Making Sunscreen
Find innovative production technology for making sunscreen and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Sunscreen is an emulsion which can be either oil-in-water or water-in-oil. To create it, you must prepare an oil phase and a water phase separately, then mix and heat them. Homogenization is a key process to guarantee that the product will have the right consistency. When manufacturing sunscreen, give special attention to protection against UV filters.
Select your sunscreen process
Tell us about your production challenge

Ultraviolet types – why do we need protection from them?
While three types of UV radiations (UVA, UVB and UVC) exist, sunscreens’ ingredients only protect us from two: UVA and UVB. UVA goes deeper in the skin and is photoaging, meaning that skin gets old prematurely because of exposure to it. It can also damage collagen, elastin and hyaluronic acid, which are produced in this deeper layer. UVB only reaches the top part of your skin and is responsible for getting the pigment, but is also the one that can cause skin cancer. UVC, the most harmful of the three, doesn’t “trespass” the ozone layer – so it doesn’t reach us, luckily.
Do the math for the sunbath
Ever wondered what are the numbers on the sunscreen bottles? That’s the SPF, or the Sun Protection Factor. It is the result of a simple math that determines how long it takes for your skin to get red due to sun exposure. You calculate it running tests with UVB, one of the three different ultraviolet (UV) radiation types. Apart from SPF, European sunscreens usually also have a PPD factor. Meaning “persistent pigment darkening”, it’s the equivalent to SPF for UVB.

Back to math, the SPF number on the bottle is the amount of radiation it takes to make your skin red using the sunscreen versusthe amount it takes without the sunscreen. Translating into English, it means that with an SPF 50 sunscreen, you need to get exposed 50 times longer to the sun to get burned compared to being exposed without the product.
PPD, in its turn, indicates the sunscreen efficiency protecting you from longer-lasting tanning caused by UVA. Like SPF, PPD compares the effect with the sunscreen and without it. It’s important because high exposure to UVA can cause erythema.

Different filters: how to make sunscreen?
To make sunscreen, you can use chemical, physical or mixed filters, which are the main components of sunscreen and the ones that protect you from radiation. Chemical filters absorb part of the photon energy of the radiation and turn it into heat. This makes us feel hot for 20 to 30 minutes after applying the product. Chemical sunscreen types also have a lighter consistency.
Physical filters don’t absorb, rather reflect part of the radiation, and leave a white coating on the skin. Some producers try to avoid them due to esthetics. They also include nanoparticles which help spread the product better. Some scientists, though, raised questions regarding whether they can cause damage and penetrate the skin.
To get the most efficiency, you can combine both chemical and physical filters to get a safe and photostable product. Make sure you include protection from UVA and UVB.
Processing steps involved in sunscreen making
Which sunscreen technology do you need?

Rotary indexing sealer for cup filling
Streamline your production line with precise cup filling and sealing, ideal for a wi...

Vacuum de-aeration unit for liquid to pasty products
Optimize your product consistency and stability with continuous de-a...
Tube filling machine for cosmetics and food products
Achieve precise and efficient packaging with this advanced twin-head...

Tube filling solution for plastic and laminate tubes
Ensure precise tube filling and sealing with quick changeovers, enha...

Tube filling solution for plastic, laminate, and aluminum tubes
Optimize your production line with a versatile tube fill...

Hig Speed Tube Cartoner
Achieve seamless integration into your high-speed packaging line with a cartoning solution that ensur...

Cartoning solution for tube applications
Streamline your cartoning operations with a machine designed for flexible size cha...
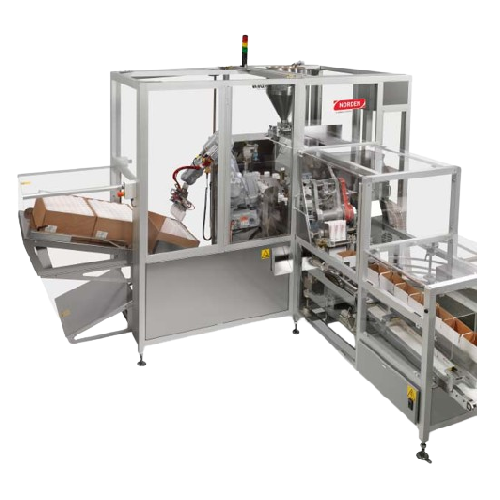

Pick & place robot for packing tubes in boxes
Efficiently streamline your packaging line with this compact case packer, de...
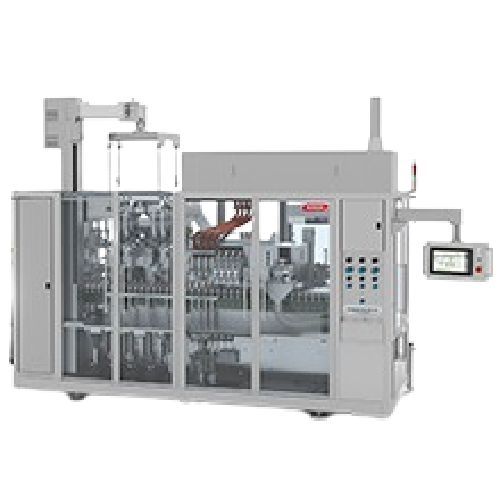

Tube filling station for plastic, laminate, and aluminum tubes
Efficiently seal and fill various tube materials, ensurin...
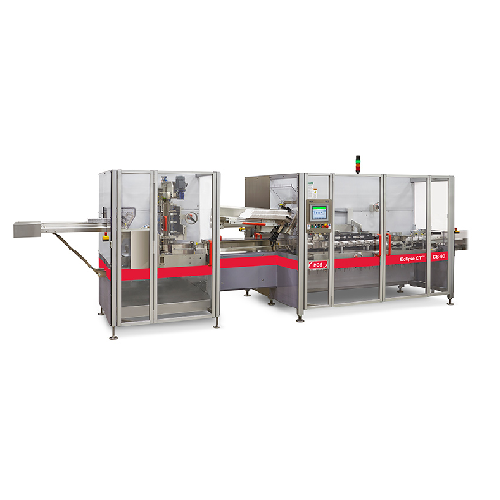

Horizontal cartoner for diverse industries
Streamline your packaging process with precise cartoning capabilities, effectiv...
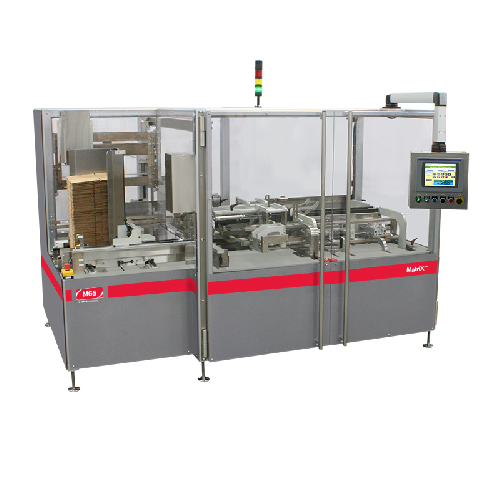

Case packer for pharmaceutical and healthcare products
Streamline your packaging line with a versatile case packer design...
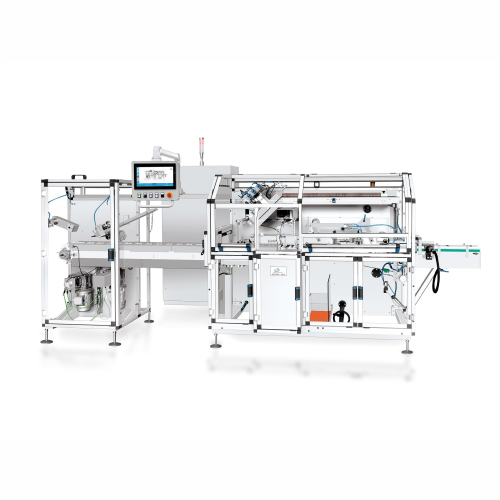

Automatic horizontal cartoning solution
Optimize your production line efficiency with a versatile cartoning system that acc...
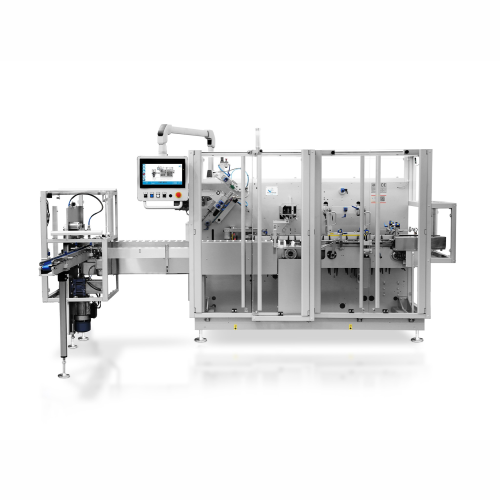

Automatic horizontal cartoning solution for various products
Optimize your packaging line with this advanced cartoning s...
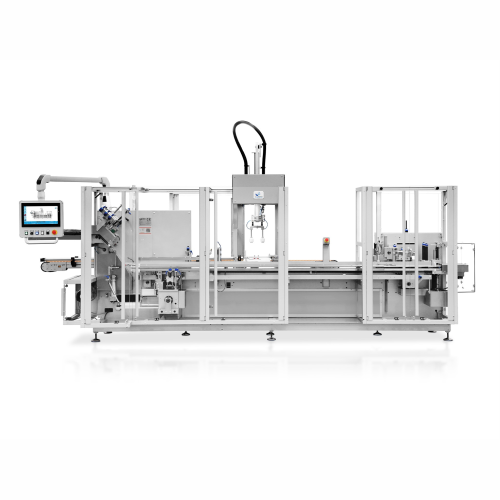

Automatic vertical cartoning solution for jars and bottles
Streamline your production line with a versatile packaging so...
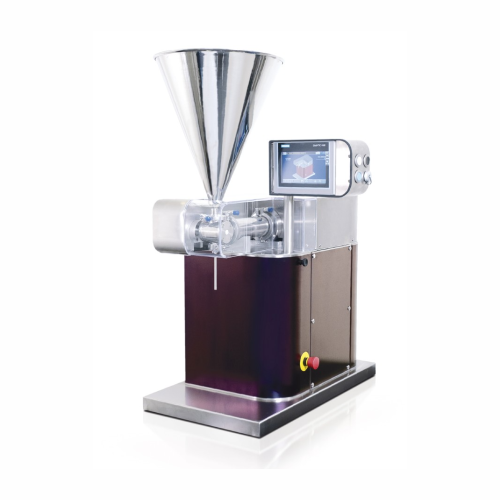

Lab-scale liquid and cream filling system
Streamline your lab production with precise filling of liquids, creams, and past...
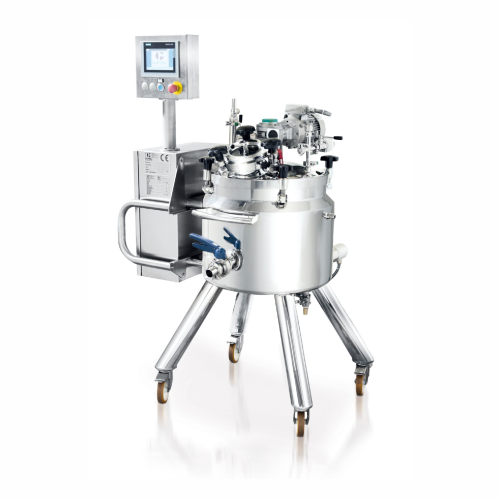

Industrial melter for cosmetic product processing
Streamline your production with this versatile melter, designed to effi...
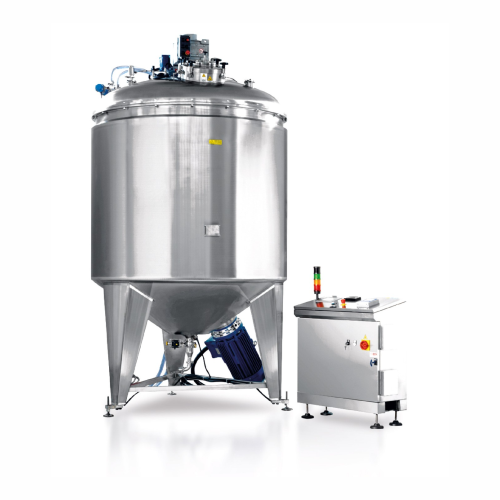

Vacuum turboemulsifier for liquid and creamy products
Achieve precise emulsification and mixing of liquid and creamy form...
Vacuum turboemulsifiers for liquid and creamy products
Simplify your production workflow with high-capacity vacuum turboe...
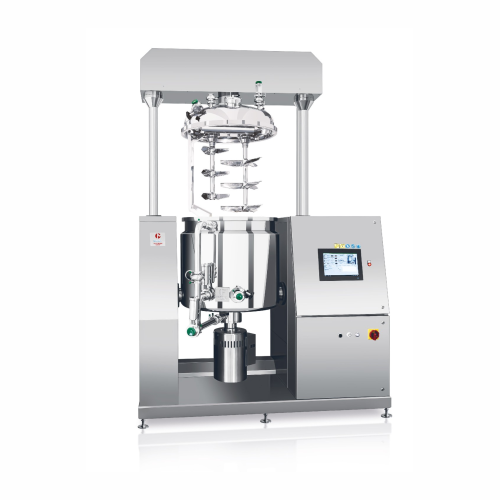

Vacuum turboemulsifier for medium-scale production
Achieve precise emulsification and consistent quality in liquid and cr...
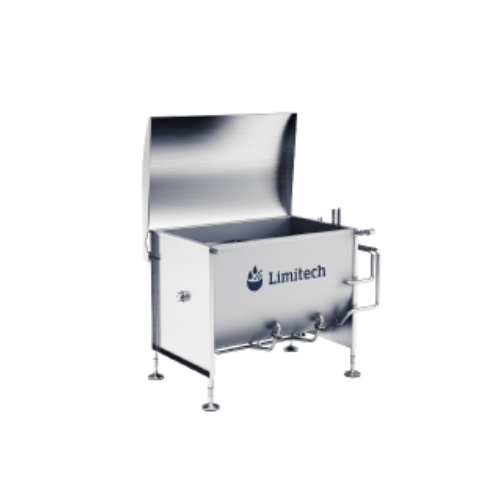

