Fuel Processing Technology
Find innovative fuel equipment and connect directly with world-leading technology suppliers
Energy is constantly changing, but it finds rest in a fuel. Once exposed to heat, though, these natural materials release their captured energy. Every aspect of everyday life – from manufacturing to digital services – is powered by the mastery of this complex conversion from fuel to energy.
Select your fuel process
Tell us about your production challenge
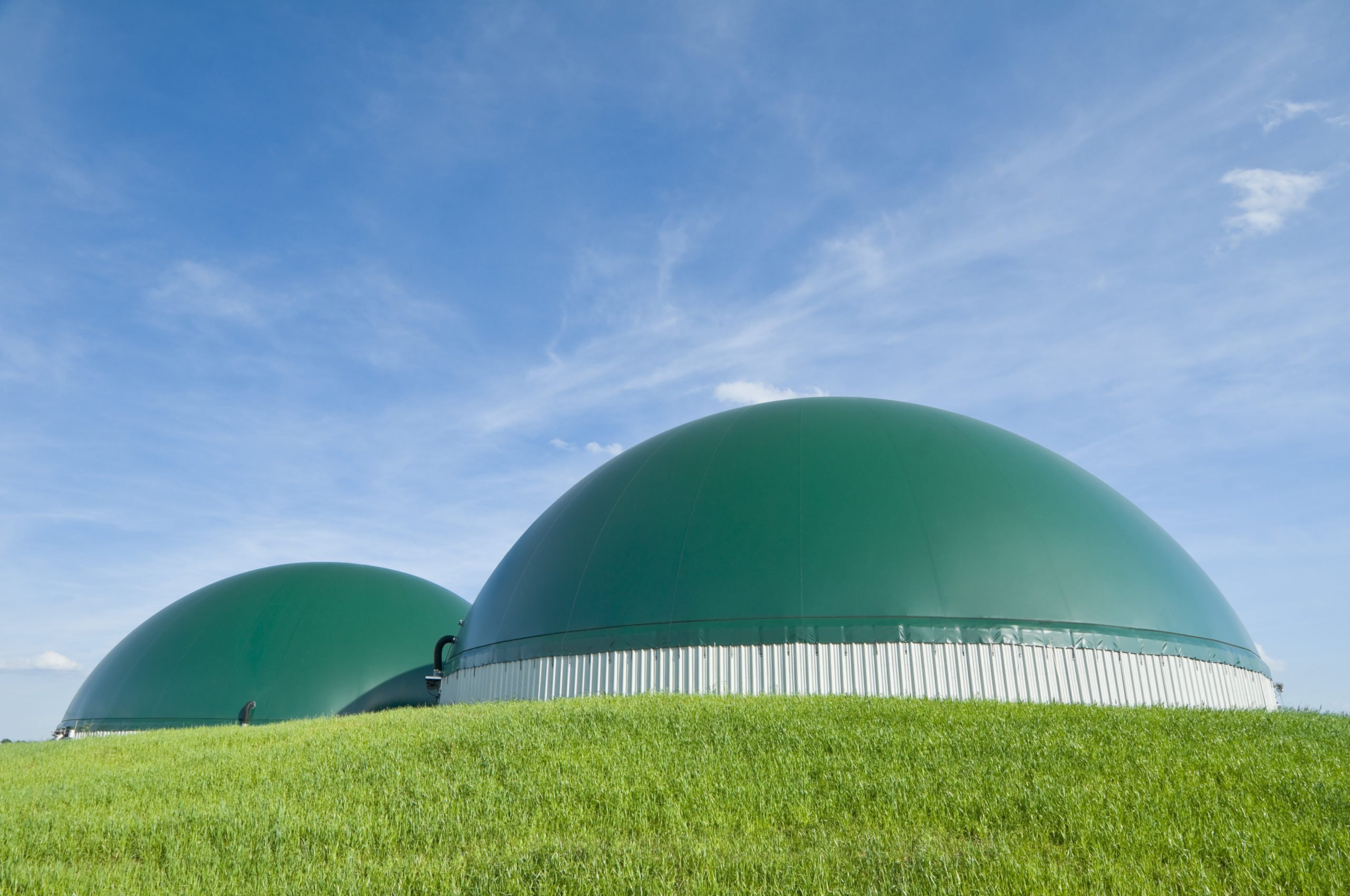
Going bio with primary fuels
Natural resources like bitumen or coal have long been used to generate heat and produce mechanical work. These primary fuels store energy that can either be used immediately or refined into a secondary fuel without causing any energy loss in the process.
Fossil fuels account for over 85% of primary energy consumption globally. In the last decade, however, alternatives such as biomass and modern biofuels have been making modest but steady inroads.

Making the most of raw resources with artificial fuels
Secondary fuels are produced to maximize their potential for combustion. Their prominent characteristics are derived from primary fuel using a process of distillation and refining.
These so-called artificial fuels are distributed for both industry and domestic use in solid states (e.g. charcoal) liquid (e.g. gasoline), or gas (e.g. methanol). New methods are producing more environmentally-responsible fuels such as ethanol or sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) that reduce the reliance on fossil fuels.
How fuels came of age with the combustion engine
Secondary fuels were developed with the arrival of the combustion engines. In fact, early refineries used to discard petrol as a waste material until technologies became efficient enough.
Today, most industrial applications, from trains to factory generators, rely on diesel compression engines. Concern over the ecological impact of diesel and limited raw resources, however, is encouraging sectors to pivot to sustainable alternatives such as biodiesel.

Revolutionizing power with the fuel cell
The combustion engine has literally propelled the industrial transformations in the last two centuries. The future, however, is looking to rely less on combustion and more on electrochemical reactions. Enter the fuel cell.
Fuel cells are versatile technologies that leverage hydrogen to generate electricity and power. The cells are more efficient and, when green hydrogen is used, they emit no greenhouse gases. The only discharges are heat and water, which can both be harvested for other applications.
Which fuel technology do you need?
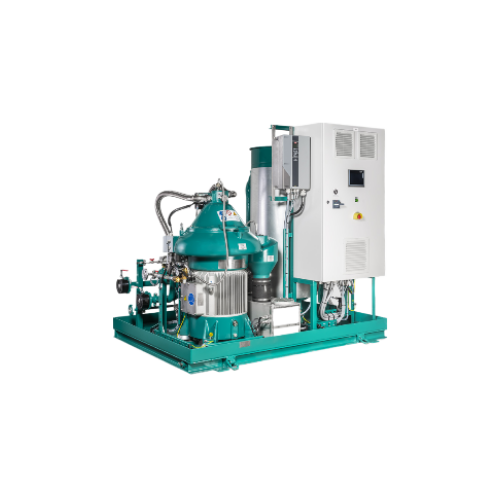

Biofuel separator for marine applications
Efficiently separate and purify marine biofuels while meeting the stringent envi...
Hydrogen refueling stations planning and construction
Facing challenges in setting up hydrogen infrastructure? Our soluti...
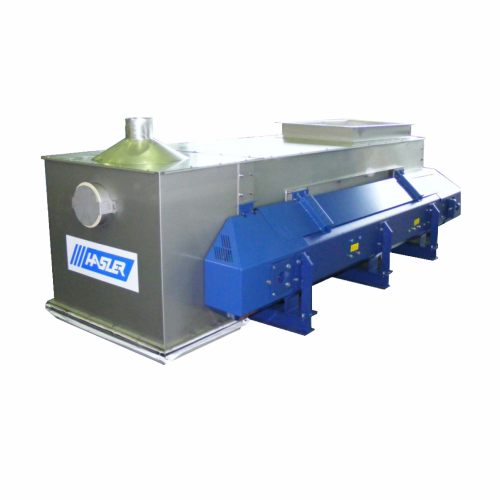

Belt feeder for alternative fuels
Maximize fuel efficiency with this belt feeder designed for seamless dosing of alternativ...

Fuel gas conditioning system
Optimize your fuel gas for efficient turbine operation and pipeline distribution with an advanc...
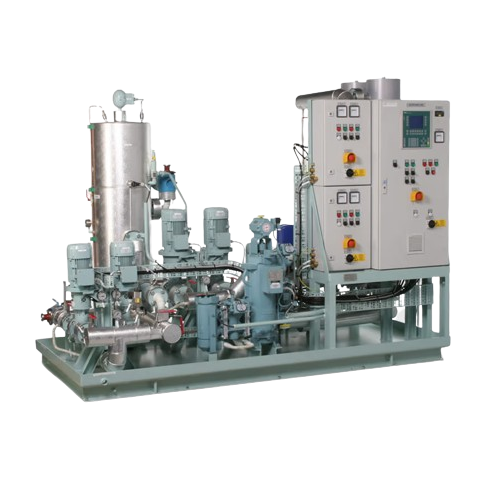

Fuel conditioning systems for diesel engines
Ensure optimal fuel quality for your diesel engines by precisely controlling ...
Industrial air classifiers for pulverized fuel production
Optimize your fuel production process with precision disc turb...
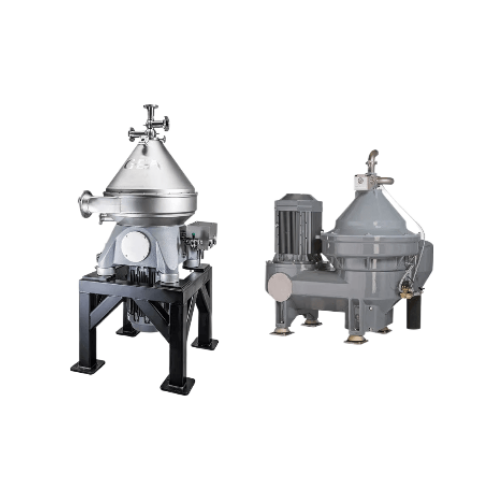

Crude oil dehydration and desalting system
Efficiently handle challenging crude oil compositions with a centrifugal system...
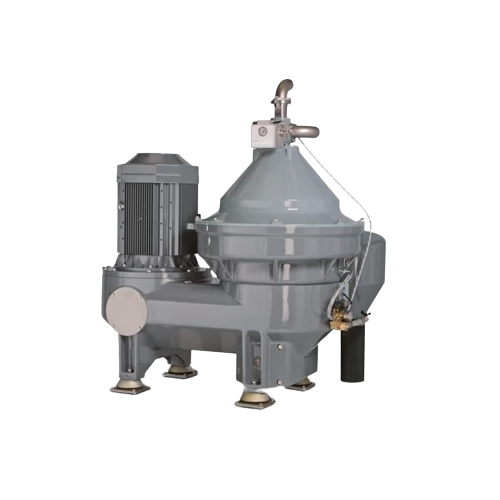

Clarifier for industrial fluids
Optimize fluid purity and extend equipment lifespan by efficiently separating contaminants f...
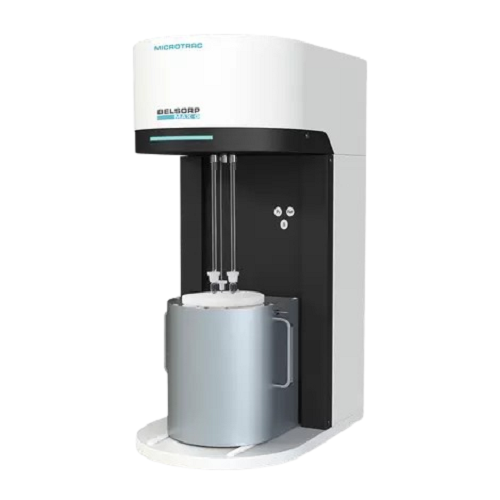

Specific surface area & pore size analyzer for materials
Achieve unparalleled precision in material characterization by m...

Catalyst characterization analyzer
Achieve precise catalyst characterization and optimization with advanced techniques like...

Automotive assembly and leak testing systems
Optimize your production line with versatile assembly and testing systems, en...
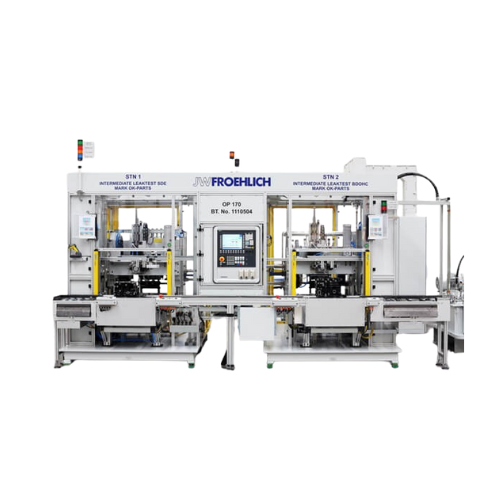

Cylinder block leak testing system
Ensure reliability and quality by detecting and addressing leaks in cylinder blocks with...
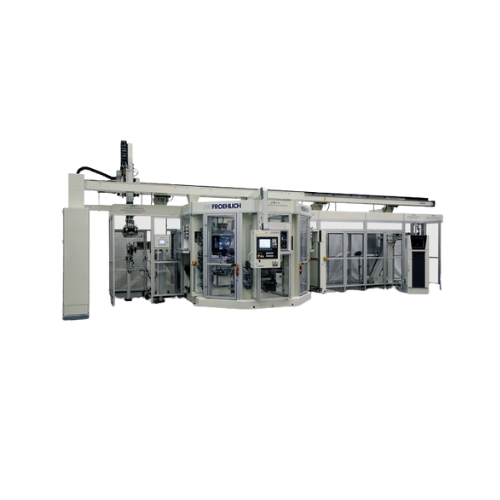

Leak testing system for automatic transmissions
Ensure the integrity and functionality of your automatic transmissions wit...
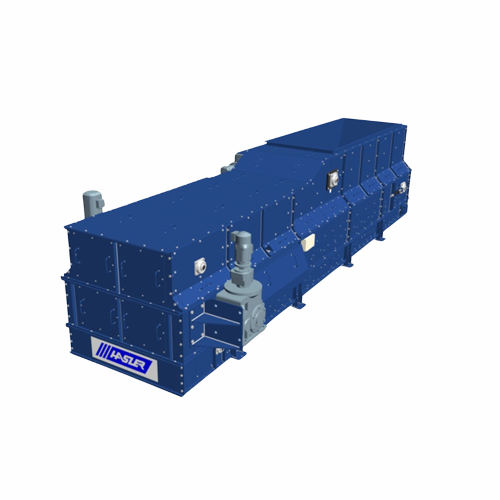

