Making Uncoated Tablets
Find innovative production technology for making uncoated tablets and connect directly with world-leading specialists
It is strange how two tablets can belong to the same but at the same time to a different category depending on how the tablet itself is classified. For example, chewable tablets and effervescent tablets have two different routes of administration but both belong to the category of uncoated tablets. Uncoated tablets are prepared by compression of granules in which no coating is added after compression. They may be single-layer or multi-layer tablets.
Stories about uncoated tablets
Select your uncoated tablets process
Tell us about your production challenge
Difference between coated and uncoated tablets – When is the coating necessary?
If you’re wondering when coating a tablet is necessary, there’s not just one answer. Uncoated tablets are rougher and don’t really taste good. This makes them harder to swallow especially for children, as they also leave a bad aftertaste in the mouth. So coating is important to mask an unpleasant taste. Another reason may be that the active ingredient the tablet is made of is acid sensitive, so an enteric coating may help resist stomach acidity.
On the other way around, the enteric coating can also help protect the stomach from a more aggressive drug. Apart from that, the coating reduces also tablet friability and it can modify or control drug release. In uncoated tablets, any excipient or added substance is not specifically intended for this purpose.
Problems that can occur during uncoated tablets manufacturing
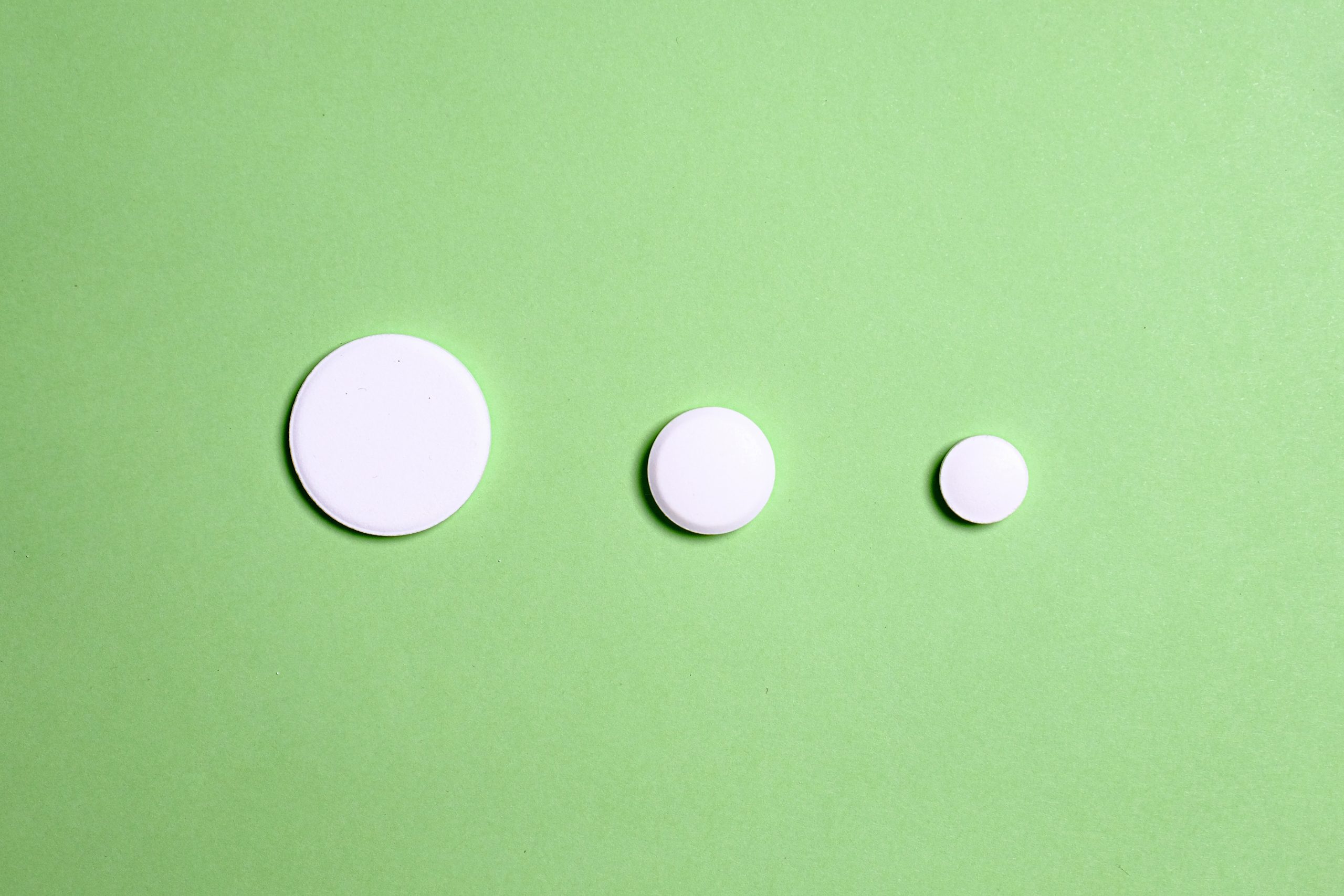
During uncoated tablet manufacturing, various problems can arise. Capping and lamination are two of these and refer to the separation of the tablet. Capping is the horizontal separation of the upper or lower part of the tablet from its main body; while lamination is the separation of the tablet into several horizontal layers.
Capping and lamination may occur immediately after compression or after several hours or days. To avoid this, it is advisable to test the tablet for friability to see if the problem is present or not.
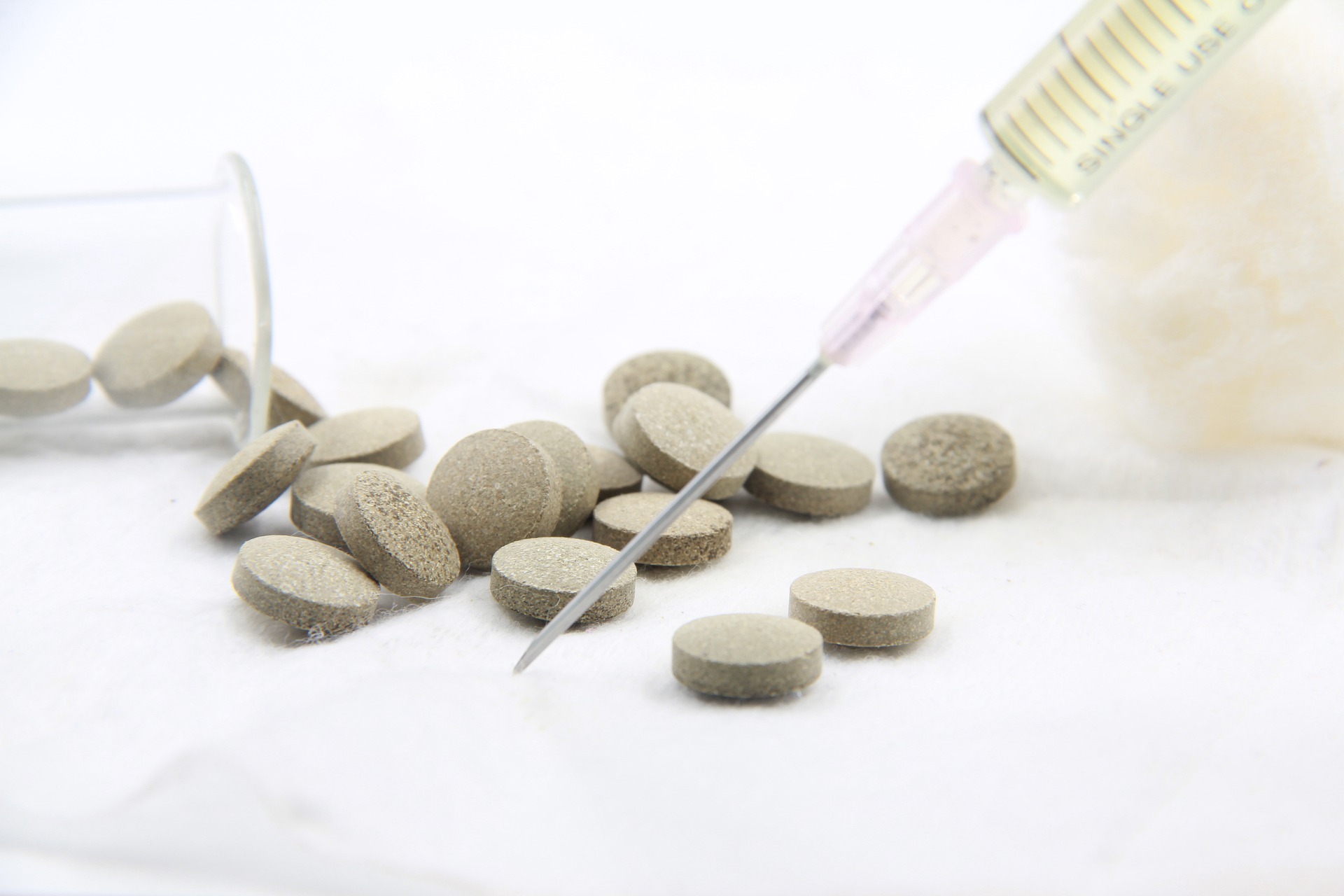
The main causes can be air entrapment in granules or particles, granules that are too dry, improper tooling, or incorrect setup of the press. Tablet lamination and capping can be prevented by precompression.
If the tablet has excessive binder, sticking can happen. It refers to when tablet materials adhere to the die wall. Picking is used to describing when a portion of material is removed from the tablet surface by a punch due to embossing design. Plating punch faces with chromium can be a solution to produce non-adherent punch faces.
Disintegration time for uncoated tablets
Disintegration is the ability of a tablet to break down into smaller particles to allow the drug to be absorbed by the body. The disintegration test is paramount for tablets that are intended for mouth administration except for chewable tablets.
The disintegration tester consists of a basket that can hold six tablets. The basket is raised and lowered into a beaker that has water as the immersion fluid, unless there is another medium specified, having the temperature at 35 °C to 39 °C.
After running the device for the specified time, if all the tablets are disintegrated completely, they are good to go. If one or two tablets fail the test, it must be repeated on 12 additional tablets. If not less than 16 out of 18 tablets tested are disintegrated, the requirements are met.
Friability test for uncoated tablets
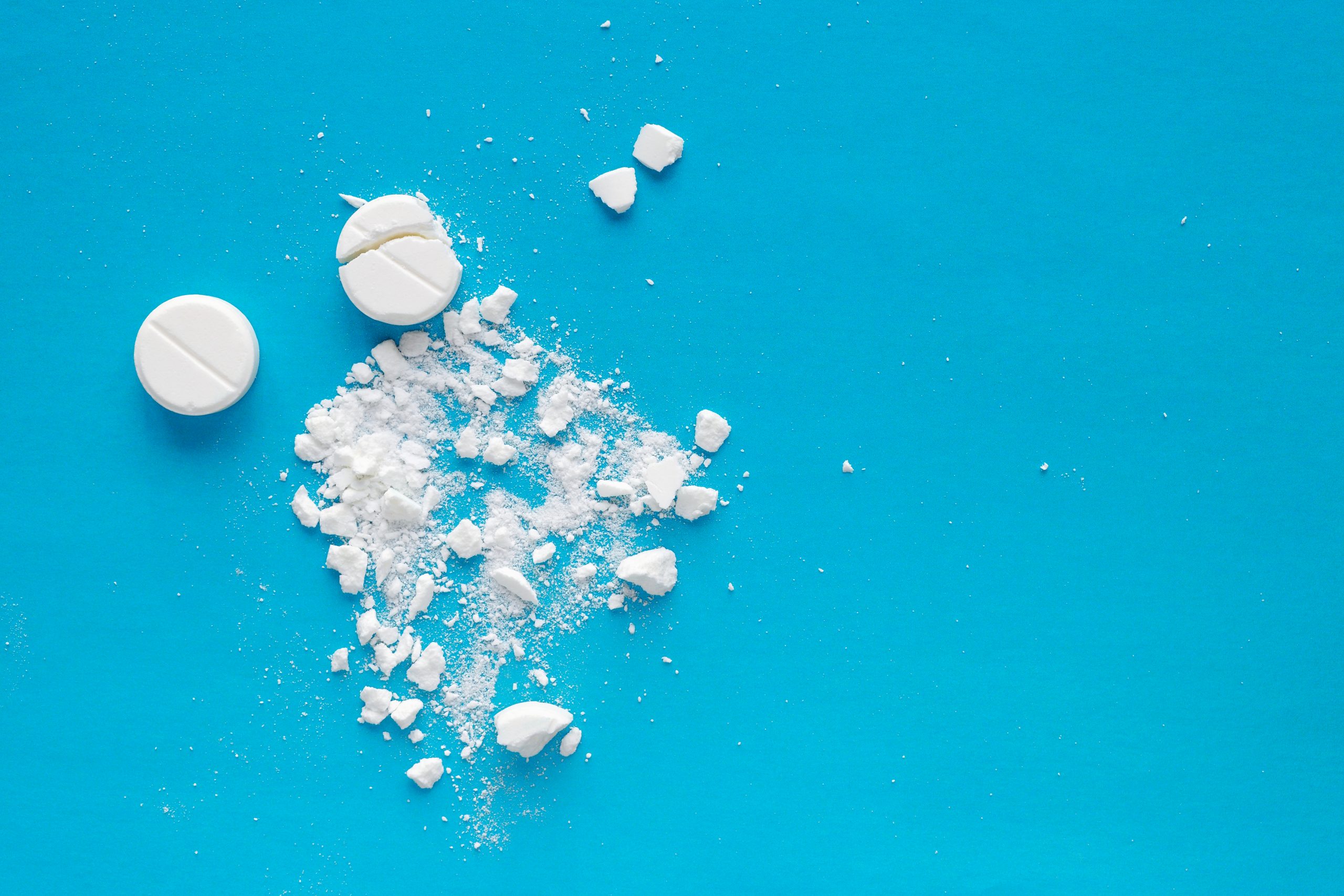

Friability test says to you how much mechanical stress tablet withstand during manufacturing, packaging and transit or when they are handled by consumers. A Friabilator is the laboratory instrument used for friability test. The device consists of a plastic chamber, the rotating drum, where you can place your preweighed tablets. Now you can rotate the drum 100 times and after removing them from the drum, just weight the tablet again.
If they have lost less than 0.5 to 1.0%, they are considered acceptable. Chewable and effervescent tablets have high friability weigh losses, so they have different specification and require special packaging. Basically, with the friability test, you can know the difference in the weight of uncoated tablets before and after the test. In this way, you can evaluate the physical strength of uncoated tablets
Which type of excipients do you have to use in uncoated tablets?
During uncoated tablet manufacturing, you cannot think to start without having your excipients. They play an important role and fulfill different functions – they can improve the taste or modify the disintegration time or the time and place of substance release. Saying that they are everything other than APIs, i.e. active pharmaceutical ingredients. When making uncoated tablets, there are some types of excipients you have to use.
For example, excipients used in orally disintegrating tablets (ODT) are sucrose, mannitol or sorbitol. Since this type of tablet disintegrates very quickly upon contact with saliva, disintegrants such as polyvinylpyrrolidone or sodium starch glycolate play a fundamental role here. In effervescent tablets instead, excipients used are citric acid, sodium citrate, fumaric acid, tartaric acid, with citric acid being one of the most important.
Processing steps involved in uncoated tablets making
Which uncoated tablets technology do you need?
Micro-dosing system for pharmaceutical powders in vials
Ensure accurate aseptic dosing of sensitive pharmaceutical powder...

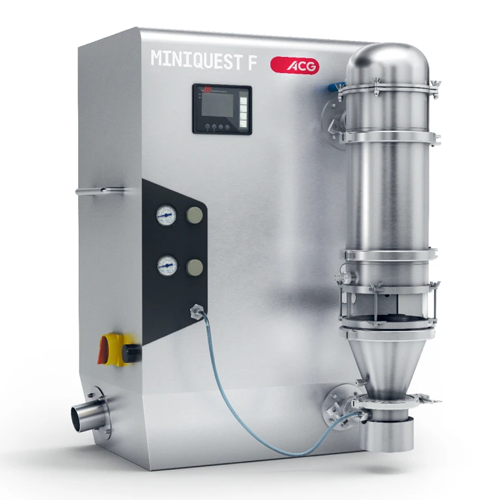
High-containment diverter for continuous tablet and capsule filling
Enhance your production line with a versatile solut...

High-speed blister packaging with integrated cartoner
Optimize your blister packaging process with a solution that seamle...

Tablet pressing system for solid chemicals and cosmetic products
Optimize your tableting process for diverse solid produ...

