Making Silicone
Find innovative production technology for making silicone and connect directly with world-leading specialists
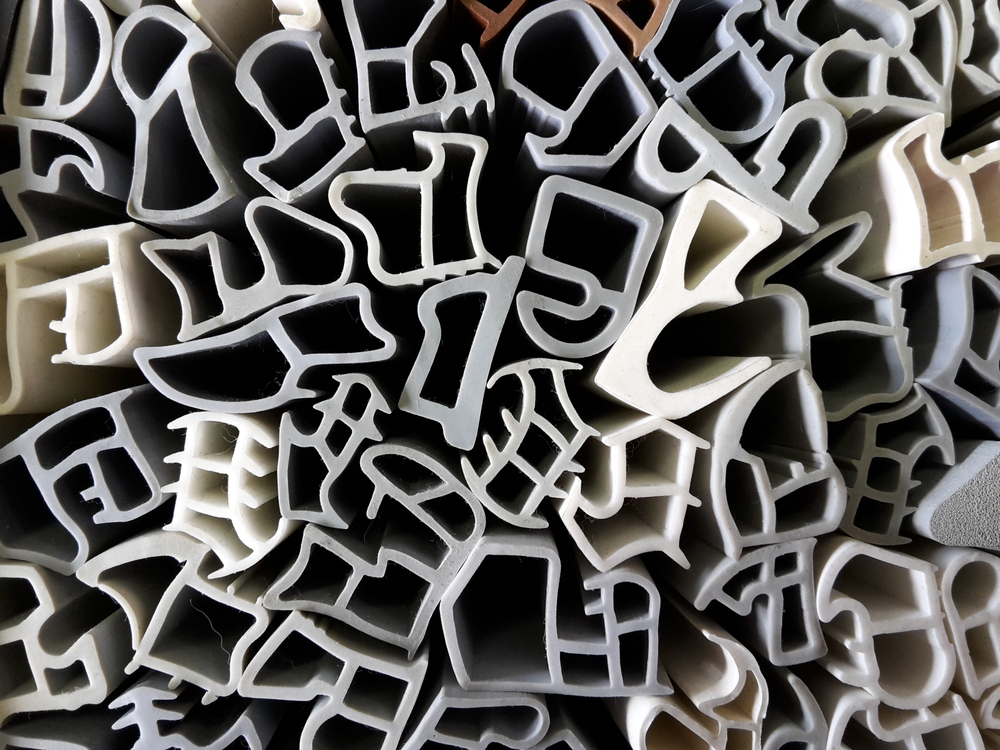
Despite only one letter difference, silicon and silicone are two different things. While silicon is the 14th chemical element on the periodic table, silicone is a synthetic material that, among other chemical elements, contains silicon. Although commonly observed as plastic, technically silicone is rubber. Among others, silicone processing equipment mainly involves several high-temperature machines, mixers and molds.
Select your silicone process
Tell us about your production challenge
Silicone processing equipment and techniques
Silicone is a synthetic material composed of silicon, oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. Being one of the main ingredients in silicone, the chemical element silicon is most commonly found in quartz, chemically known as silicon dioxide, from which it is reduced in a silicon furnace at temperatures as high as 1800°C. The leftovers of metallurgical-grade silicon are ground into fine powder. For silicone synthesis, it is crucial to add methanol to silicon to create chloromethane. Subsequently, a Müller-Rochow process starts by using a fluidized bed reactor heated at 300°C to trigger a reaction among particles forming a crude silane mixture.
The mixture is separated into various chlorosilane versions during a distillation process, and each version can further be processed depending on the desired end-product. Converted to polysiloxane chains via hydrolysis and polycondensation, difunctional chlorosilanes can be used as silicone fluids in cosmetics, textiles, and silicone rubber. As water-repellent yet breathable, trifunctional chlorosilanes are used in the construction industry. The three-dimensional silicone-resin networks are produced by undergoing hydrolysis and catalytic condensation. Finally, tertrafunctional chlorosilanes is used to manufacture pyrogenic silica, made by burning a crude silane mixture under a stream of hydrogen and air.
Silicone rubber production methods: extrusion
Silicone rubber is a highly versatile material that can be produced by a number of methods such as extrusion, injection molding, liquid injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and transfer molding.
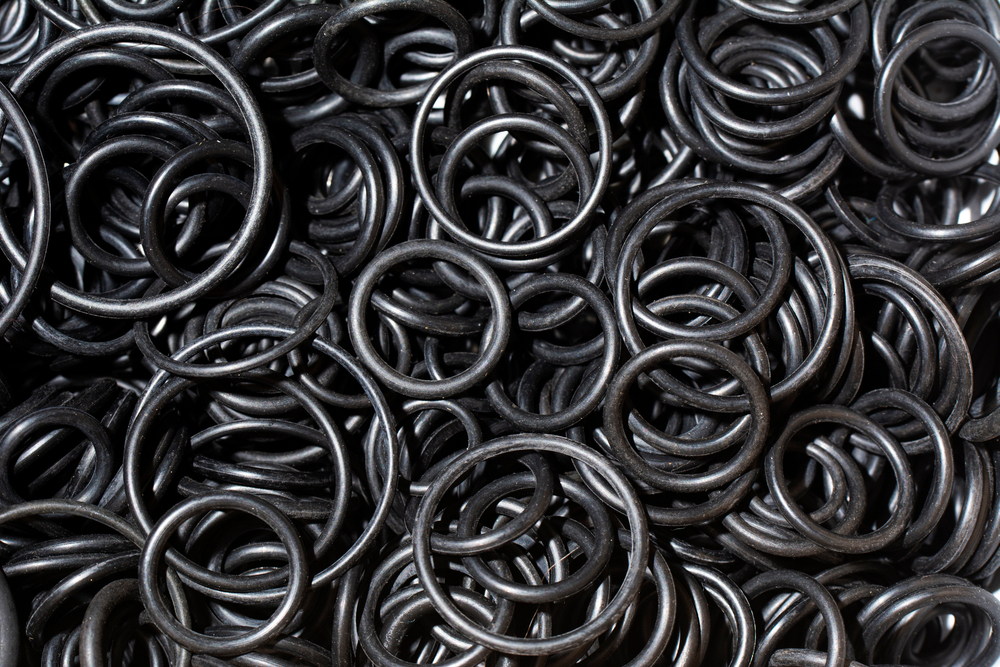

Extrusion is a preferred method for producing silicone rubber due to its practical and cost-effective nature. The essential silicone processing equipment in this method is an extruder through which all raw materials, once shaped into strips or slabs, are pressurized, heated and molded using a designed heated die. After exiting the die, the silicone is processed in ovens that circulate hot air vertically and horizontally, steam vulcanization, salt bath cure, and infrared radiation cure. Extrusion transforms fine silica particles into a translucent paste which is practical for its flexibility and ability to be aesthetically altered for the desired product specifications. This method produces silicone for end products such as gaskets, tubing, and seals.
Silicone rubber production methods: liquid injection molding
Liquid injection molding (LIM), also known as liquid silicone rubber (LSR), is used to produce high-volume durable parts and is suitable for creating complicated geometries.
The process starts in the pumping system where the base-forming silicone and the platinum catalyst parts of the liquid silicone rubber compounds are injected using supply drums, in addition to a separate container containing additives and pigments. The liquid silicone is pressurized into the machine’s pumping section with the injectors’ help. There, the metering pump will ensure that the liquid components mix and maintain a consistent ratio. Once it exits the metering pump, the mixture of base-forming silicone, catalyst, additives and pigments are combined by a static or dynamic mixer and forwarded into the nozzles. It travels from the cooled runner systems into the heated mold cavity, where the mixture is poured via the nozzles with automated shut-off valves to avoid leakage. Once the molding process is done and the product is cooled, the mold opens up.

Injection molding or liquid injection molding: where does the difference lie?
Among the production above methods, injection molding is the most common due to its ability to create products with a wide range of sizes, complexity, and application. The difference from liquid injection molding is the presence of mold halves and the raw material is forced into the hot cavity with a ram or screw-type plunger. The mold halves are clamped together, allowing for different shapes and sizes, from simple to complex and from small parts to large automobile body panels.
Solid and liquid silicone rubbers
Silicone rubber can be classified based on its viscosity – the difference between solid and liquid silicone rubber. Long chains of polymers with a high molecular weight result in a high consistency rubber, which is solid. Solid silicone is used for a variety of daily and industrial products. On the contrary, silicone rubber has a liquid texture when it contains polymers of lower molecular weight and shorter chains.
Due to it being safe as there were no added chemicals such as vulcanizing agents during molding, this type of silicone is used in the production of baby products as well as kitchen and medical supplies. Concerning the difference in production liquid silicone is injected into the mold through a vulcanization screw at a mold temperature of 170-200°C. Solid silicone, however, is cut into suitable size pieces and compression-molded.
Processing steps involved in silicone making
Which silicone technology do you need?

