Making Gypsum!
Find innovative production technology for making gypsum and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Gypsum is a naturally occurring mineral that serves many purposes, with the United States producing the largest crude gypsum in the world. Cover walls, ceilings, plasters, fertilizers, cosmetics and some foods: gypsum’s vast applications granted it the recognition of "wonder mineral". Gypsum making equipment helps in making gypsum powder or board for industrial use.
Select your gypsum process
Tell us about your production challenge
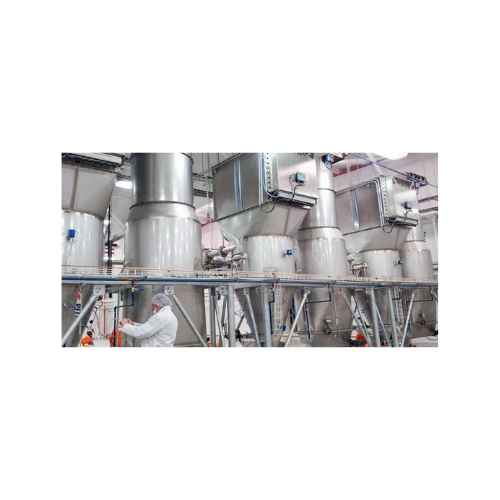
Getting fine particles with gypsum making equipment
Gypsum crystals go through crushing to achieve a desired degree of fineness. To achieve this, you can use a reclaim crusher, which depending on the design can also give room for recycling. Another key process in making gypsum is heating. This helps achieving the desired moisture content of the gypsym. To dry the product, feed the fine raw materials into the hot gas flow of the calciner. It is important to control and keep the temperature in check when operating gypsum making equipment. Heating above 152 ⁰C (305.6 ⁰F) may cause total water loss and dead-burnt gypsum.
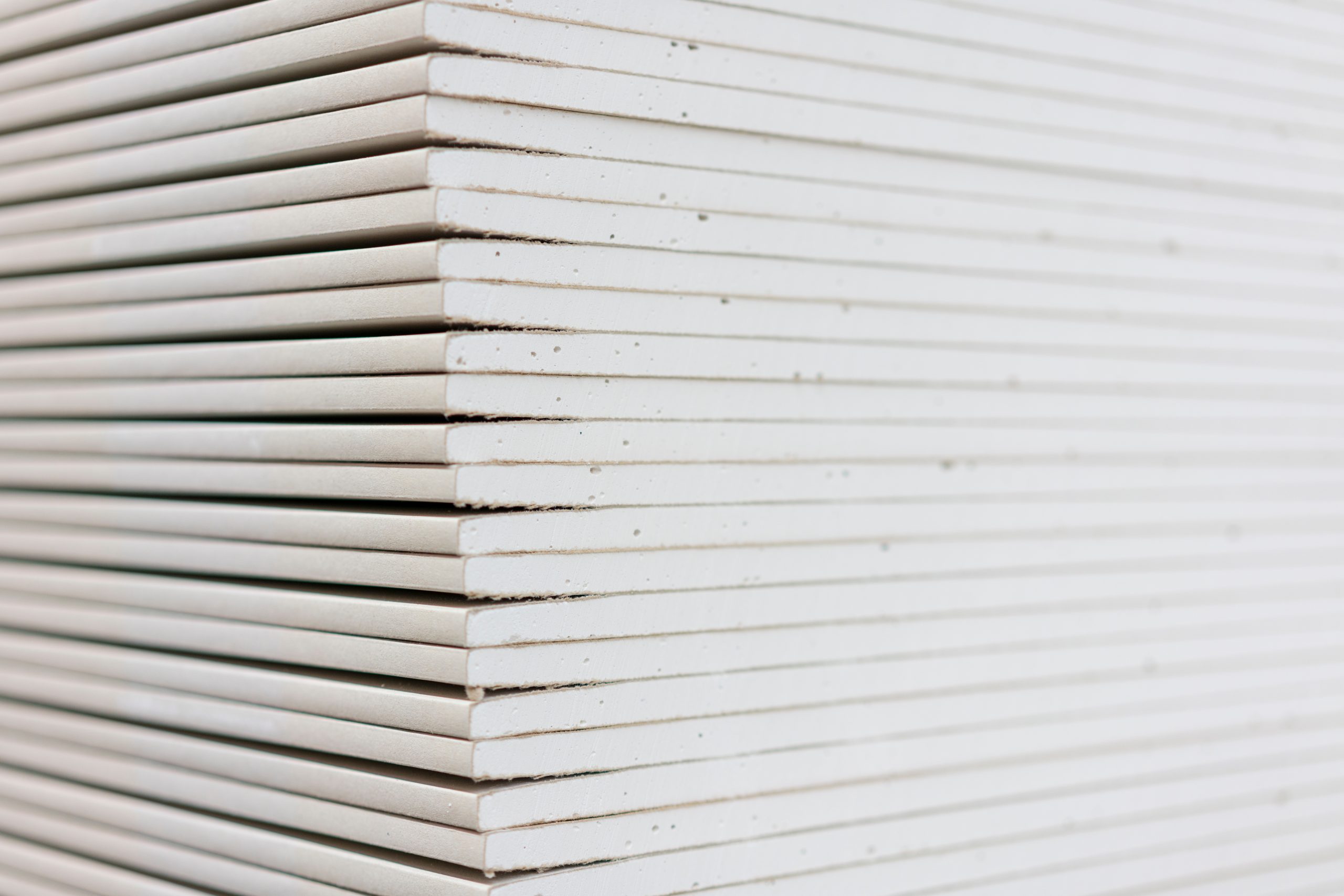

Gypsum boards, a common end-product of gypsum
The construction industry commonly uses gypsum because of its resistance to heat. The most common end-product is the gypsum board (drywall) or plaster board to produce false ceilings.
To make gypsum board, mix the calcined gypsum with water and additives to form slurry. Then feed the mixture between stacked papers on a gypsum board making machine. The mixture recrystallizes and bonds with the paper. It must dry to remove water before adding finishing touches such as coating and painting. Aesthetically, false ceilings are more appealing, and it’s also possible to install lights on them. This type of ceiling doesn’t conduct heat and prevents fire. They are good sound insulators and durable depending on how they’re managed.
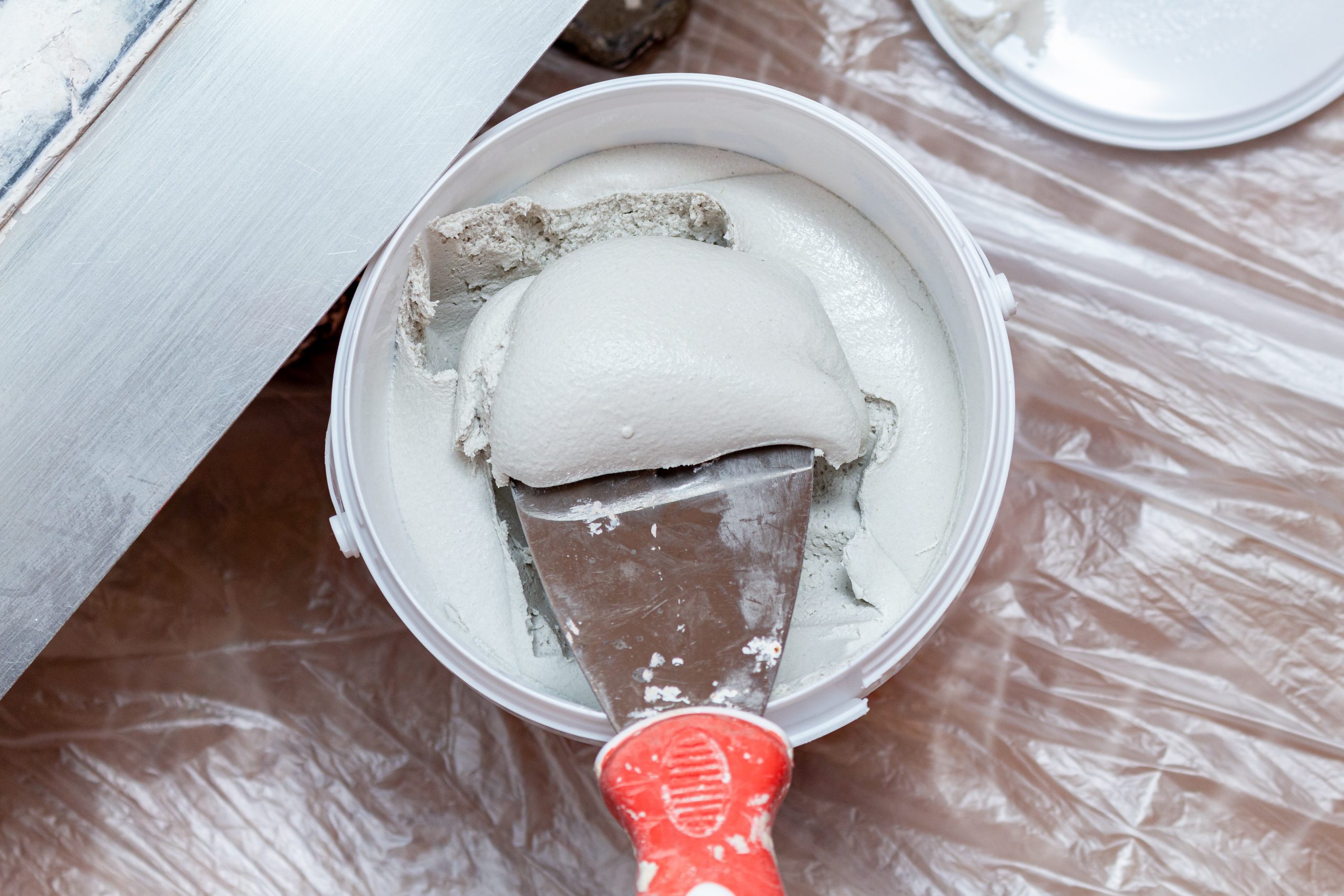

Post-industrial activities: environmental impact of making gypsum
Like every other mineral, gypsum processing releases chemicals. But by-products like sulphur are mostly reintroduced into the process, which makes tit more sustainable. It also reduces the effect of gypsum mining activities and waste disposal on ground water and on the atmosphere. Another alternative is to use synthetic gypsum produced from burning fuels for power generation. It is an easier substitute because instead of releasing it as a by-product, it is reused as it has the same chemical properties as the natural ones. Post-industrial recycling activities help produce new gypsum products while retaining its quality.
Gypsum, a cost-effective alternative for cement sand
Asides from making plaster of Paris, you can build concrete blocks and partitions with a gypsum making machine. When plastering, gypsum reduces construction time and cost compared to using typical cement sand. It is lightweight and, most importantly, reduces greenhouse gas emissions. To produce high-quality gypsum boards and build consumer confidence, you have to meet the standard codes and regulations bodies like ASTM in order to facilitate trade. For example, ASTM C1264-19 specification covers sampling inspection, rejection, certification, packaging, marking, shipping, handling, and storage of gypsum panel products.
Processing steps involved in gypsum making
Which gypsum technology do you need?

Cross beater mill for fine and coarse size reduction
Achieve precise size reduction of medium-hard and brittle materials ...

Laboratory drum mill for large sample volumes
Efficiently process large volumes of diverse materials into precise particle...
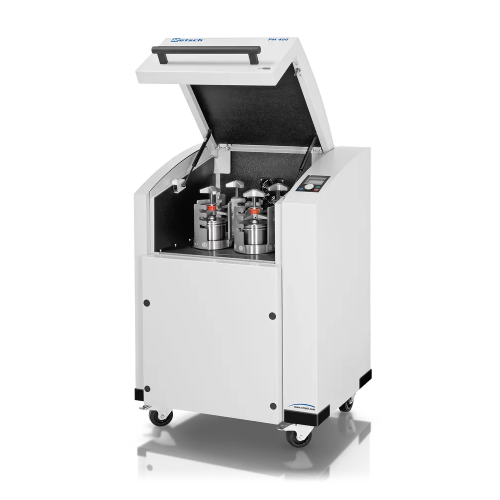

Planetary ball mill for high throughput grinding
For precise material engineering, achieve efficient size reduction, homog...
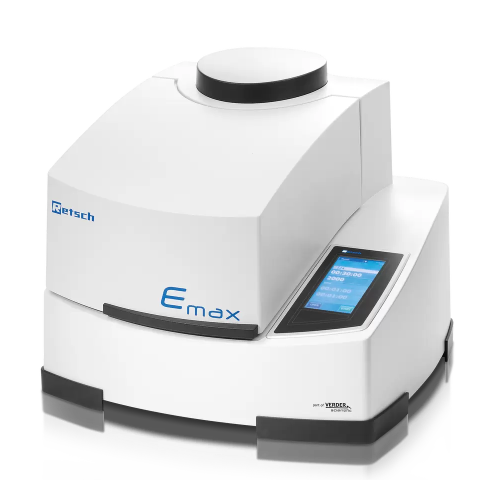

High energy untra fine ball mill
Achieve ultra-fine particle sizes rapidly with this high energy milling solution, designed ...