Laboratory film coating system for development and clinical batches
Achieve precision in tablet coating with a versatil...
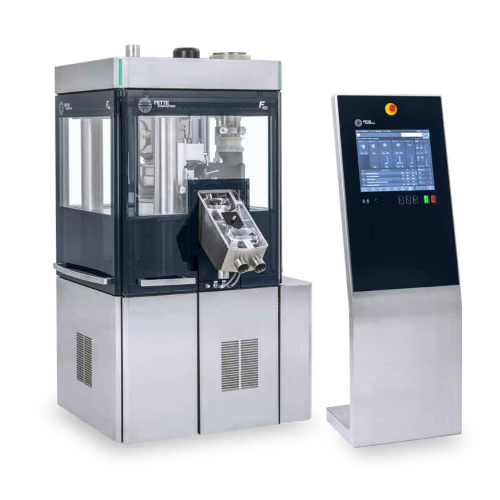

Industrial tablet press for high output production
Achieve precise control and efficient production with advanced rotary ...
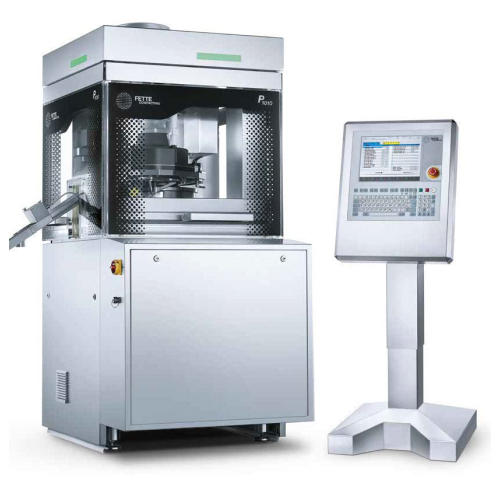

High performance tablet press for large batches
For manufacturers aiming to boost tablet production without sacrificing pr...
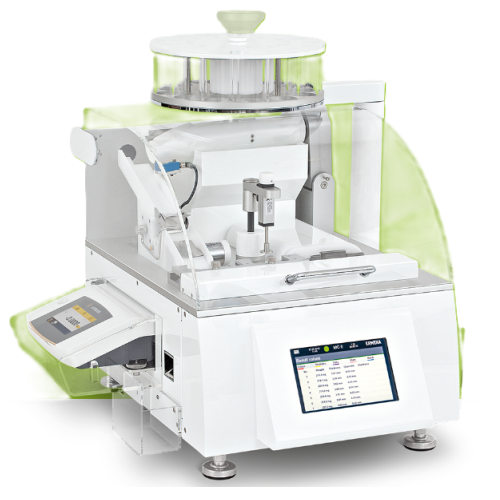

GMP automatic tablet hardness tester
Ensure precise control over tablet quality with a fully automated tester that seamless...
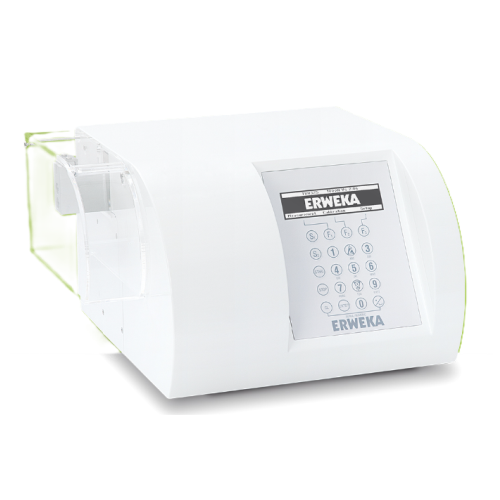

Tablet hardness tester
Ensure consistent tablet quality by precisely measuring hardness, thickness, diameter, and weight with...
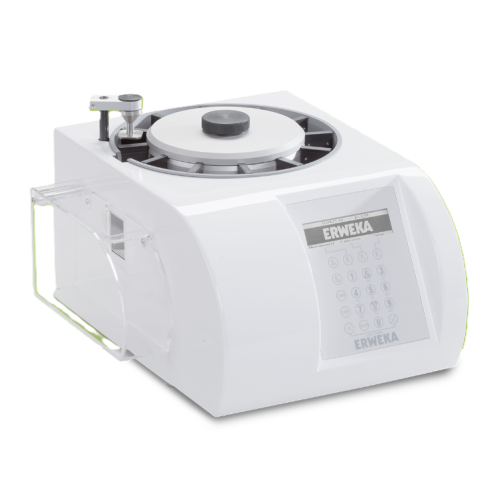

Tablet hardness and combination tester
Ensure consistent tablet hardness and precision across multiple parameters with this...
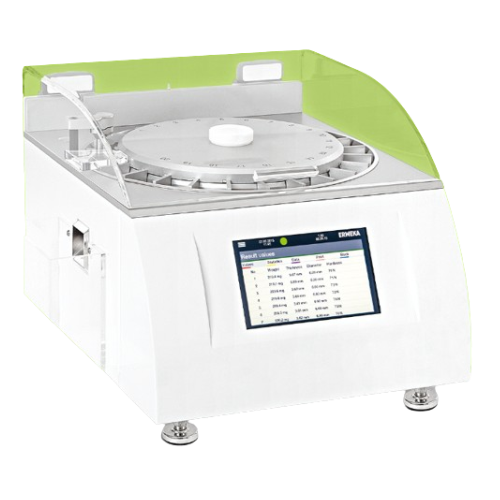

pharmaceutical-tablet hardness testing system
Ensure consistent tablet quality and compliance with pharmacopeia standards ...
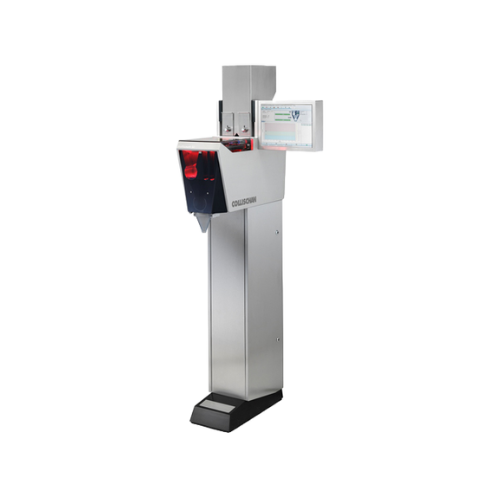

Tablet counting solution for pharmaceutical industry
Maximize dosing precision and reduce miscounts in high-speed pharmac...
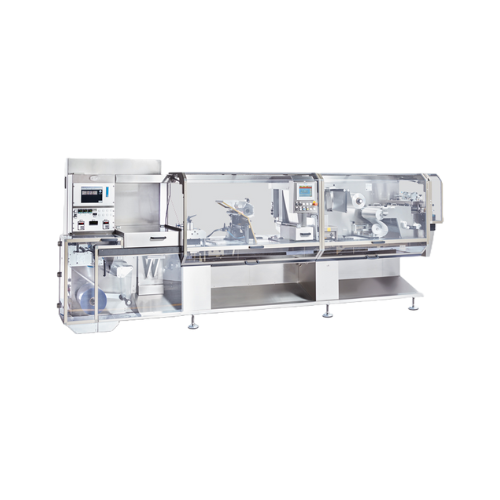

High speed blister packaging for pharmaceuticals
Need efficient packaging with quick format changeovers for various capsul...

Loose mould line for chocolate production
Streamline your chocolate production with a high-throughput line that seamlessly...

Efficient blister packing for pharmaceutical tablets
Streamline your production with a blister packing machine that enhan...

Single rotary tablet press for small and medium-batch production
Optimize your tablet production with precision compress...

Tablet and capsule visual inspection system
Achieve unparalleled precision in tablet and capsule inspection with a high-sp...
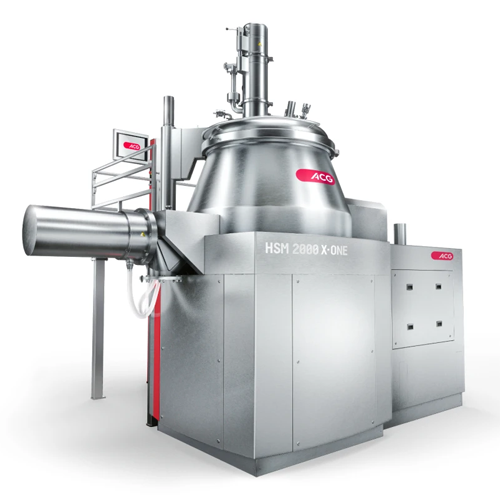

High-shear mixer granulator for pharma and nutraceuticals
Optimize your batch and high-speed production with a powerful ...
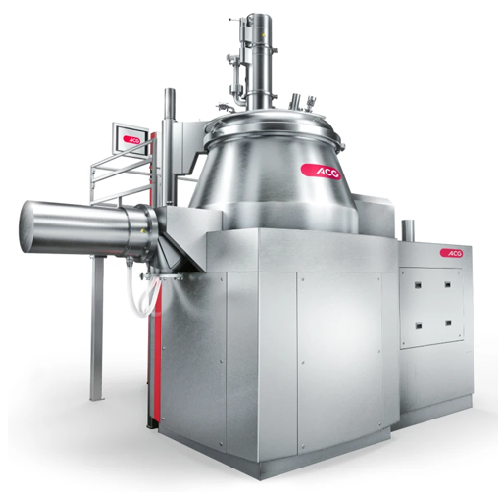

High-shear mixer granulator for small batches
Achieving consistent particle size and mix uniformity in pharmaceutical and ...
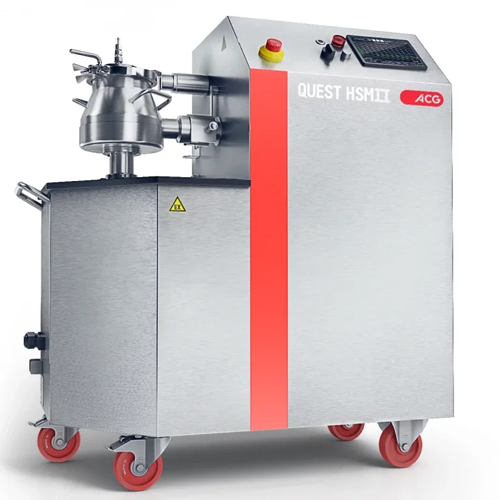

High-shear granulator for wet granulation
Achieve precise content uniformity with advanced high-shear granulation, designe...
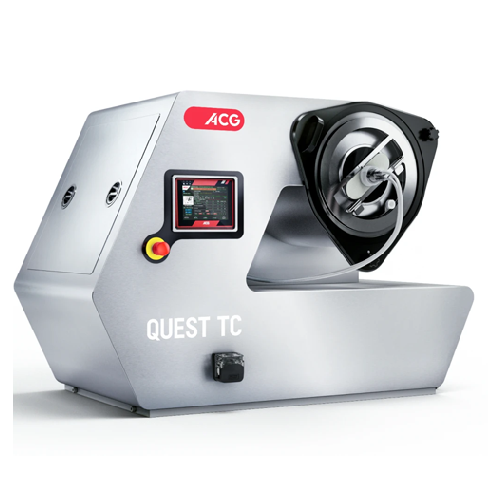

Tablet coating for r&d and small-scale production
Achieve precise, efficient tablet coating with a compact, versatile mac...

Tablet coating system for high-capacity operations
Streamline your tablet production with a coater that maximizes through...

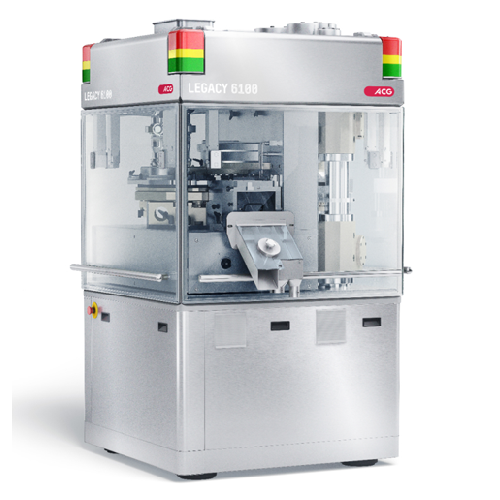
Double rotary press for high-volume tablet compression
Achieve high-speed, precision tablet compression with a machine th...

Single rotary tablet press
Streamline your tablet production with enhanced efficiency and precision, ensuring consistent tab...

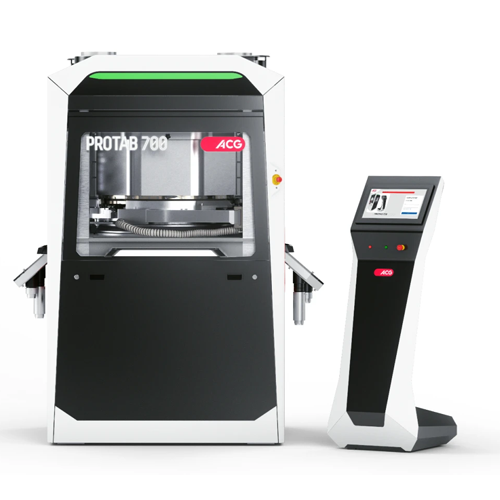
Tabletop granulation system for small batches
Enhance R&D capabilities with this innovative solution designed for gra...
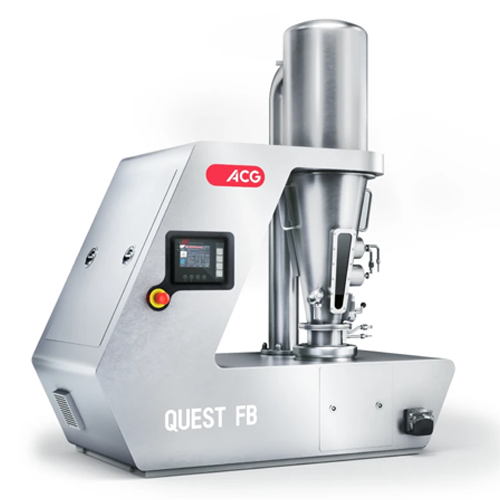

Versatile fluid bed combo for granulation and coating
Optimize lab-scale R&D with an adaptable fluid bed system, sea...
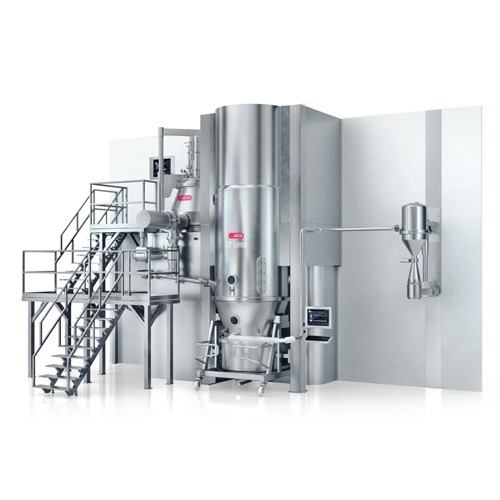

Integrated granulation train for pharmaceutical processes
Achieve precise granulation, uniform mixing, and efficient dry...
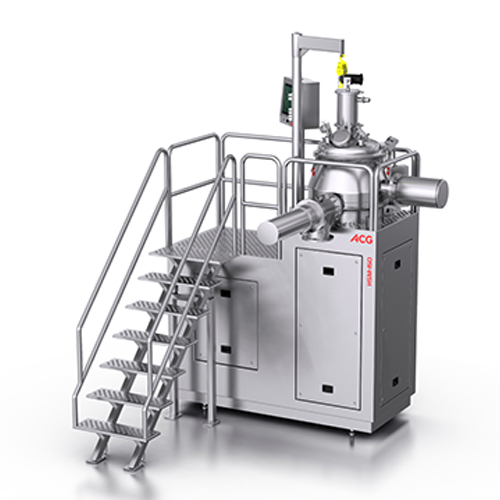

High-shear mixer for small batch granulation
Enhance your production efficiency with a high-shear mixer designed for preci...
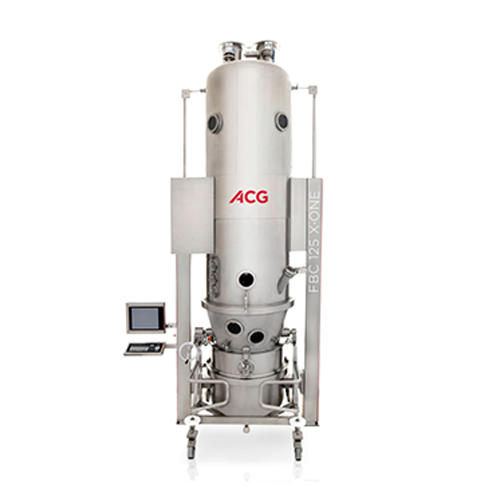

Fluid bed dryer with granulation and coating
Enhance your processing efficiency with a versatile system capable of combini...
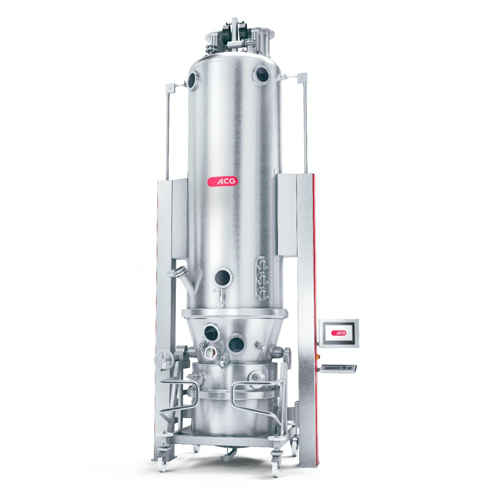

Fluid bed combo for granulation and coating
Achieve seamless granulation and coating with batch and high-speed operations,...
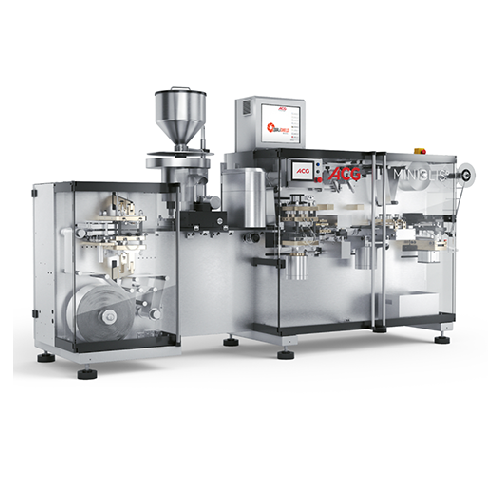