Weigh belt feeder for low-density materials
Optimize high-volume feeding accuracy for light materials while reducing your ...
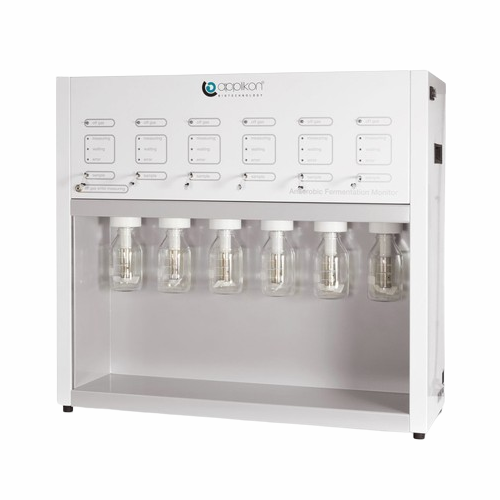

Fermentation monitor for alcohol production
Optimize anaerobic yeast fermentations with precise monitoring of carbon conve...
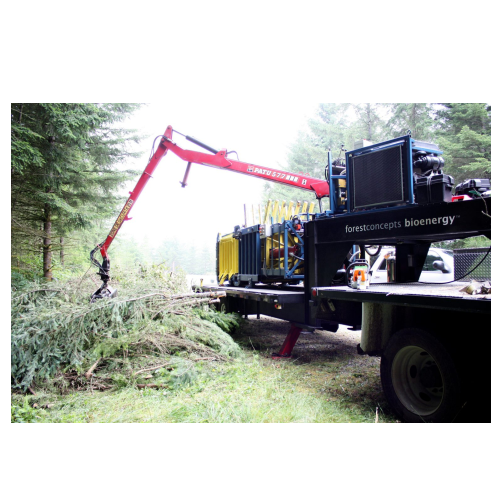

Biomass baler for woody biomass collection
Optimize woody biomass management with a mobile solution that reduces noise, du...
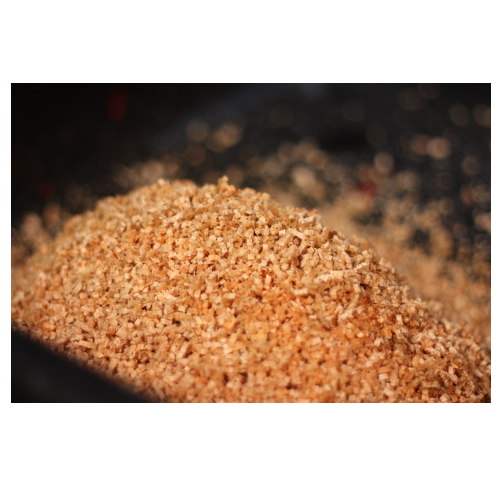

Precision feedstocks for biomass energy production
Optimize your biomass conversion with precision-sized feedstocks desig...
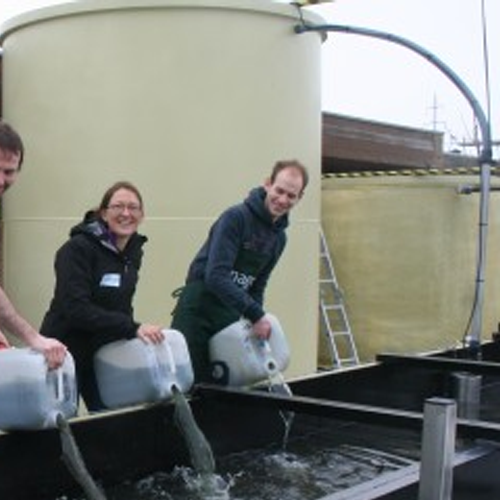

Microalgae photobioreactors for bioenergy production
Optimize your microalgae’s growth and conversion processes wit...
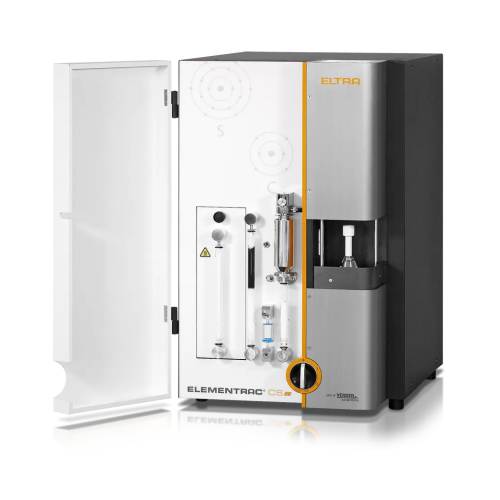

Carbon/hydrogen/sulfur analyzer for organic sample analysis
Ensure precise elemental analysis of carbon, hydrogen, and s...

Zero effluent discharge system for solvent extraction plants
Eliminate wastewater in your solvent extraction process whi...

Biodiesel pretreatment system
Optimize your biofuel production by efficiently reducing impurities and unwanted components, e...

Renewable diesel pretreatment system
Extend hydrotreater catalyst life and boost plant uptime by optimizing feedstock purit...
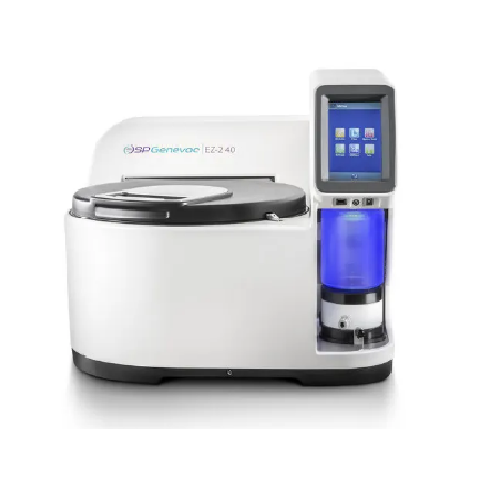

Centrifugal evaporator for medicinal chemistry
Achieve precise evaporation and crystallization with innovative anti-bumpin...
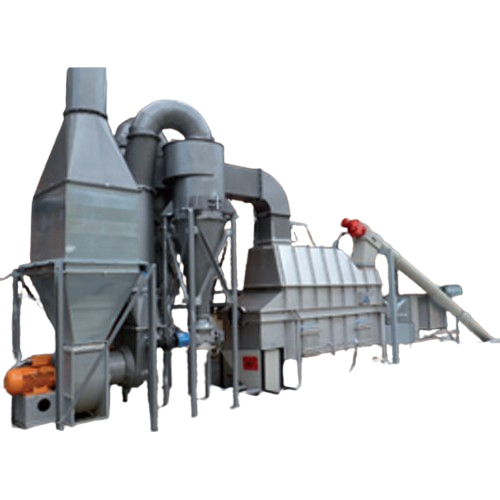

Biomass drying solution
Achieve efficient and gentle biomass drying with innovative heat exchange technology, ensuring optima...
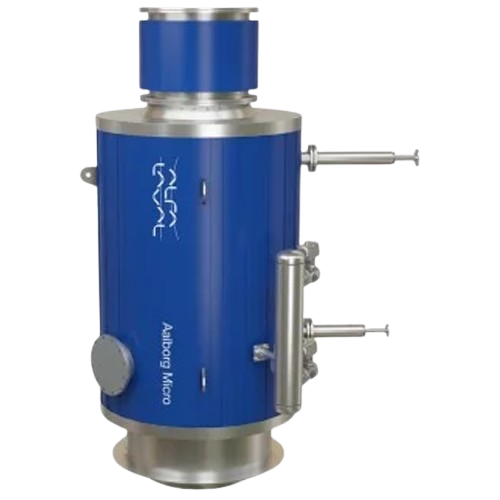

Compact marine boiler economizer for auxiliary engines
Efficiently reclaim waste heat from auxiliary engine exhaust to bo...
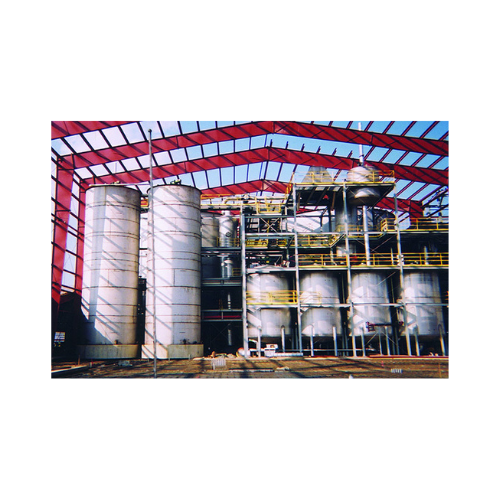

Custom fabricated industrial tanks
Optimize your production with these industrial tanks, designed to handle a diverse range...
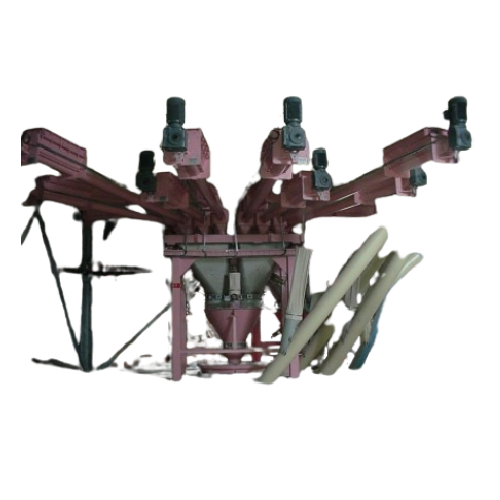

Dosing screw system for precise ingredient management
Achieve unparalleled precision in formulating mixtures with our dos...
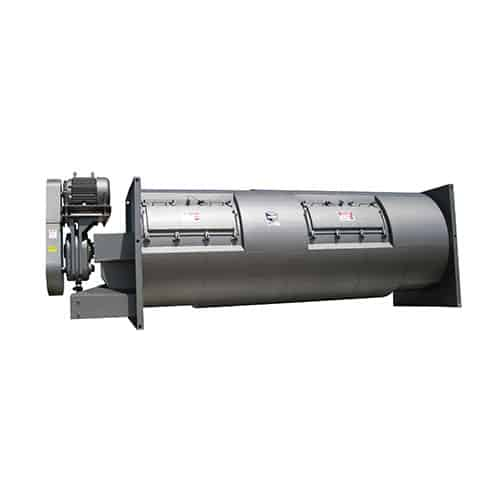

Slurry blender for ethanol production
Optimize your ethanol and beverage alcohol production with a solution that ensures pr...
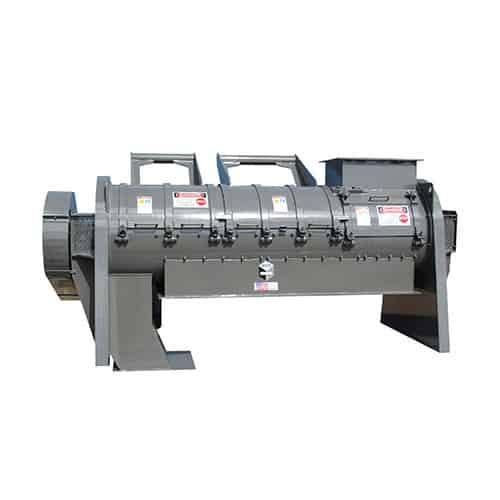

Turbo separator for Ddg agglomeration
Efficiently eliminate clumping and improve flow in your distillation process, ensurin...
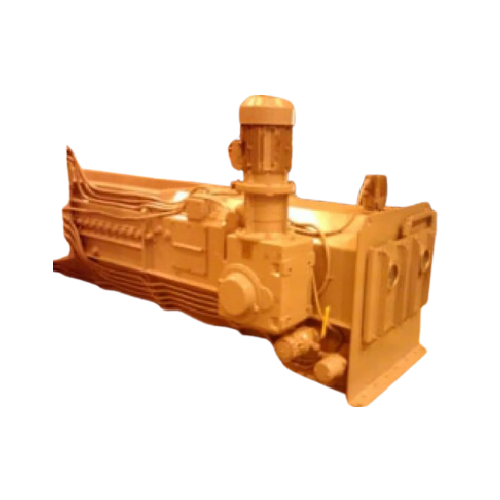

Medium pressure gravimetric feeder for pulverized coal boilers
Achieve precise combustion control and optimize fuel effi...

Wood chip gas syngas generator
The recovery of energy from biomass isn’t all advantages, it has its shortcomings as well. Bi...

