Biogas Production Equipment
Find innovative production technology for making biogas and connect directly with world-leading specialists
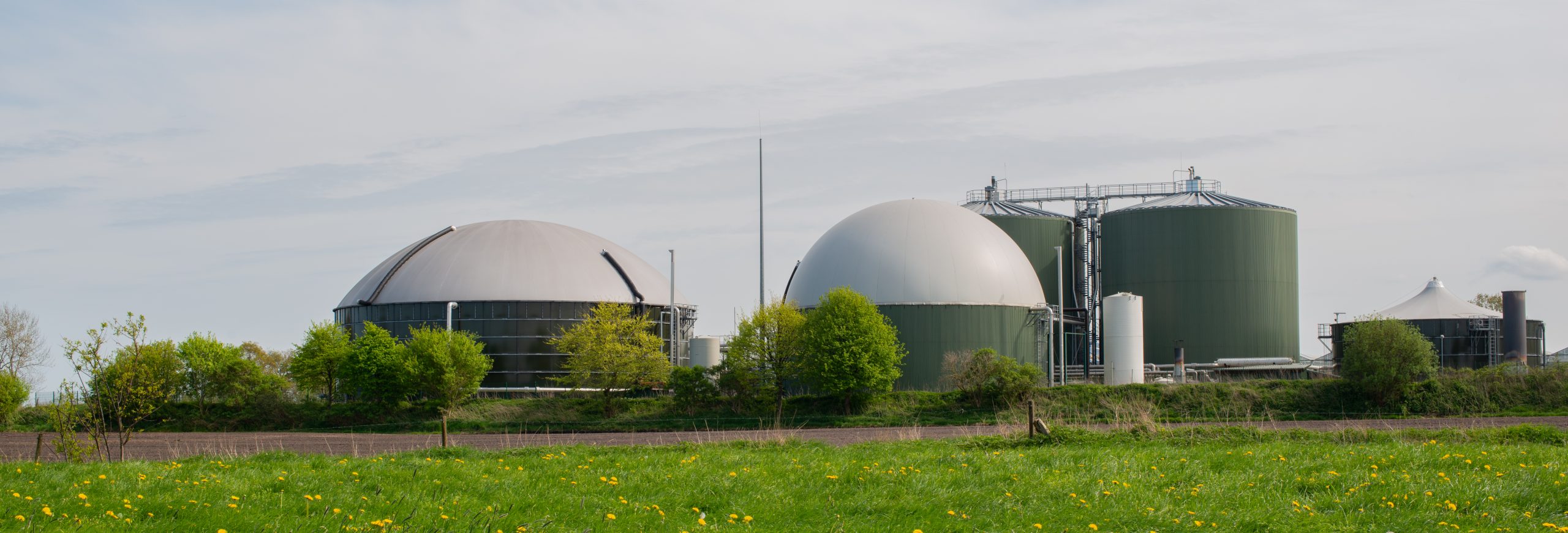
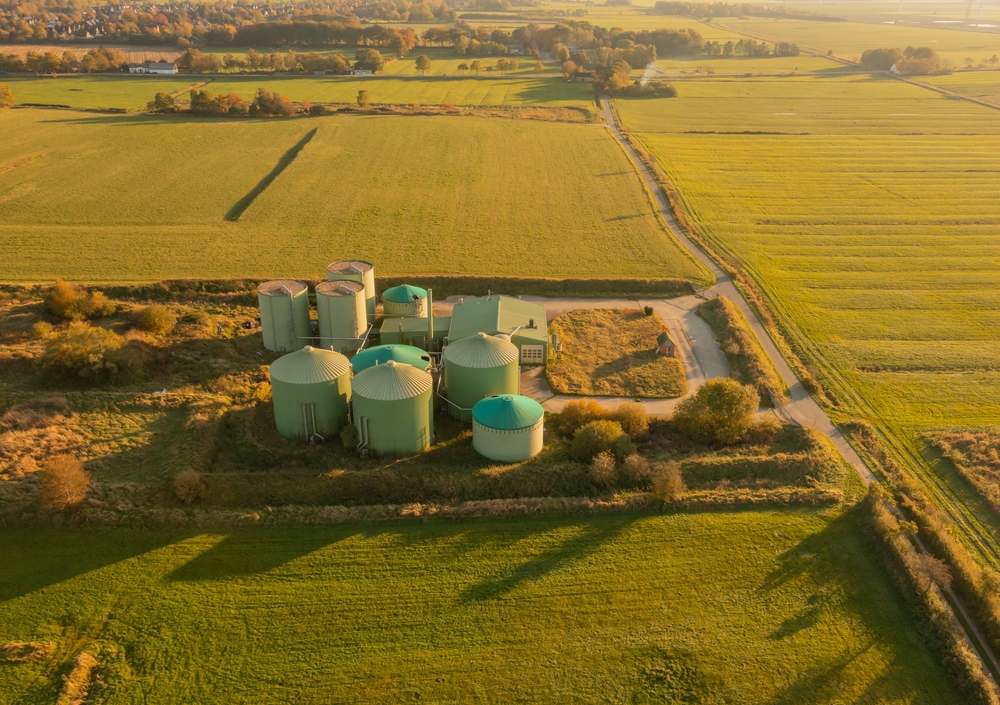
As an alternative to conventional fuels, biogas is produced from the processing of biomass resources as an industrial feedstock. Biogas is a renewable and local energy source that contributes to sustainable heat and power production. Besides making use of agricultural wastes such as crop and forest residues and animal manure, biogas production converts organic wastes from industrial and municipal waste to energy. This is usually achieved by implementing the anaerobic digestion process in biogas plants.
Technology picks for biogas processing
Tell us about your production challenge
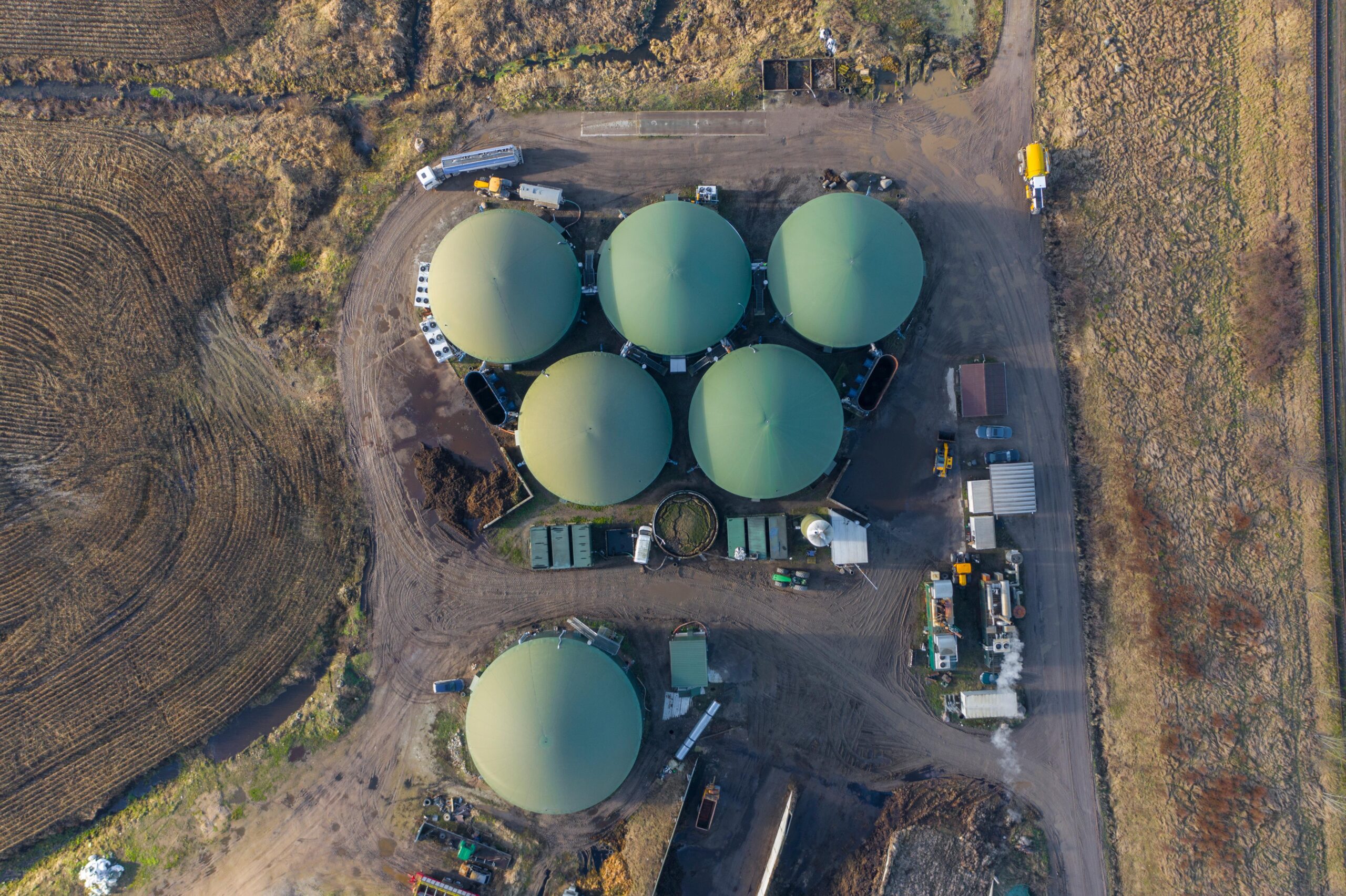

