Let's make whipped cream
Find innovative production technology for making whipped cream and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Neige de lait in French or neve di latte in Italian, as referred to in very old texts and both meaning milk snow, has been used in recipes since the 15th century. Withstanding the test of time, whipped cream is still one of the most beloved dessert toppings. What starts with milk ends as a silky delicacy with the help of whipped cream equipment and specified manufacturing processes.
Stories about whipped cream
Tell us about your production challenge
Raw materials for the large-scale production of whipped cream
Large-scale manufacturing of whipped scream starts with obtaining the main raw materials – whole milk. In order to inactivate the heat-resistant lipase in the milk, which can lead to an unstable fat emulsion, the milk is pasteurized at 72°C for 15 seconds. Once the cream is separated from the milk, its fat content should be at least 35% to have the ability to be successfully whipped. In order to obtain crystalline fat, the cream is aged for 24 hours at 4°C.
The heavy cream is then ready for further processing, mixed with sugar, and homogenized in a high-shear homogenizer or high-pressure homogenizer to form a uniform, stable emulsion of fat and sugar crystals and desired viscosity. Since homogenization can negatively impact the whipping properties of heavy cream, it is recommended to add an emulsifier. The cream is pasteurized again and cooled down to 5°C, which is crucial for its high-quality whipping properties.
Whipped cream equipment and the final steps in the production

Once the heavy cream preparations are done, it is time to transform it into whipped cream through the process of whipping. Although one way to manufacture whipped cream is by aeration in a continuous in-line rotor-stator whipping device using a neutral gas, such as nitrogen, the more traditional method is mechanical whipping in large industrial whipping machines or high-speed mixers. The process of mechanical whipping introduces air bubbles while, simultaneously, proteins are adsorbed onto their surfaces.
Fat globules accumulate on its surface , forming a network of fat-globule aggregates. In order for the whipped cream to maintain its form and structure, it has to undergo a process of stabilization through the adsorption of an appropriate surface active material such as proteins and polar lipids. If this step is not done correctly, the whipped cream structure will gradually shrink.

Consistency challenges in whipped cream production
One of the challenges manufacturers face is the ultra-pasteurization of whipping cream, the process in which cream is rapidly heated to a temperature that kills virtually all organisms. It has the advantage of increasing product shelf life but affects the product quality. Another major challenge in whipped cream production is maintaining volume and texture during manufacturing.
An important role in maintaining quality and consistency is played by controlling mixing time, ingredient ratio, and proper incorporation of air. Furthermore, the product should not be exposed to temperature, and it is important to keep the temperature range between 7.5 and 12.5°C during the whole process
Plant-based whipping cream alternatives – Meet Aquafaba
Plant-based alternatives to whipping cream are becoming a more common sight on supermarket shelves. Unlike dairy whipping cream, commercial plant-based whipped cream is based on vegetable fats, in addition to salts, veggie protein, stabilizers, and water. To transform this list of ingredients into stable and fluffy whipped cream, the primary ingredients are actually emulsifiers, which are used to hold on to the water and fat they come across and create the structure of the whipping cream we all know.
Furthermore, whipped cream manufacturers try to make their products healthier by avoiding carrageenan or ingredients such as gums, artificial ingredients, or coloring agents.
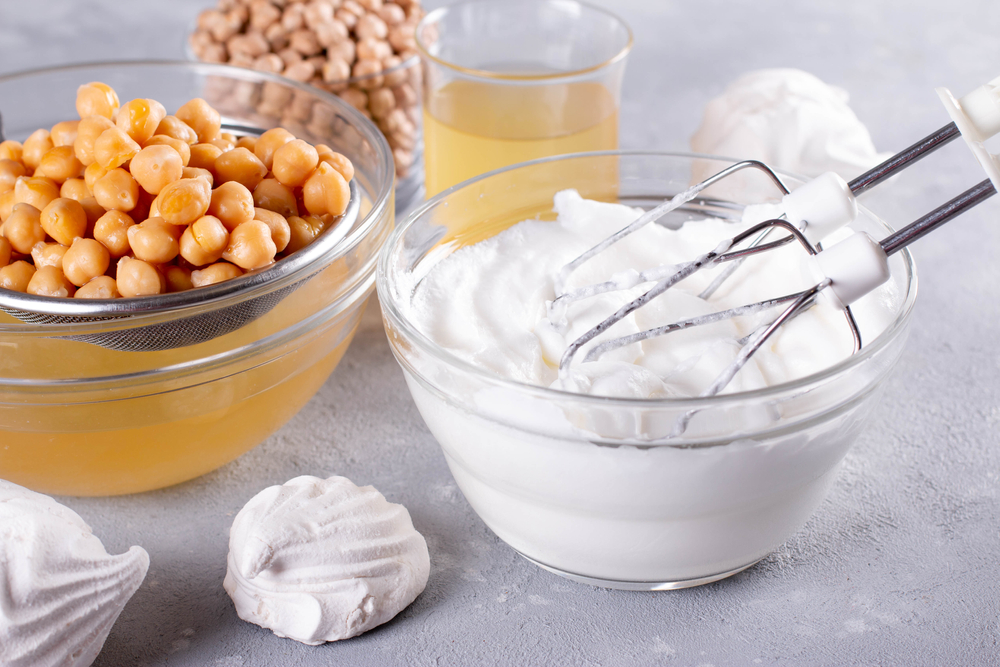

One popular plant-based alternative to whipped cream is Aquafaba. But what is it?
Believe it or not, Acquafaba is the liquid from cooked or canned chickpeas. Surprisingly, it is just water – a component often discarded without much consideration when using beans or chickpeas in recipes. Aquafaba, however, possesses a light and airy texture reminiscent of traditional whipped cream, and it offers a fat-free, dairy-free, and gluten-free option, making it remarkably versatile and delectable, particularly for individuals adhering to vegan or dairy-free diets.
Processing steps involved in whipped cream making
Which whipped cream technology do you need?

Uht sterilization for drinkable milk
Ensure long shelf-life and food safety without compromising the natural qualities of y...

Pasteurizer for extended shelf-life (esl) milk
Extend the shelf life of milk while maintaining its taste and nutritional i...

Wine clarification system
Enhance your wine production by effectively removing unwanted solids and reducing oxidation risk, ...

Milk collection system for bulk tankers
Optimize milk transfer and storage with a reliable system that reduces discharge ti...

Milk skimming separators for dairy applications
Enhance dairy production with high-efficiency skimming separators that opt...

Milk standardization system
Achieve precise milk and cream fat standardization with this advanced inline system, optimizing ...

Pasteurizer for fresh milk
Ensure your dairy and beverage lines achieve optimal product safety and quality by leveraging adv...

Blending and mixing unit for dairy and beverages
Achieve precise recipe control and high-quality results by seamlessly int...

Cheese forming units for hard and semi-hard cheeses
Optimize your cheese production process with advanced moulding and pr...
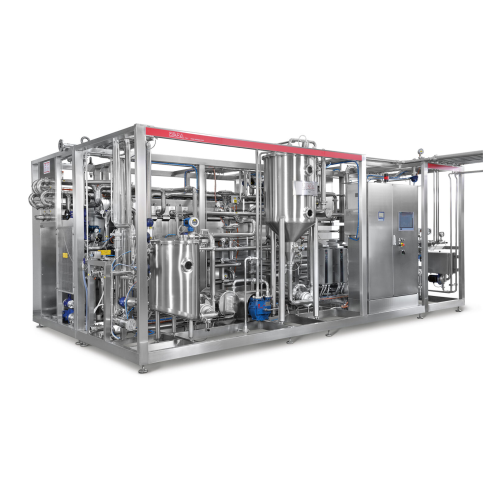

Milk evaporator for dairy industry
Optimize your liquid food production with precise control over evaporation processes, en...
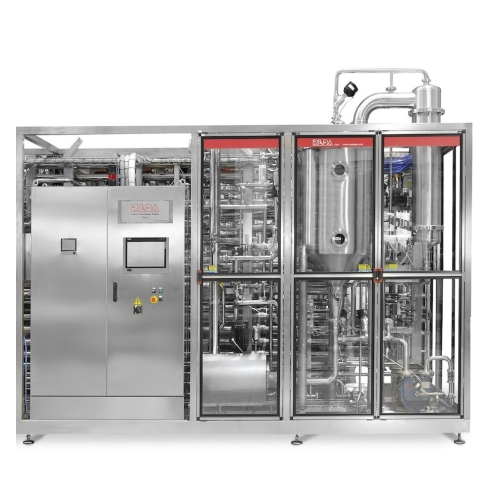