Food mixing and blending system
Enhance your production line with a versatile system designed for gentle processing needs, o...
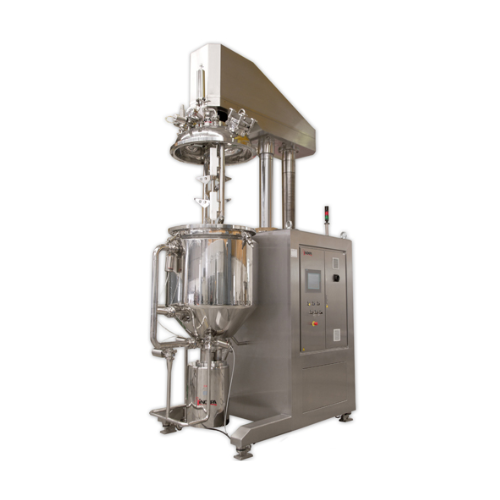

Counter-rotating blender for cosmetic and pharmaceutical mixing
Achieve precise mixing and homogenizing of complex formu...
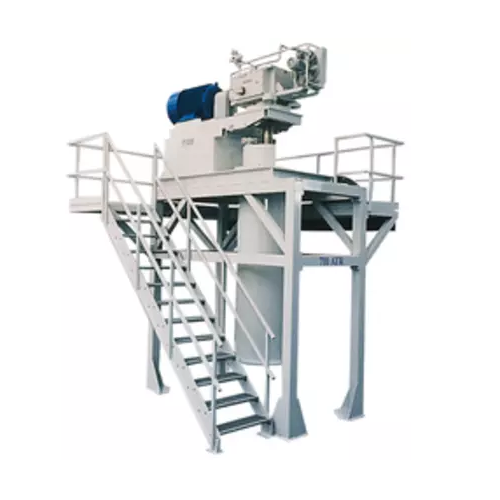

Ultra-fine grinding with ball mills and agitated media mills
Achieve precision in ultra-fine grinding for demanding mate...
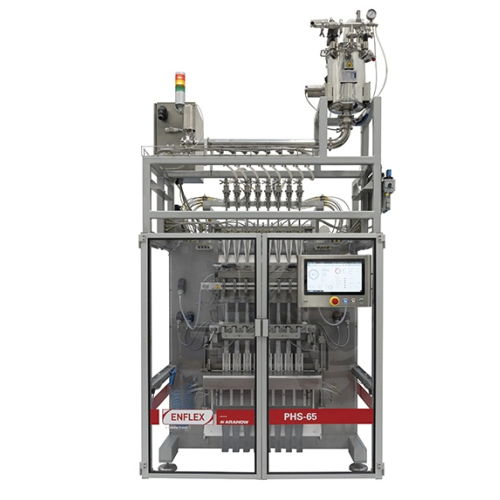

Intermittent stick pack system for pharmaceuticals
Effortlessly streamline your packaging process with a high-speed, mult...
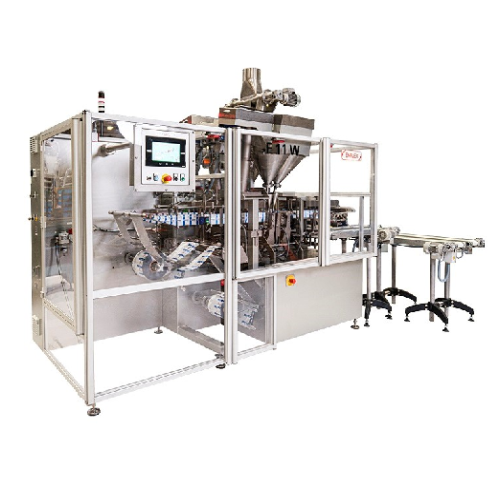

Horizontal flat pouching line for liquid soaps
Streamline your liquid product packaging with a dual-lane flat pouching lin...

Vacuum processing units for high-viscosity products
For manufacturers seeking to streamline production of high-viscosity ...

Vertical cartoning solution for fragrance and skincare products
Effortlessly carton even the most delicate cosmetics wit...

Tube filling solution for health and beauty products
Achieve rapid production with precision in tube filling for personal...

Cosmetic jar filling solution
Reduce product contamination and ensure precise filling with an intermittent jar filling solut...

Tube in-feed conveyor for cosmetic packaging lines
Streamline your packaging process with precision by efficiently transf...

Industrial mixer for liquid and viscous products
Achieve precise mixing and homogenization of high-viscosity liquids and s...

Vacuum mixer for liquids and semi-solids
Achieve precise mixing and homogenization of liquid and semi-solid formulations wi...

Colloidal mill for fine grinding and homogenisation
Optimize your liquid and semi-solid processing by achieving precise p...
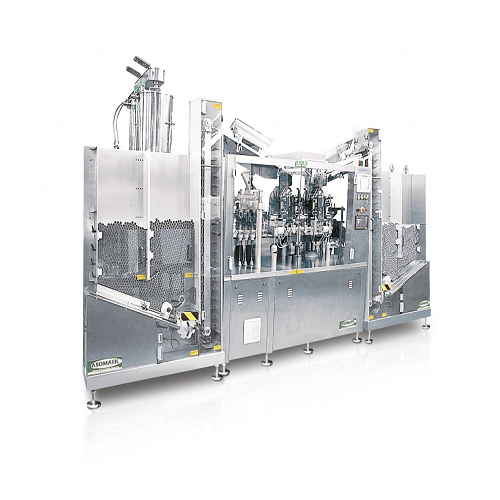

Automatic tube filling and closing system
Enhance production efficiency with a high-speed tube filling and closing system ...
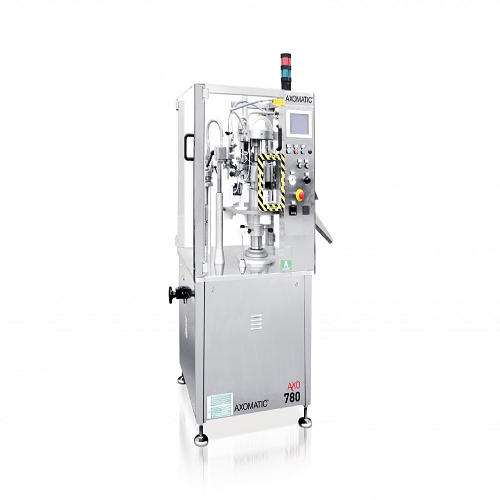

Semi-automatic tube filling and closing system
Achieve precise filling and secure closing for diverse tube types, optimizi...
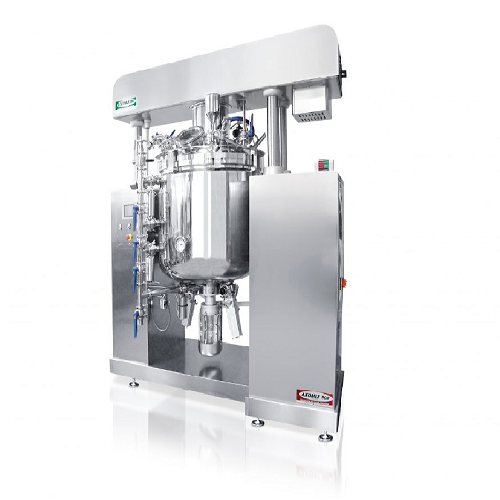

Undervacuum homogenizer for cosmetic and pharmaceutical creams
Optimizing the production of creams and lotions, this und...
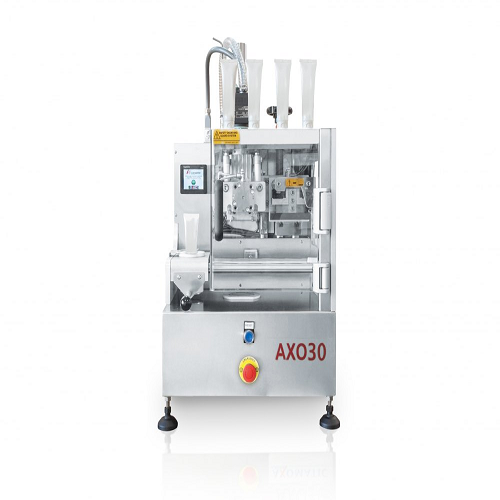

Manual tube sealer for plastic and laminated tubes
Secure precise and reliable seals on plastic and laminated tubes with ...

Automatic tube filling and closing solution
Optimize your production line with a high-speed machine for precise tube filli...

Tube feeder for pharmaceutical and personal care industries
Optimize your production line with this high-speed tube feed...

Drum decanting unit for high viscosity liquids
Efficiently decant high viscosity liquids like solvent-based paints and ess...

Rotary filler capper for personal care products
Ensure consistent filling and capping of liquid products with high-speed p...

High-performance mill for paint and varnish industry
Achieve superior fine dispersing and grinding efficiency for liquid ...

Stand-up pouch packaging for various industries
Elevate your packaging capabilities with a high-speed horizontal pouching ...
Continuous stand-up pouching solution for up to 1000ml
Maximize efficiency in high-speed production lines with precise st...

Vacuum homogenizers for cosmeto-pharma and fine chemistry
Bring precision and efficiency to your formulation processes w...

Vacuum homogenizer for cosmetics and pharmaceuticals
Optimize your production with precision mixing and homogenizing, ess...
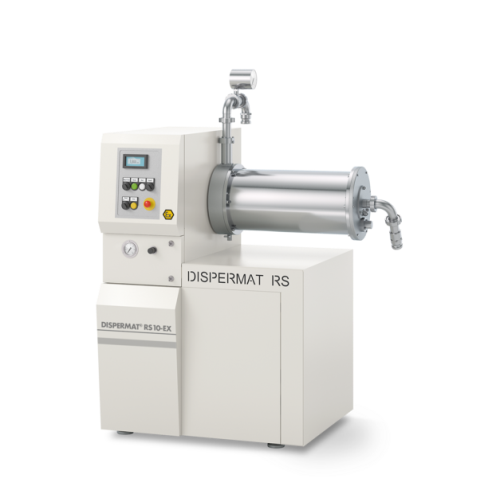

Explosion-proof bead mill for industrial grinding applications
For manufacturers seeking precise particle size control, ...
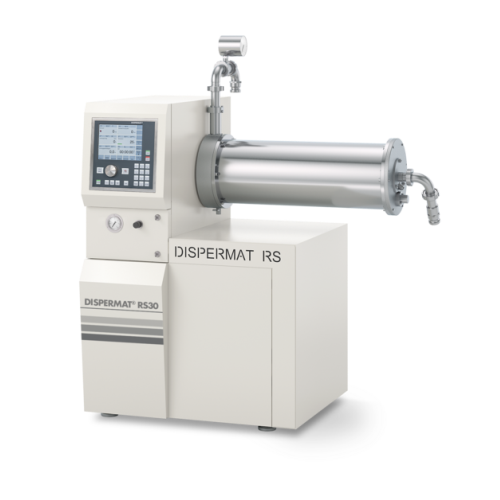

Horizontal bead mill for industrial nano grinding
Achieve precision in nano-scale grinding with this advanced bead mill, ...
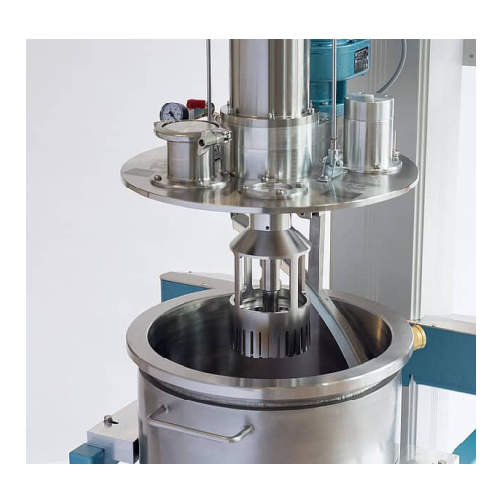

Efficient high-volume dissolver with scraper
For high-viscosity formulations, this advanced dissolver with integrated scra...
Automatic tube filling for coextruded products
Maximize efficiency in high-volume production with precision co-extruding c...
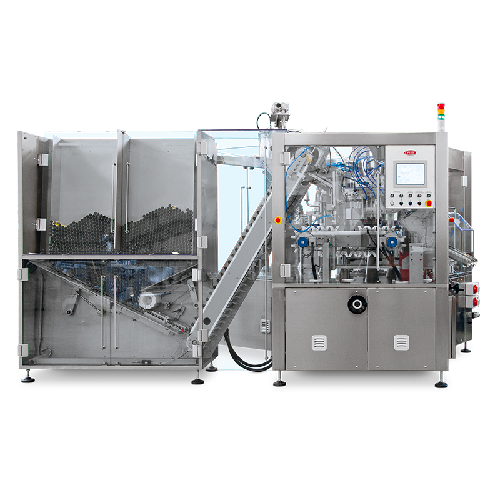

Automatic tube filling solution for high-volume production
Effortlessly streamline your production with this high-speed ...
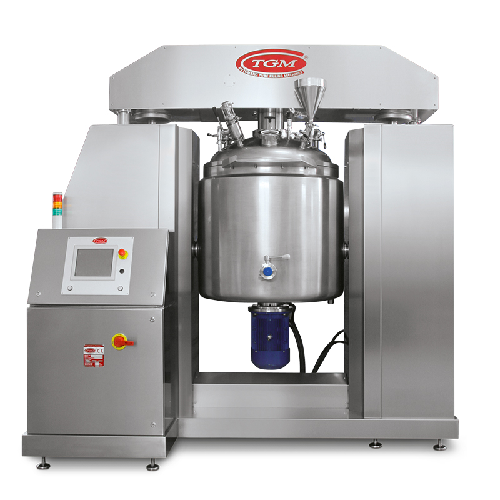

Turbo emulsifier for creams, gels, toothpastes
Achieve perfect emulsification and homogenization for your creams, gels, an...