Pendulum mill for fine grinding and drying
Achieve efficient and precise grinding for soft to medium-hard materials while ...
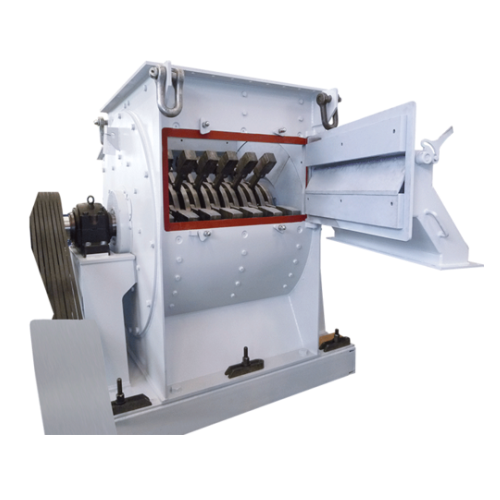

Industrial hammer mill for mineral processing
Optimize your material processing with an advanced hammer mill designed to e...
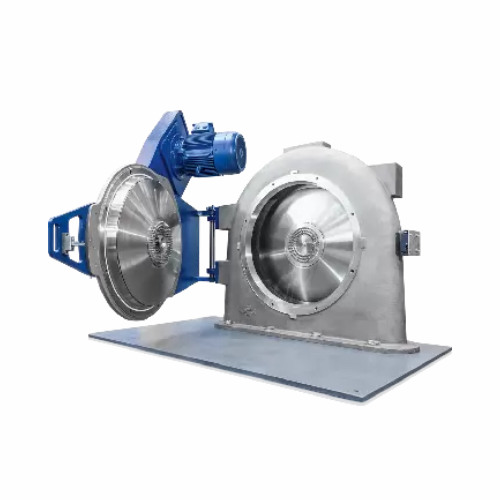

Industrial powder grinder
Achieve precise particle size reduction and classification with advanced equipment designed for co...
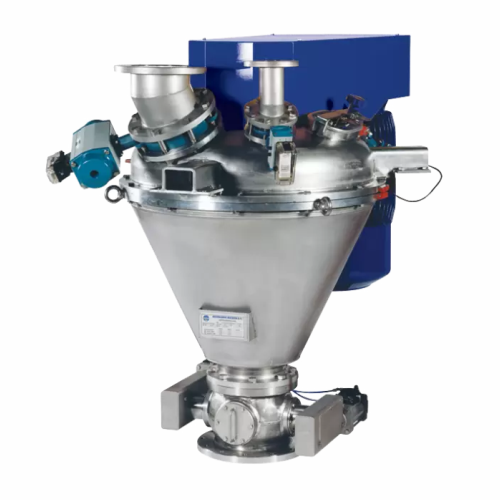

High shear impact mixer for agglomeration and dispersion
Achieve precise homogeneity and efficient agglomeration with a h...
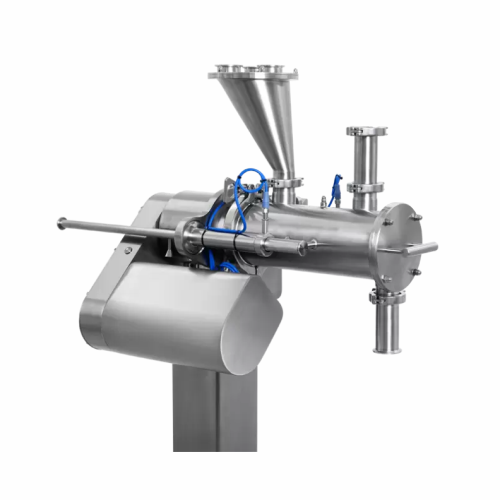

Continuous mixing for fine and cohesive powders
Achieve unparalleled mixing precision for cohesive powders while reducing ...
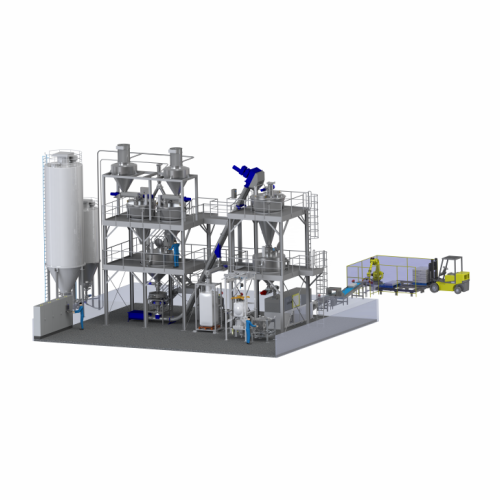

Powder mixing systems
Optimize your production line with precision powder mixing systems that ensure uniformity, enhance prod...

Choppers and disintegrators for industrial size reduction
Enhance your production efficiency by mastering size reduction...
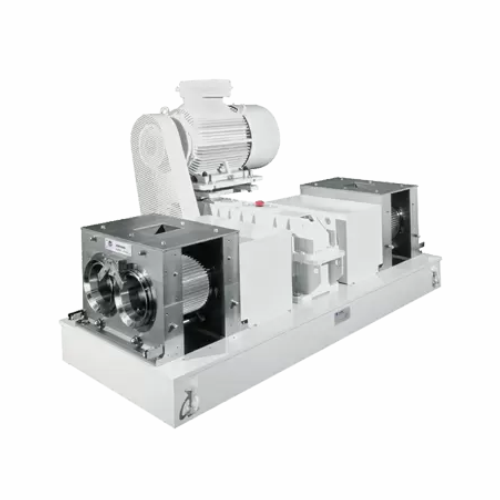

Compactors and granulators for powdery products
Transform loose powders into dense, free-flowing granules that enhance han...
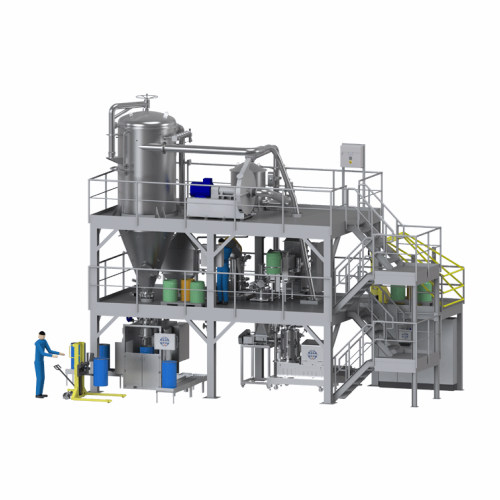

Drying systems for powders and bulk solids
Enhance your production line with precise control of moisture content in powder...
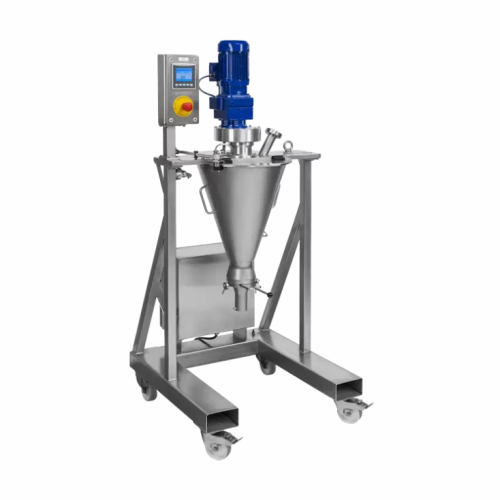

Lab mixer for high-accuracy powder and paste mixing
Achieve precise mixing of powders and pastes with a gentle convective...
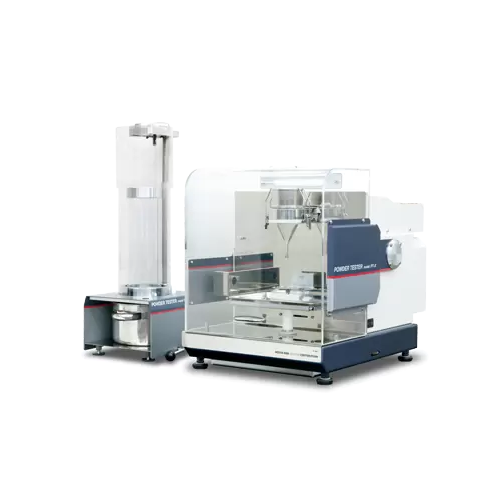

Powder characteristic evaluation
Ensure precise powder analysis and testing in your laboratory to optimize production qualit...
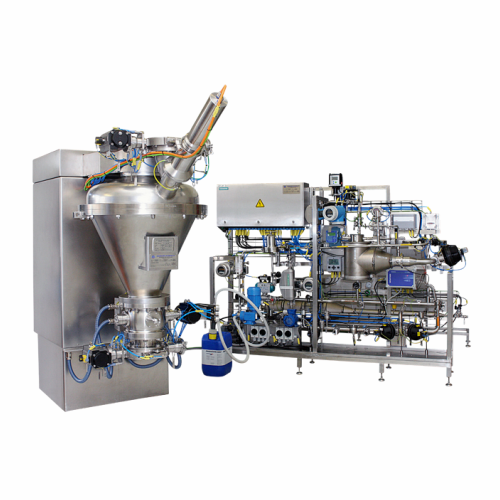

Cip/sip cleaning for solids processing systems
Ensure seamless transitions and maintain hygienic production environments w...
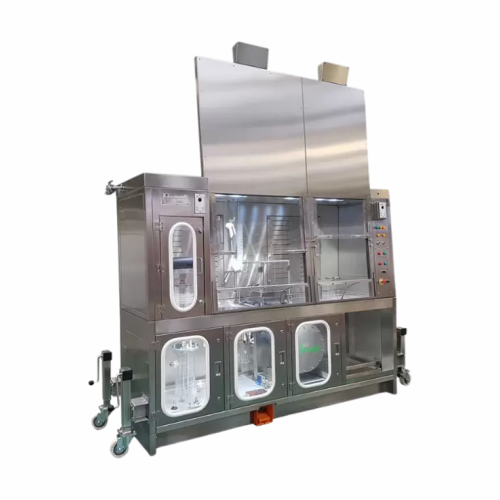

Containment solutions for hazardous material processing
Ensure safe and efficient processing of hazardous materials with ...
Conical screw mixer for powder blending
Achieve precise and homogeneous blending with the conical screw mixer, ensuring uni...
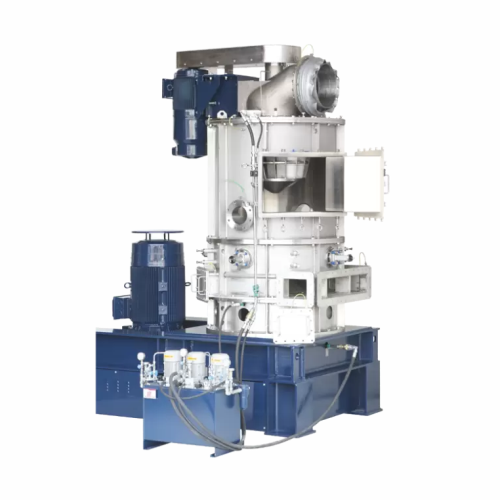

Ultra-fine powder flash drying system
Achieve rapid moisture removal and particle refinement with this integrated system, d...
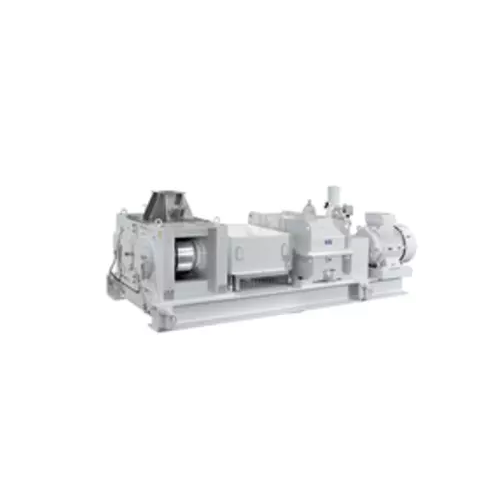

High pressure roller mill for medium-fine crushing
Achieve precision in particle size with high-pressure roller mills, id...
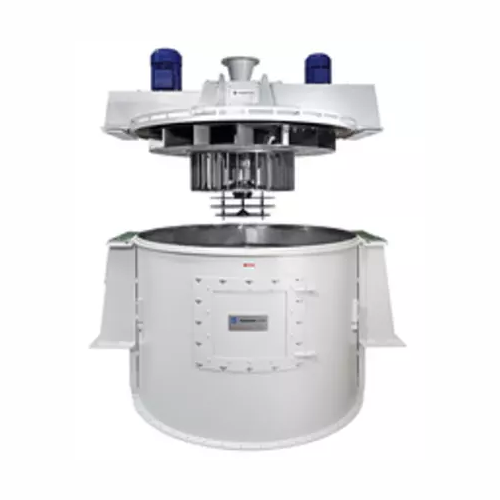

High precision air classifier for fine powder processing
Achieve precise particle separation and optimize throughput in y...
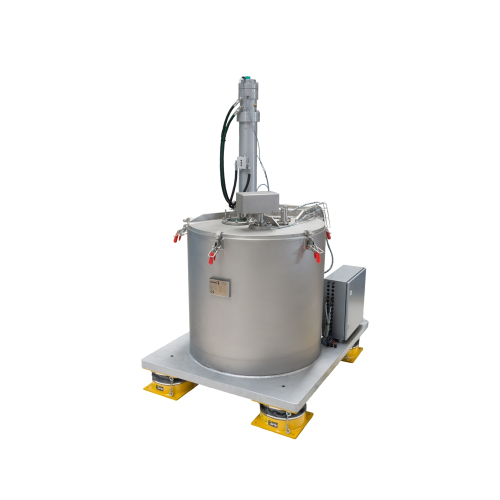

