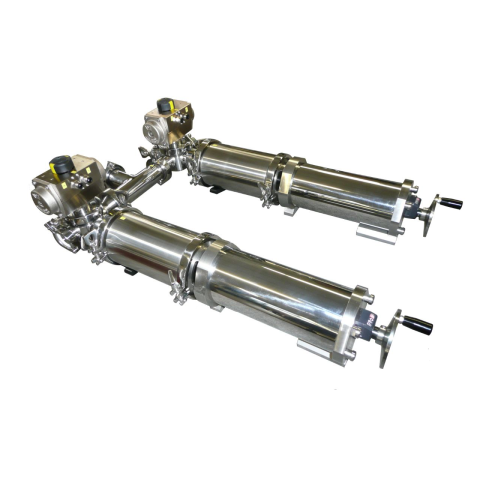

Pneumatic dosing syringes for precise liquid dispensing
Achieve precise and reliable liquid dosing with pneumatic syringe...
Select your liquid dosage forms process
What are you making?
Tell us about your production challenge
Use water or pure alcohol as a solution in the liquid dosage manufacturing process
The liquid dosage form is prepared by dissolving the active ingredient within a liquid vehicle to form a solution. Depending on the type of liquid vehicle used, you obtain either aqueous or non-aqueous solutions.
The aqueous solutions have water as the solvent, while the non-aqueous solutions have hydro-alcoholic (water and alcohol as solvents) and alcohol (only alcohol as solvent). Elixirs and tinctures are examples of hydro-alcoholic solutions. The concentration of alcohol in elixirs is 3%-25%, while the concentration of alcohol in tinctures is 25%-60%.

Apply size reduction to raw materials to facilitate solubility
Drops, syrups, elixirs, and draughts are monophasic liquid dosage forms, retaining the components in a single liquid phase. The APIs in most dosage forms of this type are weak acids or weak bases with low solubility properties. The formulation, therefore, requires adjustment of pH levels.
One method to improve solubility is by reducing the particle size of pharmaceutical powders. Using a mill or a spray drying system, grind the materials to 10 microns or less.

Apply gravimetric measurement in the liquid dosage manufacturing process
The volumetric measurement risks a high variability in liquids as the ingredients may be subjected to volume contraction or expansion.
The gravimetric method bypasses the effects of temperature and ambient forces acting on the ingredients. By measuring the density of the total contents, the technique gives a more reliable reading of the liquid dosage before filling and packing.
Which liquid dosage forms technology do you need?
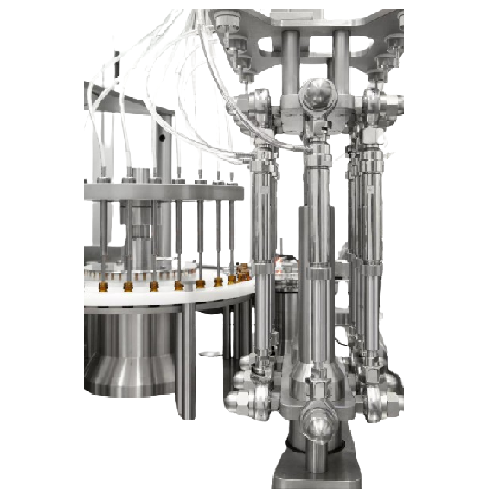

Filling and capping solution for oral liquid products
Achieve precise, high-speed filling and capping of oral liquids wit...
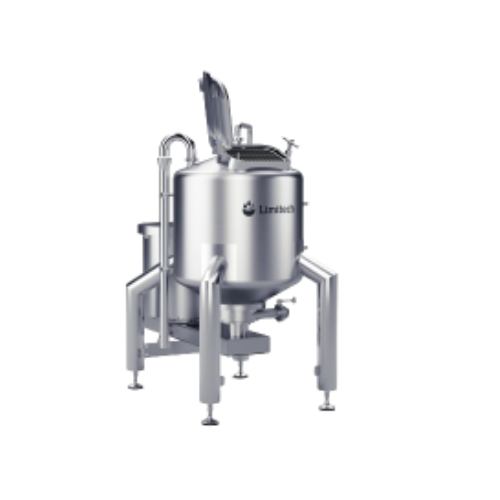

Inline high shear mixer for low to medium viscosity liquids
Efficiently dissolve large quantities of powders into liquid...
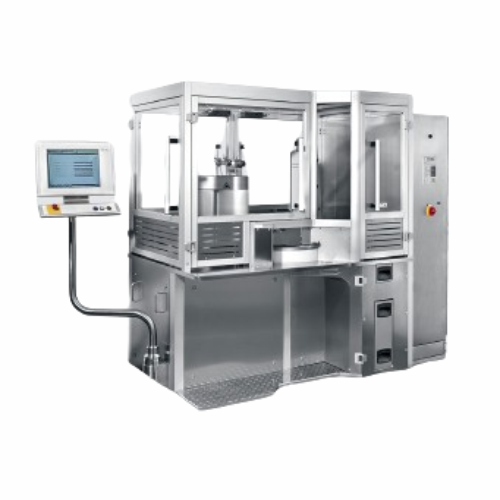

Liquid filling system for medical and pharmaceutical products
Enhance your production capabilities with high-speed liqui...
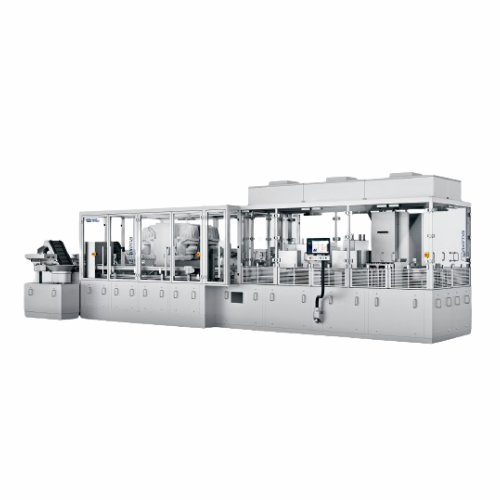

Liquid dosing and assembly platform for pharmaceutical products
Optimize your production line with a seamless solution f...
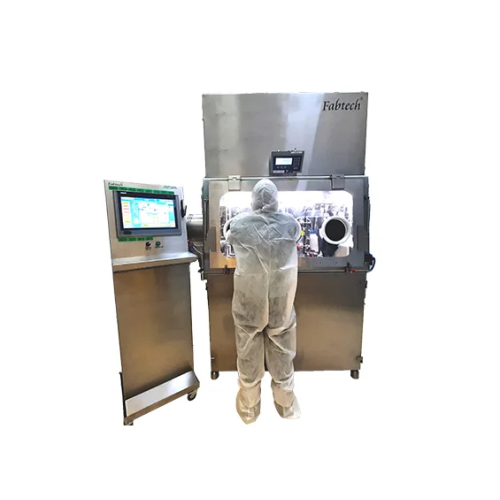

Liquid dispensing isolator for sterile environments
Maintain product sterility by utilizing a liquid dispensing isolator ...
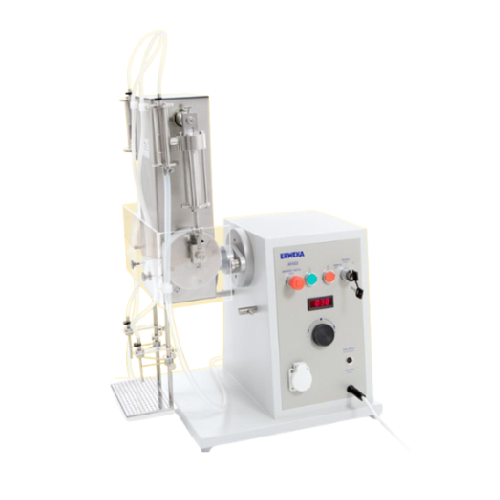

Industrial liquid filler for small to medium volume operations
Ensure accuracy and efficiency in liquid formulation with...
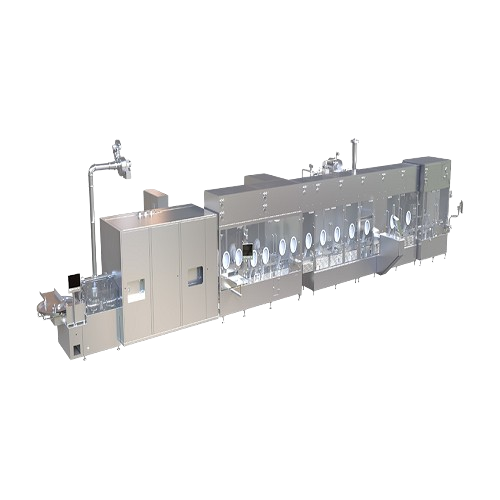

Sterile filling line for liquid and powder
Achieve seamless integration of filling, sterilization, and packaging with this...
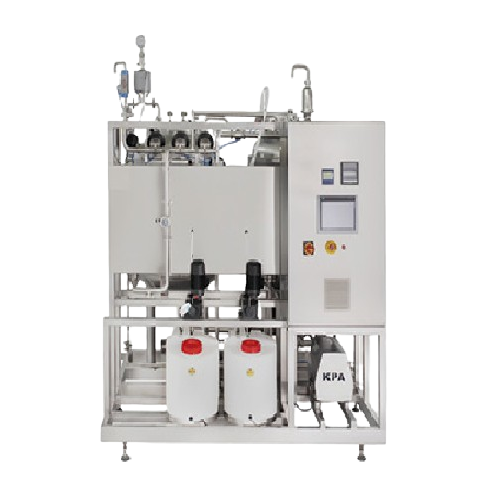

Cip workstation for pharmaceutical liquid preparation systems
Optimize your liquid formulation process with precise clea...

Sterile liquid preparation system for pharmaceutical use
Ensure the sterility and precision of your liquid formulations w...
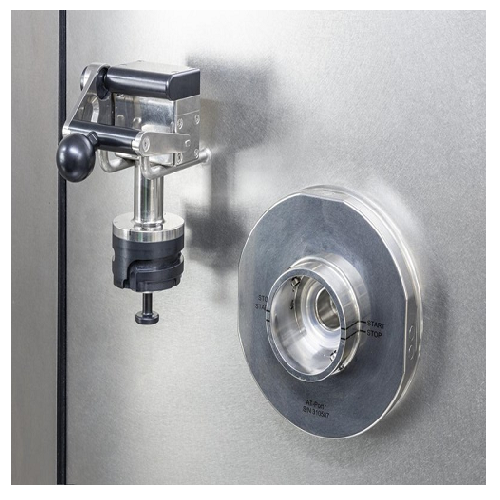

Aseptic liquid transfer connection system
Ensure sterile liquid transfer between containment areas with minimal product lo...
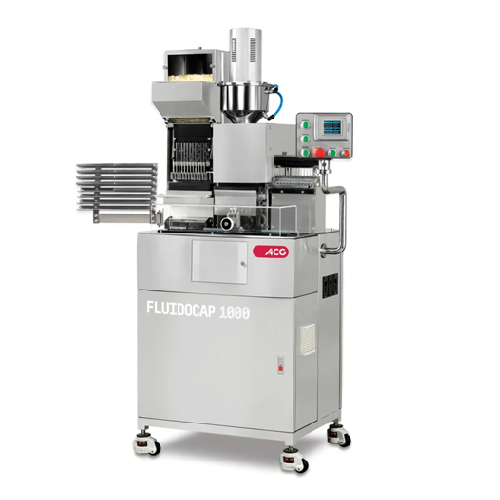

Liquid capsule filling for r&d and pilot-scale production
Optimize liquid capsule production with a compact machine that...
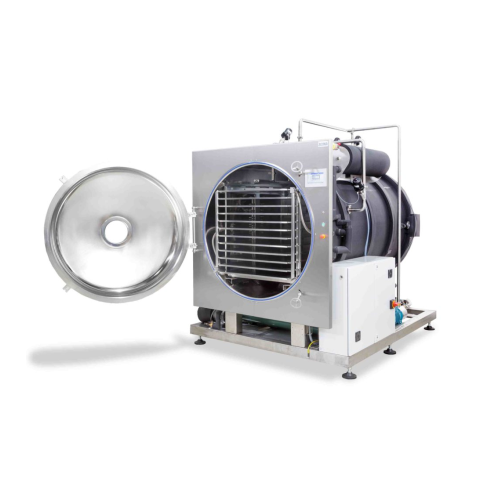

Single-chamber freeze dryer for liquid products
When precision drying of sensitive liquids is crucial, this single-chamber...
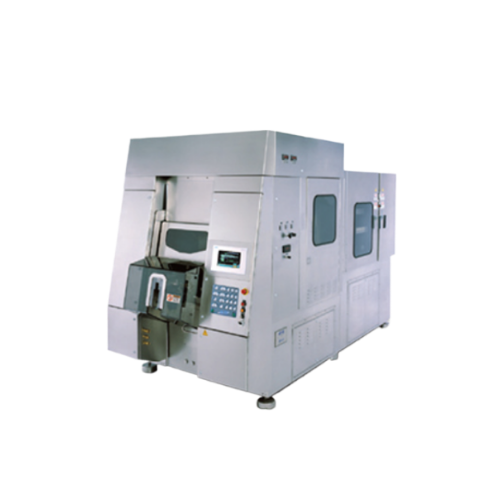

Blow/fill/seal packaging system for sterile liquid products
Streamline your liquid product manufacturing with high-speed...
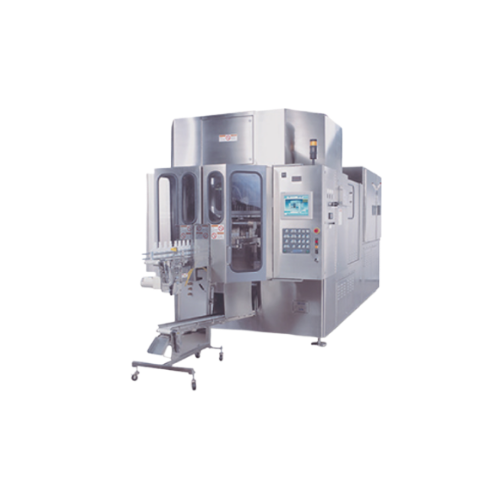

Blow/fill/seal system for aseptic liquid packaging
Achieve efficient aseptic packaging with a system that combines blow m...
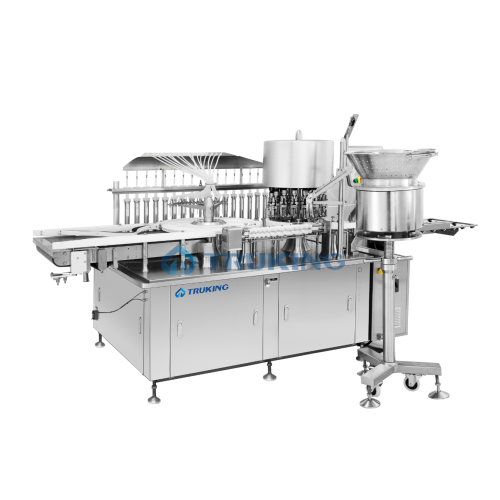

Oral liquid bottle filling & capping system
Streamline your liquid manufacturing processes with precise filling and secure...
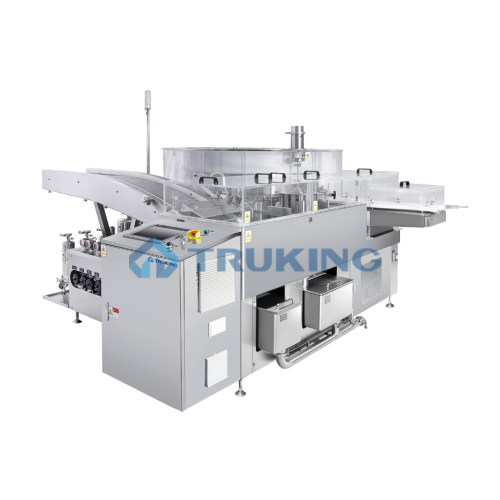

Vertical ultrasonic washing system for oral liquid bottles
Ensure optimal cleaning and sterilization with a compact vert...
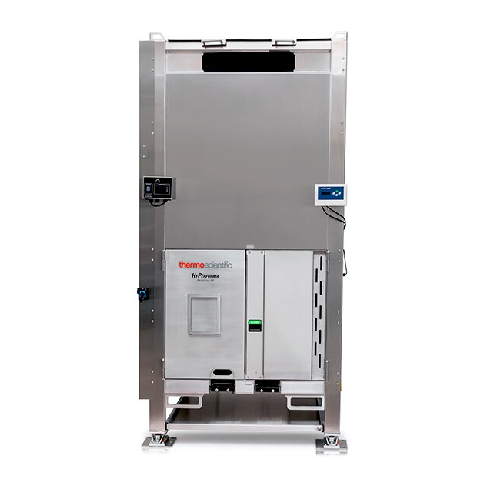

Large-volume sterile liquid storage solution
Efficiently store and transfer large volumes of sterile process liquids with ...
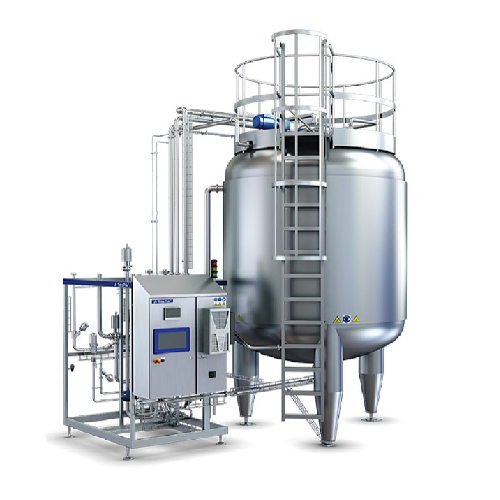

Aseptic tank with blending function for liquid food storage
Achieve seamless integration of aseptic buffering and in-lin...
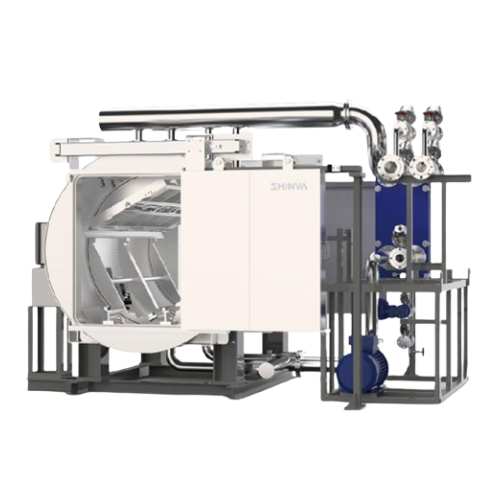

Moist heat sterilizer for liquid preparation
Ensure precise sterilization of pharmaceutical liquids and injectable biologi...
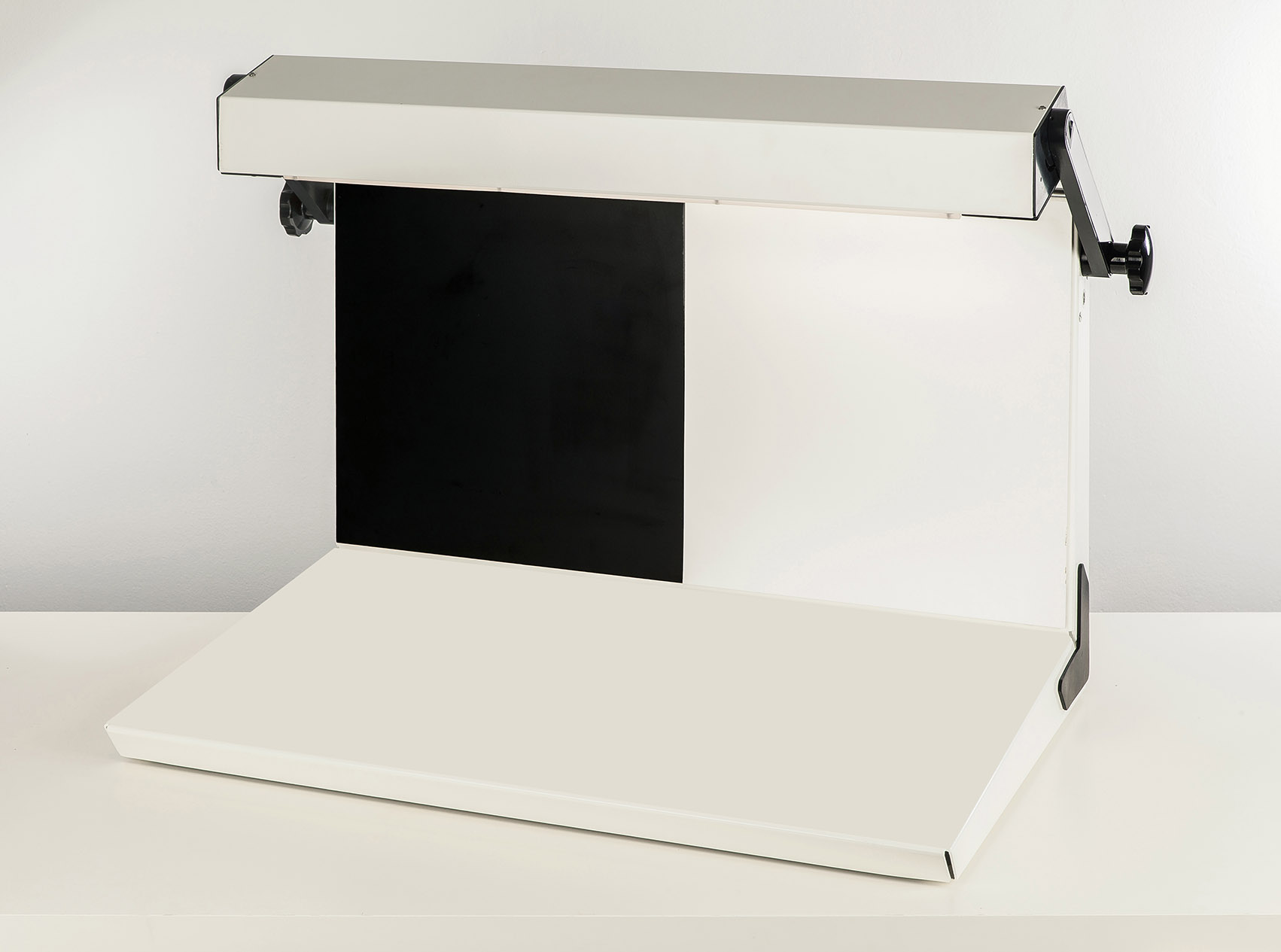