Flat-forming blister packager for small production batches
Ideal for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical firms seeking effi...
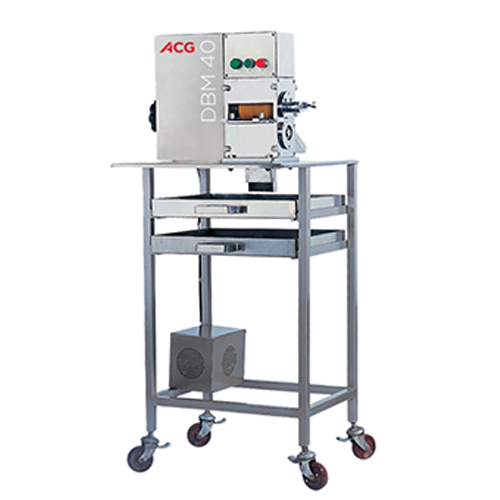

Semi-automatic de-blistering solution for Pvc and alu blister packs
Streamline your packaging operations by swiftly rec...
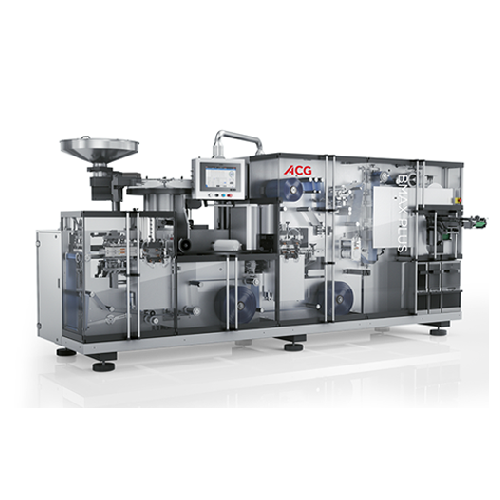

Flat forming and sealing blister packaging solution
Enhance your blister packaging process with a solution that ensures p...
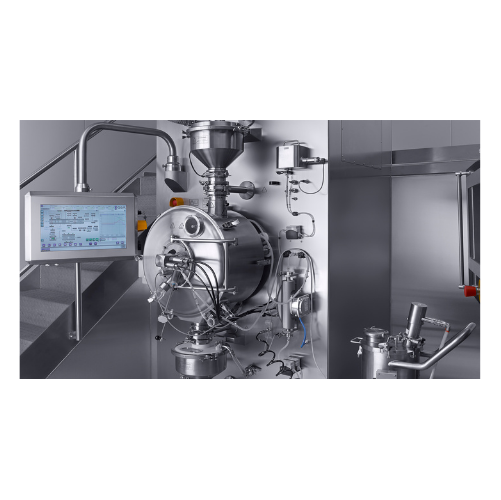

Pharmaceutical tablet coating system
Achieve precise and efficient coating of pharmaceutical tablets to enhance product sta...
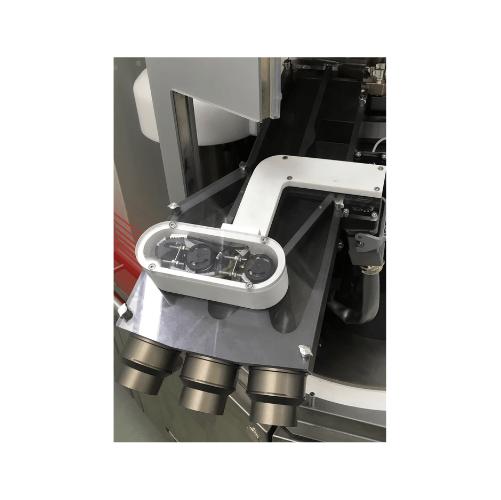

Rotary tablet press for abrasive powders
Achieve precise tablet sizing and bilayer production, even with abrasive powders, ...
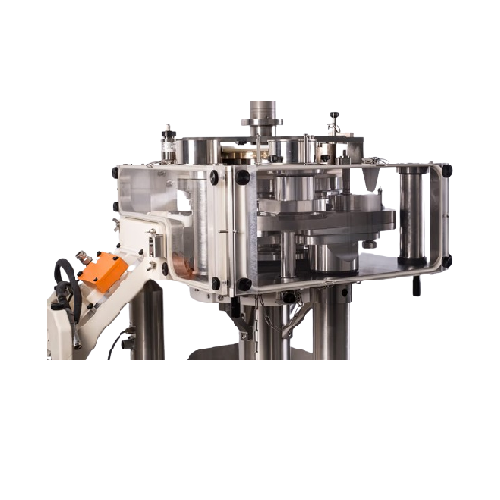

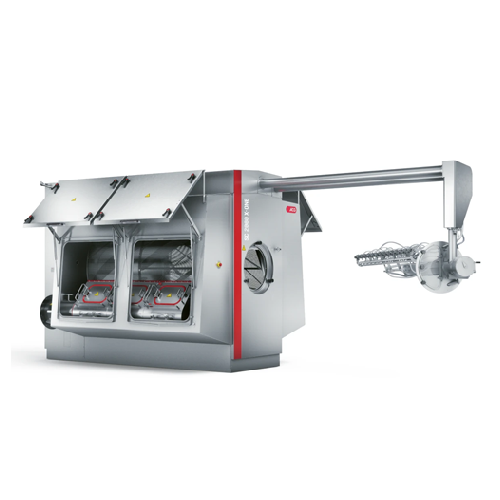
Wash-off-line system for pharmaceutical plants
Optimize your production with a versatile wash-off-line system, ensuring pr...

Automated sample preparation workstation for content uniformity testing
Streamline your laboratory workflows with autom...
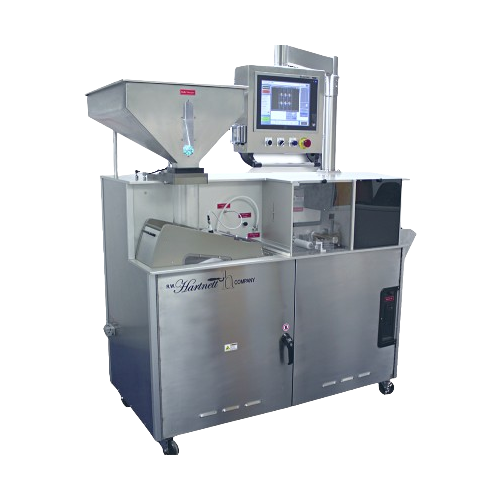

Flatbed laser drilling for tablet manufacturing
Optimize your tablet production with high-speed laser drilling, ensuring p...
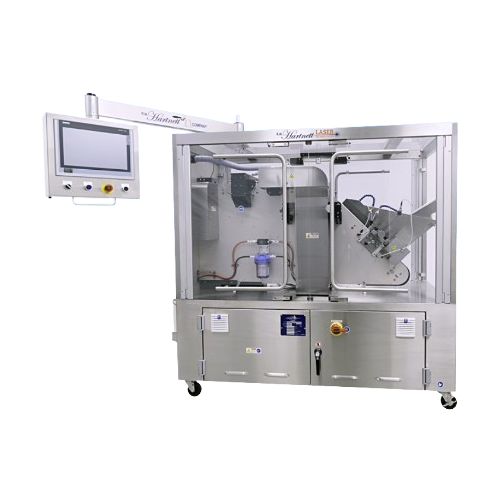

Precision laser drilling for osmotic controlled release tablets
Enhance tablet precision and control drug release with h...

Agitator bead mill for API
To achieve precisely defined API properties and safe and reproducible production, rigorous implem...
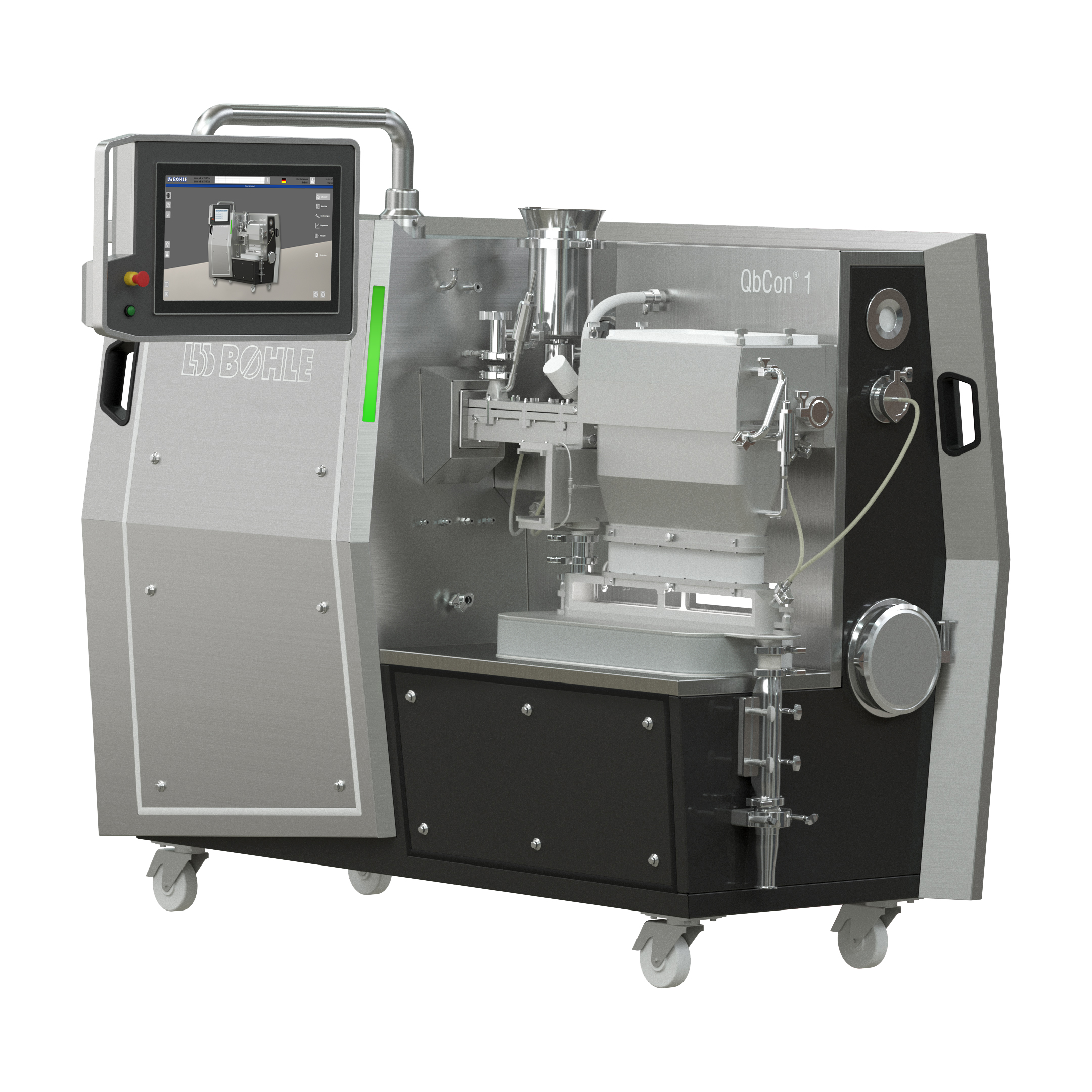

Continuous wet granulator and dryer for R&D
Pharmaceutical laboratories need compact equipment to handle and produce small...
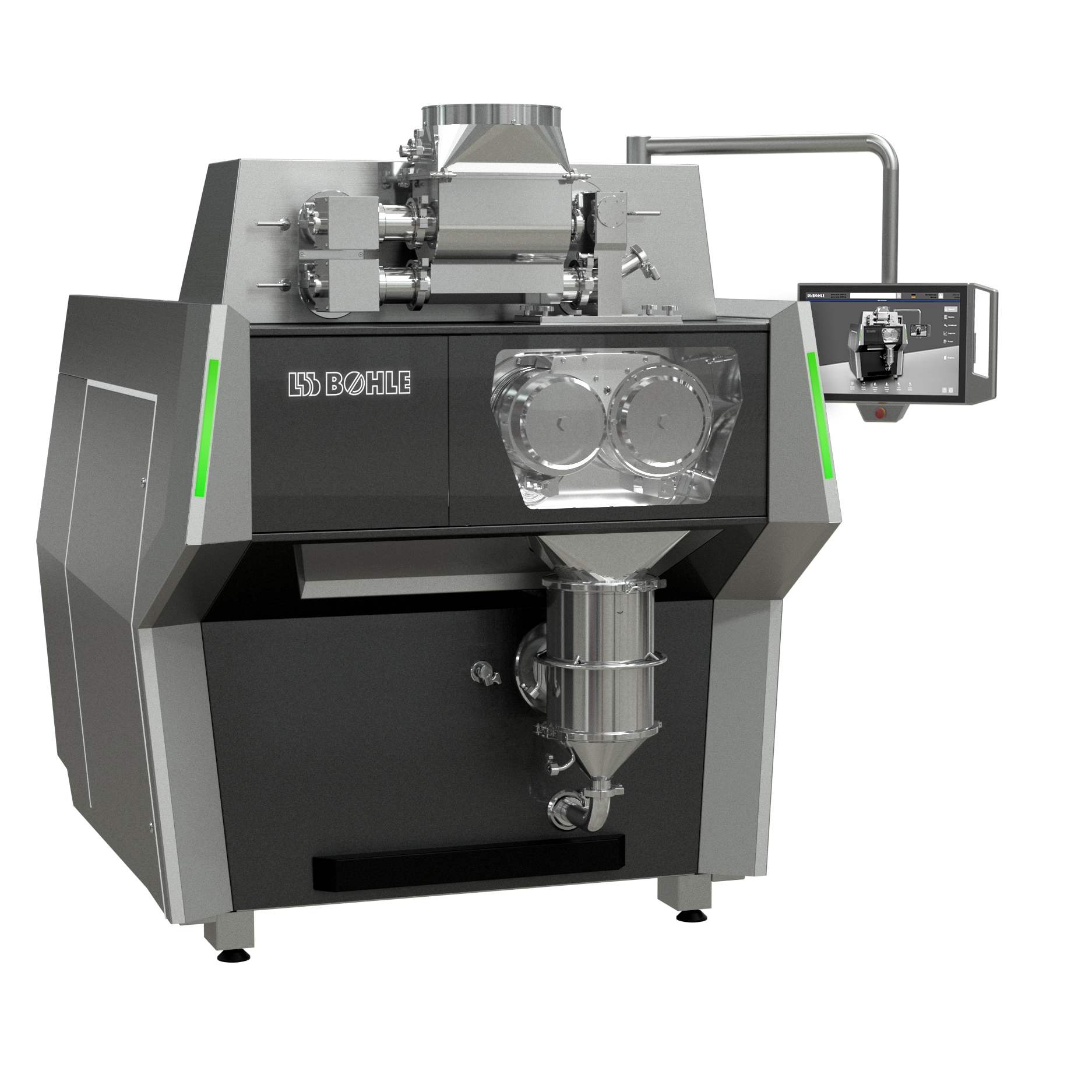

Dry granulator for pharmaceutical powders
In pharmaceutical industries, where large-volume production is the norm, compact...
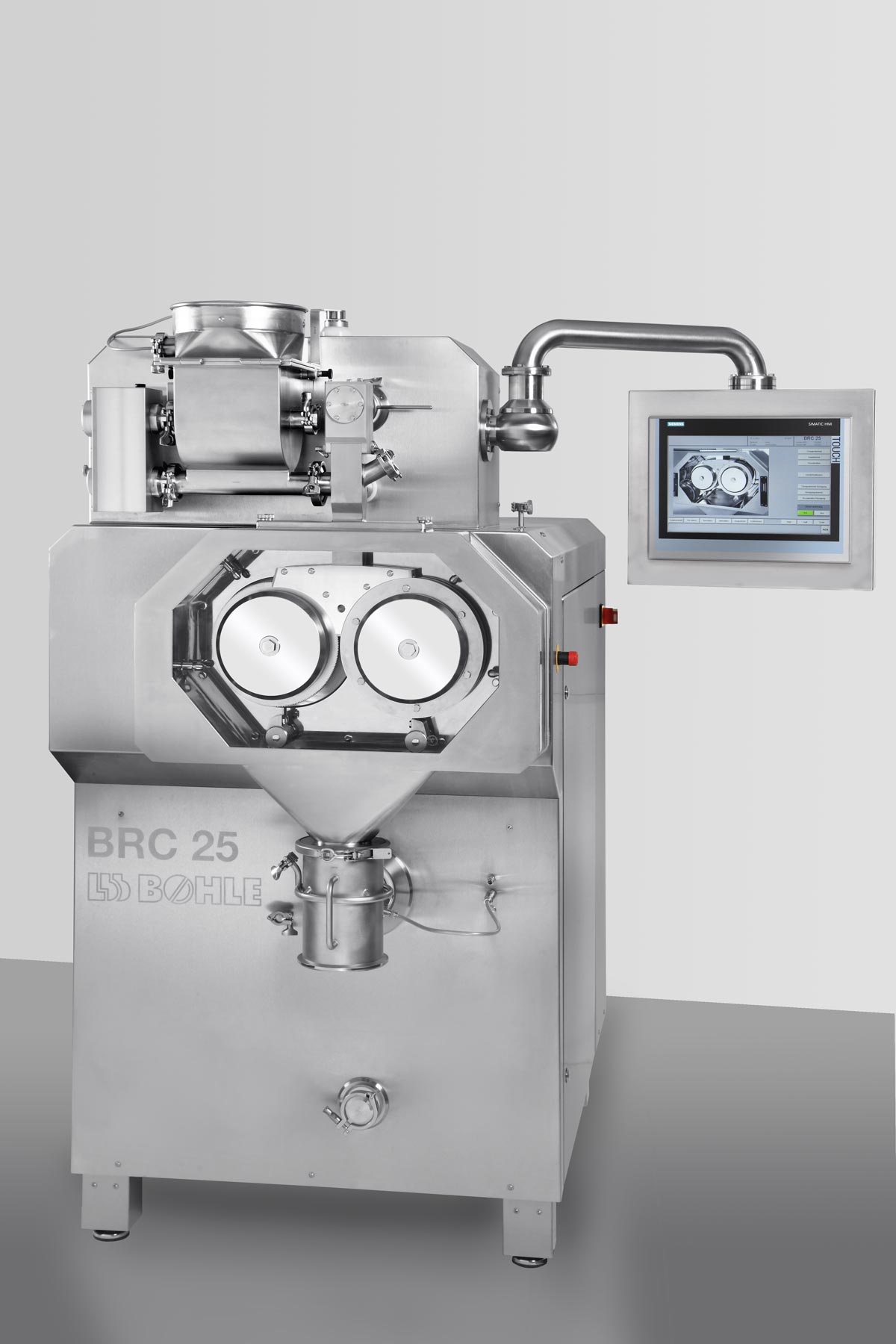