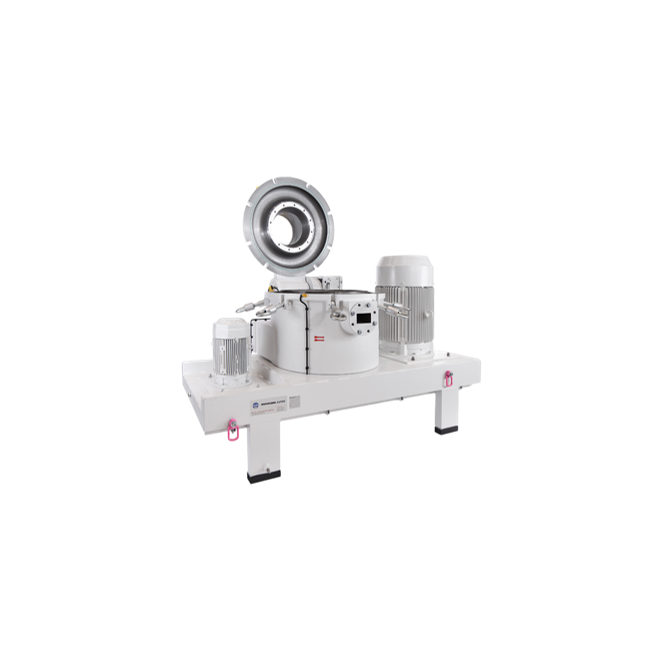
Vertical peeler centrifuge for gypsum dewatering
Effectively dewater gypsum with minimum residual moisture and optimized w...
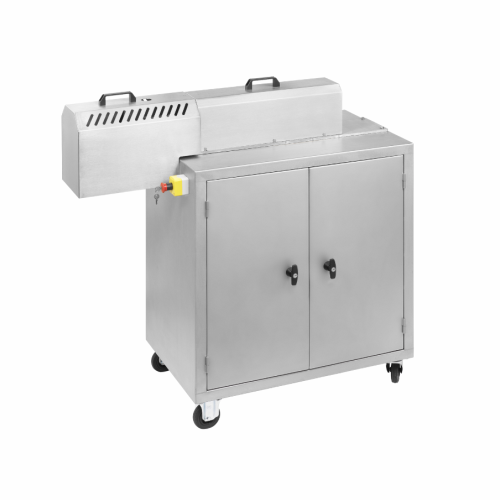

High-viscosity continuous industrial kneader for small volumes
Achieve consistent high-viscosity material processing wit...

Carbon and sulfur analyzer for organic and inorganic samples
Achieve precise and simultaneous carbon and sulfur analysis...

Carbon and sulfur analyzer for inorganic samples
Achieves precise carbon and sulfur measurement in varied inorganic materi...

Carbon dioxide and water analyzer for cement and lime
Ensure precise moisture and carbon dioxide quantification in constr...

Carbon and water analysis for lime and gypsum
Achieve precise carbon and water measurement in diverse materials like cemen...

Evaporative gas cooling system for industrial gases
Optimize exhaust gas management with precision cooling and conditioni...
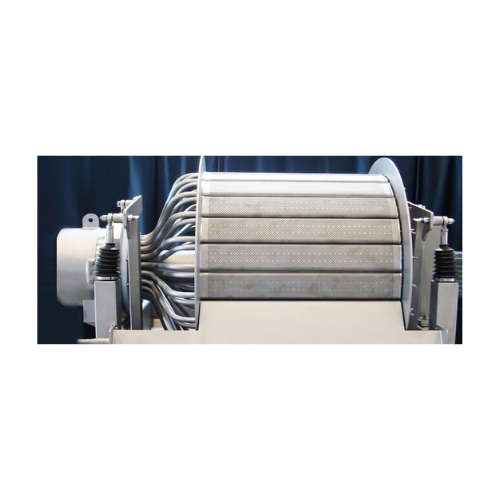

Industrial drum vacuum filter for filtration and washing
Efficiently manage filtration, washing, and dewatering tasks wit...
Paddle dryer for industrial sludge
Achieve consistent drying and pasteurization of complex materials with this advanced pad...
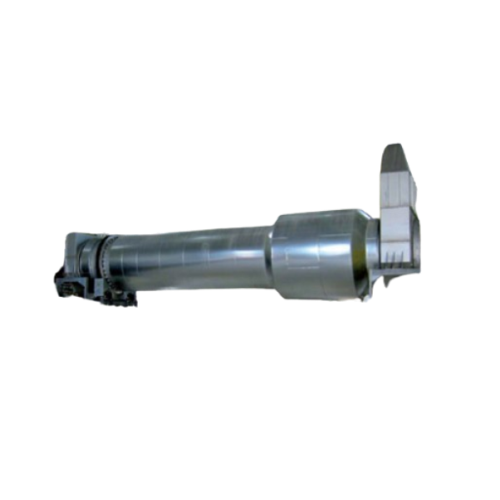

Indirect drying drums for solvent-based products
Optimize energy use and safety with our indirect drying drums, ideal for ...
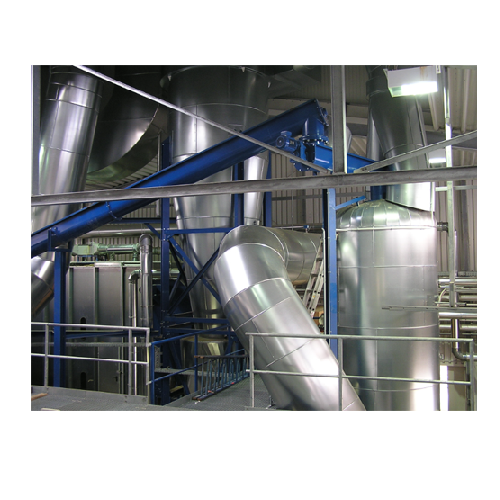

Flash dryer for high-moisture bulk materials
Tackle high-moisture challenges head-on with rapid drying solutions that effi...
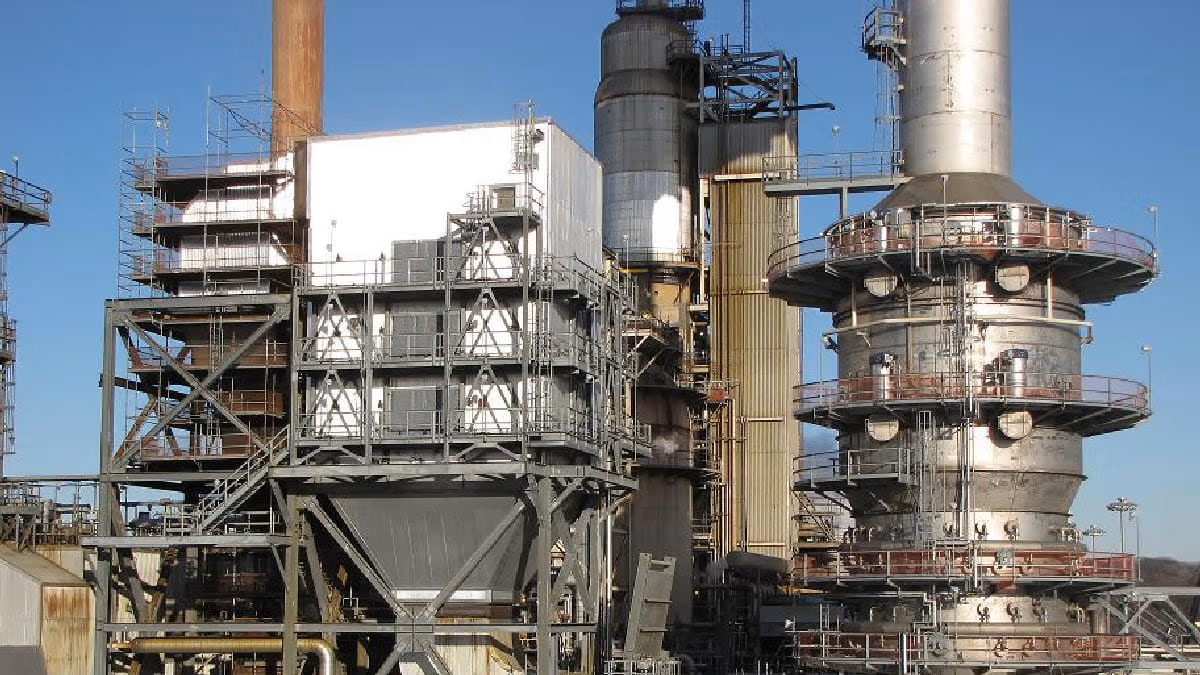

Wet scrubbing for So2 removal in industrial applications
Effectively eliminate sulfur oxides from flue gases using advanc...
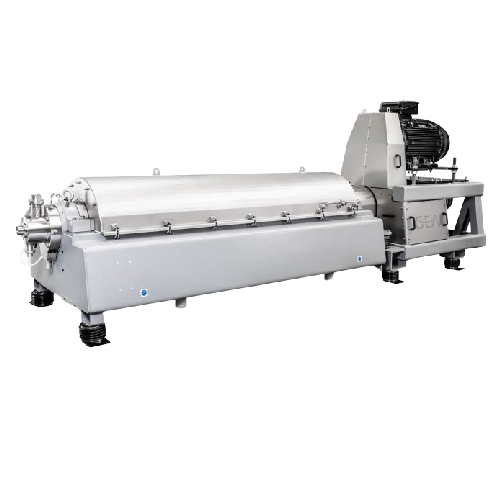

2-phase separating decanter for chemical and mineral processing
Ensure precise separation and optimal moisture control i...
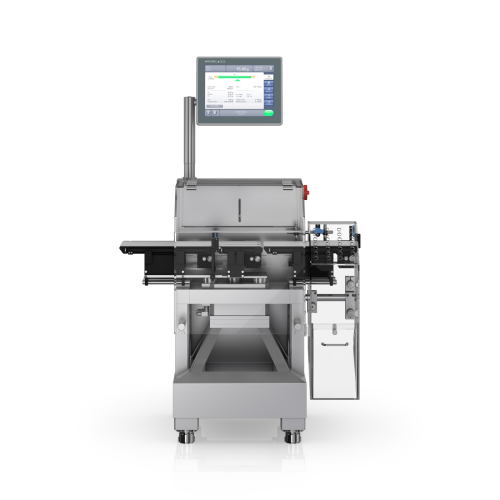

High-speed checkweigher for dynamic weighing
Achieve precision and consistency in high-speed production environments with ...
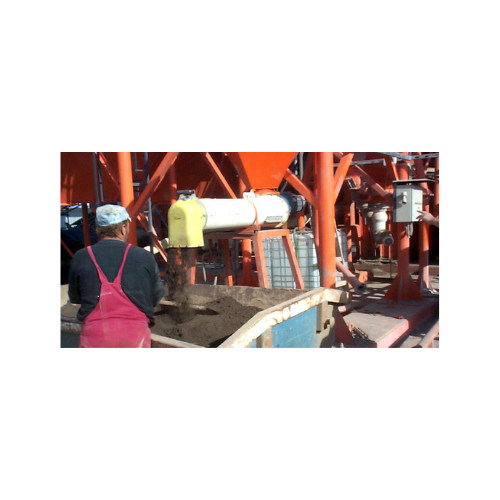

Industrial dust conditioner for heavy-duty processes
Tackle industrial dust challenges with a solution designed for effic...
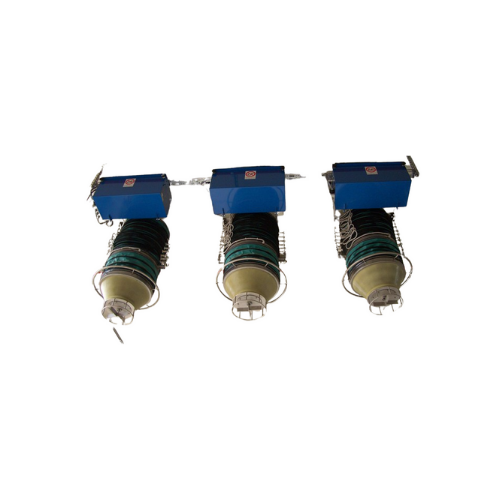

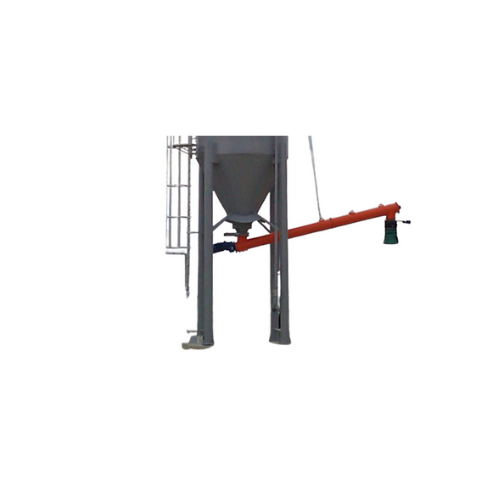
Tanker loading bellow for dust-free bulk solids loading
Optimize tanker loading while minimizing dust emissions with this...