Laboratory liquid viewer for colored glass bottles
In the pharmaceutical industry, an inspection to detect any particulat...
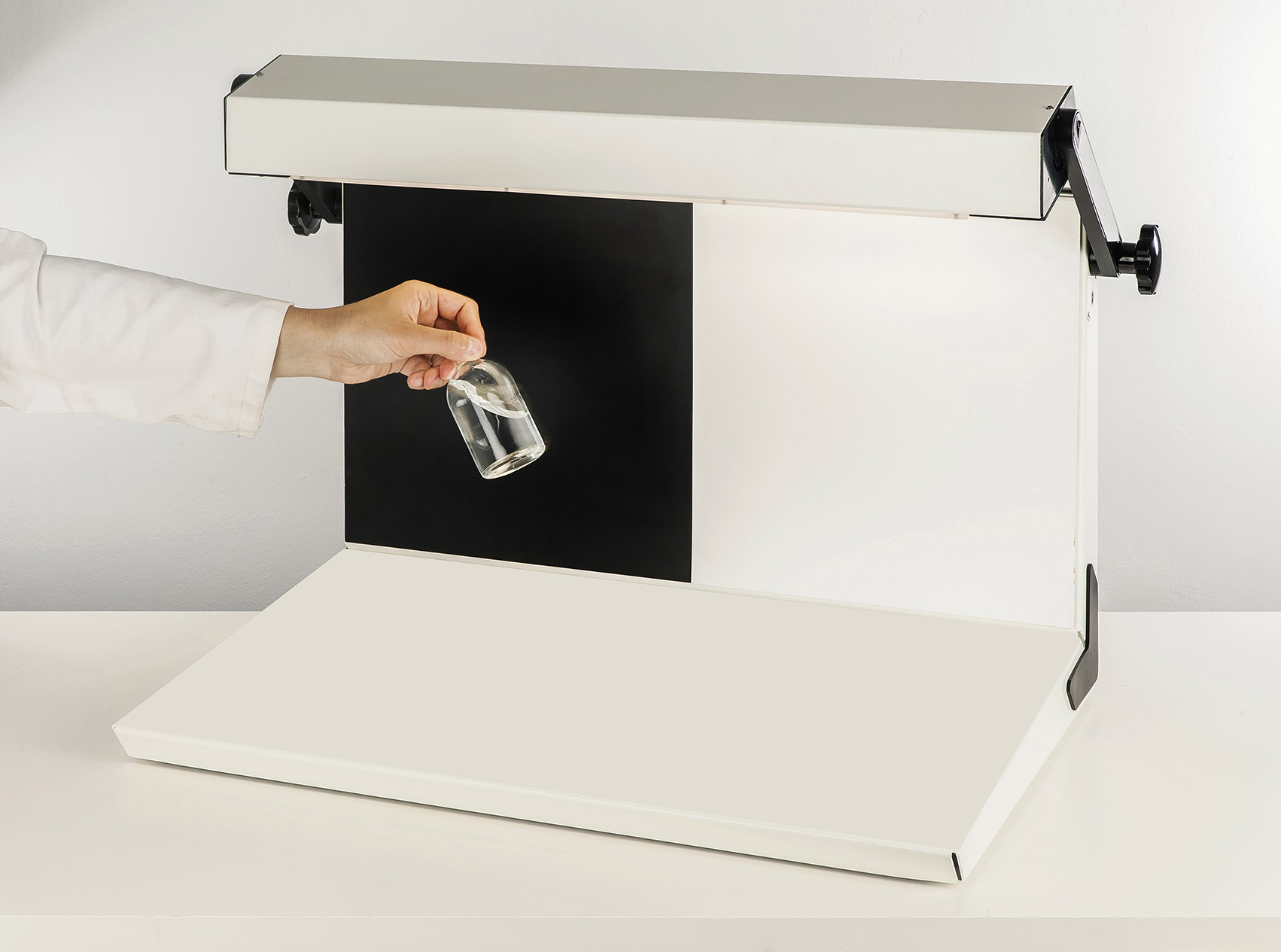

Laboratory liquid viewer for varying light conditions
In the pharmaceutical industry, you must inspect liquids in vials o...

Laboratory liquid viewer for transparent glass bottles
Impurities like hair, fibers, or glass, sourced from the environme...
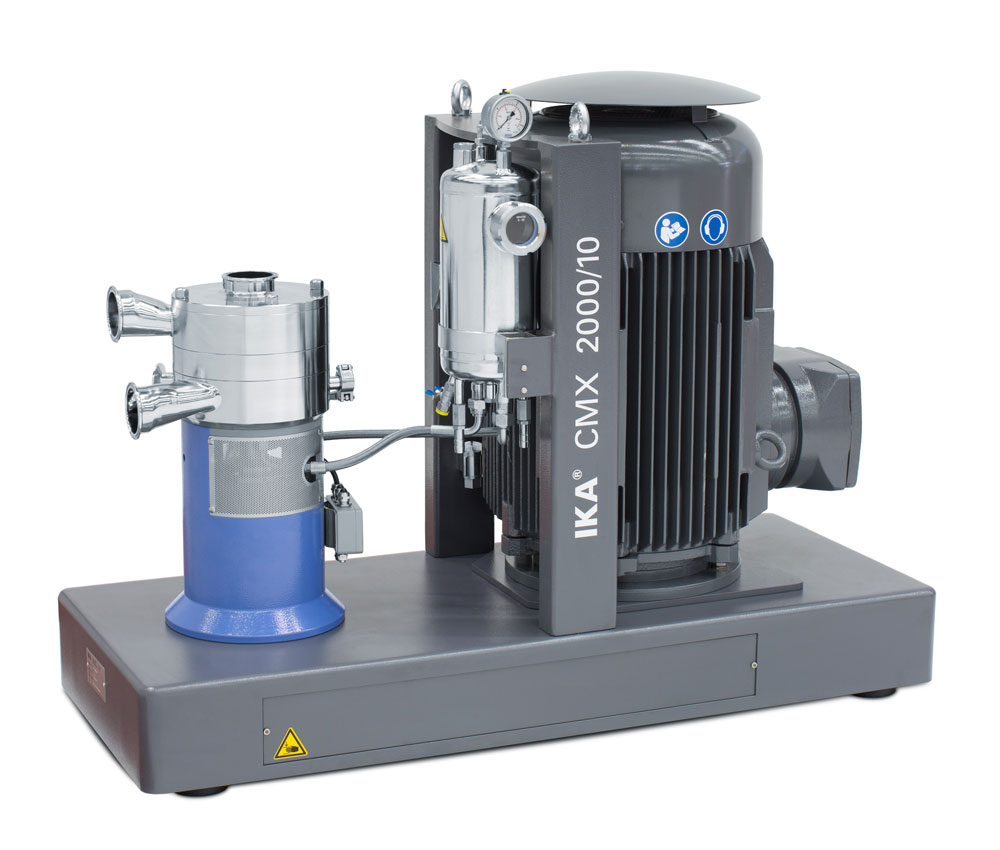

Inline batch mixer for solids and liquids
Several issues often arise when your process requires batch-wise mixing of powde...
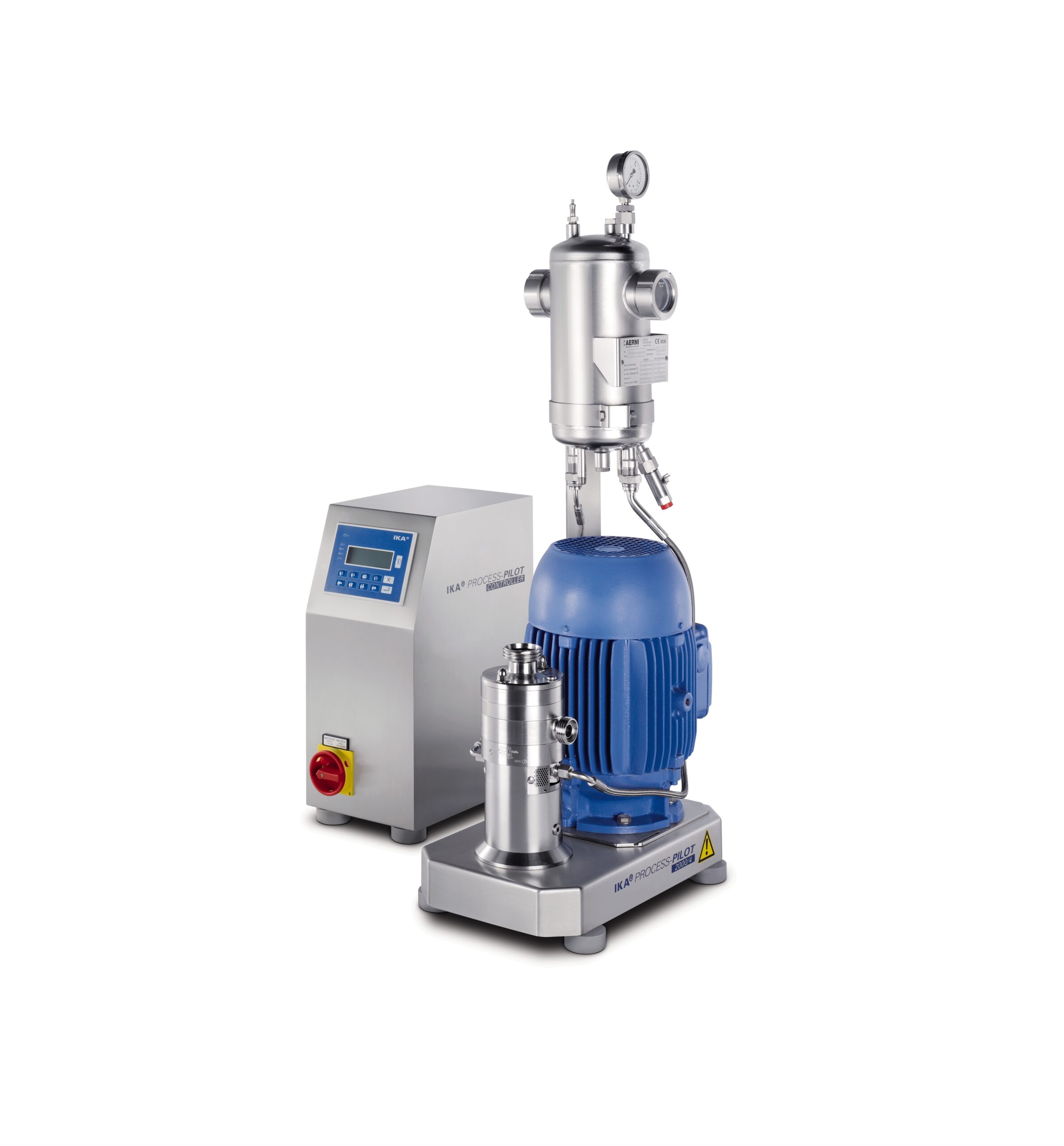

Dilution system for two or more liquids in one pass
Onsite dilution of liquid process ingredients has historically been a...
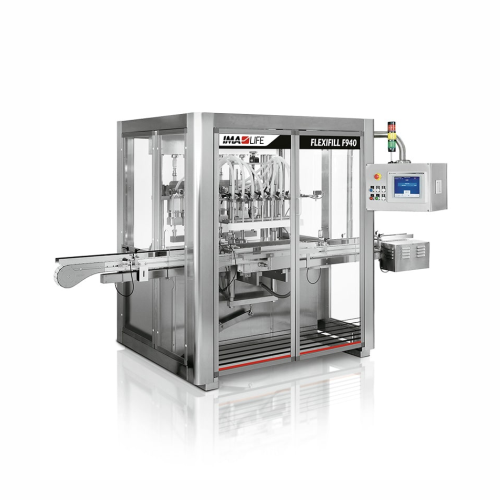

In-line filling system for pharmaceutical products
Ensure precise and flexible filling of liquids, from sterile saline to...
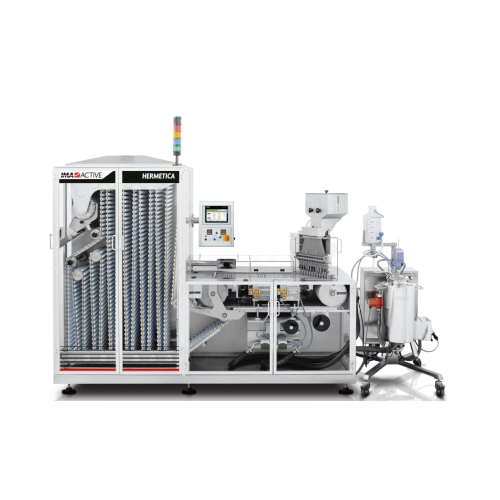

Capsule banding system for tamper-evident sealing
Ensure tamper-evident integrity for capsules by utilizing a precise ban...

Thermoforming solution for clinical trials
Designed for precision and flexibility, this compact thermoforming machine stre...
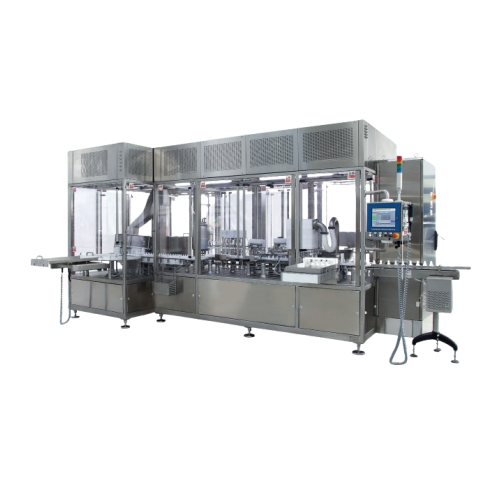

Filling solution for non-injectable pharmaceutical products
Streamline your pharmaceutical production with a versatile s...
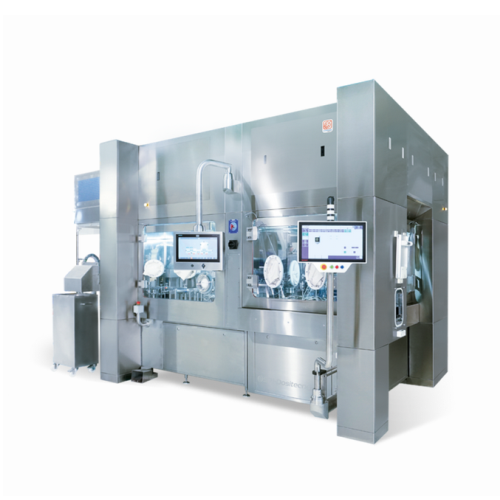

Rotary filling system for Rtu vials in pharma production
Optimize your sterile liquid and powder handling with a versatil...
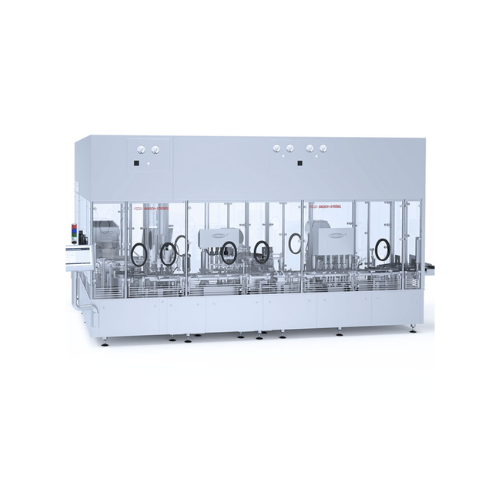

Filling and closing solution for plastic bottles
Efficiently sort, fill, and close a variety of plastic bottles with preci...
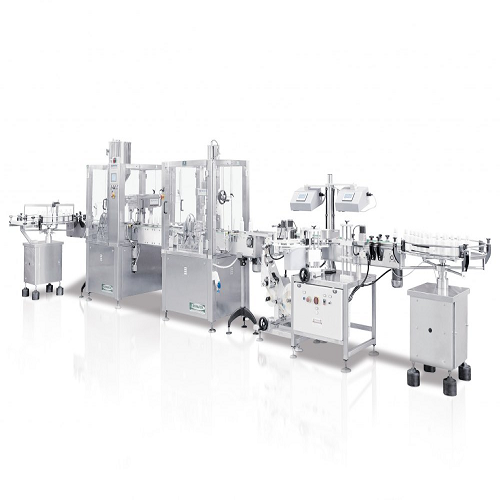

Automatic bottle filling and capping line
Streamline your liquid product packaging with this high-speed solution, integrat...
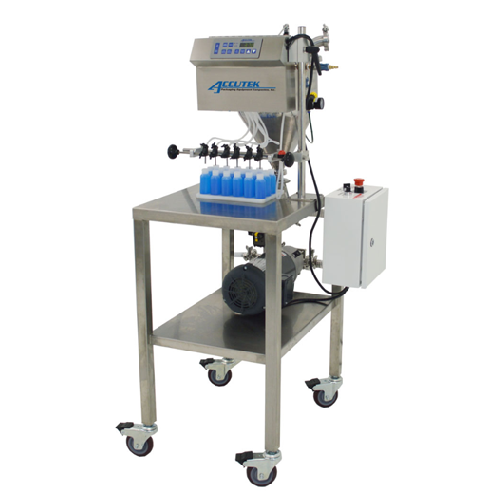

Semi-automatic timed flow filler for aqueous solutions
Handle diverse liquid filling needs with precision, from thin oils...
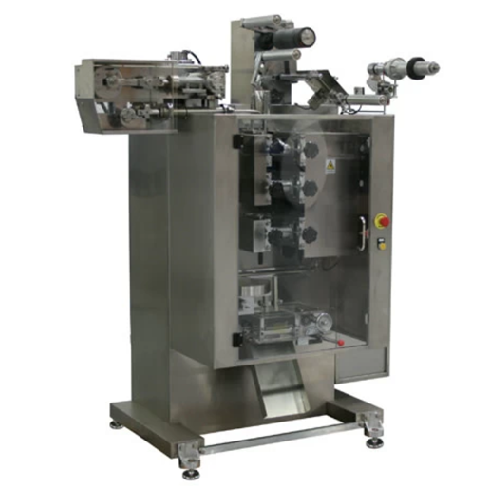

Form, fill, and seal system for single-use pouches
Achieve precise portion control and secure sealing with an integrated ...
Continuous in-line blender for beverage industry
Enhance your blending precision and process flexibility with a system des...