Vacuum deaeration with aroma recovery for juices
Eliminate oxygen from liquid foods to prevent oxidation while retaining v...
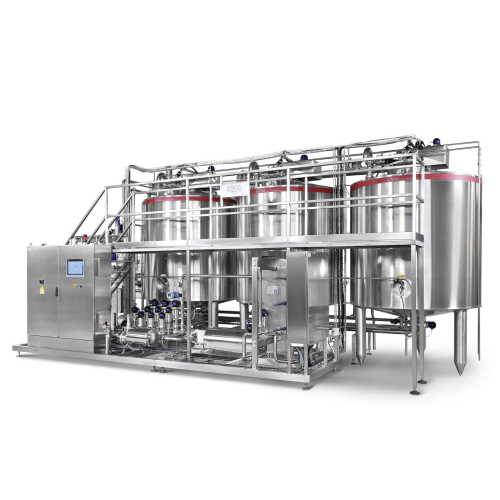

Fermentation tank for yoghurt and fermented dairy products
Optimize your dairy and plant-based drink production with eff...
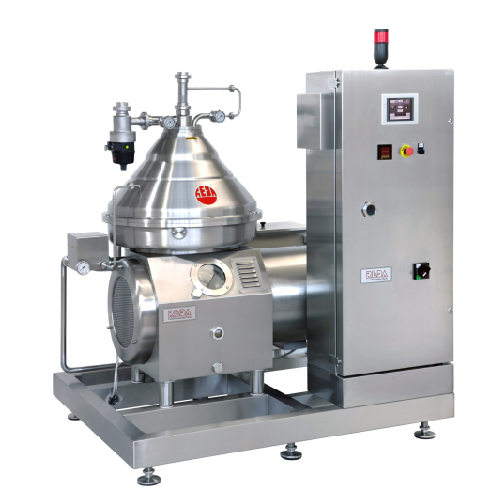

Bacteria removal separator for dairy products
Ensure top-quality dairy and plant-based products with reliable bacteria rem...

Juice clarification system
Ensure consistent beverage clarity with advanced separation technologies, enhancing production ef...

Curd making equipment for cheese production
Optimize your cheese production with versatile curd making equipment, designed...

Aseptic tank for sterile liquid food storage
Ensure sterility and maximize shelf life for liquid foods by utilizing an ase...

Uht sterilization for milk
Enhance your production line with advanced UHT sterilization, ensuring extended shelf-life and un...
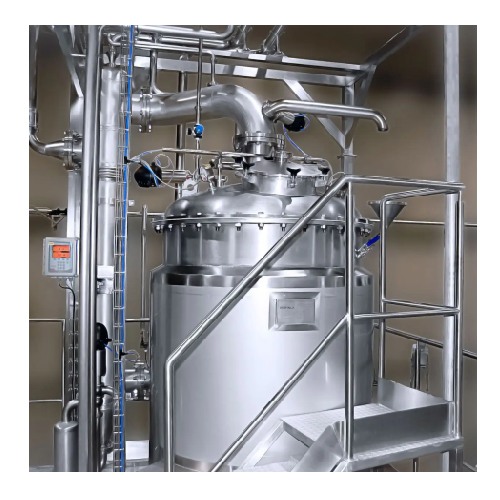

Inline processing system for food and beverage production
Optimize your production line with a versatile inline processi...
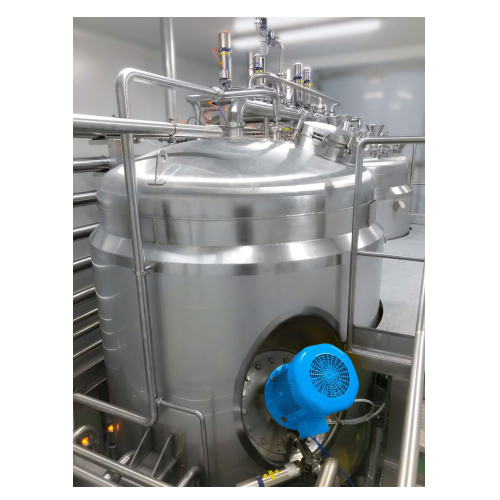

Industrial cooling vessel for ready meal components
Enhance your production with precise cooling and gentle handling of t...
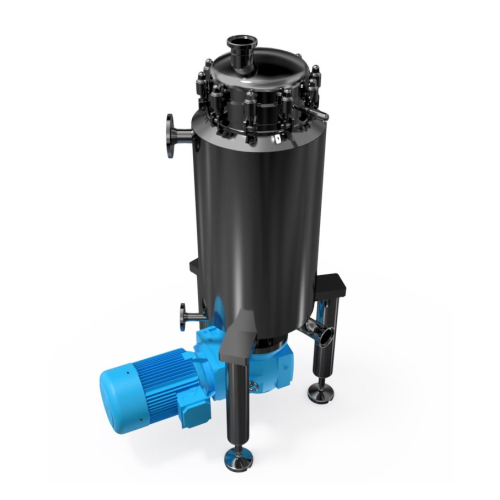

Scraped surface heat exchanger for food processing
Efficiently handle temperature-sensitive food products with a compact ...
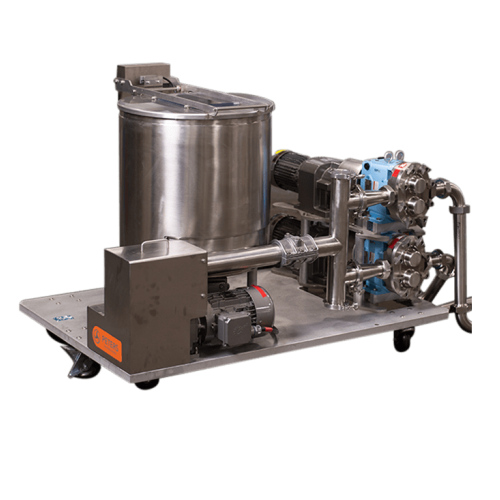

Cream delivery solution for sandwiching lines
Achieve precise cream delivery with enhanced control and efficiency, optimiz...

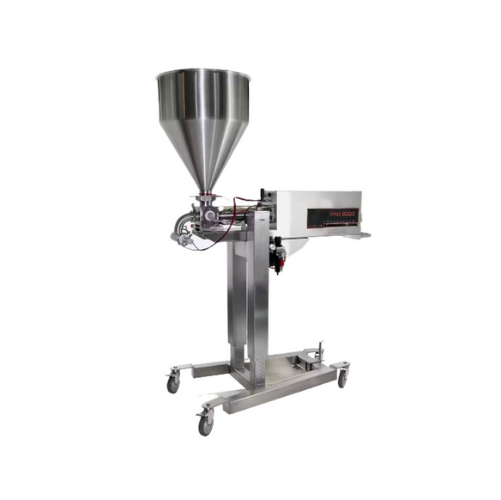
Crystallizer for small-scale aeration and crystallization processes
Streamline your production with a versatile crystal...

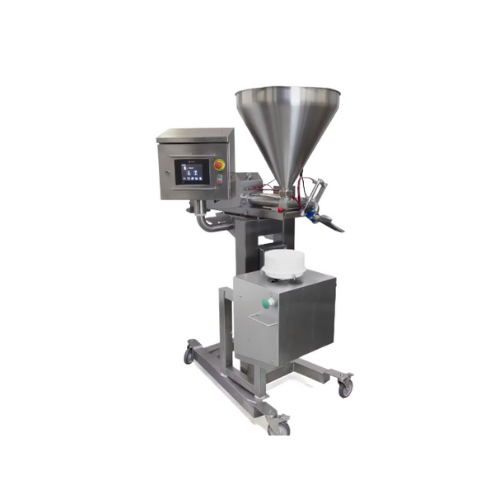
Professional dosing system for creams and sauces
Streamline your production with precise dosing of creams and sauces, tail...

Fermenting tanks for beer production
Optimize your beverage production with advanced fermenting tanks designed to enhance t...