Anaerobic digestion is a process of decomposition of organic material in the absence of oxygen. During anaerobic fermentation of organic matter, the feedstock material breaks and degrades; in the meanwhile, different bacteria populations generate biogas. The produced biogas is in general a mixture of mostly methane, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and water vapor. The high concentration of methane in biogas indicates its potential to be injected into existing gas grids thanks to equipment for biogas purification and upgrading technology.
Upgrading biogas to biomethane
When biogas comes out from the digestion tanks, is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, air, hydrogen, Volatile Organic Components (VOCs), and siloxanes. Upgrading or purifying biogas means removing any CO2 and other contaminants present in biogas to produce biomethane.
In the membrane separation process, biogas produced in an anaerobic digestion plant enters the installation and is cooled and dehumidified. It is then transported to the active carbon filter system where it is purified by removing hydrogen sulfide and other contaminants. Once cleaned, the gas is compressed to the required pressure. The biogas flows to the membrane system in which methane is separated from carbon dioxide. The actual separation takes place because CO2 diffuses more easily than methane through the membrane straws, leading to separation.
Anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion is the process through which organic matter is broken down in an oxygen-free environment to create biogas. Therefore, biogas is created by food waste, wastewater, animal manure, and various other organic wastes and is used to generate electricity and to provide heat.
When organic waste arrives at the plant, it is pre-treated and mixed with liquid waste to create a slurry. Then, it is fed into the digestion tank where there is no oxygen. Bacteria within this slurry eat organic matter. As they eat and break down organic matter, they create biogas (methane, carbon dioxide, and other gases). Gas flows at the top of the tank and is captured to create electricity and heat. Methane can also be cleaned up and used as vehicle fuel. The remaining slurry can be collected to act as manure for plants.
Convert waste to energy
Biogas is considered a solution to biomass and sustainability. The basic form of biomass comes mainly from firewood, charcoal, and crop residues, which is commonly used in the combustion process of dry raw materials to generate heat and power. However, biogas production through anaerobic digestion reduces greenhouse gas emissions. And, it is widely used for the valorization of wet residues and liquid effluents, such as municipal wastes and sewage, and moist residues of agricultural crops and animal wastes. Biogas production technology allows for waste conversion of solids content into gaseous fuels. It is an environmentally friendly, renewable, clean biofuel. Biogas technology is also a source of nutrient-rich organic fertilizer.
Upgrading biogas to produce biomethane can help to fully utilize the potential of biogas as a vehicle fuel or as a substitute for natural gas. Therefore, it is important to improve the quality of the raw biogas to separate unwanted substances such as nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and water. Finally, by removing carbon dioxide in the biogas upgrading process, the energy content of the gas is increased, making it ready for grid injection. The removed carbon dioxide can be recovered and stored for other industrial use.
Biogas Production Videos
Wastewater treatment
Biogas upgrading
Processing steps involved in biogas making
Which biogas technology do you need?

Compressor combinations for high-pressure applications
Optimize your energy infrastructure with specialized compressor co...

Industrial piston compressors for various applications
Optimize your gas processing capabilities with versatile piston co...

Hollow fiber membranes for clarification in food and beverage industry
Optimize filtration and separation processes wit...

25kg automatic dry powder packaging system
Optimize your packaging line efficiency with precise, high-speed handling for 2...

25kg powder packaging system for sanitary applications
Achieve high accuracy and hygiene in powder packaging with a syste...

Bag break station for pneumatic conveying systems
Efficiently manage powder feeding and dust control in your production l...

Sanitary bulk bag filling system
Streamline your powder handling process with a system designed to improve stability and acc...
Bulk bag filler with integrated palletizing system
Optimize your powder packaging with a seamless system that fills and a...
Sanitary bulk bag unloader for powdered products
Efficiently manage powder discharge with enhanced dust control and stream...

Dense phase pressure conveying system for fragile powders
Ensure gentle handling and long-distance transport of fragile ...

Ultrapure water demineralizer for critical boilers
Achieve high-purity water production with minimal chemical usage and a...

Advanced hollow fiber membrane for wastewater treatment
Tackle high solid challenges in water treatment with robust ultra...

Mbr module for wastewater treatment
Optimize your wastewater management with efficient membrane bioreactors, designed to en...

Tall form bustle dryer for dairy and food products
Experience efficient drying and precise moisture control with this inn...

Milk product evaporator for high solids concentration
Efficiently concentrate milk products to high solids, optimizing pr...

High-concentration dairy evaporator
Achieve high solids concentrations with enhanced efficiency by integrating this evapora...

Gas contactor for hydrogen sulfide removal from biogas and sour gas
Efficiently convert harmful hydrogen sulfide into m...

Co2 recovery and liquefaction system for biogas upgrading
Maximize methane recovery while producing food-grade liquid CO...

Manure biogas plant for agricultural sector
Transform animal waste into renewable energy and nutrient-rich bio-fertilizer,...
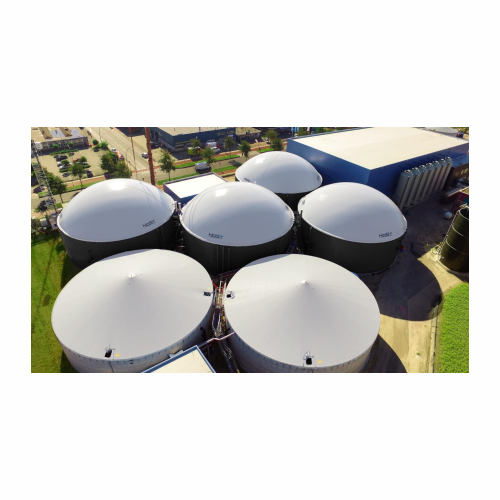

Organic waste biogas plant
Transform abundant organic waste into renewable energy and valuable byproducts with a high-effici...
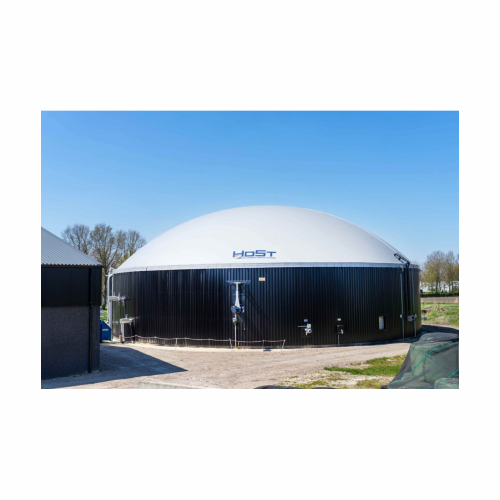