Vertical cartoning solution for manual product loading
Streamline your cartoning process with a versatile solution design...
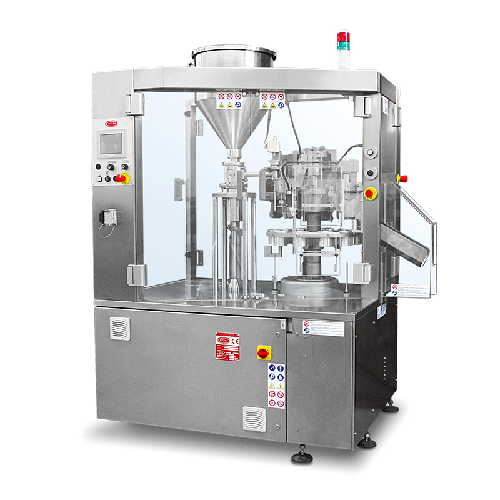

Small batch tube filling system for metal and plastic tubes
Optimize your small-batch production with precise tube filli...
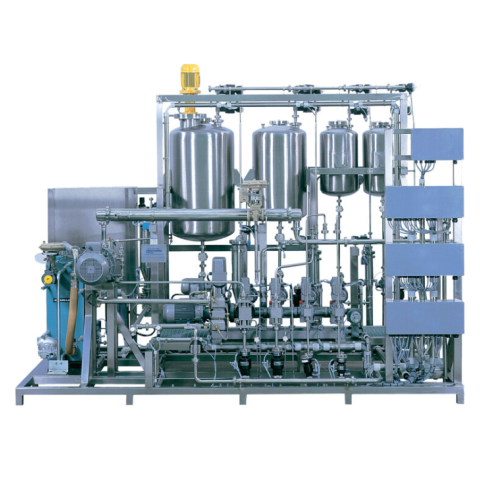

Automated body lotion blending system
Streamline your personal care product manufacturing with a seamless blending and emul...
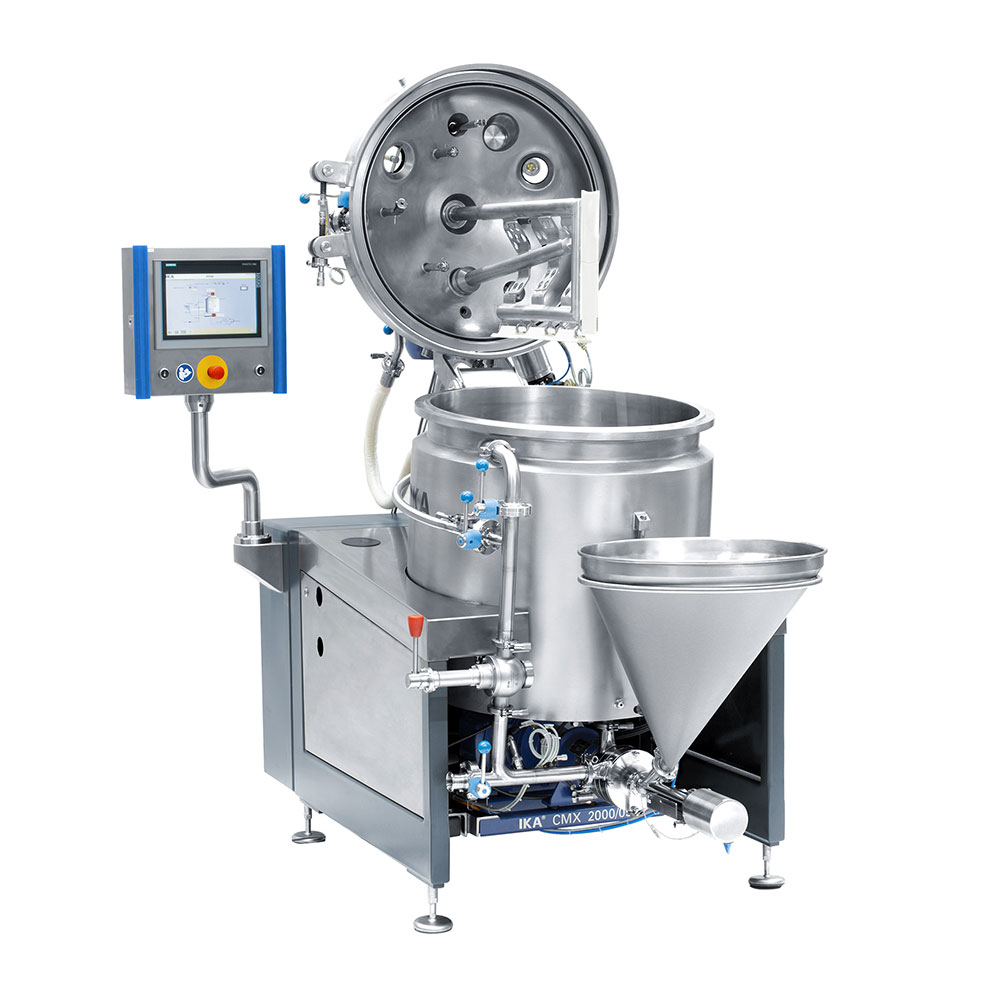

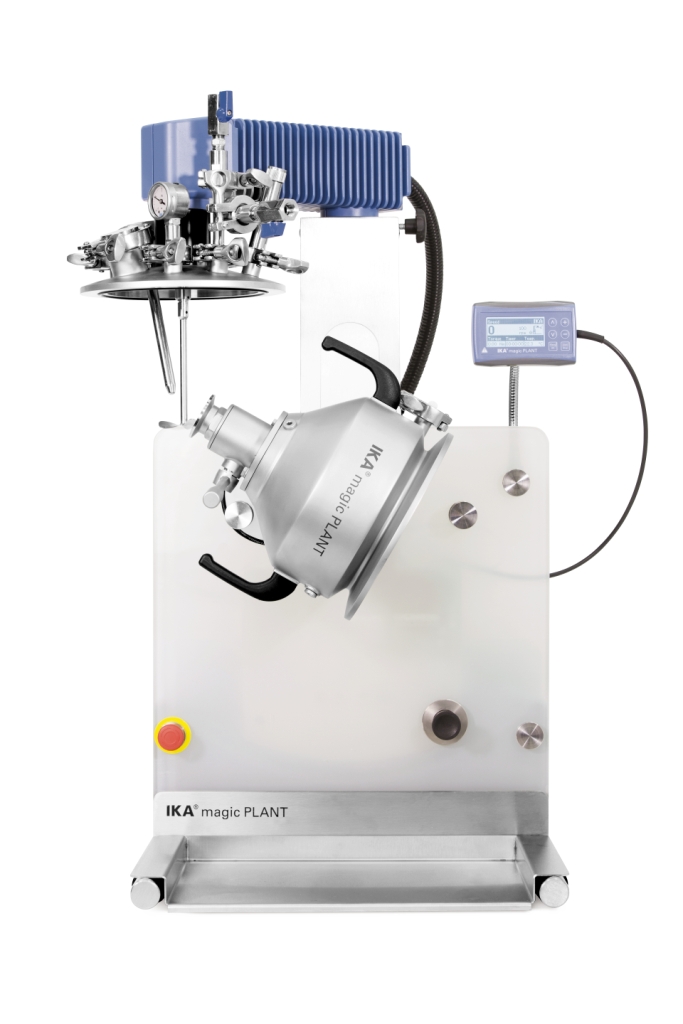
Compact Mixing Plant for Paints and Coatings
A smooth finish in paints and coatings depends on the grade of dispersal duri...
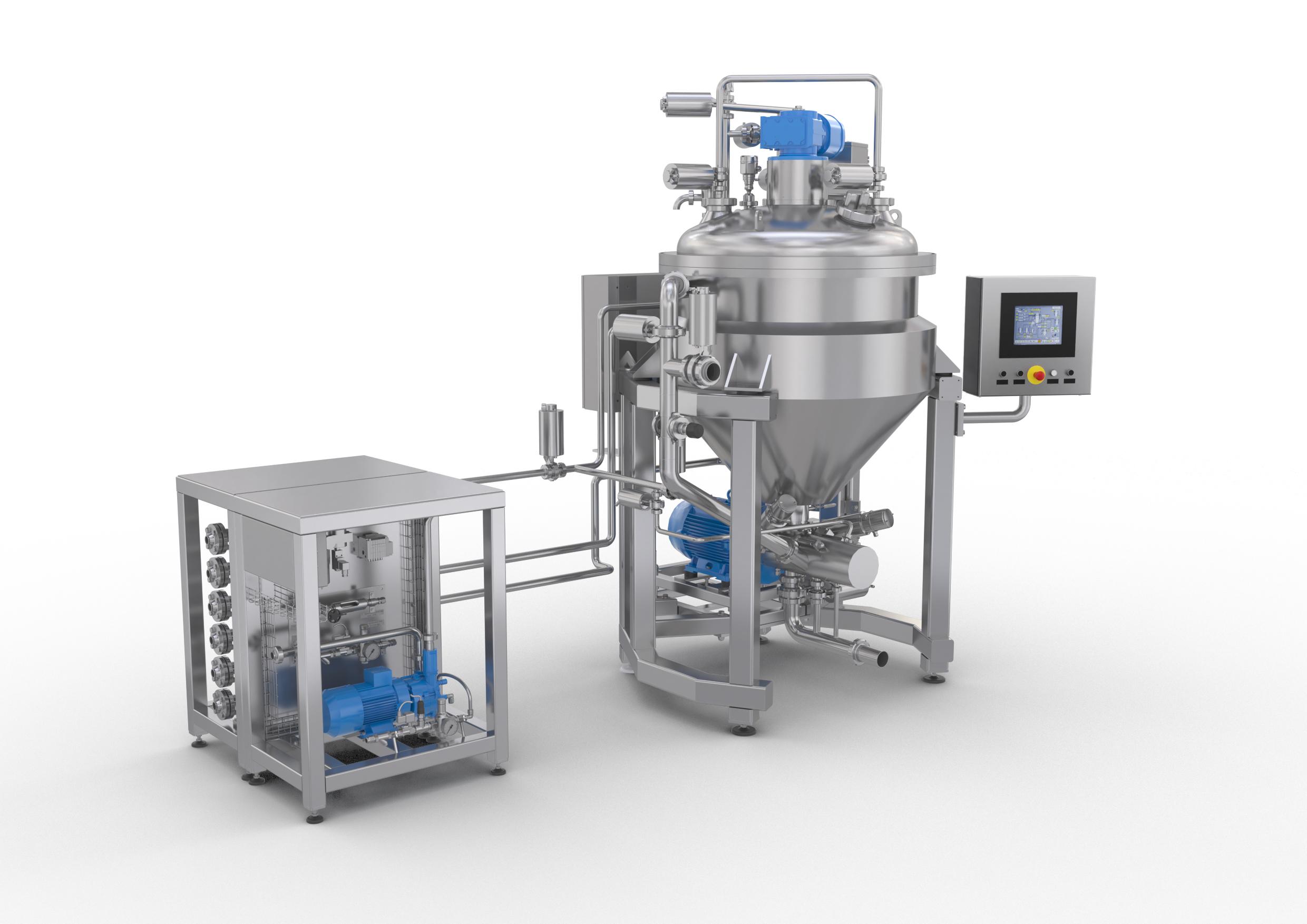

Batch vacuum mixer for emulsion-based products
The production of creams or ointments can be either be a water in oil (w/o)...

Self-adhesive linear labeling machine for bottles
It is vital to have precise and long-lasting labels on bottles to avoid...

Cosmetic cream filler
From thin liquid baby oils and perfumes to thicker lotions and creams for hair and skincare, cosmetic p...
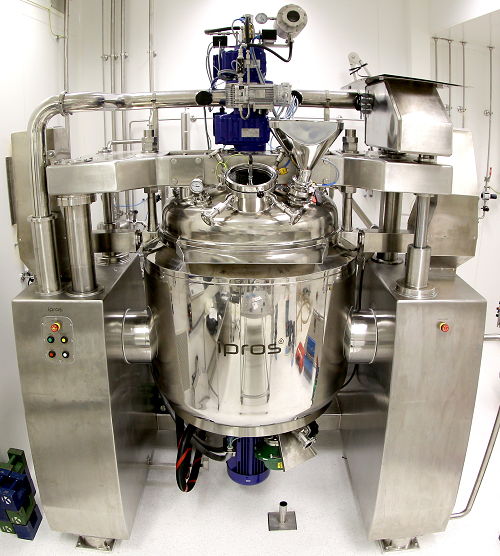

Homogenizer for creams
Homogenization (or pharmaceutical micronization) is the process of reducing particle sizes, and is a v...
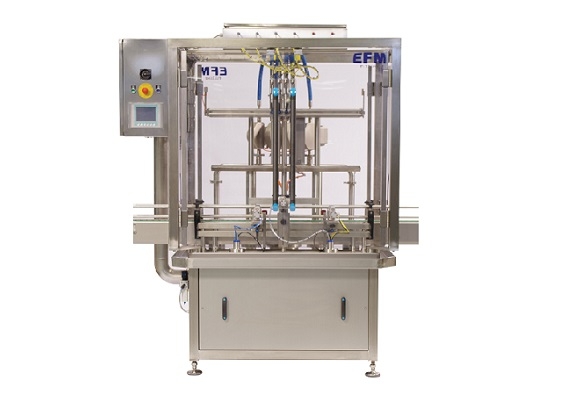