Bulk solids tanker loading bellows
For industries looking to efficiently load dry, non-dusty bulk solids into tankers, thes...
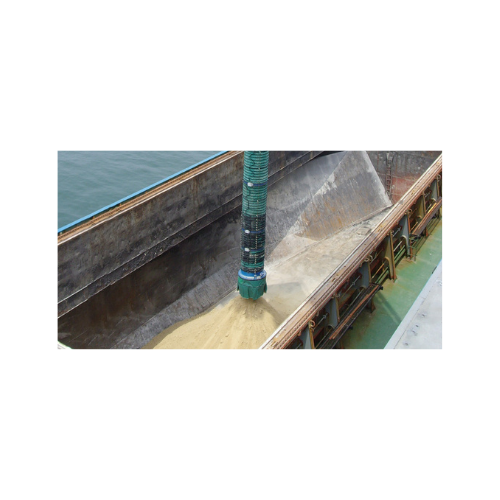

Telescopic loading bellows for bulk solids
Streamline your bulk material operations with high-capacity, dust-free loading ...
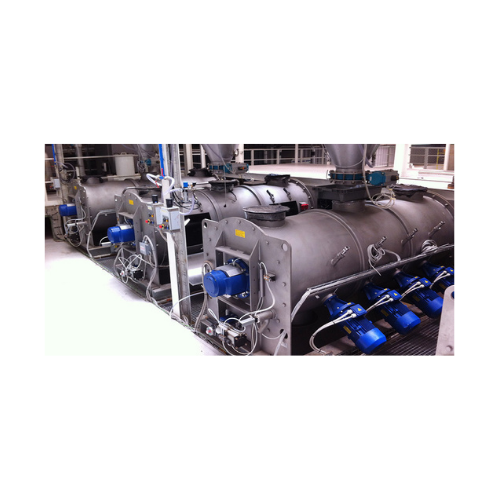

Batch-type single shaft mixer for industrial mixing
Achieve precise and uniform mixing with high-speed, single-shaft mixe...
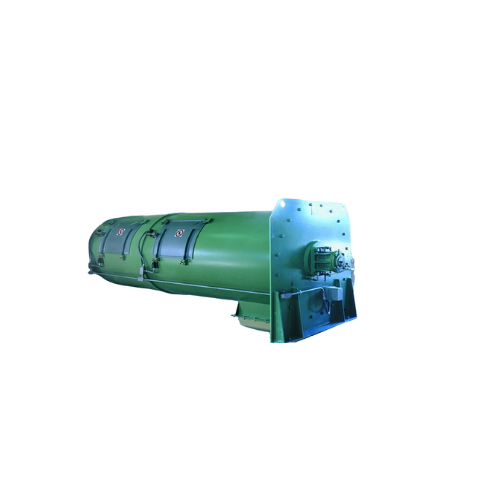

Continuous single shaft mixer for waste treatment
Achieve consistent mixing homogeneity and prevent dead spots in your pr...

Atex-certified flanged polygonal dust collectors
Ensure dust control and compliance in explosive environments with our com...

Atex certified flanged round dust collectors
Designed for potentially explosive environments, these flanged round dust col...

Flanged round dust collectors for industrial air filtration
Optimize your industrial processes with a dust collection sy...

Butterfly valves for powders and granules
Ensure precise flow control and reliable sealing for gravity-fed or pneumatic sy...

Butterfly valves for powder and granular material handling
Experience seamless material control with advanced butterfly ...

Industrial slide valve for heavy-duty applications
When managing gravity material flow in abrasive environments, achievin...

Membrane pressure relief valve for silos and bins
Ensure silo safety with our valve that instantly balances internal pres...

Low profile slide valve for controlling powder flow
Optimize your powder and granule flow management with precision-engin...
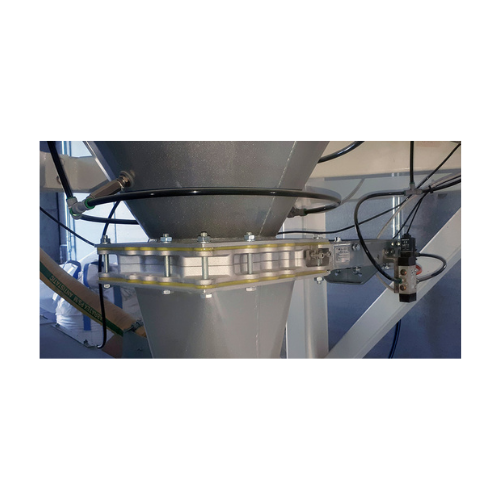

Slide valves for flow interception in powder and granular materials
Effectively manage the flow of powdery and granular...
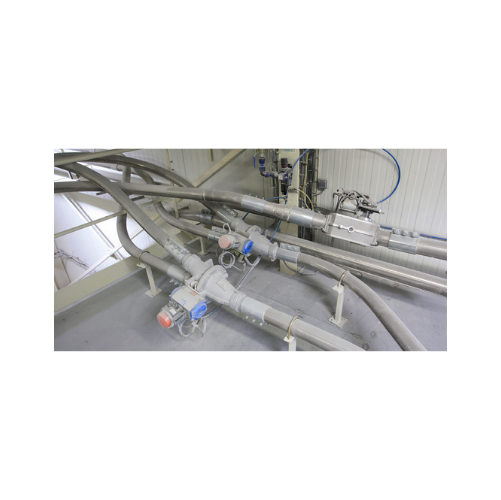

Flap diverter valves for pneumatic conveying
Streamline material flow in your pneumatic conveying system by effortlessly r...

Diverter valves for pneumatic conveying lines
Experience precise flow control in pneumatic conveying with diverter valves ...
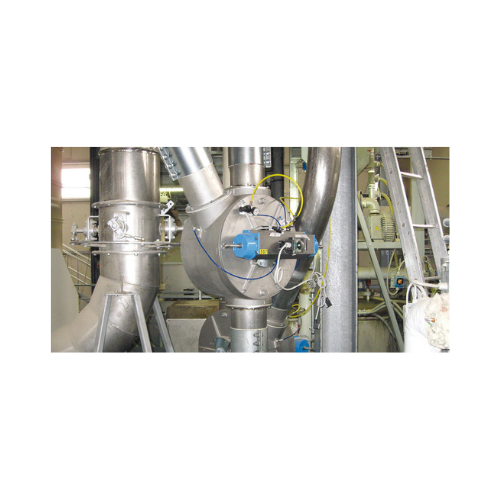

Drum-type diverter valves for pneumatic conveying
Optimize your pneumatic conveying system by effortlessly controlling th...
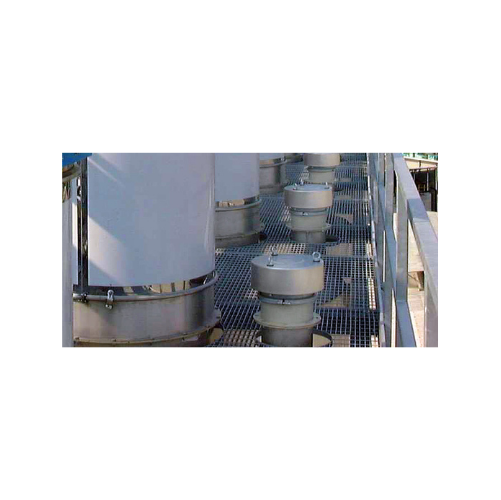

Spring-loaded pressure relief valves for silo overfill protection
Ensure safety and prevent costly overfills with press...

Double dump valves for high temperature granules
Ensure precise material flow and withstand extreme temperatures with thes...

Heavy-duty tubular screw conveyor for bulk solids
Optimize your production line with a durable solution for uninterrupted...
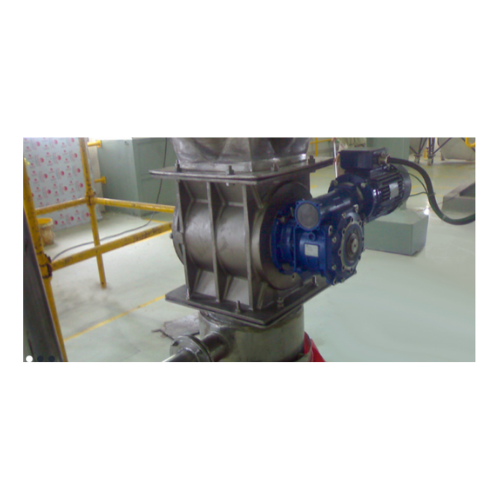

Drop-through rotary valve for powder and granular material feeding
Achieve precise control in discharging and feeding p...
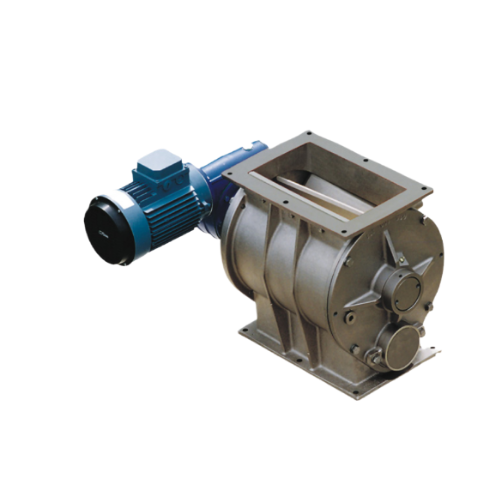

Drop-through rotary valve for precise powder and granule feeding
Ensure precise material handling with this drop-through...

Automatic bag splitter for bulk solids handling
Streamline your production line with an efficient solution to split, empty...

Continuous impact vibrators for bulk material removal
Combat material flow issues like bridging and rat-holing with our i...

Continuous impact vibrators for bulk solids discharging
Optimize your discharging process with vibrators that effectively...

Belt conveyor for automatic bag splitters
Optimize your material handling with a belt conveyor designed to seamlessly feed...
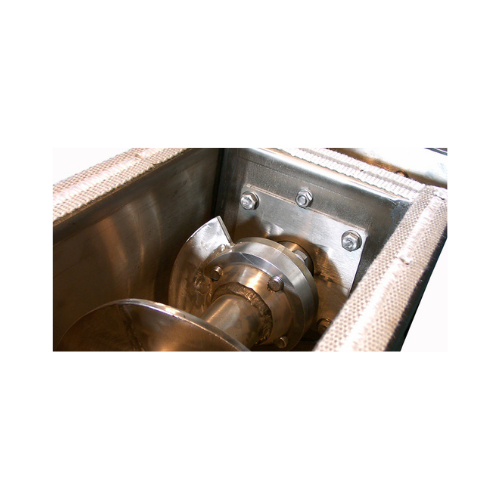

High-temperature screw conveyors for bulk solids
Designed for extreme conditions, these conveyors handle high-temperature ...
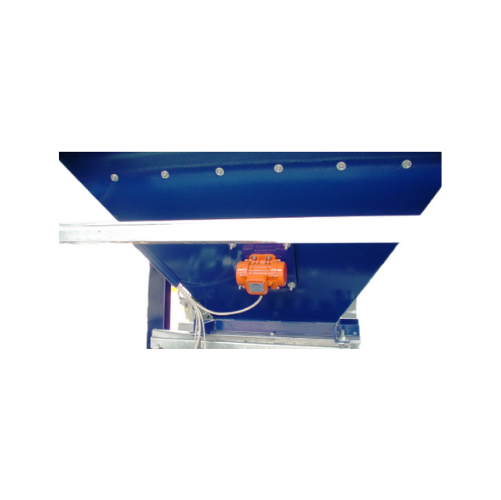

External electric motovibrators for industrial applications
Optimize material movement and improve discharge efficiency ...
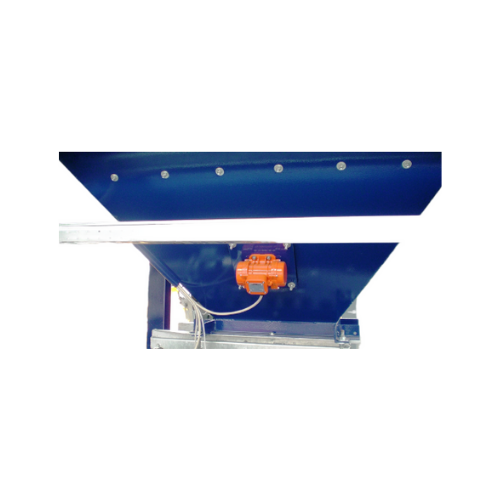

External electric motovibrators for bulk solids conveying
Enhance material flow efficiency and solve challenging dischar...
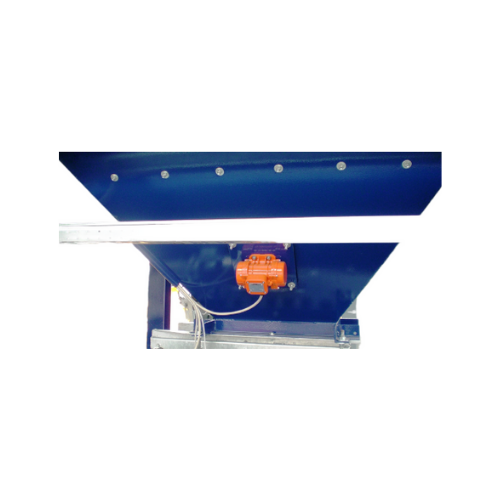

Industrial electric vibrator for bulk solids discharging
Enhance material flow efficiency and ensure consistent output ac...
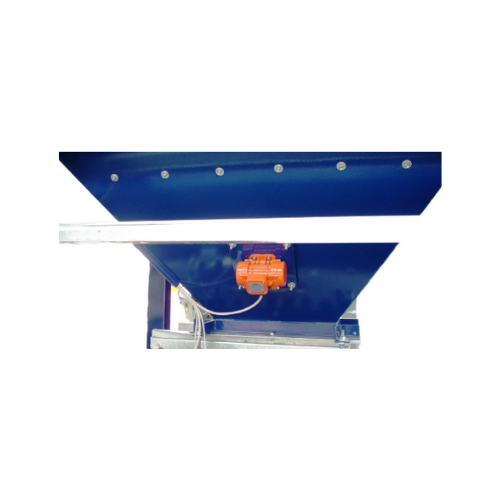

External electric motovibrators for industrial material flow
Experience enhanced material flow and precise material disc...

Silo overfill protection system
Prevent silo overfilling and excess pressurization with a system designed to safeguard silos...

