Making Chocolate Spread
Find innovative production technology for making chocolate spread and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Consumers usually eat chocolate spreads along with bread, or other grain-based items, such as pancakes, biscuits, waffles, and others. Although one particular brand has dominated this market for more than 50 years, there is still a place for new, health-friendly innovations and production ideas using chocolate spread machines.
Technology picks for producing chocolate spread

Automatic chocolate processing line
Transform your production by automating the complete chocolate-making process—from prec...

Filling machine for viscous products
Chocolate paste and other viscous liquids require special handling to obtain the optim...

Industrial spreading systems for sticky products
Effortlessly manage the spread of sticky confectionery products with prec...

Chocolate and spreadable cream dispenser
Effortlessly enhance your confection creations with a dispenser that precisely mel...
Tell us about your production challenge

Major production steps and utilization of chocolate spread machines
To produce a high-quality chocolate spread, start with the base chocolate. It is where you incorporate a pasty mass of cocoa and sugar. Specifically, the sugar grounds need to be 100 microns in terms of particle size. As you add more ingredients to the chocolate spread machine, cylinders refine the particle size further to 10-20 microns. Then, it is time to mix it with cocoa butter. Conching is also a critical process for a great chocolate consistency. It does this by gradually applying frictional heat, promoting fluidification or dispersion of sugar and cocoa particles in its fatty phase. In turn, it also releases organic compounds and volatile gasses in a process called degassing. This enables the consistency of a fluid pasty mass that can be easily molded.
Sugar substitutes and other sweetener alternatives
Sugar is a sweetening agent, as well as the responsible for the consistency and texture of the chocolate spread. In most commercial spreads, sugar has a big impact due to market, cultural, or expense purposes. As an additive, you can replace it with alternatives such as xylitol, erythritol, D-psicose/psicose, and other low-calorie sweeteners. These sweeteners are organic and a healthier choice than refined sugar. Since sweetness is subjective, the base chocolate is still a key part of the spread – whether or not you use a natural sweetener – as it will balance out all the flavors.

Demand for vegan-friendly chocolate spreads
Vegan chocolate spreads are also possible with the right ingredients and additives. Due to intolerances to lactose and other milk components, or for environmental reasons, consumers nowadays are finding alternatives to milk-based chocolates. Milk replacers such as rice milk, soy milk, and lupine milk all have the potential in replacing animal milk. In terms of fat, hazelnut, almond, and coconut fat are all feasible choices to replace milk fat. The chocolate paste-making process is still similar to the original process, with the aid of chocolate paste machines or a chocolate spread making machine.

Food standards for chocolate spreads
The FDA imposes regulations on chocolate spreads based on milk chocolate; it must contain not less than 12% by weight of nonfat milk, exclusive of any sweetener or other dairy-derived ingredient. It must also have safe and suitable vegetable-derived oils and fats, other than cacao fat. On the other hand, the EU legislation on cocoa and chocolate products allows for the use of six tropical vegetable fats, to a maximum of 5% of the chocolate component of the finished product. Both governing bodies pay close attention to appropriate labeling of fat content – you must mention fats other than cocoa butter.
Processing steps involved in chocolate spread making
Which chocolate spread technology do you need?
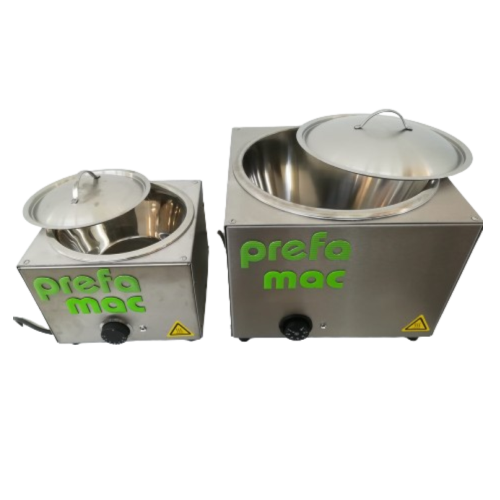

Chocolate melting trays for small-scale applications
Efficiently melt chocolate with precision and ease using compact, el...
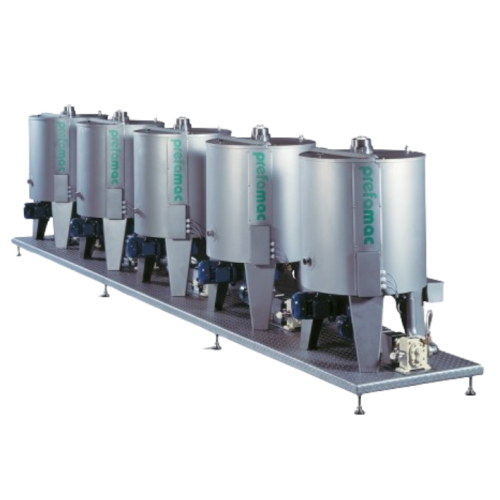

Melting and mixing kettles for chocolate production
Achieve consistent melting and mixing of chocolates, butter, and jams...
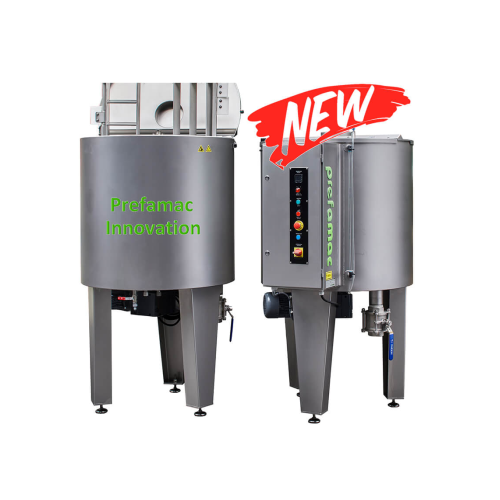

Melting and mixing kettle for chocolate production
Optimize your confectionery production with this versatile melting and...
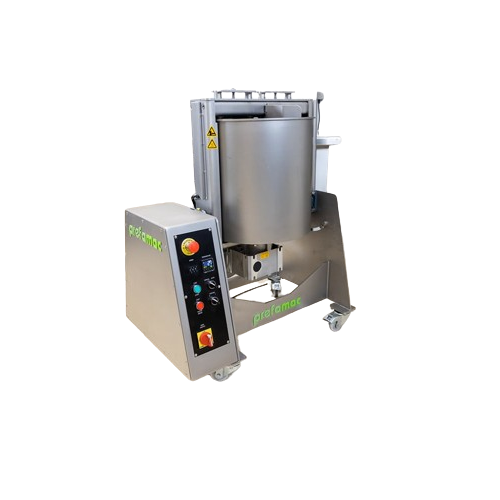

Precision chocolate production from cocoa nibs
Achieve ultra-fine chocolate textures by utilizing stone conching to bring ...
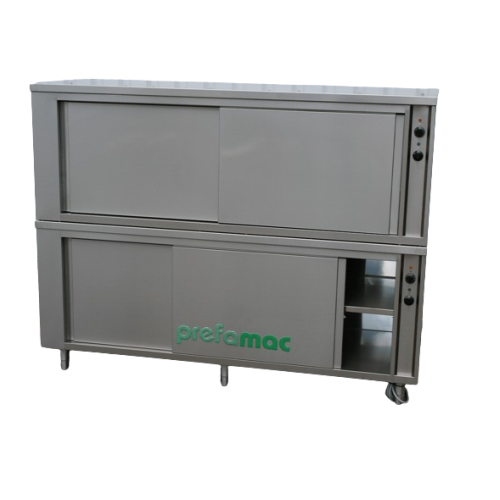

Double heating cabinet for melting and preheating chocolate
Optimize space while ensuring precise temperature control fo...
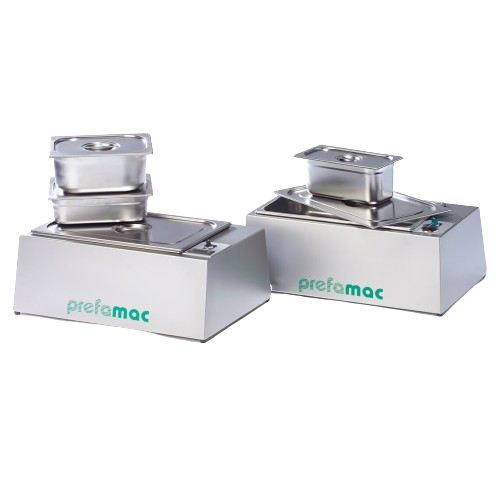