Air jet sieving system for powdered materials
Optimize particle distribution with precision air jet sieving, designed to e...

Vacuum de-aeration unit for liquid to pasty products
Optimize your product consistency and stability with continuous de-a...

Guarded hot plate for thermal conductivity testing
Ensure optimal insulation performance with precise thermal conductivit...
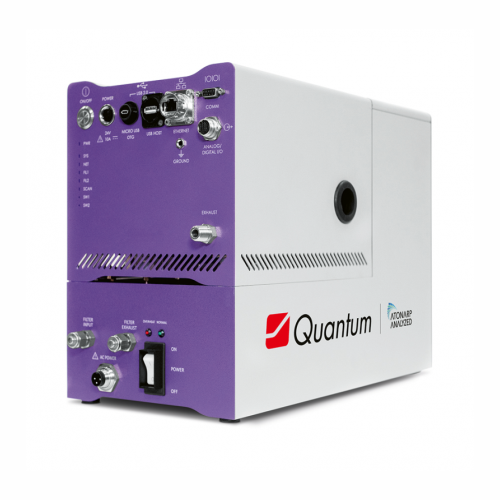

Smart miniature mass spectrometer for pharma freeze dryers
Optimize your freeze-drying process with a non-invasive tool ...

Fine impact mills for particle size reduction
Achieve precise particle size reduction with fine impact mills, essential fo...
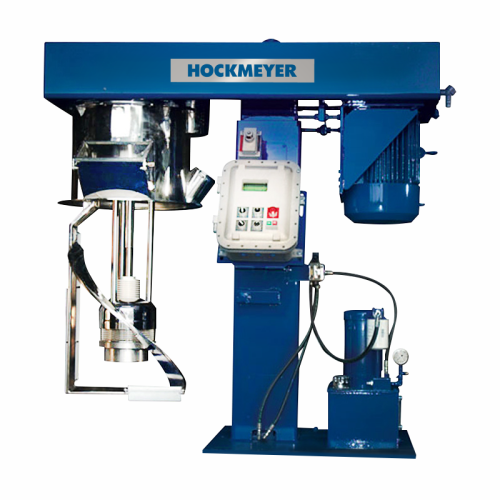

Immersion mill with sweep blade for high-viscosity products
Optimize your production line with this immersion mill desig...
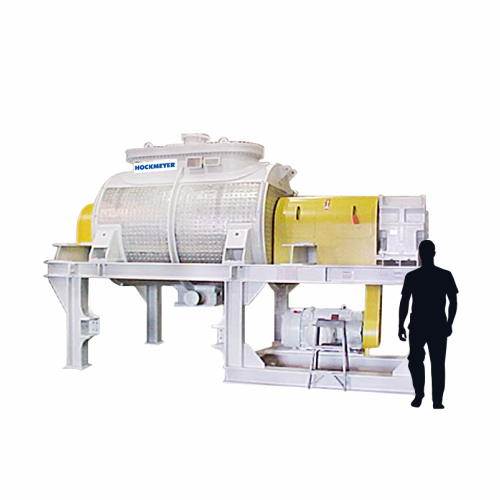

Horizontal paste mixer for high-viscosity materials
Efficiently transform high-viscosity and challenging materials into u...
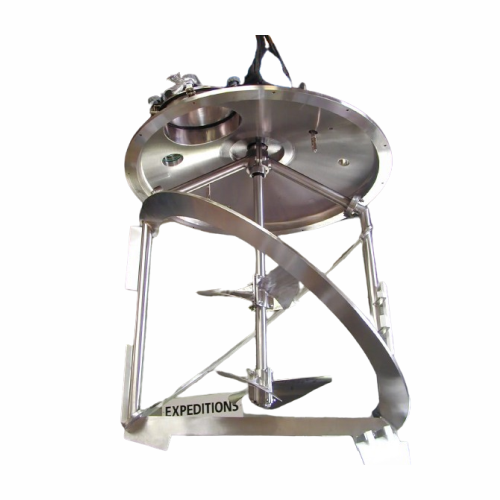

Coaxial mixer for high viscosity liquids
Achieve seamless blending of high-viscosity materials with a coaxial mixer designe...
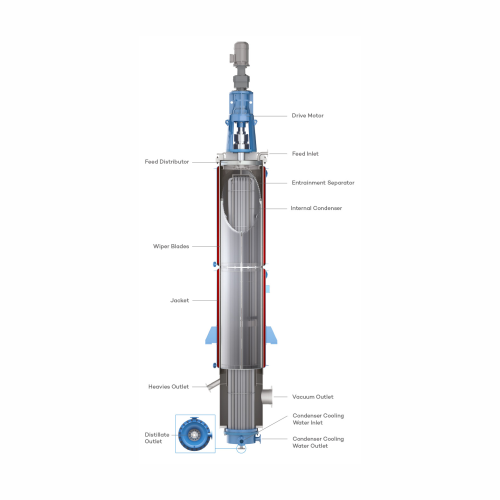
Wiped film evaporator for high boiling point materials
For challenging separations of high boiling, viscous, or heat-sens...

High-speed cutting mill for versatile material comminution
Efficiently transform diverse materials like plastics, textil...

Oil absorption testing instrument for carbon black and silica
Accurately measure oil absorption in powders to enhance fo...

Silicone spraying unit for laboratory and small-scale production
Ensure precise silicone application for cartridges, syr...

Industrial mixer for liquid and viscous products
Achieve precise mixing and homogenization of high-viscosity liquids and s...

Stirred reactors with heating and cooling system
Optimize your production line with versatile stirred reactors, designed t...

Auto-indexing filler for aqueous solutions and light oils
Streamline your bottling process with this six-head filler, pe...

Automatic positive displacement filler for various liquids
Achieve precision and versatility in liquid filling operation...

Automatic positive displacement bottle filler
Streamline your liquid filling operations with precision and flexibility, id...
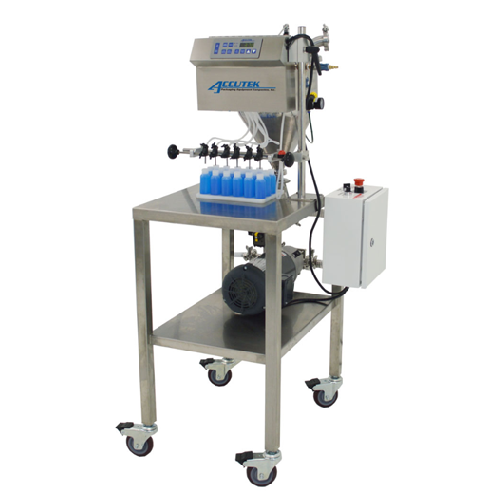

Semi-automatic timed flow filler for aqueous solutions
Handle diverse liquid filling needs with precision, from thin oils...
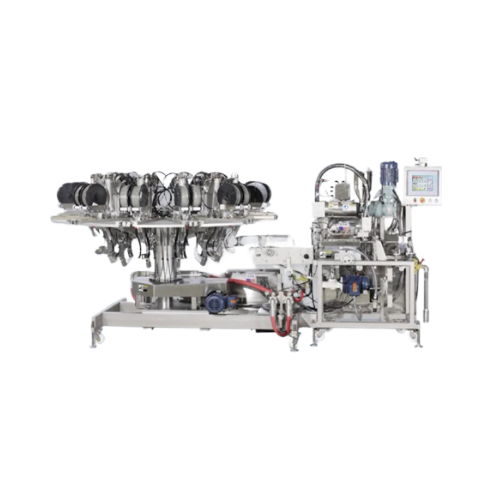

Automated clipping system for flexible packaging
Achieve precise volume control and reduce material waste with this high-s...
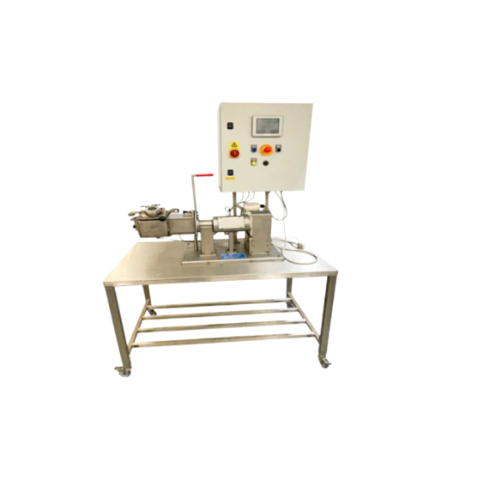