Stainless steel tanks for dairy processing
Optimize your dairy processing with customizable stainless steel solutions for ...
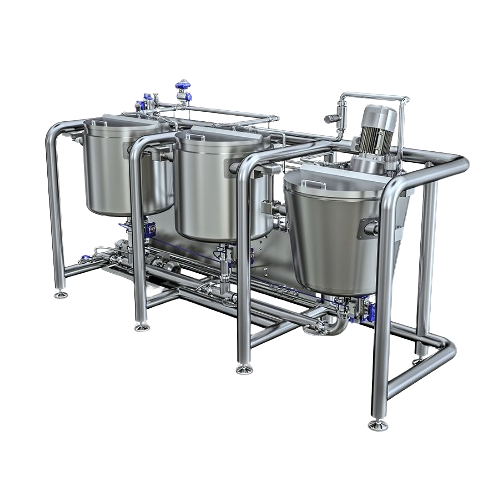

Whipping agent solution station for egg solutions
Optimize your production of delicate egg-based foams with a versatile s...
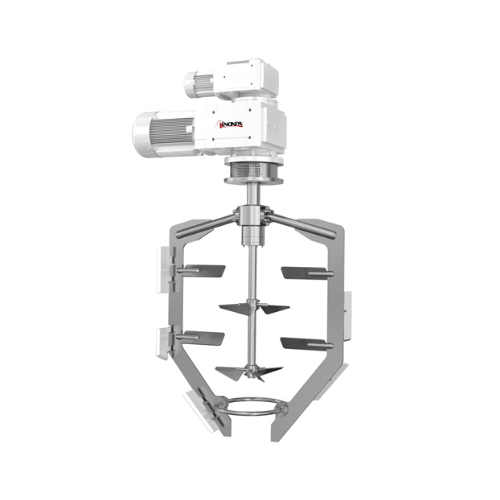

Counter-rotating agitator for high viscosity products
Achieve seamless heat transfer and precise mixing with a counter-ro...
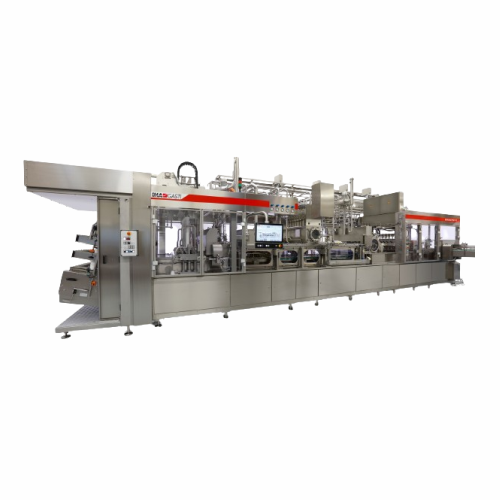

Filling and sealing pre-formed cups solution
Ensure ultra-clean and aseptic processing for pre-formed cups with a fully en...
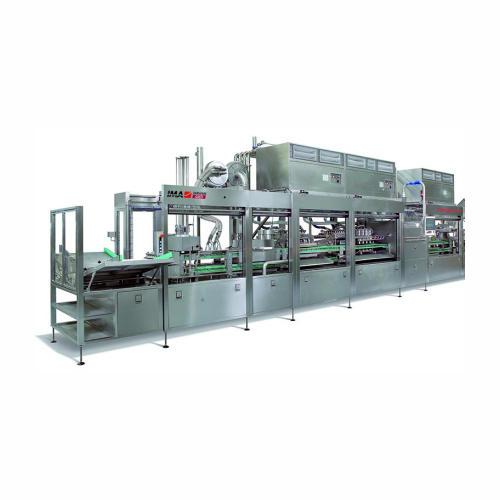

Filling and sealing solution for pre-formed cups
Optimize your liquid and solid product filling with a continuous-motion s...

Cartoning solution for cheese portions
Optimize your cheese packaging with a flexible cartoning solution designed to accomm...

Homogenizers for high-pressure applications
Achieve unparalleled product consistency and stability with precision-engineer...

High-pressure homogenizers for dairy and food products
Achieve consistent texture and stability in your liquid products w...

Contact spreading machine for cream application on wafer sheets
Ensure precise cream application with our specialized co...

Aseptic filler for bag-in-box packaging
Achieve unparalleled product safety and quality in liquid packaging with our advanc...

Aseptic filler for bag in box packaging
Optimize your bag-in-box packaging process with high-speed aseptic filling, ensurin...

Planetary stirrer for bakery and confectionery
Achieve consistent textures and presentation by effortlessly stirring, beat...

Linear intermittent motion filling system for high-density liquids
Ensure precise dosing of high-density liquids like c...

Scraped surface heat exchanger for viscous liquids
Optimize heating and cooling of viscous liquids efficiently with conti...

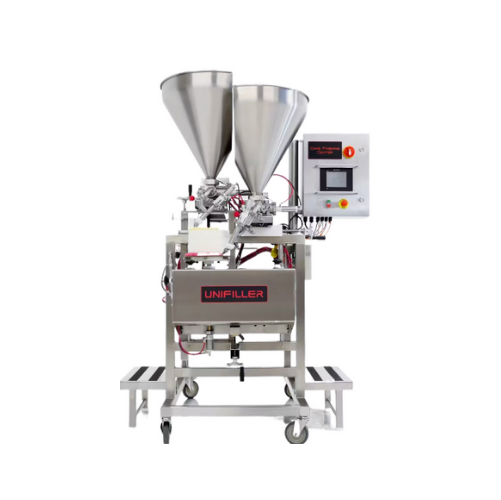
Premixer for cream production
Achieve precise mixing of liquid and solid fats for diverse cream formulations with insulated ...

Evaporator for juices and purees
Efficiently concentrate liquid products like apple juice, tomato puree, and chocolate sauce...

Evaporators for fruit and vegetable juices and purees
Optimize your juice and puree production with advanced evaporators ...

Frozen product cleaning and sizing system
Achieve precise cleaning and sizing of frozen goods effortlessly, enhancing prod...

Vacuum degasser for juices and purees
Enhance the quality of your liquid products with efficient degassing and flavor recov...

Vibrating tables for dewatering and sizing
Optimize your processing line with versatile vibrating tables designed to effic...

Turbo extractor for puree and concentrate production
Enhance your puree and concentrate production with a turbo extractor...

Storage tank for oils and greases
Efficiently store and preserve various liquid products with integrated heating, cooling, ...

Belt blancher for vegetables
Optimize your vegetable processing with efficient blanching and cooking, ensuring reduced treat...

Sterile cooling system for fruit preparations
For manufacturers seeking aseptic conditions, this cooling system ensures ra...

Scraped surface sterilizer for high viscosity liquid products
Optimize your production of high viscosity liquids with a ...
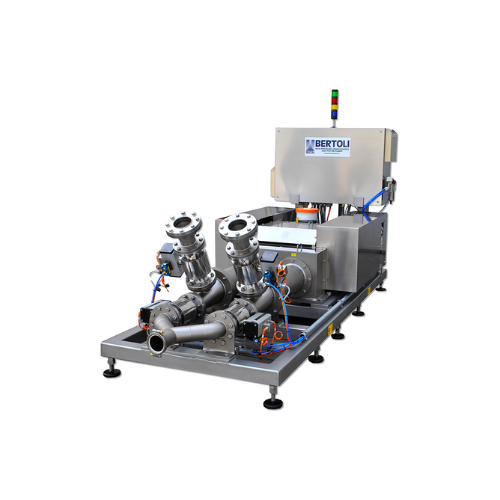

Industrial homogenizer for food and beverage applications
For manufacturers seeking consistent quality, this homogenizer...
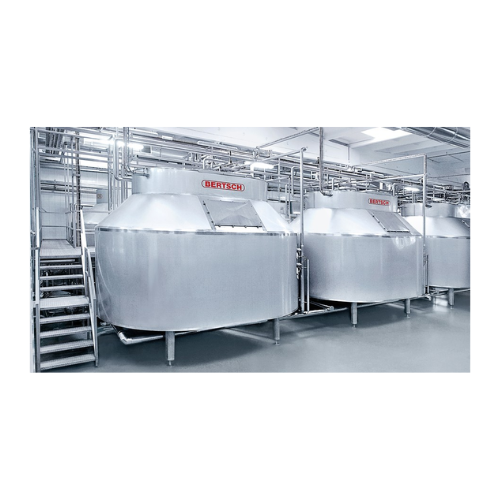