High shear mixer for low viscosity products
Achieve precise mixing and dispersion for diverse liquid applications with a h...
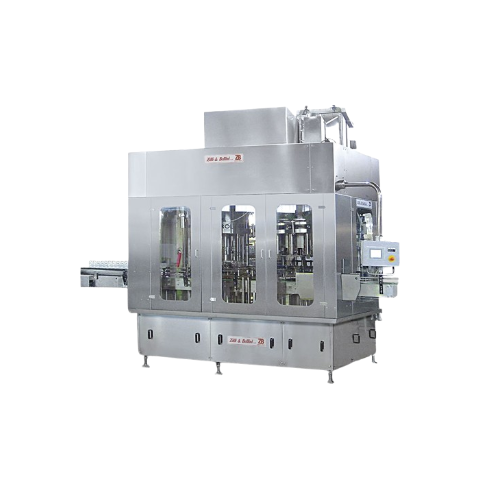

Ultraclean filling monoblocks for food industry
Enhance product safety and quality with monoblocks designed for ultraclean...
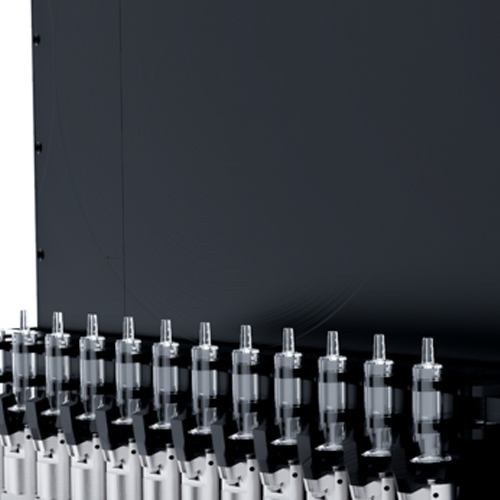

X-ray inspection module for pre-filled syringe needles
Ensure sterility and product integrity in high-speed syringe produ...
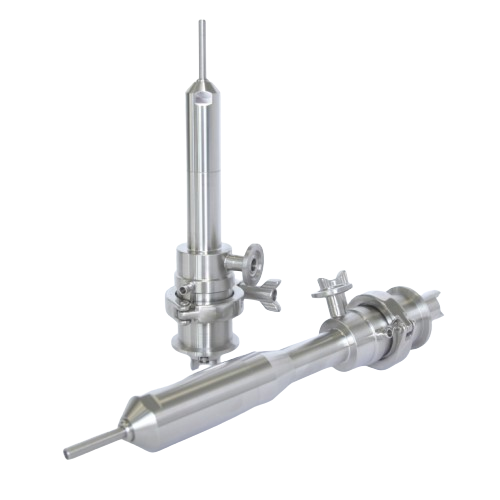

Accurate pharmaceutical dispenser for high-viscosity fluids
Achieve precise liquid dosing with ease, designed to handle ...
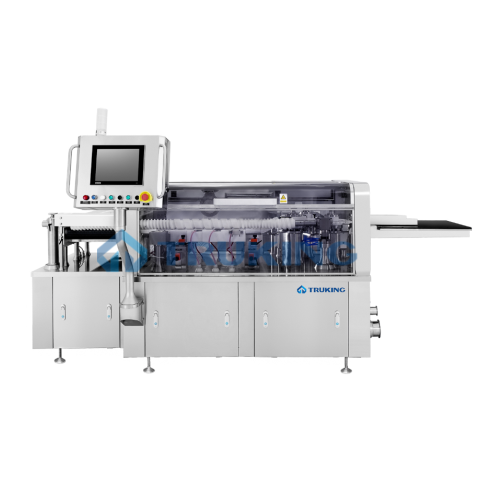

Automatic leak detection system for pharmaceutical containers
Ensure the integrity of pharmaceutical containers with pre...
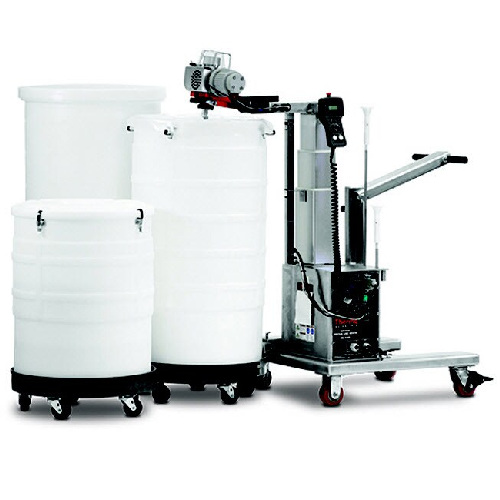

Single-use mixer for buffer sterile mixing
Enhance mixing efficiency with a versatile single-use mixer designed to handle ...
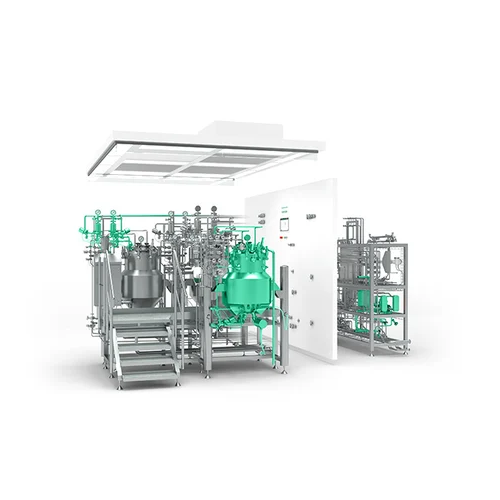
Modular pharmaceutical formulation systems
Achieve unparalleled flexibility and efficiency in liquid pharmaceutical formul...
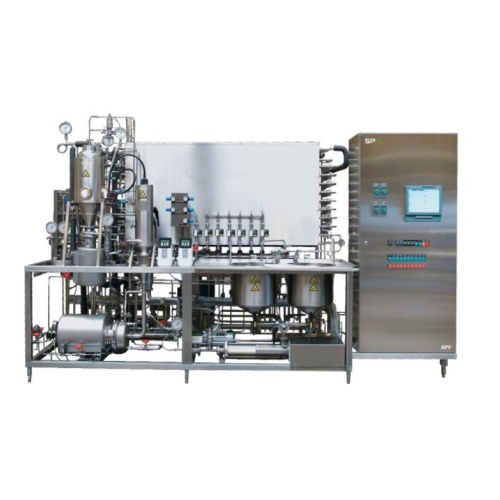

Multipurpose ultra high temperature (uht) pilot plants
Optimize liquid food production with a versatile pilot unit design...
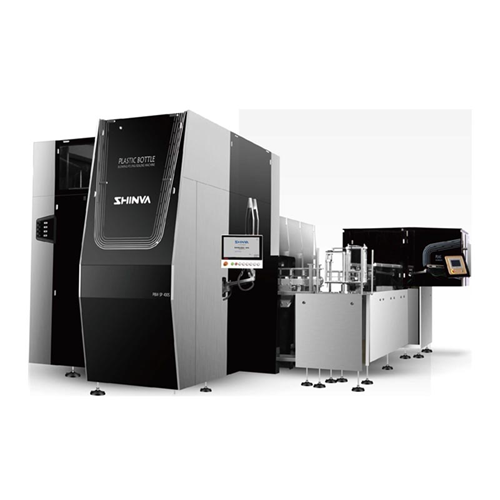

Reciprocating plastic bottle blow-fill-seal system
Achieve seamless integration of bottle forming, filling, and sealing w...
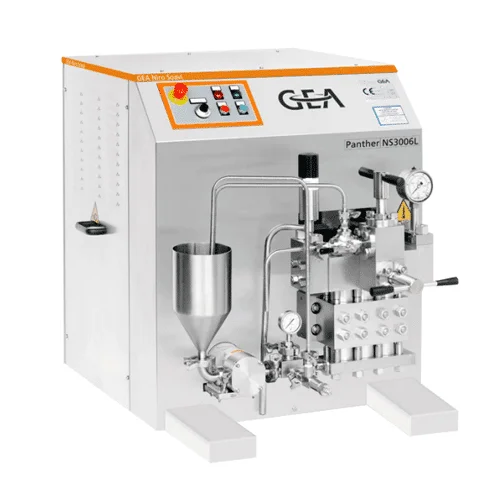

Cannabis nanoemulsification system for high-precision production
Achieve rapid bioavailability and stable formulations i...

Benchtop peristaltic dispenser
When you fill vials and ampoules, high standards of hygiene are required to avoid the risk of...
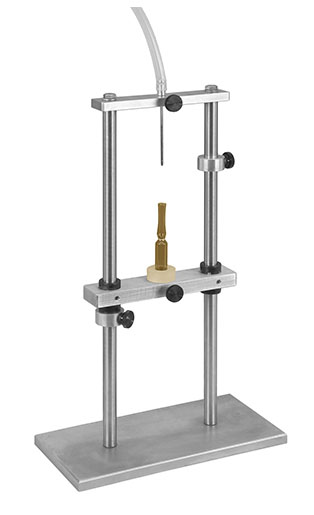
Manual ampoule filler
When you fill ampoules it is essential to avoid wetting the inside walls of the container, as it may af...
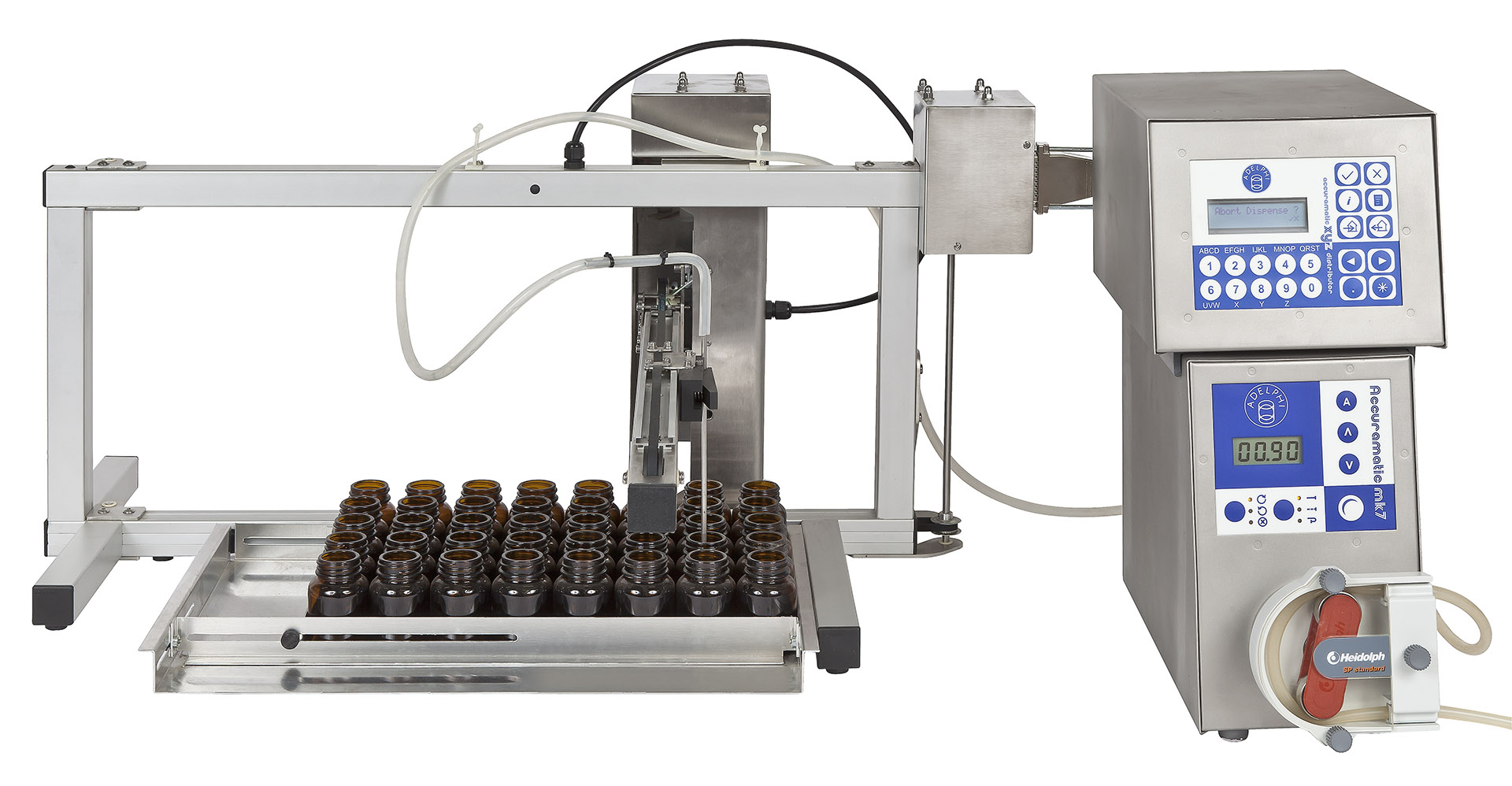

Benchtop piston filling equipment for vials in trays
Vials are difficult to fill individually through manual methods due ...

Manual stoppering equipment for pre-filled syringes
Air present in the empty space of pre-filled syringes may prevent you...
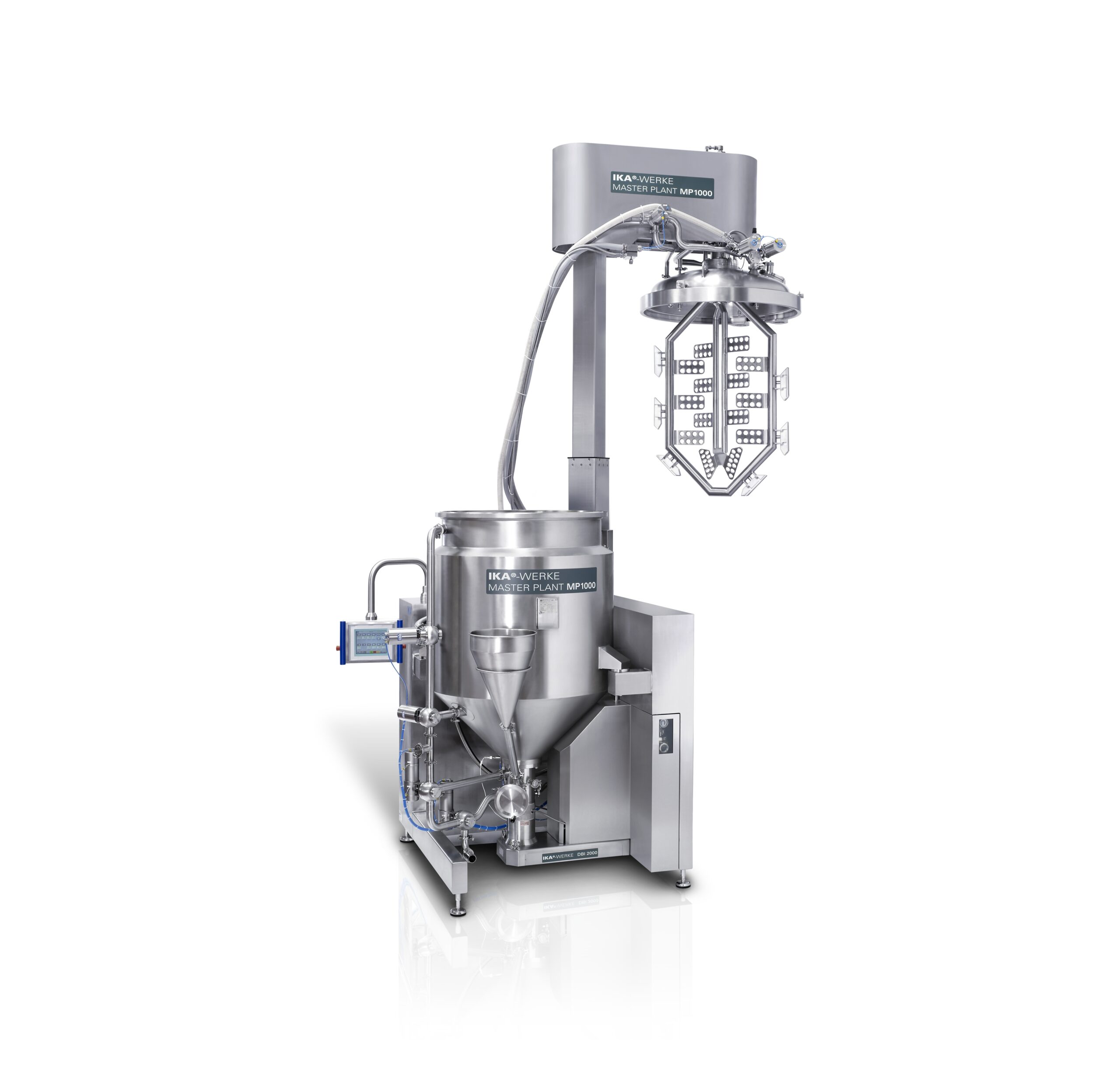

GMP homogenizing system
Manufacturers need production mixing equipment that is capable, flexible, and easy to maintain. Accur...
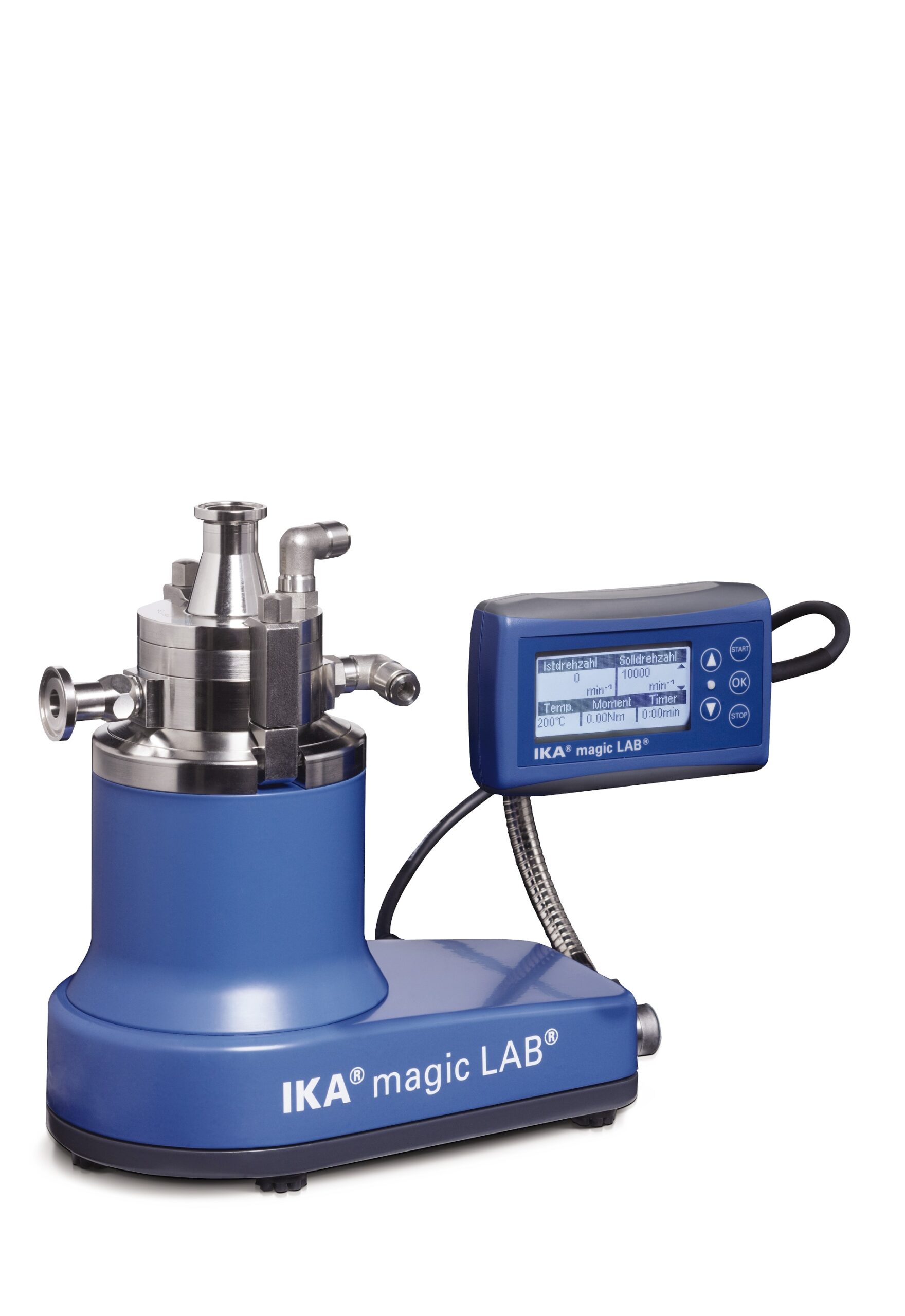

Small-scale laboratory dispersing machine
Developing and validating new processes requires reliable and highly versatile e...
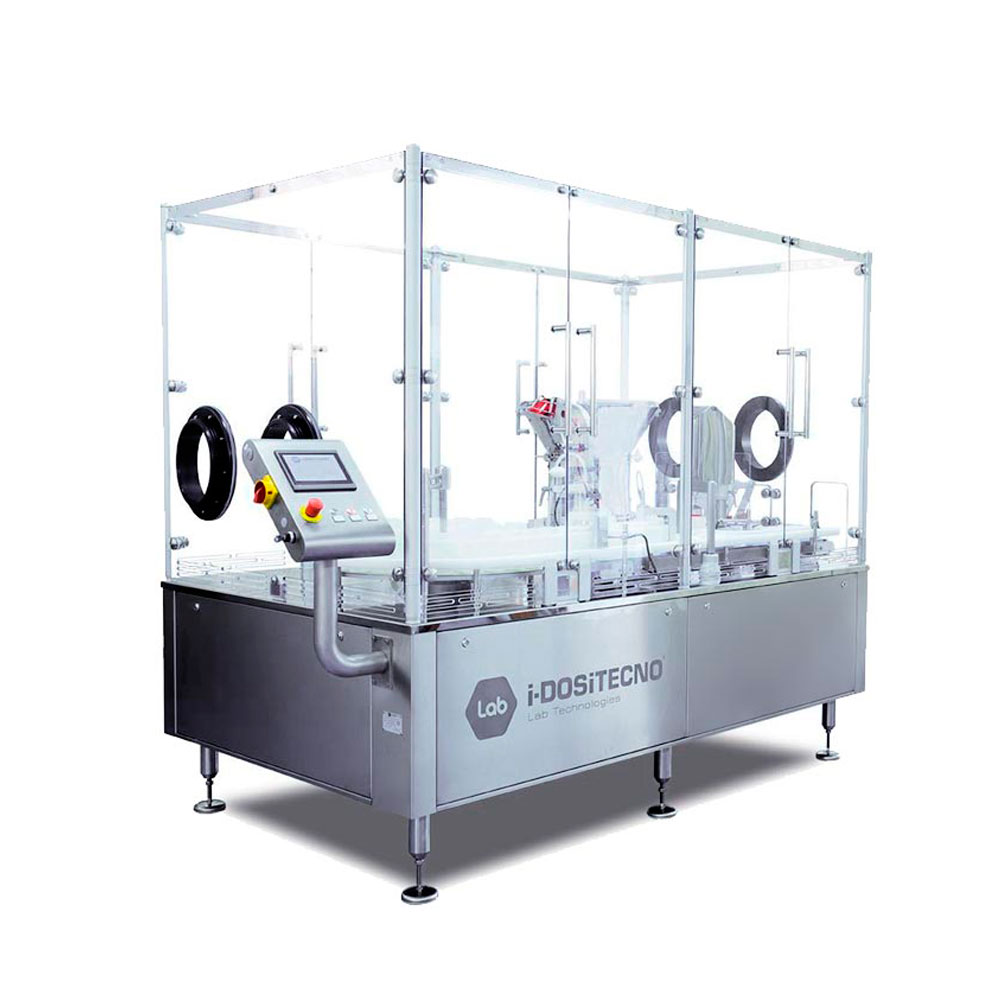