Flowmeter filler
For larger production runs of food, non-food and cosmetics industries, where accuracy and volume of filling i...
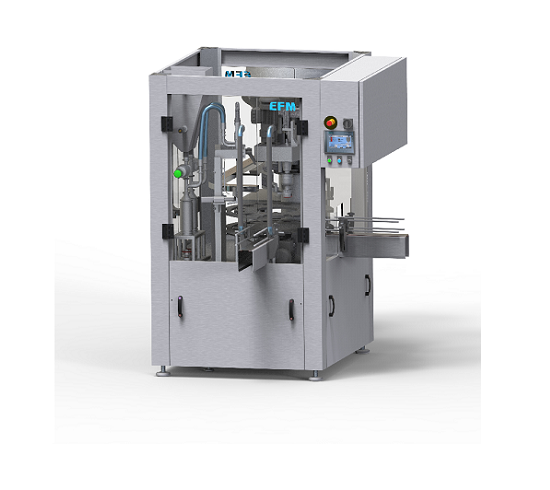

Compact monoblock filler
Filling and capping bottles and pots for food, chemical and cosmetics industries using separate mach...
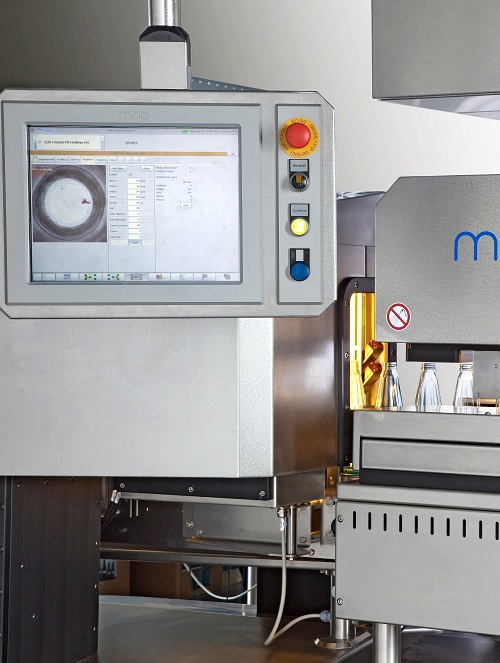

High-end empty bottle inspection system
If you are looking for a system with empty bottle inspection; base, residual liquid...
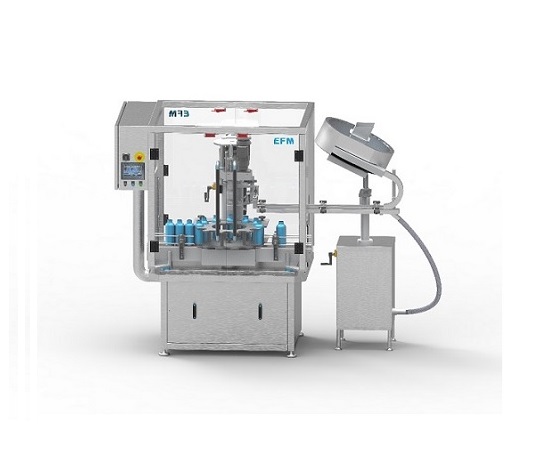

Single head capper
For the stand-alone capping of bottles of up to 30 litre capacity for smaller-scale production you need a ...
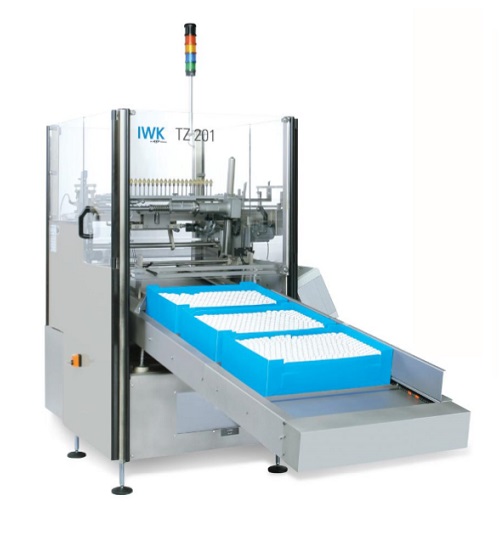

Tube unloader and feeder
The pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries utilise high speed tube fillers on large-scale production...
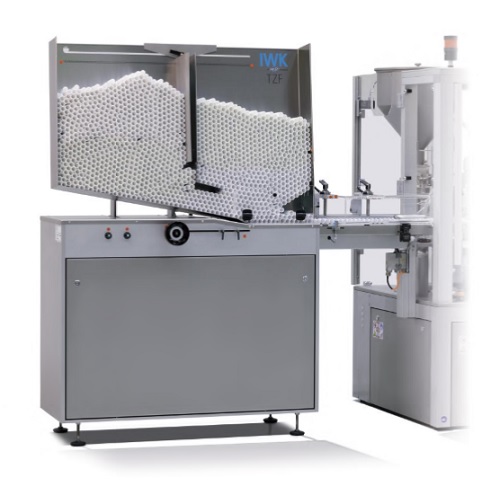

Tube feeding unit for high volume and high speed tube filler
High performance tube-filling machines are used for large s...
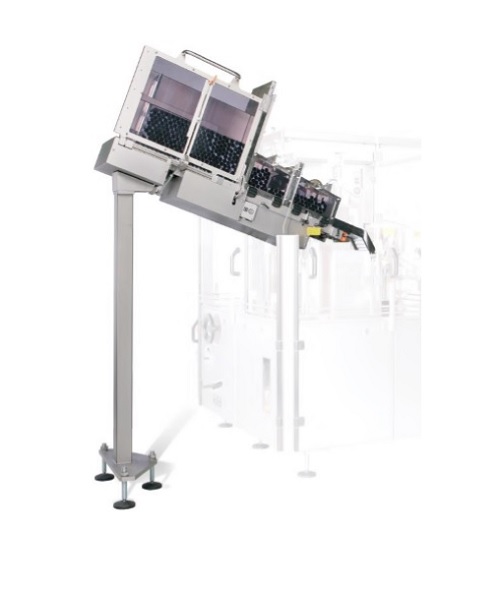

Loading cassette for a tube filler
High performance tube-filling machines are used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic indus...
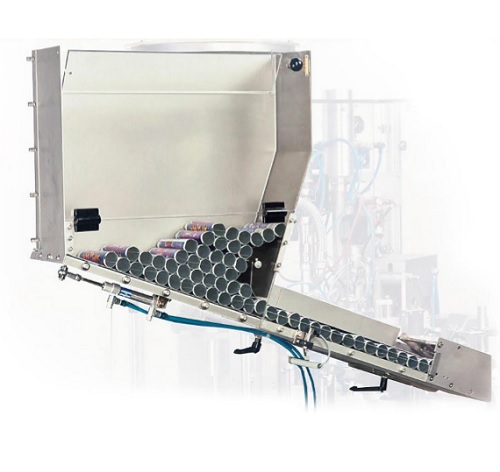

Tube feeder for a small scale production tube filler
Low speed tube-filling machines are used for small scale production ...

High speed automatic tube filler
For high-volume lines filling pharmaceutical, cosmetic or food products into tube container...

High-capacity horizontal cartoner for pharma and cosmetics appliances
Cartoners take carton blanks which are formed and...

Pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry products cartoner
A large number of cosmetic and pharmaceutical products are packed ...

Medium speed tube filler and sealer
For scale-up filling of tube packaging for pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and food products...
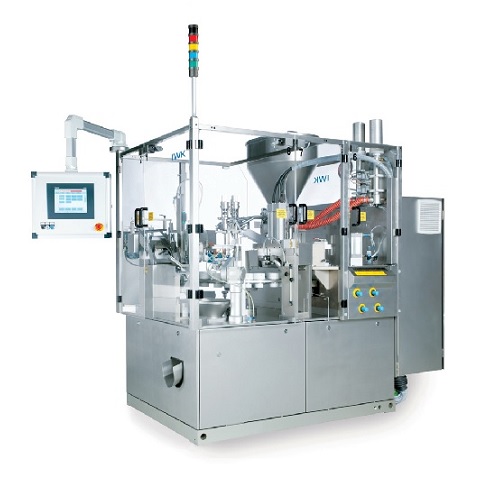

Medium and high speed range automatic tube filler
When scaling up production of pharmaceutical, food or cosmetic products...
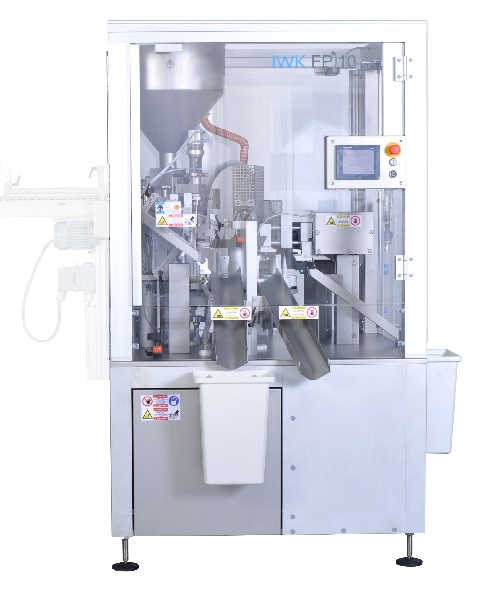

Low speed tube filler
Increasing numbers of products in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries are delivered in fle...
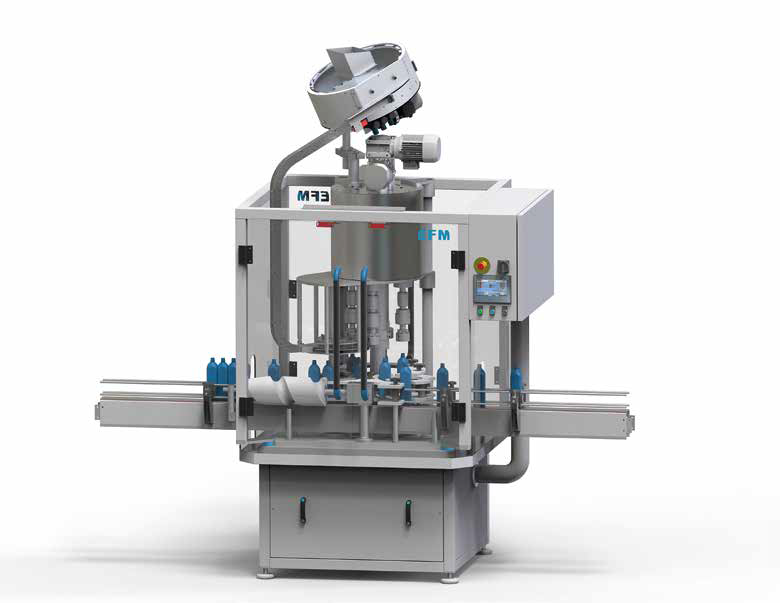

Multi-head capper
For the stand-alone capping of bottles of up to 2.5litre capacity you need a robust and flexible machine wi...
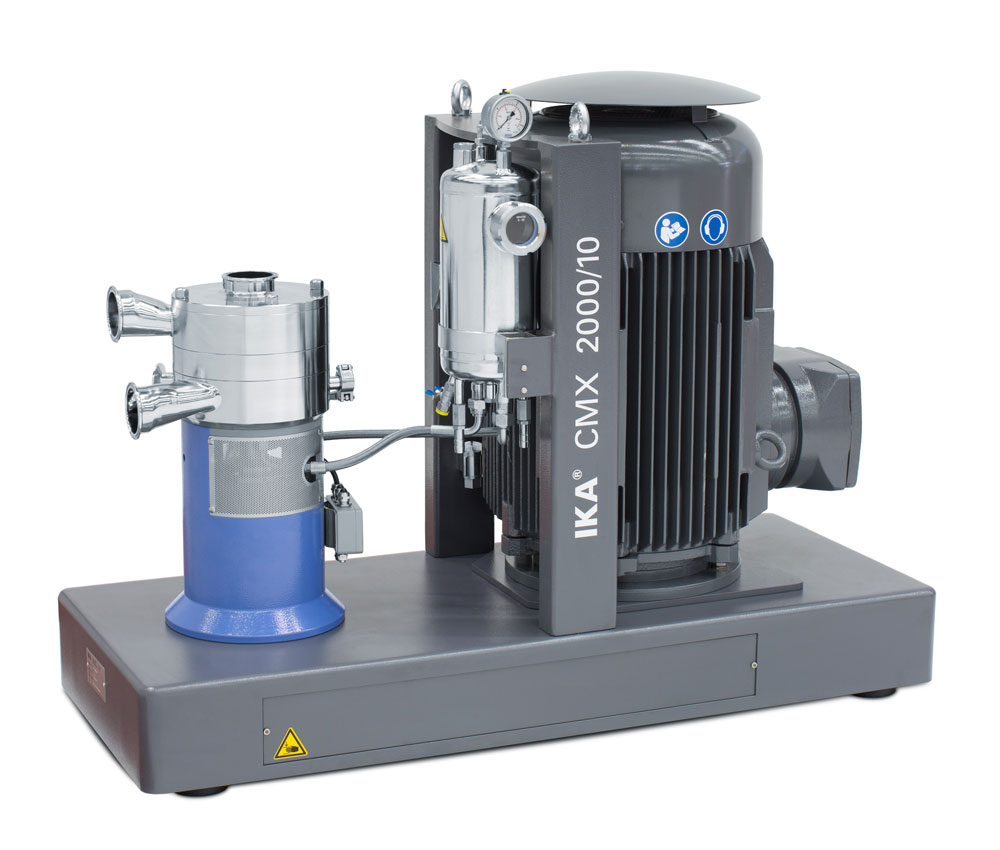