Organic residue and manure biogas plant
Transform organic waste into renewable energy while efficiently reducing carbon emi...
Biogas upgrader for high methane yield
Optimize biogas production by efficiently converting raw biogas into high-purity bio...
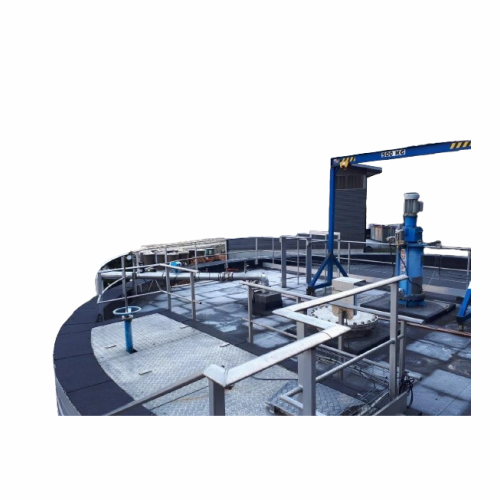

Agitator for biogas digesters in anaerobic digestion
Achieve efficient anaerobic digestion and optimal biogas recovery by...
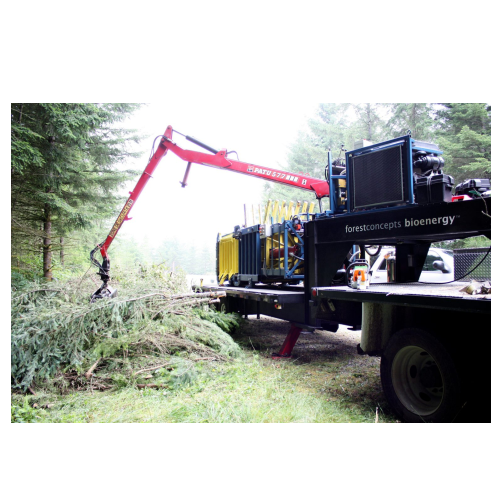

Biomass baler for woody biomass collection
Optimize woody biomass management with a mobile solution that reduces noise, du...

Industrial nozzle separator for high solids concentration
Optimize your production with high-performance nozzle separato...

Ultraclean aseptic storage tanks for hygienic liquid food
Ensure your liquid products remain uncontaminated and maintain...

Microalgae photobioreactors for bioenergy production
Optimize your microalgae’s growth and conversion processes wit...

Automated cleaning in place (cip) systems for beverage processing
Optimize your production with automated CIP systems t...
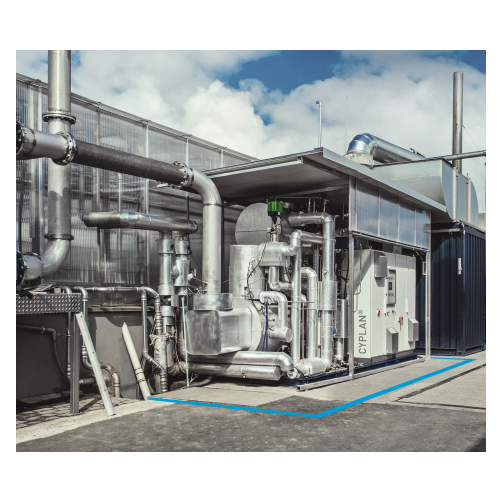

Organic rankine cycle for decentralized power generation
Harness waste heat and renewable energy sources to efficiently g...

Hydrogen sulphide adsorption filter for industrial applications
Efficiently capture and convert hydrogen sulphide emissi...
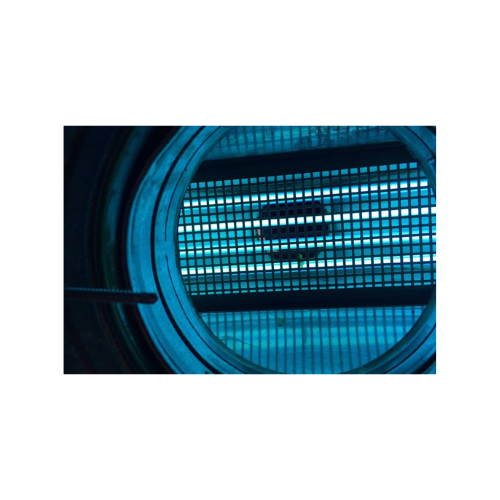

High intensity Uv reactor for industrial odor control
Achieve efficient odor elimination and VOC reduction with advanced ...
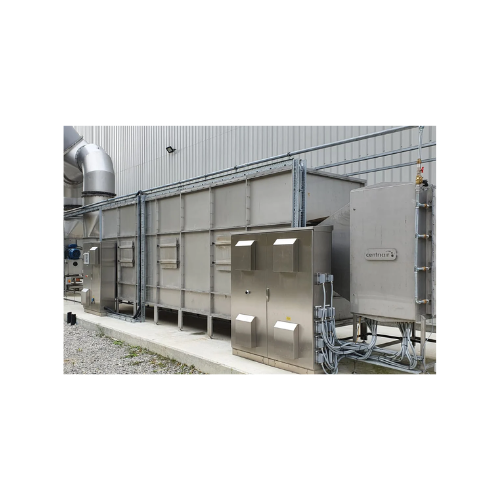

Industrial activated carbon filters for air purification
Optimize air quality control and odor management with versatile ...
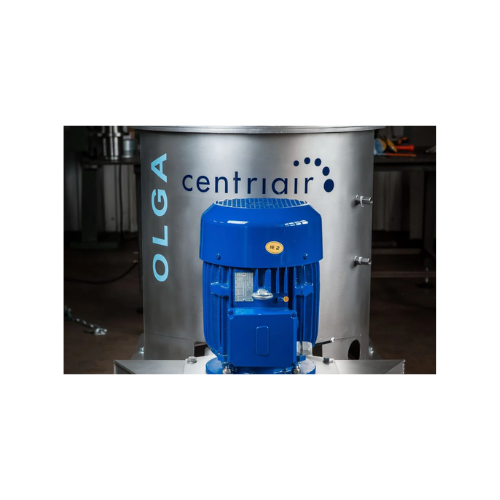

Centrifugal separator for food processing
Optimize your production line with high-speed disc stack centrifuges, designed t...
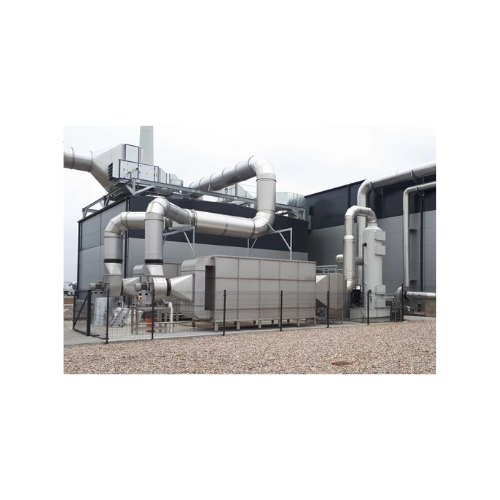

Industrial exhaust air treatment for food processing
Effectively eliminate volatile organic compounds and odors while max...
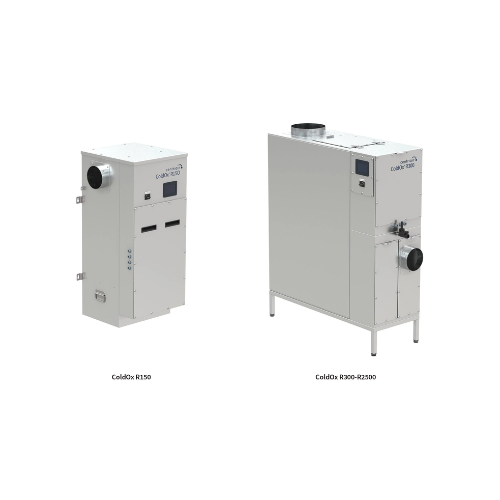

Uv reactor and activated carbon filter for odor reduction
Effectively mitigate VOC and odor emissions with a compact sys...
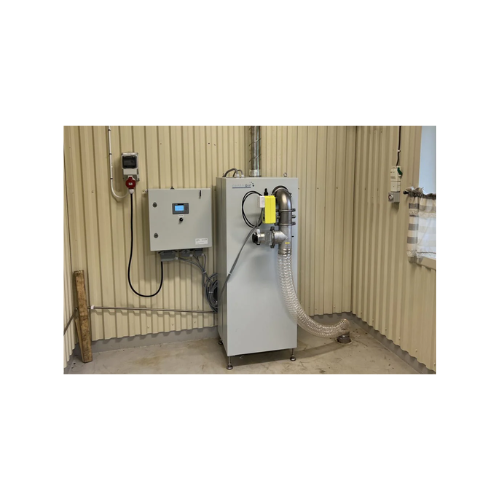

Catalytic system for industrial odour and Voc elimination
Tackle VOC and odour emissions with a versatile catalytic syst...