Cheese processing plant for hard and semi-hard cheese
Optimize your cheese production with a versatile solution designed ...
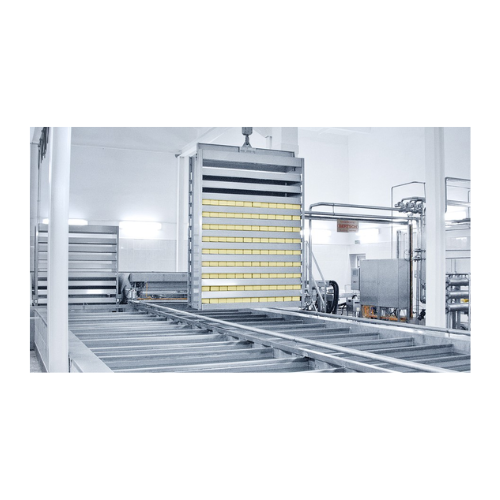

Cip cleaning systems for dairy processing plants
Optimize cheese production with precise curd handling and exceptional sti...
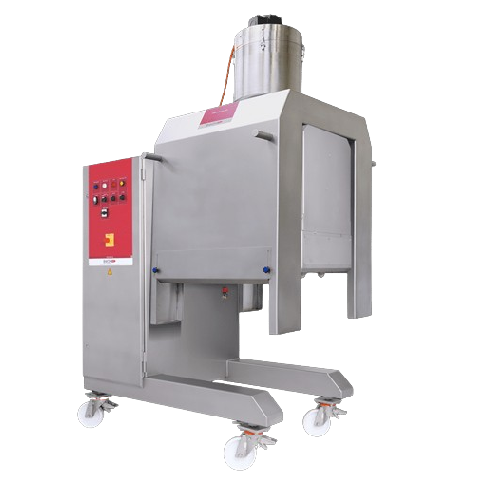

Rotating greaser for baking moulds and trays
Achieve precise greasing with minimal overspray for all your baking moulds an...
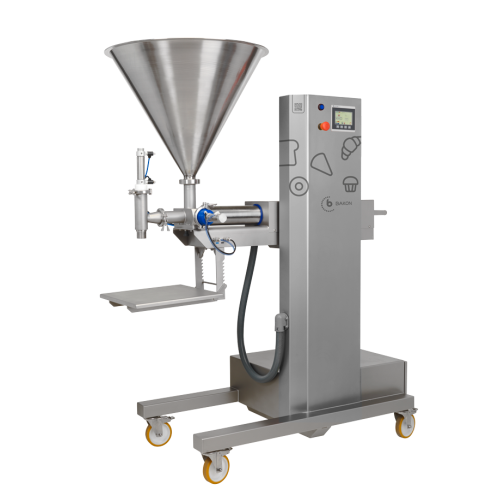

Depositing solutions for liquid and semi-liquid foods
Ensure consistent portioning and minimize waste with advanced depos...
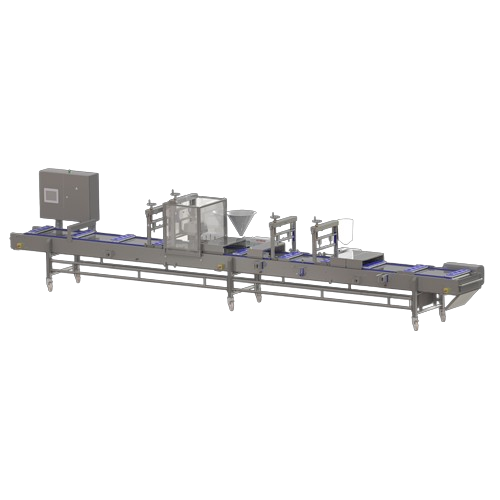

Multifunctional dessert line for layered dessert production
Effortlessly create complex, multi-layer desserts or meal co...
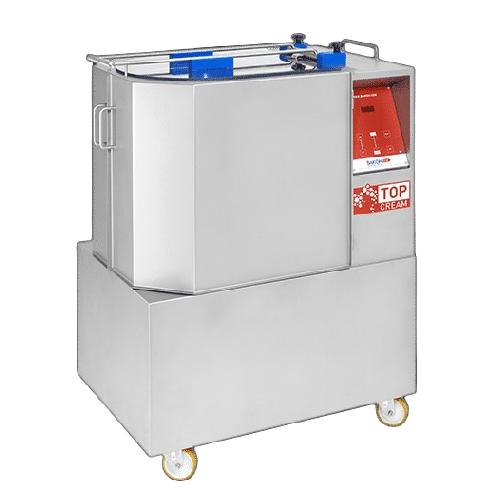

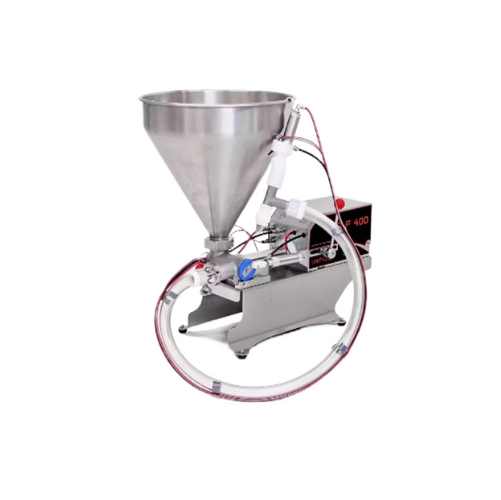
Industrial cream whipping machine
Elevate your production with a whipping machine that amplifies cream volume by up to 50%,...
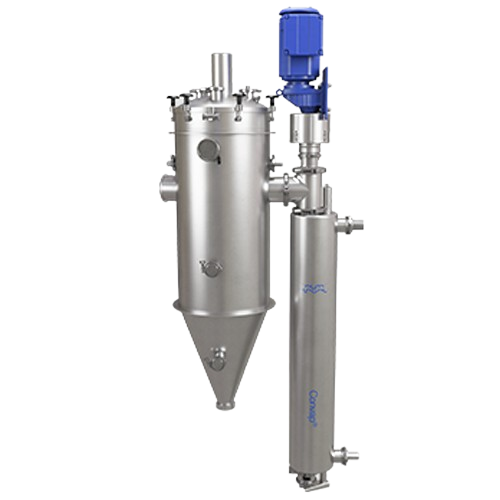

Scraped surface evaporator for high-viscosity materials
Efficiently concentrate high-viscosity and hard-to-handle materia...
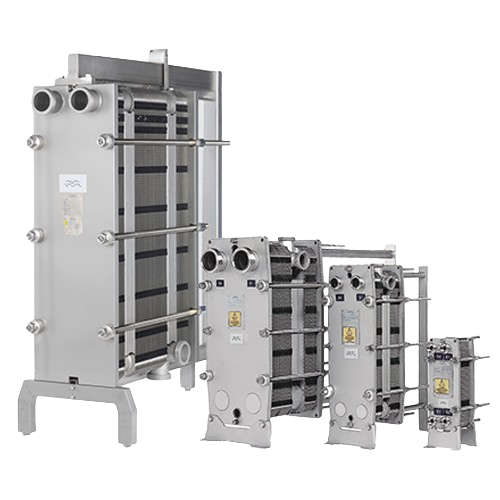

Gasketed plate heat exchangers for hygienic applications
Ensure optimal hygiene and thermal efficiency in your processing...
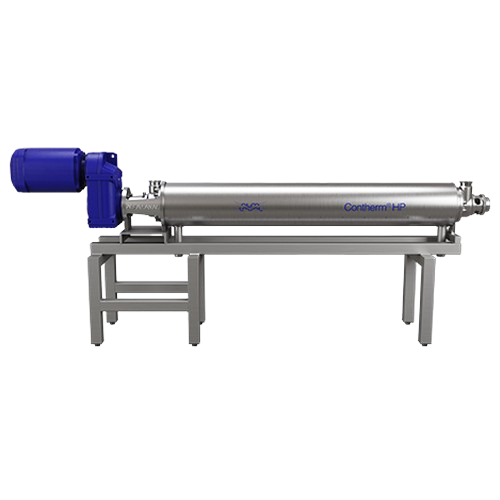