Inline batch mixer for solids and liquids
Several issues often arise when your process requires batch-wise mixing of powde...
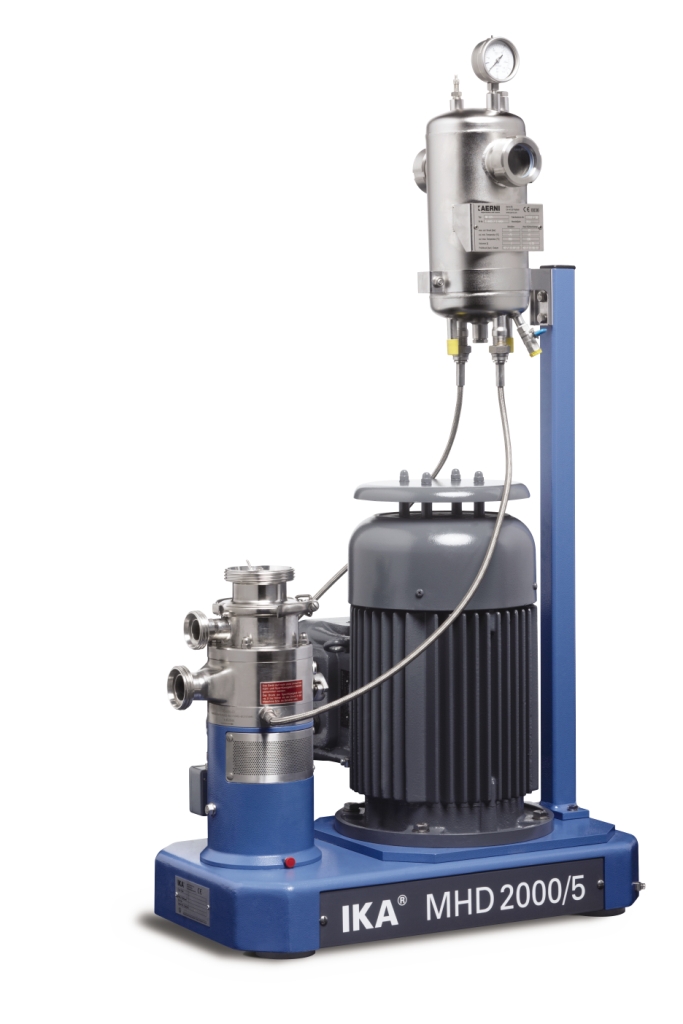

Continuous homogenizing system
Certain mixing tasks present unique challenges and manufacturers need equipment that is speci...
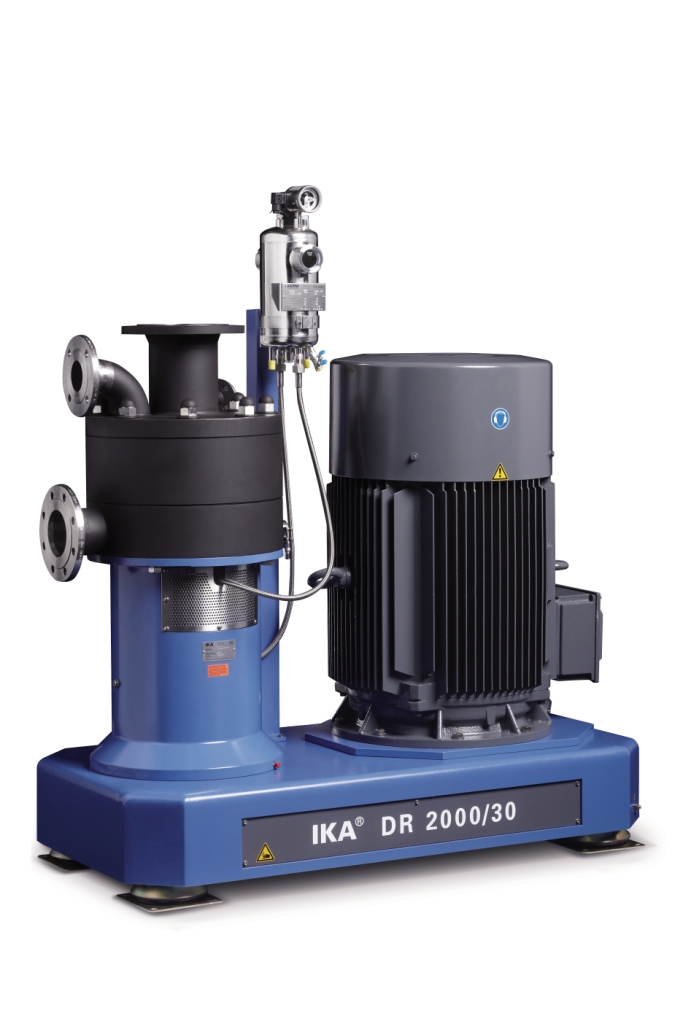

High accuracy homogenizing system
When extremely high accuracy is required in your recipe or formulation traditional mixing...
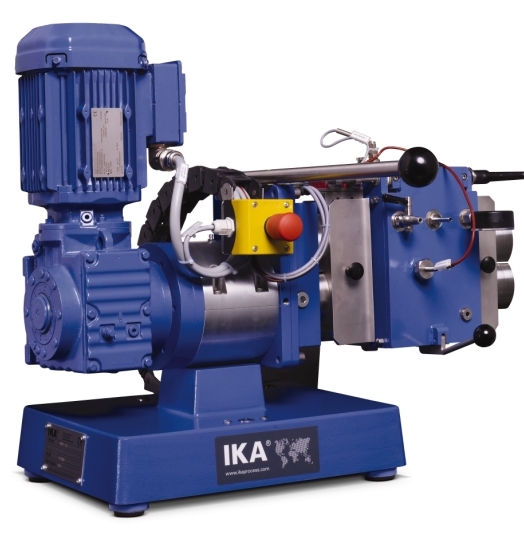

Horizontal kneader
For high viscosity products, better results and reduced process times can be achieved with kneading type r...
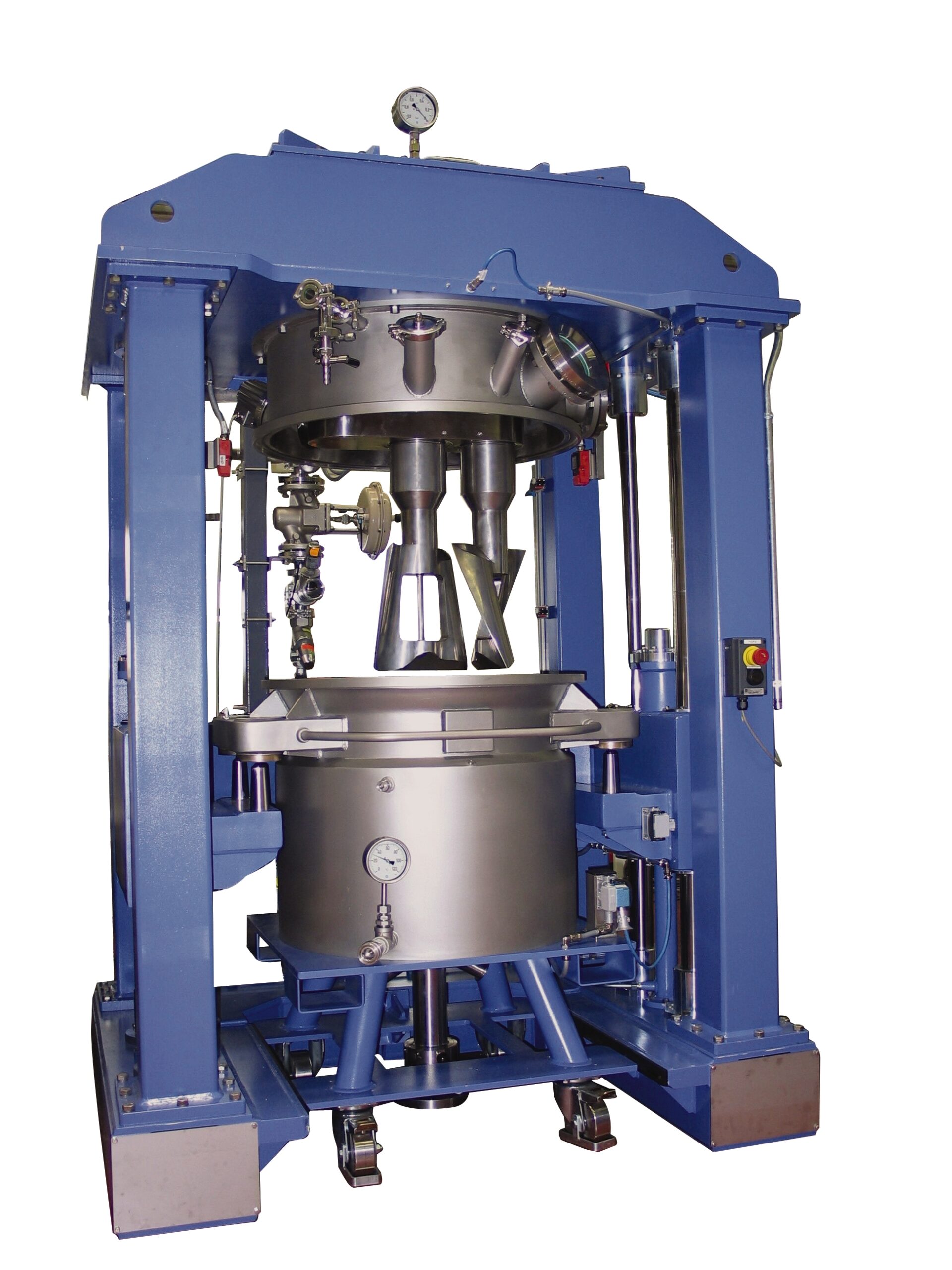

Vertical kneader
Production of highly viscous products with high solid content often benefits from kneading processes rather t...
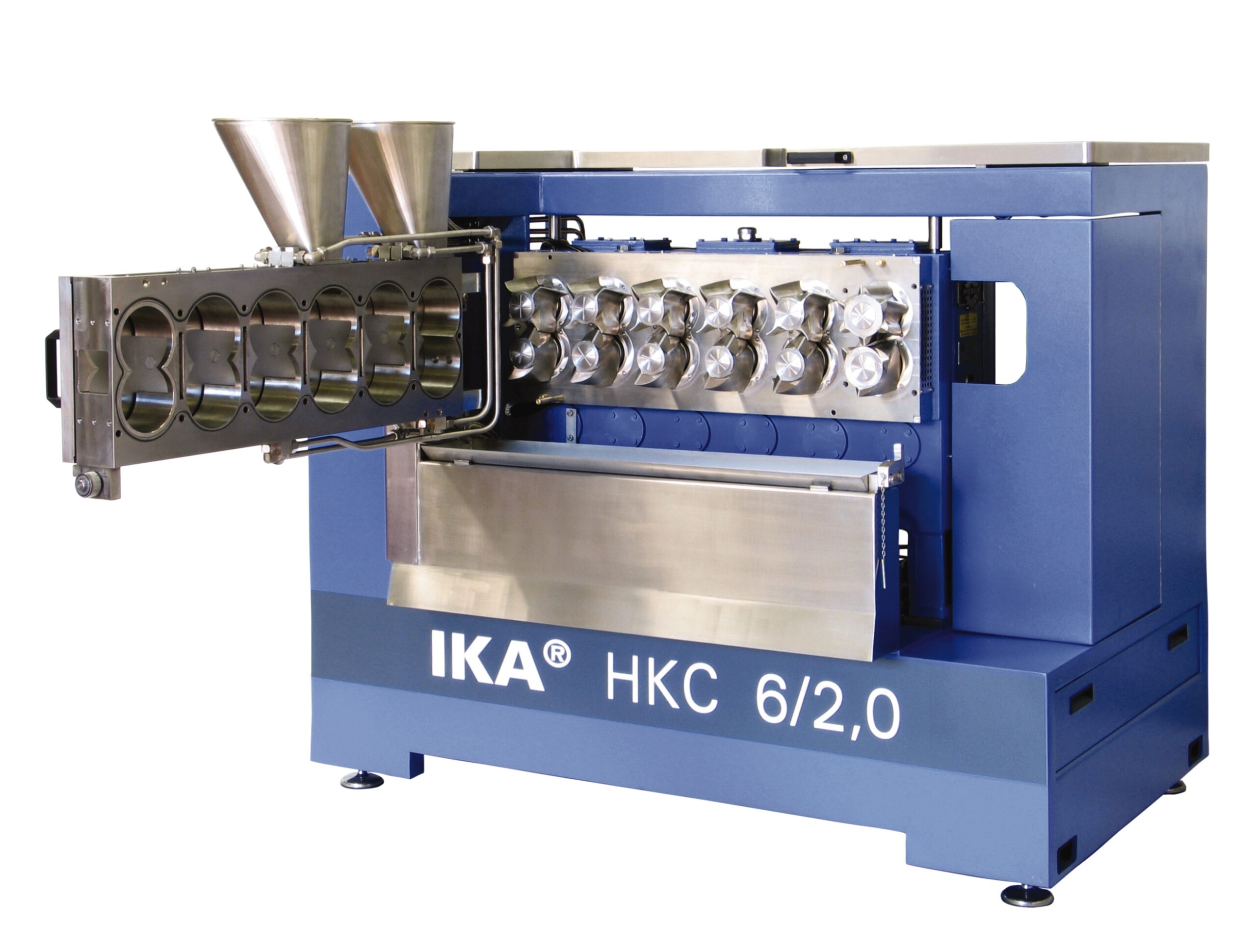