Continuous roller compactor for dry granulation of pharmaceuticals
When making tablets, pharmaceutical manufacturers ne...
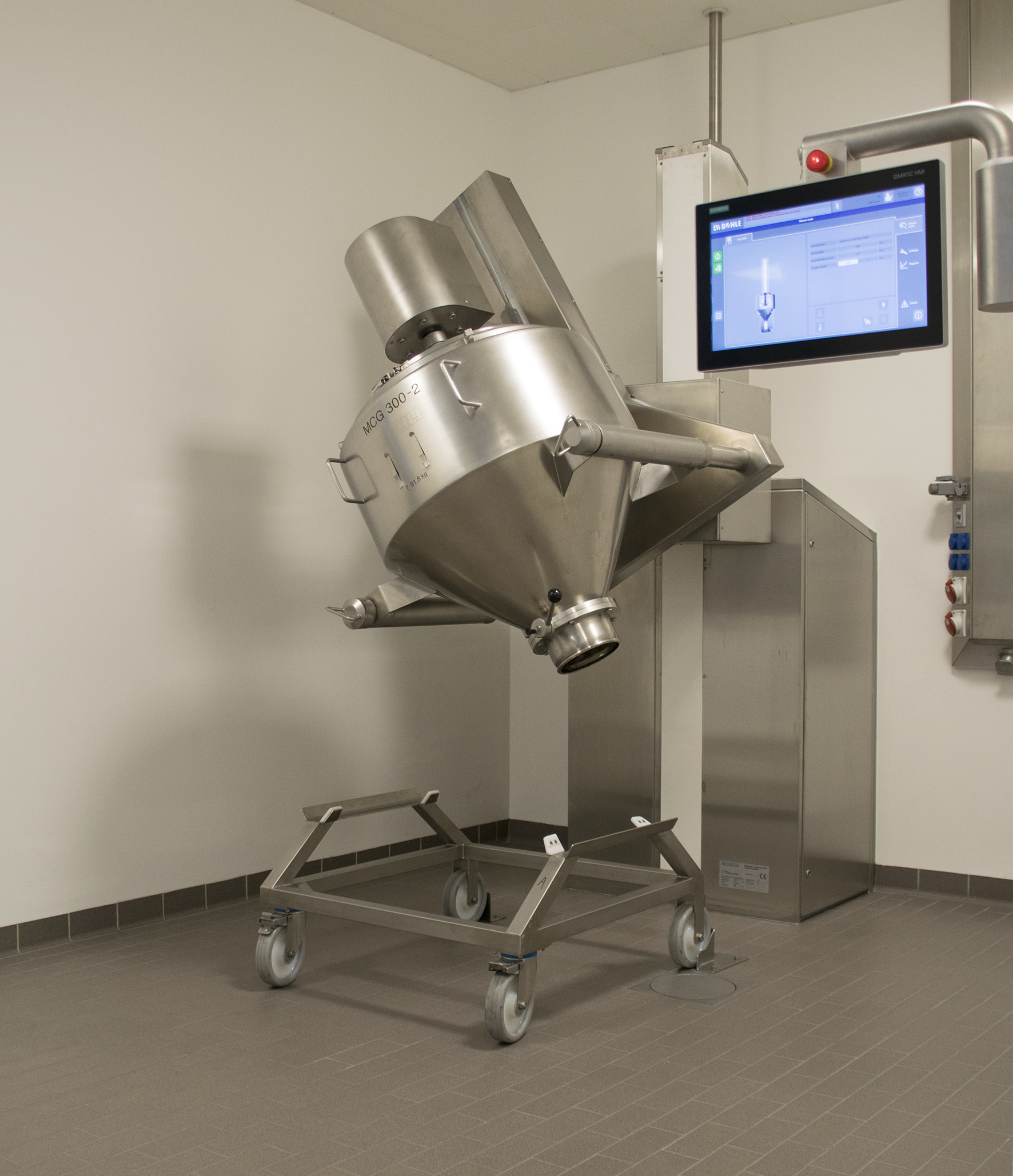

Container blender for pharmaceuticals
Manufacturing pharmaceutical solids like tablets requires using a proper blender to b...

Serialization equipment for cases
Serialization is a multi-stage process that includes printing, inspection, and labeling. ...
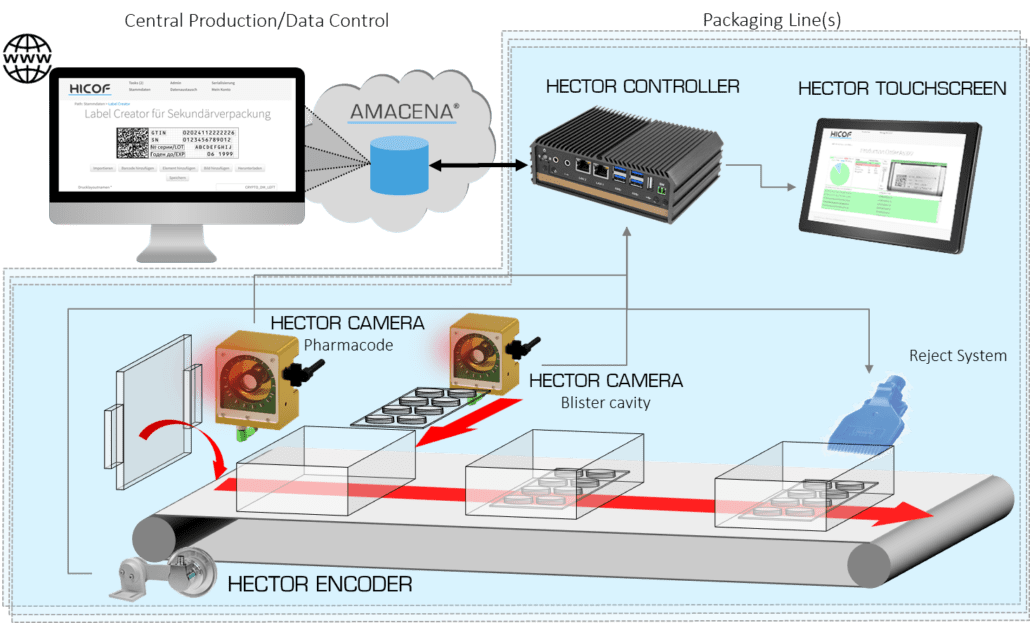
Serialization and aggregation inspection system
Including serialization and aggregation inspection systems to packaging li...

Blister inspection system
The pharma and healthcare industries widely use blister thermoforming machines to package a variet...

High Speed Visual Inspection System for Tablets
In order to ensure quality and standard specifications of tablets, capsule...

Contained Visual Inspection System
In the medicine industry, it is important to ensure there are no defects in tablets or c...
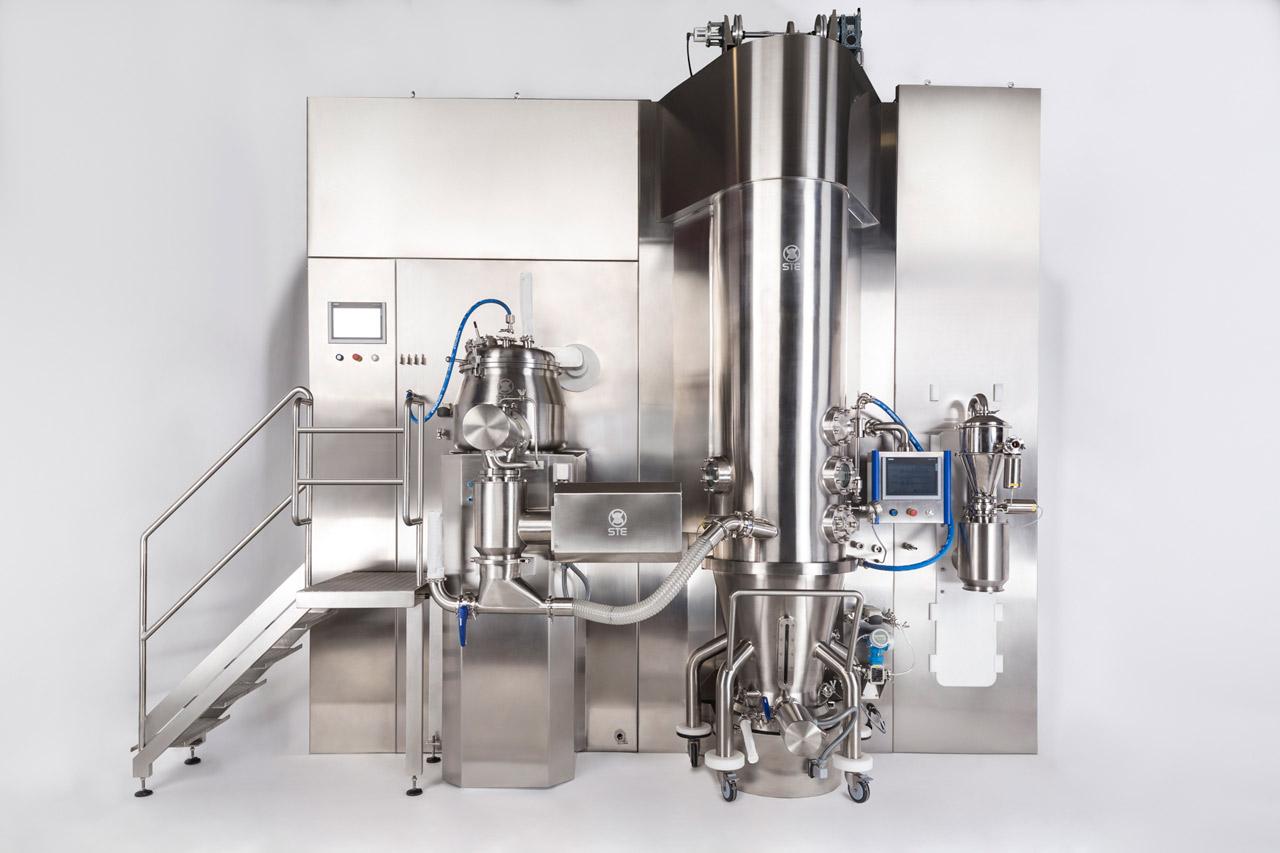

Granulation line for pharmaceutical solid dosage forms
Granulation is a common technique in production of pharmaceutical ...

Tablet counting machine
Production of pharmaceutical solid dosage forms usually require complete accuracy, flexibility, and c...

Pharmaceutical bottle unscrambler
Pharmaceutical packaging industry requires the ability to quickly manage the process yet ...

Dessicant inserting machine
Desiccant canisters play an important role in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. T...
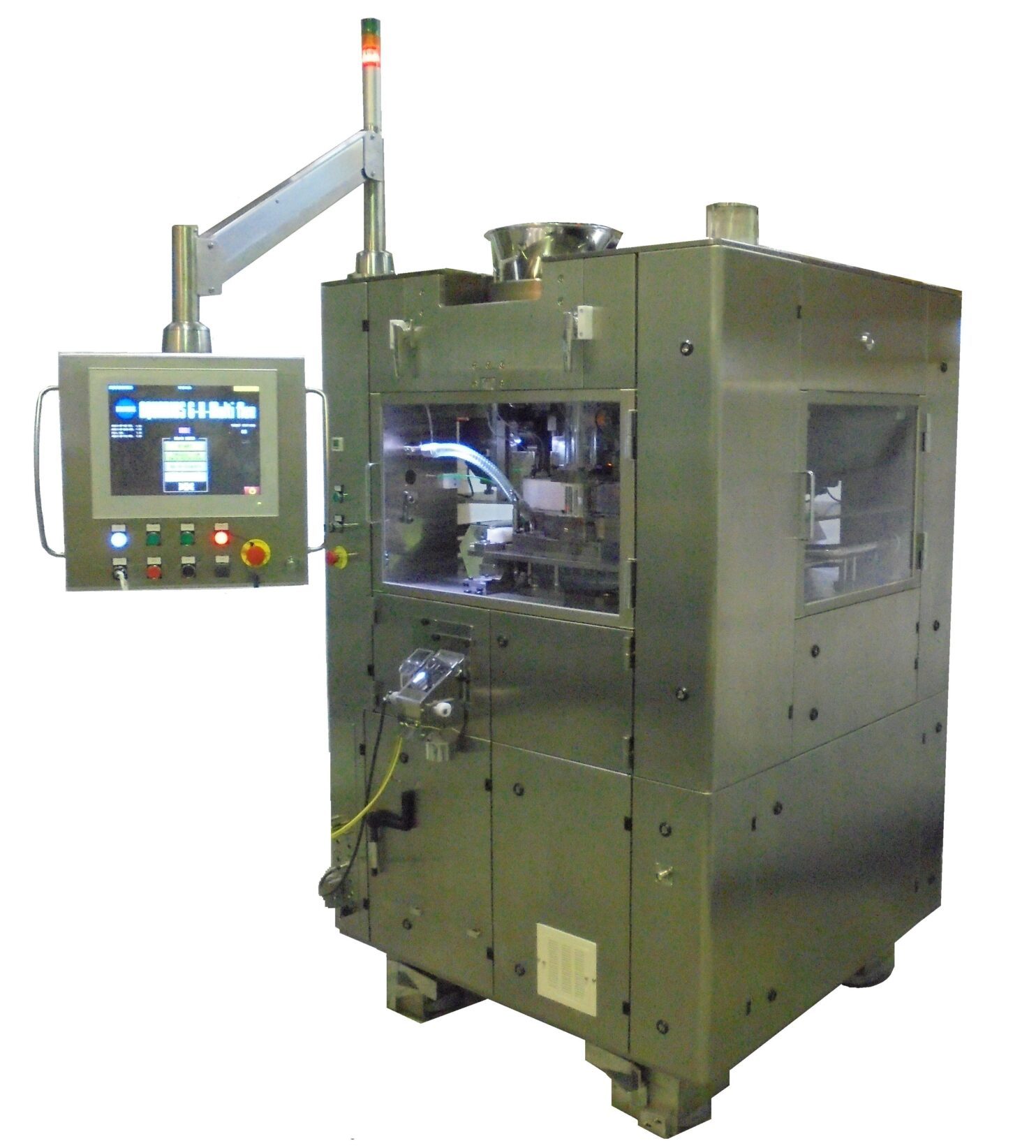

High Speed Double-Sided Tablet Press
To achieve as much as double the output of single-sided tablet press, the upper and lo...
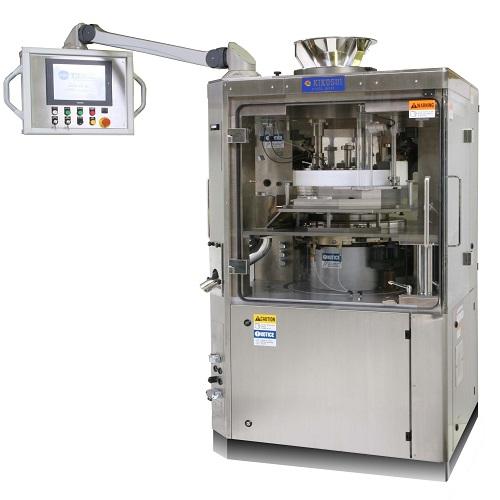

High Speed Tablet Press
High speed pharmaceutical tablet presses convert powder to tablets. The operations should be quick an...
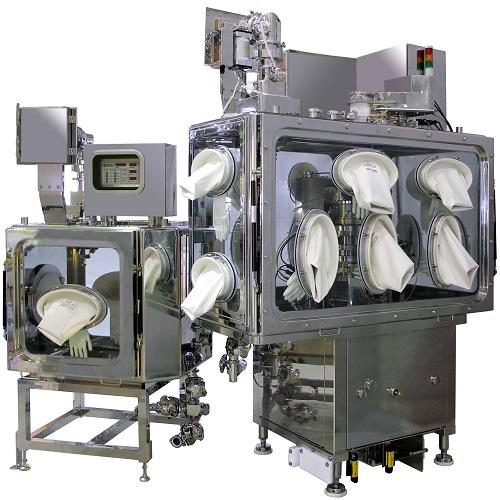

High Speed Containment Tablet Press
High speed containment presses make pharmaceutical tablets in closed environments with ...
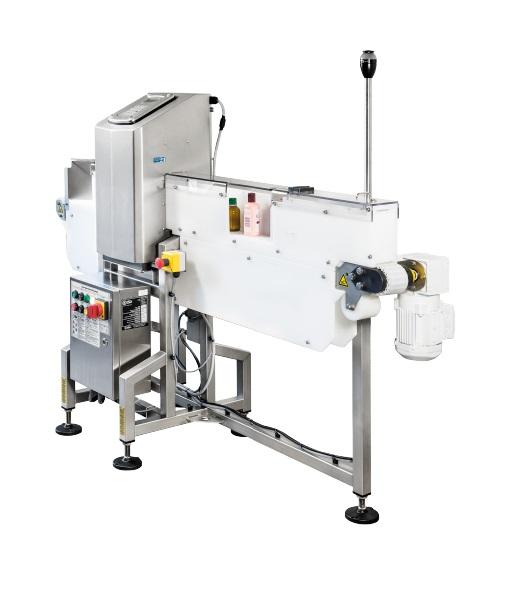

Metal detector for bottles
For metal contamination detection in finished products that are bottled, traditional solutions re...