Scraped surface heat exchanger for high-pressure applications
Handle high-viscosity and particulate-rich products with p...
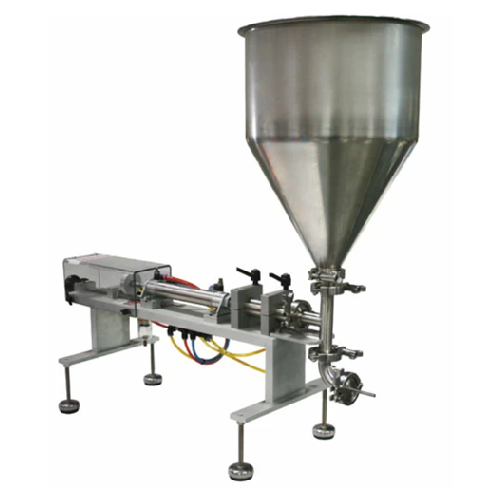

Semi-automatic piston injector for bakery products
Enhance your bakery production with precise delivery of a wide range o...
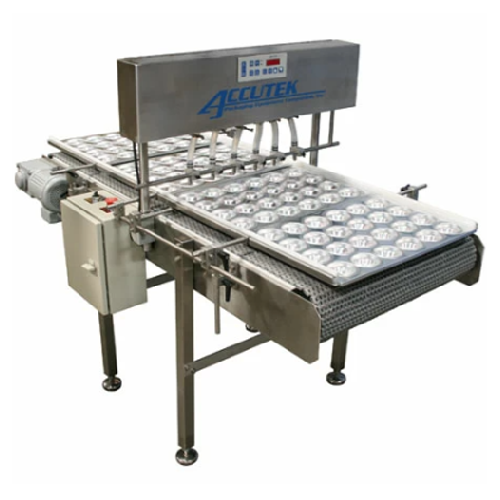

Auto bakery tray depositor for creams and batters
Efficiently deposit precise quantities of creams and batters with high-...

Industrial mixing tanks for liquid, slurry, and gas dosing
Optimize your production with versatile mix tanks, designed t...

High shear mixer for dairy and personal care products
Achieve consistent emulsification and stable homogeneity with high ...
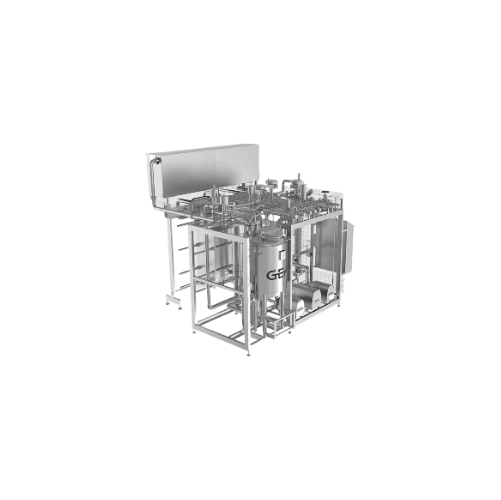
Pasteurizer system for dairy applications
Achieve optimal pasteurization with precise temperature control and energy-effic...

Standardization unit for cream fat or milk fat
Optimize your milk standardization process to achieve precise cream and fat...

Laboratory homogenizers for nanoparticles and emulsions
Tackle the challenge of achieving consistent nano-scale dispersio...

Rotary piston fillers for pumpable products
Optimize high-speed production lines with precision filling for diverse liquid...

Rotary piston fillers with plunger for viscous products
Optimize your filling process with high-speed, rotary piston fill...

Planetary mixers for baking and food industries
Achieve precise mixing and consistency across a range of products with adv...

Inline mechanical homogenizer for food processing
Achieve precise particle size and uniform texture in your emulsions and...

Storage tank integrity testing
Prevent costly contamination and streamline your operations with advanced tank integrity test...

Industrial depositor for bakeries
Enhance your bakery production with precision depositing and filling, designed to handle ...

Industrial depositor for large volume bakery products
Achieve precise and high-speed depositing for bakery items with sea...

Industrial servo-based depositor for cake production
Effortlessly manage diverse depositing tasks across high-speed baker...

Portable table top bakery depositor
Optimize your baked goods production with precise portioning and rapid depositing, all ...

Automated cake icing system
Enhance your cake production efficiency by seamlessly integrating high-speed icing and decoratio...

Icing and decorating system for cake
Enhance your production with precise cake finishing—top, side, and border icing integr...

Cake icing and decorating system
Streamline your cake production with this system that adjusts to icing texture changes, ens...

Industrial food production depositor for bakery applications
Optimize your bakery production with precision depositing a...

Servo deposition system for industrial cake production
Effortlessly streamline your food production process with precise ...

Tabletop food depositor for portion control
Streamline your food production with precise portion control, reducing waste a...

Automated icing system for cakes
Efficiently layer, fill, and ice various cake types with precision and speed, securing cons...

Aseptic filler for fruit juices and purees
Ensure product integrity and shelf stability with a versatile filler designed t...
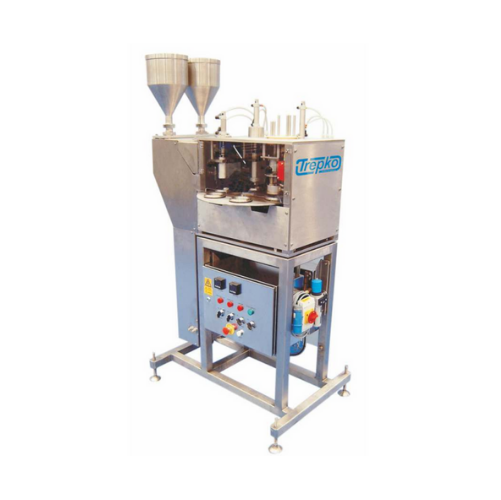

Rotary cup filling and closing system
Maximize production efficiency with a system that offers precision filling and secure...

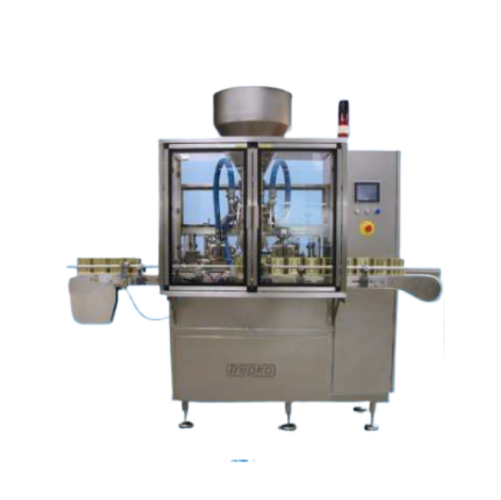
Semi-automatic filling and closing system for pre-formed containers
Streamline your packaging process with reliable sem...

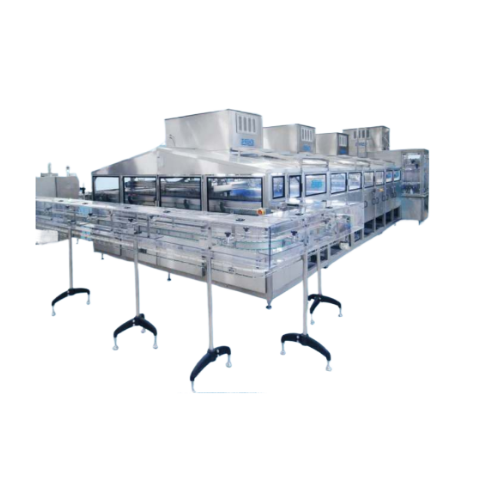
Pre-formed container filling system for multi-layer products
Efficiently handle a diverse range of products with this fl...
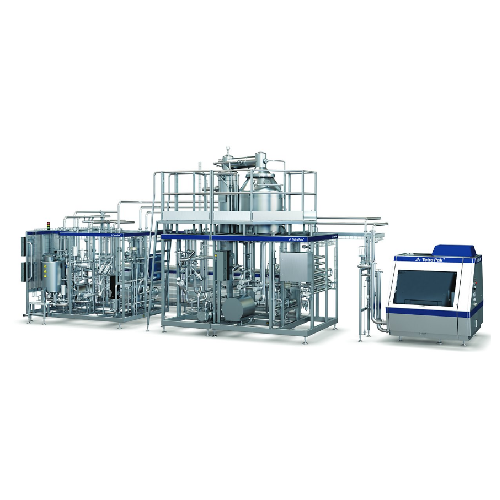