Electric melting tray for small-scale chocolate applications
Effortlessly melt and prepare chocolate with precision and ...
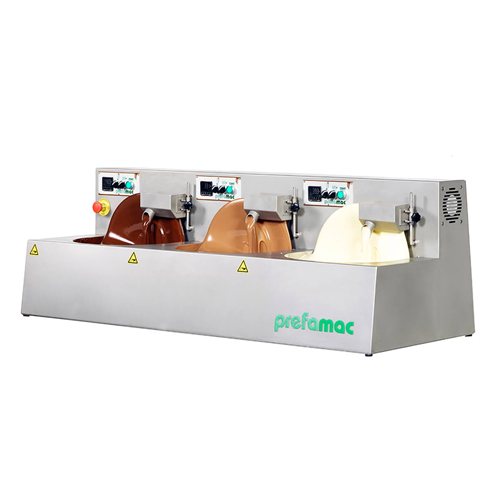

Compact chocolate moulding solution 3-in-1
Streamline your confectionery creations with a versatile 3-in-1 machine that se...
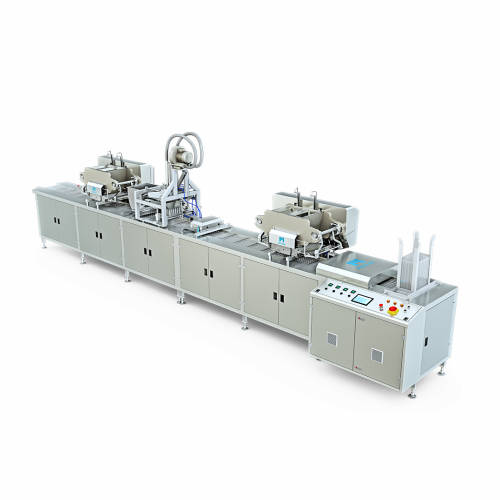

Chocolate moulding line for center-filled chocolates
Streamline your chocolate production with a versatile moulding line ...
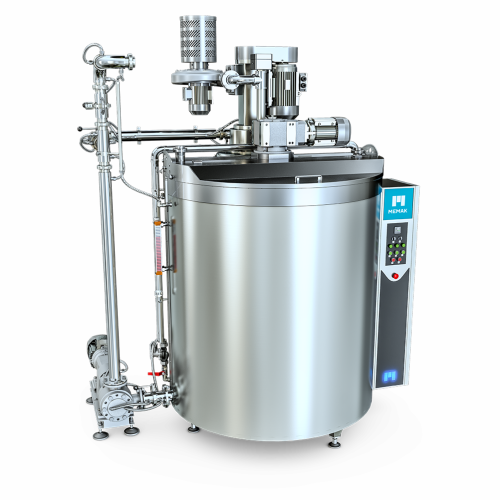

Conching solution for chocolate processing
Achieve optimal chocolate texture and flavor by ensuring efficient conching, cr...
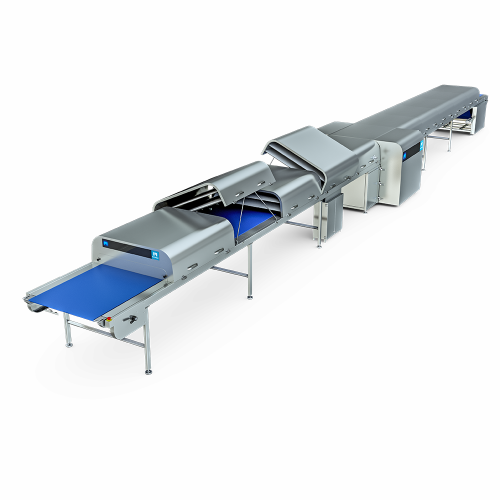

Chocolate cooling tunnel
Enhance your confectionery production with efficient cooling and precise crystallization, critical f...
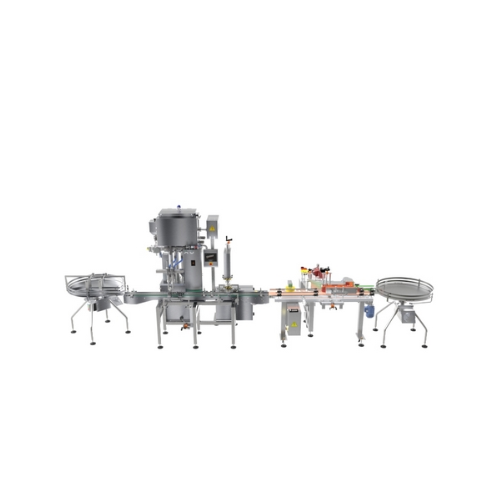

Medium capacity filling line for food and cosmetics
Streamline your production with a versatile filling line that seamles...
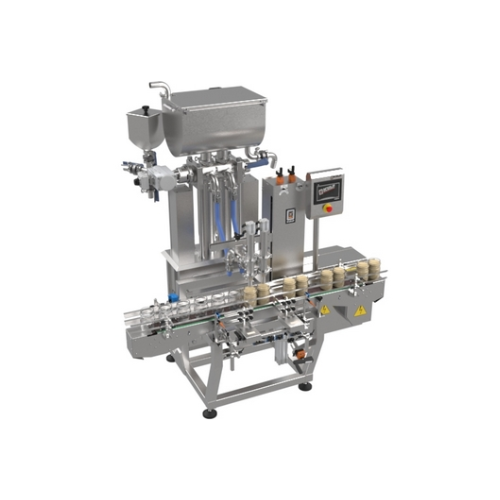

2-head liquid and viscous product filling system
Streamline your filling operations with precision and versatility designe...
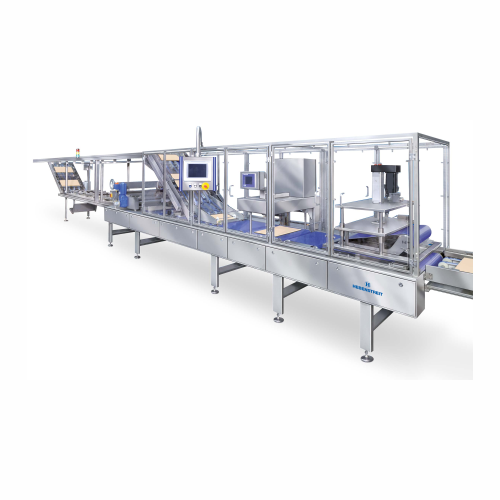

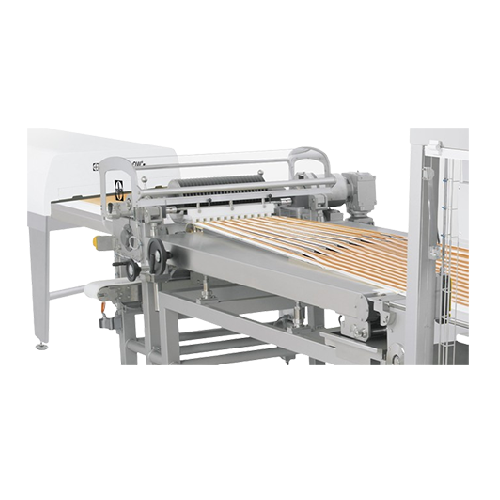
Wafer sheet cream application system
Achieve precision in cream application with high-capacity, continuous film spreading, ...
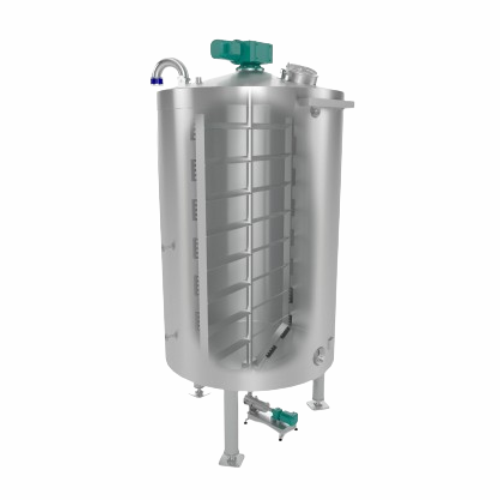