High intensity scrubber for particle separation and gas absorption
Effectively manage gas emissions and particle separa...

Synthesis gas cooler for partial oxidation of oil or natural gas
Optimize high-temperature gas streams efficiently by em...

Carbon capture membranes for Co2 separation
Efficiently reduce carbon emissions in power plants and industrial operations ...

Stirred reactors with heating and cooling system
Optimize your production line with versatile stirred reactors, designed t...

Biomass drying solution
Achieve efficient and gentle biomass drying with innovative heat exchange technology, ensuring optima...

Self-priming side channel pump for high gas content media
When handling media with high gas content, achieving efficient...

Mvr and Tvr heated distillation system
Achieve superior energy efficiency and reduced steam consumption in your distillatio...

Combined heating and cooling solution
Optimize your production with a dual-purpose system designed to efficiently manage bo...

Industrial chiller with high part-load efficiency
Optimize your cooling processes with a versatile chiller designed for p...

Natural gas compression system
Optimize gas compression and boost efficiency with advanced screw technology, designed for se...

Sludge decanter for industrial wastewater treatment
Efficiently reclaim valuable resources from wastewater and industrial...

Batch-type single shaft mixer for efficient discharging
Optimize your material mixing and discharging processes with a sy...

Compact wastewater pre-treatment plant
Optimize your wastewater treatment process with a compact solution that efficiently ...
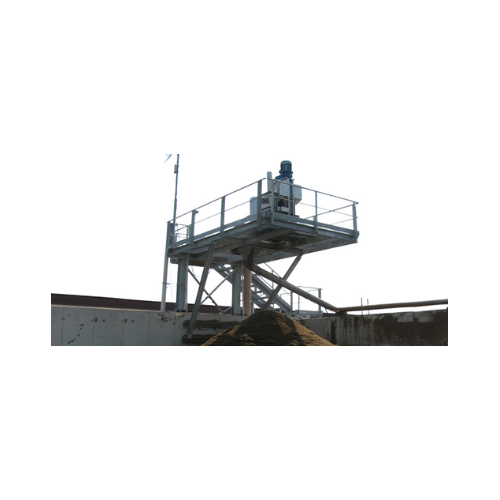

Manure treatment system for livestock breeding
Optimize waste-to-value processes with advanced systems designed to efficie...
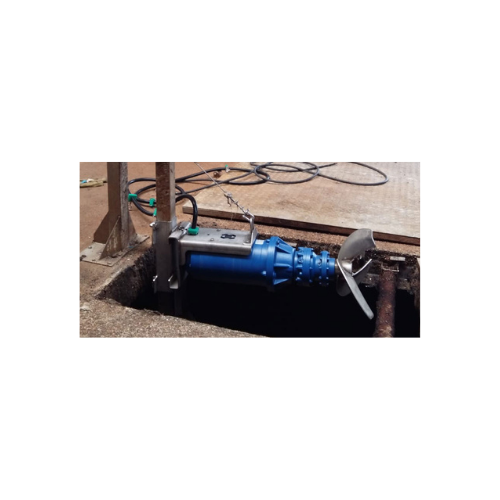

Biogas plant screw press separators
Maximize your renewable energy output and processing efficiency with cutting-edge solid...
Bulk solids conveying systems
Efficiently move and manage bulk materials with precision and reliability, ensuring seamless i...
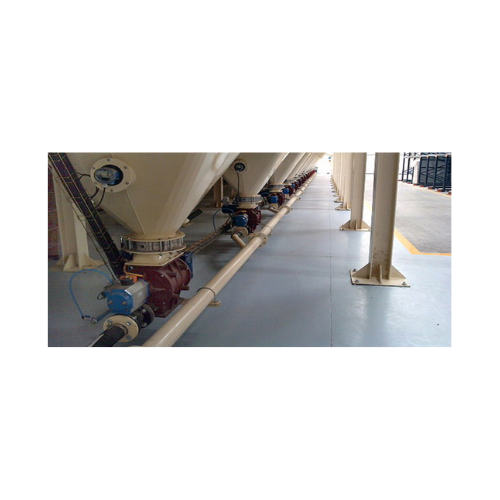

Pneumatic conveying system for bulk solids
Ensure efficient and dust-free transport of bulk materials with a pneumatic con...
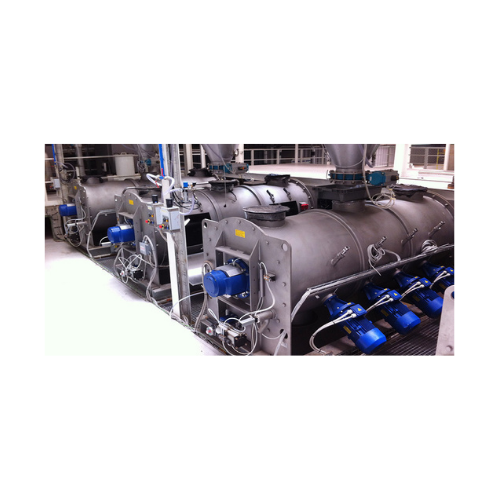

Batch-type single shaft mixer for industrial mixing
Achieve precise and uniform mixing with high-speed, single-shaft mixe...
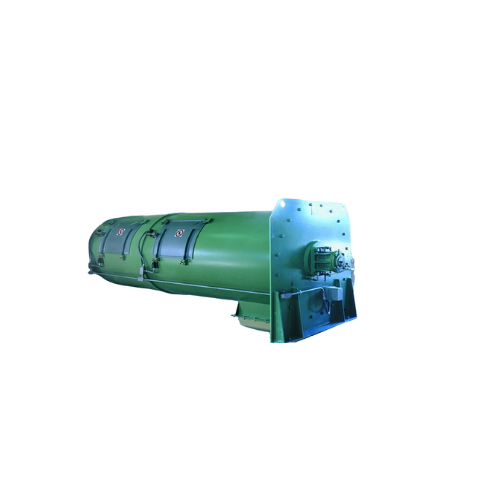

Continuous single shaft mixer for waste treatment
Achieve consistent mixing homogeneity and prevent dead spots in your pr...
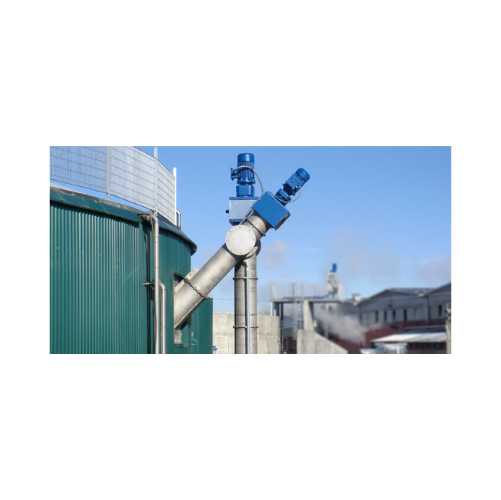

Biomass digester feeding system
Efficiently integrate biomass into your biogas production process with a system that seamles...
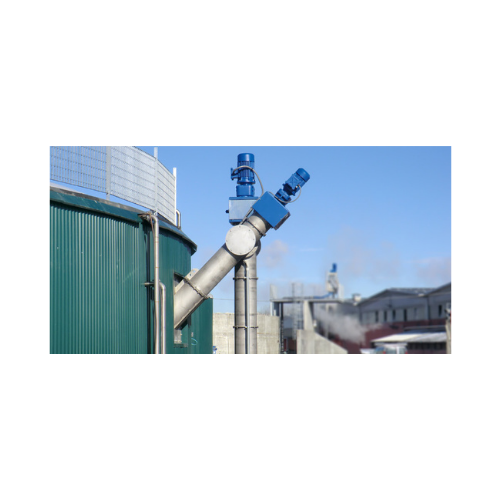