Direct Uht treatment for liquid foods
Optimize aseptic production with advanced UHT technology to preserve nutritional valu...
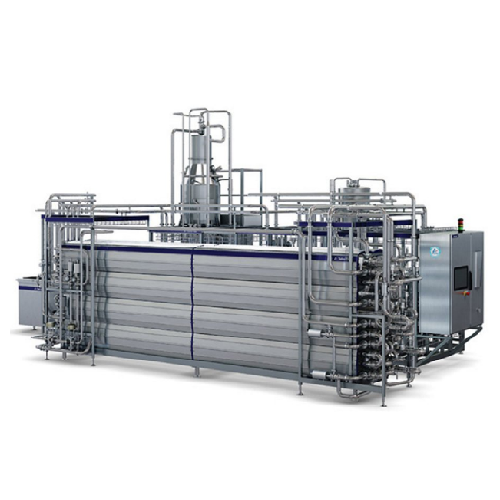

Indirect Uht treatment for dairy products
Ensure your beverages achieve extended shelf life with consistent quality using ...
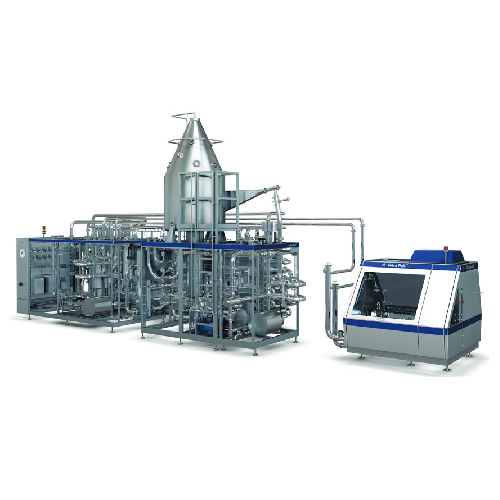

Direct Uht processing for heat-sensitive liquid products
Achieve optimal taste and nutritional value in liquid foods thro...
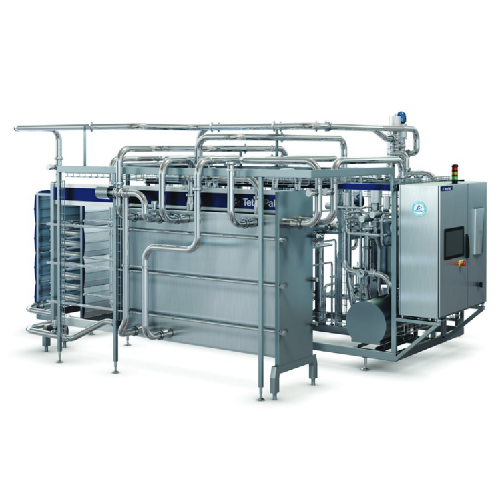

Pasteurizer for dairy products
Enhance food safety and minimize operational costs with a cutting-edge pasteurizer designed f...
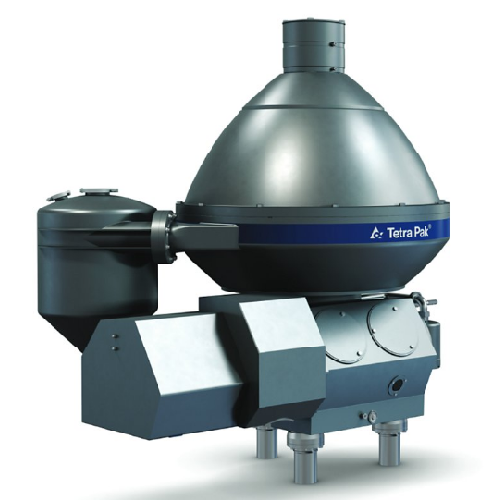

Spore and bacteria removal unit for dairy products
Ensure superior quality by precisely removing spores and bacteria from...
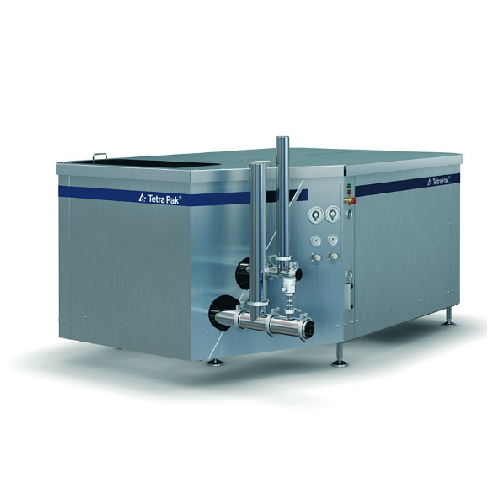

Industrial homogenizer for liquid food applications
Achieve unparalleled product consistency and quality with high-speed ...
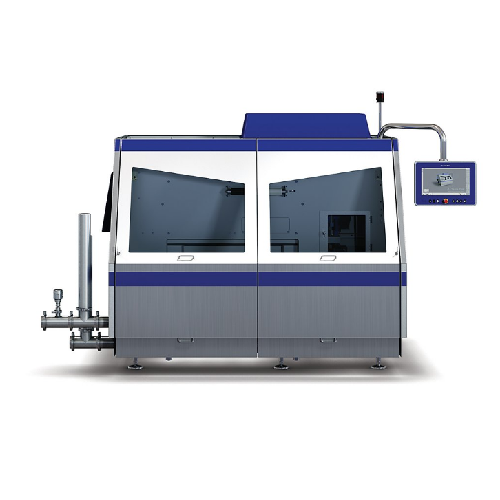

Homogenizer for high-capacity food processing
Achieve superior emulsification and suspension handling with this high-press...
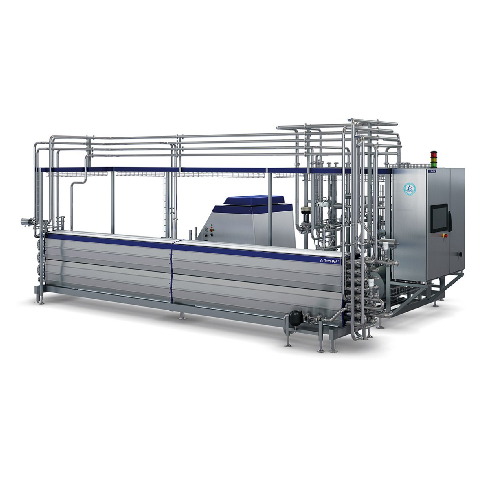

Uht processing unit for dairy products
Optimize your liquid food production with continuous, high-capacity UHT treatment th...
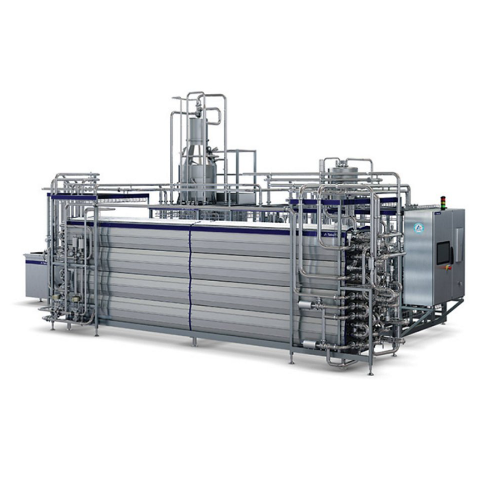

Indirect Uht processing for dairy products
Enhance your dairy and beverage operations with state-of-the-art ultra-high tem...

Dairy pasteurization system for milk, yoghurt, and cream
Ensure reliable dairy processing with an advanced pasteurization...

Efficient milk skimming separator
Optimize your dairy processing with our high-efficiency separator, designed to ensure sup...

Dairy pasteurizer
Ensure product safety and quality while reducing energy consumption and operational costs with this advance...