Stainless steel chocolate tank for storage and processing
Efficiently control temperature and consistency for chocolate ...
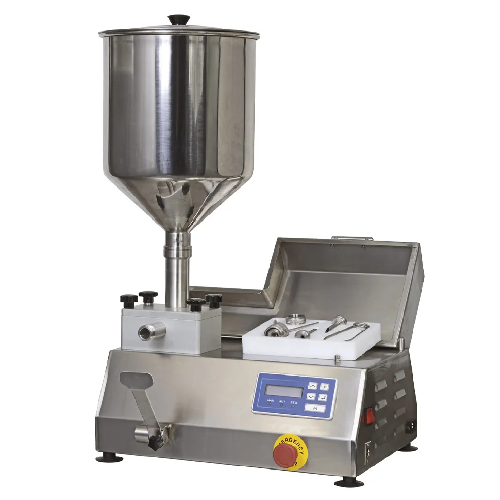

Gear or piston filling-dosing equipment for creamy and thick foods
Efficiently dose and fill dense and creamy products ...
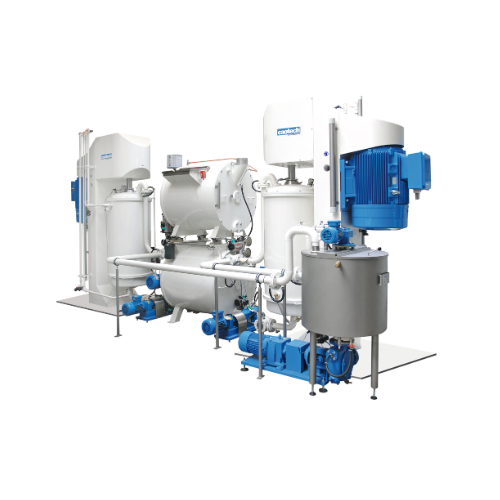

Fully automatic chocolate processing line
Accelerate your chocolate and confectionery production with this high-speed syst...
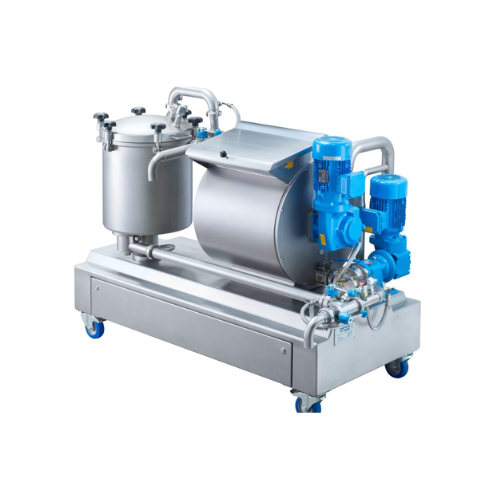

Laboratory batch chocolate processing unit
Achieve precision in developing chocolate recipes with a compact 3-in-1 unit th...
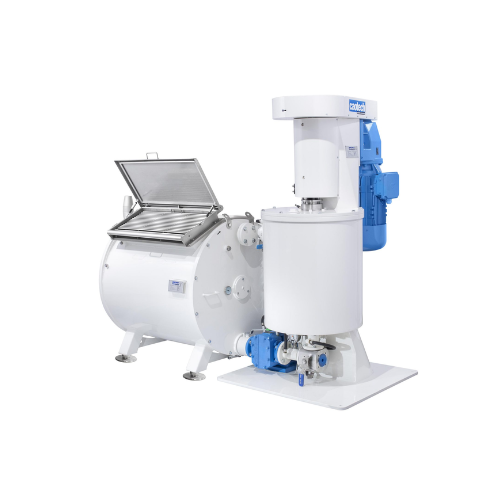

Chocolate processing unit for mixing and grinding
Achieve precise mixing and conching efficiency for premium chocolate an...

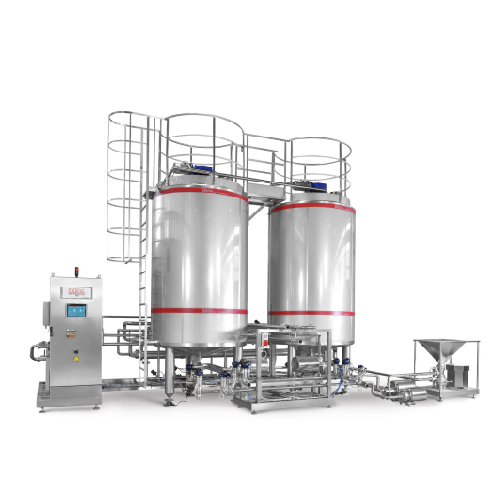
Automatic chocolate processing line
Transform your production by automating the complete chocolate-making process—from prec...
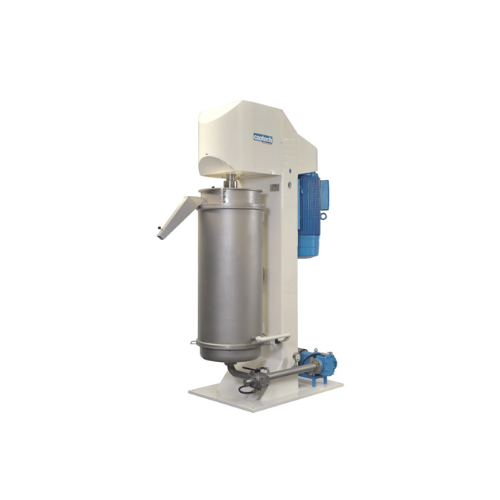

Ball mill refiner for cocoa liquor and chocolate production
Optimize your cocoa and chocolate refinement with precise gr...
Chocolate processing production line
Efficiently streamline your chocolate and compound production with a fully automatic s...
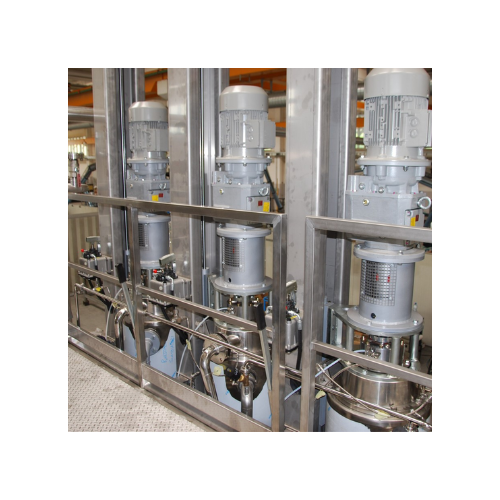

Scraped surface sterilizer for high viscosity liquid products
Optimize your production of high viscosity liquids with a ...
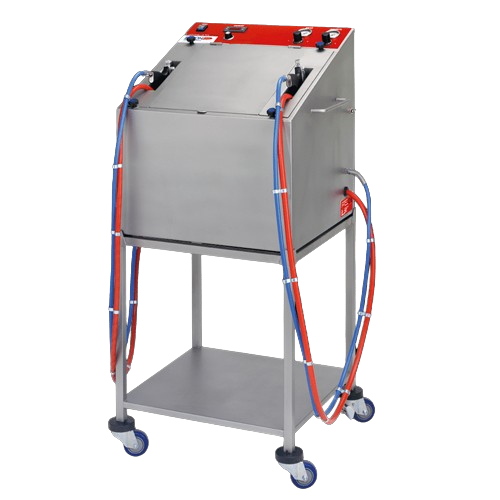

Chocolate spraying system for bakery decoration
Achieve precision chocolate coatings and intricate dessert decorations eff...
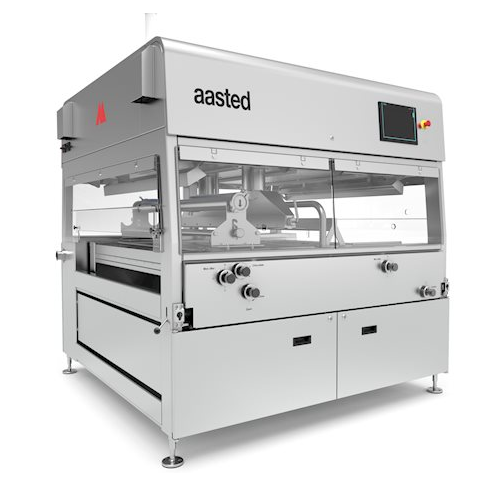