Silo overfilling safety system
Ensure safe silo filling with our system that prevents overfilling and excess pressurization,...
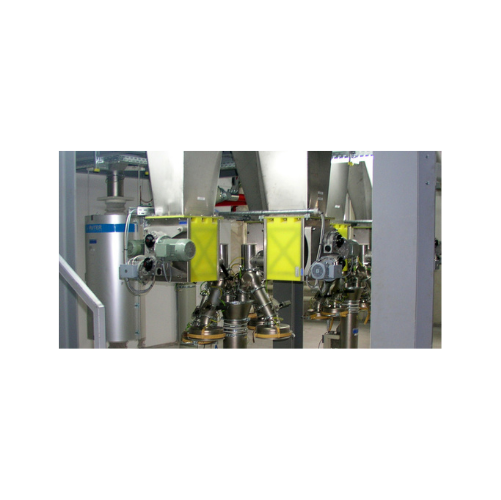

Micro-batch feeders for powder and granular material
Struggling with clog-prone powders? Gain precise control and consist...
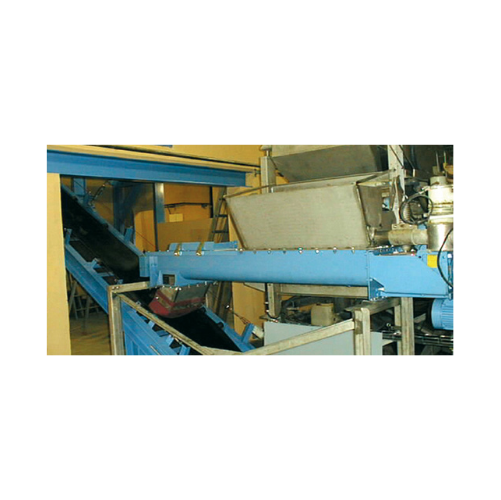

Continuous twin shaft paddle mixers for dust conditioning
Optimize your mixing process with twin shaft paddle mixers, en...
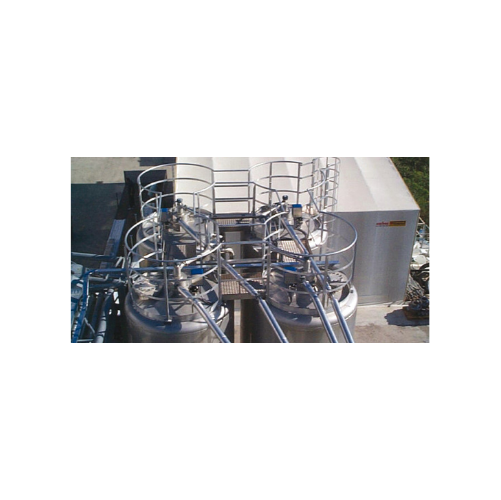

Continuous level measurement system for powdery or granular materials
Ensure precise inventory management and enhanced ...
Bin level indicator for bulk solids
Ensure precise material level detection across your production processes, minimizing th...
Bin level indicators for wastewater treatment
Ensure reliable material level monitoring in your silos and hoppers with ILT...
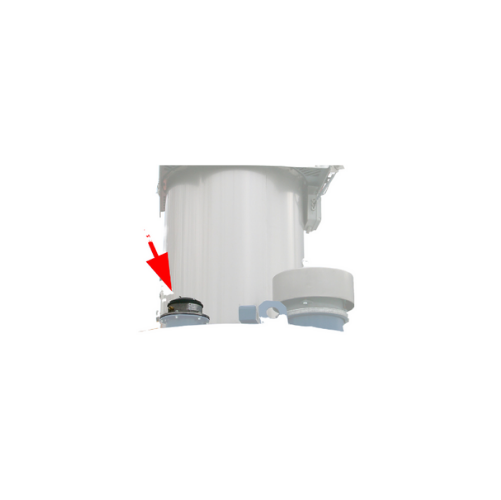

Electronic pressure meters for silo safety monitoring
Ensure precise pressure management in your systems with this advanc...
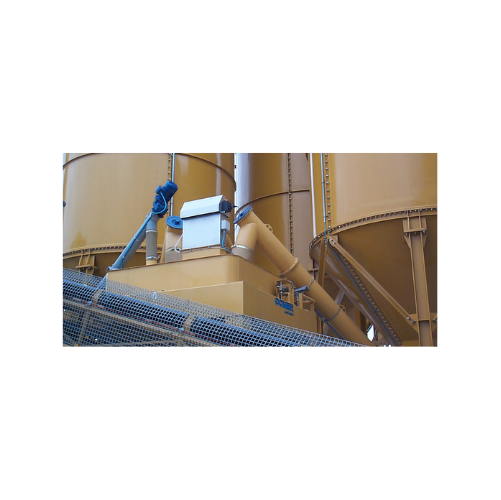

Hopper venting filter for efficient dust filtration
Achieve superior dust control and efficient material handling with a ...
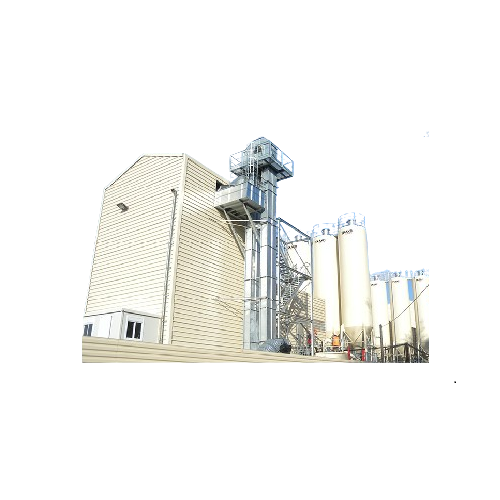

Heavy-duty vertical conveyor for aggregates and minerals
Achieve efficient vertical transport of heavy, abrasive material...
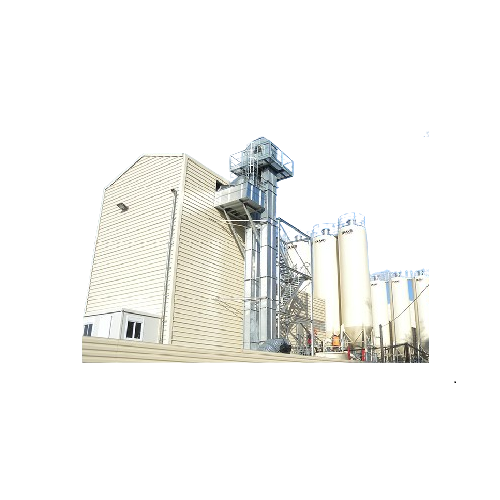

Heavy-duty vertical conveying for aggregates and minerals
Achieve efficient vertical transport of heavy bulk materials w...

Vertical conveyor for fine aggregates and minerals
Optimize the handling of abrasive materials with a vertical conveying ...

Anti-wear elbows for pneumatic conveying systems
Reduce wear and extend the lifespan of your pneumatic conveying systems w...

Dust disposal and conditioning system
Optimize your dust management operations with a superior conditioning system designed...

Open truck loading bellows with dust collector
Achieve efficient, dust-free loading of dry bulk solids into open trucks, m...

Trough screw conveyors for powdery and granular materials
Optimize your material handling process with a flexible screw ...
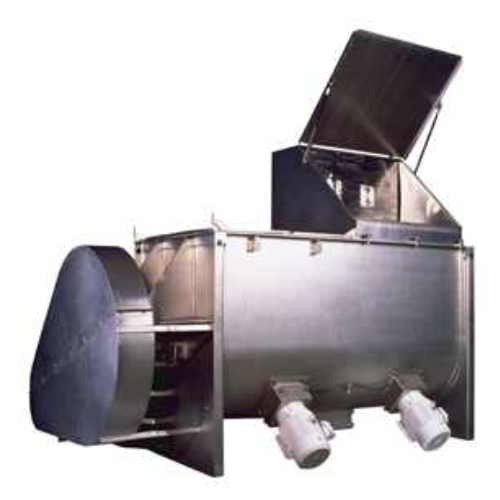

Single shaft horizontal batch mixer
Achieve consistent, high-quality blends with precise homogenization using a single shaf...
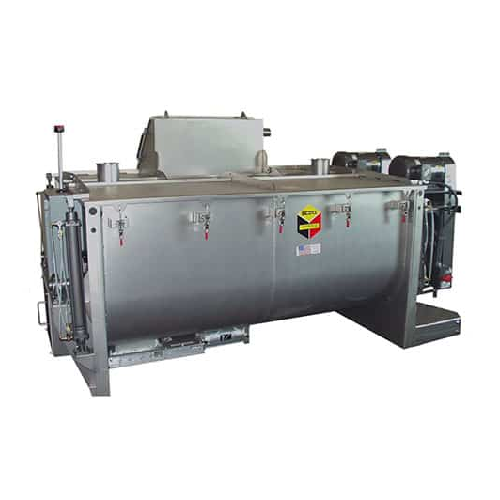

Twin shaft horizontal batch mixers for homogenous material mixing
Achieve consistent and rapid mixing of diverse materi...
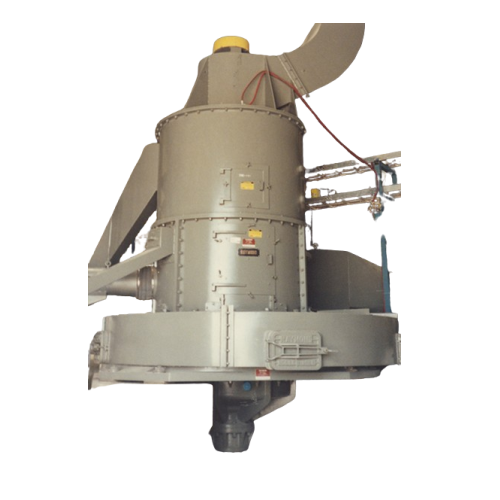

Vertical ring-roll mill for pulverizing minerals
Achieve precise particle size control and efficient material processing w...
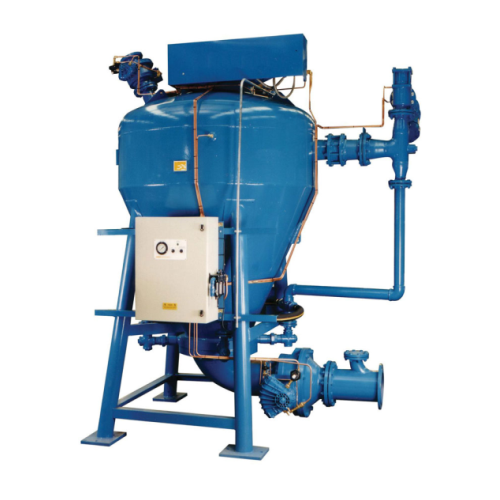

Dense phase conveying pumps for bulk material transfer
Optimize your material handling with pneumatic conveying solutions...

High volume 3D shaker mixer for ceramics
Achieving consistent homogeneity and the logistics of handling and introducing lar...
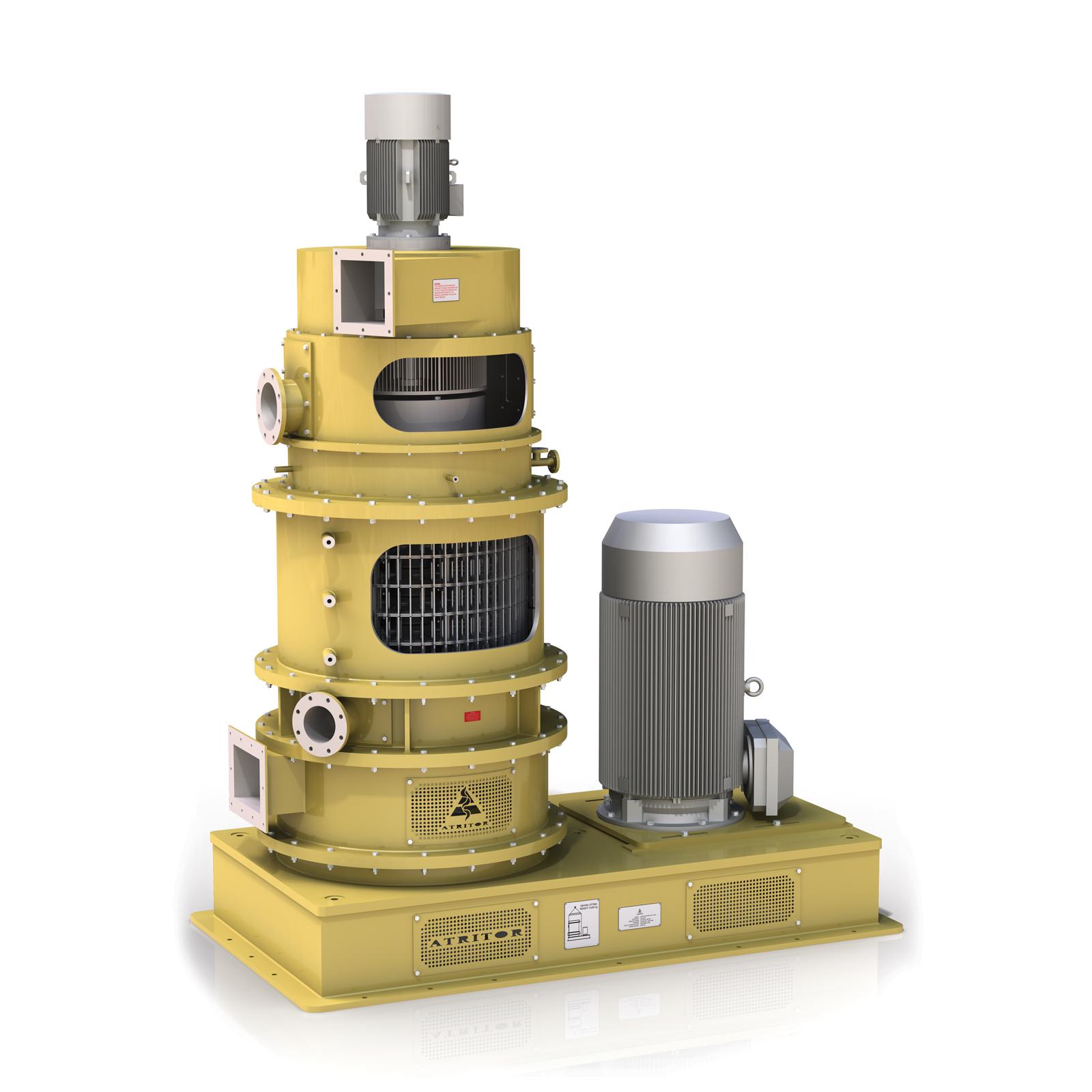