Start-up sterile filling line for ophthalmics
Commencing ophthalmic production requires sterile conditions and accurate me...
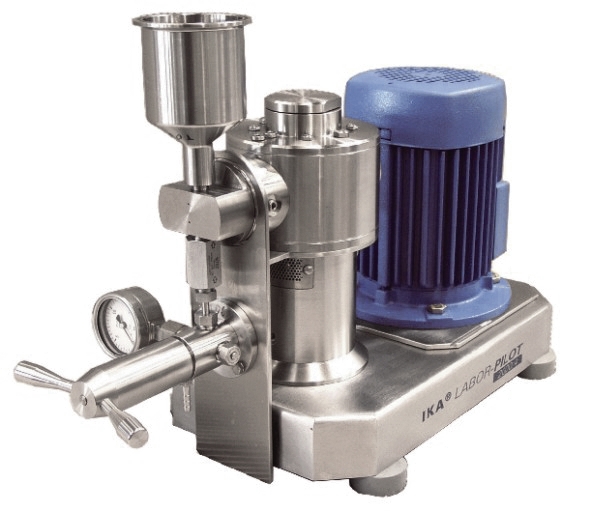

High-pressure homogenizer
When processes call for homogenized emulsions with extremely fine particle sizes the traditional t...
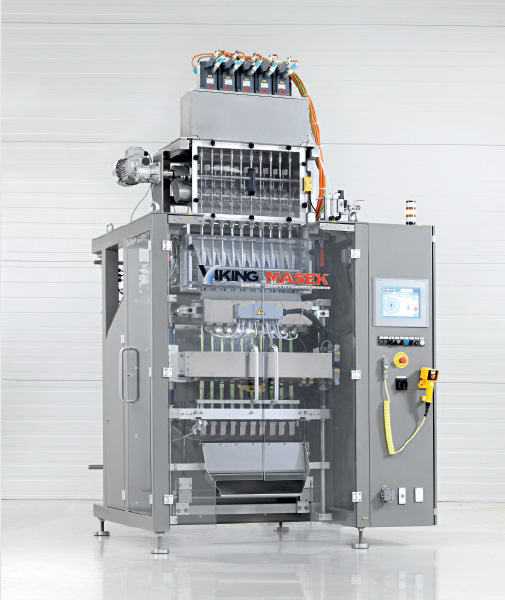

Stickpack Machine
If you are looking to pack your product into stick packs from 17 x 40 mm to 100 x 200 mm in size, you may b...
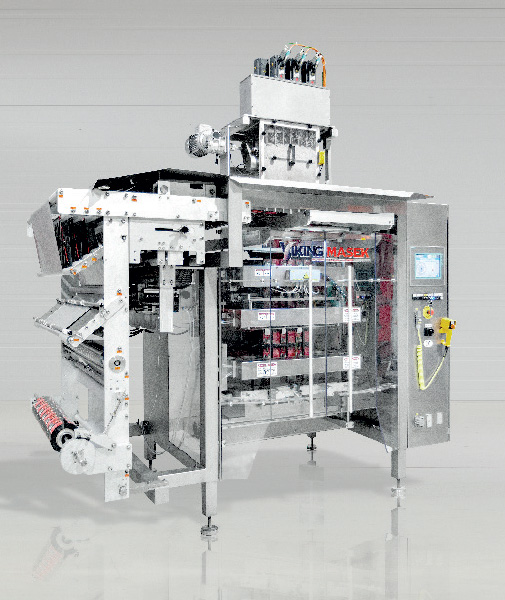

Sachet Machine
If you want to pack into eye-catching 4-side sealed sachets between 40×50 mm and 250×200 mm in size, ...
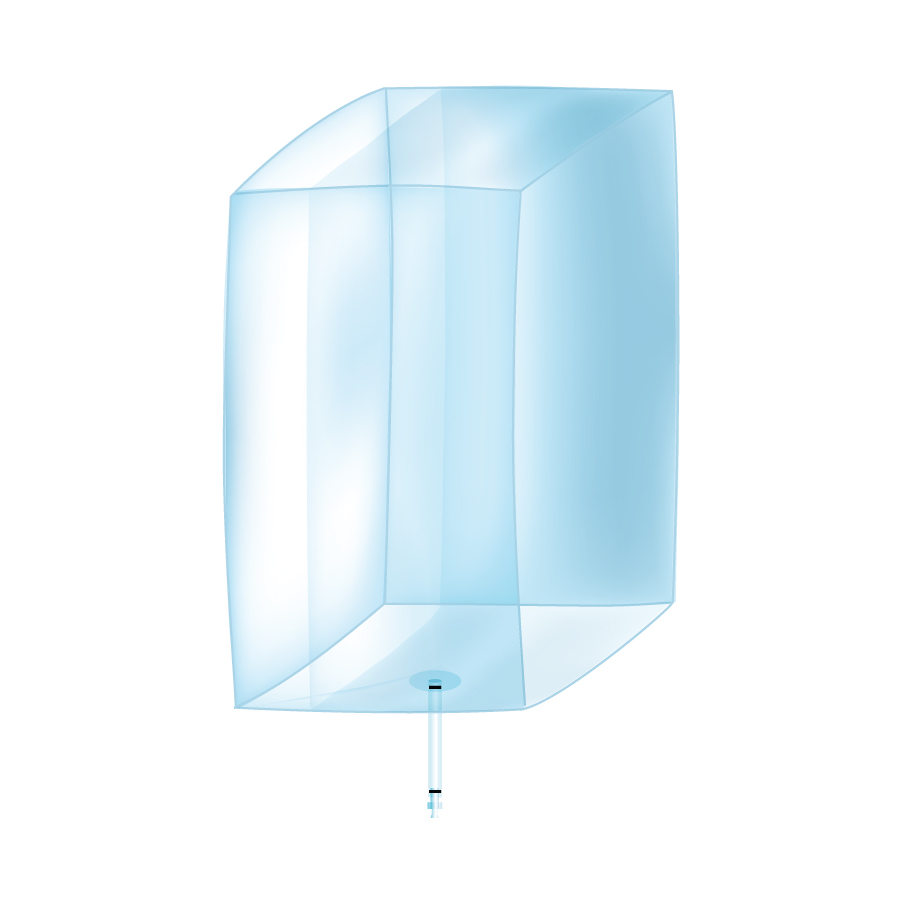
Disposable tank liners
Manufacturers in the bioprocessing industries are increasingly turning to single use solutions for the...
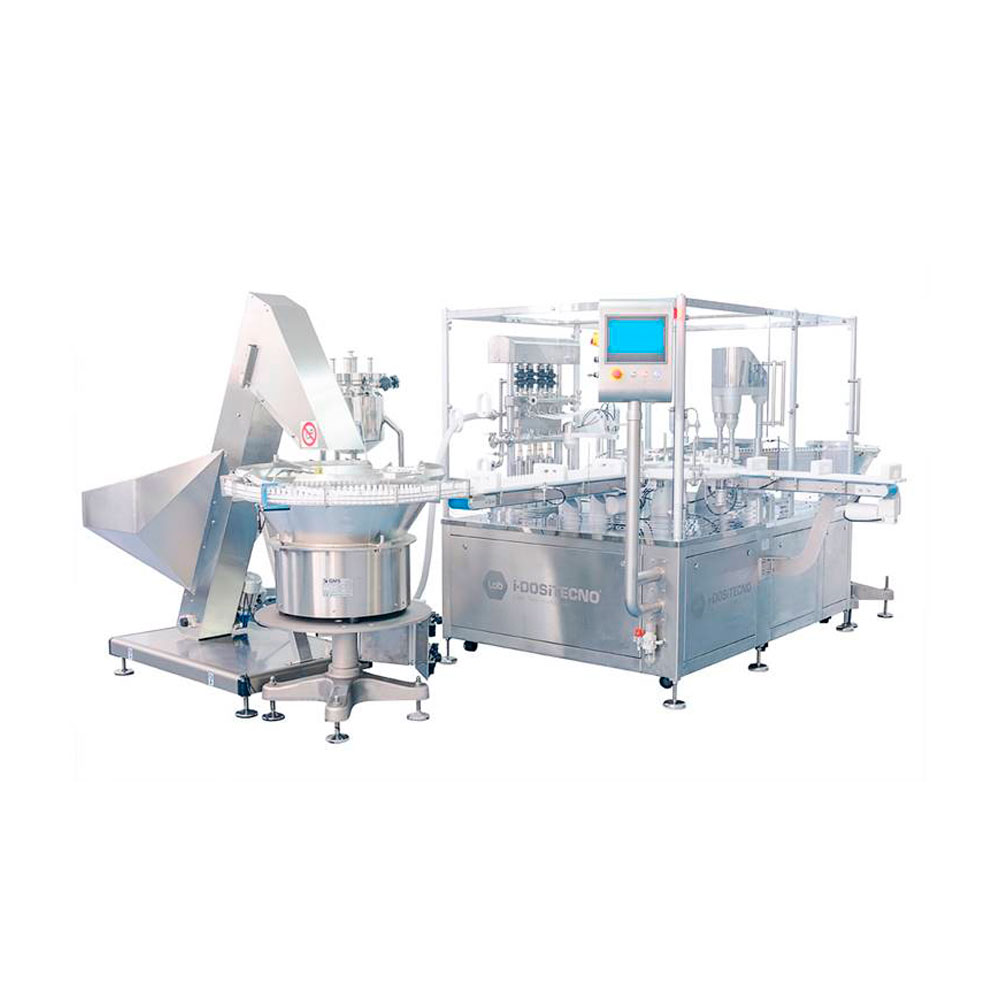

Sterile filling line for ophthalmics
Demanding very high standards, the ophthalmic market requires quality solutions for fi...
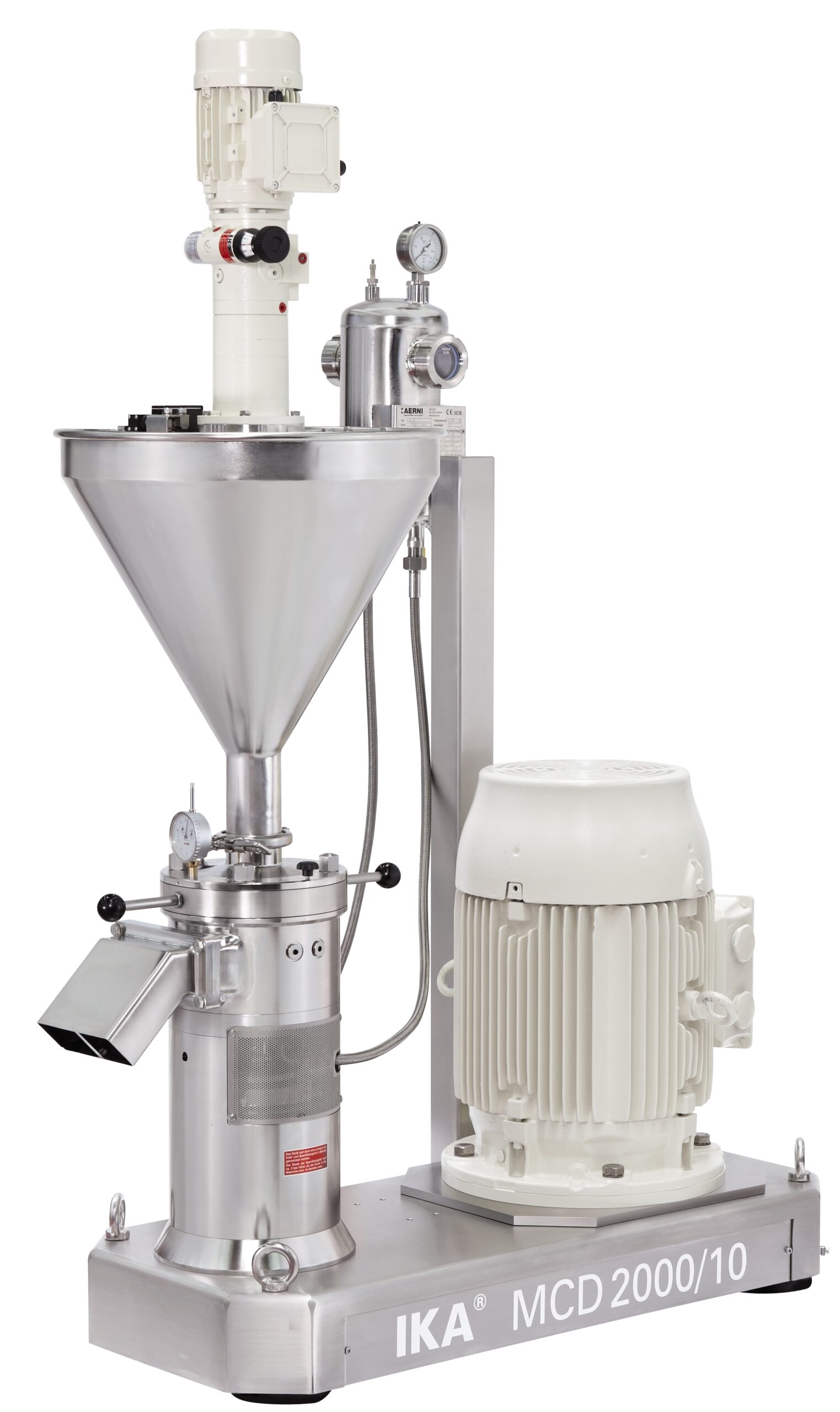

Corundum disk mill
Wet milling and grinding of viscous liquids or pastes containing solid particles such as peanut butter,mus...
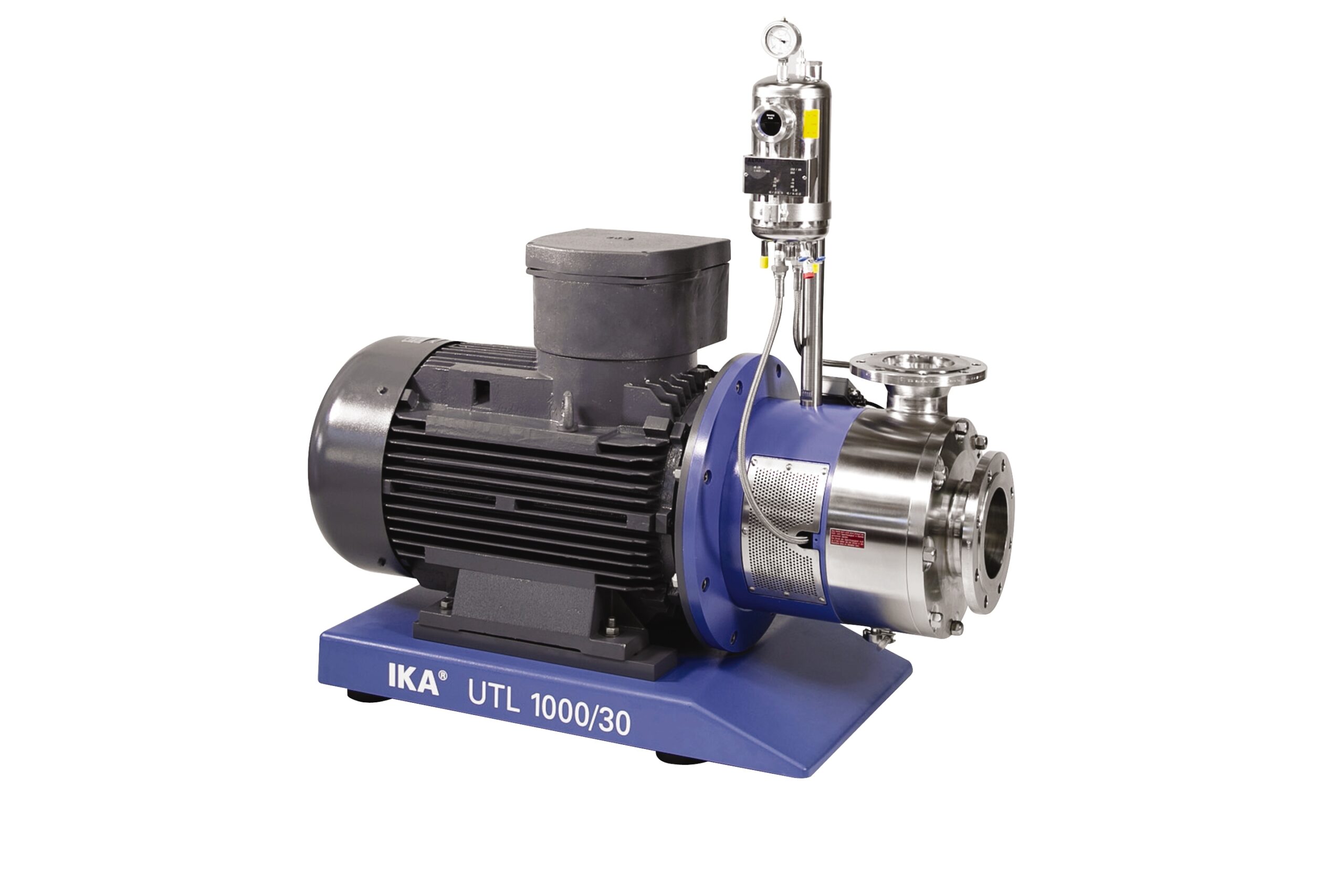

Economic dispersing machine for emulsions and suspensions
For products of medium viscosity and relatively consistent par...
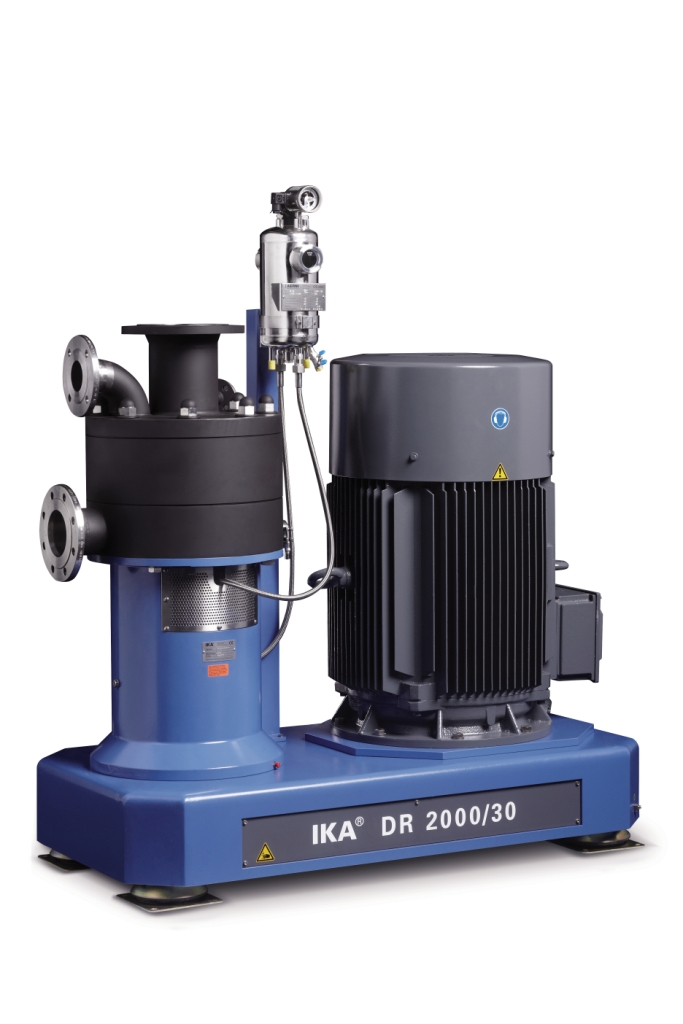