Oilseeds preparation plant
When producing customized flakes, pressed cakes, or other oilseed products, the oilseed preparati...
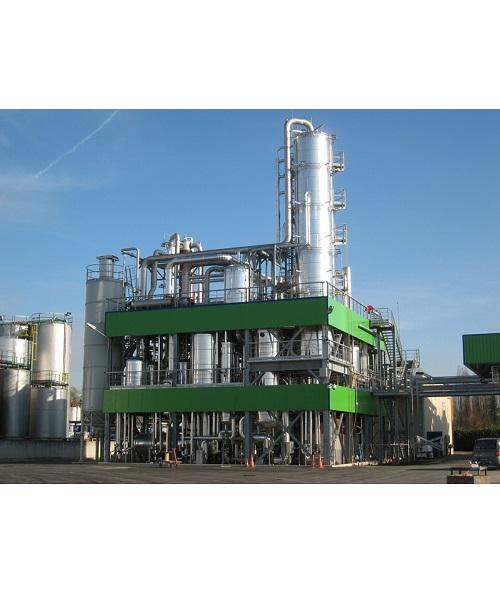

Production plant for biodiesel
As a biofuel producer, making biodiesel from several types of treated vegetable oils or anima...
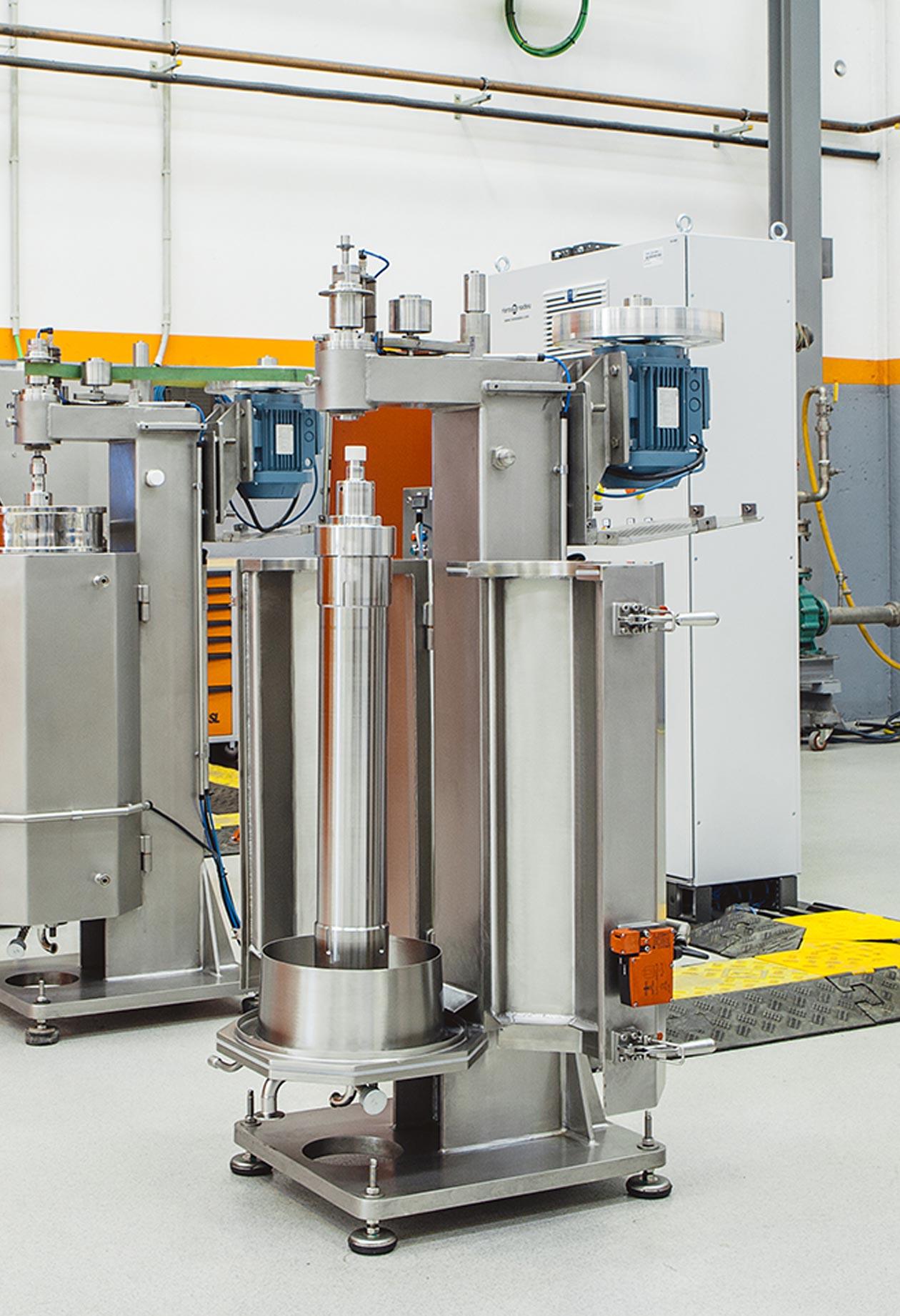

Water oil separation centrifuge
Some industries, such as petrochemical, generate large volumes of oily wastewater due to the...
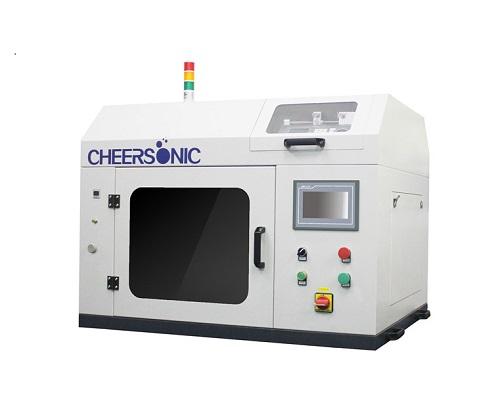

Ultrasonic spraying system for small scale coating and research processes
Ultrasonic spraying technology has the abili...
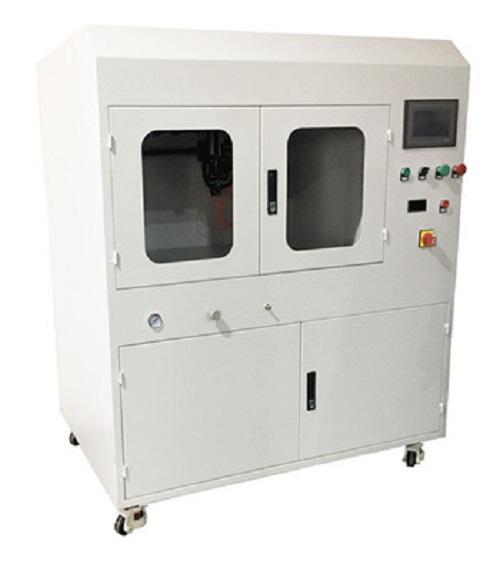

Ultrasonic spraying system for medium and large scale coating
When it comes to expensive chemical solutions and suspensi...
Efficient sized biomethane production system
Also referred to as biogas purification, biogas upgrading is an excellent alt...

Large-scale biomethane production system
Membrane separation technology for biogas purification is considered as an effecti...

Modular biogas to biomethane system
The primary purpose of biogas upgrading technology is to increase the volumetric energy...

Small-scale biogas upgrading system
Biogas upgrading refers to the process of purifying biogas through separating methane f...
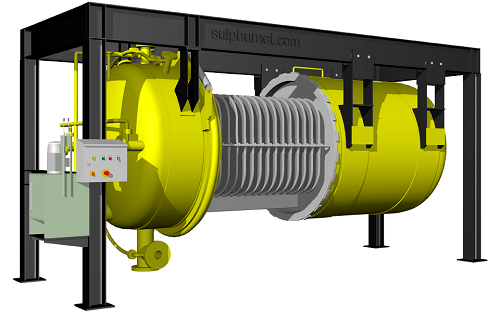
Industrial leaf filter for chemicals
In recent years the removal of sulphur has received increasing attention because of sa...
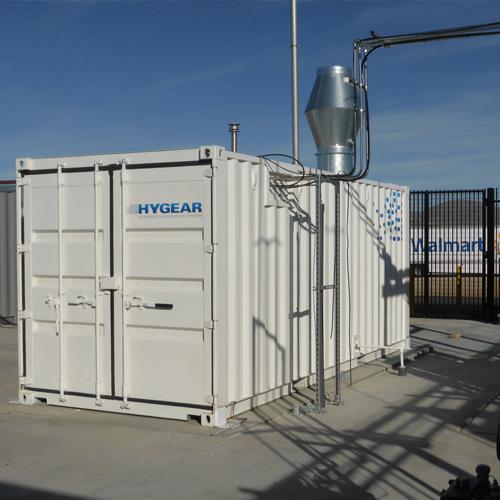

Plug and play natural gas to hydrogen generator
Hydrogen is an all-purpose element and can be simply defined as energy’s S...

Belt dryer for sewage sludge
If your water treatment plant often facing difficulties with sewage sludge deposits, drying the...
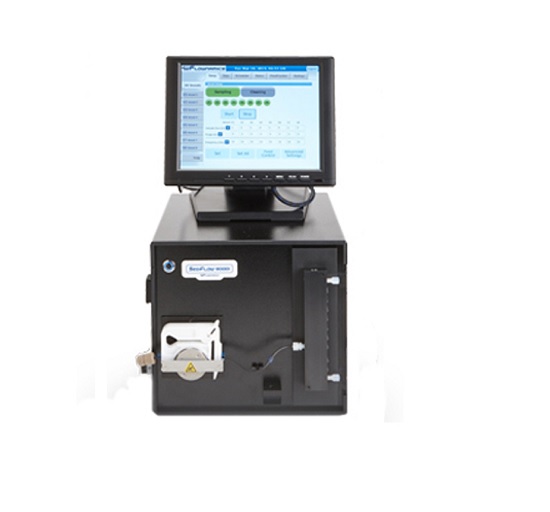

Online sampling system for larger scale bioprocesses
Accurate sampling is vital for improving a wide variety of industria...

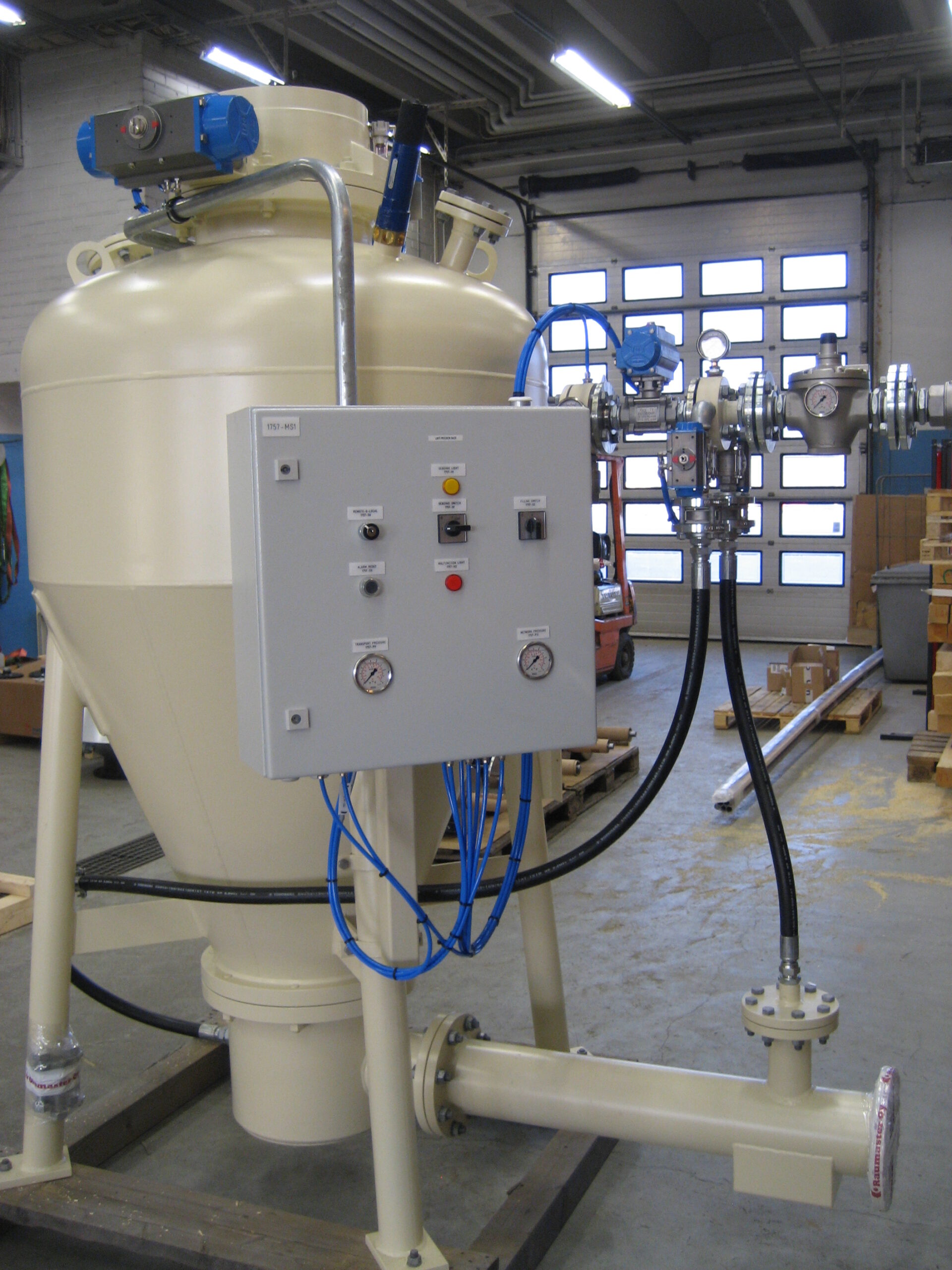
Pneumatic conveying for industrial biomass boilers
Modern boiler plants have a wide variety of conveying needs. While tr...
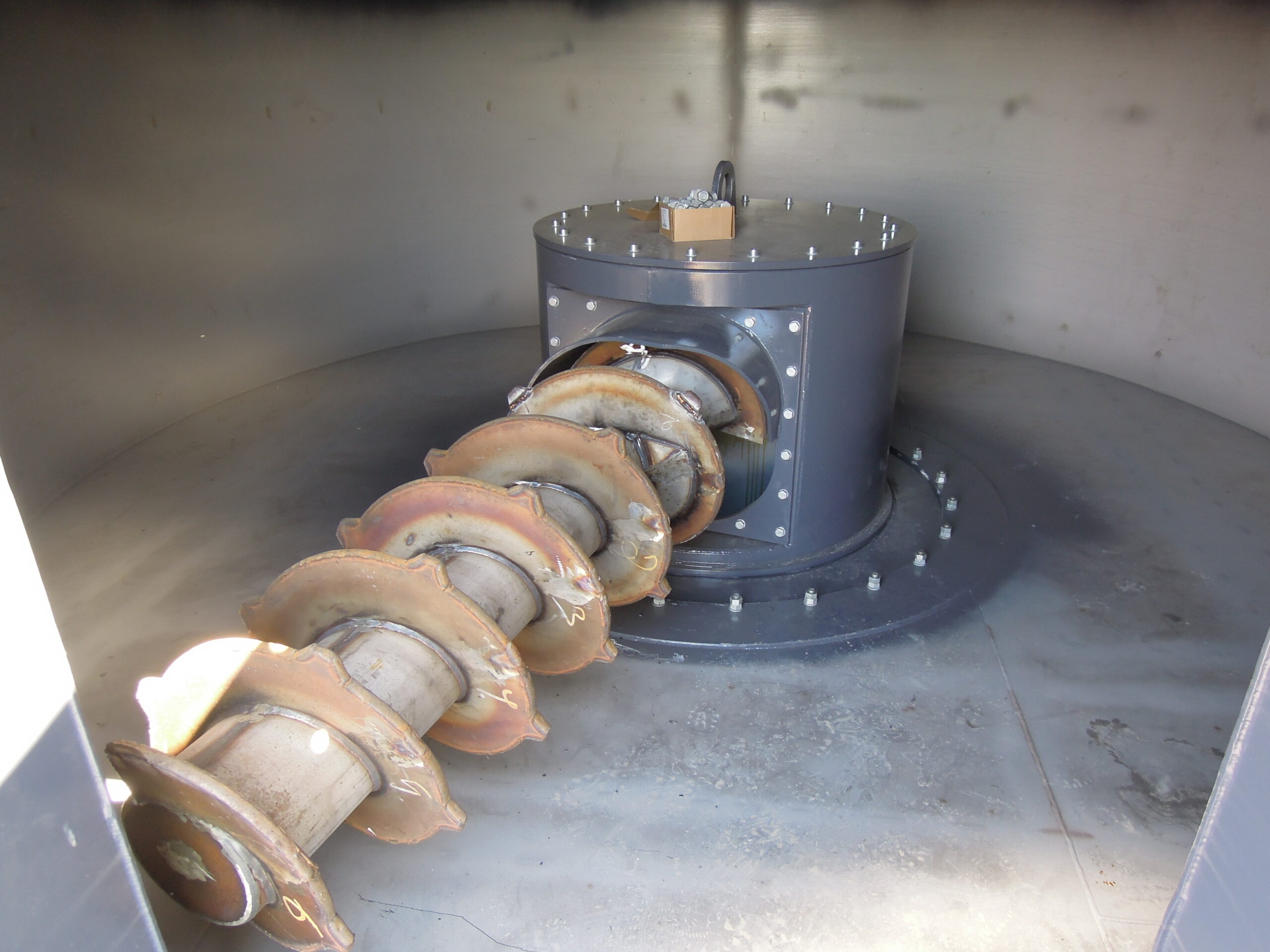