Versatile filling system for aseptic packaging
Achieve seamless integration in high-speed aseptic packaging with this flex...

Buffer tanks for dairy processing
Optimize your dairy production with versatile buffer tanks, essential for balancing flow ...

Continuous aerator for dairy products
Enhance the texture and flavor of dairy delights with precise gas infusion, transform...

Continuous aerator for r&d and small scale production
Ideal for testing and scaling aeration processes, this compact mach...

Compact continuous aerator for bakery production
Optimize your bakery production with a compact aerator that delivers prec...
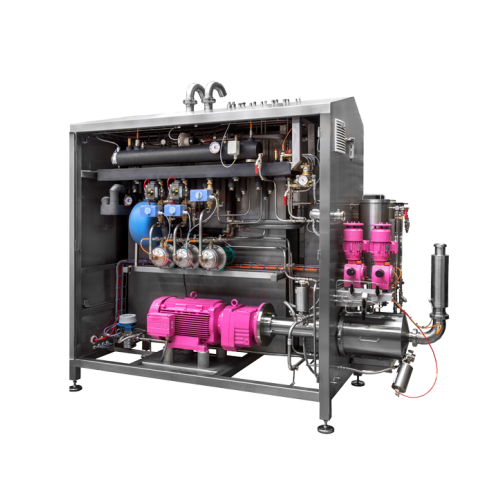

Continuous aeration system for bakery products
Optimize your bakery production with precise aeration and mixing, ensuring ...
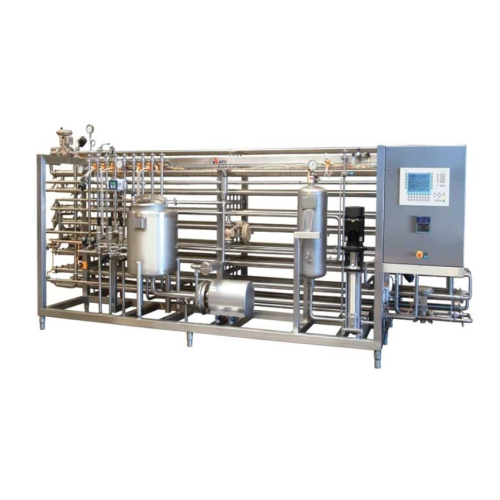
Tubular Uht processing for dairy products
Experience efficient high-pressure thermal processing with tubular UHT technolog...
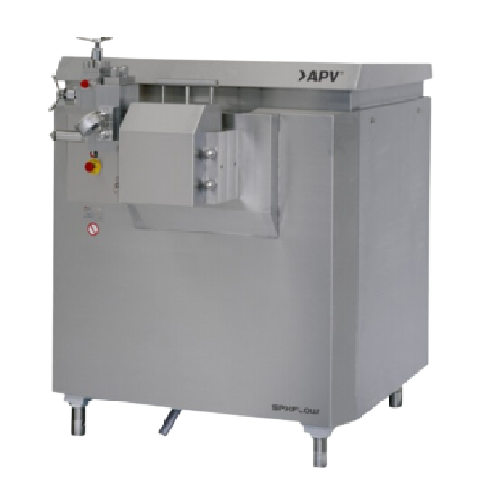

High pressure homogenizers for dairy and pharmaceutical applications
Optimize your production line with high-pressure h...
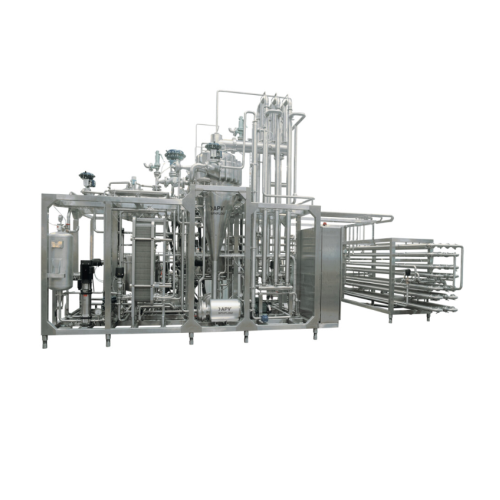

Uht system for milk and dairy products
Ensure superior product quality and extended shelf-life by utilizing rapid heat trea...
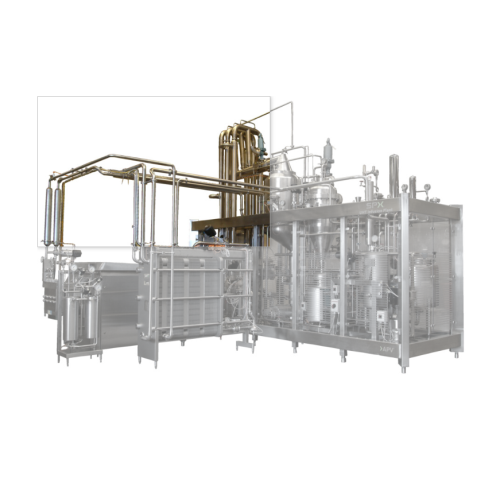

Ultra high temperature (uht) direct heating for infusion Esl plant
Achieve extended shelf life and superior flavor with...

Sanitary gasketed plate heat exchangers for clean applications
Ensure product purity and maintain hygienic standards wit...

Infusion Uht plant for dairy products
Achieve precise thermal treatment with minimal product alteration, enhancing quality ...

Clean in place (cip) system for industrial cleaning
Ensure optimal hygiene and production efficiency with a system that s...

Process tanks for mixing, cooking, and cooling applications
Efficiently tackle viscous product challenges with advanced ...

Crystallization and pin-working equipment for food processing
Optimize your food product quality with precise crystalliz...

Dairy product filling solutions
Optimize your dairy production with advanced filling systems designed to enhance product saf...

Chocolate and spreadable cream dispenser
Effortlessly enhance your confection creations with a dispenser that precisely mel...

Refiner for spreadable cream and chocolate
Achieve optimal texture and consistency for your spreadable creams and chocolat...

Homogenization and emulsifying system for fine foods
Texture and consistency are critical to foods with delicate composit...

Planetary mixer for confectionery and bakery production
For the best quality confectionary and bakery products, controlla...

Mixer for aeration of confectionery and bakery products
Aerated products can be difficult to mix thoroughly without reduc...

Temperature-treatment mixer for bakery & gastronomy
The production of creams, sauces, ragouts, ready-to-bake, and sim...
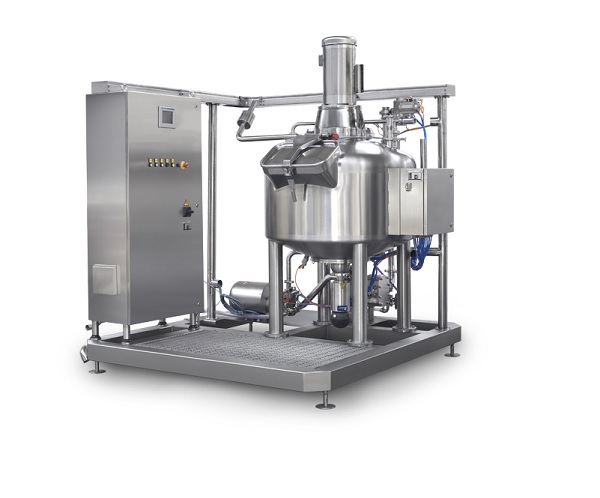

Centrifugal mixer for batters and creams
Batters, creams and other delicate sauces and emulsions take time to mix, reducing...
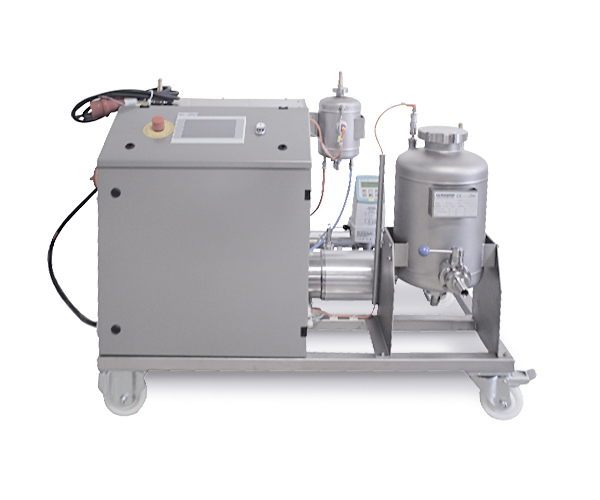