Milling and drying machine for fine powders
When you need to produce ultra-fine powders, the milling and drying process em...
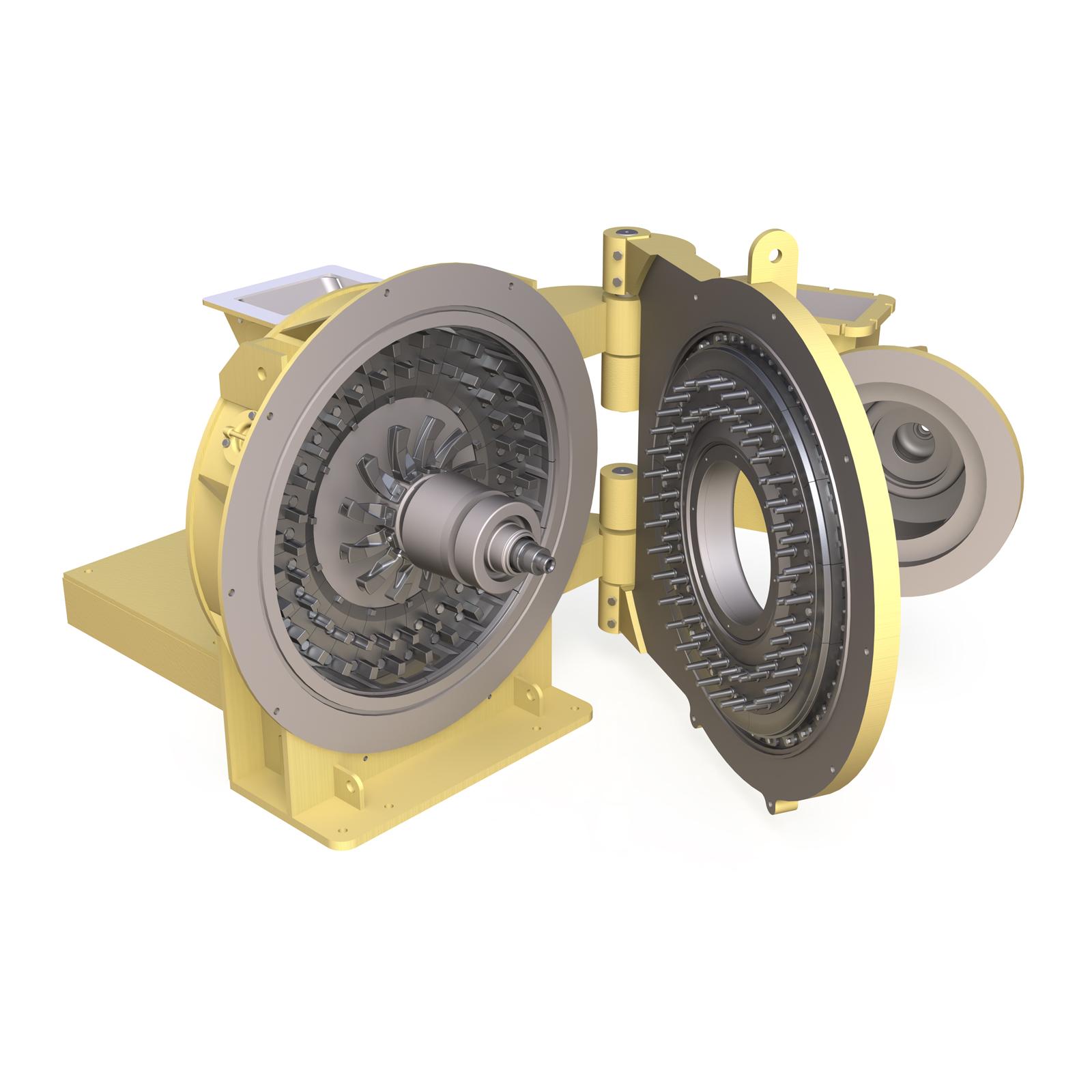

Flash drying grinder for powders
Drying and grinding can be an important feature when trying to process products such as raw...

Horizontal rotary ball mill drum
A horizontal rotary ball mill drum can be used for grinding of dry hard materials, such as ...
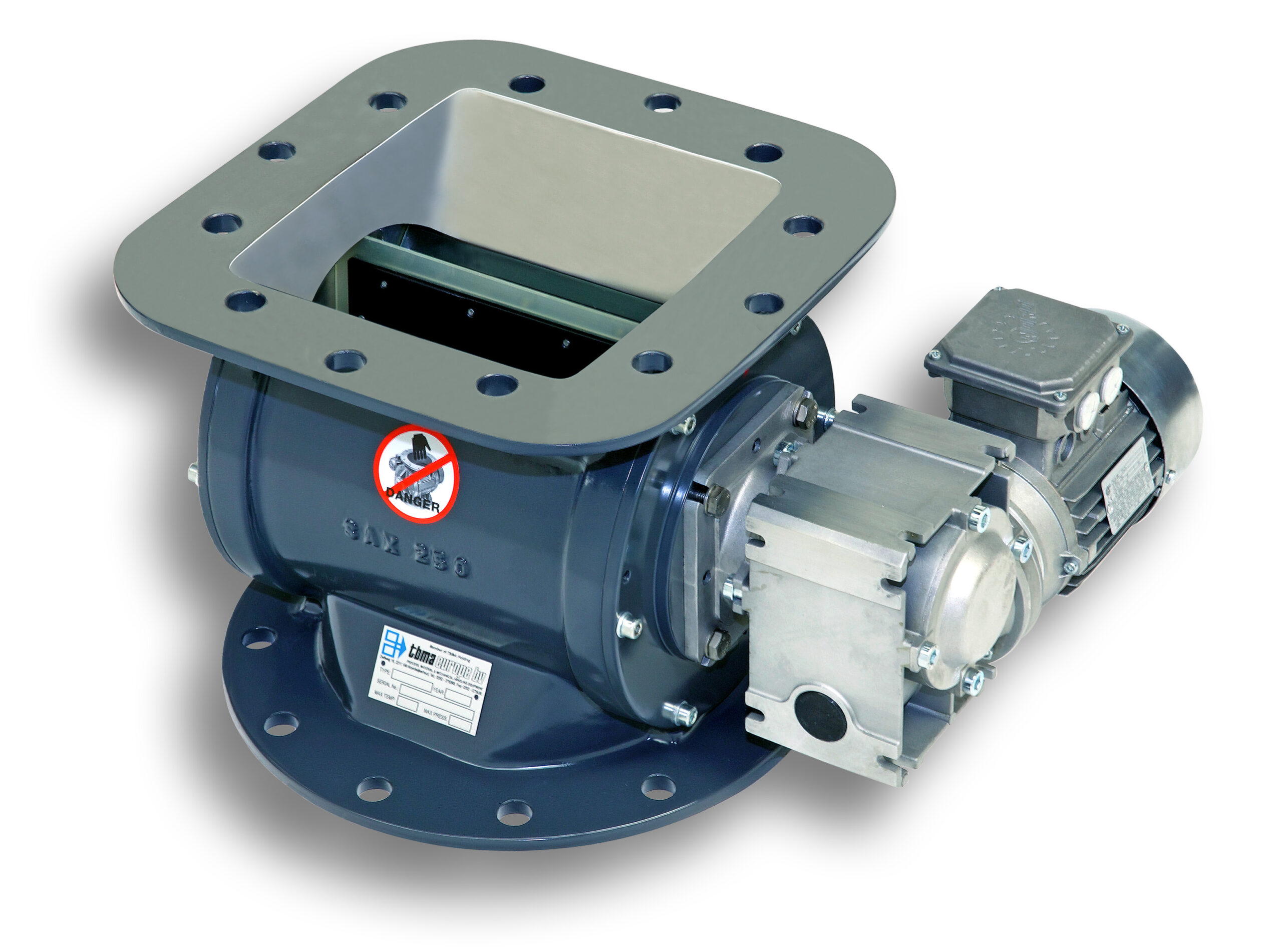

Light duty rotary dust valve
In some light industrial applications there is limited pressure differential for valve operation.
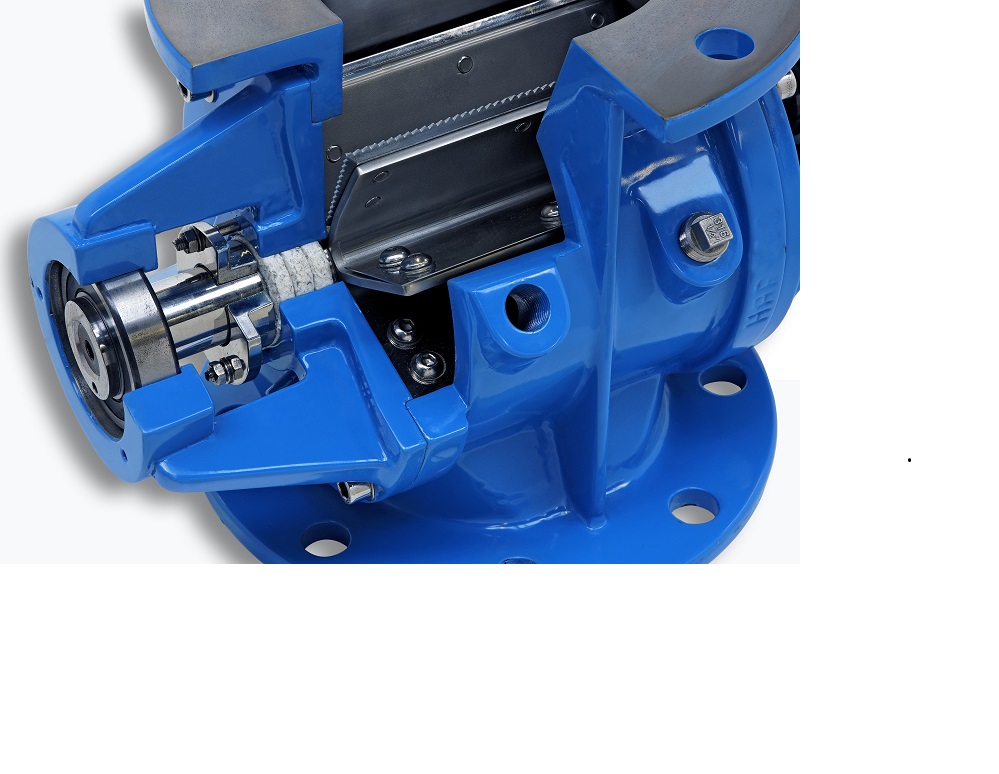

Heavy duty rotary valve
Handling powdered and granulated materials in pneumatic conveying systems requires consistent, safe v...
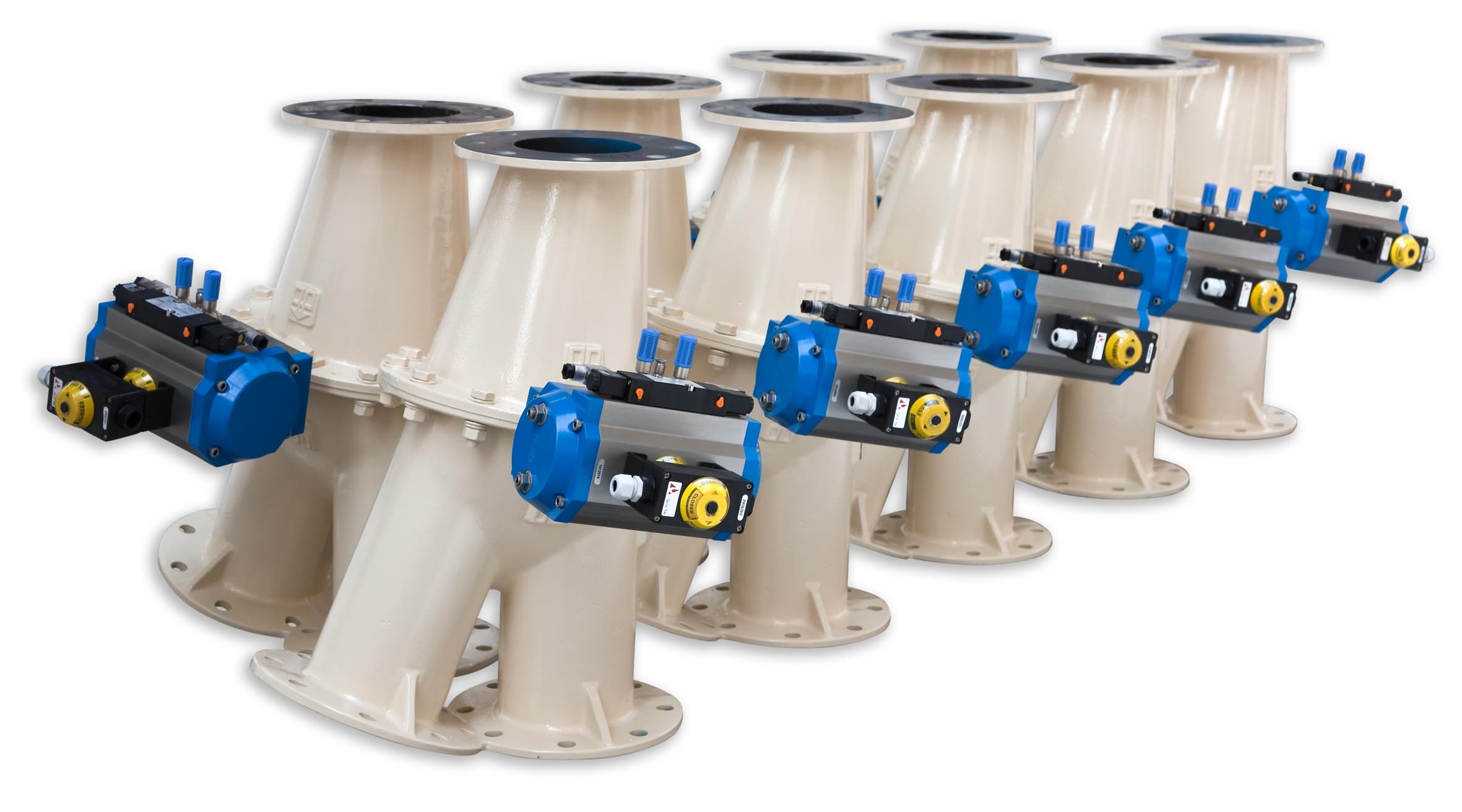