Bulk biomass digester feeding system
Optimize your biogas production with a versatile system designed for efficient biomass...
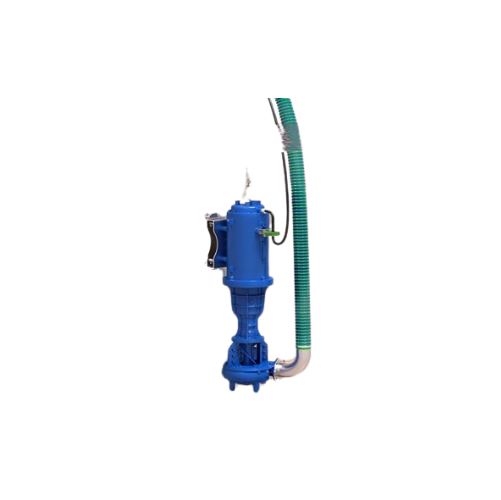

Submersible chopper pump for manure treatment
Efficiently handle slurry containing lumpy, fibrous solids with cutting-edge...
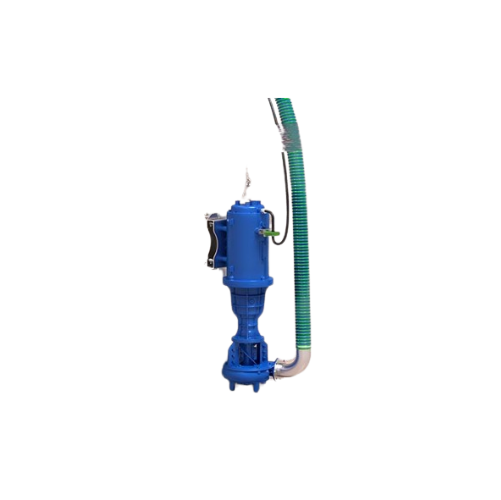

Submersible chopper pump for biogas plants
Optimize slurry management with a solution that efficiently shreds and pumps fi...
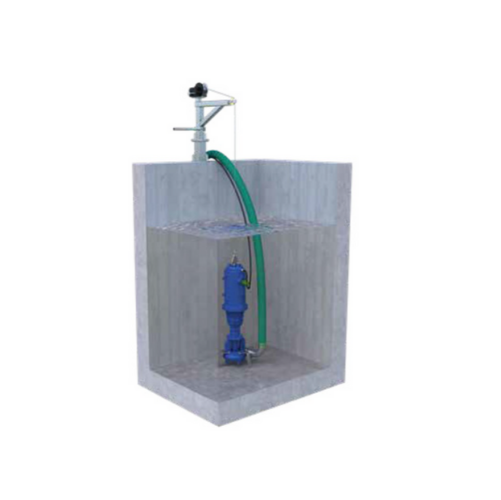

Heavy-duty submersible chopper pumps for manure treatment
Optimize your wastewater and manure handling with submersible ...
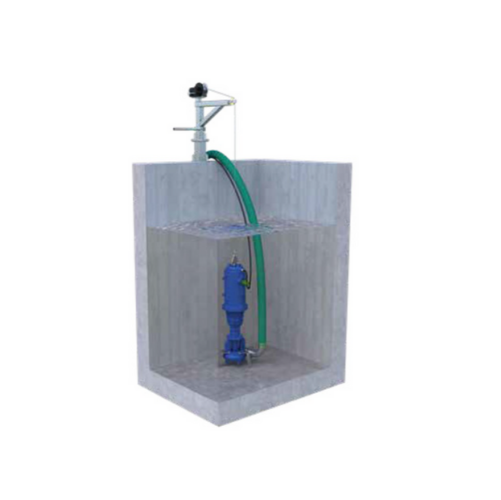

Heavy-duty submersible chopper pump for biogas plants
Effectively manage fibrous waste and prevent clogging in demanding ...

Horizontal screw press separator for biogas plants
Enhance biogas production efficiency by effectively separating high-mo...
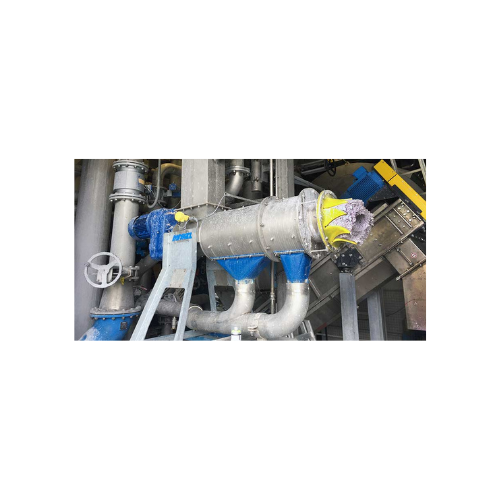

Pulp and paper horizontal screw press separator
Optimize your pulp recycling and manure treatment with high-efficiency sol...
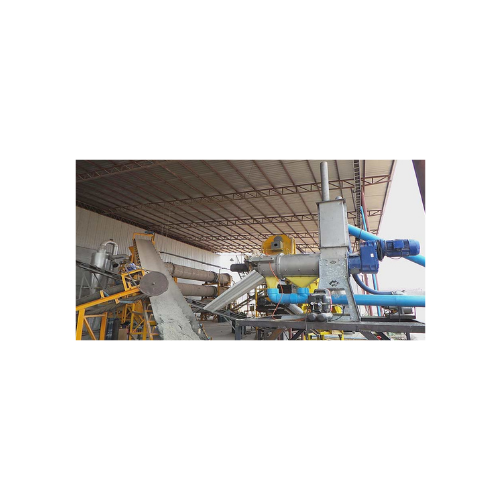

Tapioca horizontal screw press separator for biogas plants
Achieve high-efficiency separation and compaction of diverse ...
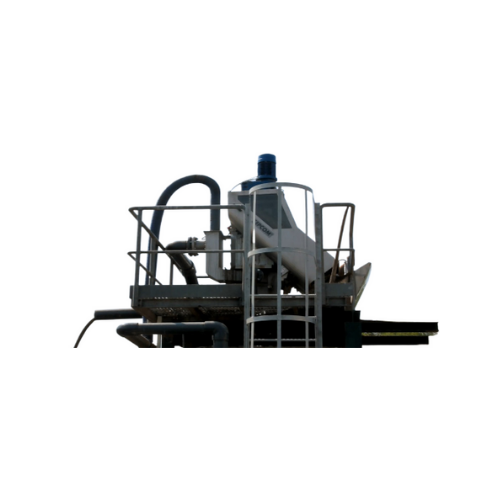

Vertical screw separator for slurries
Efficiently separate solids from liquids in diverse slurry applications, ensuring opt...
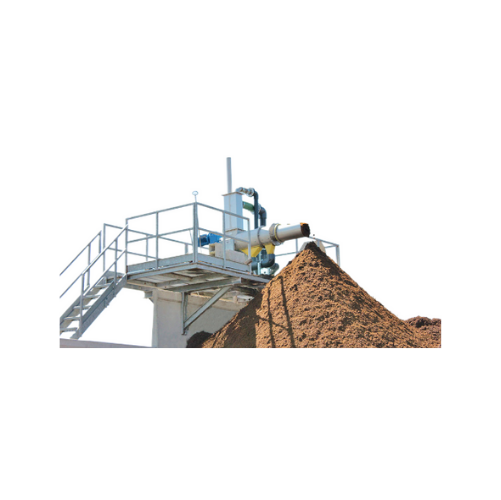