Continuous kneader
Effective mixing of highly viscous products with extremely high solids content can be difficult and the re...
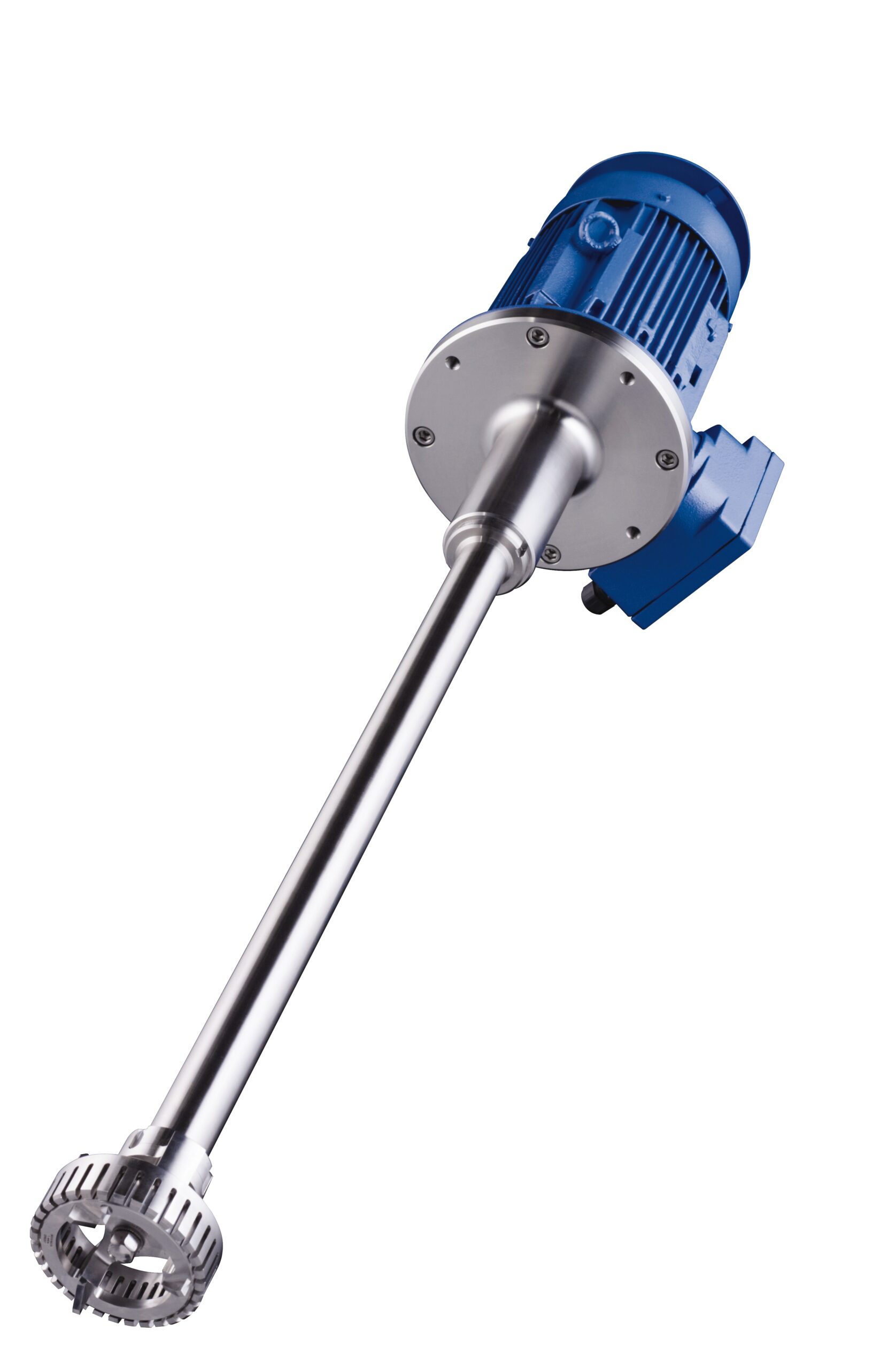

Batch dispersing machine
Equipment operating under the rotor/stator principal is often employed when more traditional methods...
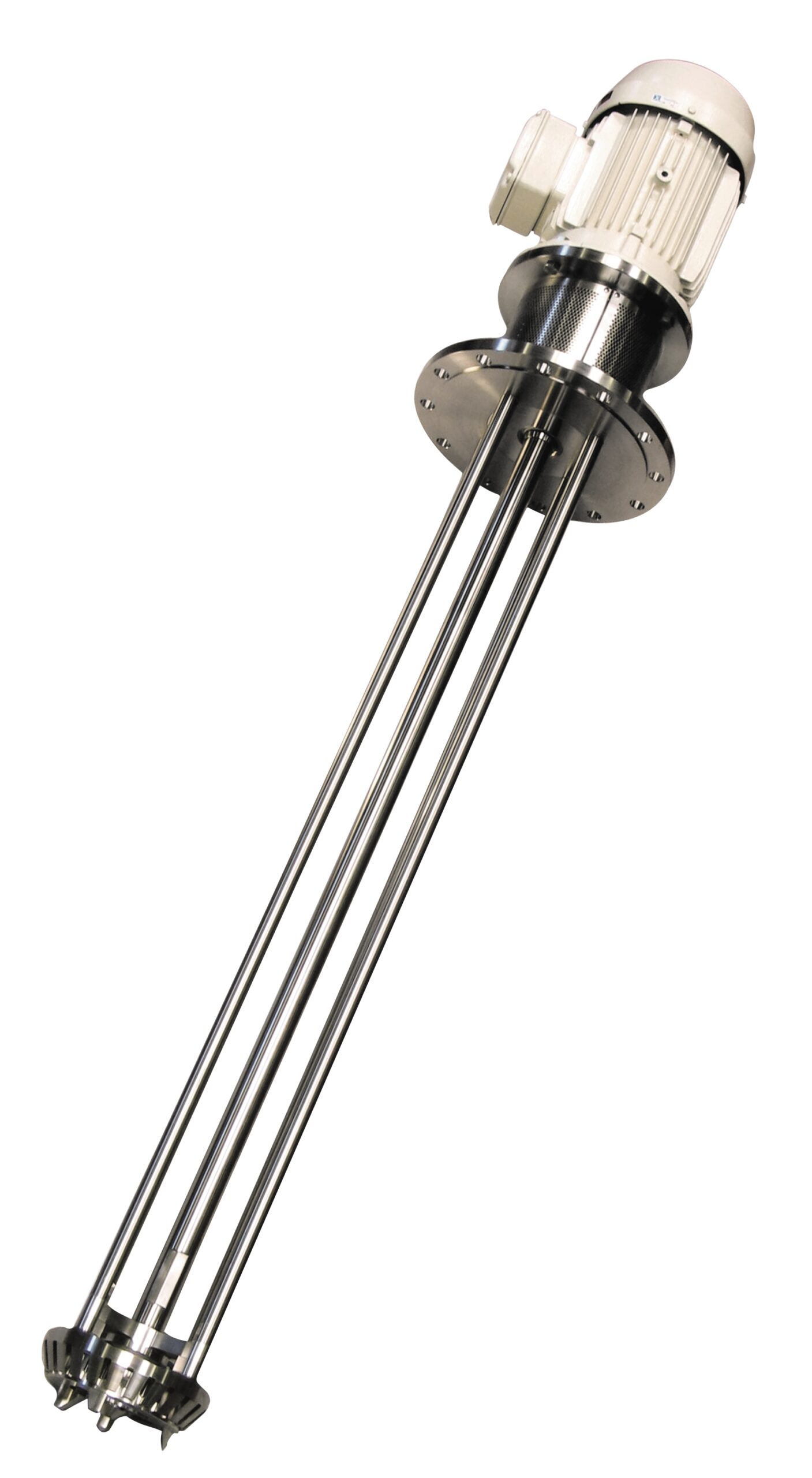

Batch dispersing machine for abrasive products
For mixing and dispersing tasks that cannot be completed by conventional st...
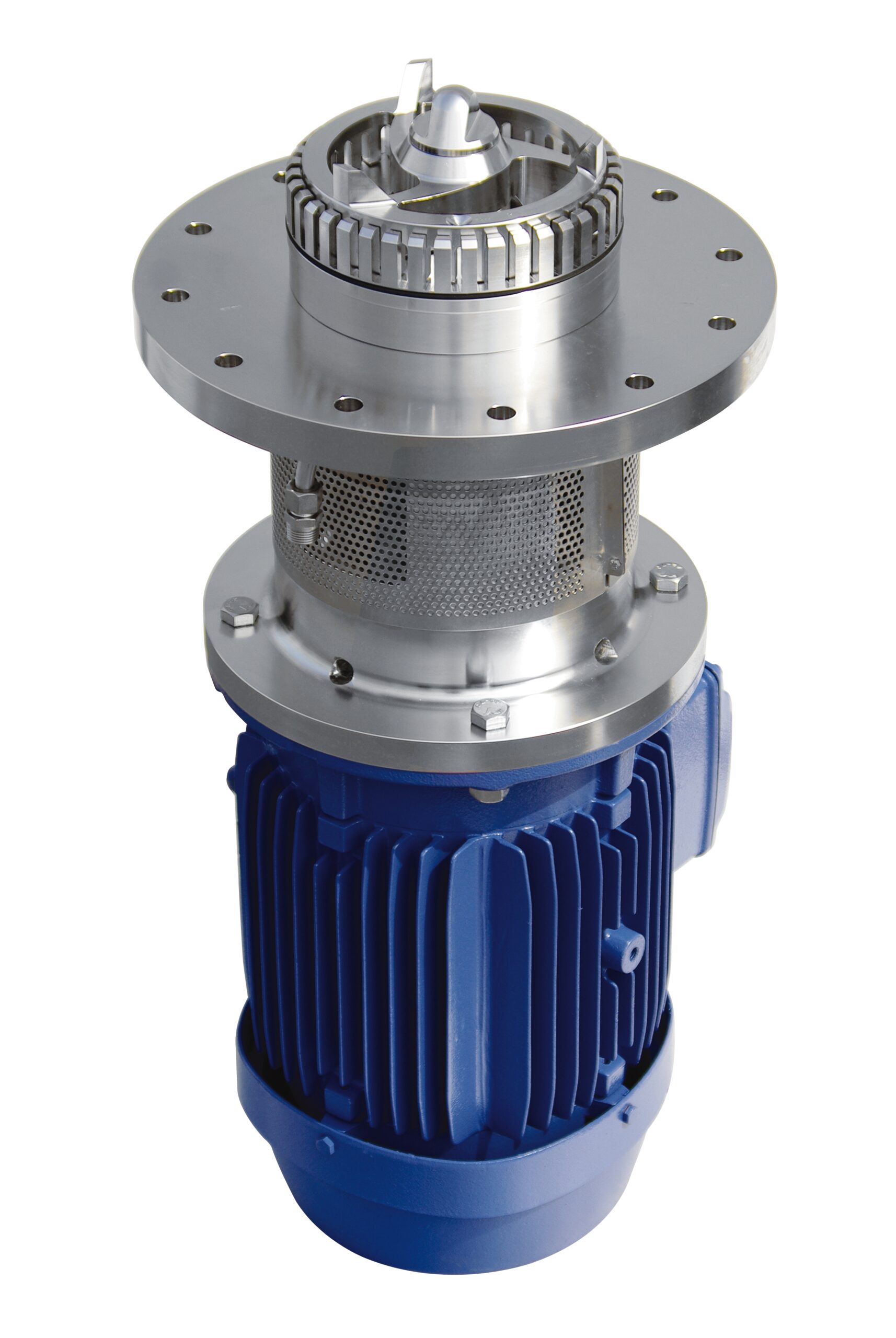

Batch dispersing machine for bottom entry into vessels
When your process requires high performance mixing or dispersion b...
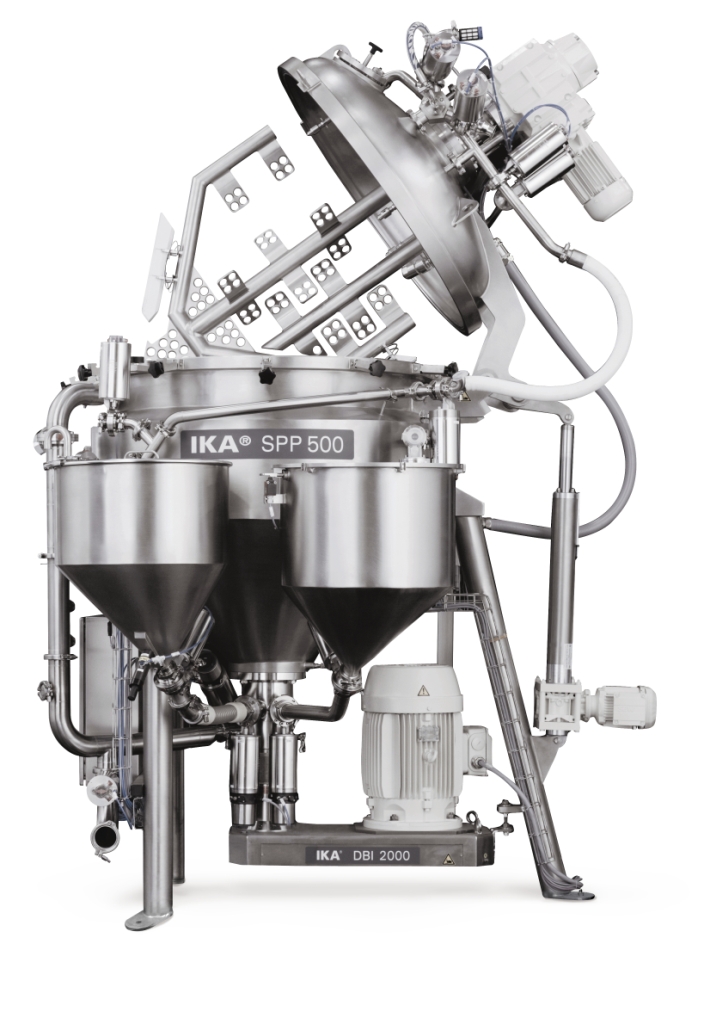