Solid biomass boiler feeding systems
Energy conversion from biomass requires efficient boiler operation which is largely in...

Conveyors for recovery boilers
Recovery boilers recapture energy otherwise wasted in organic byproducts of industrial proces...

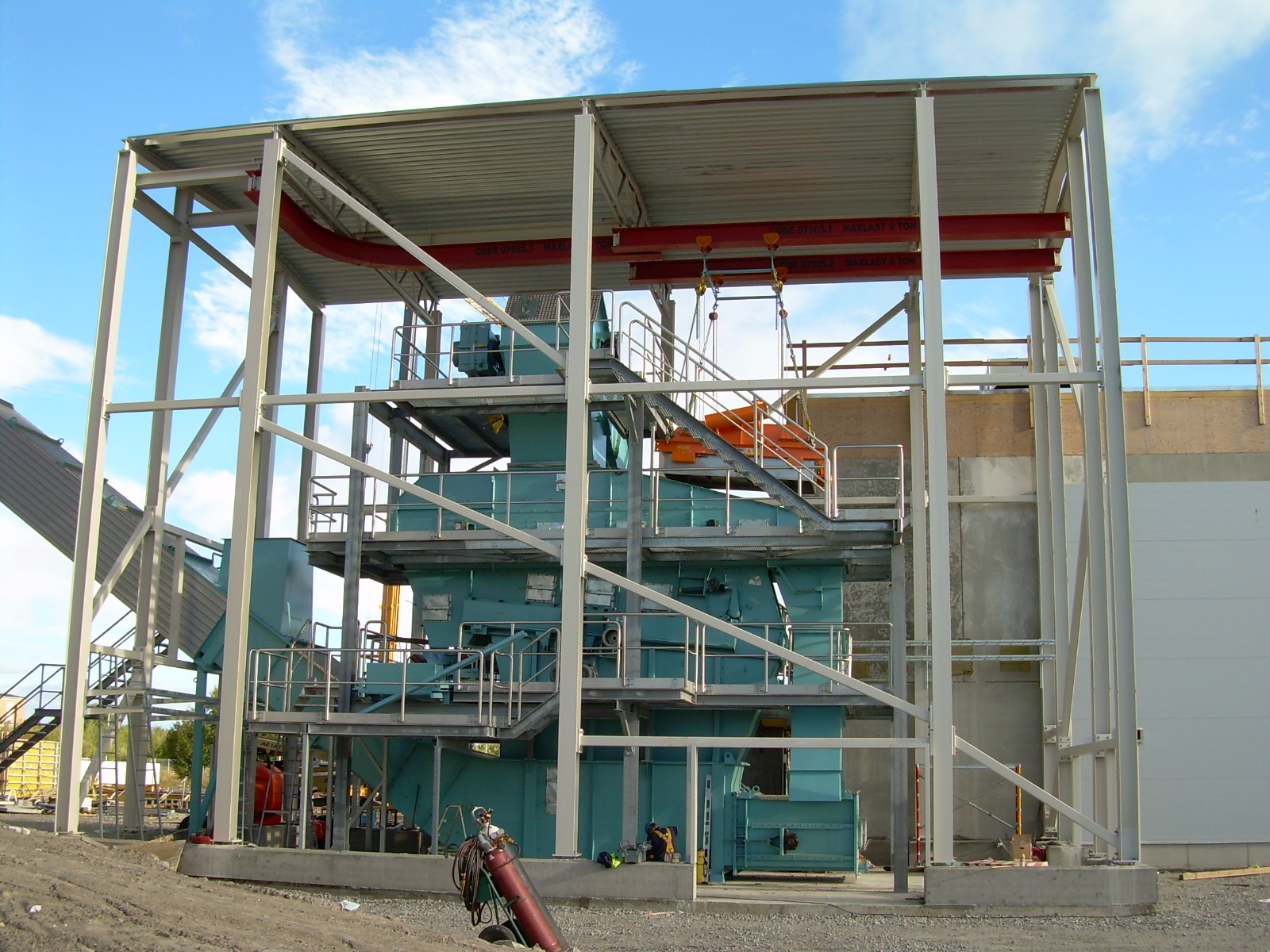
Ash handling systems for industrial biomass boilers
The increasing use of solid fuels including biomass for energy conver...

Solid biomass screening and crushing equipment
Biomass fuels come in many forms and often include impurities that can dama...
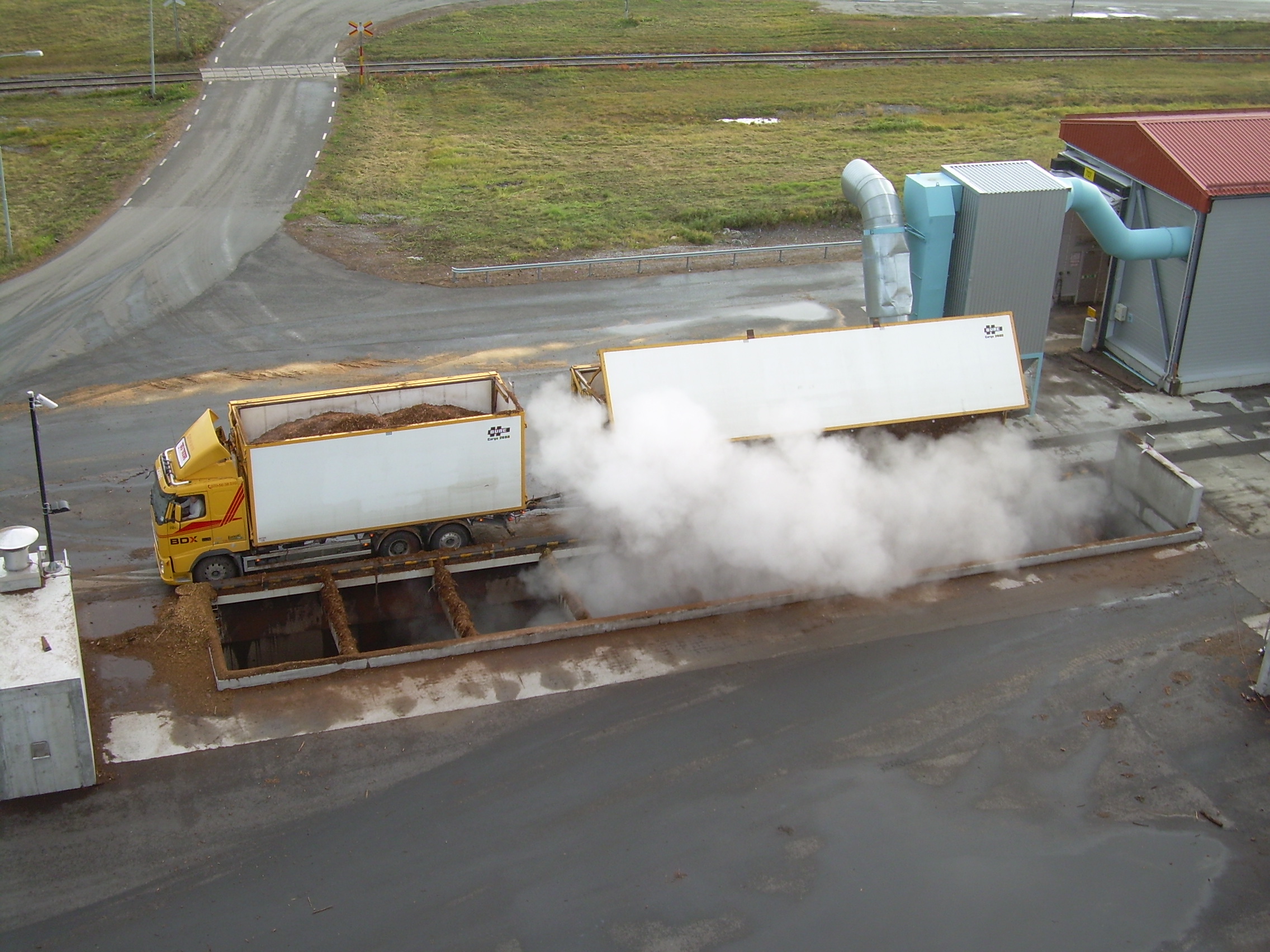

Solid biomass receiving systems
Biomass fuels come in many forms and are often handled in very large quantities. Shipment m...
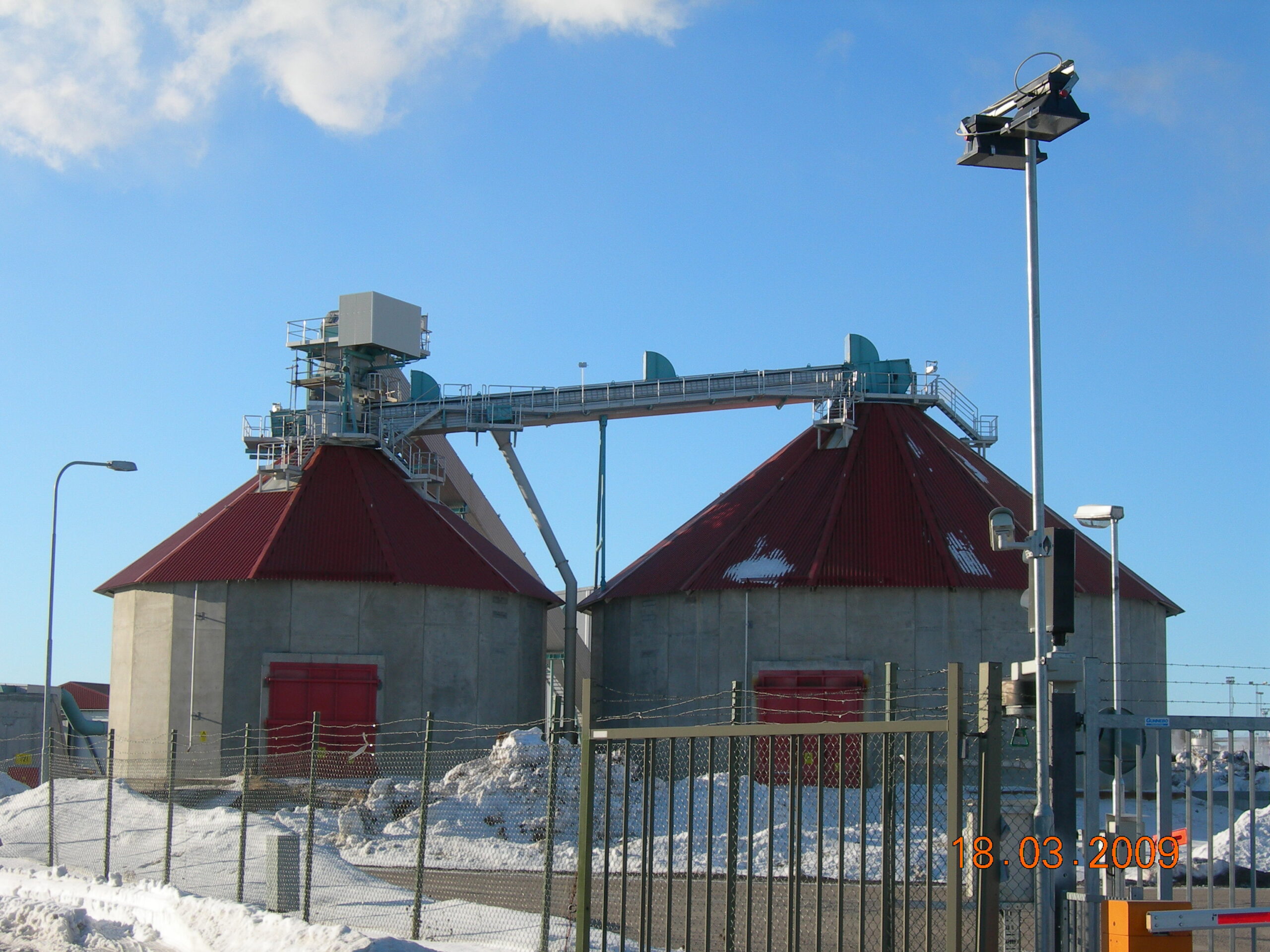

Solid biomass storage and reclaiming equipment
Biomass fuels must often be stored for additional preprocessing or prior to...