Chocolate enrober for large scale production
Efficiently enrobe a wide range of products, from chocolate bars to delicate ...
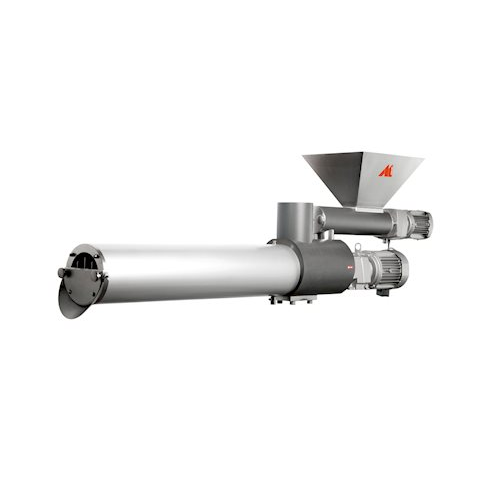

Auxiliary feeder mixer for chocolate production
Optimize ingredient incorporation seamlessly with a versatile system that ...
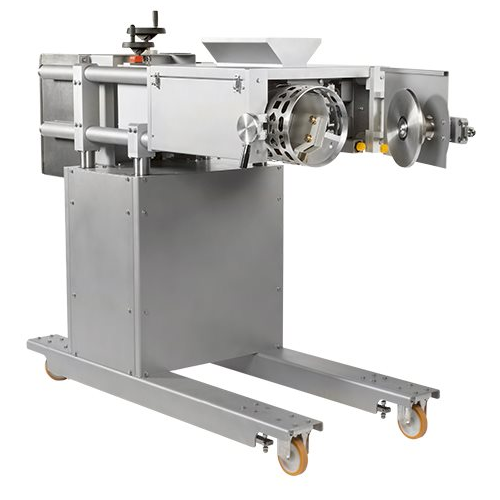

Rotating stencil depositor for confectionery products
Streamline your confectionery operations by precisely depositing in...
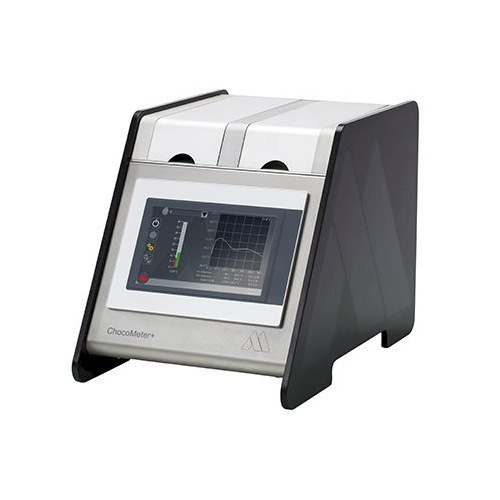

Accurate chocolate tempering measurement tool
Ensure precise chocolate tempering with real-time accuracy, enhancing qualit...
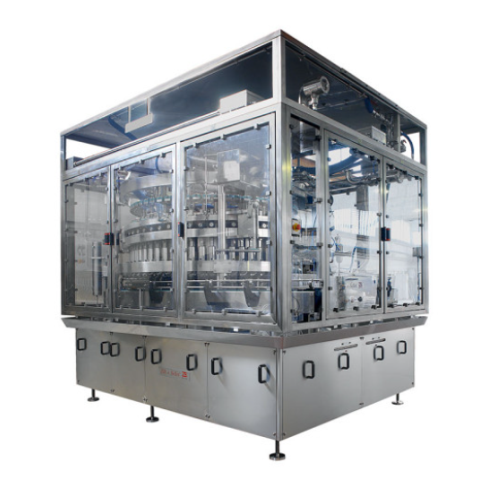

Rotary piston fillers for pumpable products
Optimize high-speed production lines with precision filling for diverse liquid...
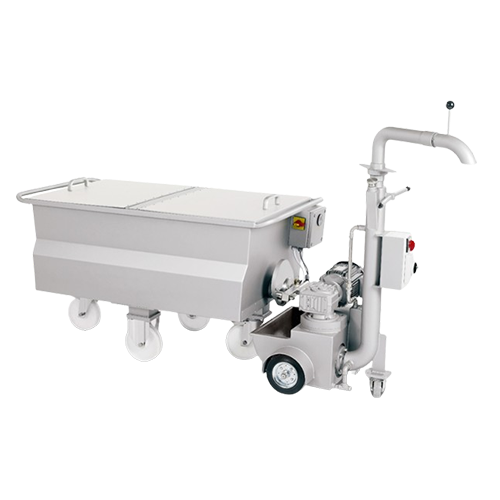

Bulk chocolate storage for confectionery production
Maximize space efficiency while maintaining product quality with our ...
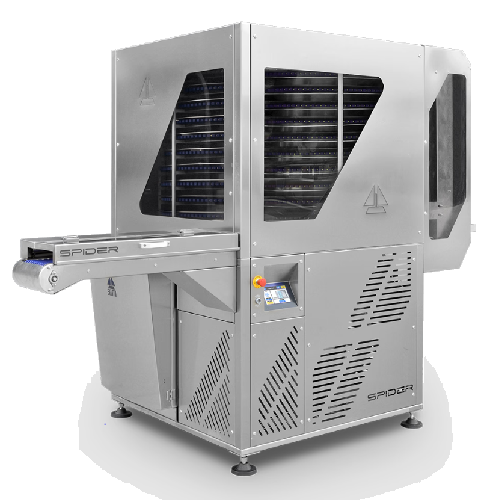

Vertical tunnel for cooling and moulding chocolate
Efficiently manage chocolate temperature control and molding precision...
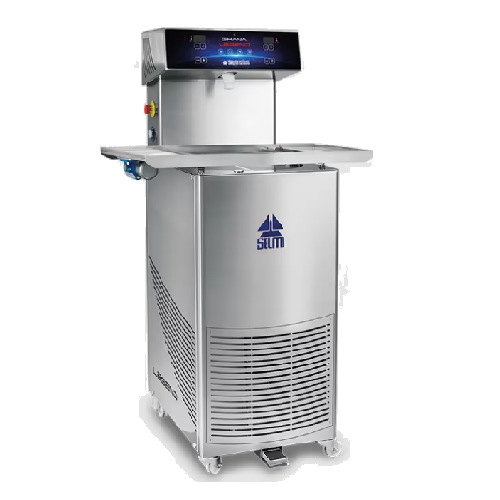

Professional chocolate tempering system for chocolatiers
Achieve precise chocolate tempering with advanced digital contro...

Chocolate and spreadable cream dispenser
Effortlessly enhance your confection creations with a dispenser that precisely mel...
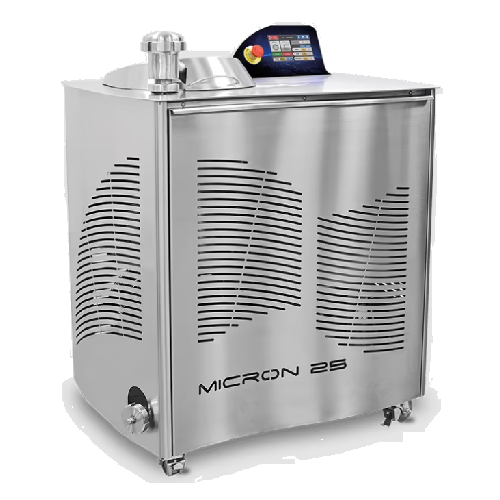