Processing vessel for liquid, sauce, or cream products
Efficiently mix and integrate liquid, cream, or slurry products wi...
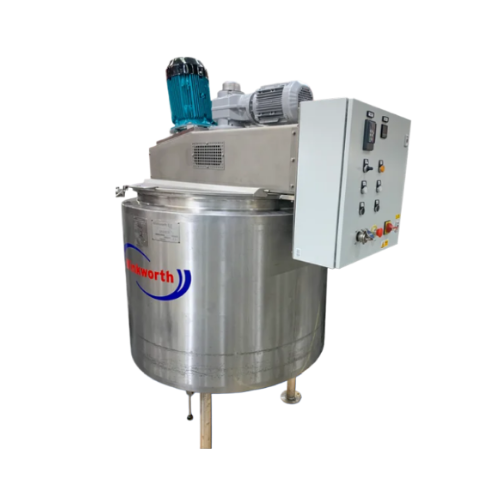

Pv processing vessels for liquid and cream mixing
Optimize your mixing operations with versatile processing vessels desig...
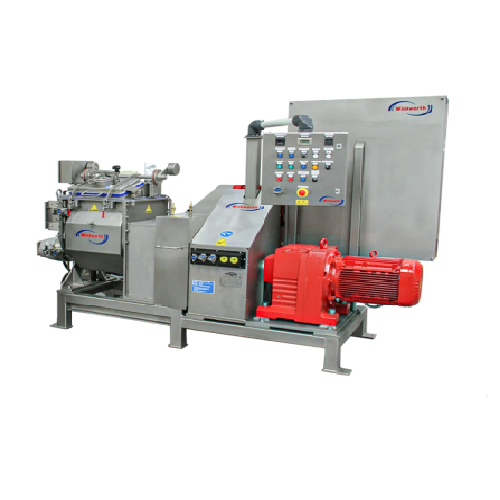

Industrial sigma mixer extruder for homogeneous mixing and extrusion
Achieve precise mixing and seamless extrusion of d...
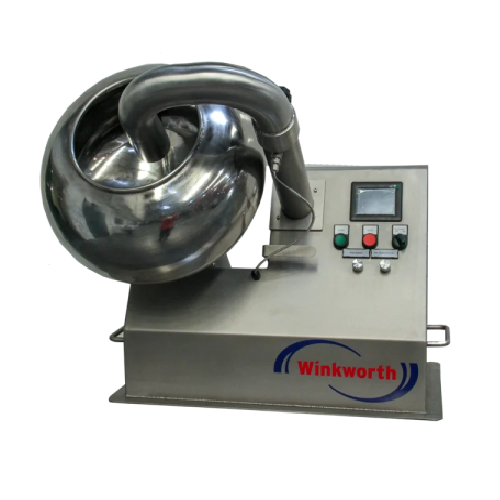

Industrial coating pan for food and pharmaceutical products
Optimize your production with precision mixing and coating, ...
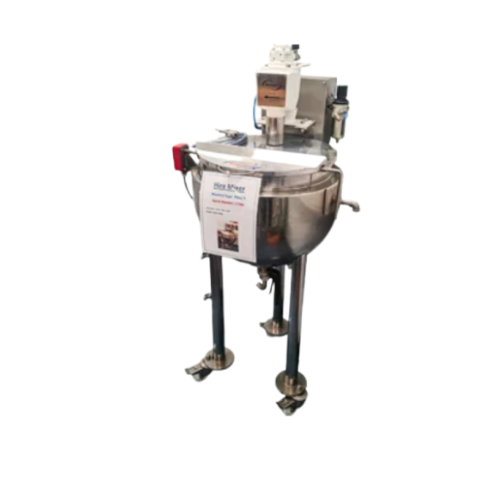

Pv mixing vessels for industrial hire
Optimize your production mix with vessels that ensure precise blending, heating, and ...
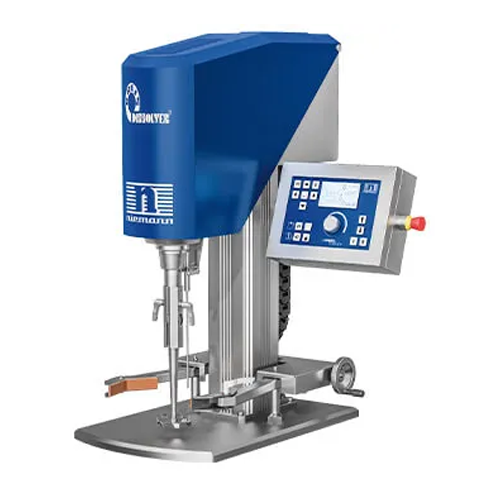

Laboratory disperser for high-viscosity products
Optimize your laboratory processes with precise mixing and dispersing of ...
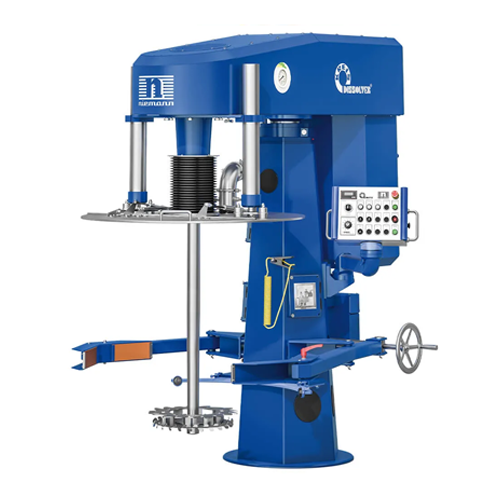

Dispersing system for high-viscous products
Achieve precise mixing and dispersing of high-viscous products with advanced f...
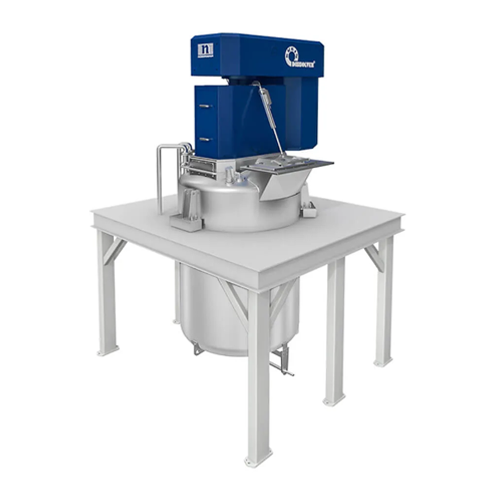

Top-mounted disperser for high-viscosity products
Achieve rapid, uniform dispersion of ultra-high viscosity materials wit...
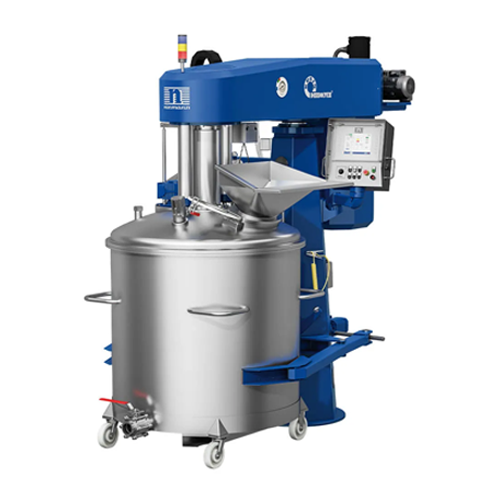

Vacuum dissolver for high-viscosity products
Elevate your production with precision mixing and deaeration, ideal for tackl...
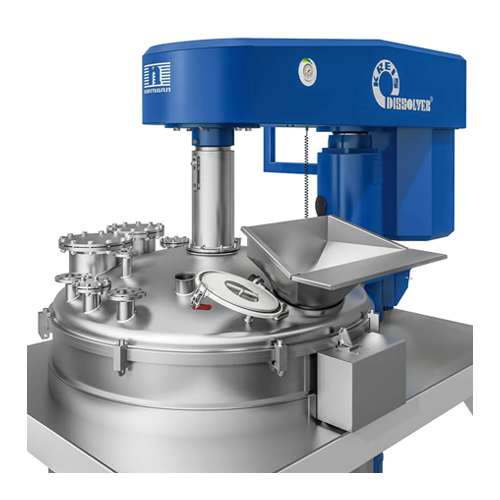

Advanced dissolver for high-viscosity products
Handle ultra-high viscosity mixing challenges effortlessly with this advanc...

Flap diverter valves for pneumatic conveying
Streamline material flow in your pneumatic conveying system by effortlessly r...