Efficient biomass screw dryers
Optimize biomass processing with screw drying technology that efficiently reduces moisture co...

Pore size distribution analyzer
Optimize your material analysis with a system that delivers precise pore size distribution a...

Gas pycnometer for true density measurement of solids and powders
Achieve highly precise density measurements of solid ...
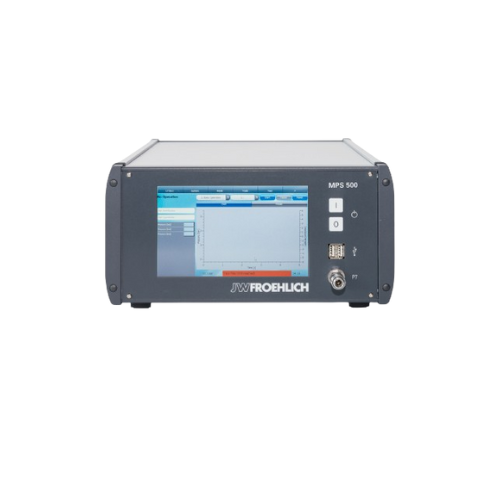

Leak test panels for industrial applications
Ensure the integrity of your critical components with precision leak testing ...
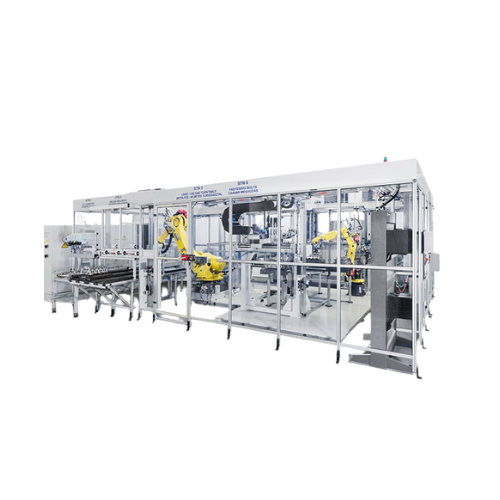

Cylinder head leak testing systems
Ensure critical sealing integrity with advanced leak testing systems designed to accurat...
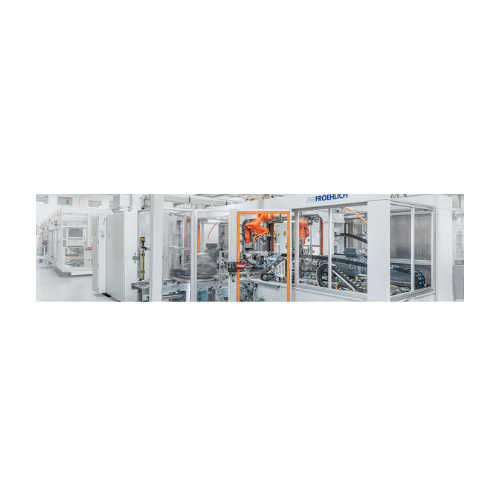

Electric drive unit testing systems
Optimize your electric vehicle production with comprehensive testing systems designed t...
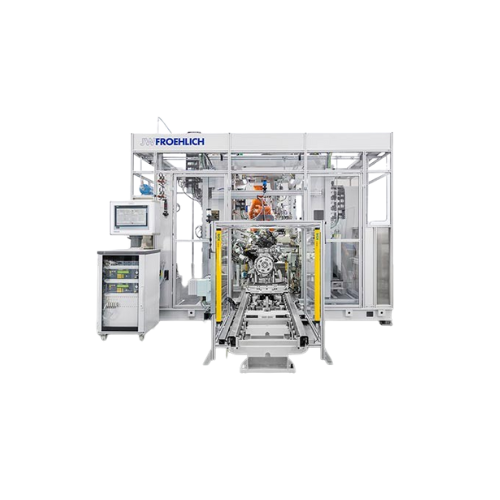

Leak test system for engine components
Ensure the integrity of engine components with precise and efficient leak detection,...
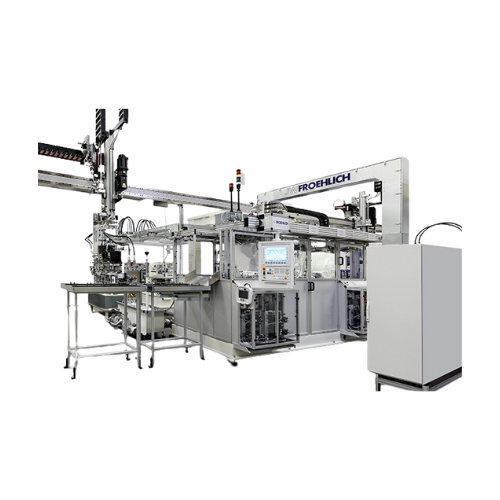

Function test for electro-hydraulic control units (ehs)
Ensure precise functionality and reliability in your production l...
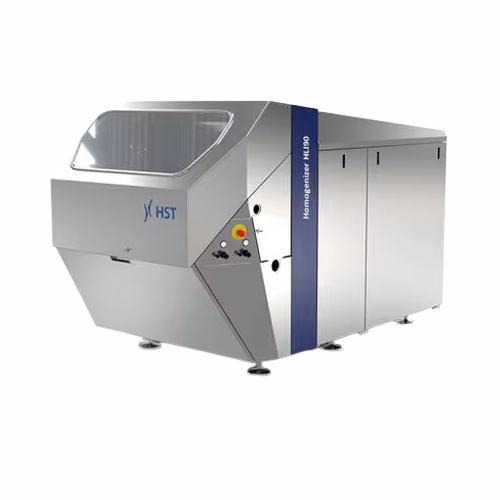

High-pressure homogenizer for food and pharmaceuticals
Achieve unparalleled consistency and stability in emulsions and di...
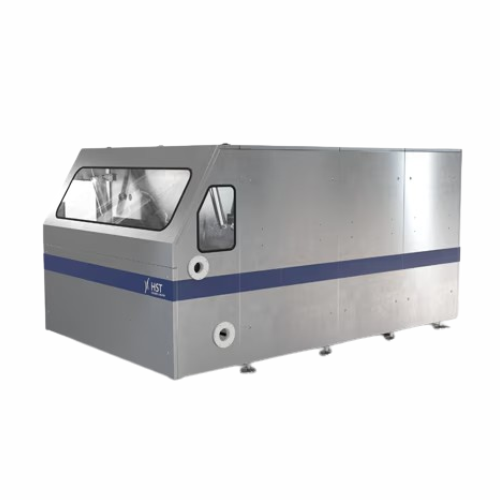

Homogenizers for high-pressure applications
Achieve unparalleled product consistency and stability with precision-engineer...
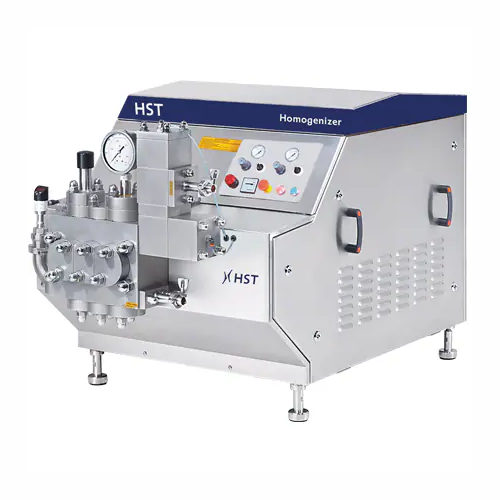

Industrial homogenizer for food and pharmaceutical applications
Ensure product consistency and stability with high-press...
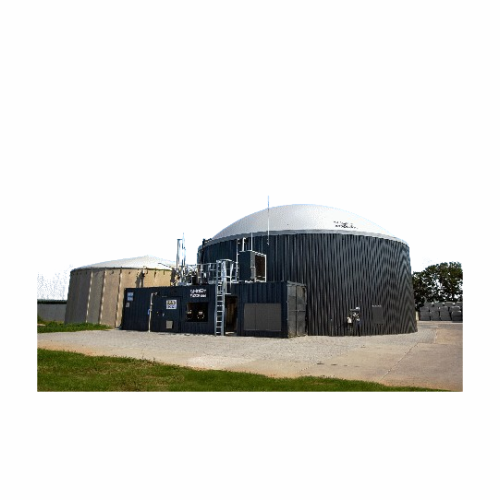

Manure biogas plant for agricultural sector
Transform animal waste into renewable energy and nutrient-rich bio-fertilizer,...
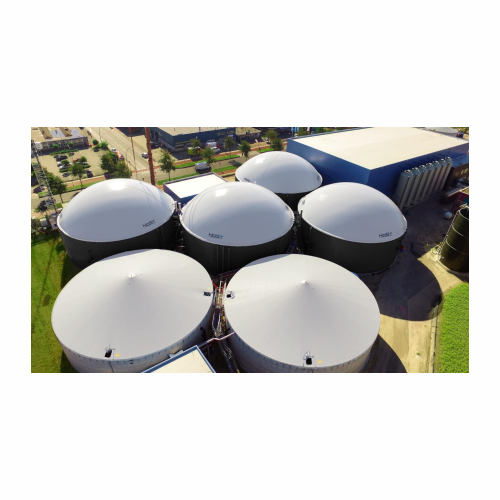

Organic waste biogas plant
Transform abundant organic waste into renewable energy and valuable byproducts with a high-effici...
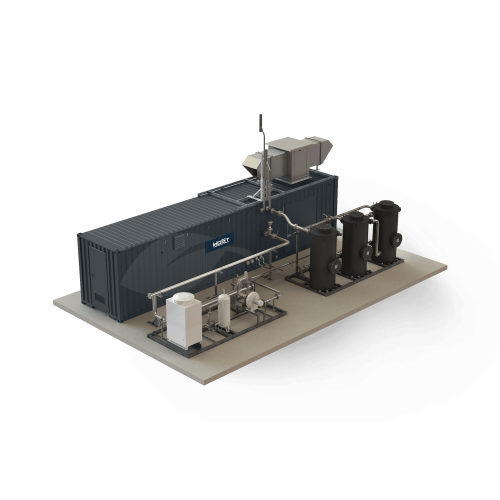
Biogas upgrader for high methane yield
Optimize biogas production by efficiently converting raw biogas into high-purity bio...
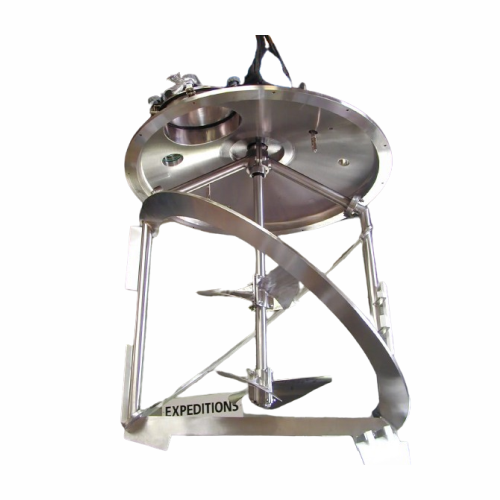

Coaxial mixer for high viscosity liquids
Achieve seamless blending of high-viscosity materials with a coaxial mixer designe...
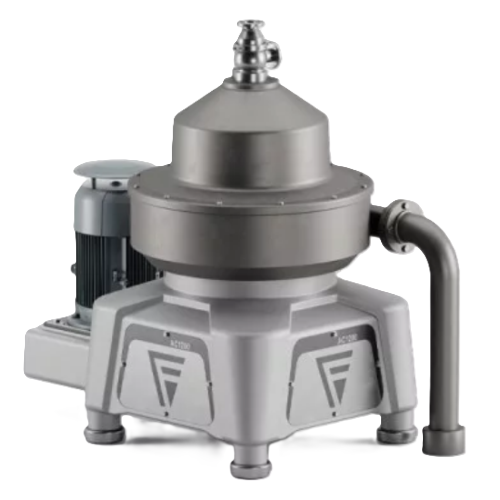

2-phase separator for clarifying liquids
Efficiently refine and clarify liquids while minimizing waste. This 2-phase separa...
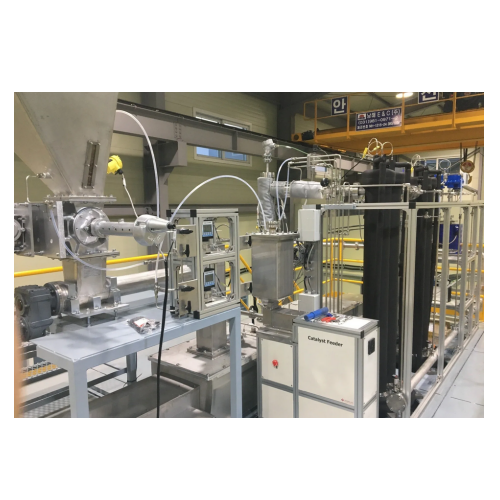