Biogas digestate screw press separator
Achieve efficient solids-liquid separation in biogas and wastewater treatment proces...
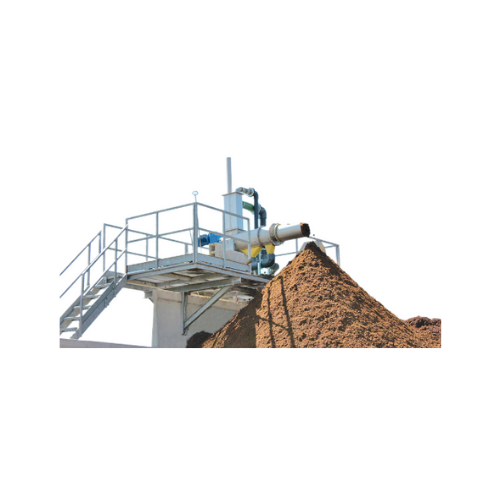

Horizontal screw press separator for biogas digestate treatment
Optimize your biogas plant’s efficiency by effecti...
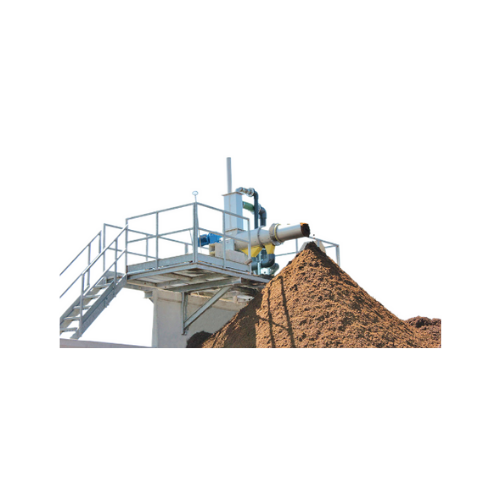

Screw press separator for biogas digestate treatment
Optimize your biogas plant’s efficiency with a robust solution...
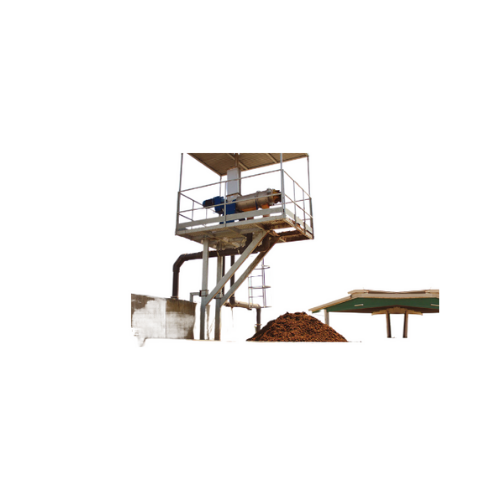

Horizontal screw press separator for sludge and manure
Achieve high-efficiency separation of solids and liquids from dive...

Horizontal screw press separator for manure treatment
Enhance your separation processes with advanced screw press technol...
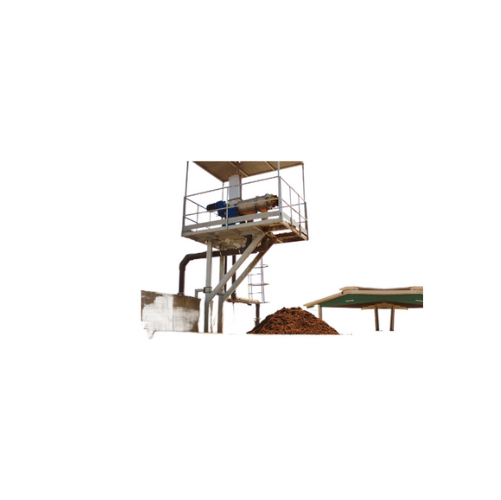

Horizontal screw press separators for biogas plants
Achieve efficient solids-liquid separation with continuous operation,...
Manure treatment micro-filter for slurries
Enhance water reuse and nutrient recovery by transforming slurry into micro-scr...

Horizontal screw press separator for pomace yield optimization
Enhance your production line by efficiently separating so...
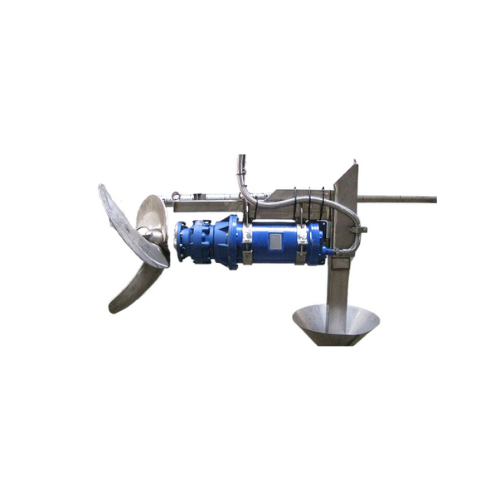

Submersible agitators for manure and wastewater treatment
Optimize mixing efficiency in manure and wastewater treatment ...

Cow bedding screw press separator
Efficiently transform cow manure into valuable green bedding with this advanced screw pr...

Air cannons for resolving bulk material flow issues
Solve bridging and rat-holing issues in bulk material storage with po...
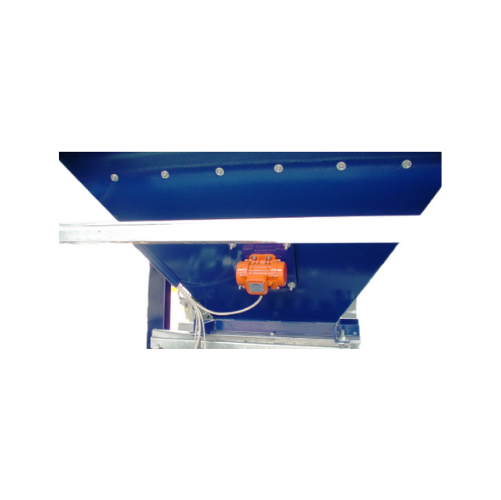

External electric motovibrators for industrial applications
Optimize material movement and improve discharge efficiency ...
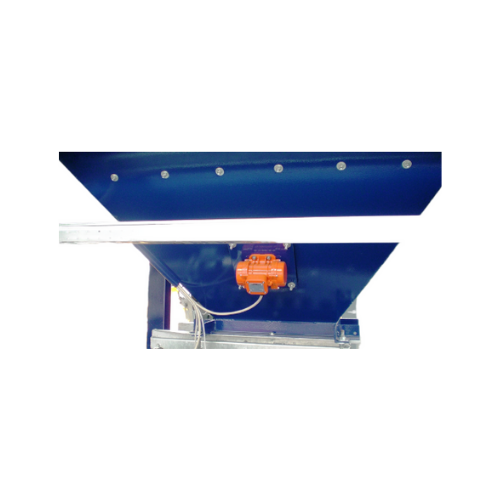

External electric motovibrators for bulk solids conveying
Enhance material flow efficiency and solve challenging dischar...
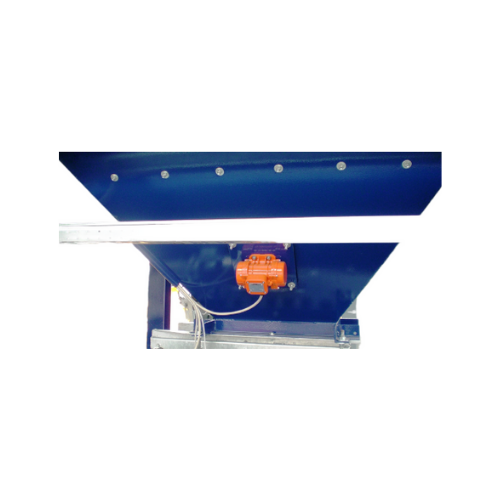

Industrial electric vibrator for bulk solids discharging
Enhance material flow efficiency and ensure consistent output ac...
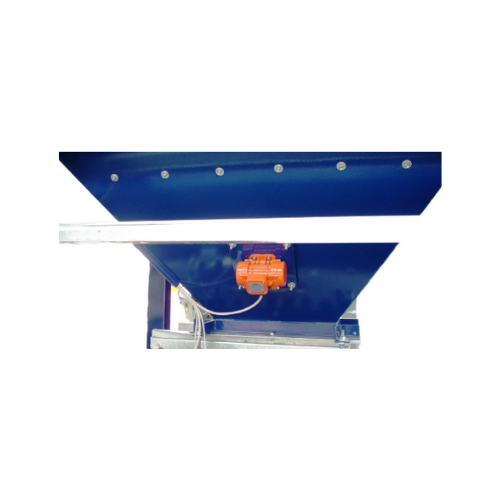

External electric motovibrators for industrial material flow
Experience enhanced material flow and precise material disc...