Two-way flap type diverter valve
Routing powder, pellets or granules from a product source to two receiving points must be d...
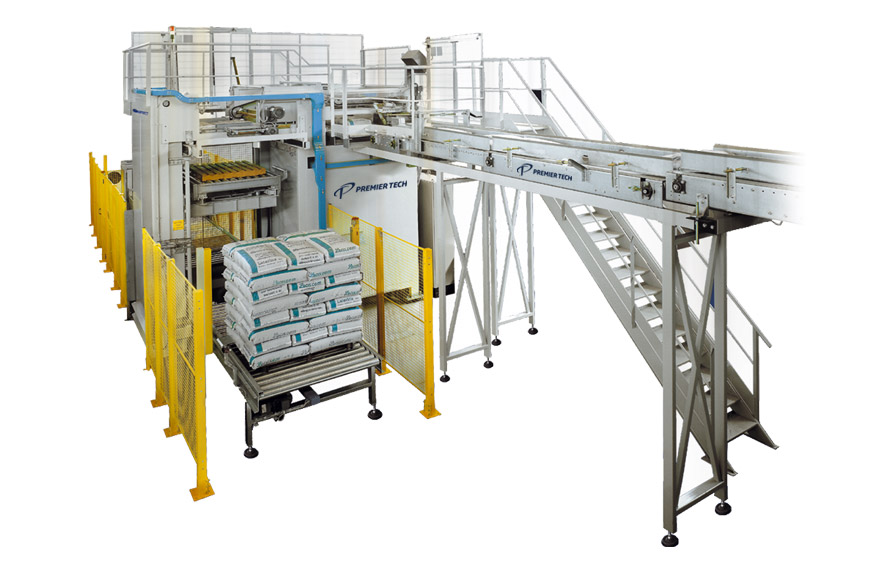

High-level layer palletizer
A palletizer that meets the middle and high-level needs of modern bagging lines. Quite suitable ...
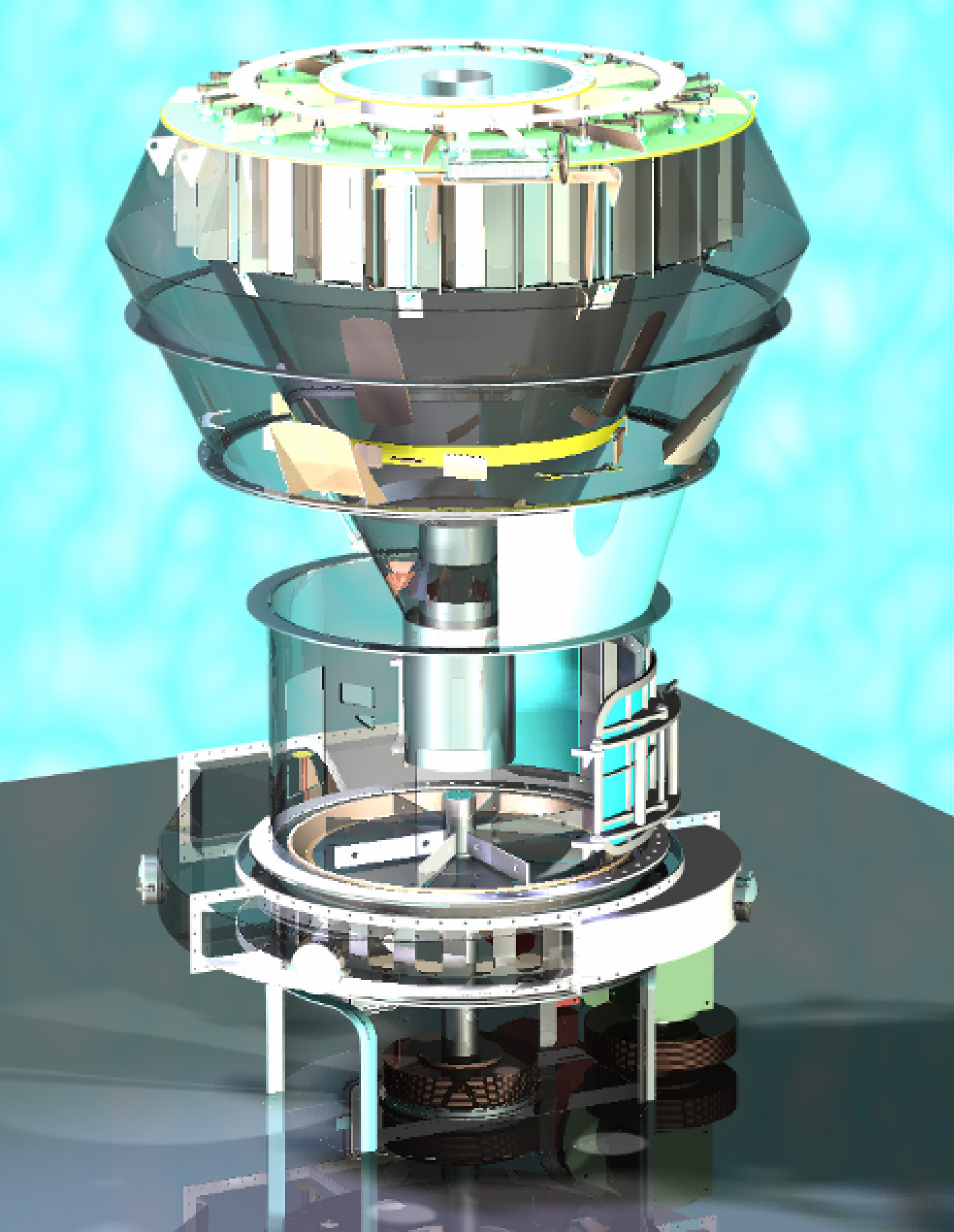
Horizontal impact calciner
Quality of synthetic gypsum and stucco products is highly influenced by the quality of the calcin...
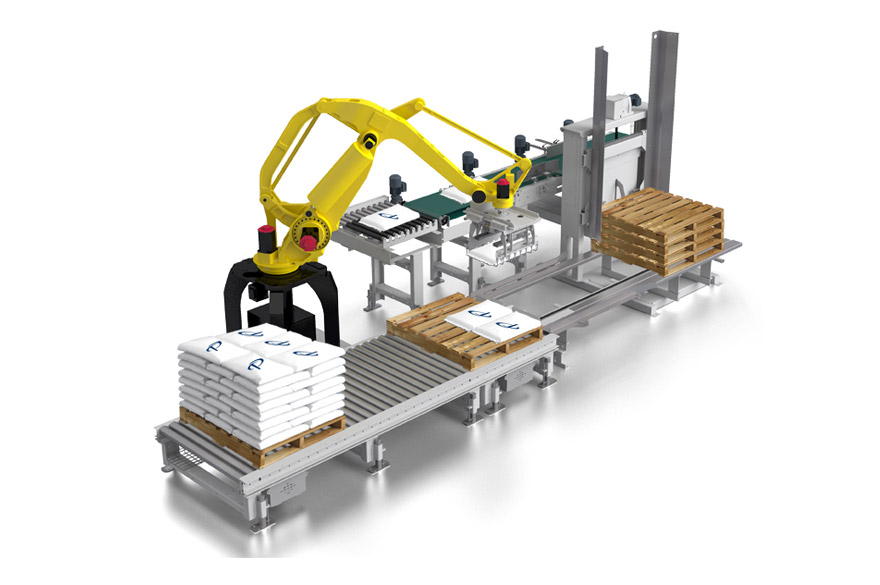

Robot palletizer
Palletize up to 1,800 large industrial bags per hour at a multi-pick-up configuration.
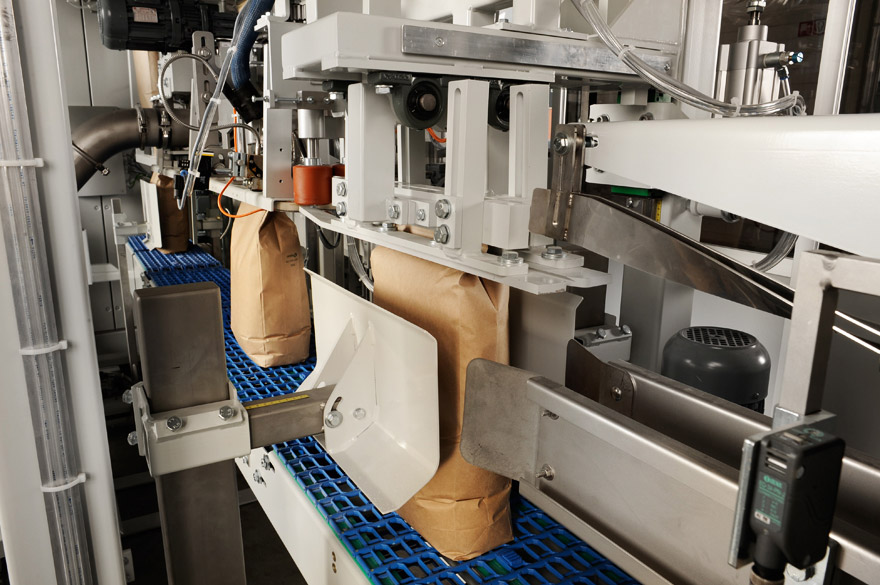

Open-mouth bottom-up baggers
Innovative bottom-up baggers for high-speed industrial packaging will help you create a dust-fr...
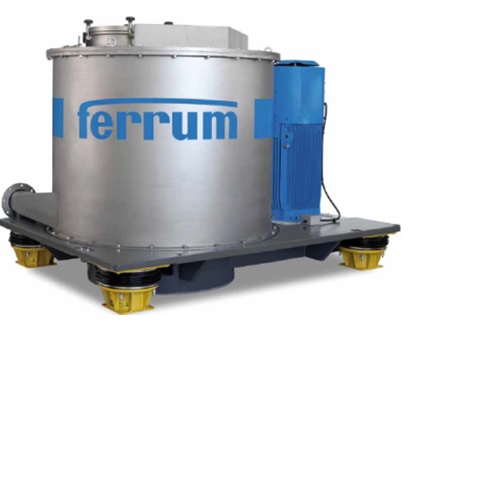

Gypsum centrifuge
Especially designed for flue gas desulphurization, applications in coal fired power plants and waste incine...
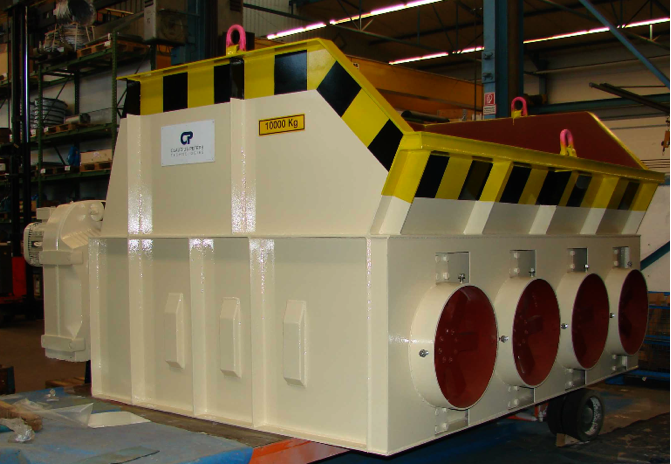