Pyrolysis for biomass conversion
Transform diverse waste materials into valuable bio-commodities and energy through advanced...
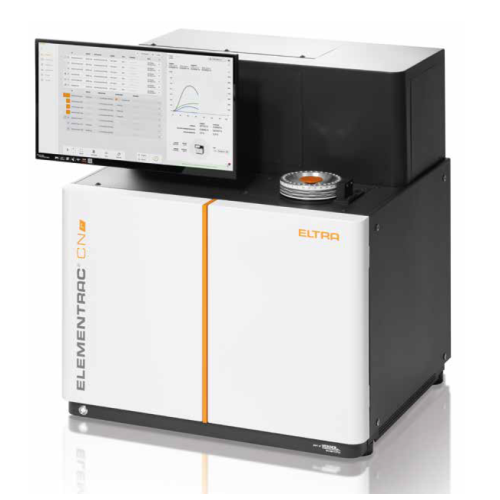

Carbon/nitrogen analyzer for organic samples
Optimize your lab’s efficiency with fast, reliable nitrogen and carbon ...
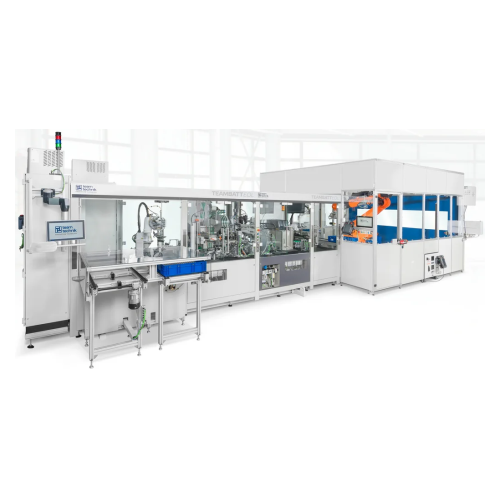

Production systems for battery cells with end-of-line testing
Optimize battery cell production with a flexible system of...
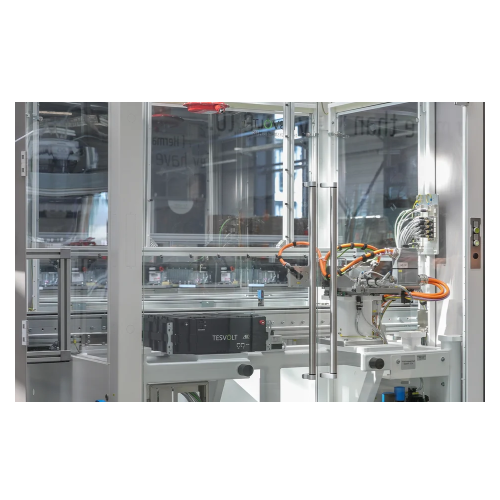

End-of-line battery pack testing system
Ensure the quality and reliability of your battery packs with comprehensive end-of-...
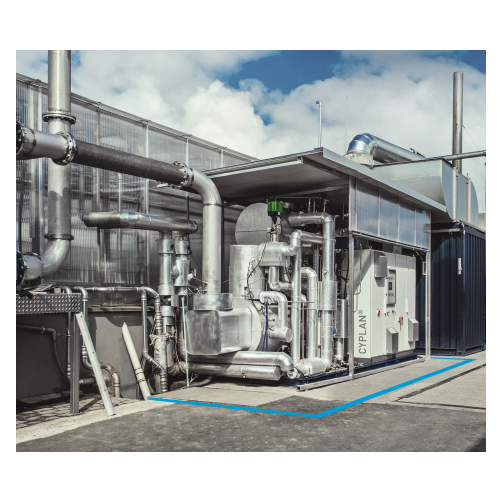

Organic rankine cycle for decentralized power generation
Harness waste heat and renewable energy sources to efficiently g...

Rectification column for close boiling point separation
Achieve high-purity separation and distillation for compounds wit...
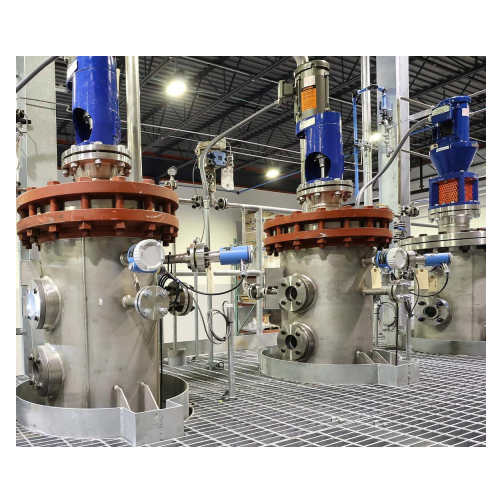

Biodiesel distillation process
Improve biodiesel quality by enhancing cold flow characteristics and removing impurities thro...
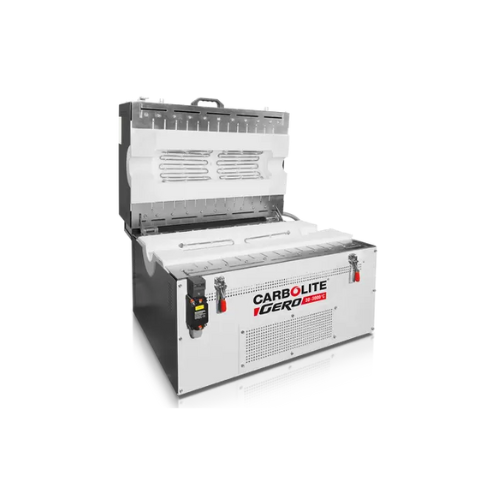

Split tube furnace for high-temperature applications
Enhance your thermal processing operations with a split tube furnace...
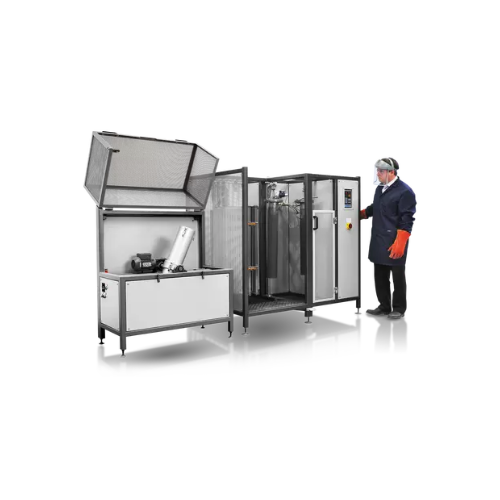

Coal and coke pilot plant testing equipment
Enhance your material testing precision with versatile equipment designed for ...
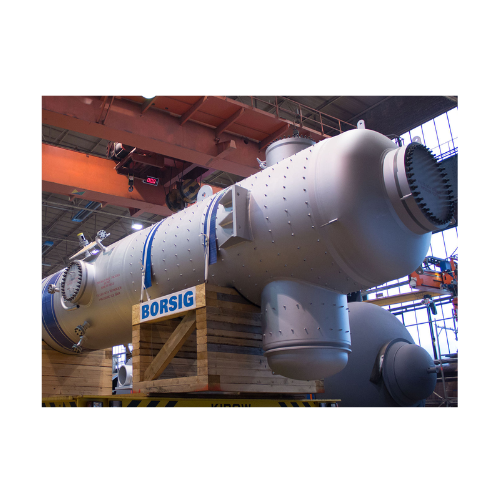

Synthesis gas cooler for partial oxidation of oil or natural gas
Optimize high-temperature gas streams efficiently by em...
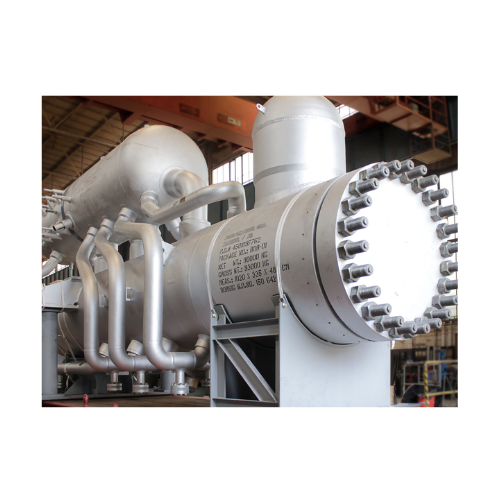

Synthesis gas waste heat boiler for ammonia plants
Enhance your ammonia production with cutting-edge waste heat recovery ...
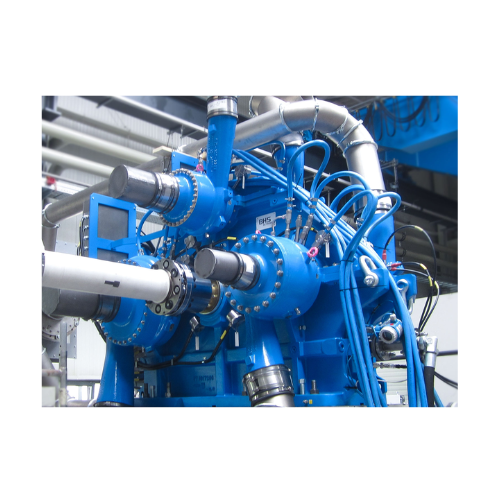

Integrally geared centrifugal compressors for process gases
Optimize your production efficiency with our integrally gear...
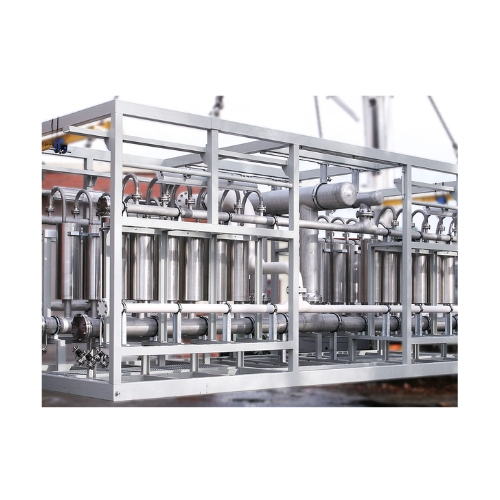

Carbon capture membranes for Co2 separation
Efficiently reduce carbon emissions in power plants and industrial operations ...
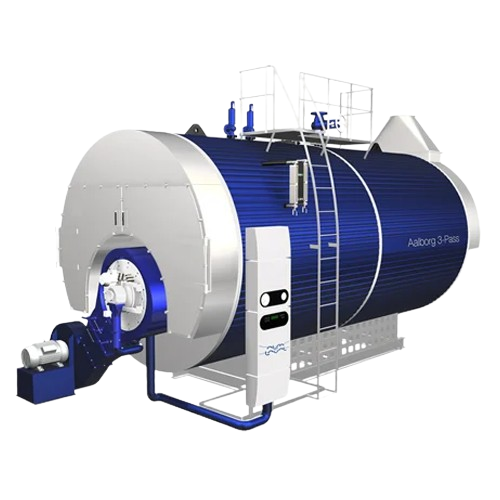

Oil and gas-fired industrial boiler
Enhance steam production efficiency with a robust three-pass combustion system designed...
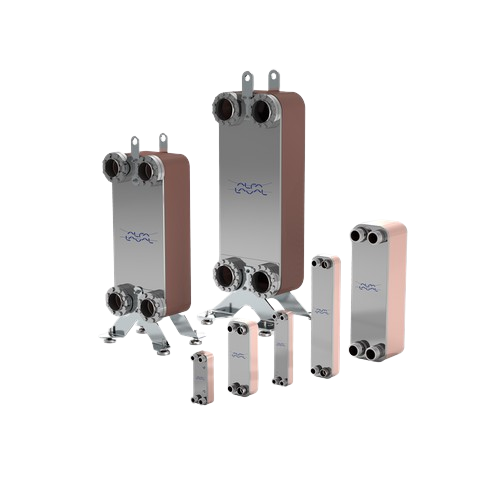

High-efficiency brazed plate heat exchanger
Optimize your thermal processes with compact, high-efficiency heat exchangers,...
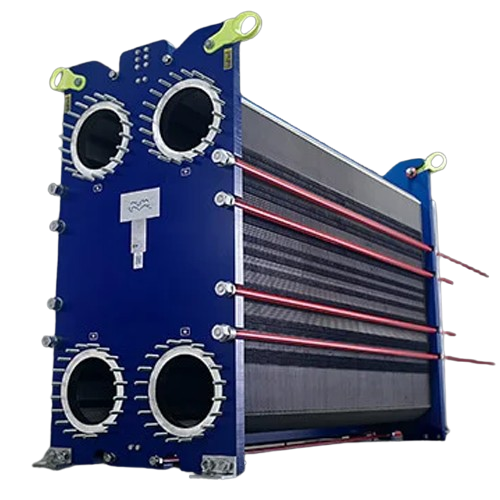
Gasketed plate-and-frame heat exchangers for industrial applications
Optimize your production with precise thermal mana...
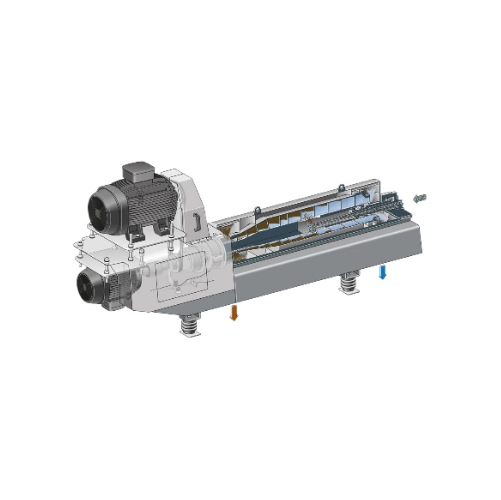
Decanter centrifuge for bioethanol production
Optimize bioethanol production with enhanced separation efficiency, enabling...
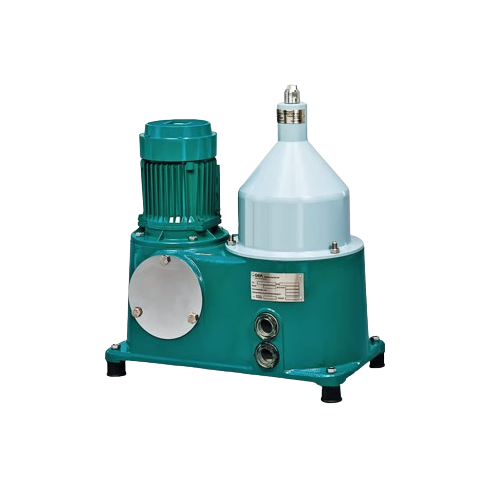

Solid-wall bowl separator for power plant lube oil purification
Optimize your power plant’s performance by address...