Hopper venting filter for efficient dust filtration
Achieve superior dust control and efficient material handling with a ...

Industrial mixing dissolver for medium to large batches
Achieve precise mixing and dispersion of medium to large batch fo...

Explosion-proof dissolver for production applications
Ensure safety and efficiency in volatile environments with a robust...

Explosion-proof dissolver for chemical processing
Ensure safe and efficient dispersion in volatile environments with this...

Vacuum homogenizer for cosmeto-pharma applications
Optimize your formulations with our vacuum homogenizers, ensuring prec...

Vacuum basket mill for high viscosity products
Achieve efficient fine grinding of high-viscosity products while minimizing...

Vacuum dissolver for large batch production
Optimize your mixing processes with a versatile vacuum dissolver designed for ...

Explosion-proof horizontal bead mill for paint production
Ensure ultra-fine particle size and consistent quality with an...

Horizontal bead mill for fine grinding in continuous process
Achieve ultrafine particle dispersion and consistent mixing...

Horizontal bead mill for ultrafine particle grinding
Achieve precision in ultrafine grinding with a system that allows fo...

Modular basket mill for industrial dispersion
Effortlessly enhance your production efficiency with this versatile solution...
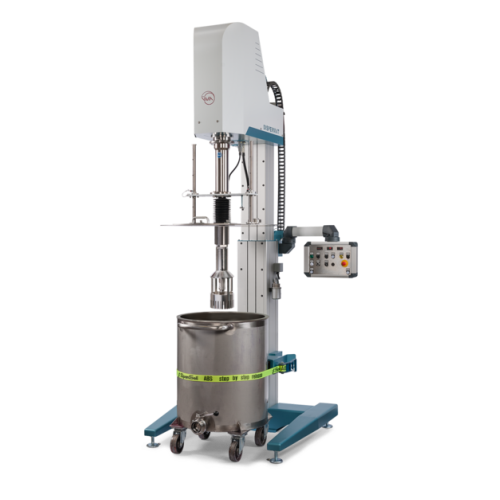

High shear batch process homogenizer for production
Achieve efficient emulsifying, homogenizing, and dispersing with prec...
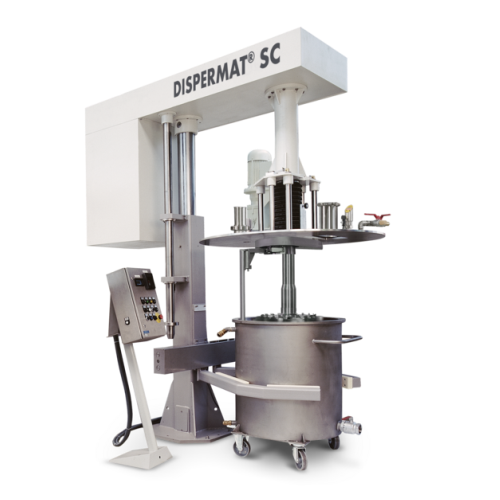

Explosion-proof production vacuum disperser for viscous products
Achieve precise and reliable dispersion of high-viscosi...
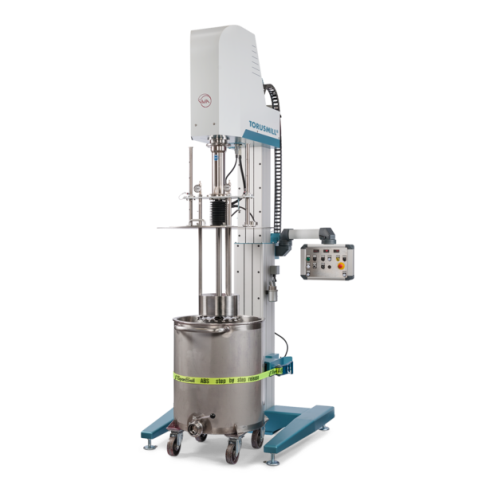

Industrial basket mill for medium viscosity products
Achieve precise particle size reduction and rapid pigment dispersion...
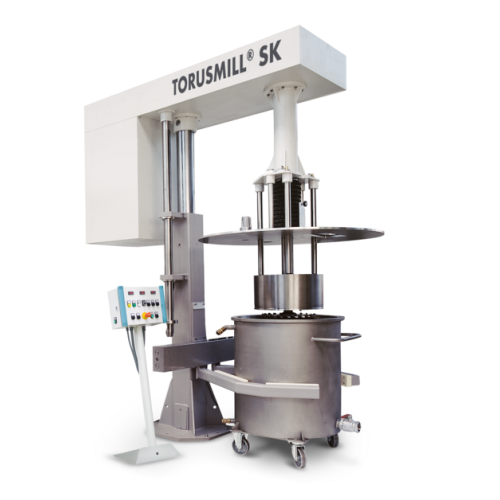

High-efficient industrial immersion mill
Achieve rapid, efficient dispersion and fine grinding in demanding production envi...
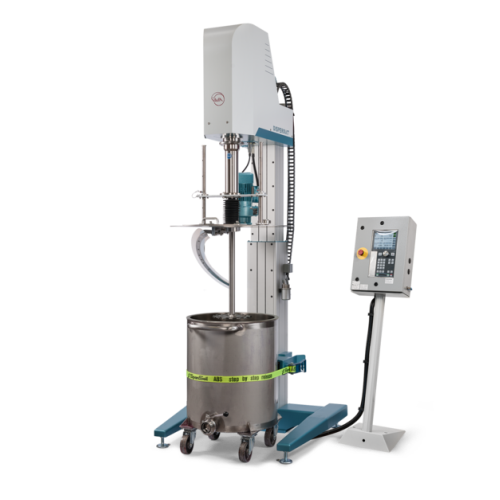

Explosion-proof dissolver with scraper for high viscosity substances
Ensure flawless dispersion with enhanced safety, d...
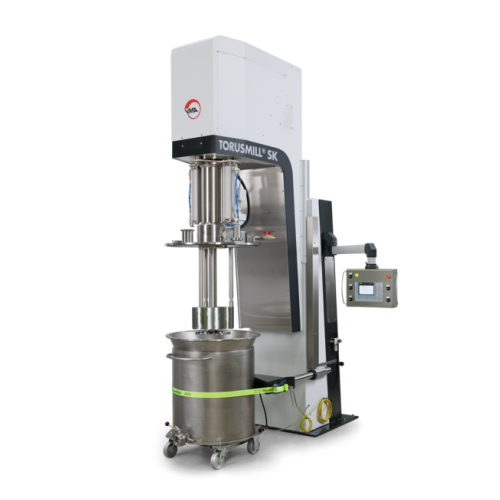

Vacuum basket mill for high-viscosity product milling
Achieve refined particle size and smooth texture in your high-visco...
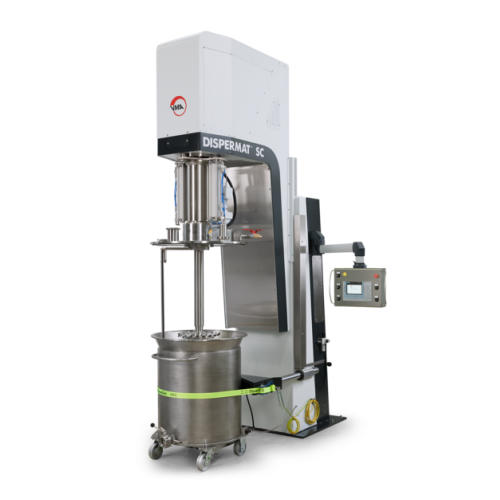

Explosion-proof vacuum disperser for high-viscosity substances
Achieve precise dispersion and eliminate air inclusions w...