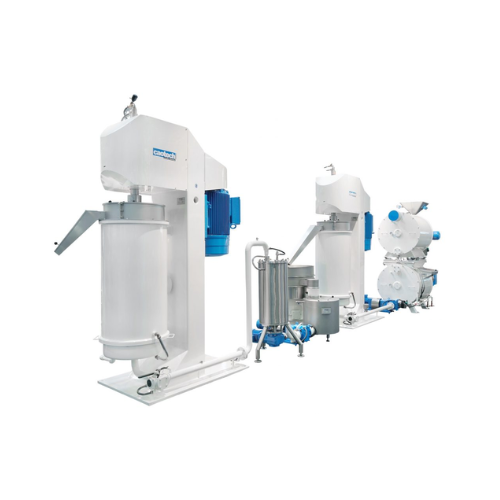
Refiner for spreadable cream and chocolate
Achieve optimal texture and consistency for your spreadable creams and chocolat...
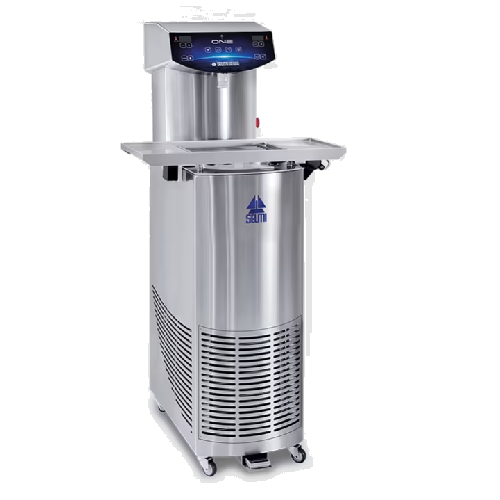

Chocolate tempering solution for small scale production
Efficiently temper chocolate for diverse confectionery creations ...
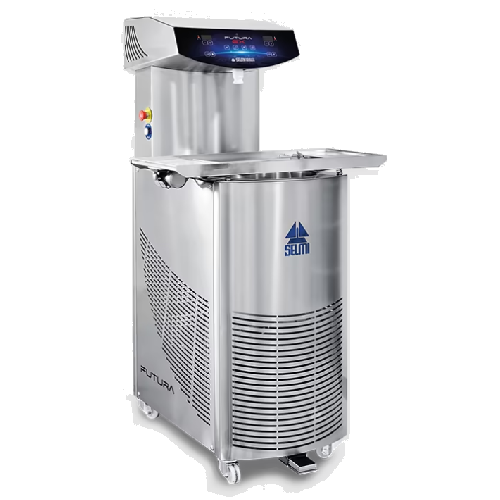

Professional chocolate tempering equipment for efficient production
Enhance your production capabilities with a versati...
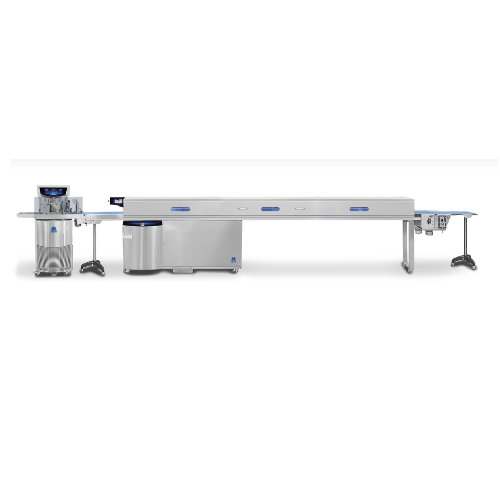

Chocolate enrobing and cooling tunnel 300/400 mm
Ensure seamless enrobing and precise cooling for chocolate products with ...
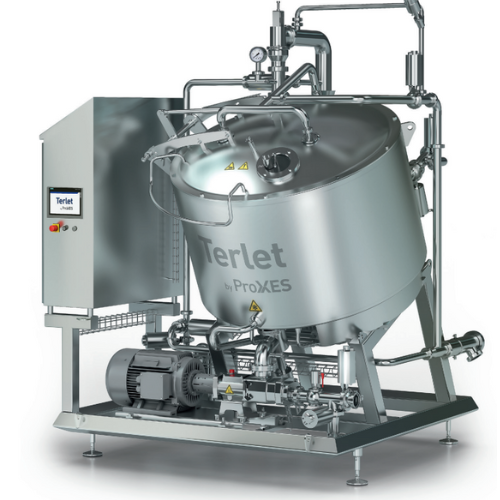

Energy-saving cooling system for vegan products
High-viscosity products like hummus or chunky pasta sauces must be cooled ...
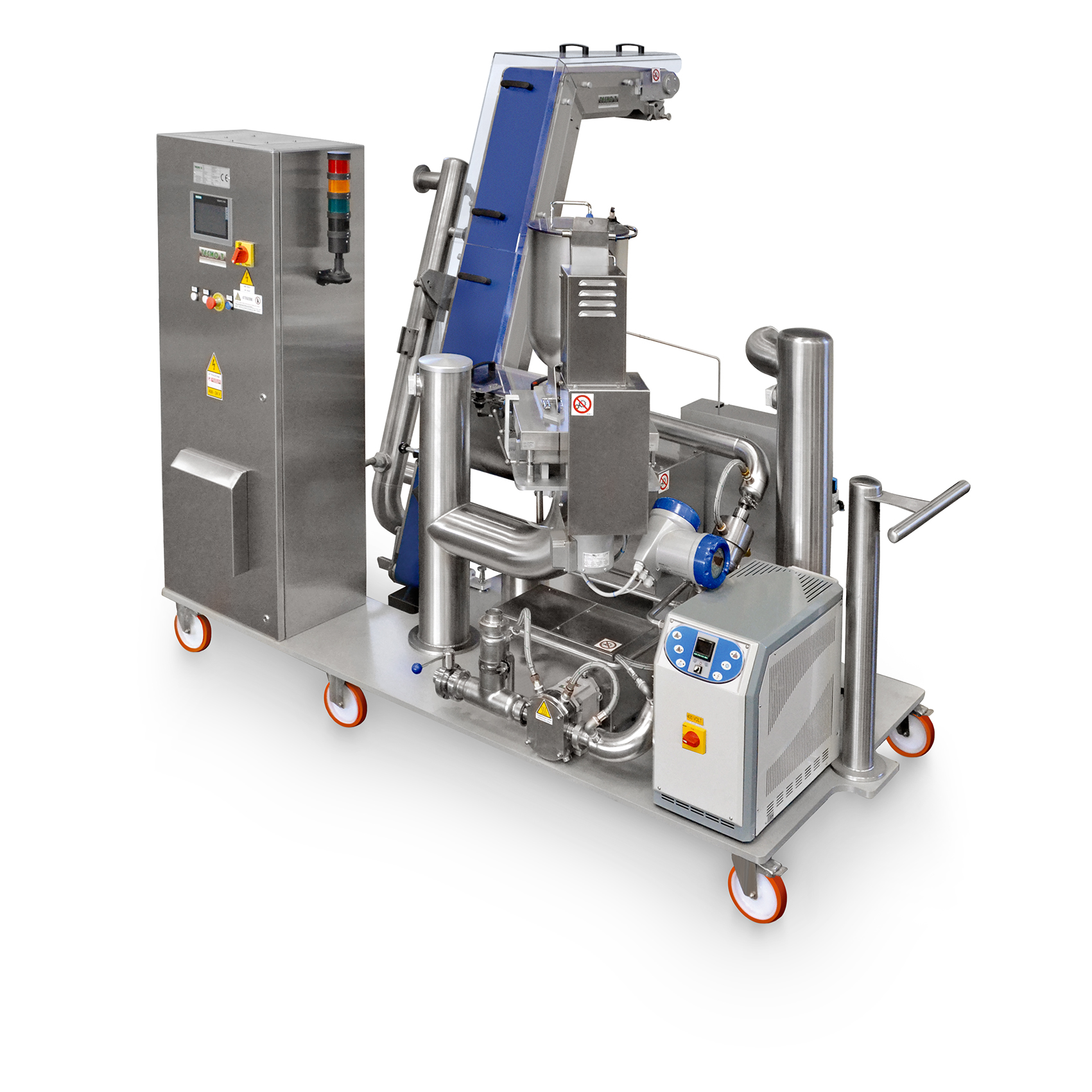