Aerator for high-viscosity media
Highly viscous ingredients in both the food and chemical processing industries require spec...
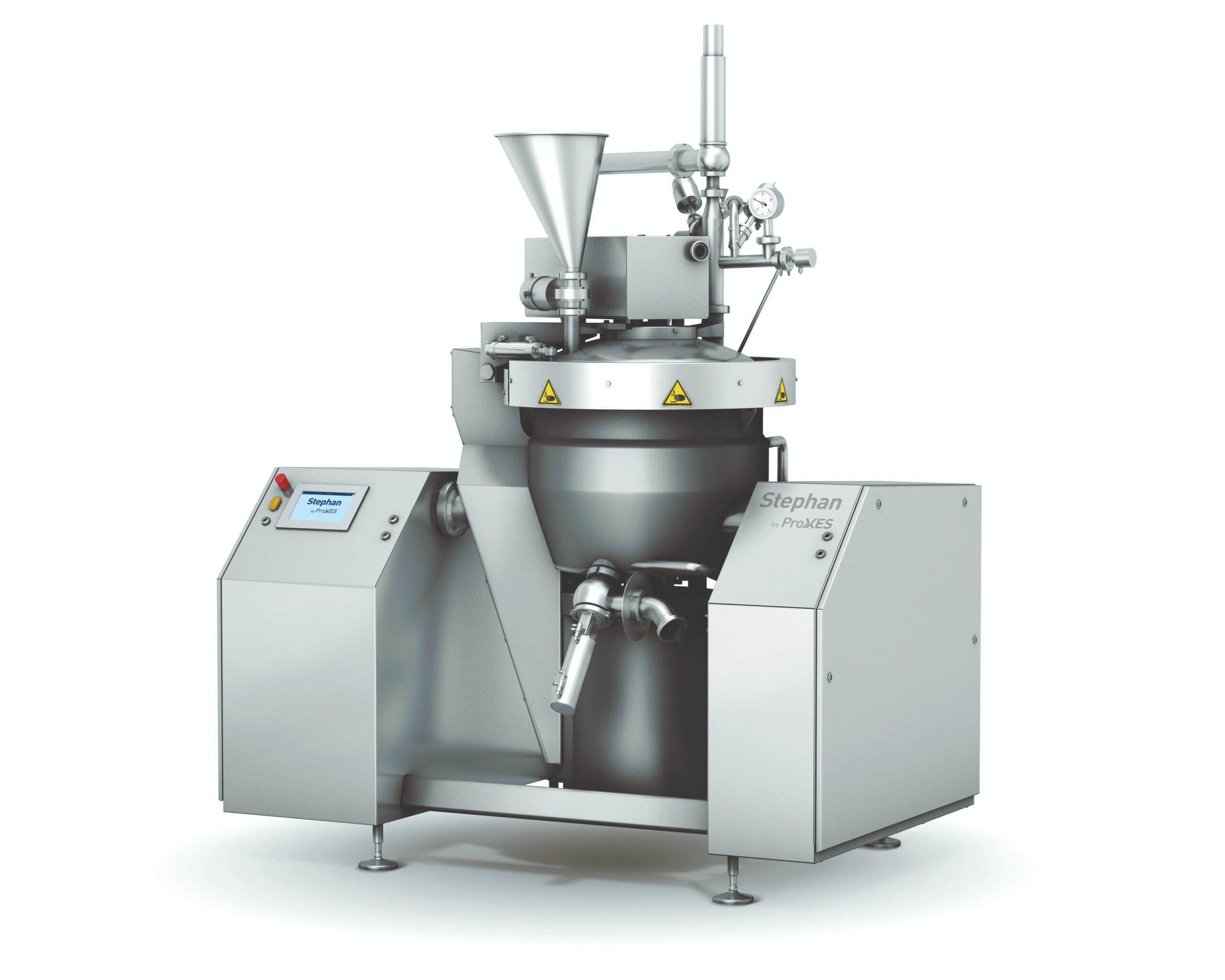

Complete cutting, mixing, emulsifying and heating system
From laboratory scale to large volume food or cosmetic productio...
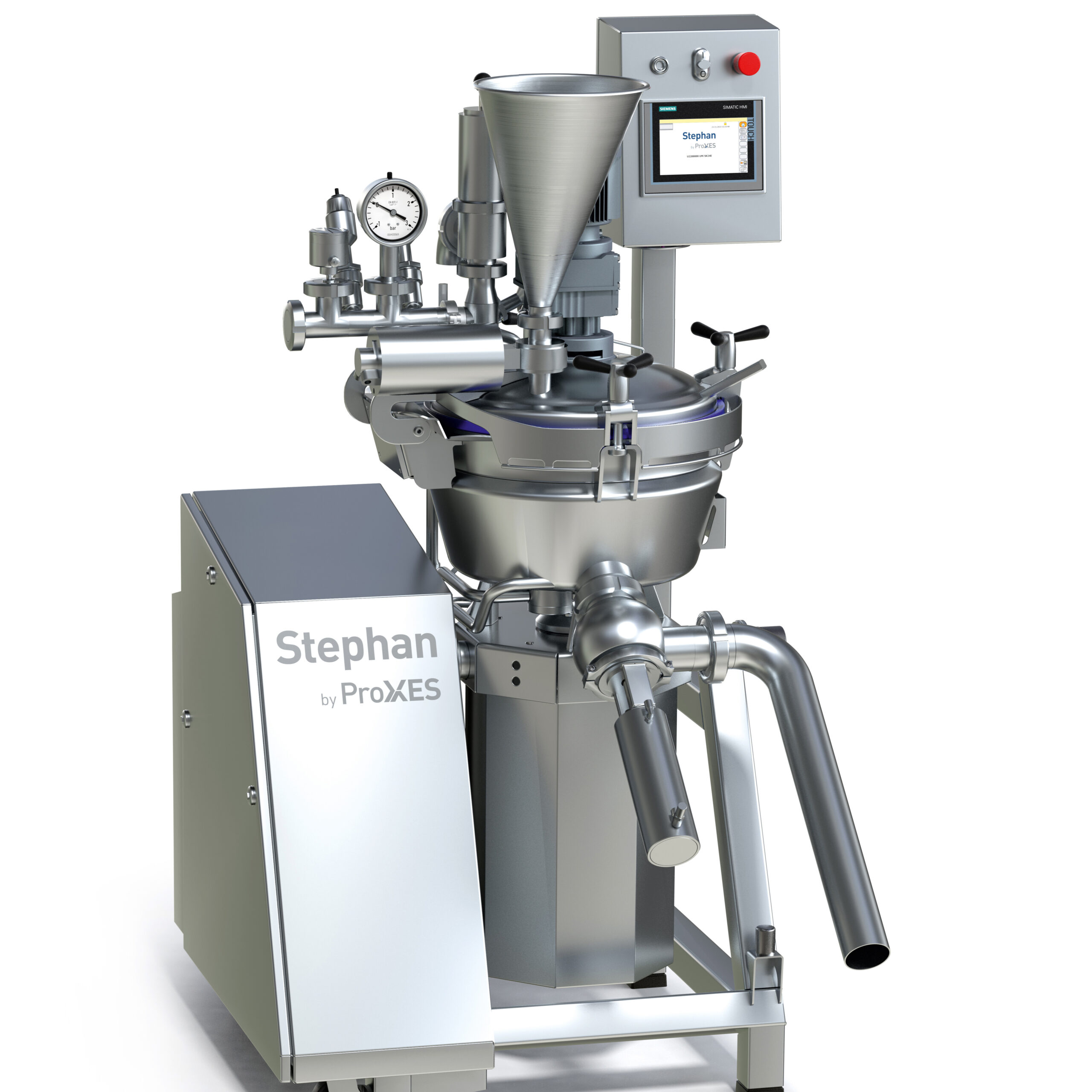

Flexible mixing system for whipped cream and pastries
Delicacies such as meringue, ganache, and marzipan undergo various ...

Batch processing system for emulsions and suspensions
Emulsions enhance foods with a creamy mouthfeel and richer flavors....