External electric motovibrator for increased safety in hazardous environments
Designed for environments with explosive...

External electric motovibrators for hazardous materials
Ensure safety and efficiency in hazardous environments with relia...

Bar screens for wastewater treatment
Efficiently remove coarse debris from wastewater streams with high-capacity sub-vertic...

Electric gear motor actuators for slide valves
Achieve precise control over industrial slide valves in high-speed operatio...

Hand wheel actuators for Vg slide valves
Effortlessly control flow interception in high-demand settings with these hand whe...

Wet spent grains pre-dewatering system
Optimize your brewery operations with a dewatering system that efficiently reduces m...
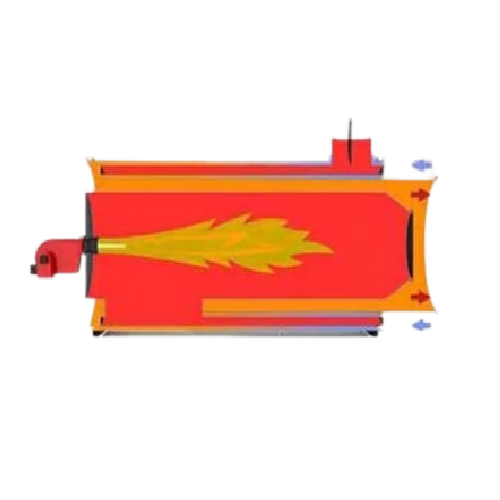

Industrial air heater for agriculture and industry
Optimize energy efficiency and maintain high air quality in your produ...

Hybrid dryer for agriculture and industrial applications
Achieve efficient moisture reduction in varied materials, from f...
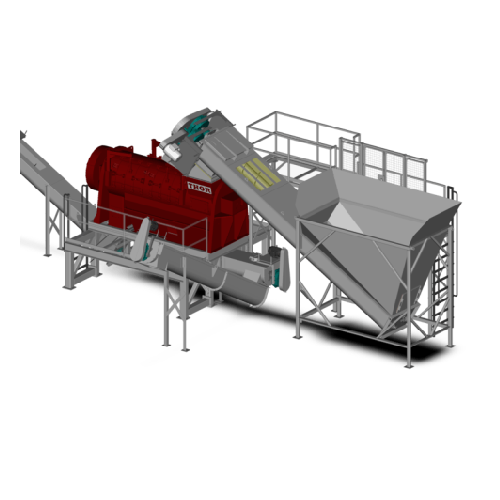
Organic material extraction for recycling
Achieve high-efficiency organic material separation for versatile end products l...

Exergy pressurized superheated steam dryer
Traditional dryers and heat transfer systems, like belt-, drum- or bed dryers a...
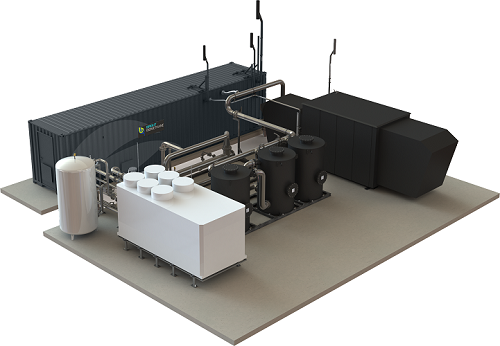
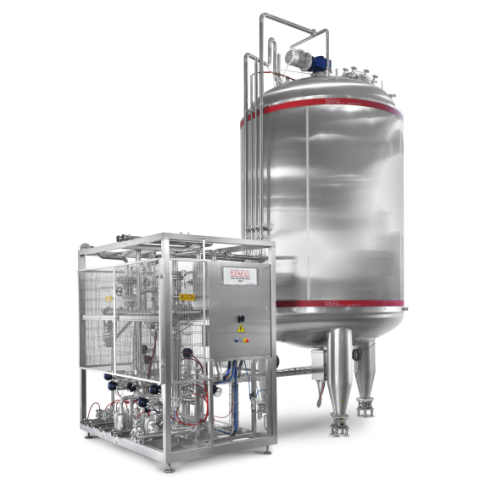
Efficient sized biomethane production system
Also referred to as biogas purification, biogas upgrading is an excellent alt...

Large-scale biomethane production system
Membrane separation technology for biogas purification is considered as an effecti...

Modular biogas to biomethane system
The primary purpose of biogas upgrading technology is to increase the volumetric energy...

Small-scale biogas upgrading system
Biogas upgrading refers to the process of purifying biogas through separating methane f...
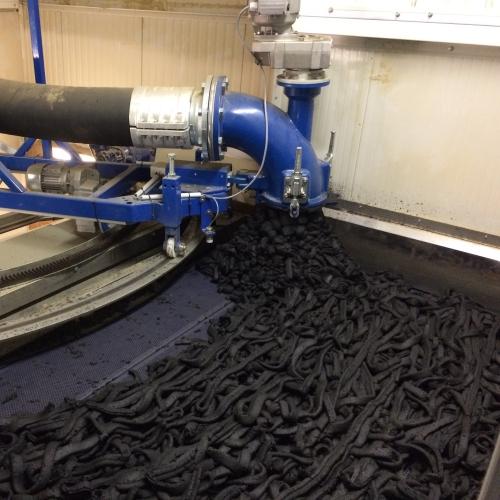

Belt dryer for sewage sludge
If your water treatment plant often facing difficulties with sewage sludge deposits, drying the...
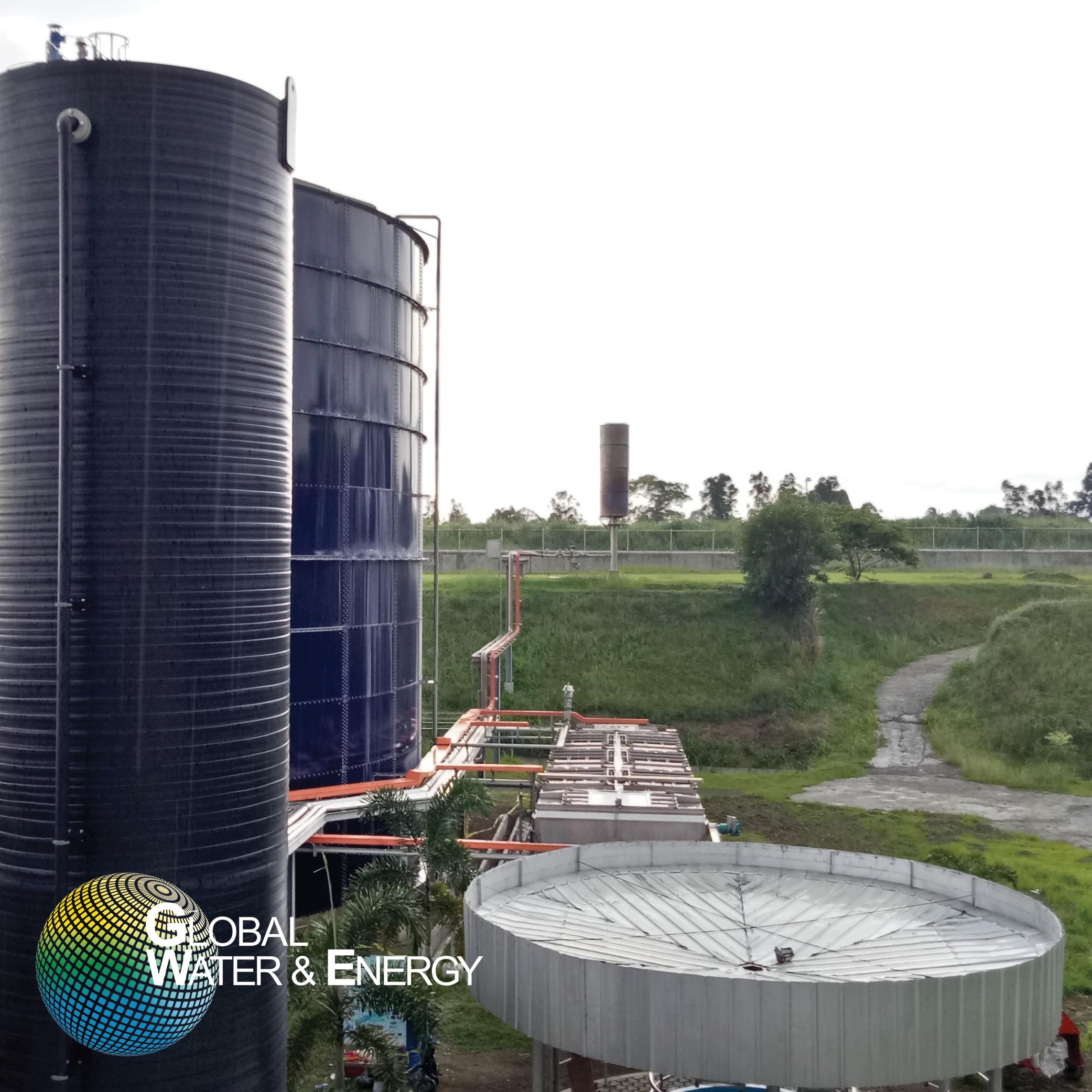