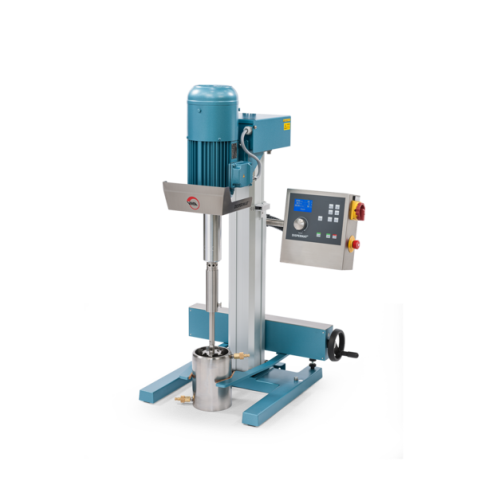
Laboratory stirrers for high viscosity materials
Efficiently mix and stir high-viscosity materials with ease, enabling pre...
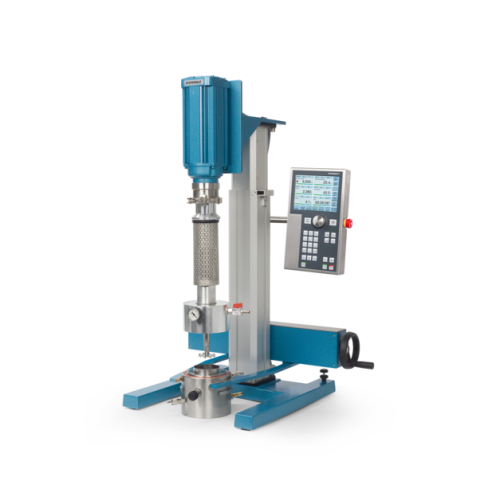

Vacuum dispersion system for laboratory applications
Achieve precise mixing and homogenization under vacuum conditions, e...
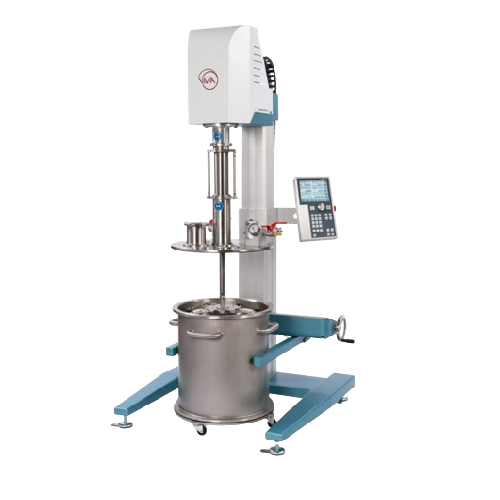

Vacuum dispersion system for single-walled containers
Optimize your production line with an adaptable vacuum dispersion s...
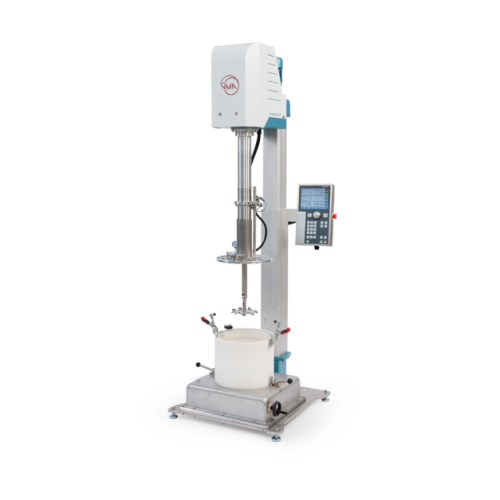

Laboratory vacuum dissolver
Experience precision vacuum processing for your high-viscosity formulations, ensuring optimal di...
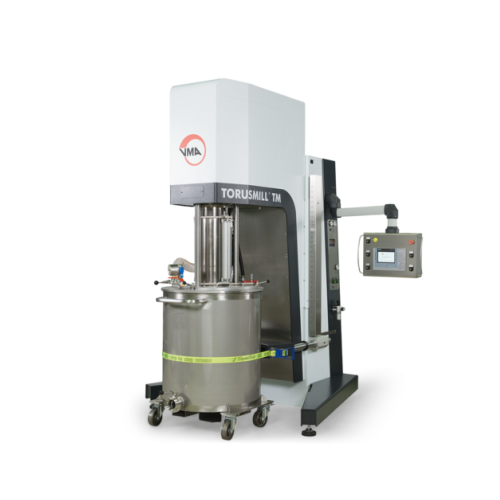

Dissolver for high-volume industrial dispersion
Achieve precise and efficient mixing with this dissolver, designed for sea...
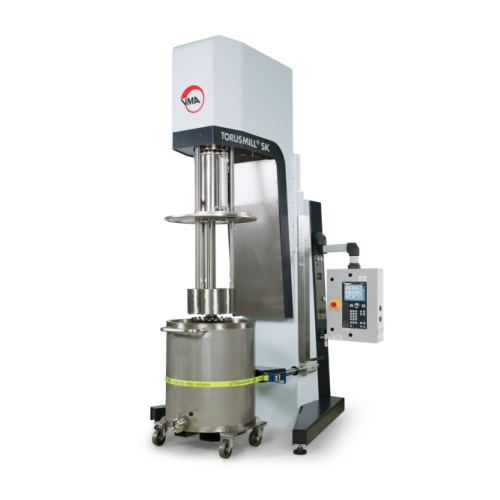

Explosion-proof immersion mill for paints and varnishes
Optimize high-performance coatings production with an explosion-p...
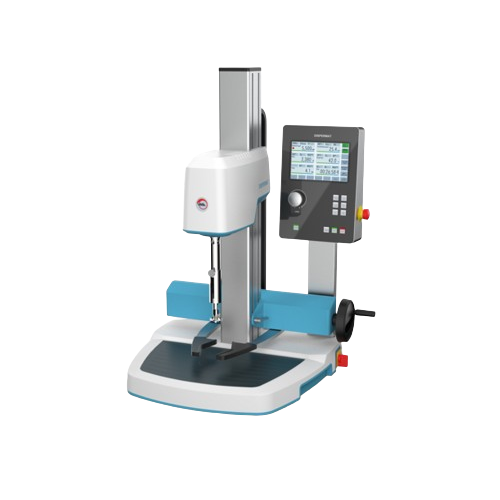

Laboratory dissolver for multiple applications
Efficiently streamline your laboratory processes with this versatile dissol...
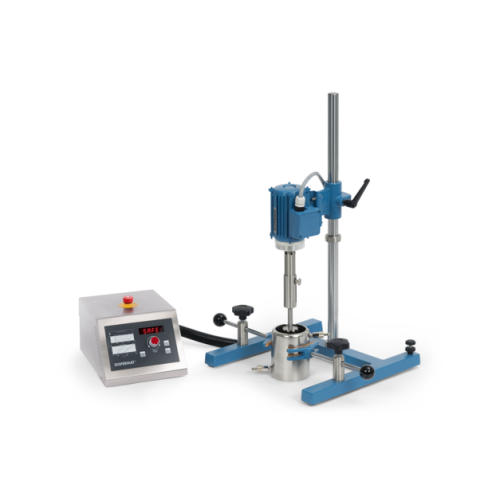

Lab and pilot plant dissolver for dispersion and fine grinding
Achieve efficient dispersion and fine grinding in laborat...
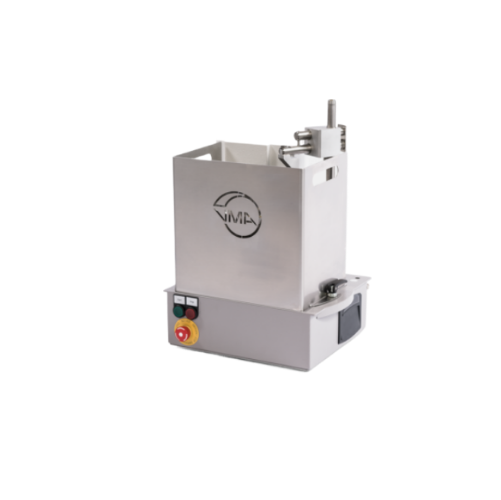

Industrial dissolver for high-viscosity materials
Efficiently disperse and mix high-viscosity materials with precision, e...
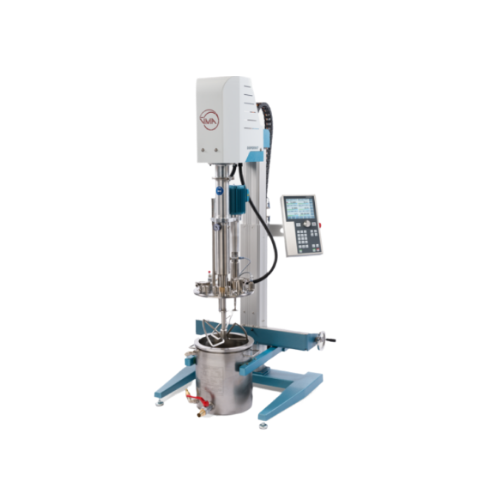

Vacuum dissolver for highly viscous products
Efficiently mix and disperse high-viscosity substances under vacuum to ensure...

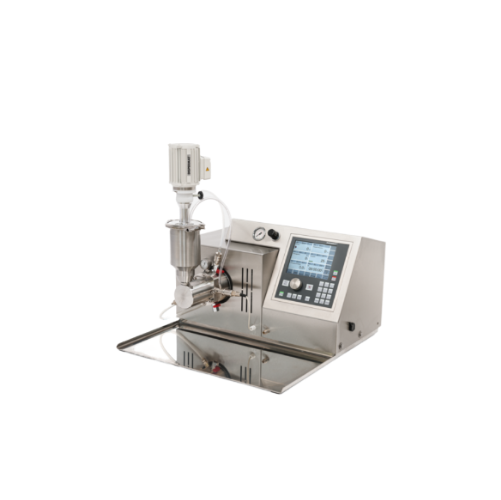
Atex horizontal bead mill
Ensure precision and safety in explosive environments with a robust solution that finely grinds an...