Dust-tight metal detector for tablets
For FDA-compliant production of tablets, the elimination of airborne dust containing ...
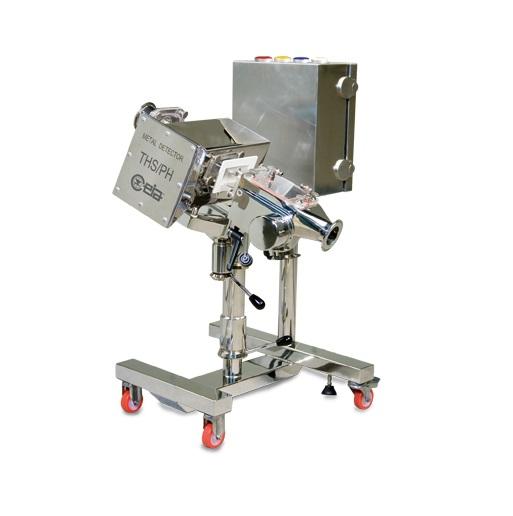

Wash-in-Place metal detector for tablets
Where hygiene and decontamination are vital, traditional pharmaceutical metal dete...
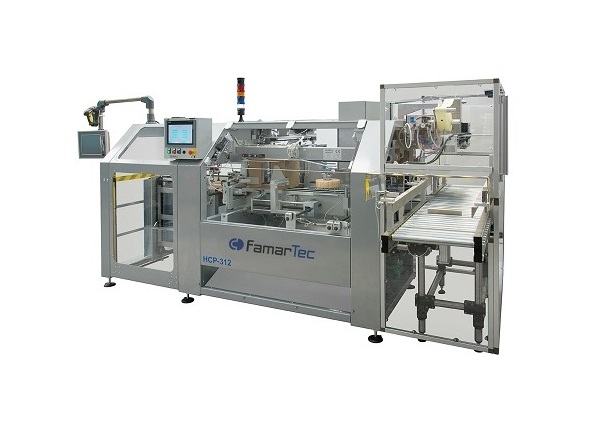

Side-load case packer
As the final stage in the packaging process, an automated case-packing solution can ensure that your co...
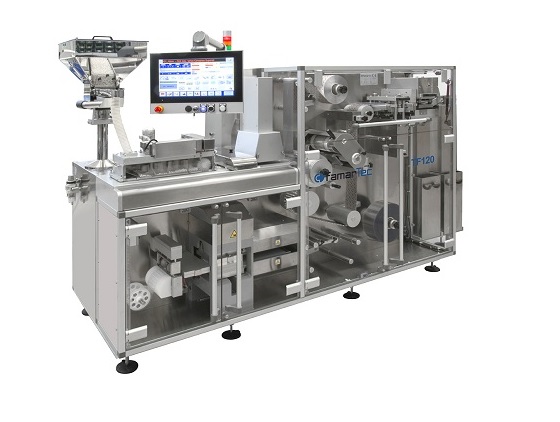

Entry-level blister packaging machine
Blister packaging is a popular packing method in the pharmaceutical industry thanks t...
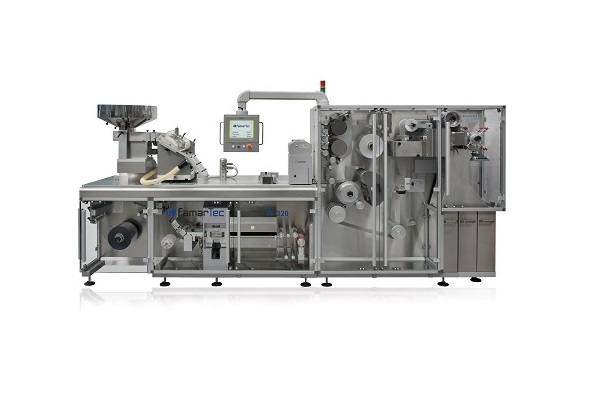

Industrial blister packaging machine
High-volume, fully-automated blister packaging is the perfect choice for large scale p...
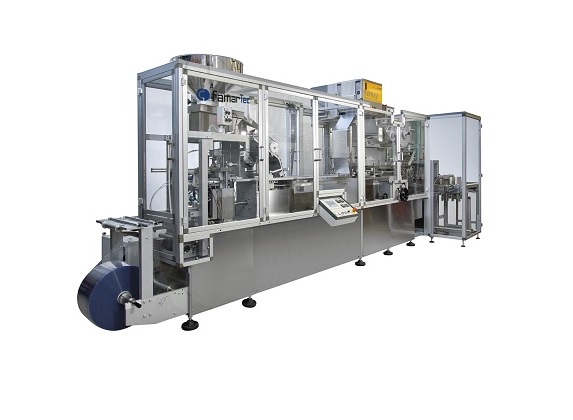

Plate sealing blister machine
Blister packaging is the preferred choice for most large-scale pharmaceutical lines, and a pla...

Automatic blister packaging machine
Automated blister packaging is a popular choice for pharmaceutical production thanks to...
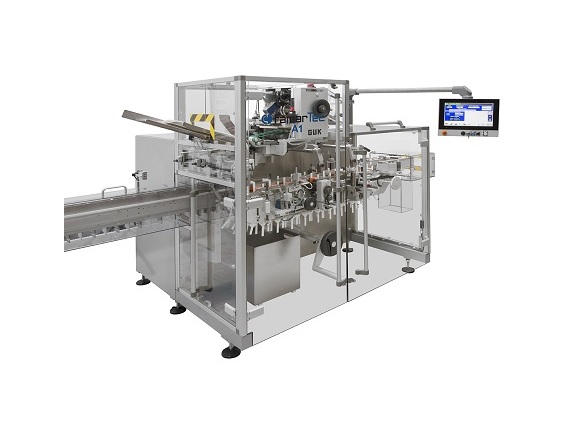

Horizontal cartoner for pharmaceutical applications
Automatic cartoning for cosmetic or pharmaceutical products is a requ...
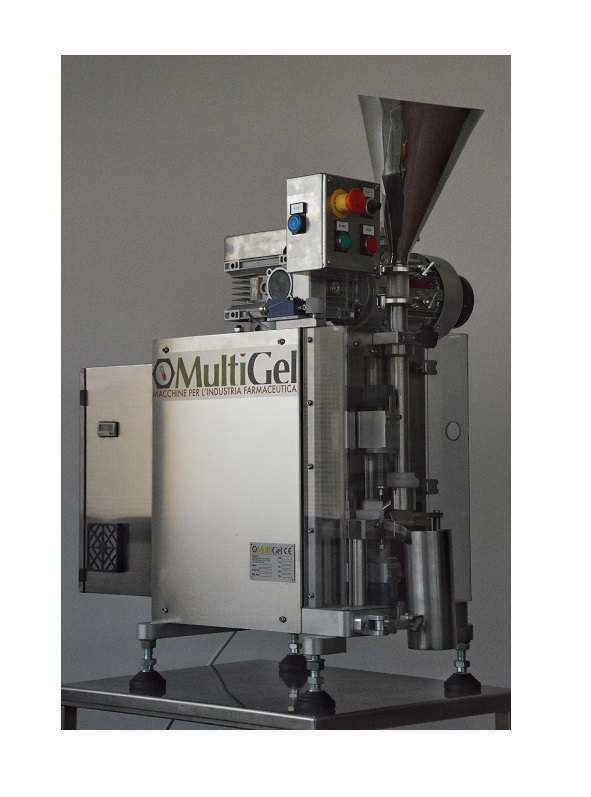

Benchtop tablet press
For lab work or small-scale production, a purpose-designed tablet press that meets your exact requireme...
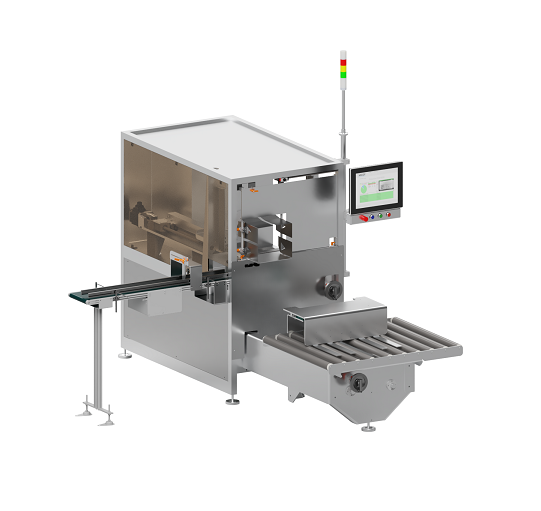

Semi-automatic case packer
Pharmaceutical products require complete traceability throughout the production cycle. For smalle...
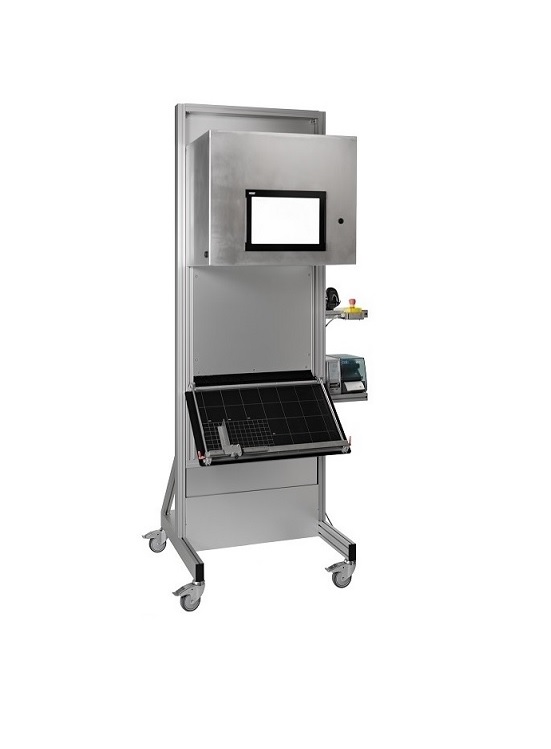

Stand-alone aggregation station
The aggregation of pharmaceutical products for tracking purposes is already compulsory in ma...
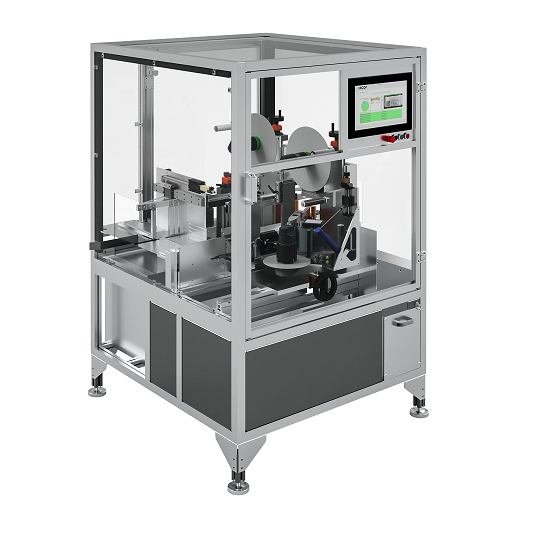

Serialization coding and labeling equipment
In the pharmaceutical industry, product serialization is the cornerstone of al...
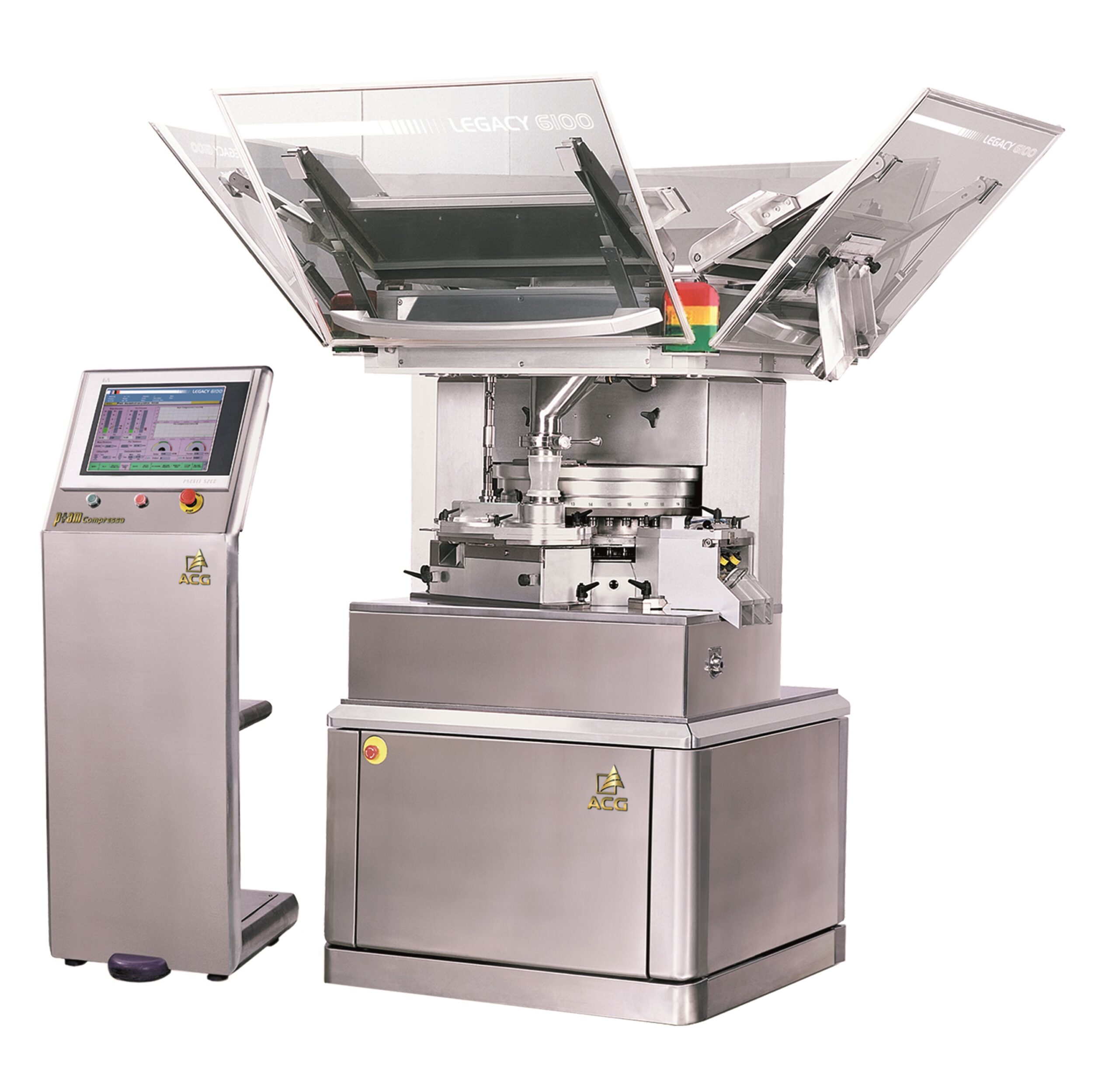