Mixer for production of chocolate with inclusions
Using the same mixing equipment for different recipes in chocolate manu...
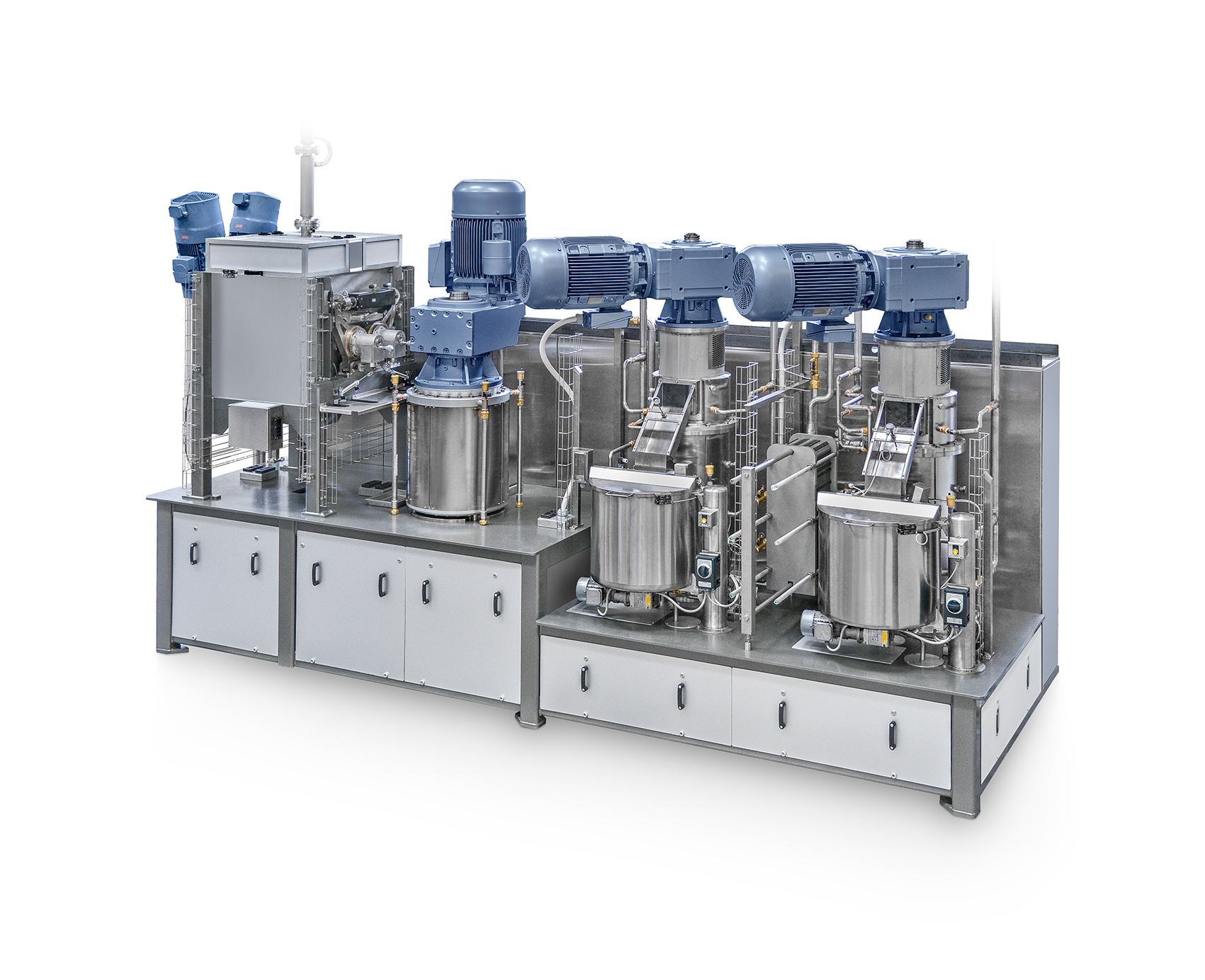

Refining plant for chocolate
Achieving a balanced, velvety mouthfeel in chocolate is challenging. Larger particles in chocol...
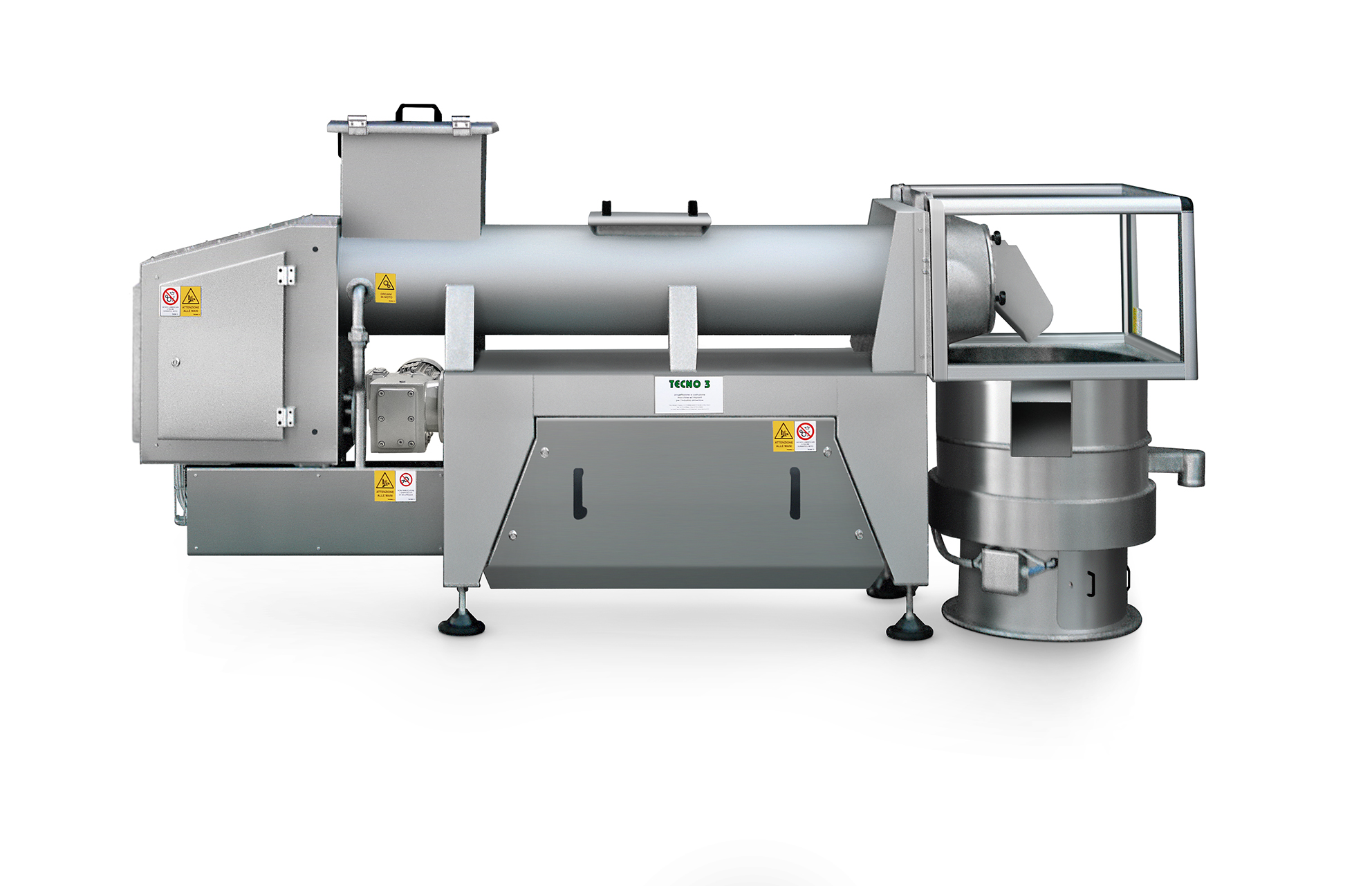