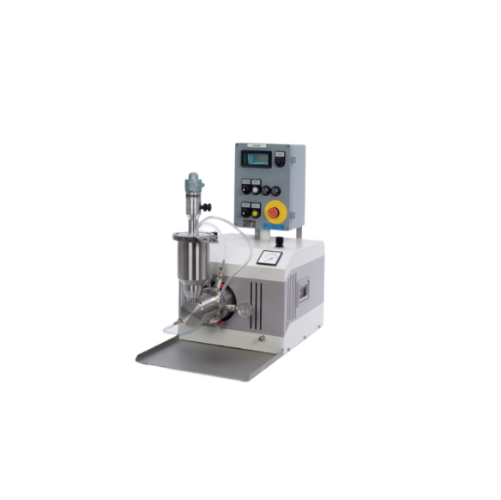
Explosion-proof dissolver for hazardous area mixing
When operating in hazardous environments, maintaining consistent and ...

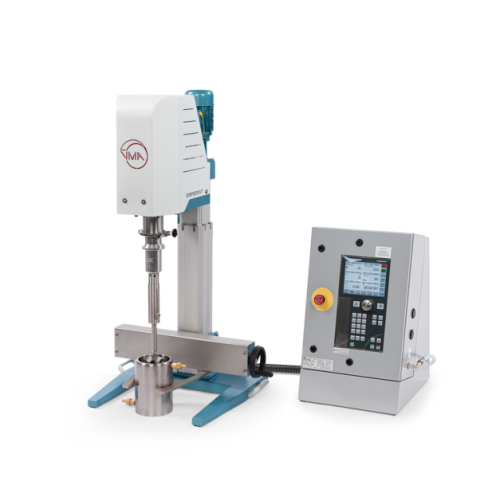
Lab stirrer for high-viscosity substances
Need precise, high-torque stirring for your complex formulations? This lab stirr...

Entry-level vacuum dispersion system for laboratory applications
Achieve precise dispersion and milling with this versat...

Laboratory and pilot plant horizontal bead mill
Achieve precision milling with minimal product waste, ensuring consistent ...
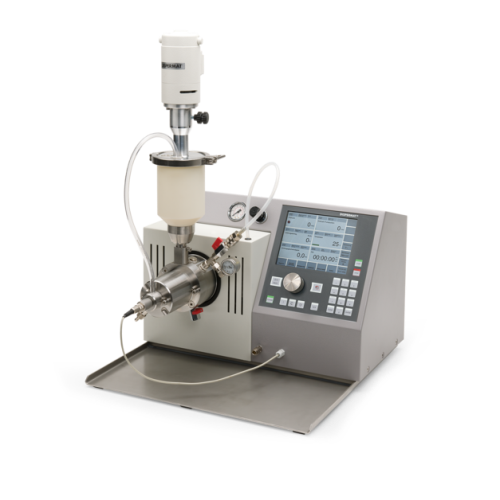

Nano bead mill for laboratory wet grinding
Achieve ultra-fine particle dispersion and consistent milling results with this...

Rotary homogenizer for laboratory and pilot plant
For achieving optimal dispersion in complex formulations, this solution...
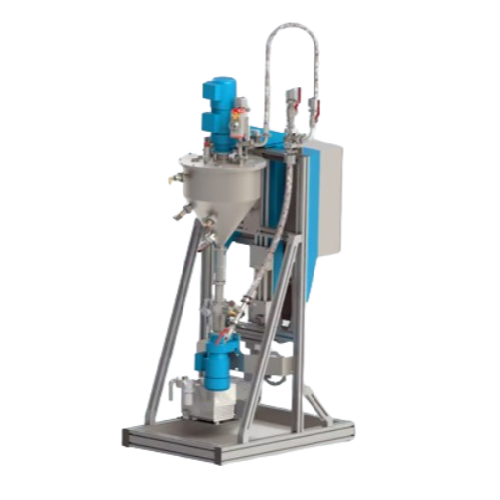

Consistent material supply system for industrial applications
Ensure seamless production with a system designed for cont...
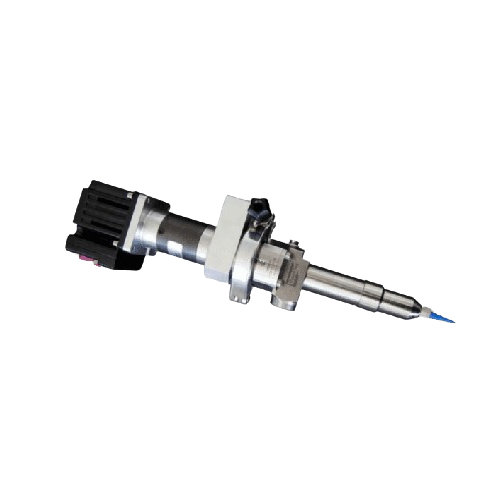

Precision dispenser for high-viscosity fluids
Achieve unparalleled precision in dosing and application with a dispenser de...
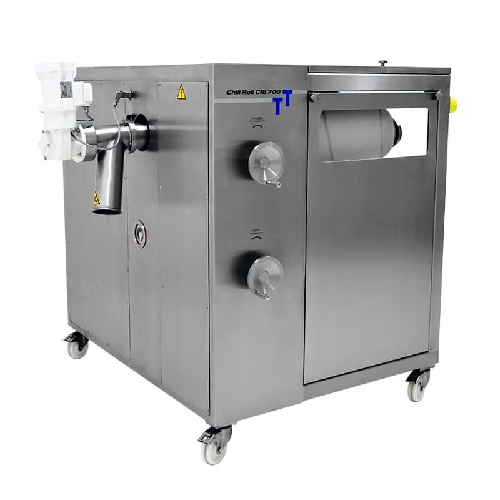

Continuous cooling roller for extrudates
Ensure rapid and efficient cooling of high-heat capacity extrudates with a compact...

Benchtop x-ray diffractometer for routine analysis
Achieve high-precision phase analysis and crystalline characterization...

Laboratory extruders for feasibility studies and r&d
Optimize your testing with laboratory extruders designed for precise...

Terrier extruder for high volume material processing
Ideal for continuous high-volume processing, this extruder efficient...

Twin shaft feeder for optimized material feeding
Achieve precise material flow and optimize downstream processing with adv...

Vacuum extruder for high-viscosity materials
Optimize material processing with precision de-airing and temperature control...

Automatic tube filling solution for medium to high volume production
Boost your production line efficiency with a robus...

Food processing scraped surface heat exchanger
Enhance your production line with precise temperature control and continuou...

Portable and fixed mount mixing system
Optimize your mixing operations with a versatile system that adapts seamlessly betwe...

High shear lab mixer for laboratory work and r&d
Achieve unparalleled precision and consistency in laboratory and pilot-sc...
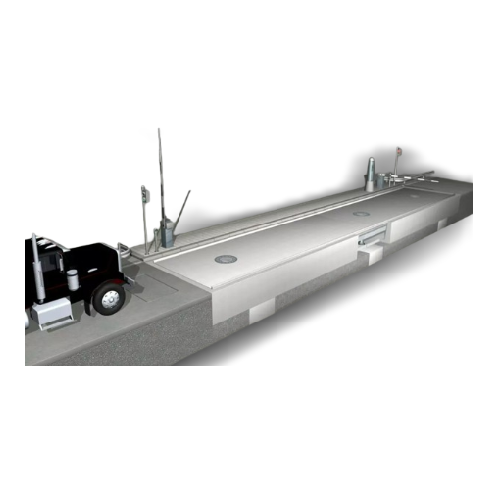

Pit scales for industrial weighing
Optimize material flow and ensure precise load determination with a robust pit scale sol...
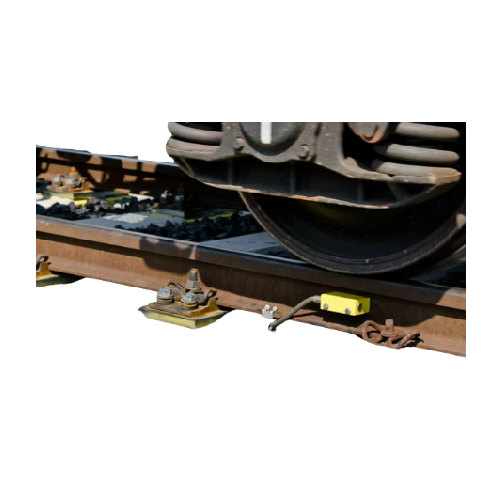

Dynamic weighing for solids and liquids
Ensure precision in rail transport with innovative dynamic scales that provide lega...
Crane weighing system for precision measurement
Ensure precise and temperature-resistant weighing during high-demand opera...