Economic tablet press
Successful pharmaceutical manufacturers know that high quality, reliable equipment is essential in orde...
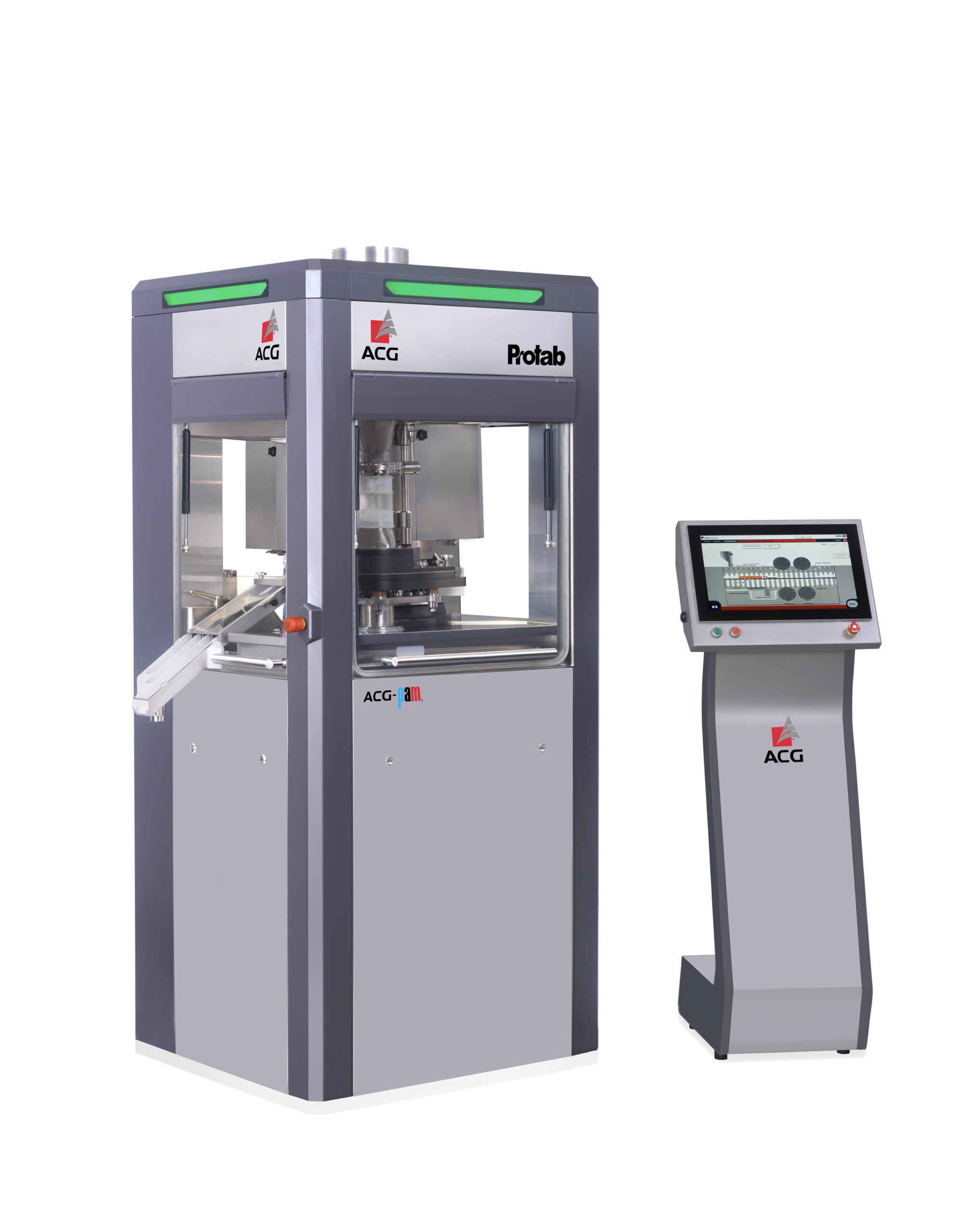

Single rotary tablet press
Creating batches of consistent high quality pharmaceutical grade tablets from your powdered ingre...
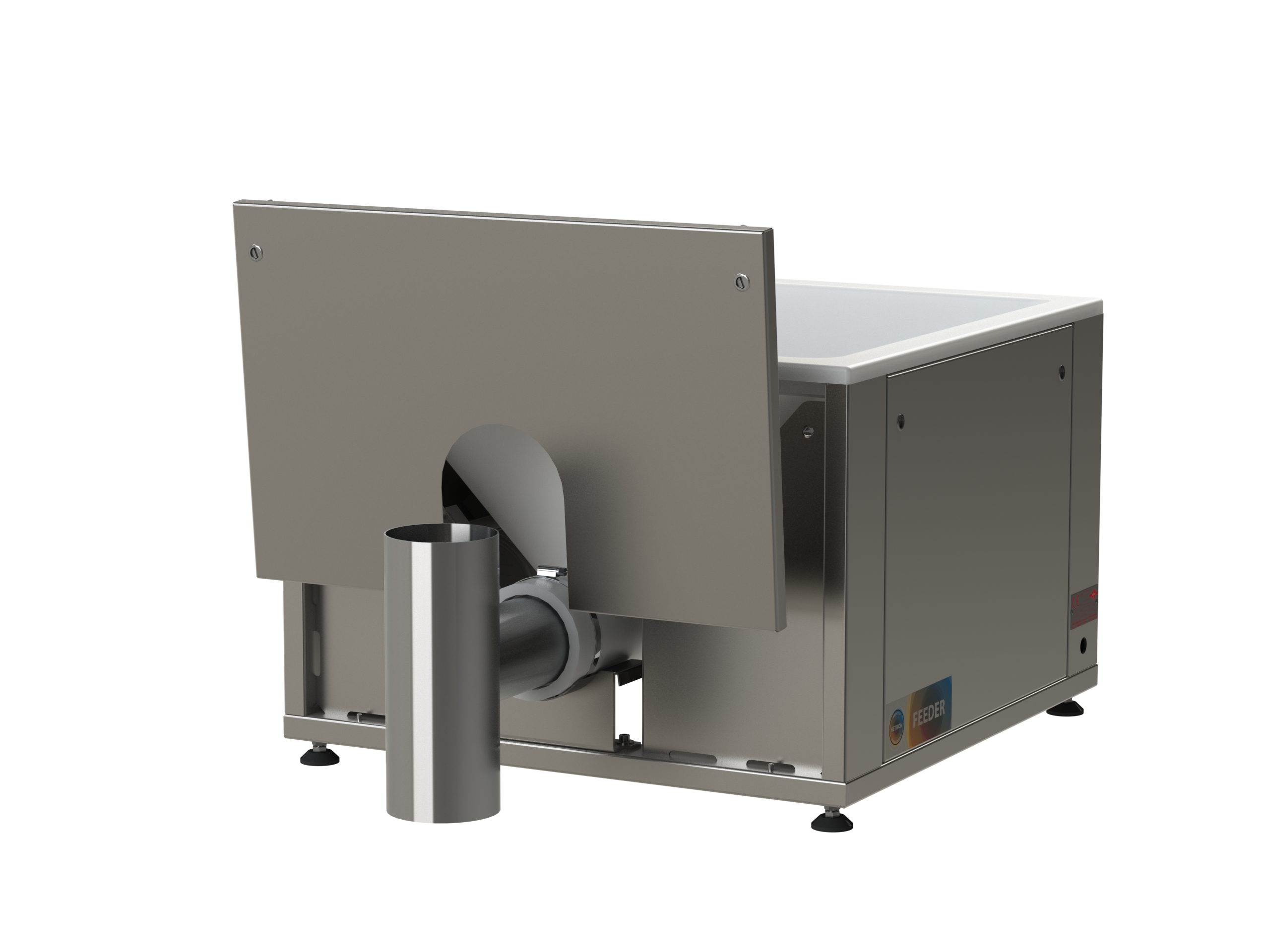

Feeder with flexible wall hopper
The varying properties of dry powder products mean that specialized feeders are required fo...
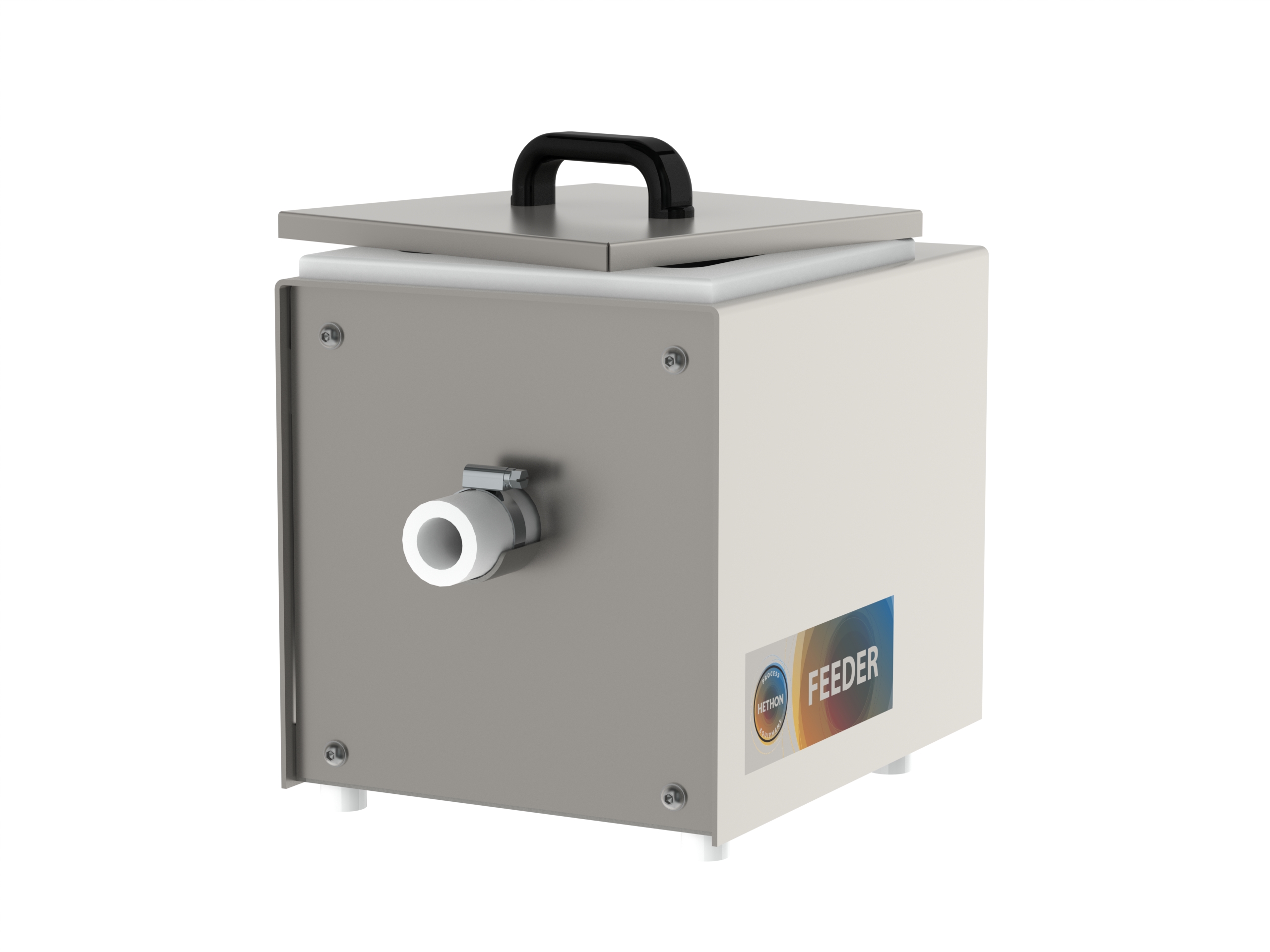

Small feeder with flexible wall hopper
In many laboratory applications and production processes, smaller quantities of powd...
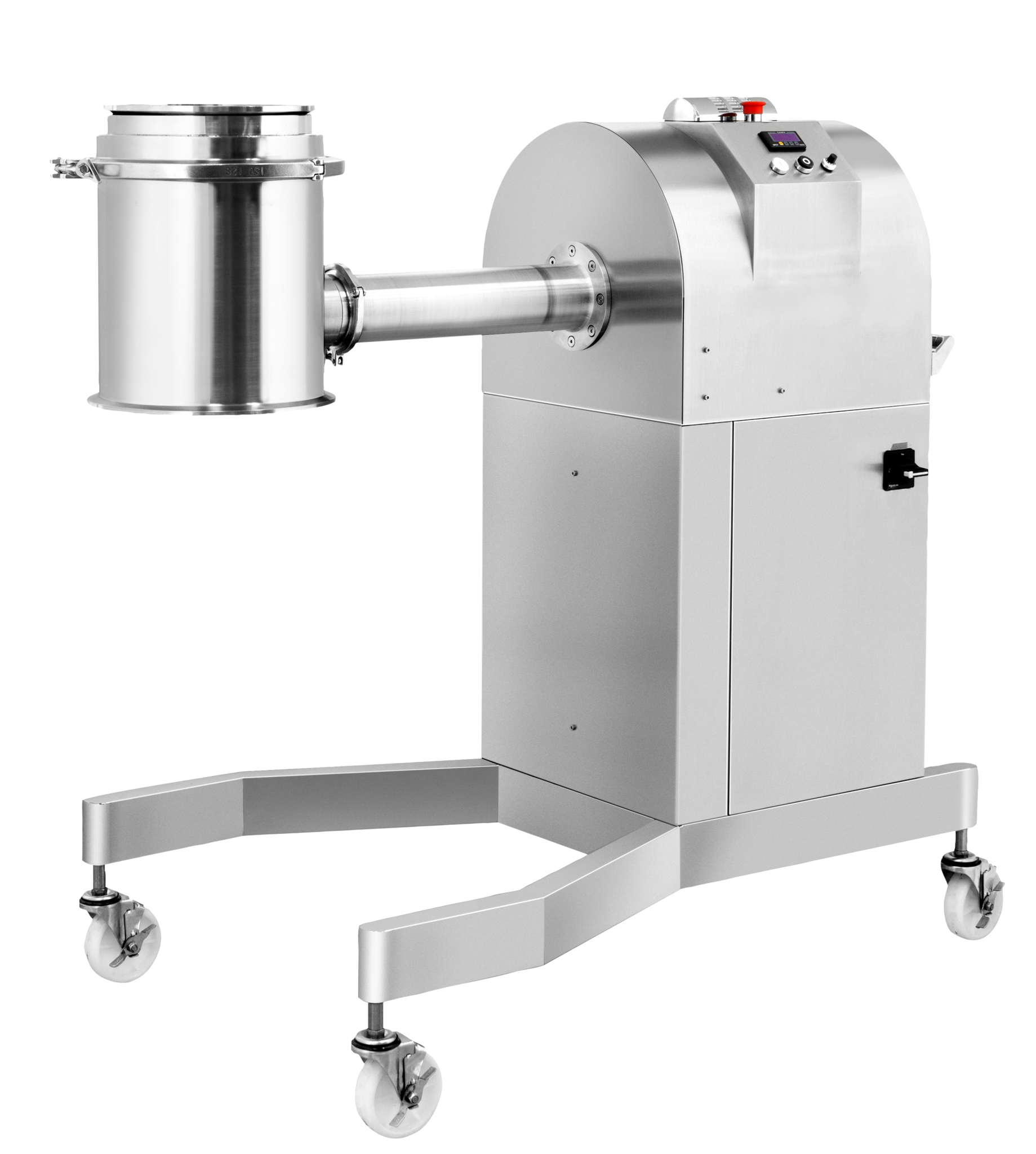

Conical mill for drug formulation
The efficient size reduction of granular powders is a key step in many pharmaceutical pro...
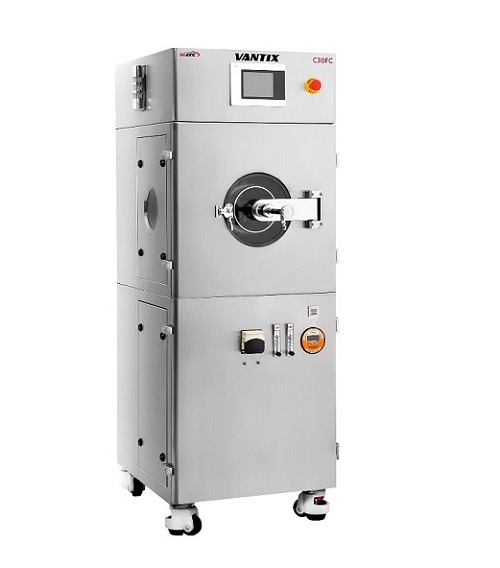

Automatic tablet coater for lab scale
The ability to coat tablets in an even and controlled way is an important stage in th...
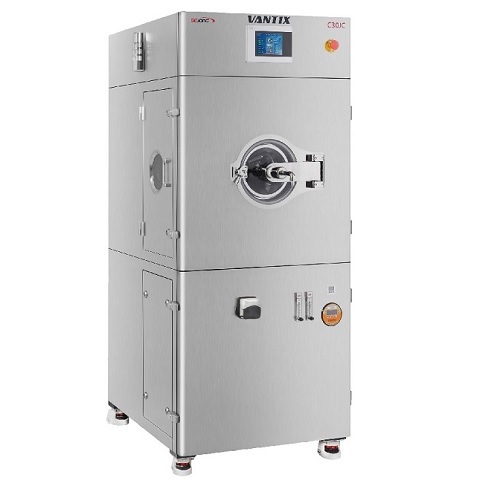

Tablet auto coater for lab scale
Many pharmaceutical doses in tablet form require a coating before they are ready for use. T...