Cost-effective homogenizing and emulsifying system
Manufacturers of cosmetic products need mixing equipment that is capab...
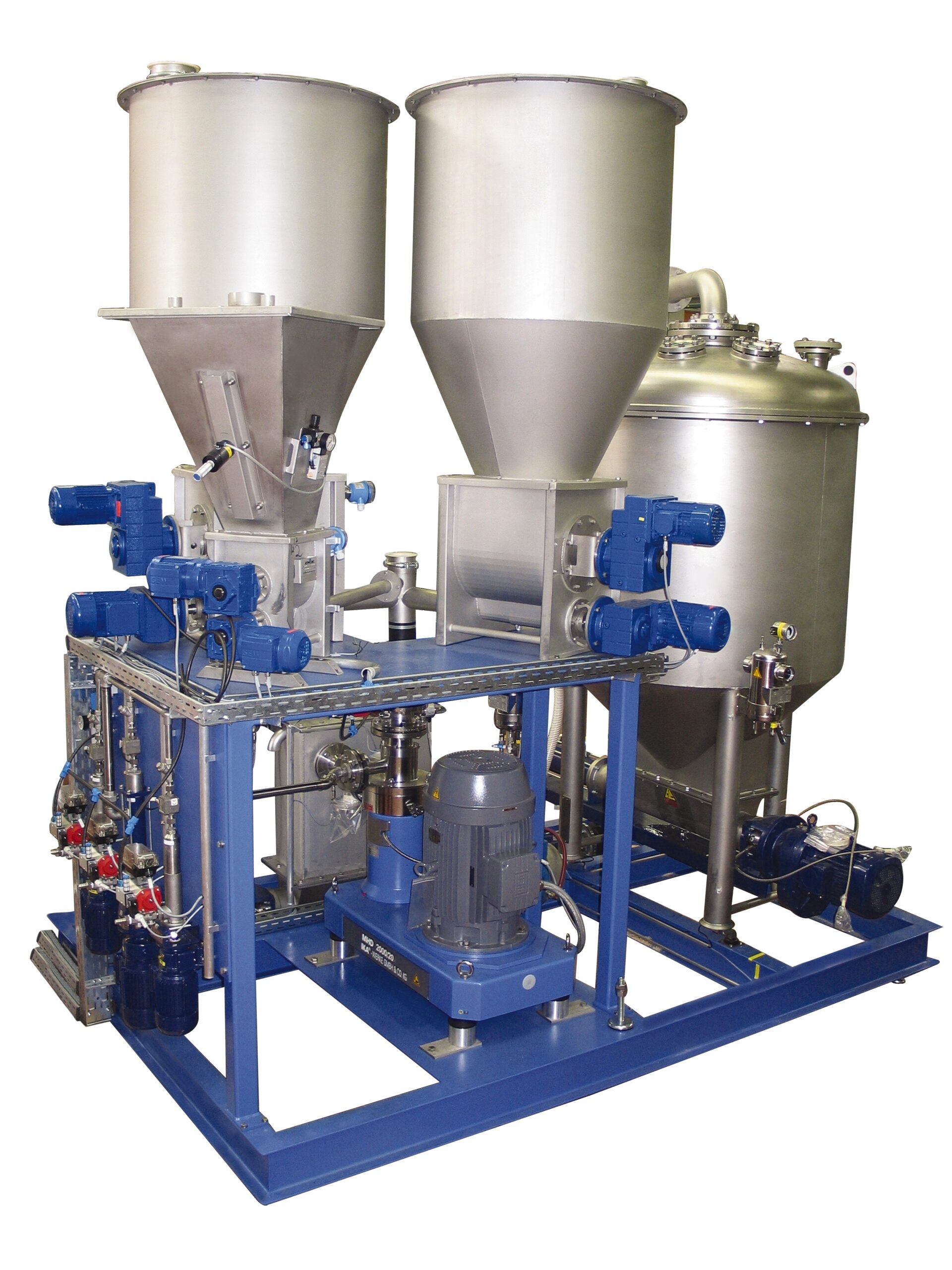

Dust-free continuous homogenizing system
Producers in a wide variety of industries benefit from equipment that can continuo...
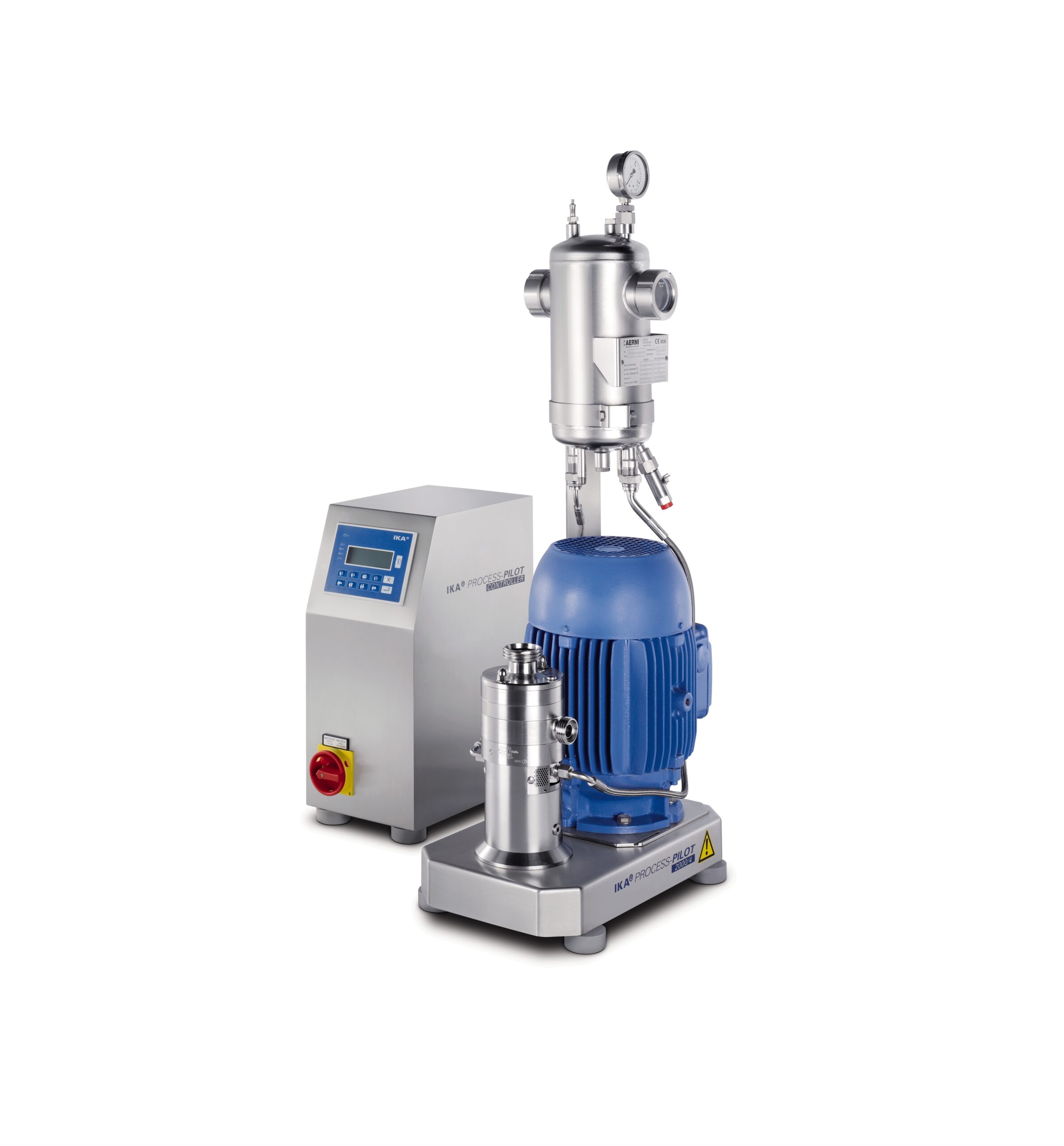

Dilution system for two or more liquids in one pass
Onsite dilution of liquid process ingredients has historically been a...

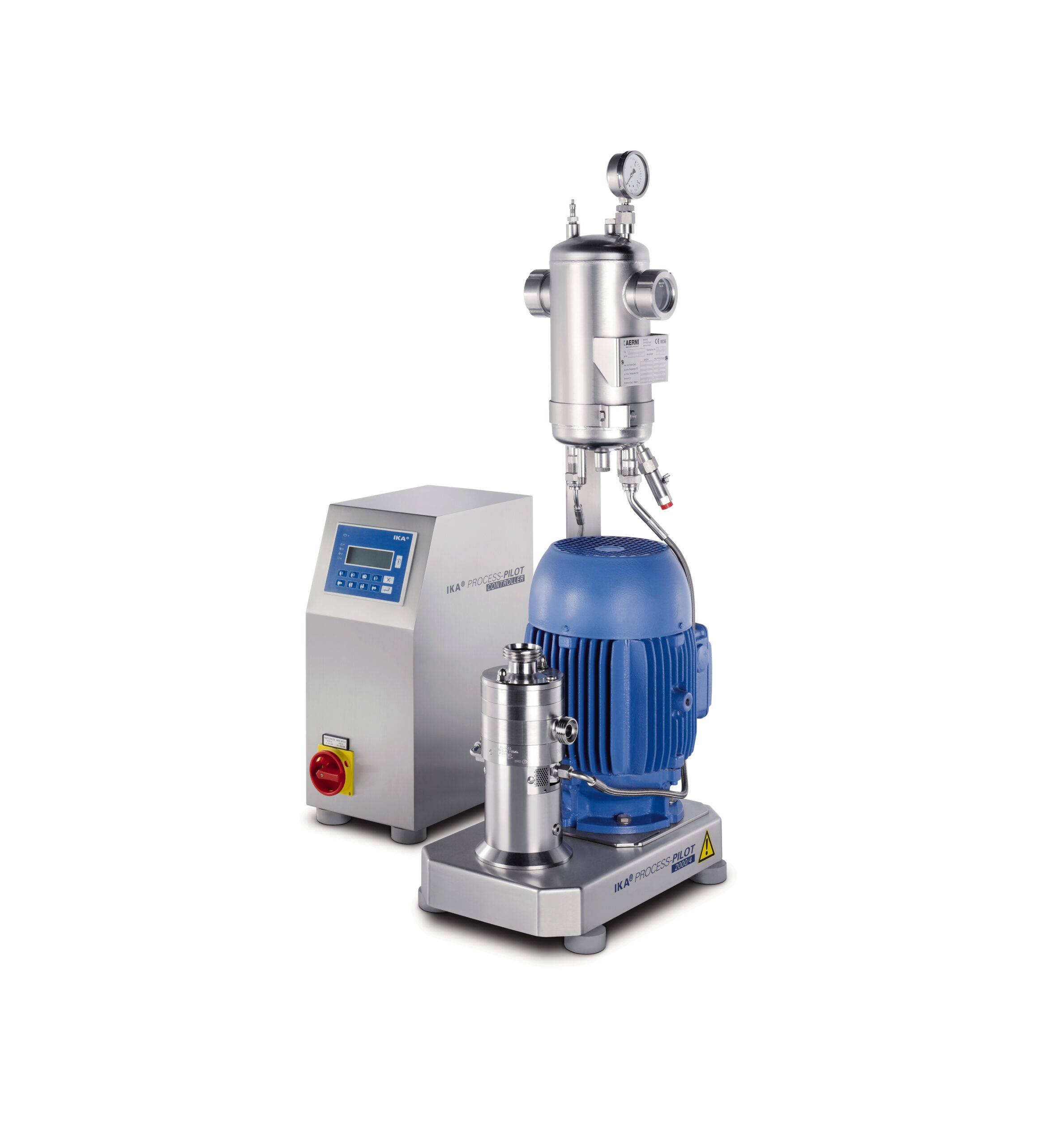
Pilot dispersing machine for testing and scale-up
Innovators in process development need laboratory equipment that helps ...

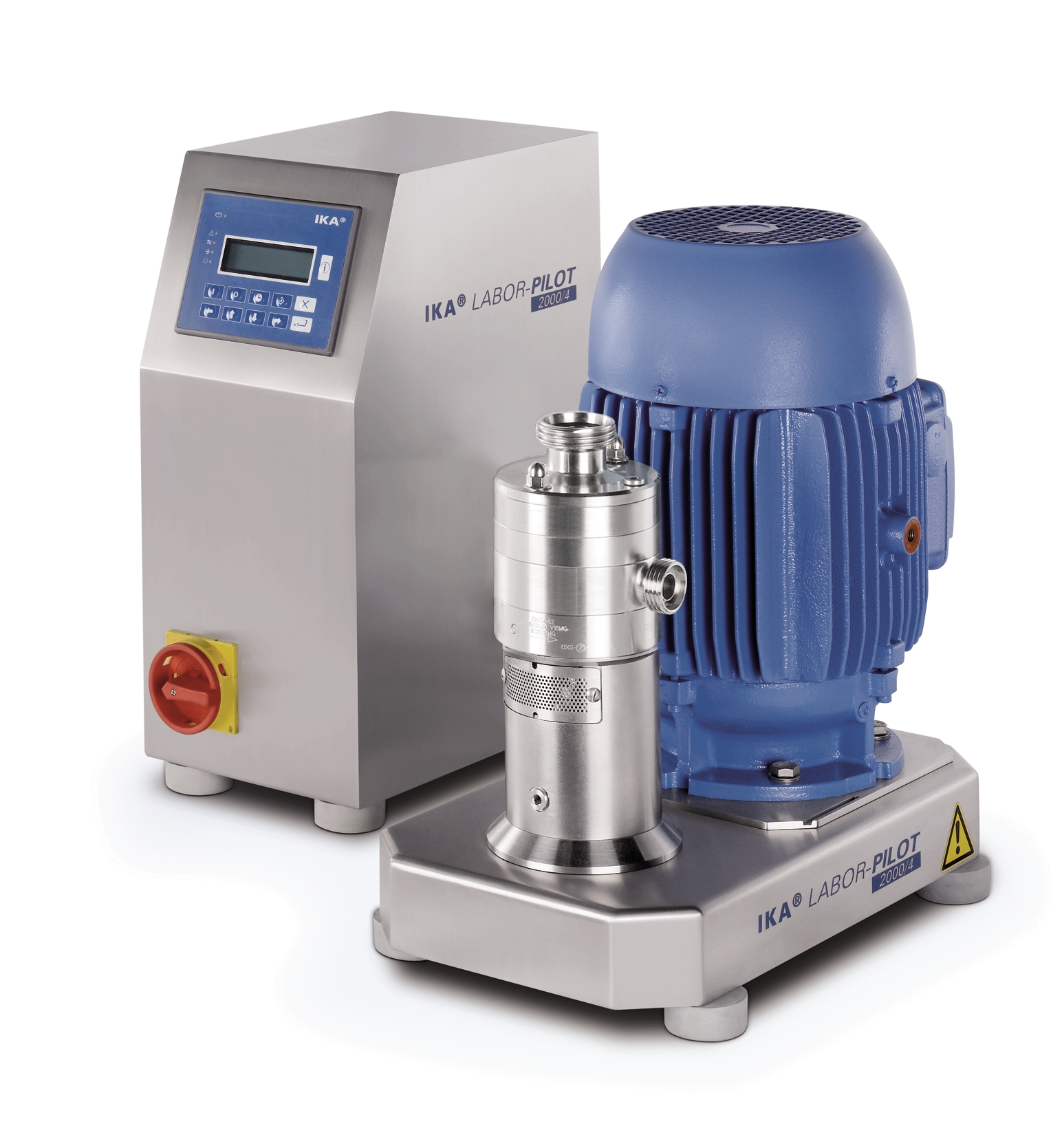
In-line laboratory dispersing machine
Innovators in a wide variety of industries need laboratory equipment on which process...