Mass flow rate feeder for bulk powders
Achieve precise control and consistent material flow in high-speed manufacturing env...

Industrial grinding mill replacement parts service
Optimize production efficiency with high-precision grinding solutions ...
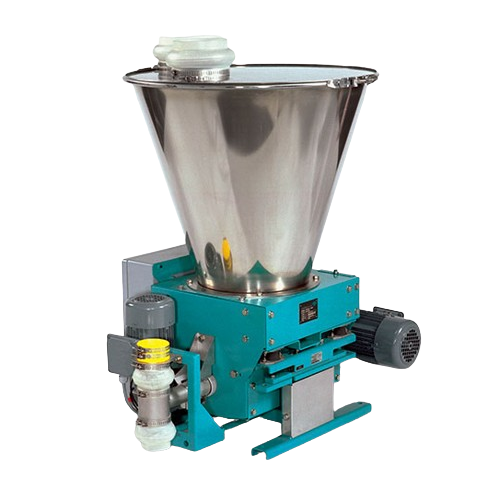

Loss-in-weight feeder for bulk solids
Ensure precise and reliable dosing of bulk solids with a compact feeder that eliminat...
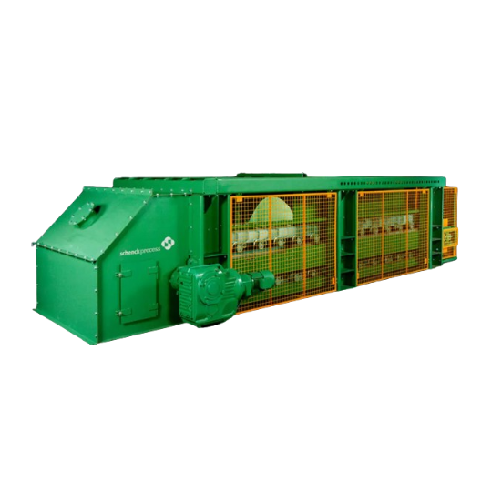

Apron weighfeeder for sticky bulk materials
Optimally handle challenging, sticky materials with precision and consistency ...
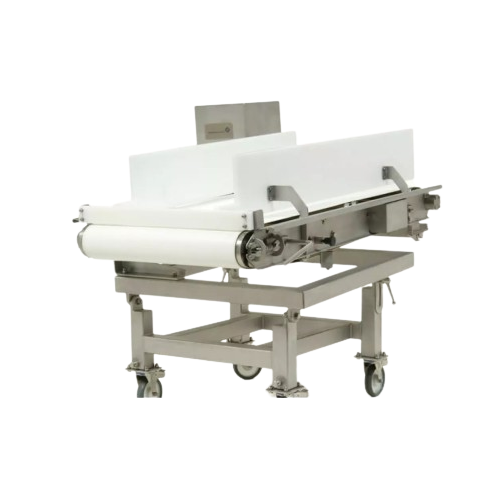

Industrial weighfeeder for hygienic applications
Achieve precise mass flow control with a hygienic design, ideal for appli...
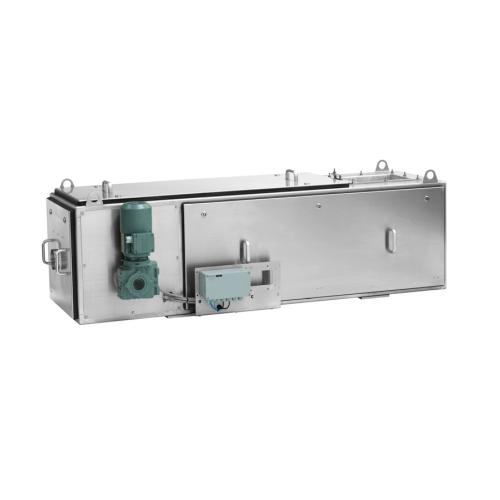

Continuous and batch feeding system for bulk materials
Achieve precise bulk material feeding with seamless integration in...
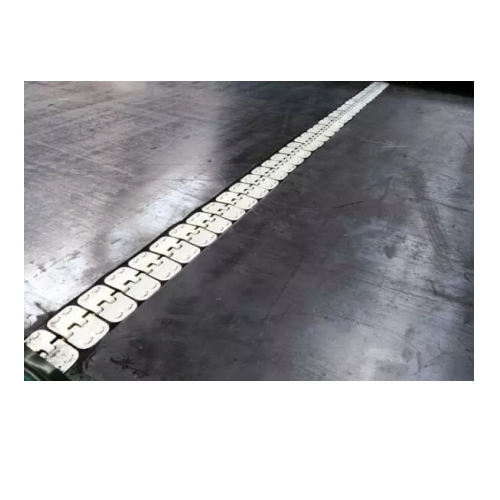

Optimal maintenance solution for industrial weighfeeders
Streamline your processing operations with a solution that minim...
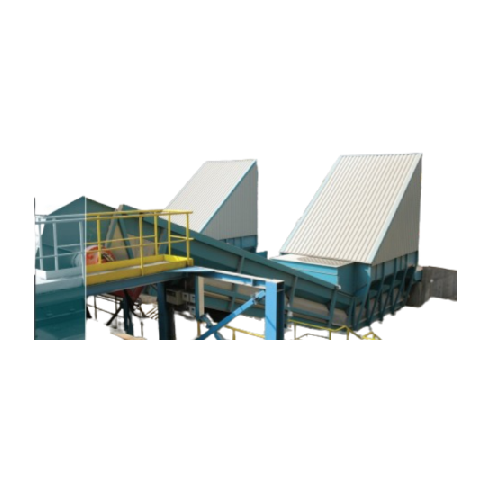

Bulk reception solution for industrial material handling
Optimize your operations with an above-ground bulk reception sys...
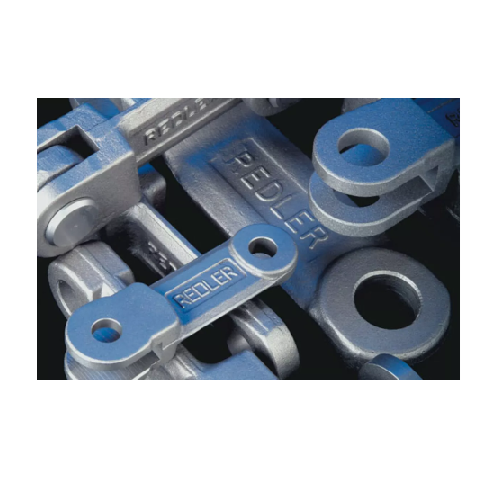

Drop forged chain for drag chain conveyors
Enhance your material flow efficiency with a robust drop forged chain designed ...
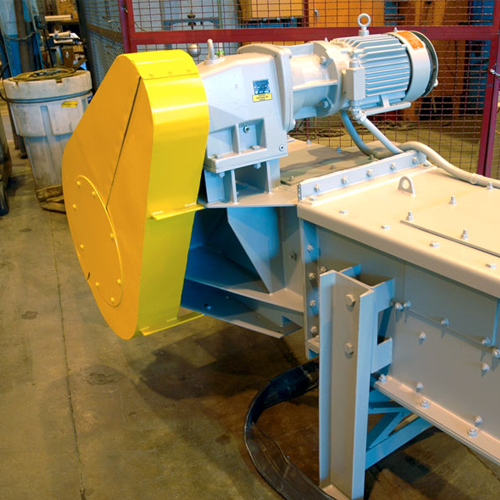

Bulk material handling with chain conveyor
Optimize your material transport with a solution designed for reliability in de...
Grinding and drying of CaCO3
Widely used in the construction industry as filling materials, calcium carbonate is usually mad...