Industrial melter for chocolate rework
Wastage or out-of-specification products are not uncommon in the chocolate manufactu...
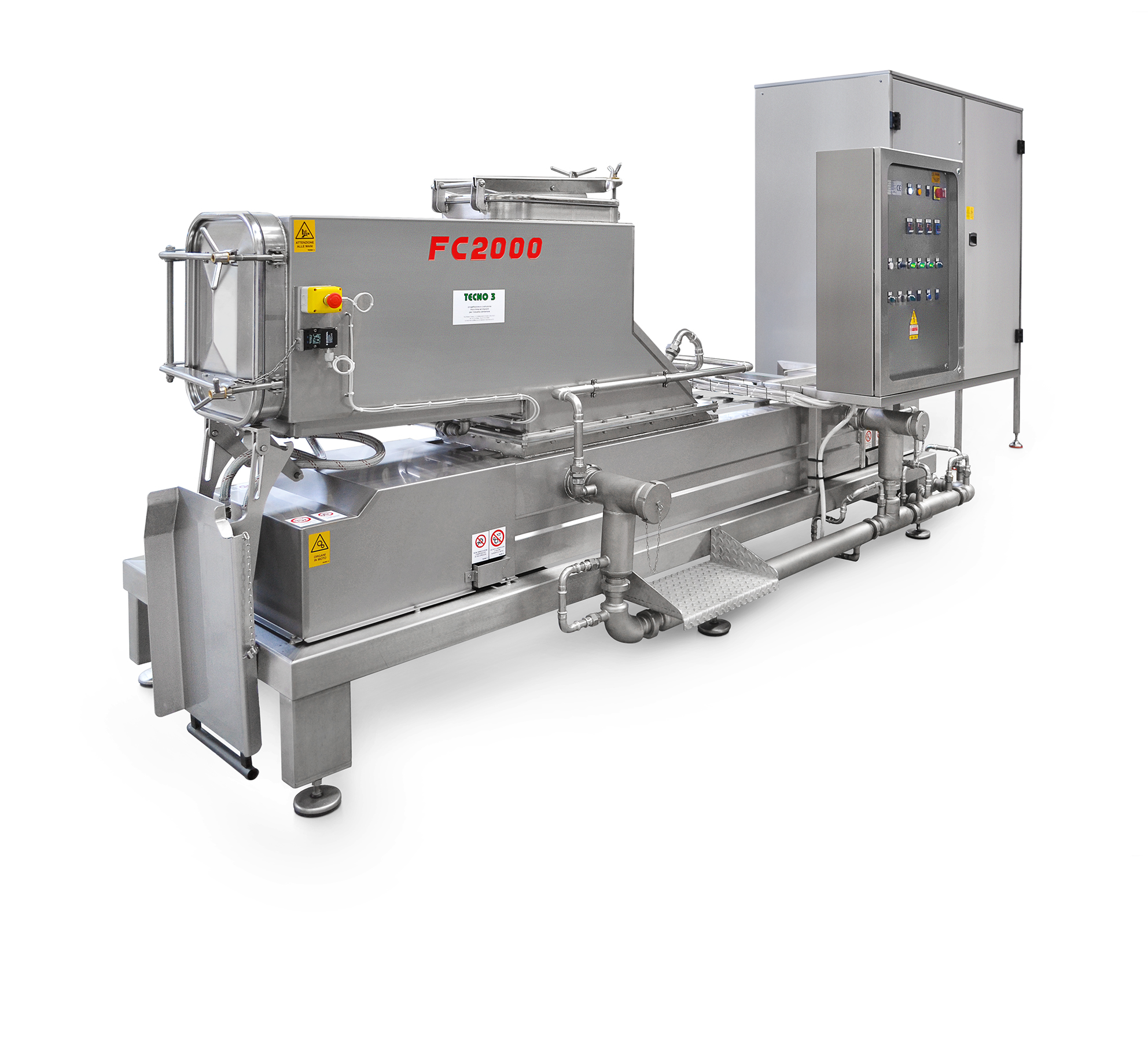

High-speed chocolate block melt machine
If you produce chocolate using larger blocks instead of cocoa beans, chocolate melt...
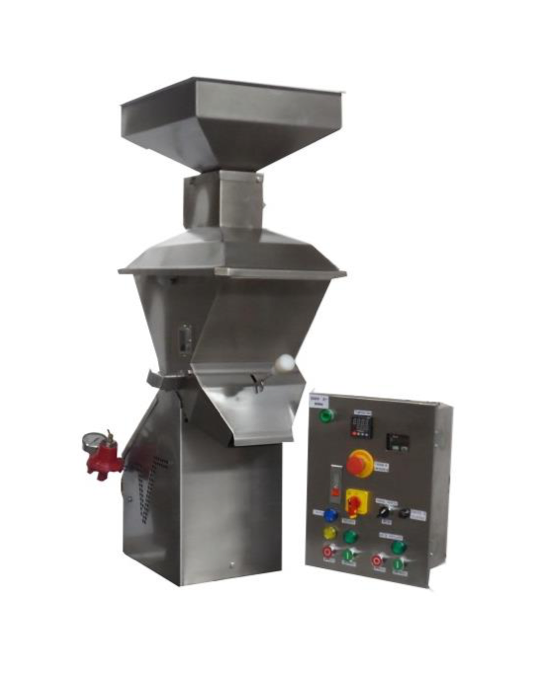

Entry level cocoa roaster
The biggest challenge that small-scale cocoa processing manufacturers face is even and thorough ro...
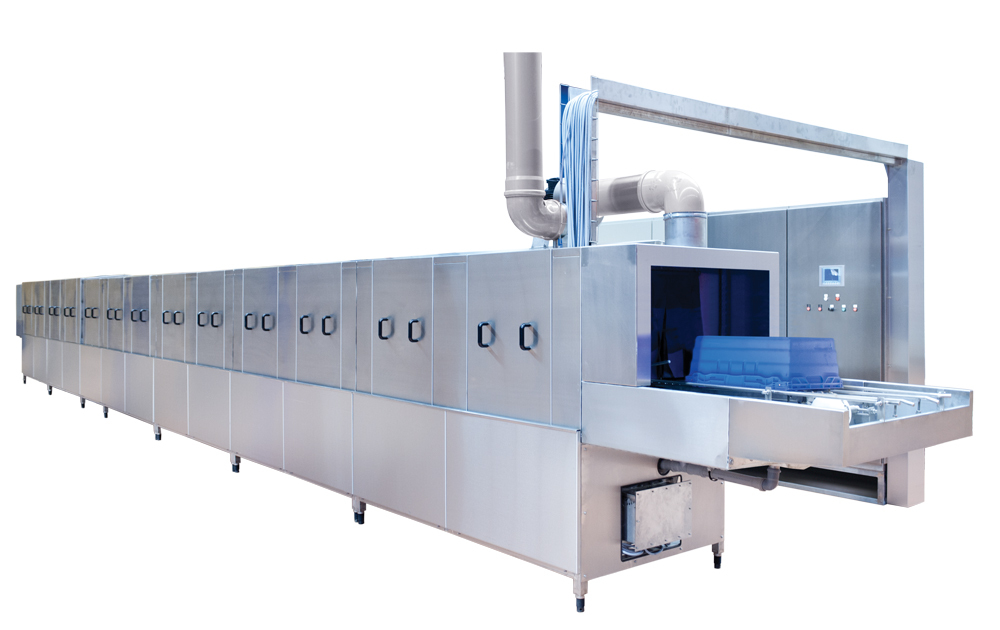

Industrial washer for plastic crates
In the food production sector, hygiene regulations are getting stringent by the day. E...

Industrial fine milling equipment for nuts
In a bakery environment fruit jams are often used for the decoration or filling...

Small capacity cocoa grinder
The first step of producing almost any kind of chocolate starts with grinding cocoa beans to ge...

Entry level bean to bar line
One of the challenges when setting up a small-scale cocoa processing factory is making all of t...