Single and double layer tablet press
High performance tablet presses that are capable of producing both single and double-l...
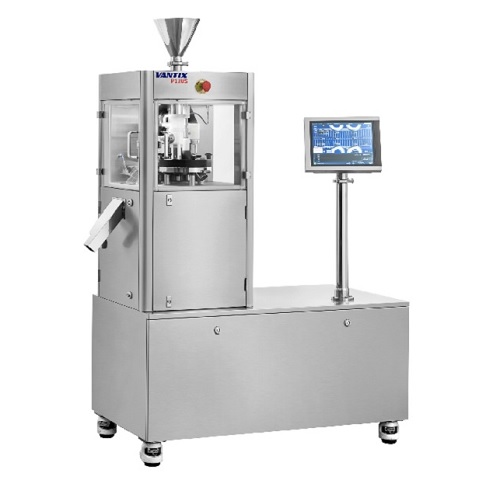

Lab scale single layer tablet press
Automated pressing of tablets saves time and improves quality. In R&D or laboratory...
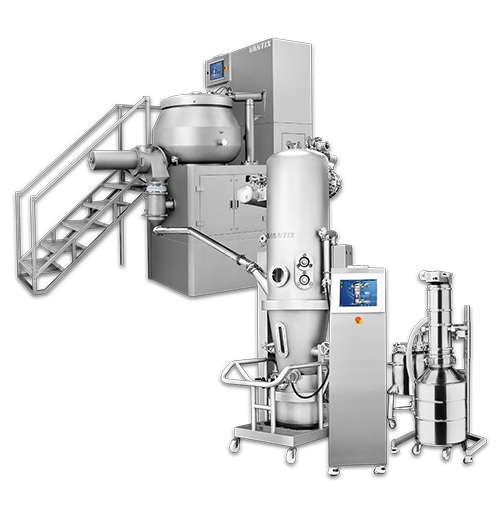

Granulation line of mixer and fluid bed dryer
A complete granulation line allows for the mixing and granulation of pharmac...
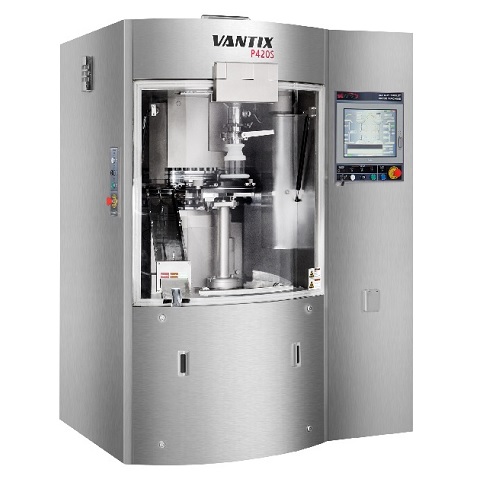

Single layer tablet press
High performance tablet presses for the modern production environment need to be fast, accurate an...
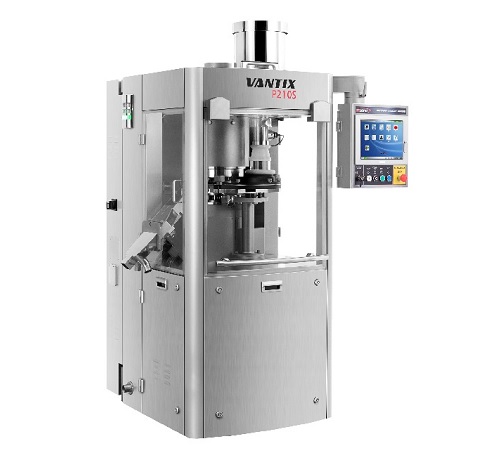

Rotary tablet press
For pharmaceutical tablet producers looking to reduce waste, costs and increase production volume, a hig...
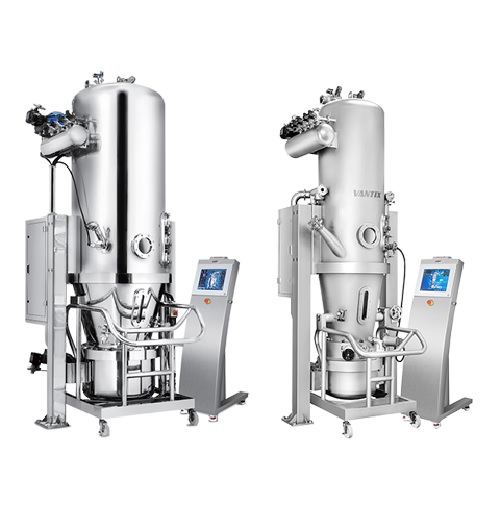

Fluid bed dryer for production scale
Fluidized bed drying (FBD) is a common process in the pharmaceutical industry for dryi...
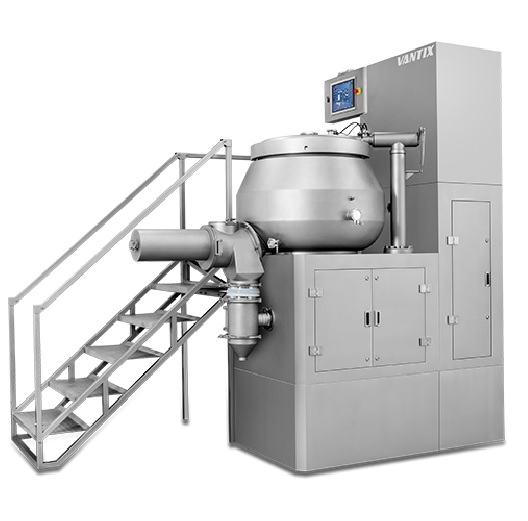

High-shear mixer
For the efficient mixing of larger batches of pharmaceutical compounds and high-shear mixer provides the opti...
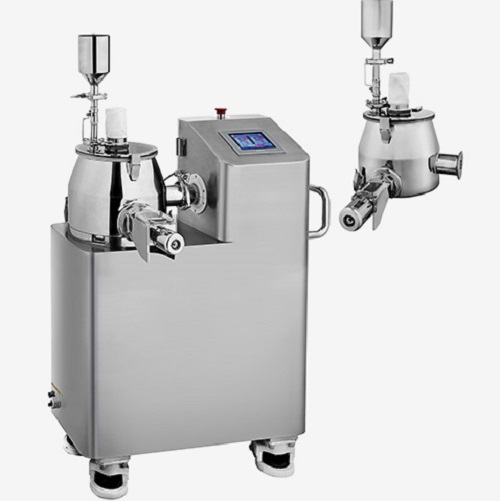

Entry-level high-shear mixer for drug formulation
For pilot and lab-scale pharmaceutical formulations, a high-shear granu...
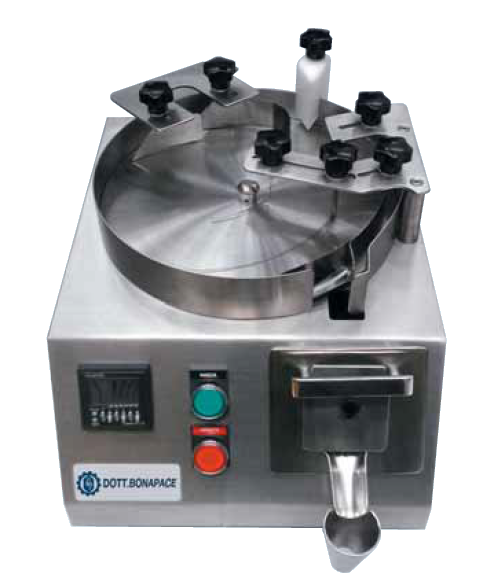

R&D electronic counter for capsules and tablets
This machine has been designed to offer an ever-precise and reliable count...
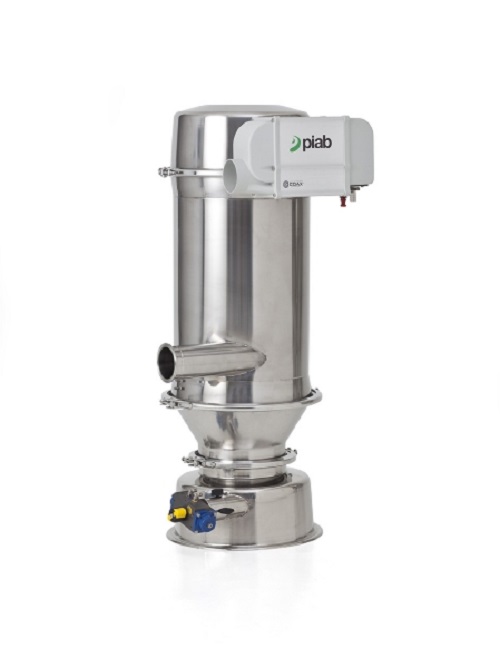

Premium vacuum conveyor
When you have a need to tailor make your conveyor and still have the high requirement on hygiene, e.g...
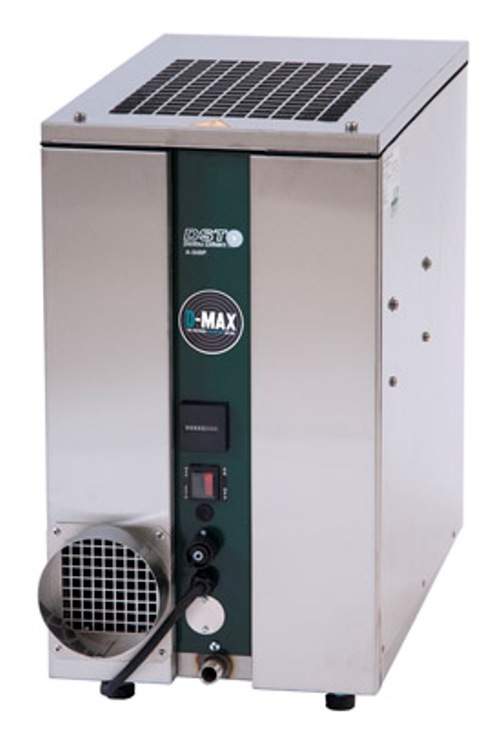

Sorption dehumidifier with air-chilled condenser
It is not always possible to duct out the wet air from a dehumidifier ser...
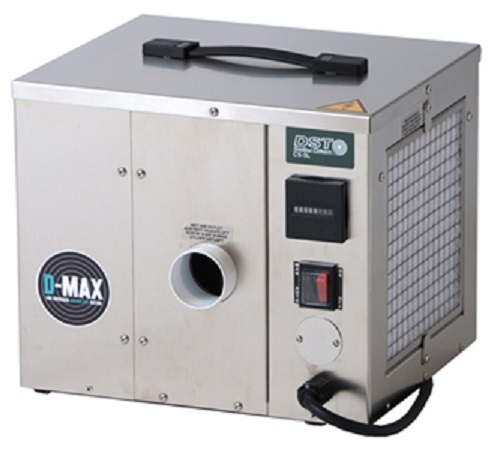

Small portable dehumidifier
Water damaged areas require dehumidification to limit the damage and prepare the area for restor...
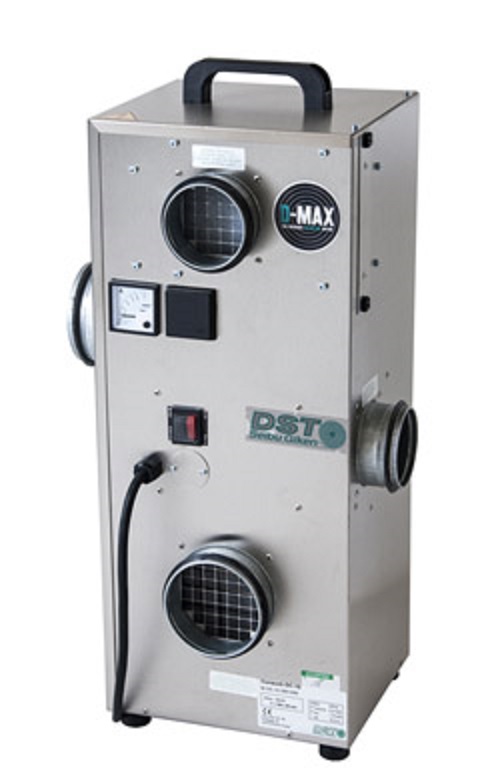

Sorption dehumidifier for large temperature differences
Small, humid areas can be difficult to dehumidify in humid ambien...
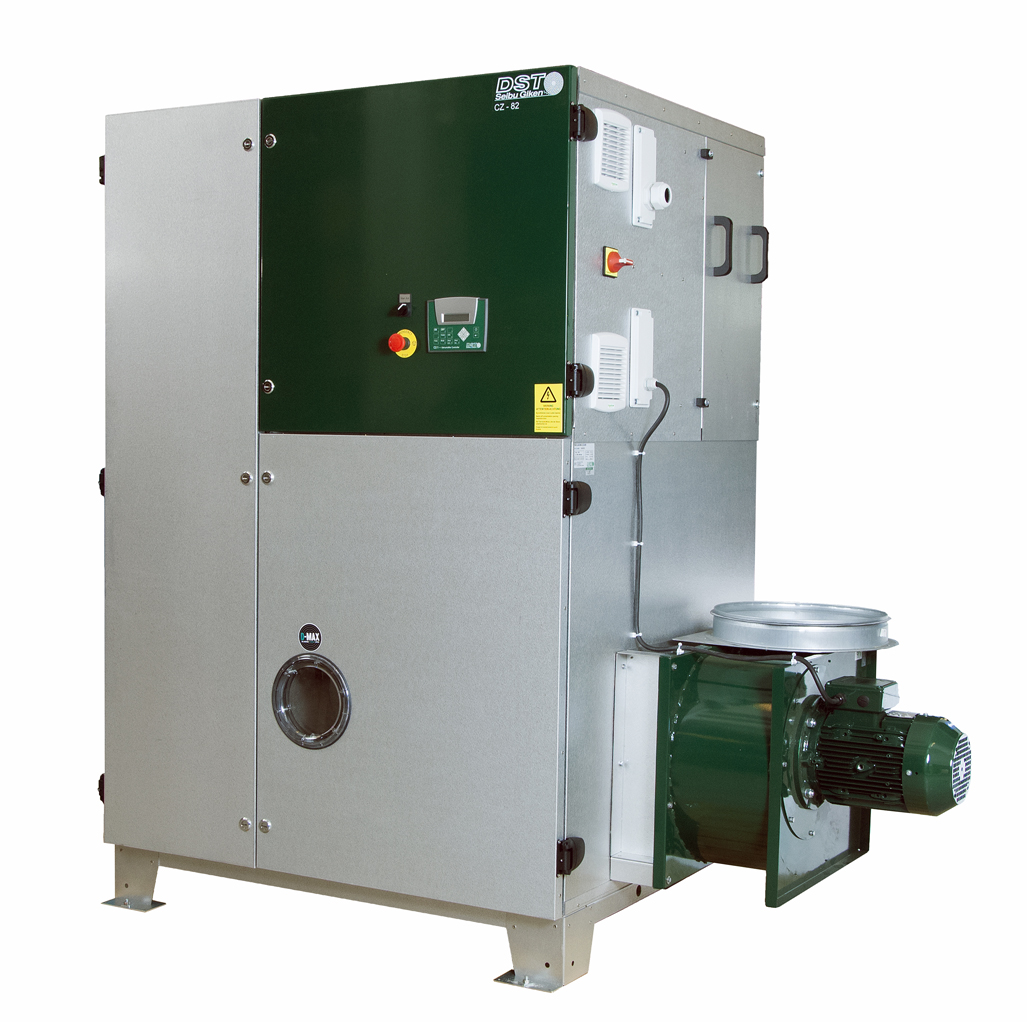

Sorption dehumidifier for deep drying
Humid ambient conditions such as those in tropical climates make dehumidification mor...
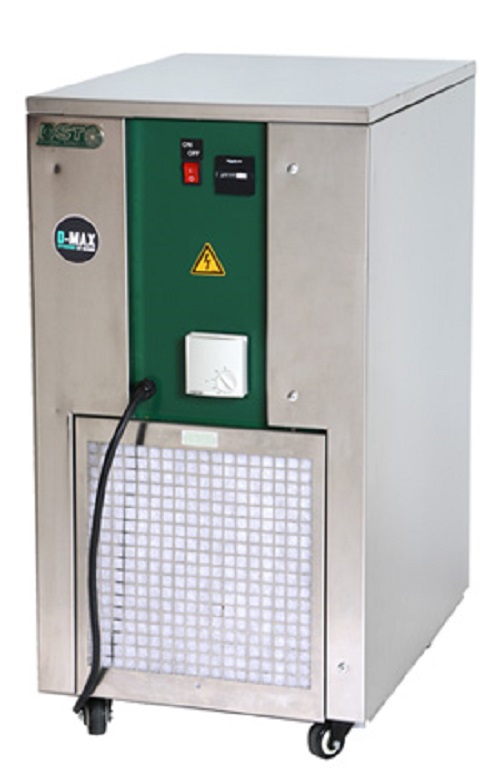

Dehumidifier for difficult wet airflows
Sealed rooms can be challenging to dehumidify with ordinary dehumidifiers. The wet ...
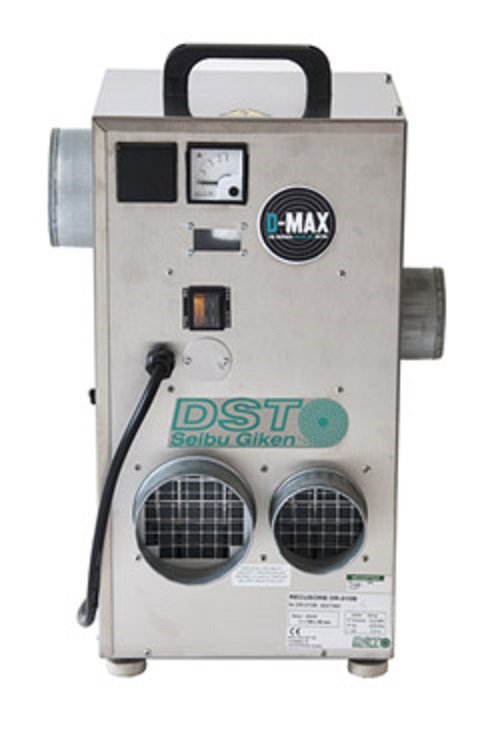