Advanced anaerobic digestion with external separation
Factories of dairy products, palm and coconut oil, slaughterhouses,...
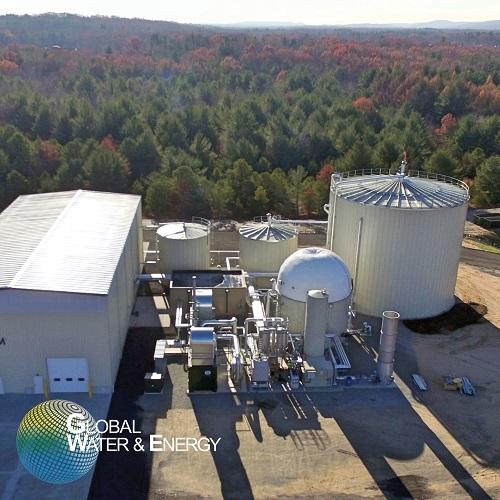

Waste to energy anaerobic digestion system
The food industry produces tremendous amounts of waste at food production facil...
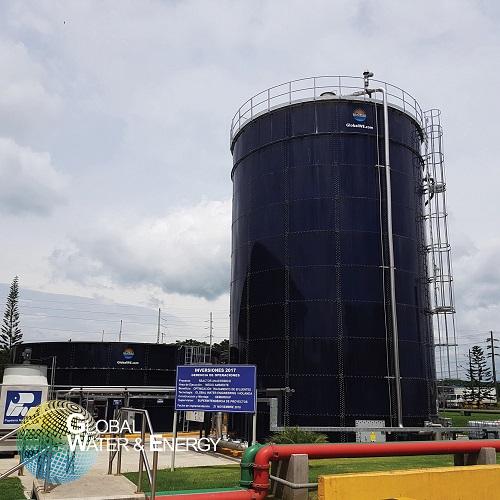

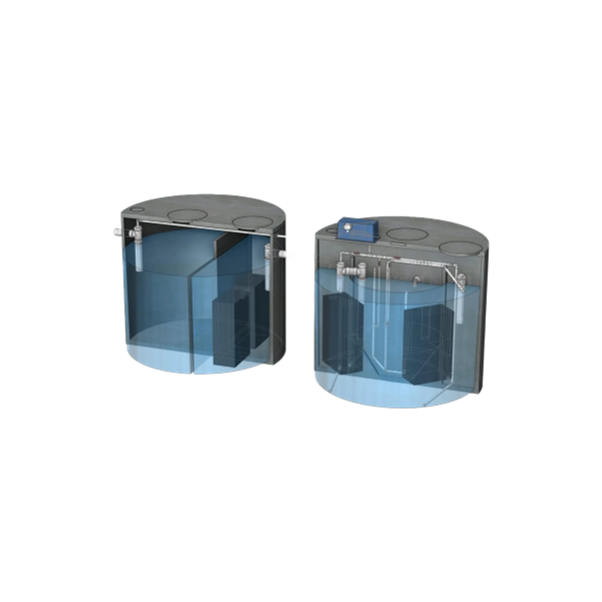
Anaerobic EGSB wastewater treatment
If you are looking for a compact and sustainable solution to remove organic pollution f...
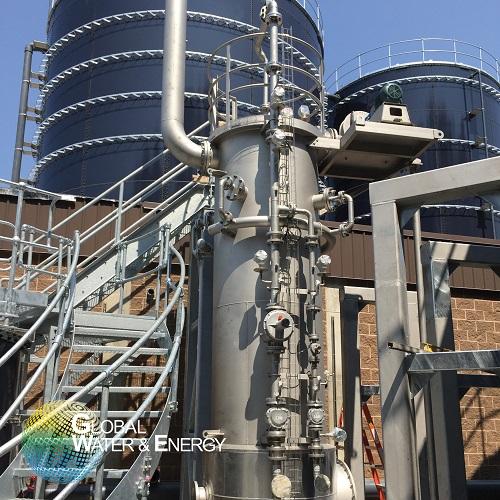

Biogas heating system
Traditionally, heating of wastewater would use boilers and heat exchangers. Biogas is a natural by-prod...
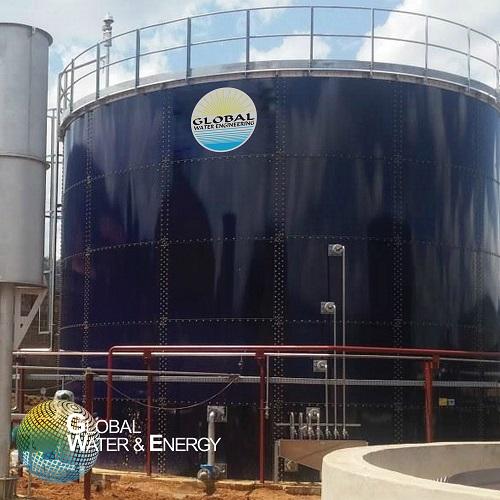

Anaerobic UASB wastewater treatment
If you need to remove organic compounds from your wastewater, the up-flow anaerobic slu...
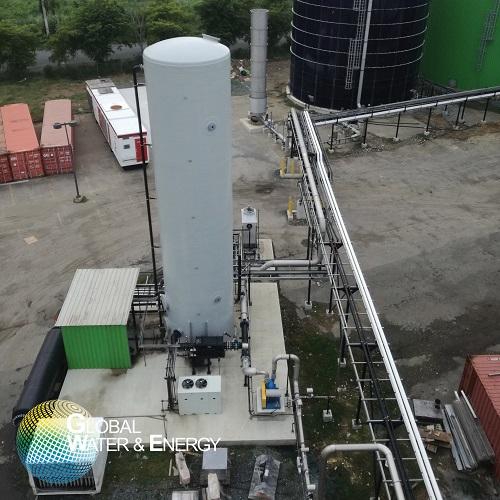

Biological H2S scrubber
Raw biogas produced by digestion, for example during an anaerobic process is approximately 60% methan...
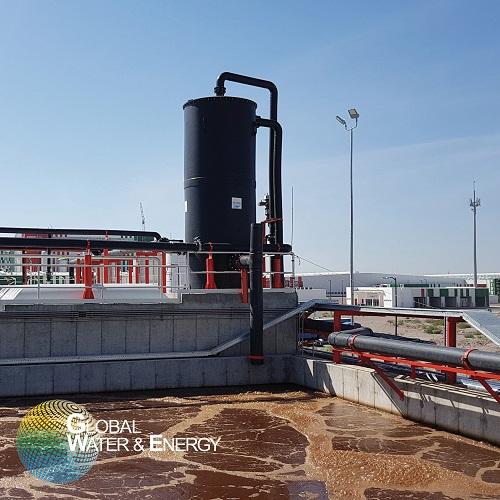

H2S scrubber for biogas
Raw biogas produced by digestion, for example during an anaerobic process is approximately 60% methan...