Dispersing machine for very fine emulsions and suspensions
For continuous high performance mixing of solid and liquid ra...
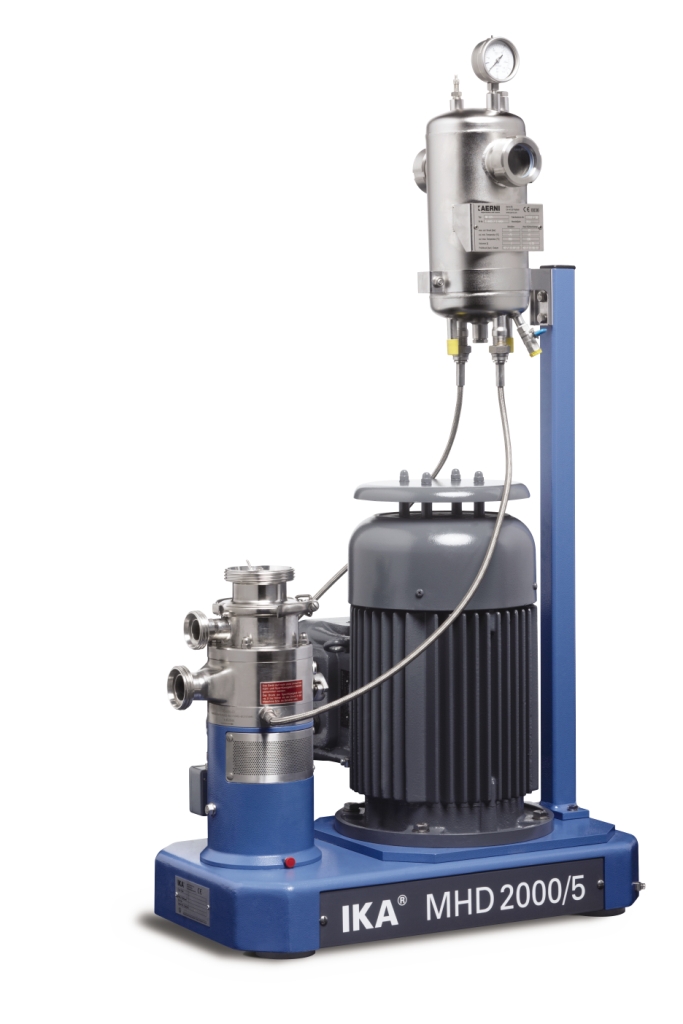

Continuous homogenizing system
Certain mixing tasks present unique challenges and manufacturers need equipment that is speci...
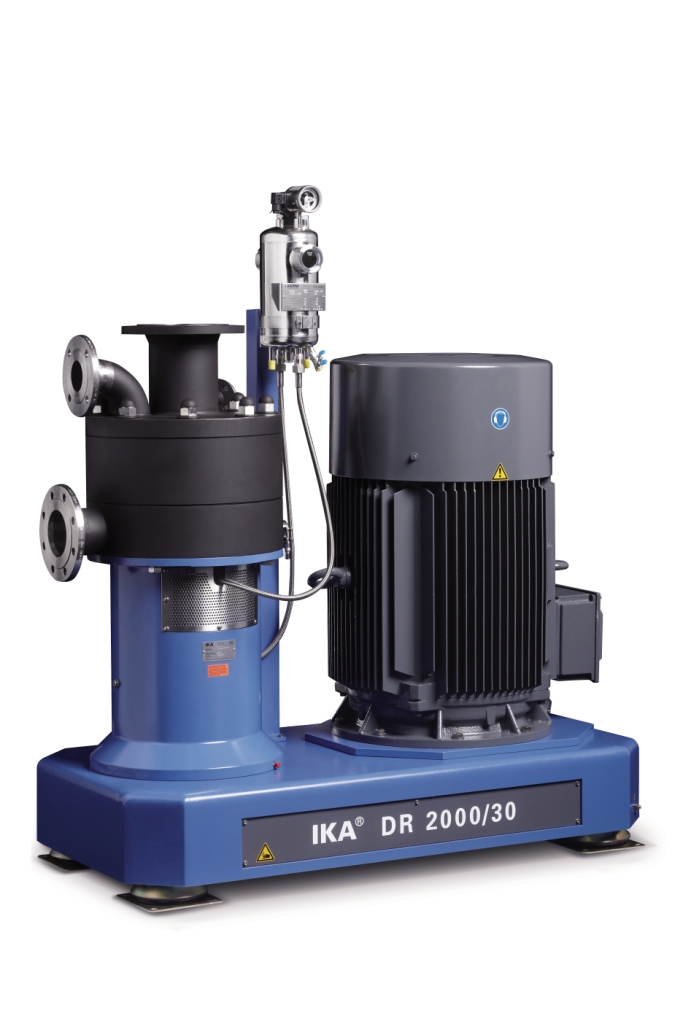

High accuracy homogenizing system
When extremely high accuracy is required in your recipe or formulation traditional mixing...
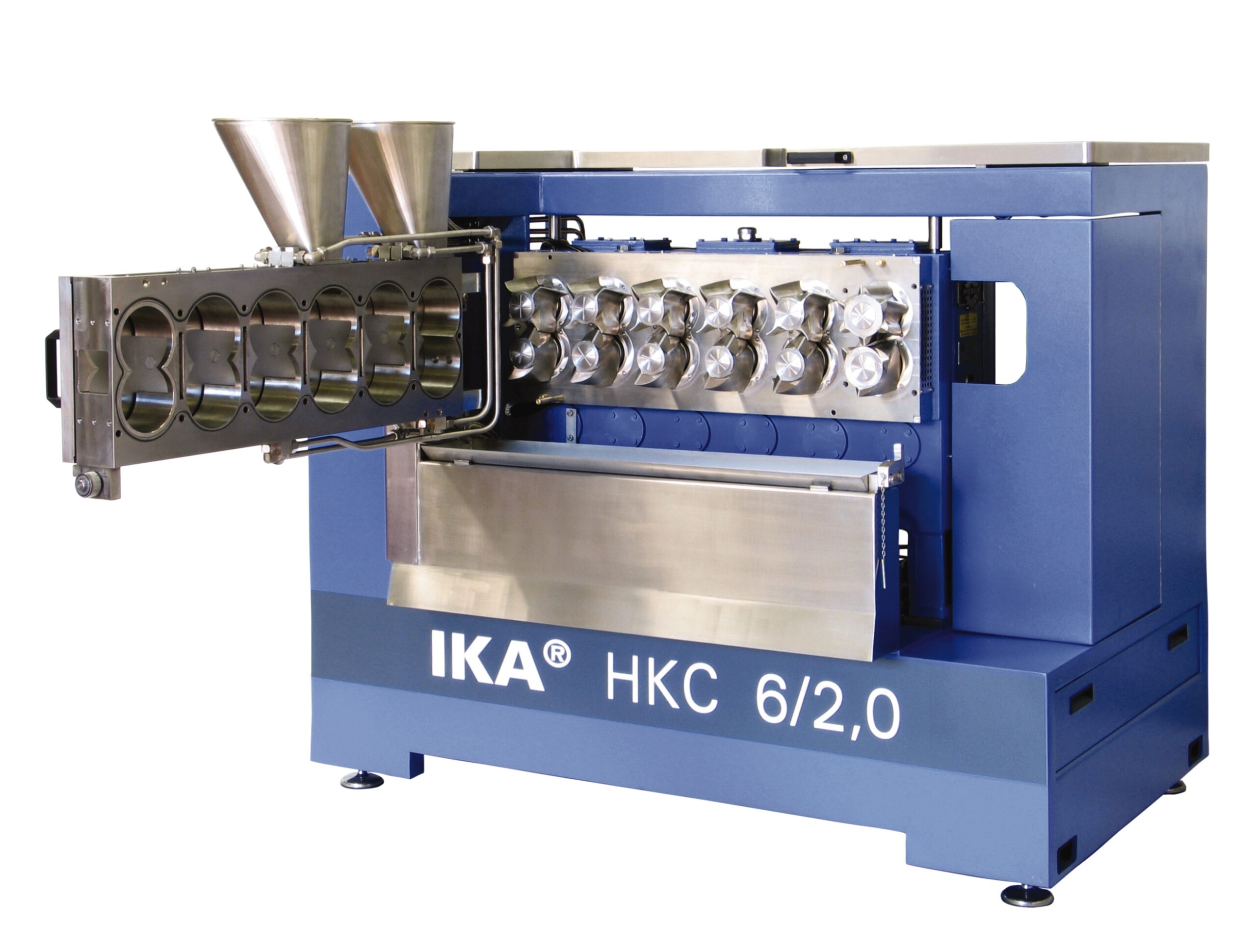

Continuous kneader
Effective mixing of highly viscous products with extremely high solids content can be difficult and the re...
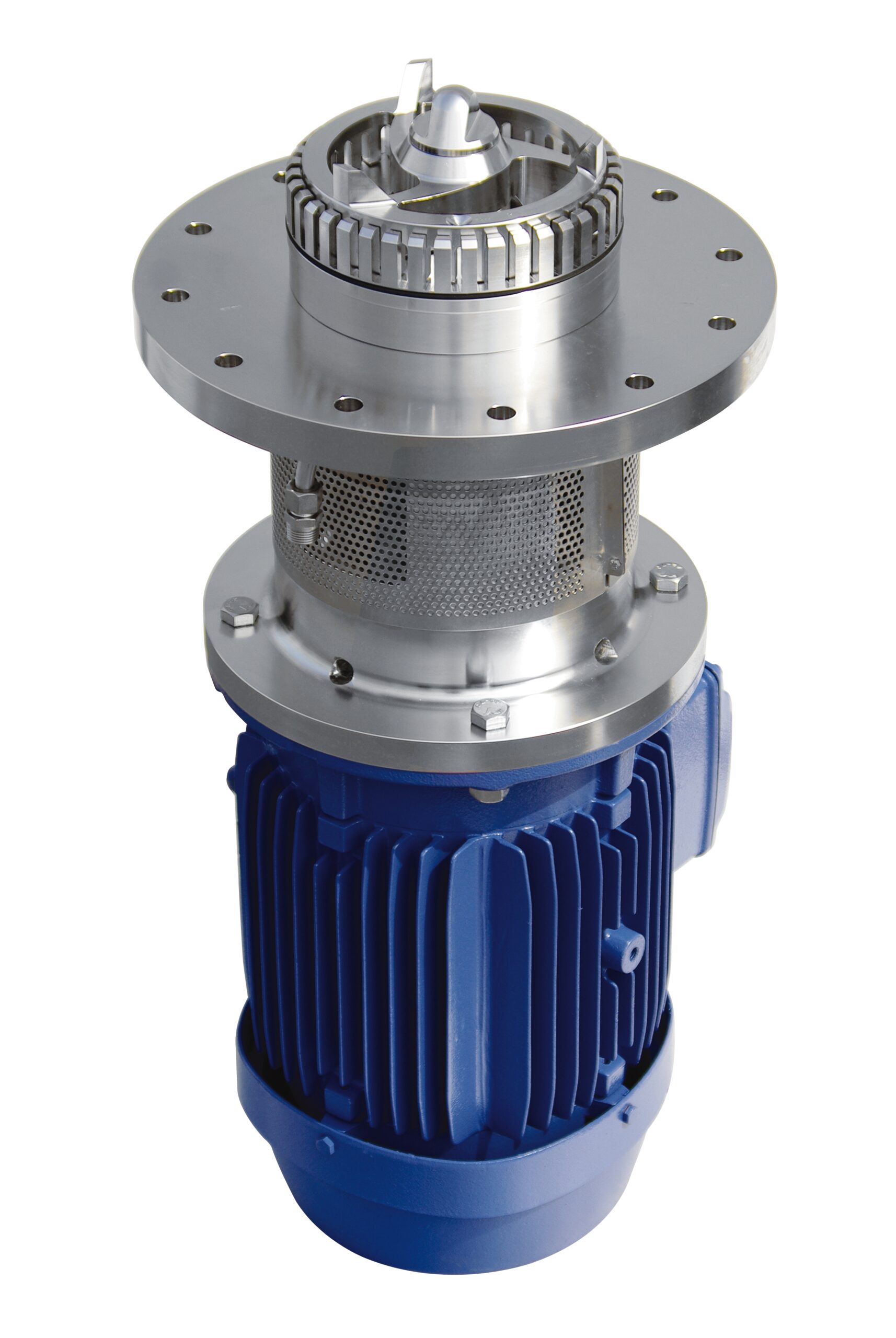

Batch dispersing machine for bottom entry into vessels
When your process requires high performance mixing or dispersion b...
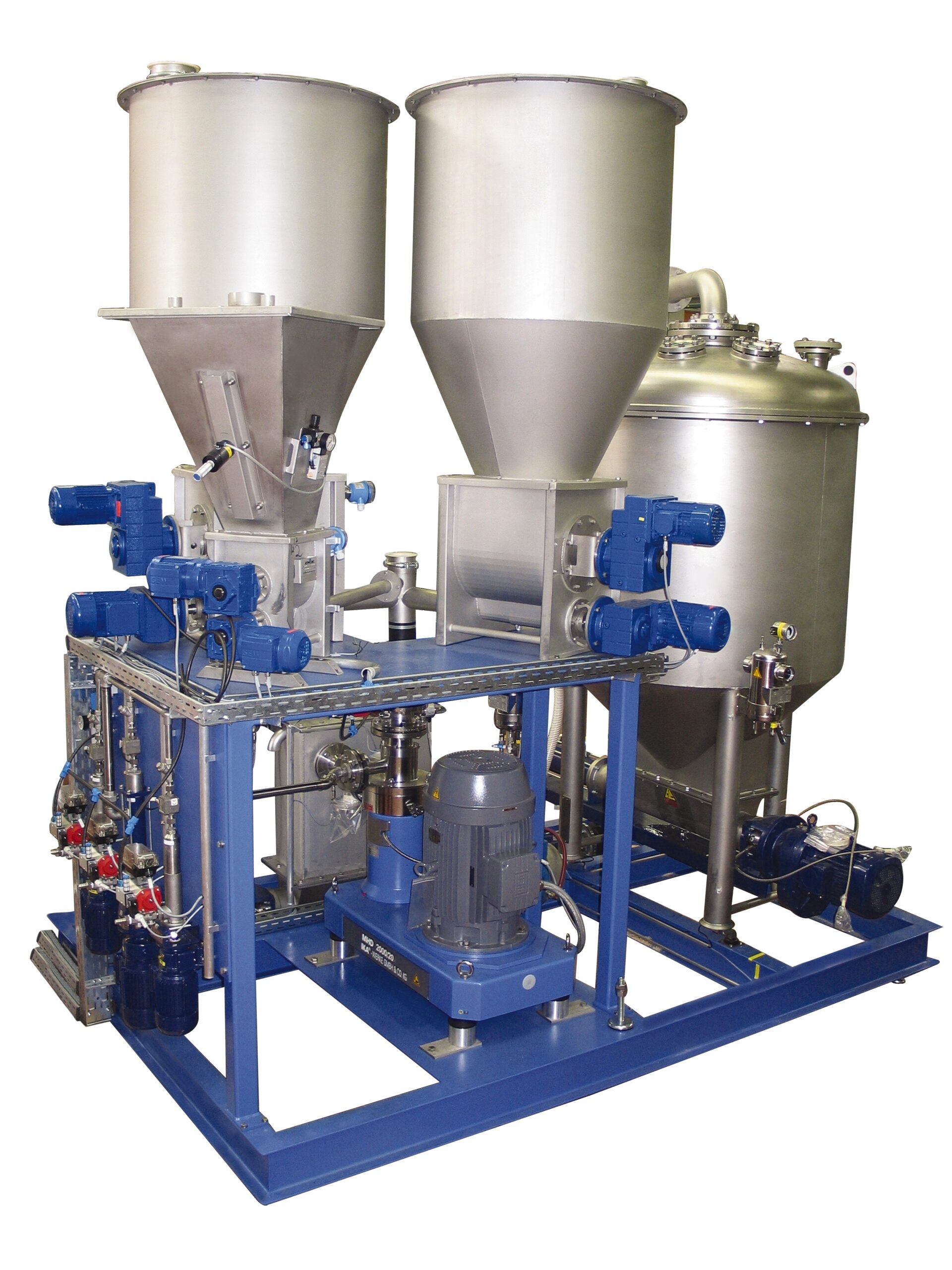

Dust-free continuous homogenizing system
Producers in a wide variety of industries benefit from equipment that can continuo...
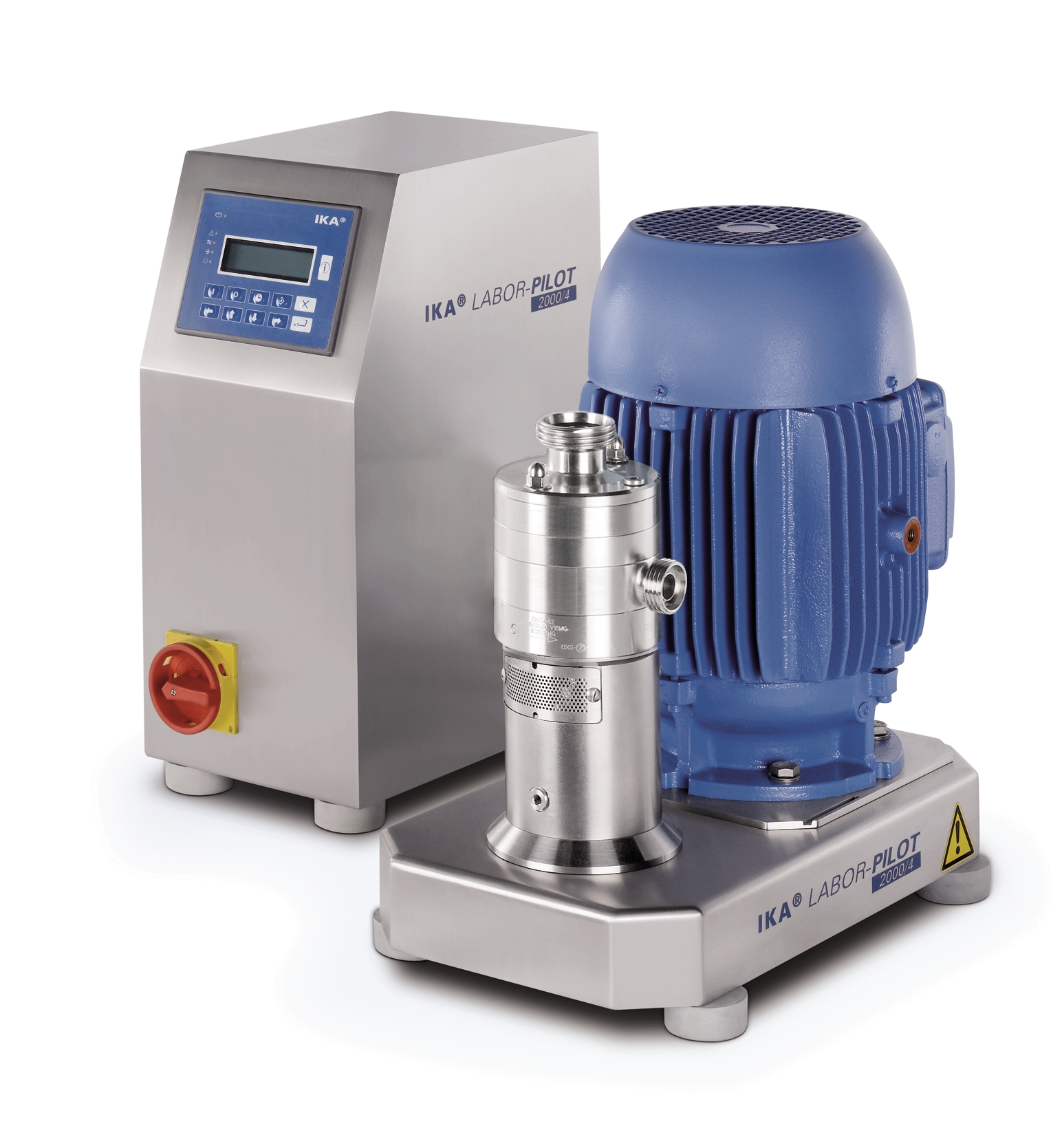