Sorption dehumidifier for overpressured rooms
Small humid spaces, used for processing or storage, often need a simple dehu...
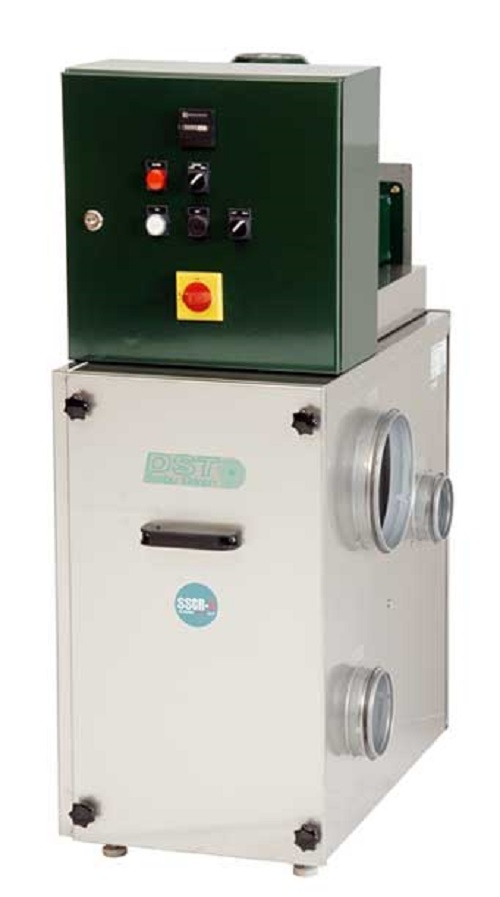

Heat recycling sorption dehumidifier
Facilities that handle large amounts of water can become very humid. High humidity may...
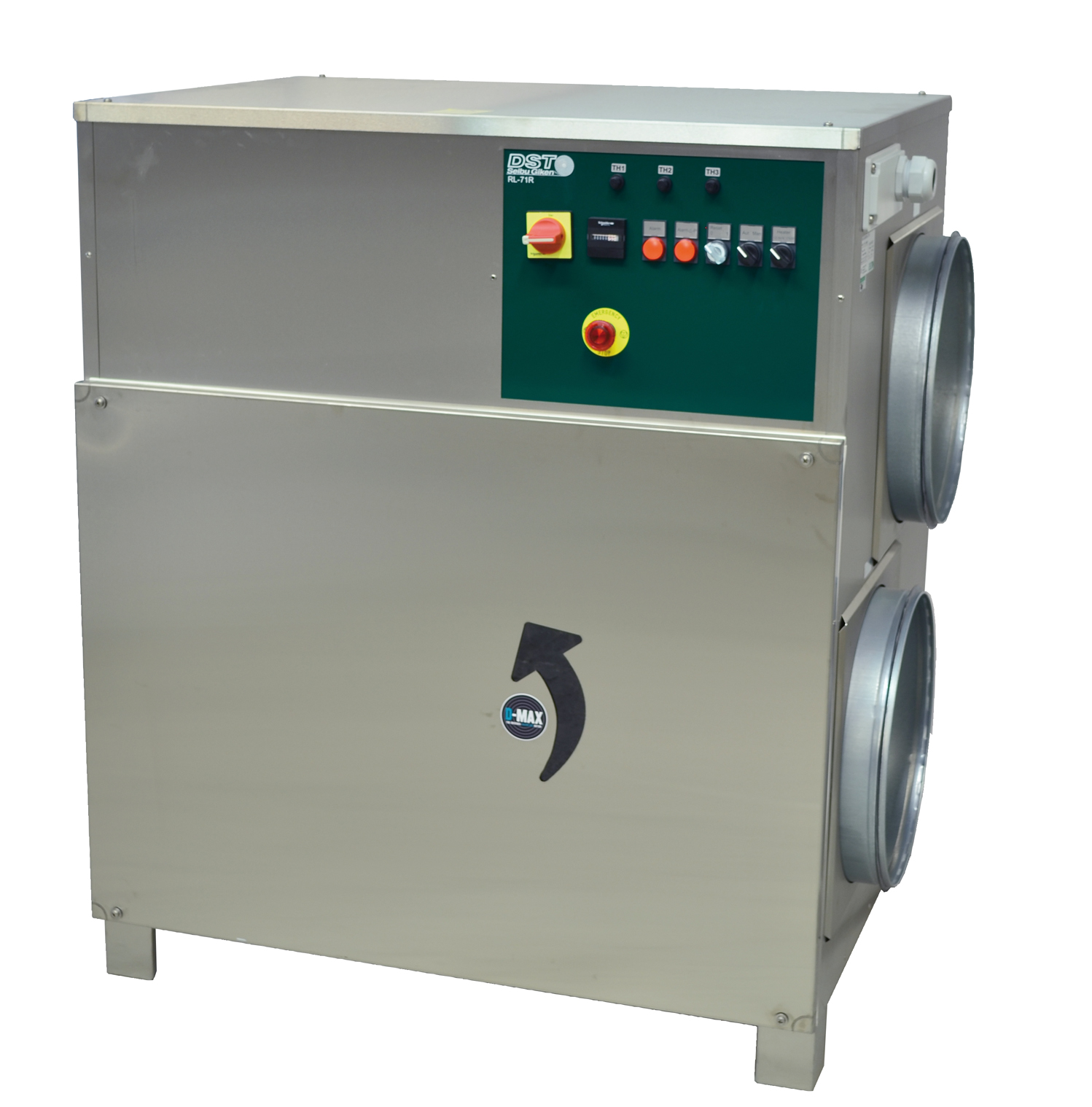

Industrial desiccant dehumidifier
Dehumidification of medium sized manufacturing and processing facilities can be a dauntin...
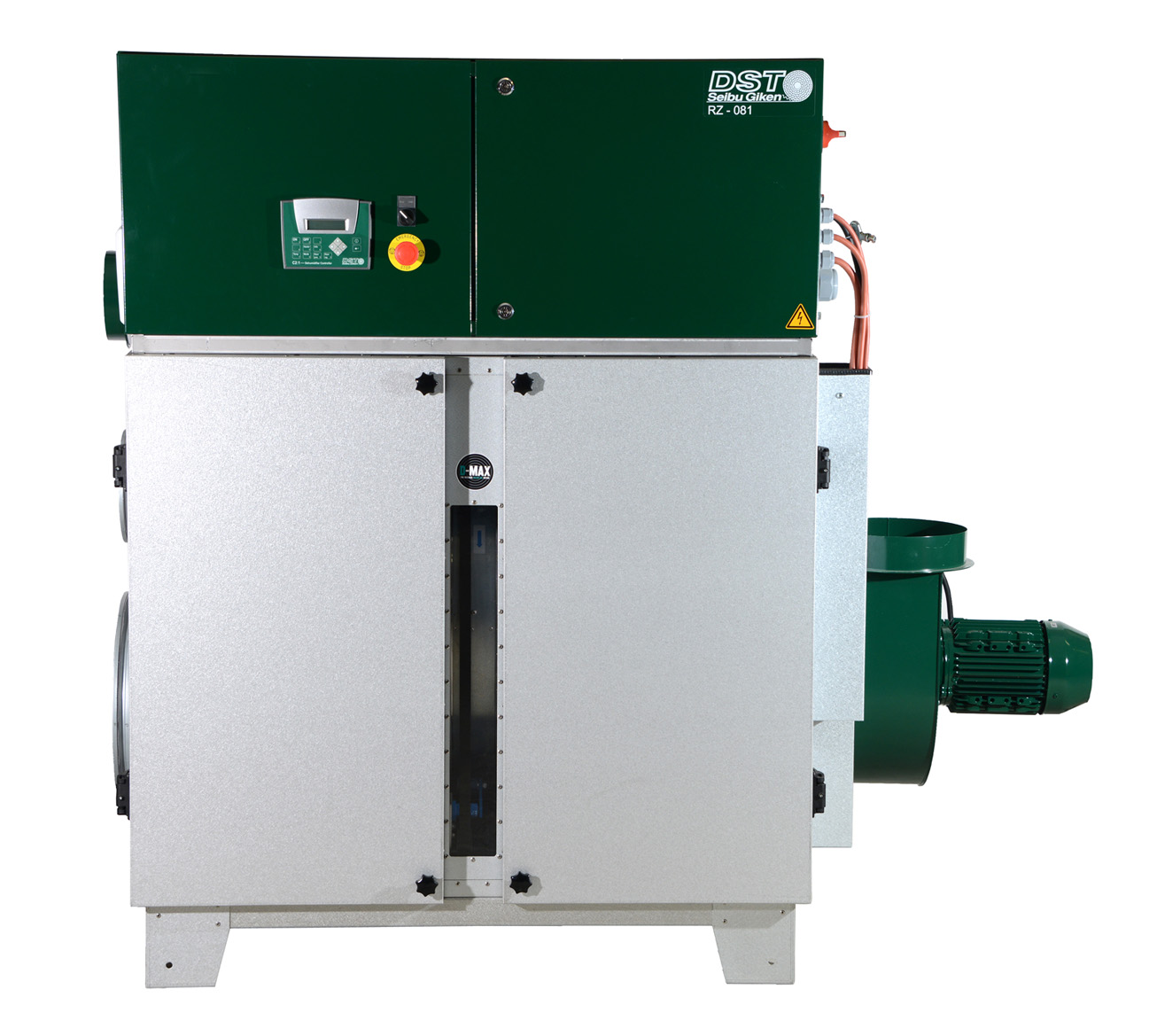

Large scale desiccant dehumidifier
Moisture sensitive processing and storage facilities need low humidity environments to s...
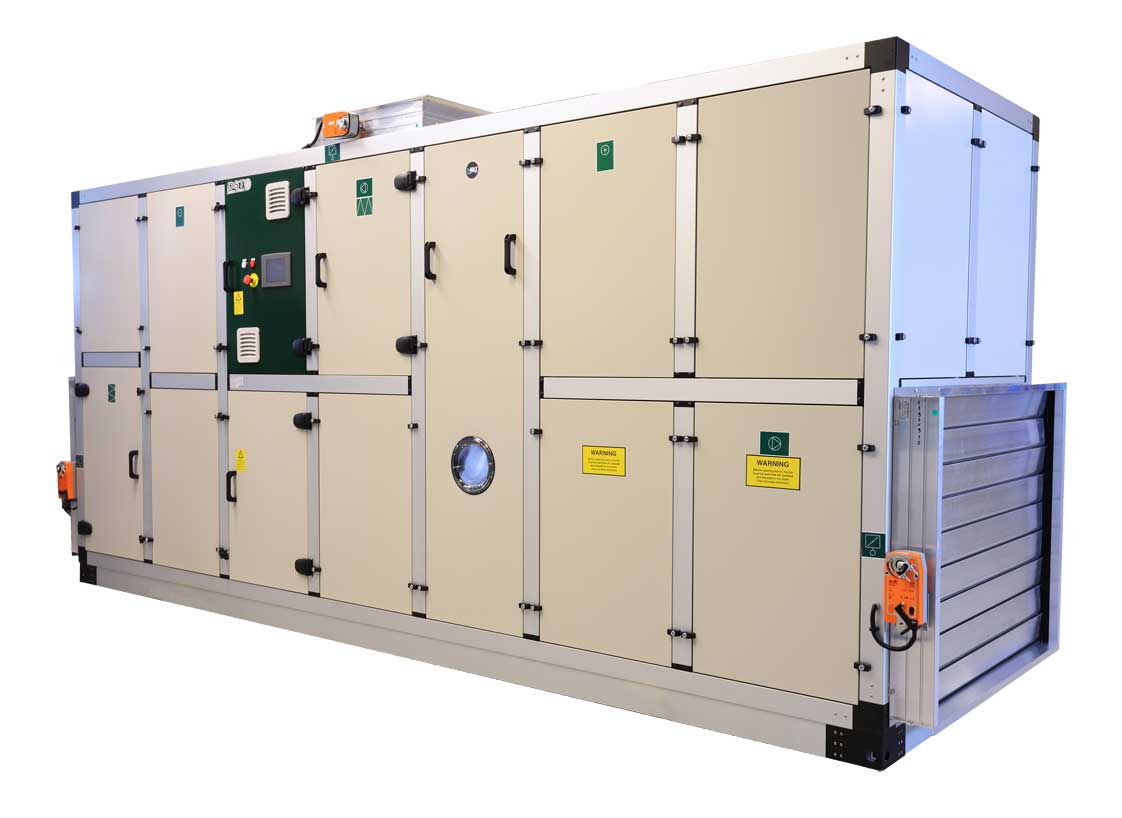

Customizable dehumidifier
Dehumidification needs can vary significantly from one project to another. Dehumidifiers with a fi...
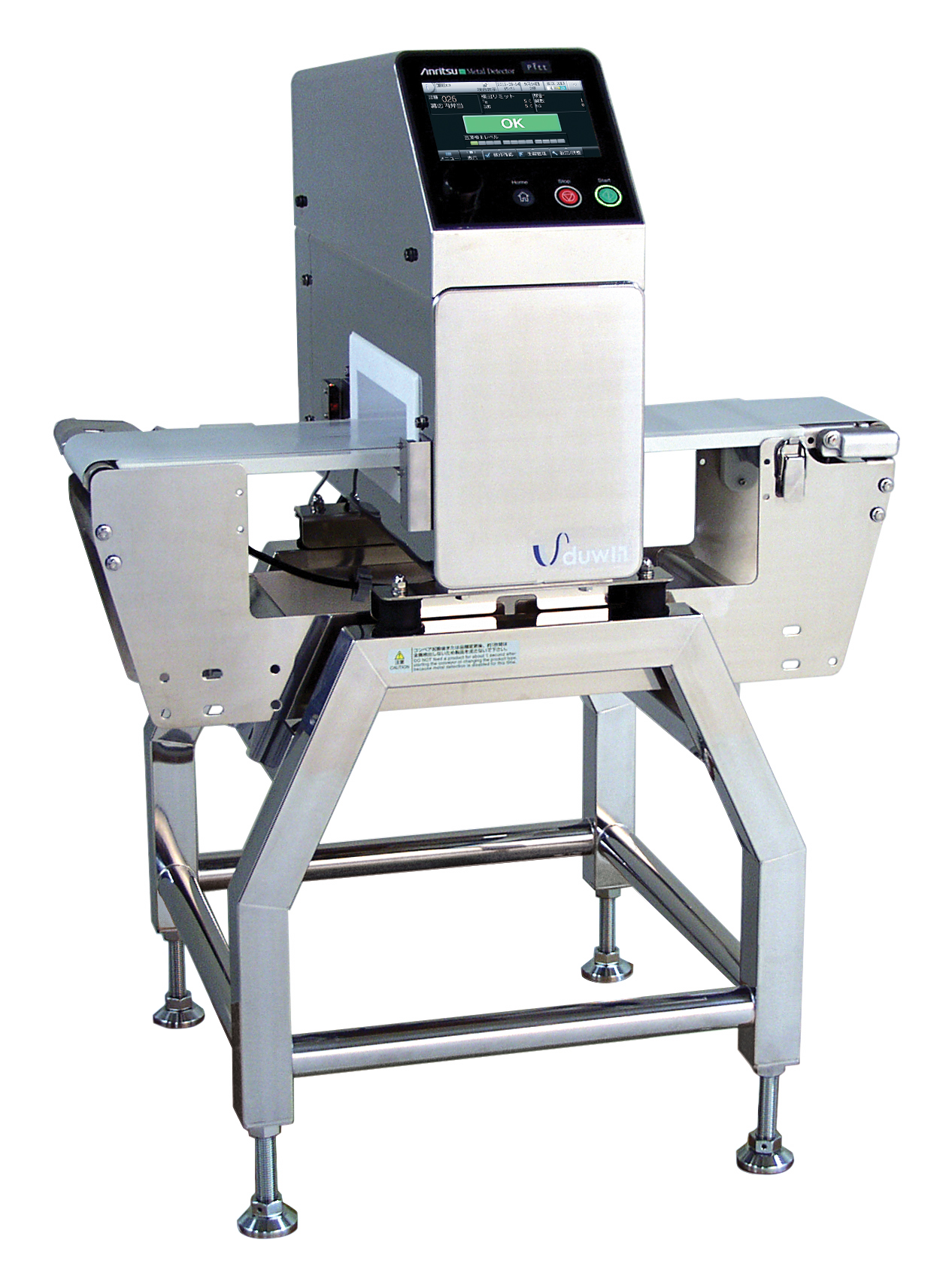

High-sensitivity metal detection system
Highly efficient metal detector with enhanced quality control and reporting capabil...
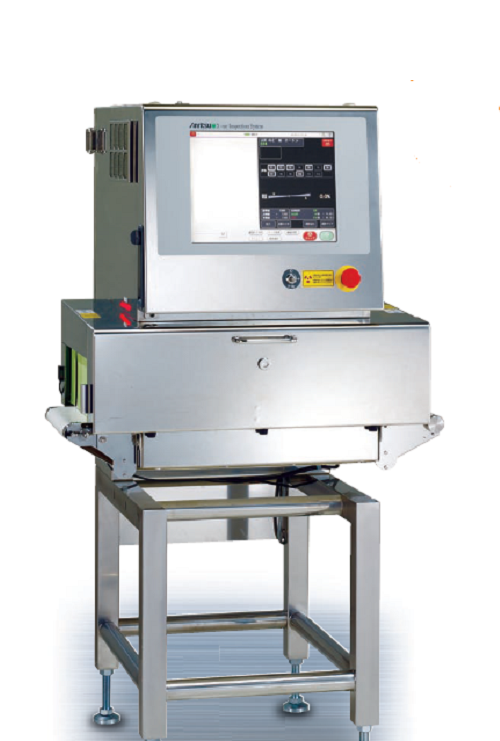

Entry-level X-ray inspection system
Without compromising on performance, if you need an entry level x-ray inspection system...