Laboratory dispersing machine for low-viscous masses
Laboratory mixers have not always been easy to work with. Getting a...
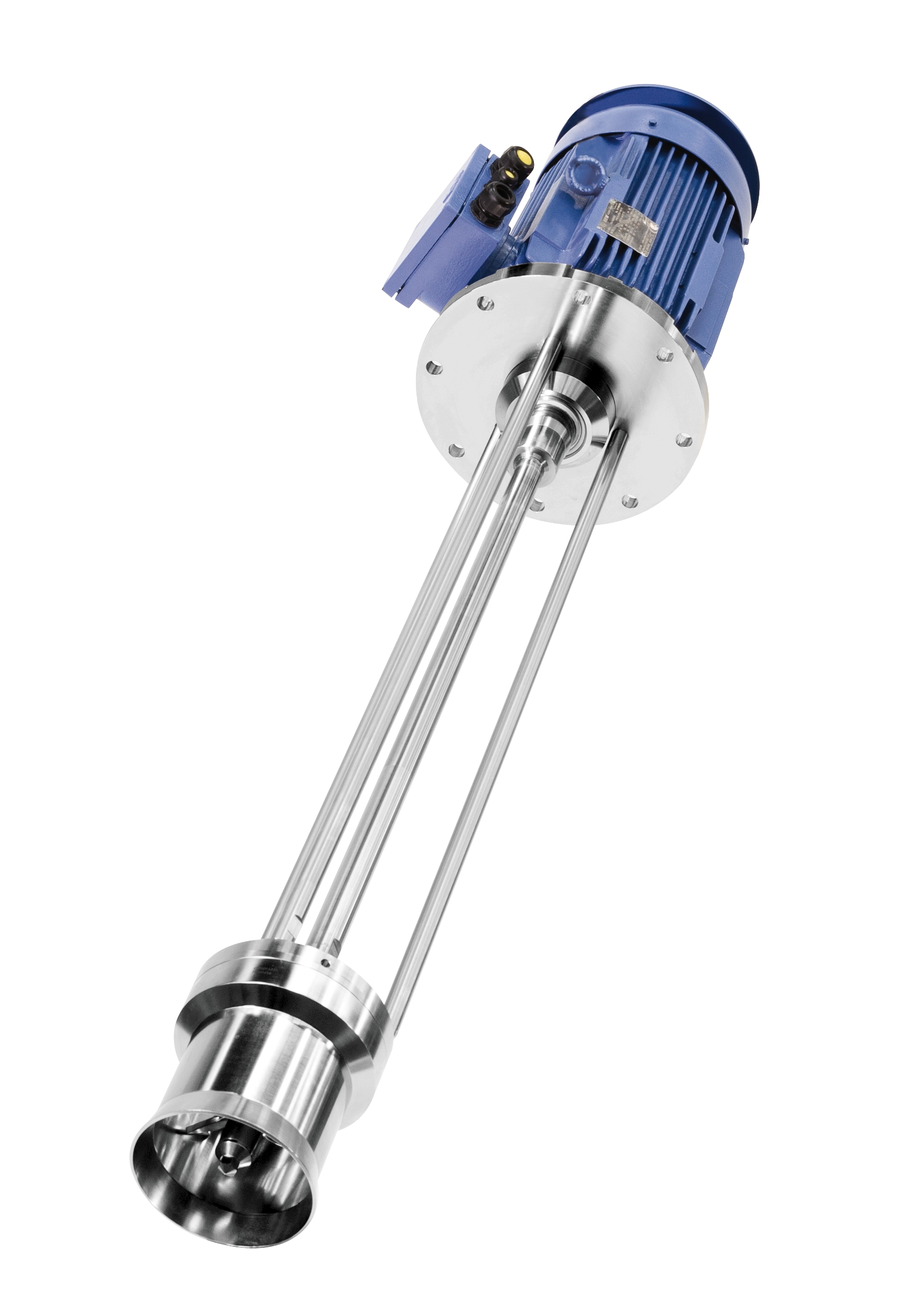

Jet flow agitator for high-viscosity media
Processes including homogenization, dispersing, suspension, emulsification and ...
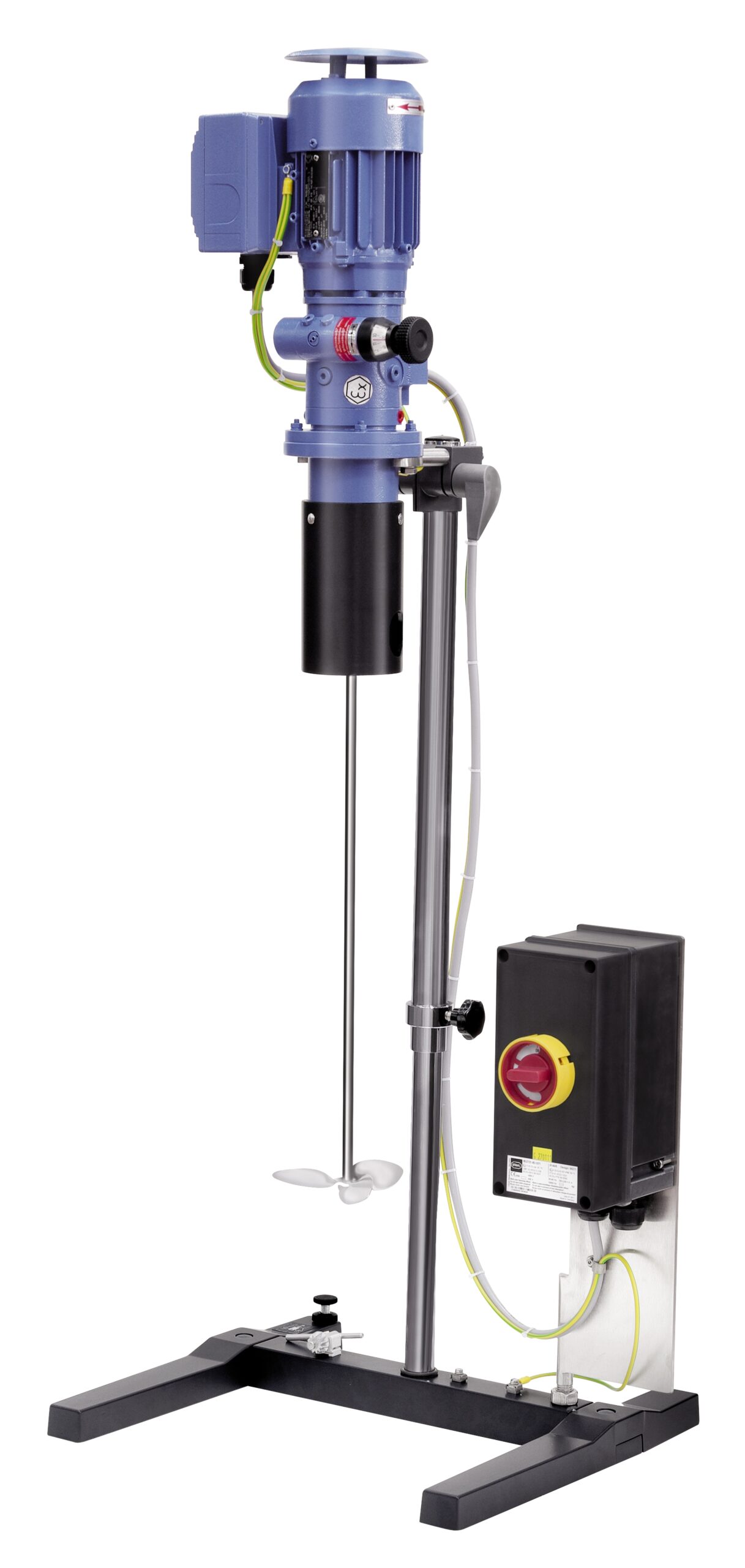

Agitator for medium viscosity media
Mixing fluids of medium viscosity for many production processes requires an agitator wi...
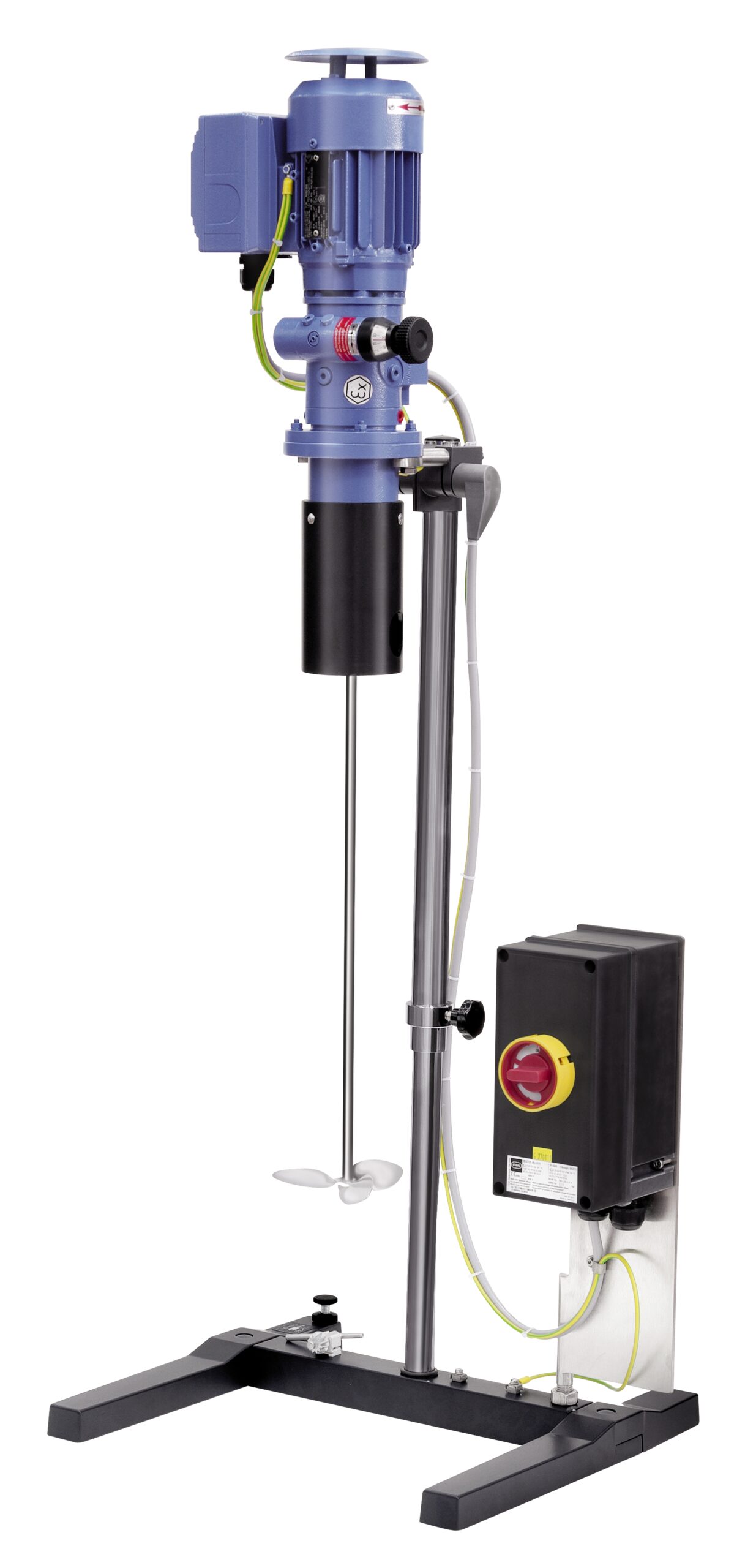

Agitator for low viscosity media
Reliably agitating fluids in open or pressure-less vessels in a laboratory or small scale p...
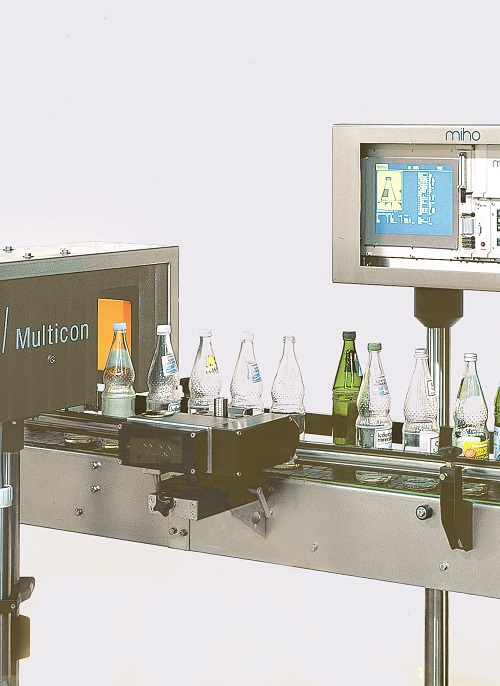

Empty bottle shape, colour and size sorting system
Accurate bottle sorting system that differentiates between the bottles...