Pilot dispersing machine for testing and scale-up
Innovators in process development need laboratory equipment that helps ...
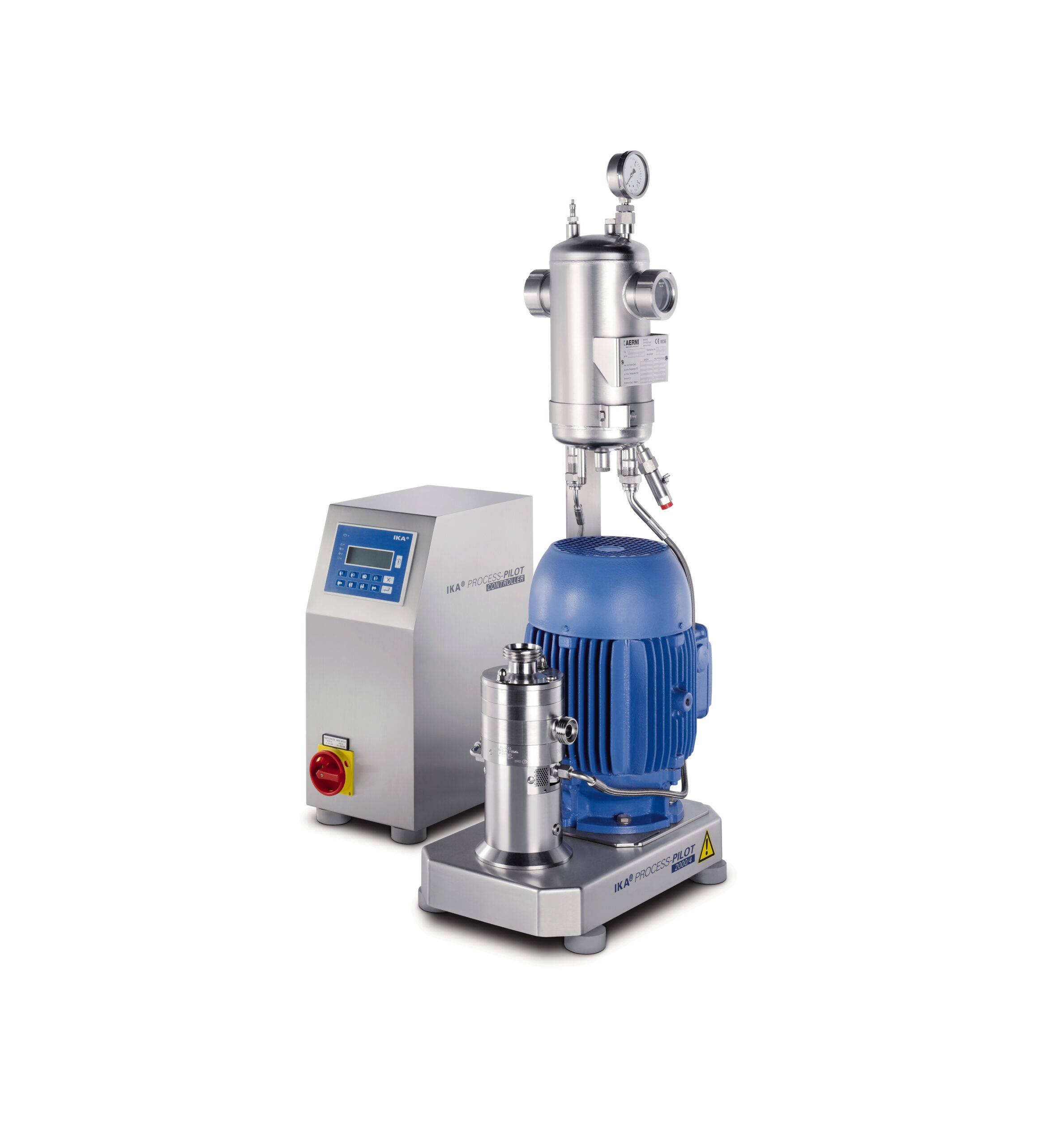

In-line laboratory dispersing machine
Innovators in a wide variety of industries need laboratory equipment on which process...
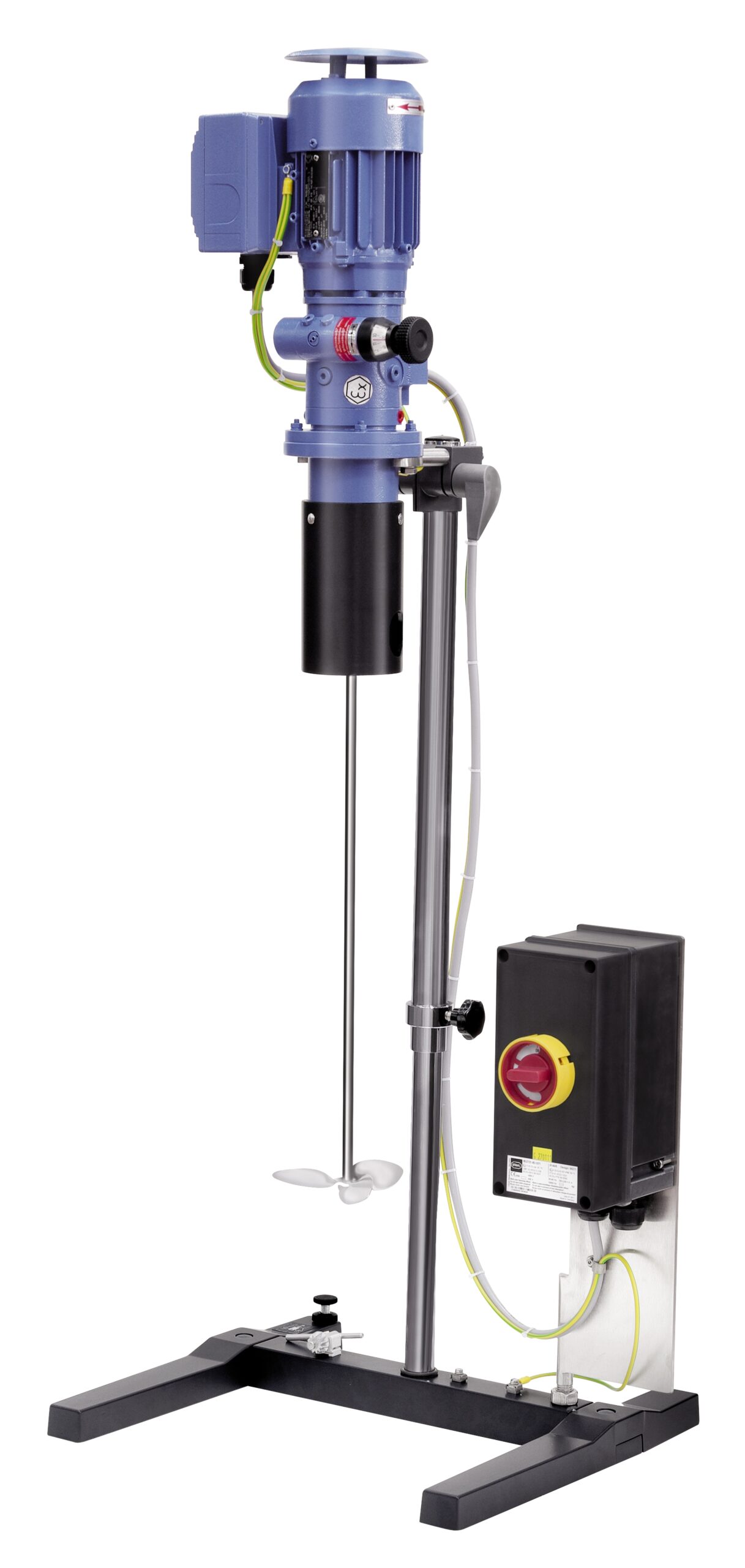

Agitator for medium viscosity media
Mixing fluids of medium viscosity for many production processes requires an agitator wi...
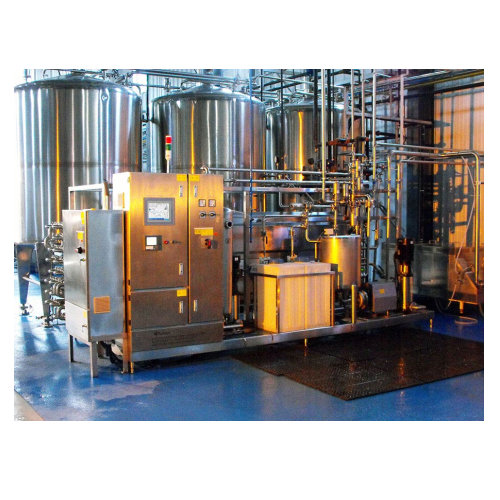

Soya milk production system
Efficiently transform soybeans into high-quality, non-beany soy milk with advanced processing te...
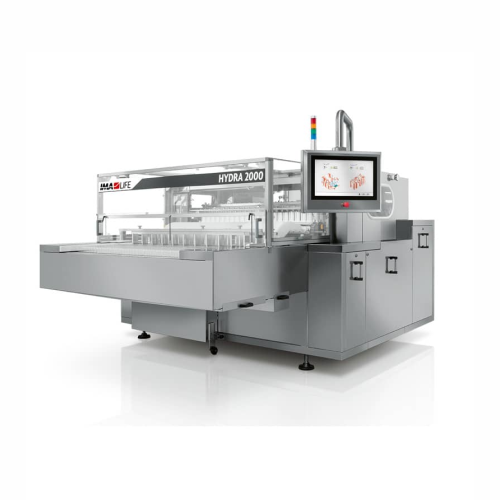

Linear vial washer for injectable drug containers
Achieve sterile conditions by efficiently removing contaminants from va...
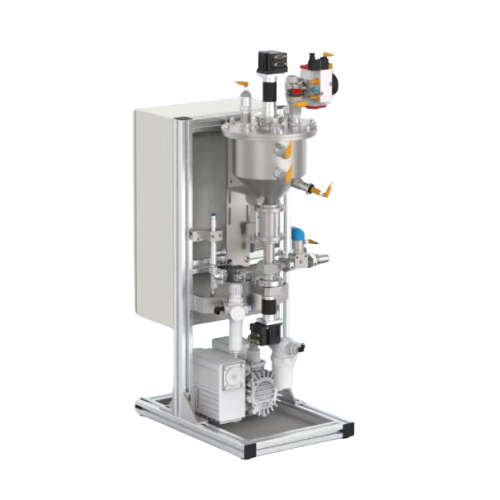

Industrial fluid and paste preparation system
Eliminate air bubbles and achieve uniform viscosity in fluids and pastes to ...

Pharmaceutical isolator system for aseptic production
Ensure aseptic conditions and operator safety with a robust isolati...
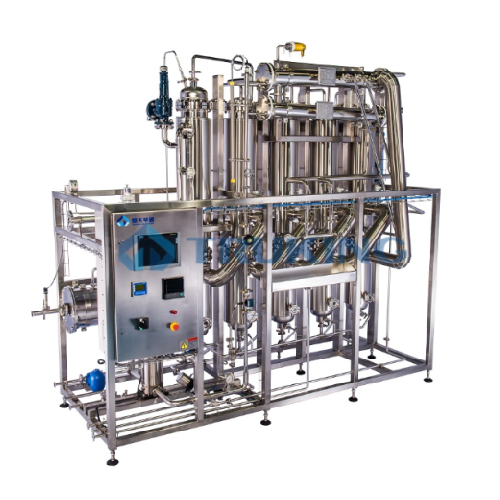

Multi-effect water distillator for pharmaceutical applications
Ensure your production line meets stringent regulatory st...
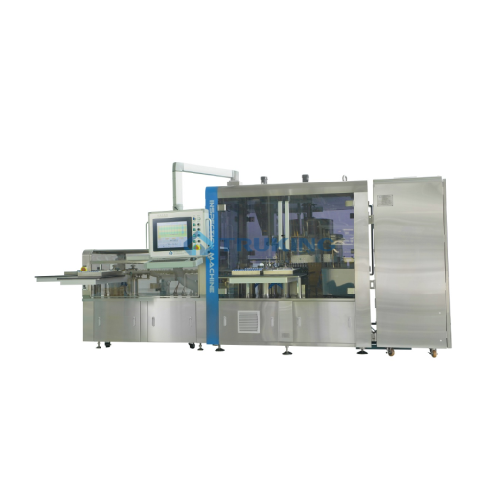

Automatic inspection and leak test for pharma containers
Ensure container integrity for injectables with high-speed inspe...

Ophthalmic filling solution for eye drops
Enhance your ophthalmic production line with a solution designed for precision f...

Semi-automatic vial crimper
In a small production line, crimping vials manually can cause fatigue to your operator due to mu...
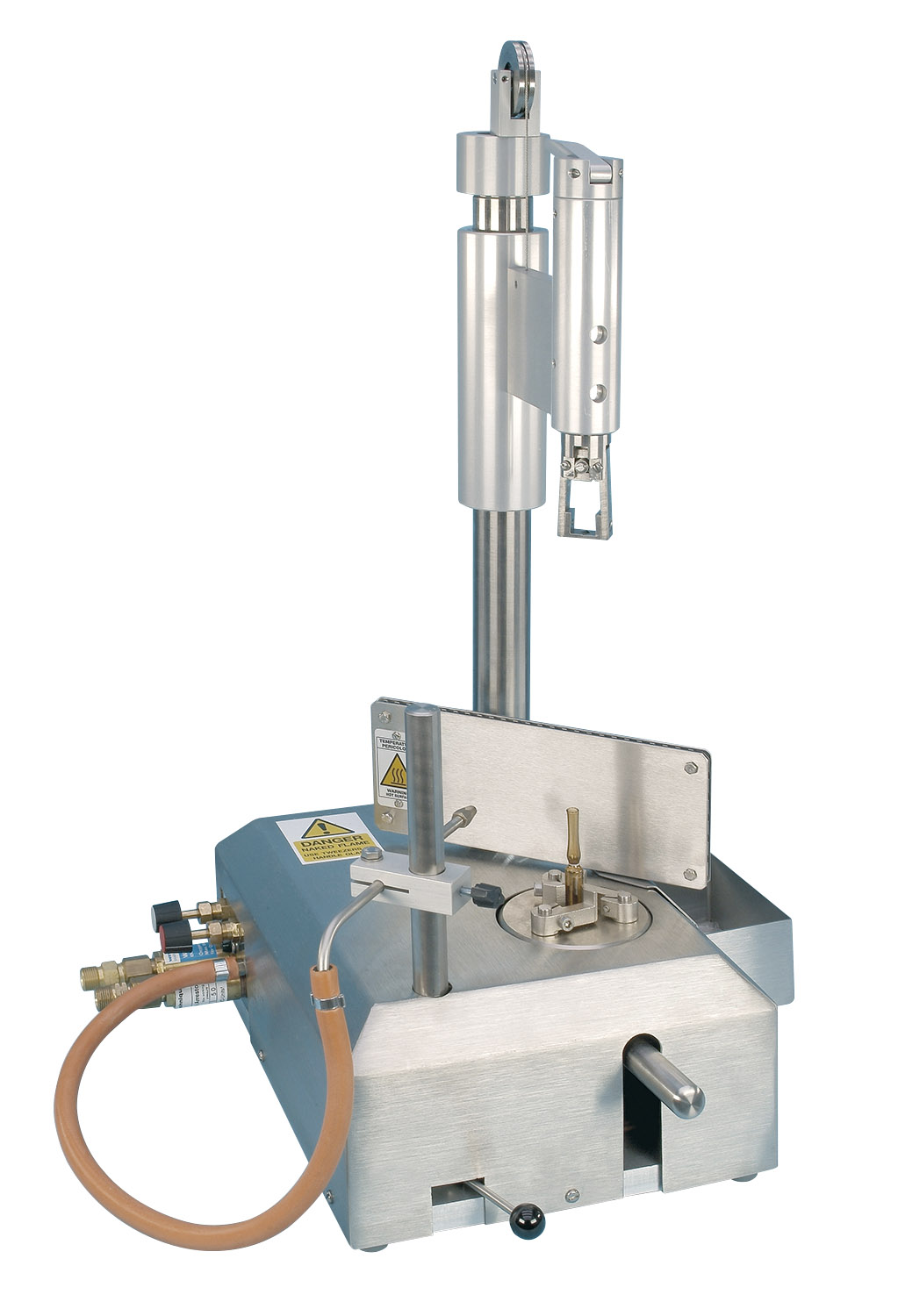

Benchtop ampoule opening and closing equipment
The procedure for opening or closing ampoules requires you to handle gas an...

Labeling machine for ampoules
It’s essential for pharmaceutical companies to provide the highest quality ampoules to custome...
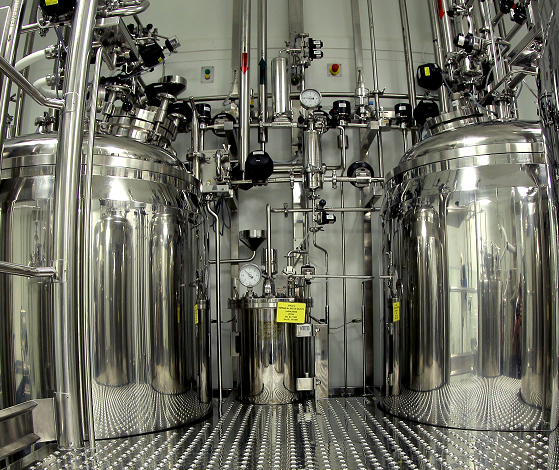

Syrup preparation tank
Syrups and suspensions are typically produced under the same high-quality conditions as used for steri...

Loading basket for GMP washer
To ensure perfect cleaning of contact parts they must be placed in the GMP washer in such a wa...
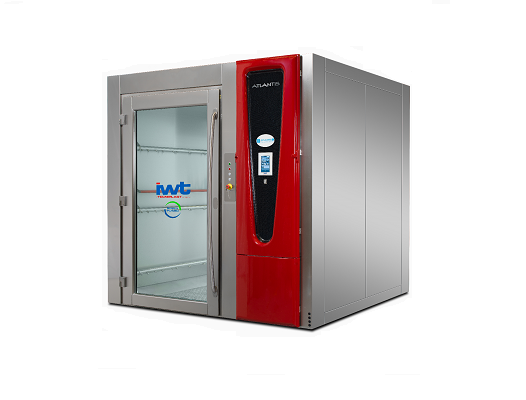

Bulk chamber washer
The production of cosmetics, nutraceuticals or unregulated pharmaceuticals often requires the cleaning an...
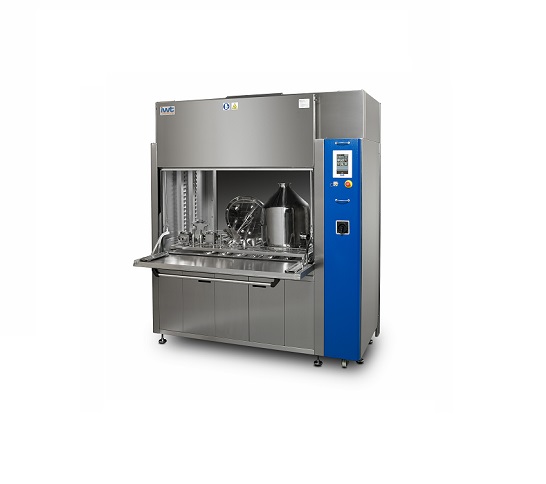

Entry-level chamber washer
When cleaning smaller products contacting filling or compressing components used in the productio...
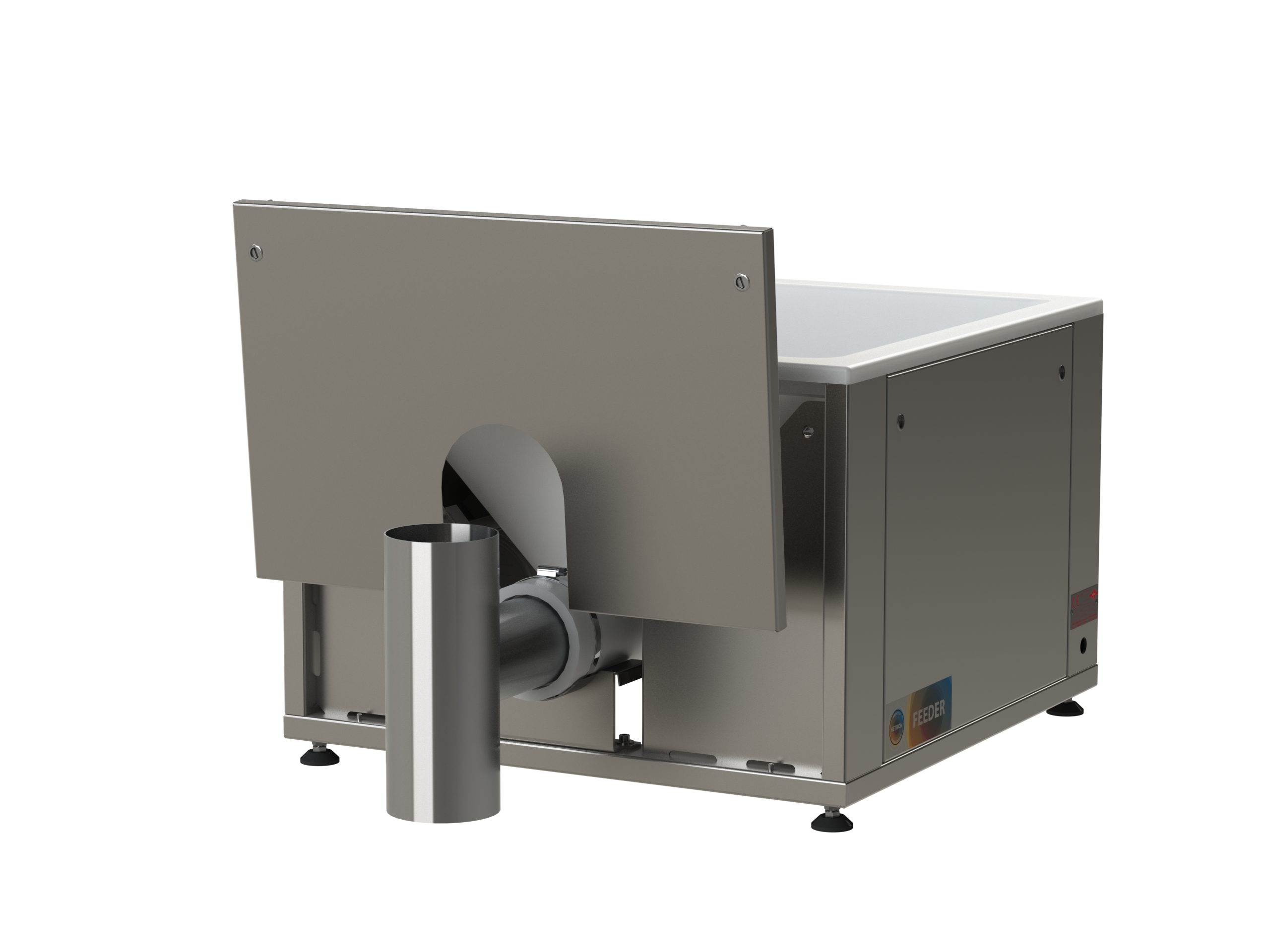