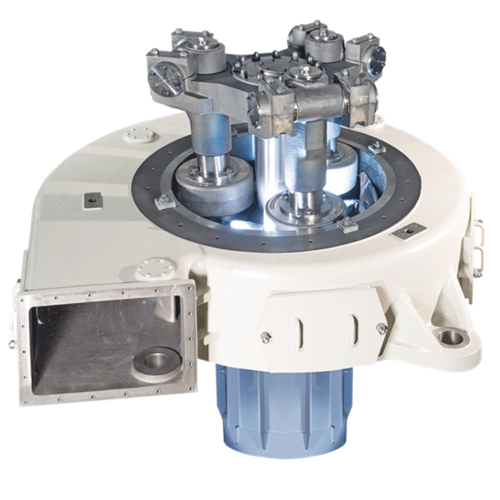
Reclaim crusher
Waste products and rejected materials are inevitably generated from any gypsum products manufacturing process....
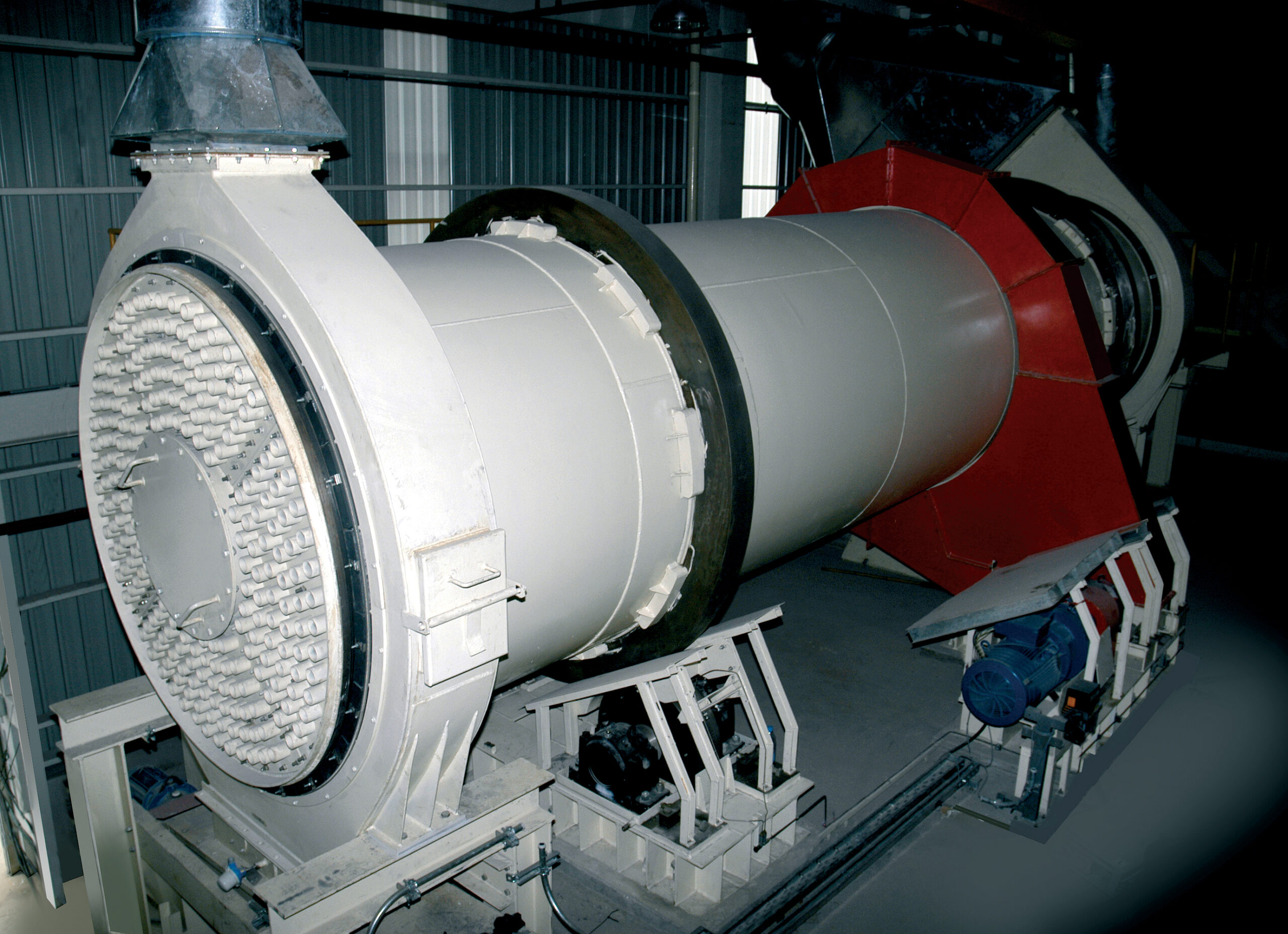
Rotary drum cooler for calcined gypsum products
After the calcining process gypsum products must be cooled from temperatur...
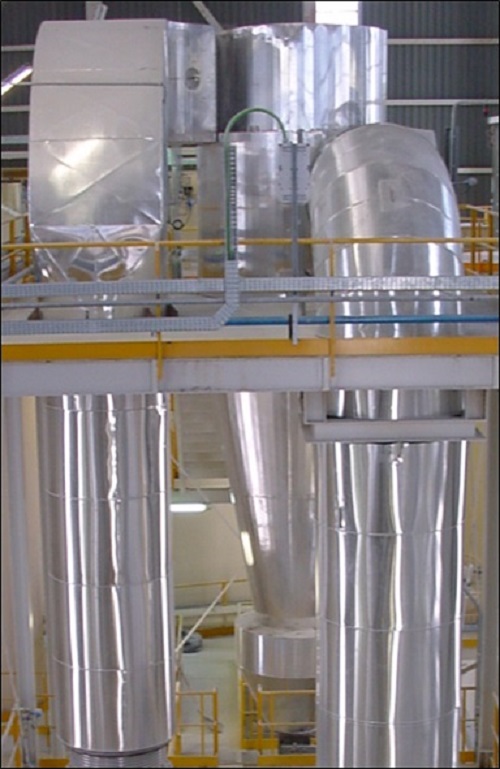

Flash calciner
Quality of gypsum plaster products is highly influenced by the quality of the calcining process employed in pro...
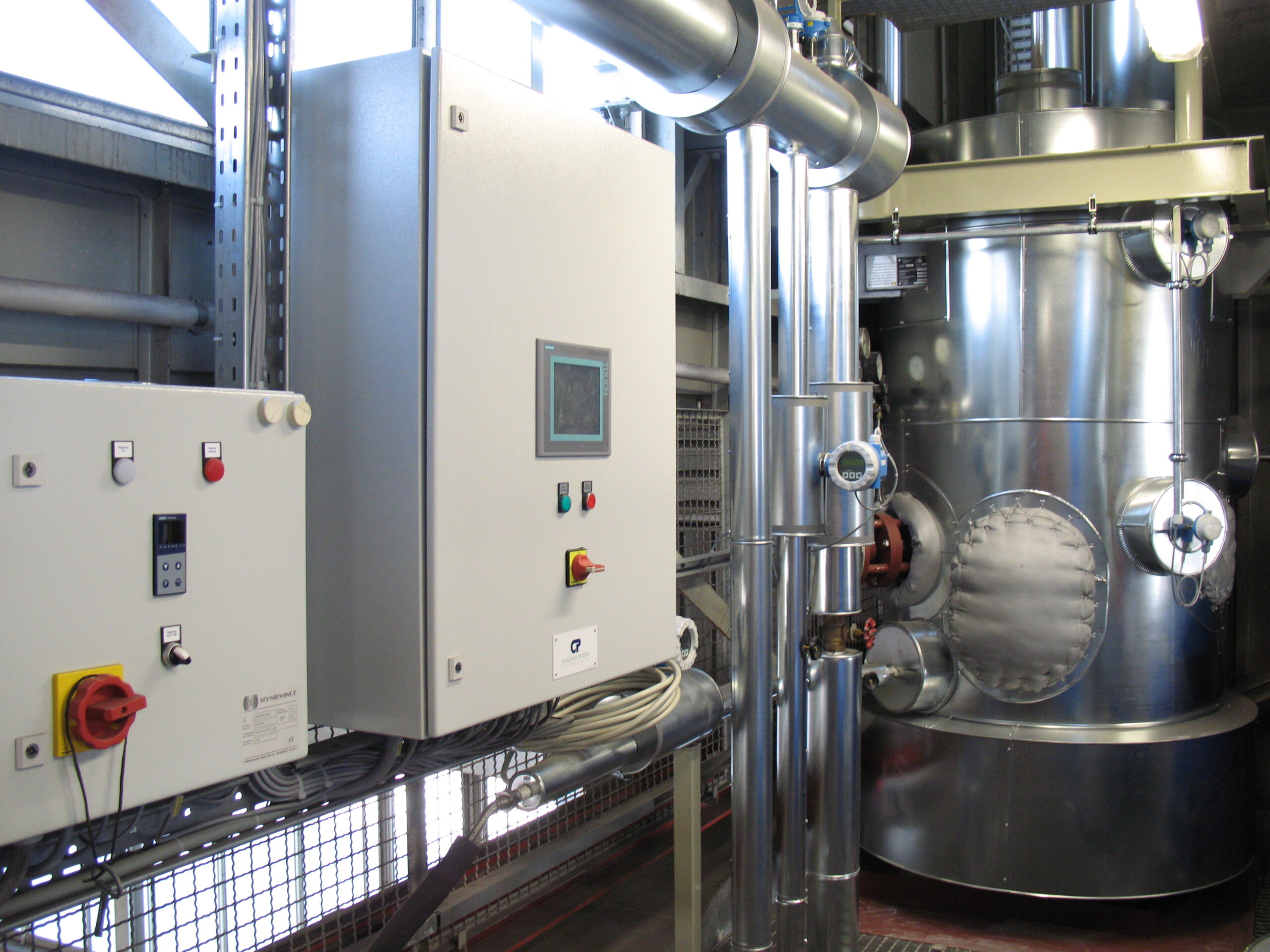

Gypsum homogenizer
The quality of gypsum and stucco products is highly influenced by the quality of the calcining process uti...
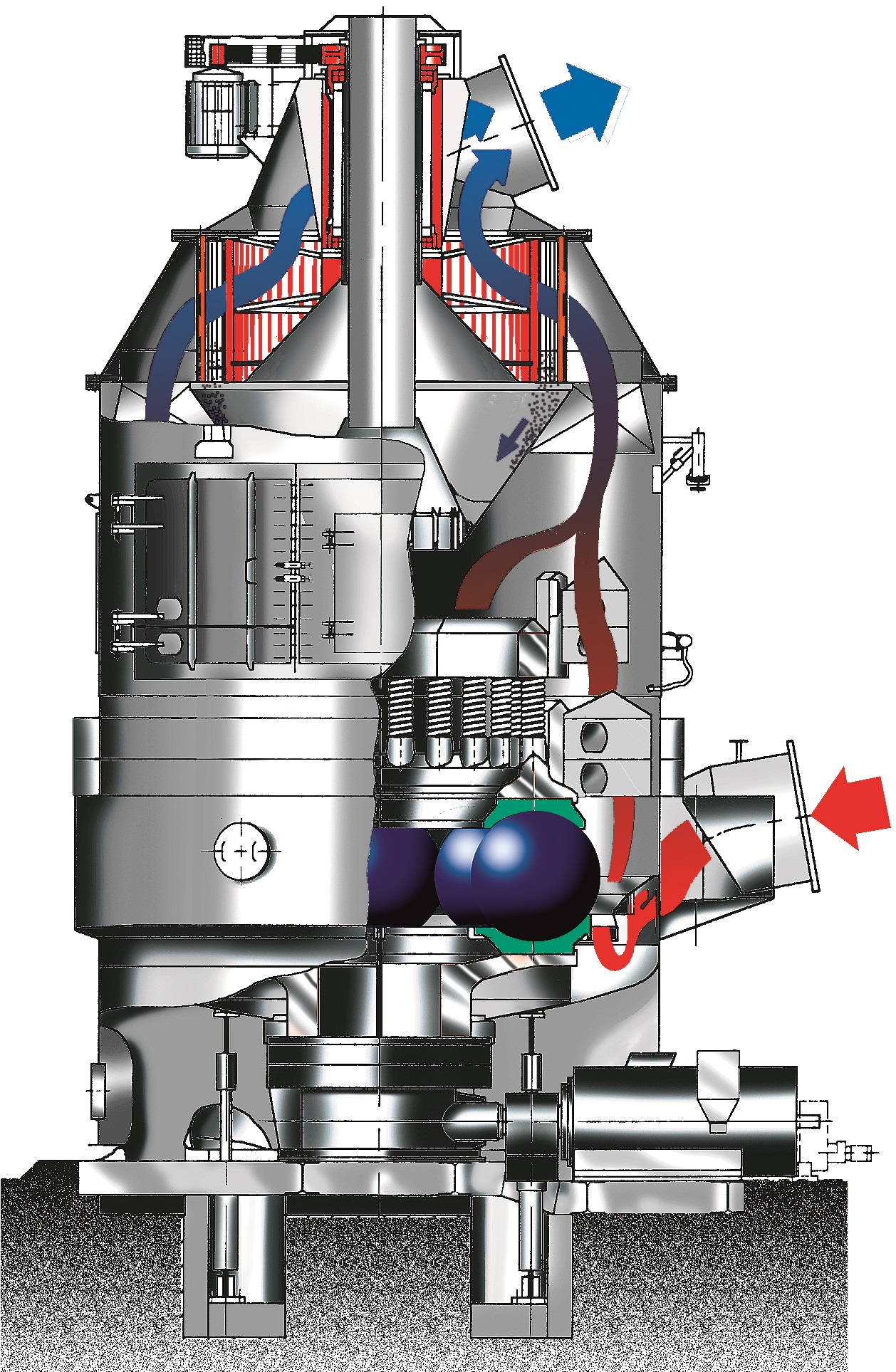
Mill for calcining gypsum
Quality of gypsum and stucco products are highly influenced by the quality of the calcining proces...