Autonomous process control for petrochemical and food industries
Streamline your production with autonomous control syst...
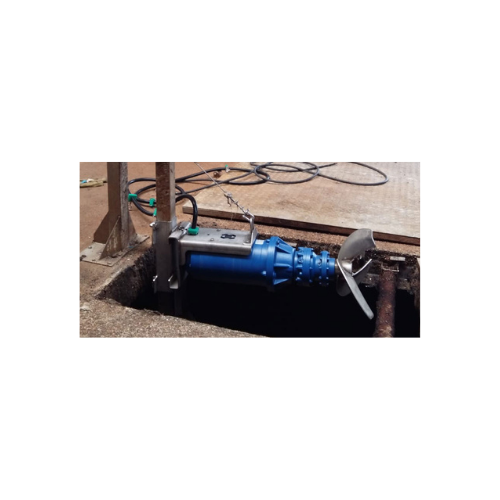

Biogas plant screw press separators
Maximize your renewable energy output and processing efficiency with cutting-edge solid...

Explosion-proof external electric motovibrators for oil & gas industry
Ensure safety and efficiency in hazardous enviro...

Explosion-proof production disperser for paint manufacturing
Ensure safe and efficient dispersion in volatile environmen...

Explosion-proof dissolver for chemical processing
Ensure safe and efficient dispersion in volatile environments with this...

Vacuum basket mill for high viscosity products
Achieve efficient fine grinding of high-viscosity products while minimizing...
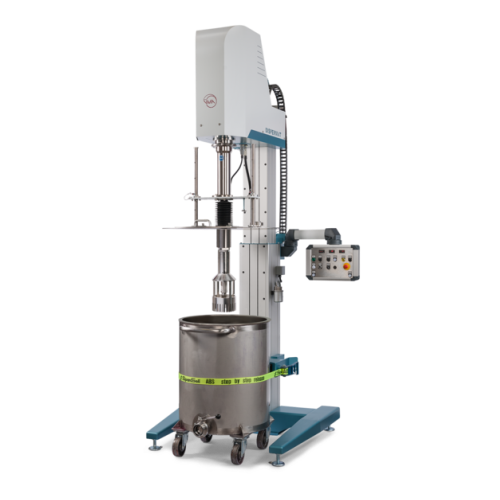

Rotor-stator homogenizer for high shear batch processing
Achieve ultra-fine particle distribution and stable emulsions wi...
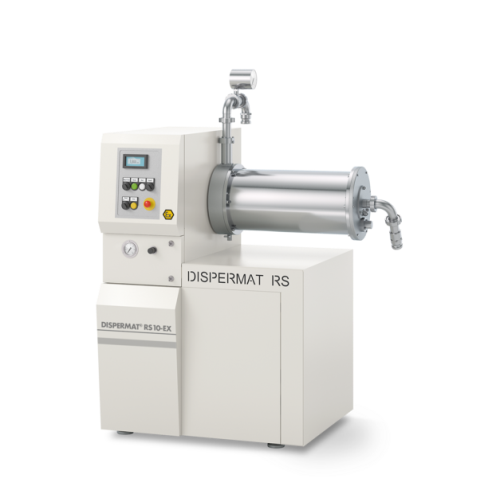

Explosion-proof bead mill for industrial grinding applications
For manufacturers seeking precise particle size control, ...
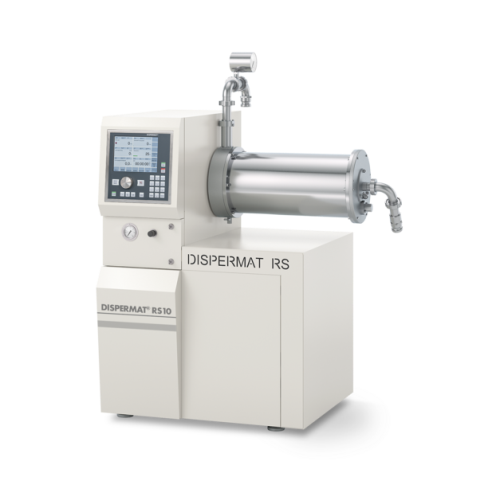

Horizontal bead mill for industrial production
Ensure ultra-fine particle size reduction in high-demand processes with thi...
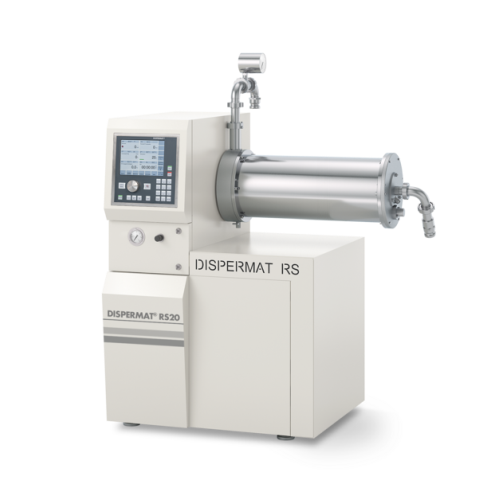

Horizontal bead mill for fine grinding in continuous process
Achieve ultrafine particle dispersion and consistent mixing...
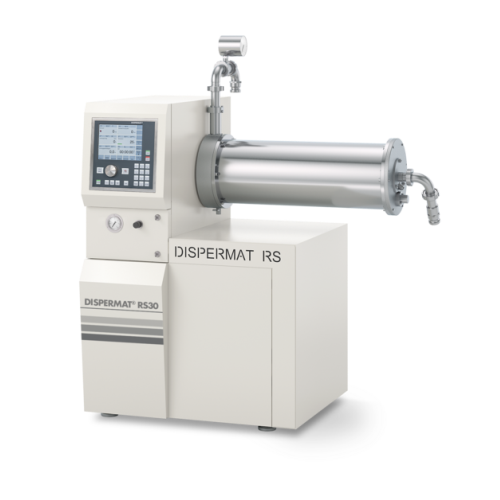

Horizontal bead mill for industrial nano grinding
Achieve precision in nano-scale grinding with this advanced bead mill, ...
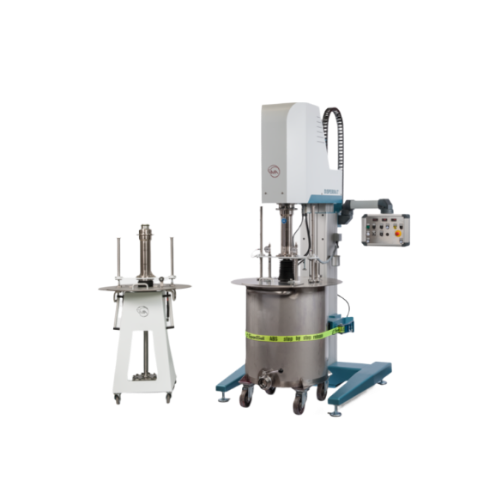

High-capacity dissolvers for industrial mixing
Enhance your production line with precision mixing, achieving consistent di...
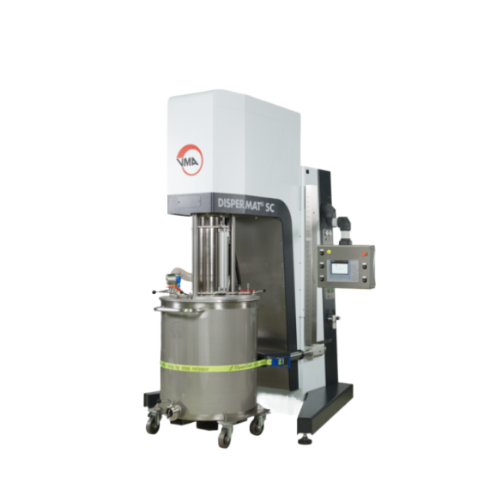

Modular basket mill for industrial dispersion
Effortlessly enhance your production efficiency with this versatile solution...
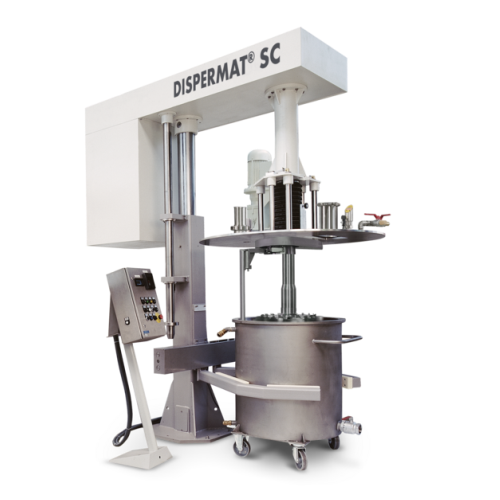

Explosion-proof production vacuum disperser for viscous products
Achieve precise and reliable dispersion of high-viscosi...
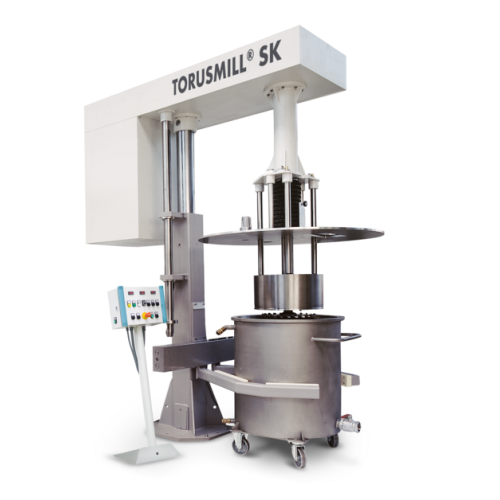

High-efficient industrial immersion mill
Achieve rapid, efficient dispersion and fine grinding in demanding production envi...
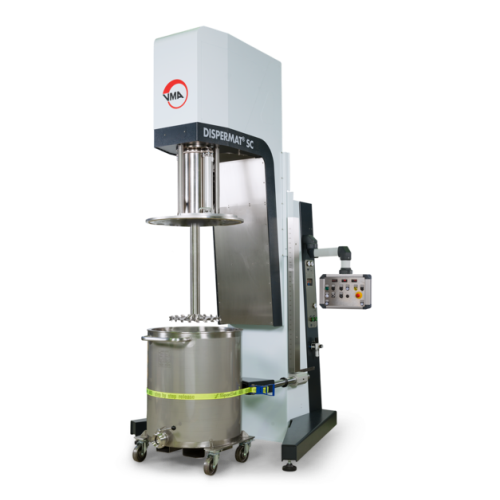

High-performance dissolver for industrial dispersion processes
Optimize your dispersion processes with this advanced dis...
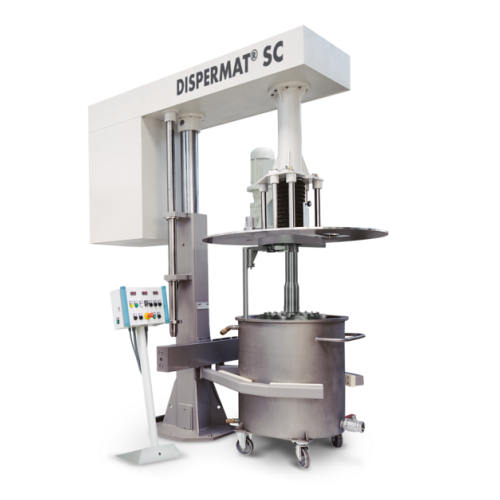

Industrial dissolver for high viscosity products
Optimize high-viscosity product dispersion with a robust dissolver design...
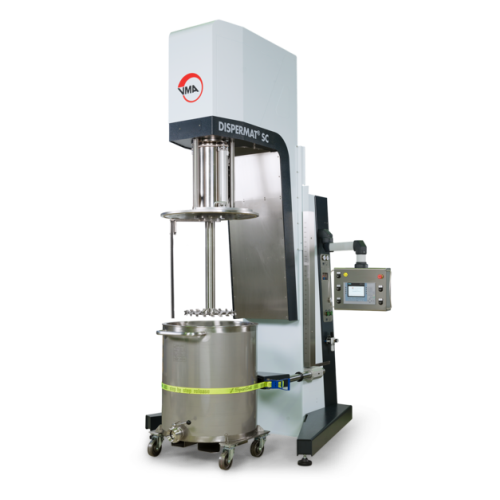

Explosion-proof dissolver for high-viscosity products
Optimized for safely processing high-viscosity products, this explo...
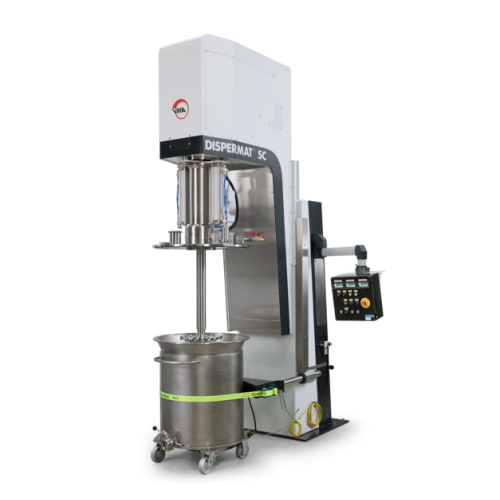

Explosion-proof vacuum dissolver for high-viscosity products
Optimize your production by eliminating air inclusions and ...