Feeder with flexible wall hopper
The varying properties of dry powder products mean that specialized feeders are required fo...
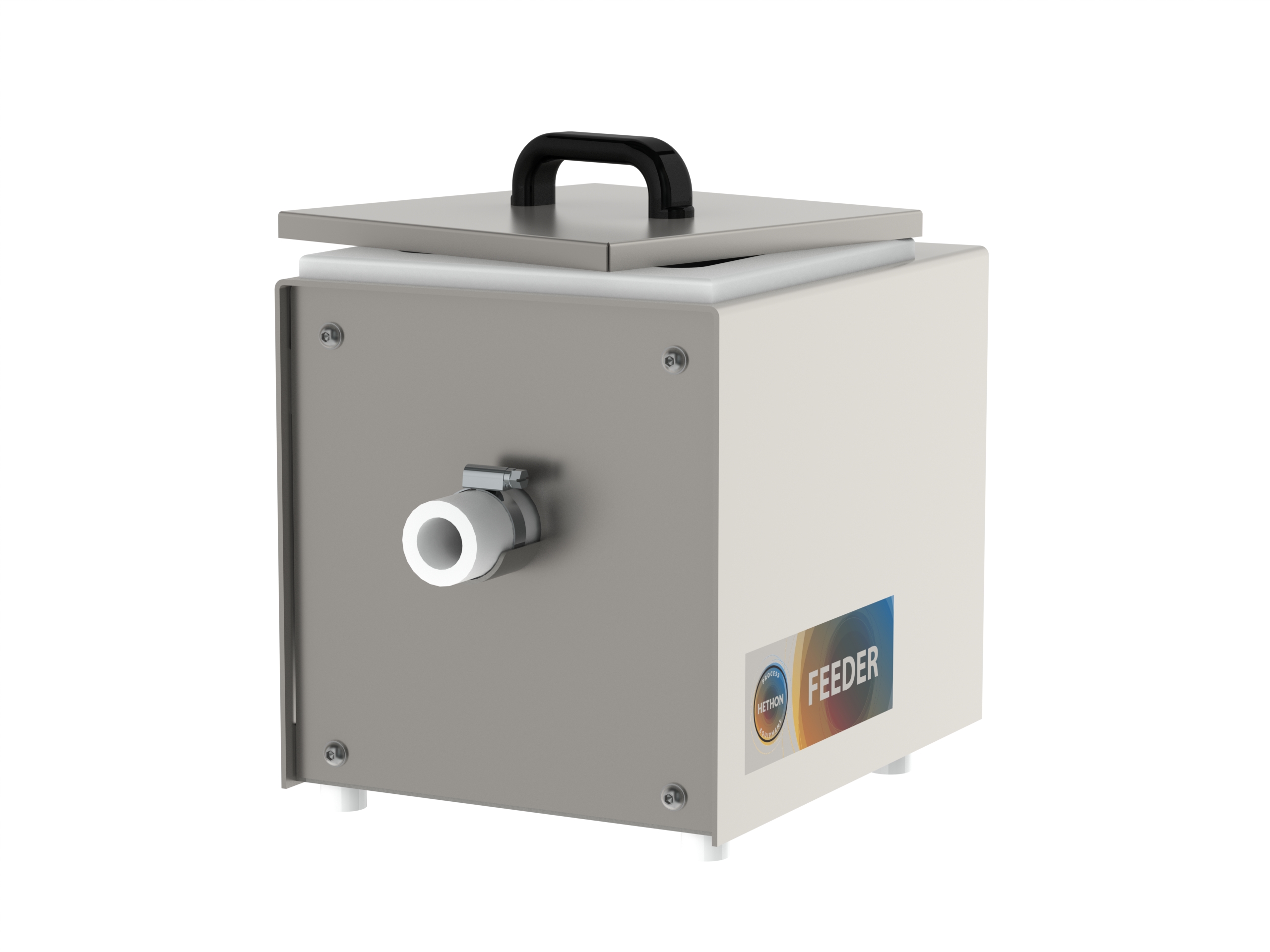

Small feeder with flexible wall hopper
In many laboratory applications and production processes, smaller quantities of powd...
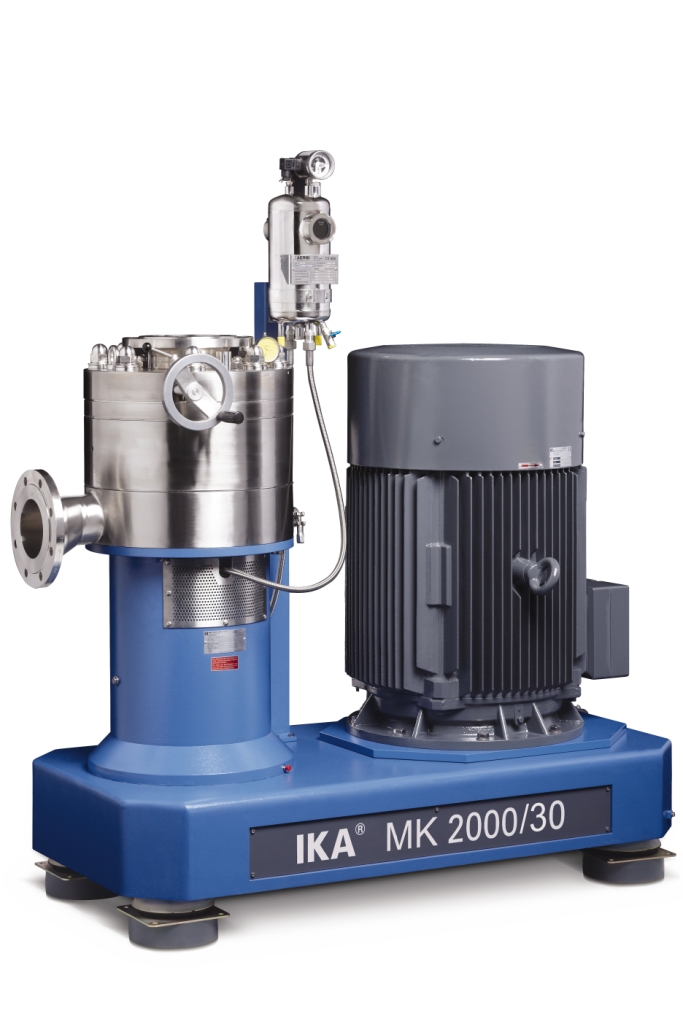

Colloid mill
For creating extremely fine emulsions and high quality dispersions a high pressure homogenizer is often chosen. ...
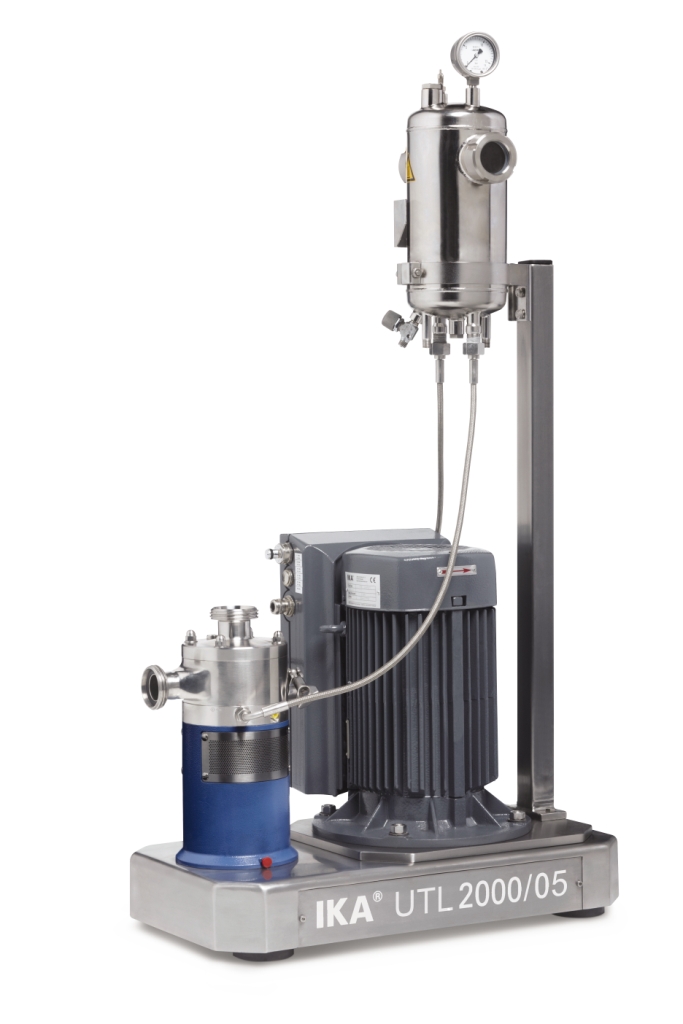

Dispersing machine for emulsions and suspensions
Equipment operating under the rotor/stator principal is often employed wh...
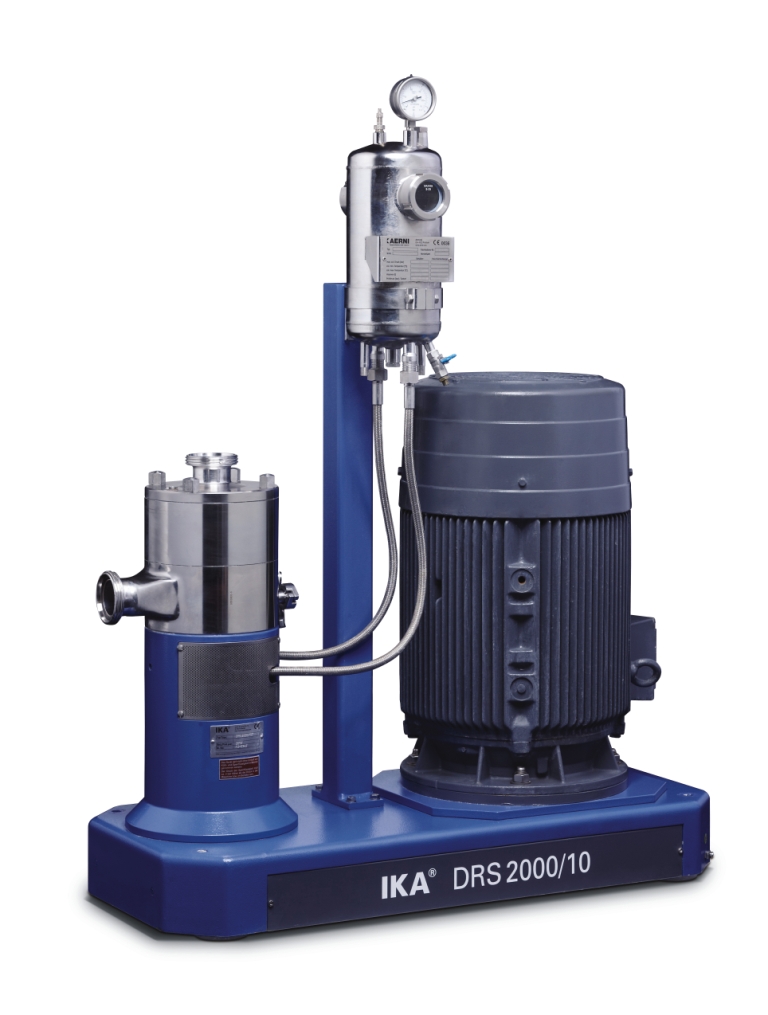

Ultra-fine dispersing machine for emulsions and suspensions
Producing the finest micro-emulsions and suspensions require...
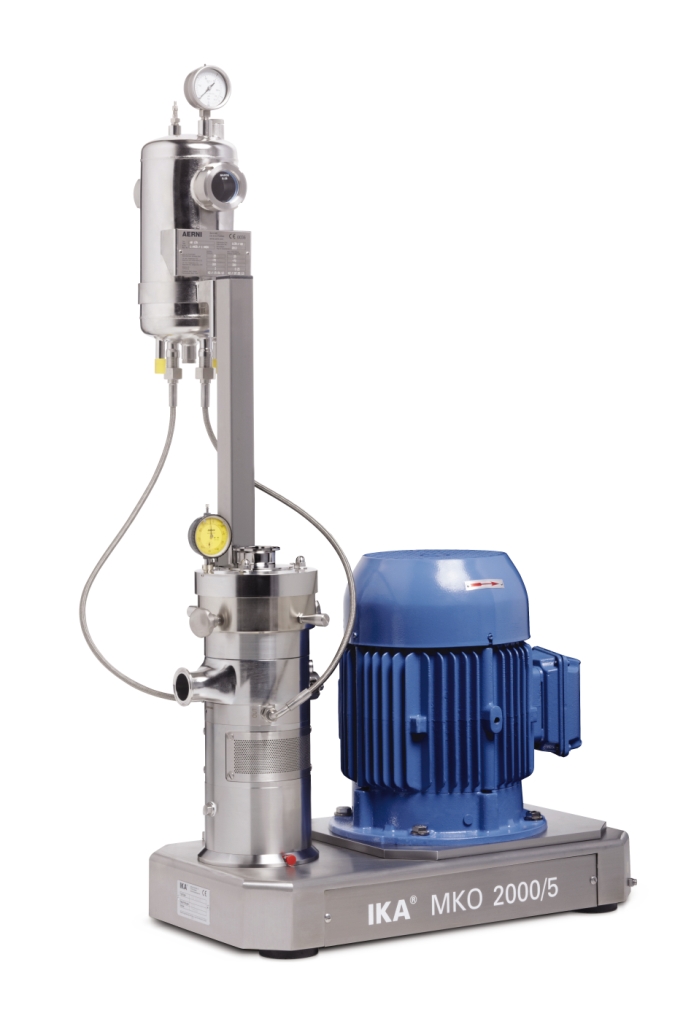

Cone mill machine
When your raw materials include agglomorated suspensions of grainy or crystalline solids and your process n...
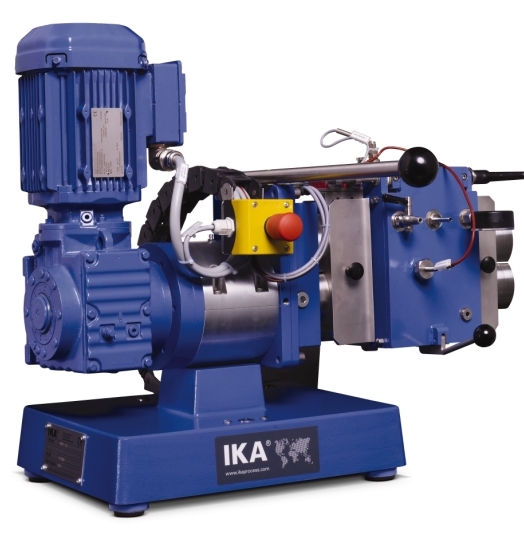

Horizontal kneader
For high viscosity products, better results and reduced process times can be achieved with kneading type r...
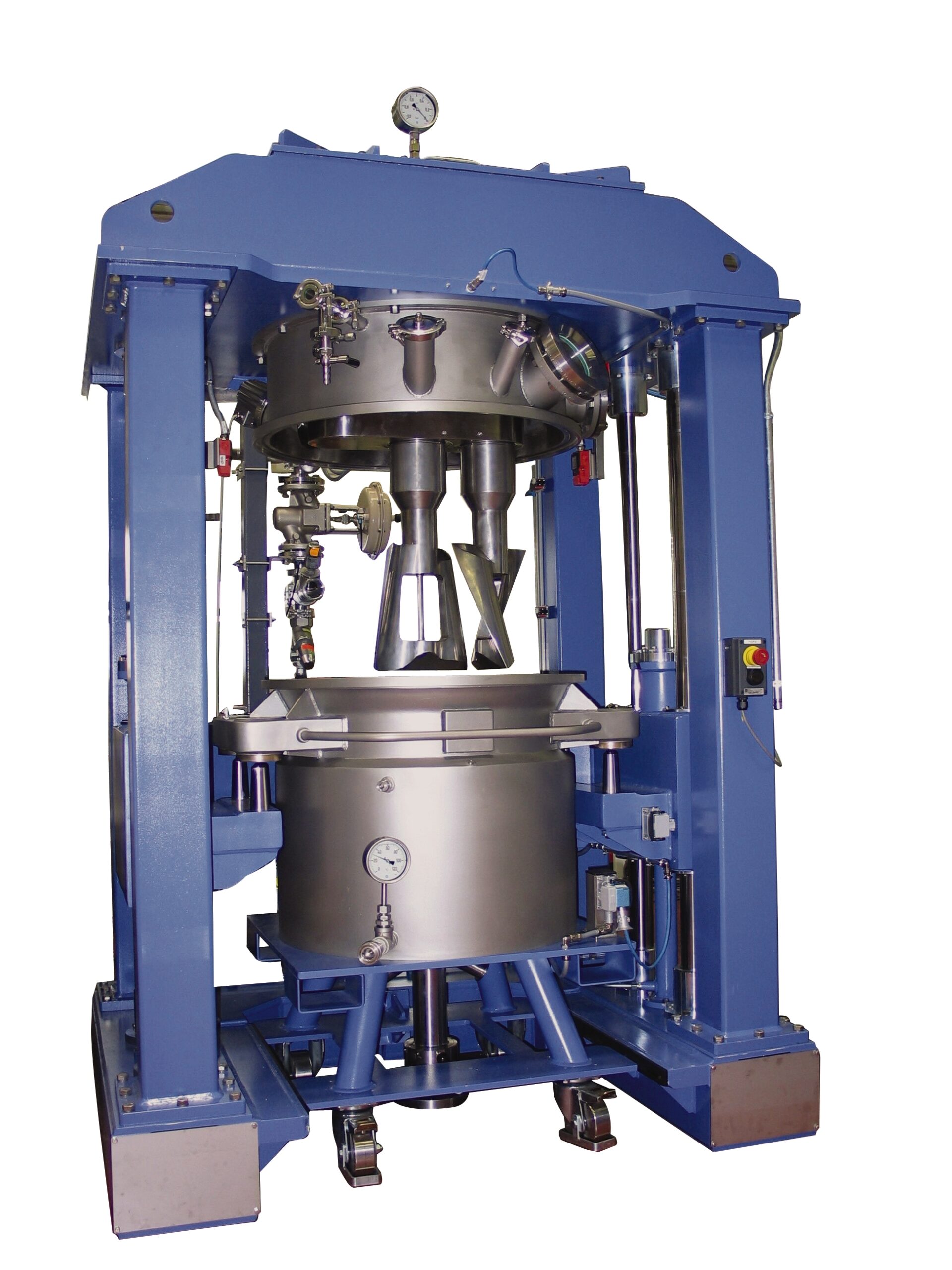