Grinding and drying of bentonite
After crushing and drying mined bentonite, this clay mineral is usually processed through a...
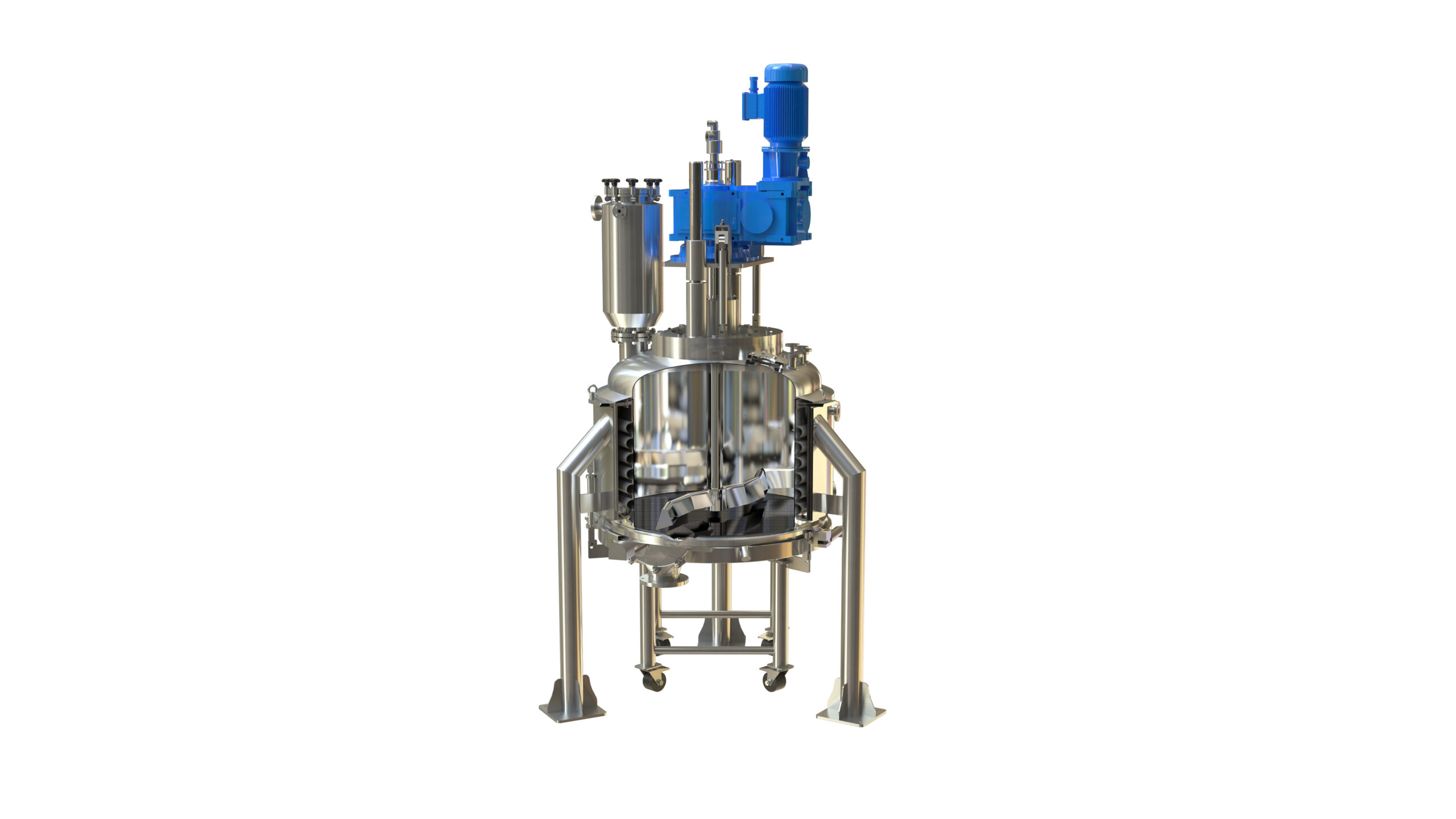

Filter dryer
The pharmaceutical and bioprocess industries need filtration processes of particularly high quality to ensure the...
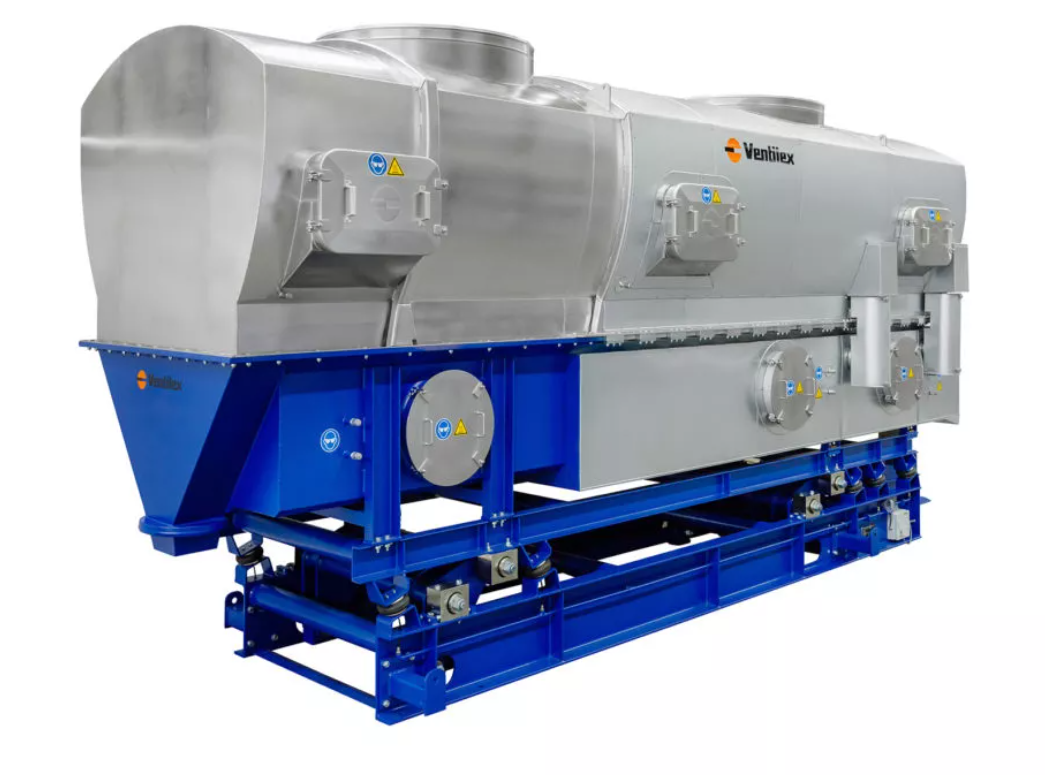

Continuous fluid bed dryer
In a Fluid Bed, a product or solid is made fluid by an upward moving flow of gas. The mechanical ...
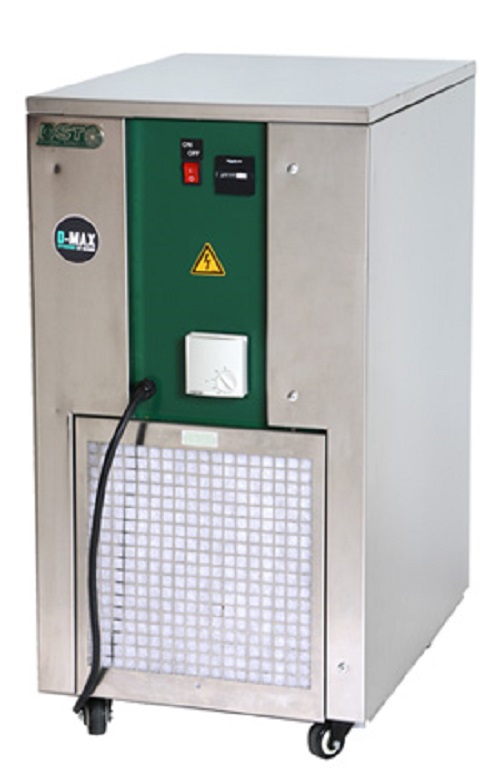

Dehumidifier for difficult wet airflows
Sealed rooms can be challenging to dehumidify with ordinary dehumidifiers. The wet ...
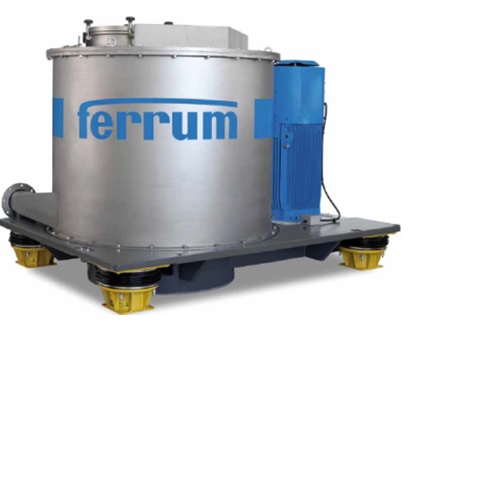

Gypsum centrifuge
Especially designed for flue gas desulphurization, applications in coal fired power plants and waste incine...