Laboratory stirrers for high viscosity materials
Efficiently mix and stir high-viscosity materials with ease, enabling pre...
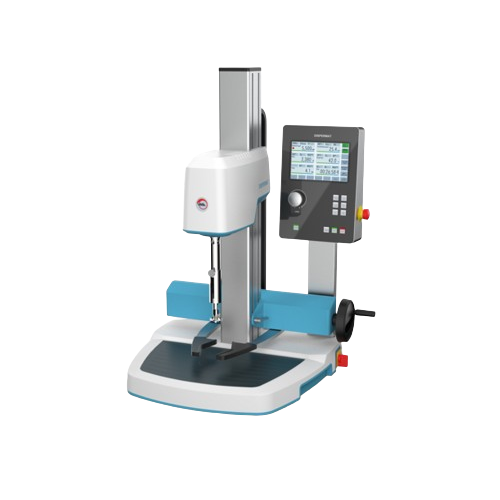

Laboratory dissolver for multiple applications
Efficiently streamline your laboratory processes with this versatile dissol...
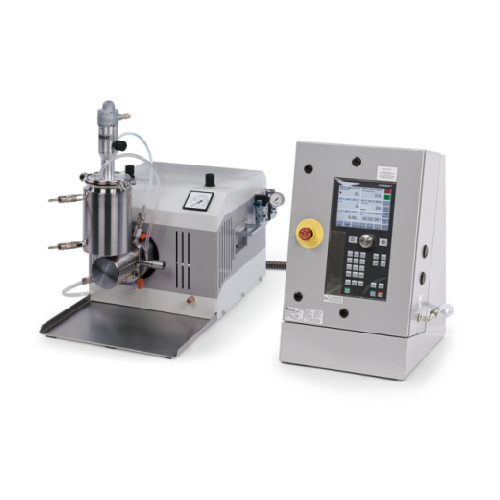

Explosion-proof horizontal bead mill for fine grinding
Ensure precise, explosion-proof grinding in hazardous environments...
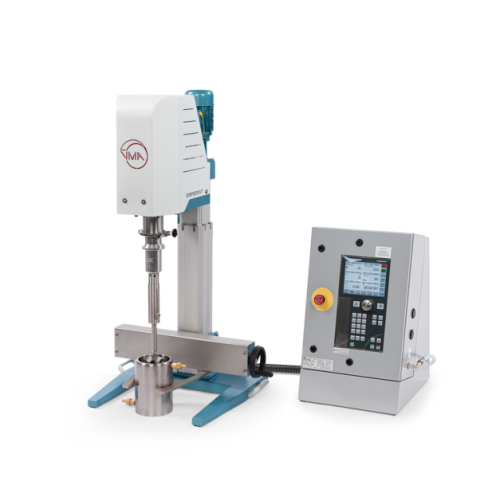

Explosion-proof dissolver for hazardous area mixing
When operating in hazardous environments, maintaining consistent and ...

Explosion-proof dissolvers for laboratory use
Ideal for safely dispersing and mixing chemical substances in potentially ex...
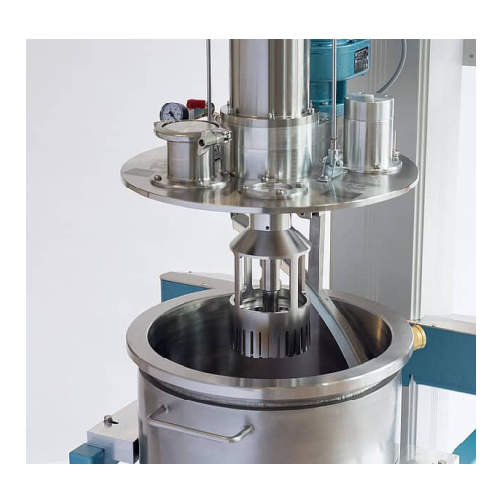

Efficient high-volume dissolver with scraper
For high-viscosity formulations, this advanced dissolver with integrated scra...
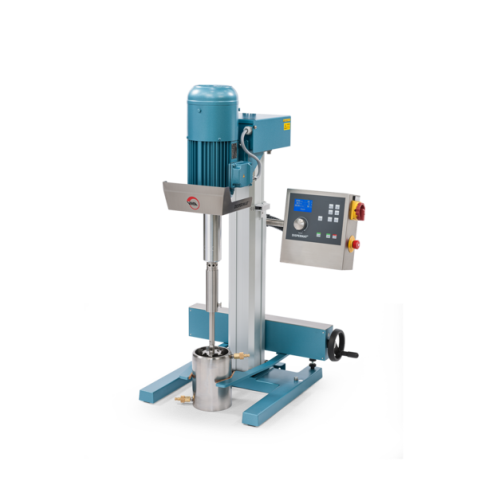

Lab stirrer for high-viscosity substances
Need precise, high-torque stirring for your complex formulations? This lab stirr...
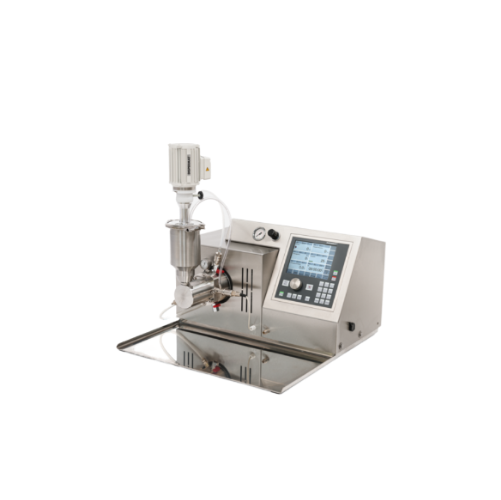

Laboratory and pilot plant horizontal bead mill
Achieve precision milling with minimal product waste, ensuring consistent ...
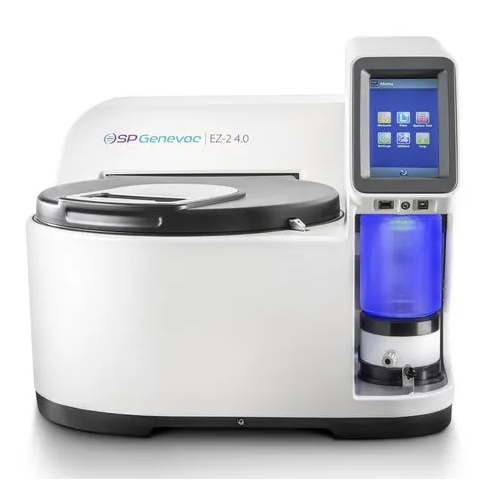

Centrifugal evaporators for medicinal chemistry
Streamline your solvent evaporation and drying processes with this solutio...
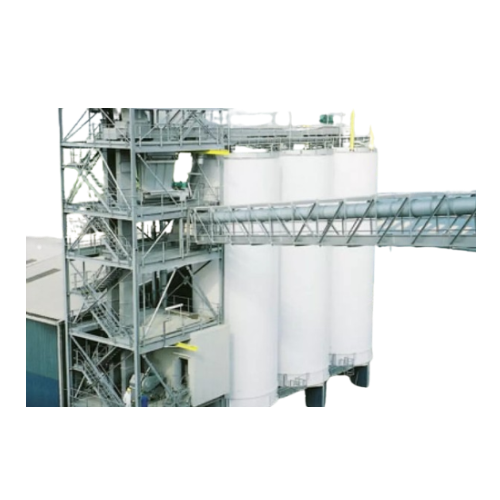

Industrial belt and bucket elevators
Optimize your material handling with elevators designed for high-speed conveying and e...
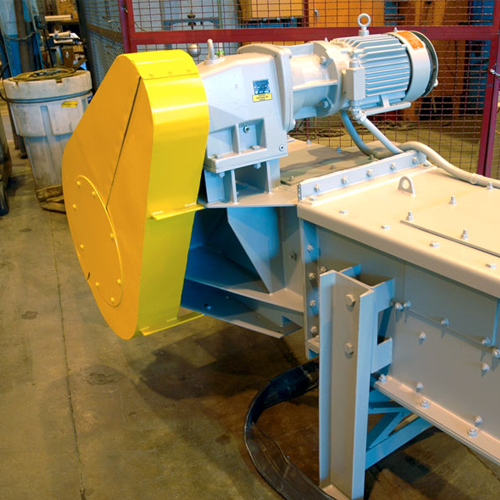

Bulk material handling with chain conveyor
Optimize your material transport with a solution designed for reliability in de...
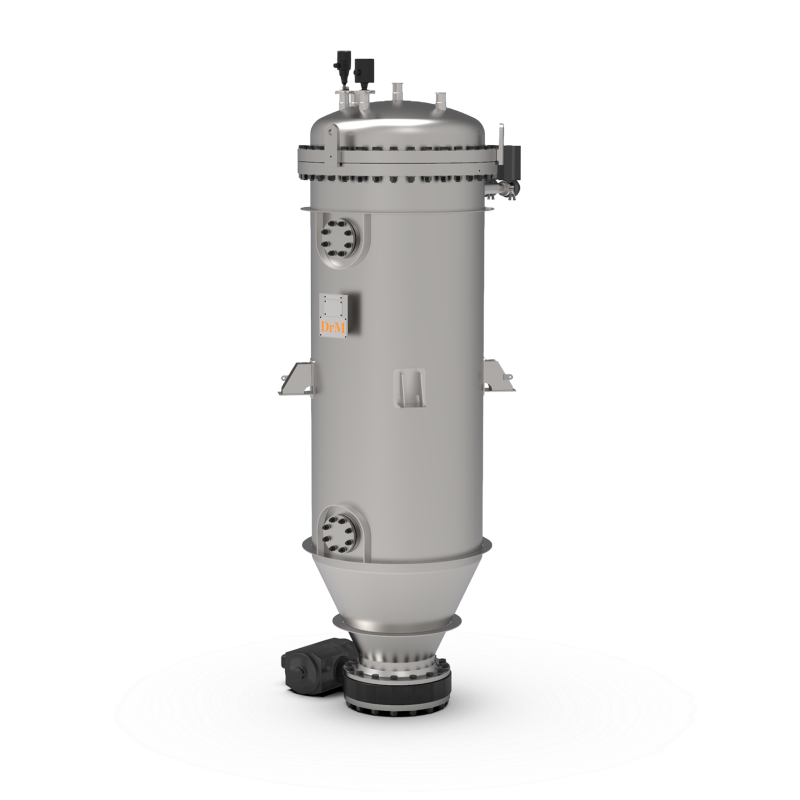

Self-cleaning candle filtration system
Separating solids from liquids by filtration requires frequent cleaning or replaceme...
Complete pellet line
Large industries are shifting towards more environment-friendly technology, such as recycling wastes and...
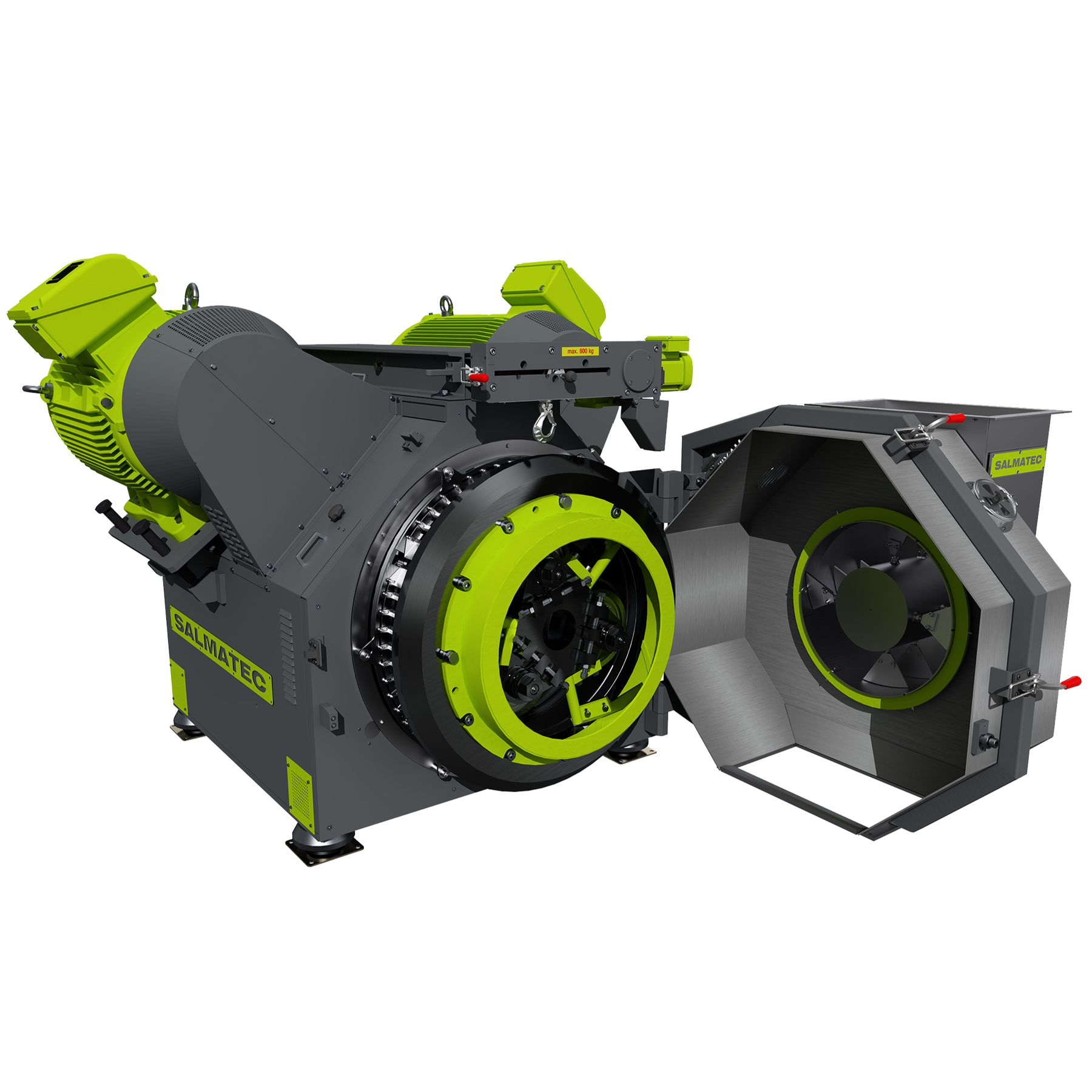

Industrial pellet mill
At the industrial level, the application areas of pellets range widely in fields such as feeds, biomas...