Vertical kneader
Production of highly viscous products with high solid content often benefits from kneading processes rather t...
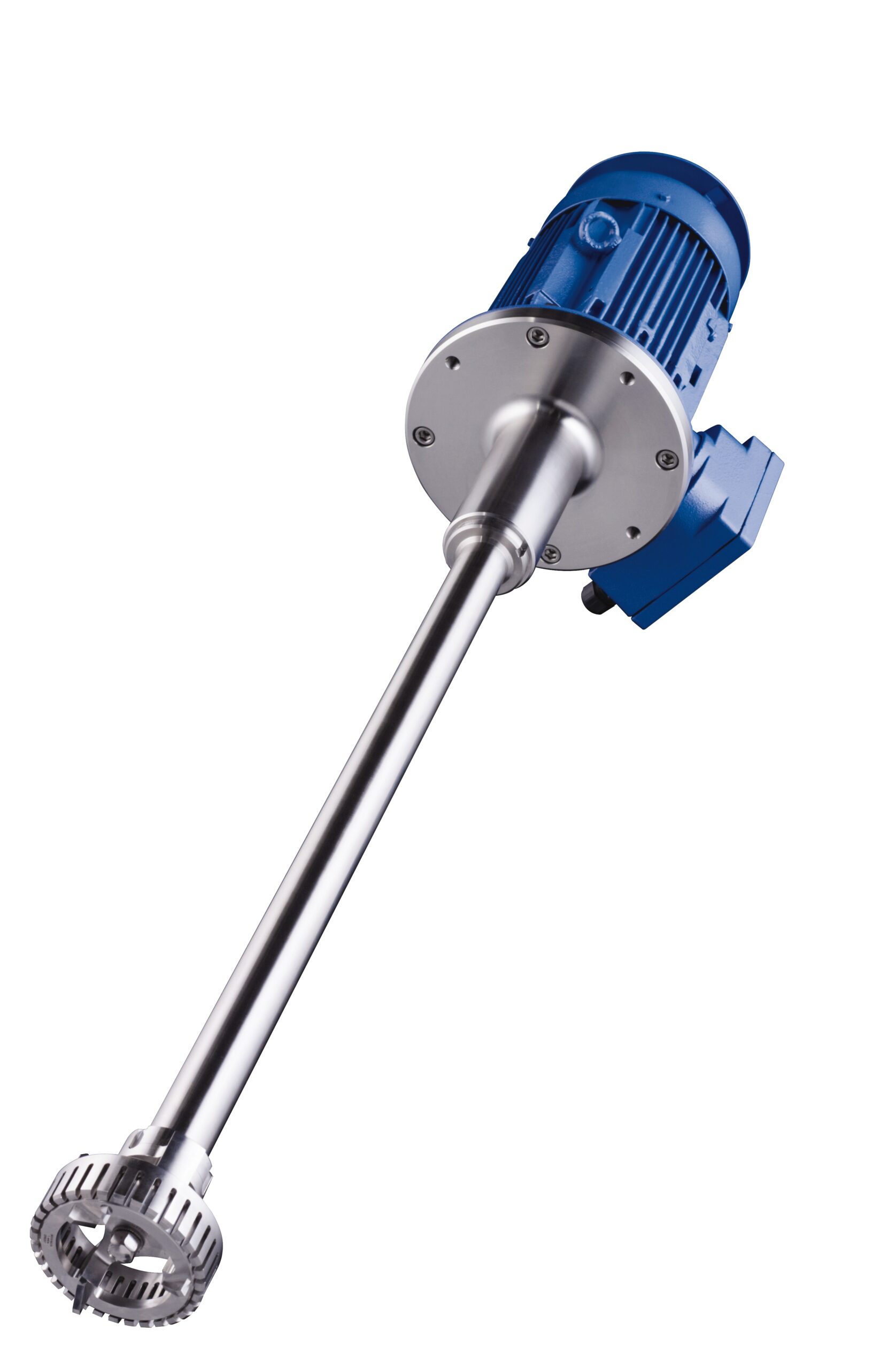

Batch dispersing machine
Equipment operating under the rotor/stator principal is often employed when more traditional methods...
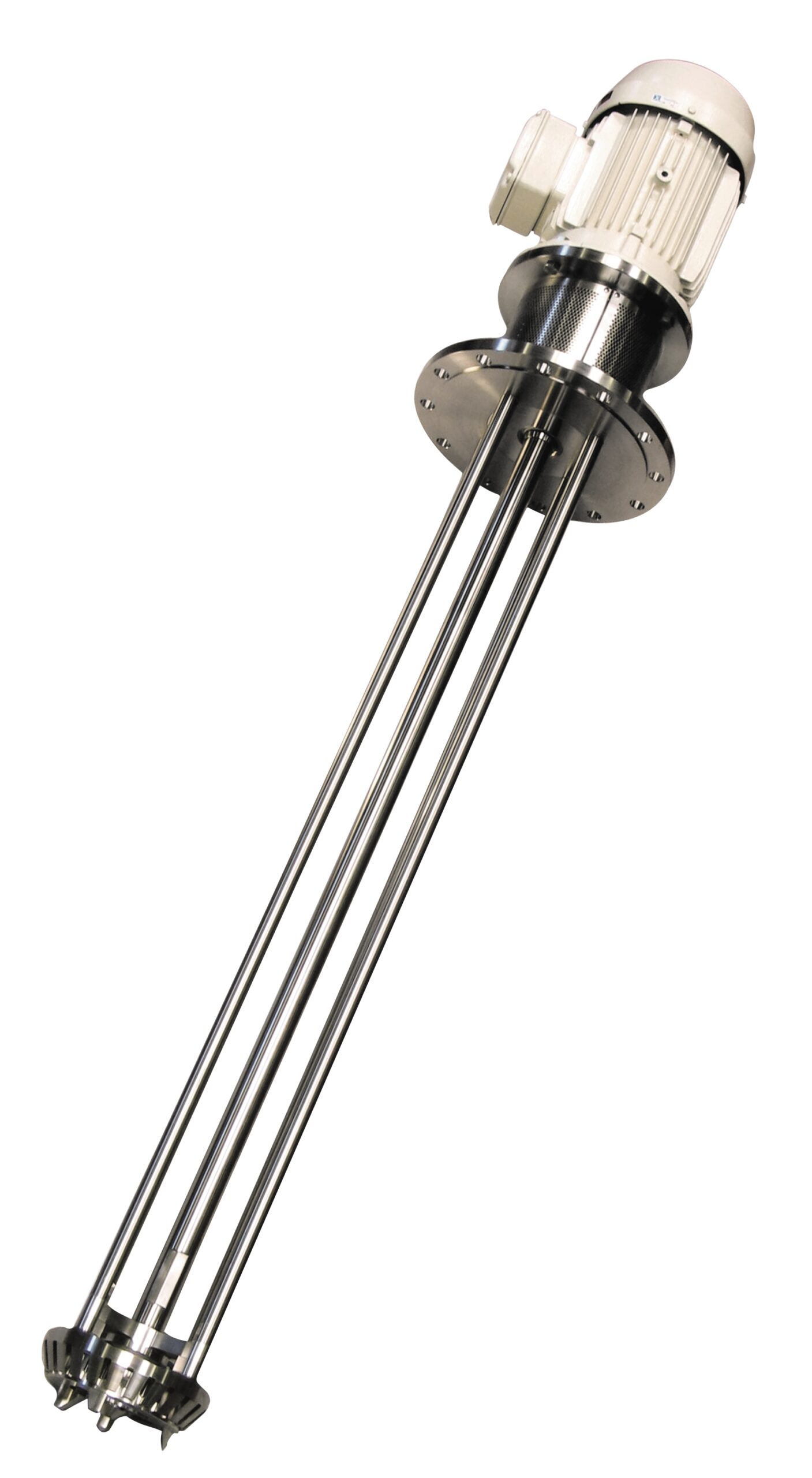

Batch dispersing machine for abrasive products
For mixing and dispersing tasks that cannot be completed by conventional st...
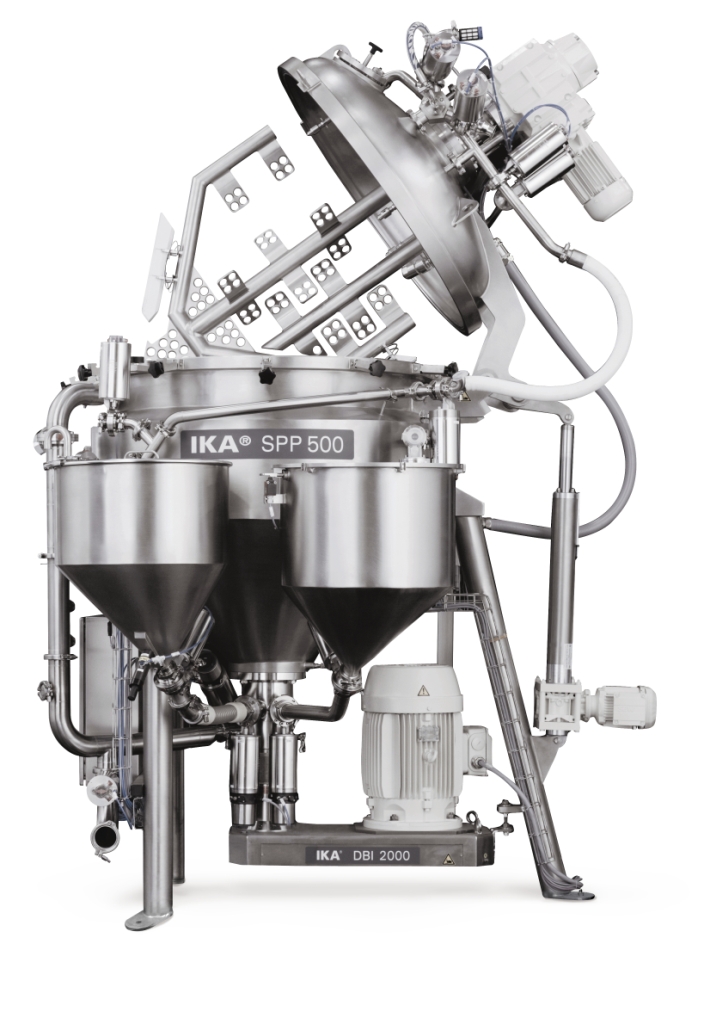

Cost-effective homogenizing and emulsifying system
Manufacturers of cosmetic products need mixing equipment that is capab...
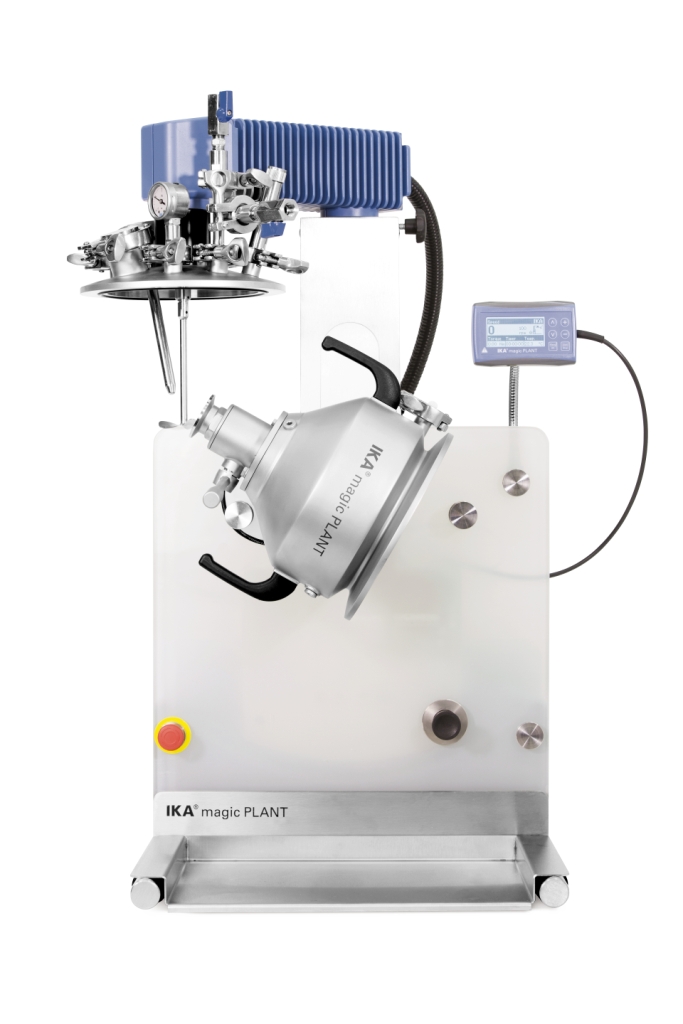

Laboratory dispersing machine for low-viscous masses
Laboratory mixers have not always been easy to work with. Getting a...
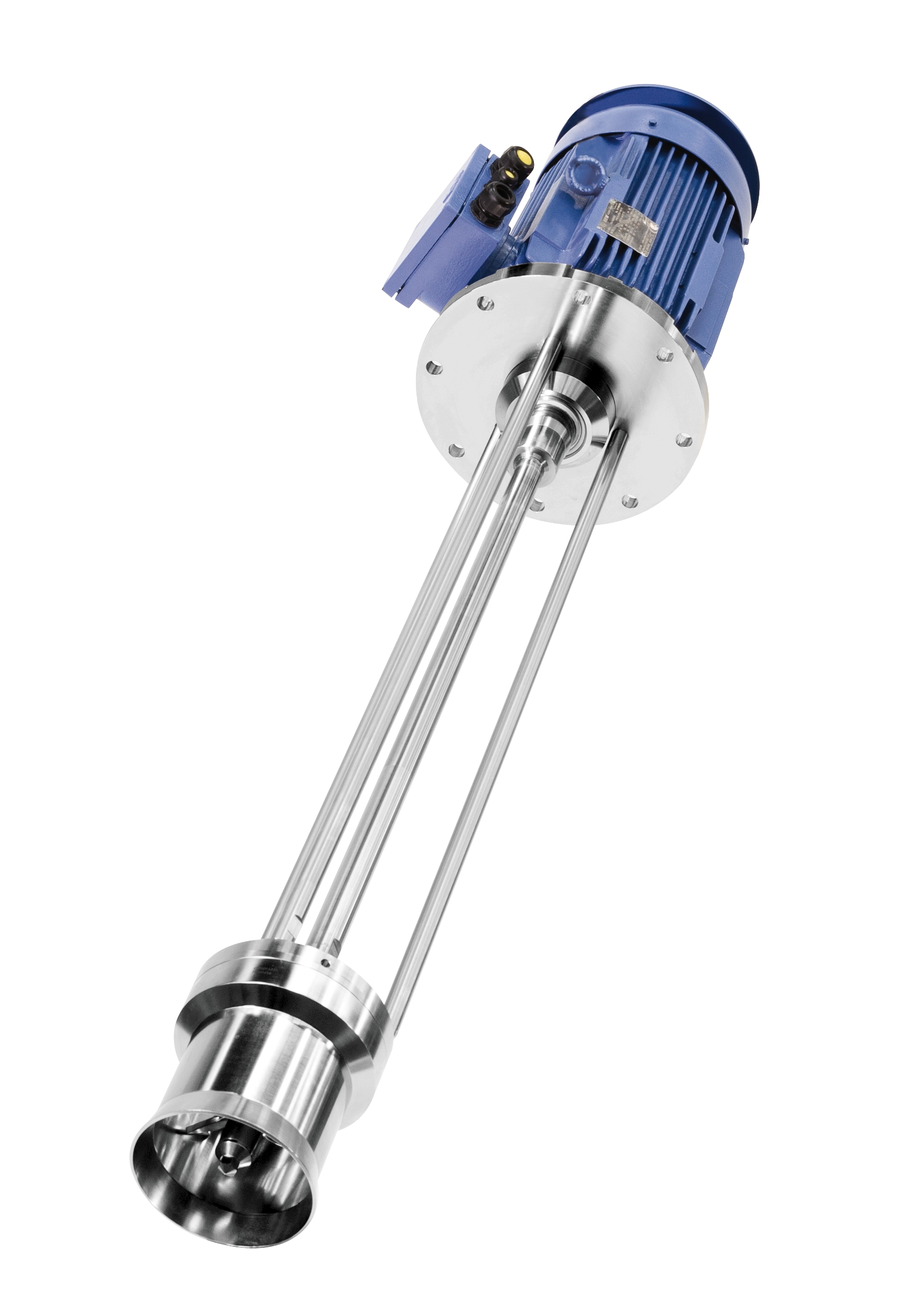

Jet flow agitator for high-viscosity media
Processes including homogenization, dispersing, suspension, emulsification and ...
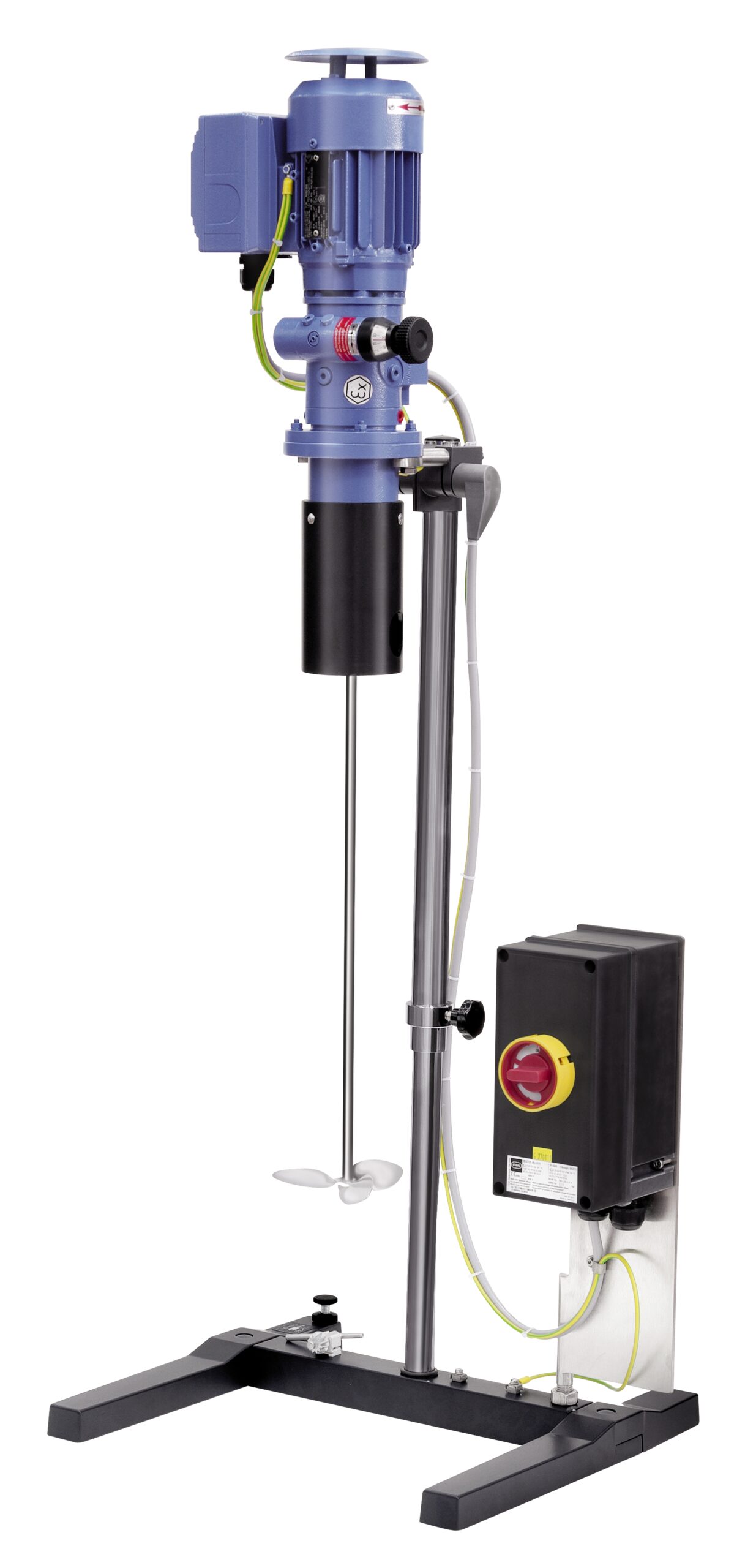

Agitator for low viscosity media
Reliably agitating fluids in open or pressure-less vessels in a laboratory or small scale p...
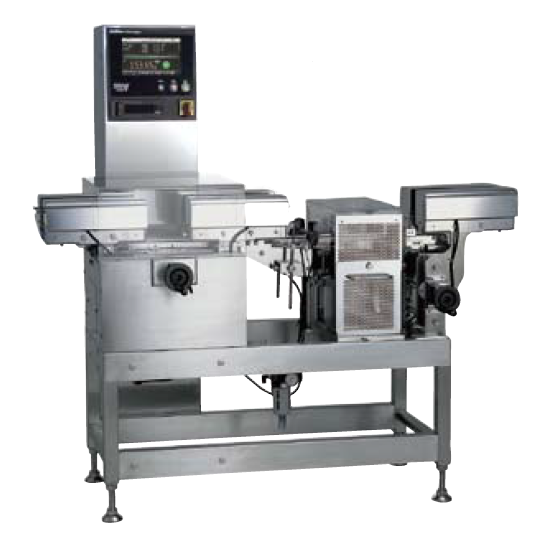

Small bottle checkweigher
Any small-diameter bottle, containing prescription medication or cosmetic applications, can be pro...
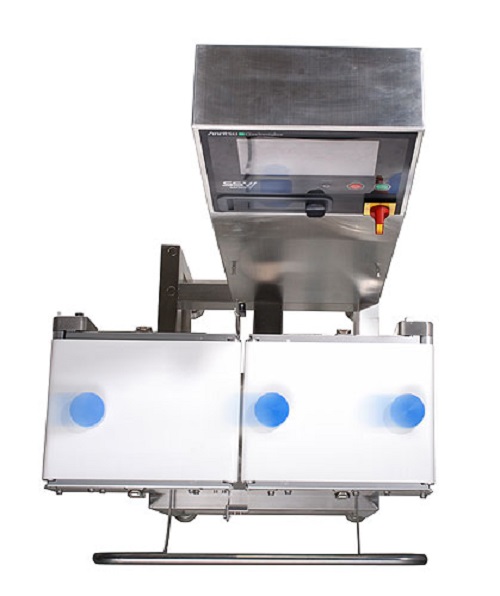

Versatile checkweigher
This Versatile checkweigher is equipped with a highly versatile strain gauge load cell. It is also sui...