Vertical cartoning machine
In the food industry, a large number of bulk products like for example pasta, need to be packed i...
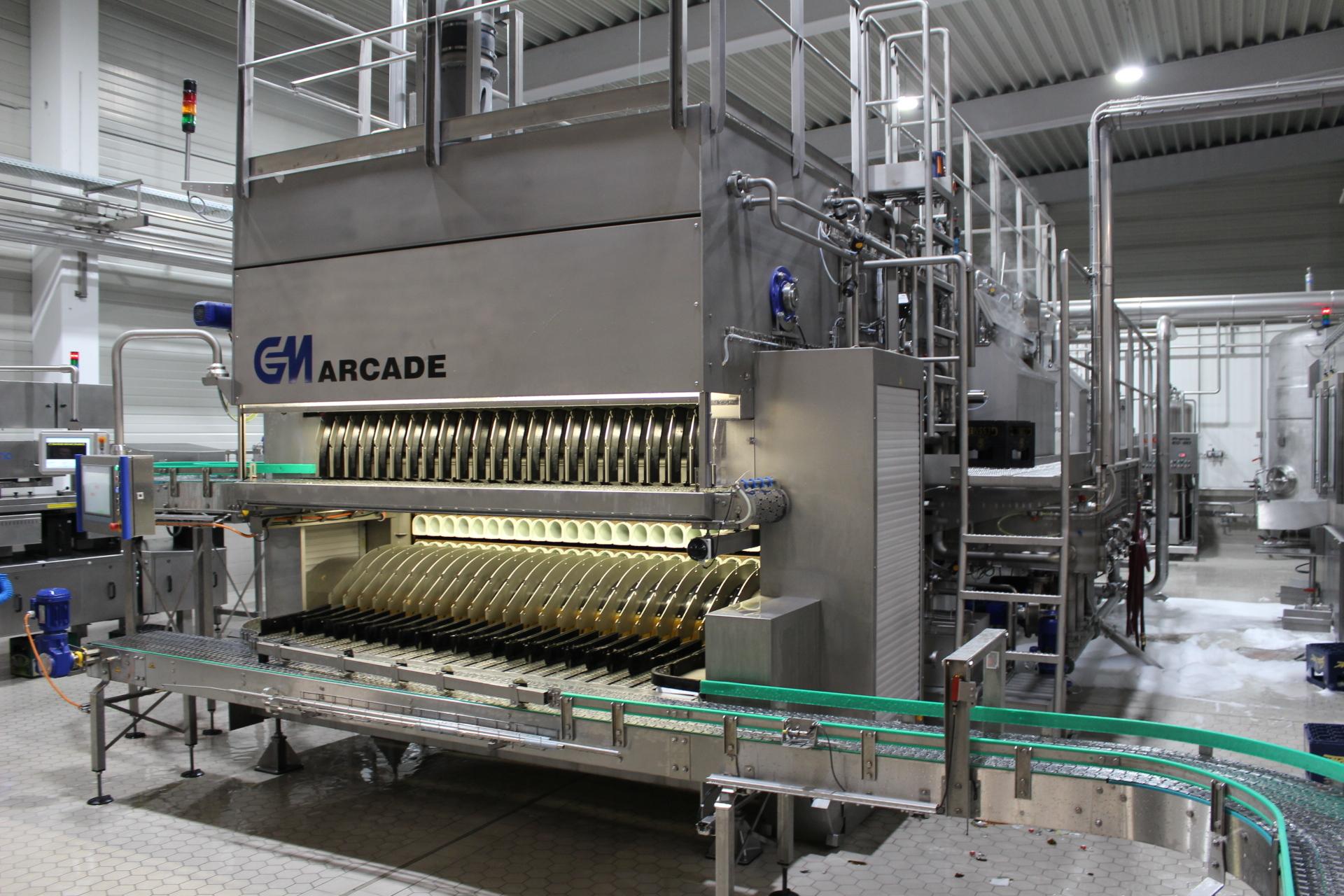

Industrial bottle washing machine
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and glass bottles are widely used in the beverage indust...

Filling machine for viscous products
Chocolate paste and other viscous liquids require special handling to obtain the optim...
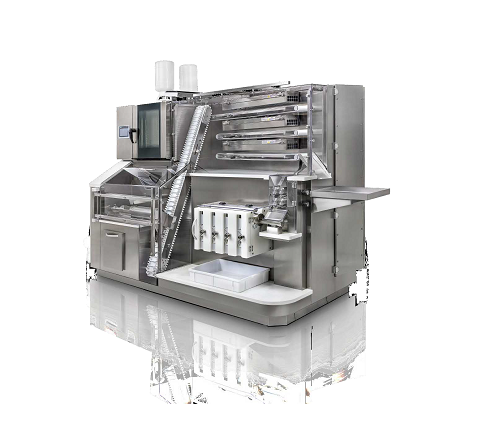

Small scale cocoa beans processing machine
For the highest quality chocolate production, complete control of the entire pr...
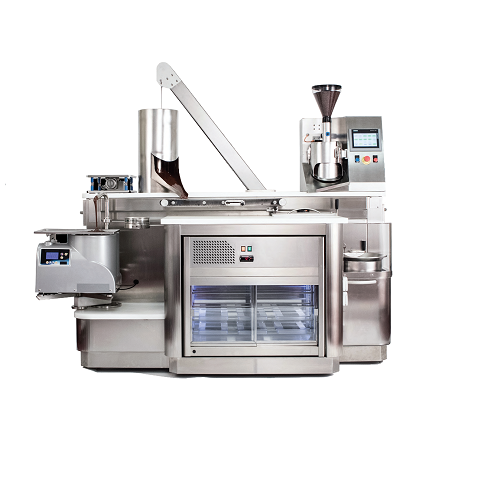

Entry level bean-to-bar machine
The production of high-quality chocolate from the bean can often be out of the reach of smal...
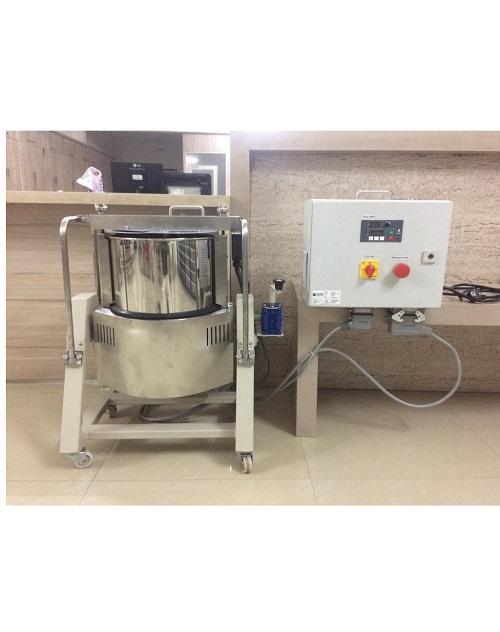

Small capacity chocolate melangeur
In order to produce the finest of chocolate products, you need the cocoa nibs to be grin...
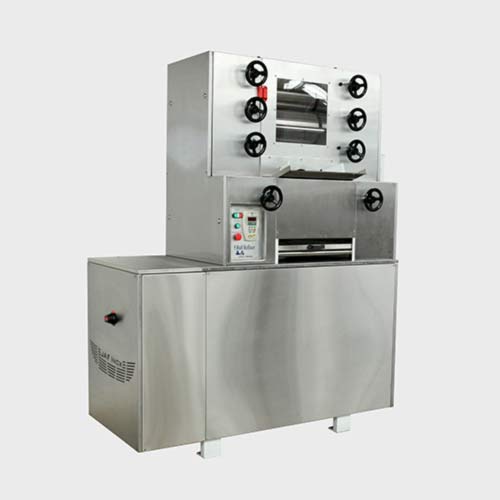

Chocolate refiner with chiller
Milled beans need further reduction in particle size before they can be sent to a conche for ...
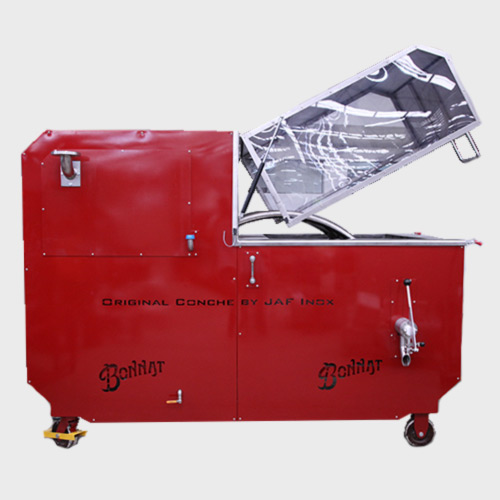

Longitudinal chocolate conche
High-quality chocolate requires specialized conching. Precise control of temperature and mixin...
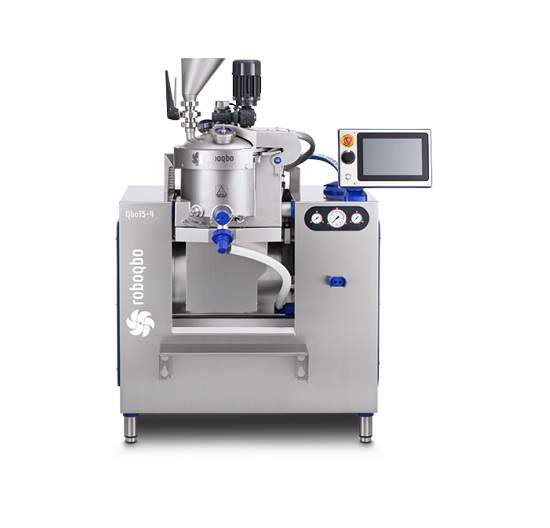

Multi-functional food processor for a high sugar percentage pastes production
For the development and production of hi...
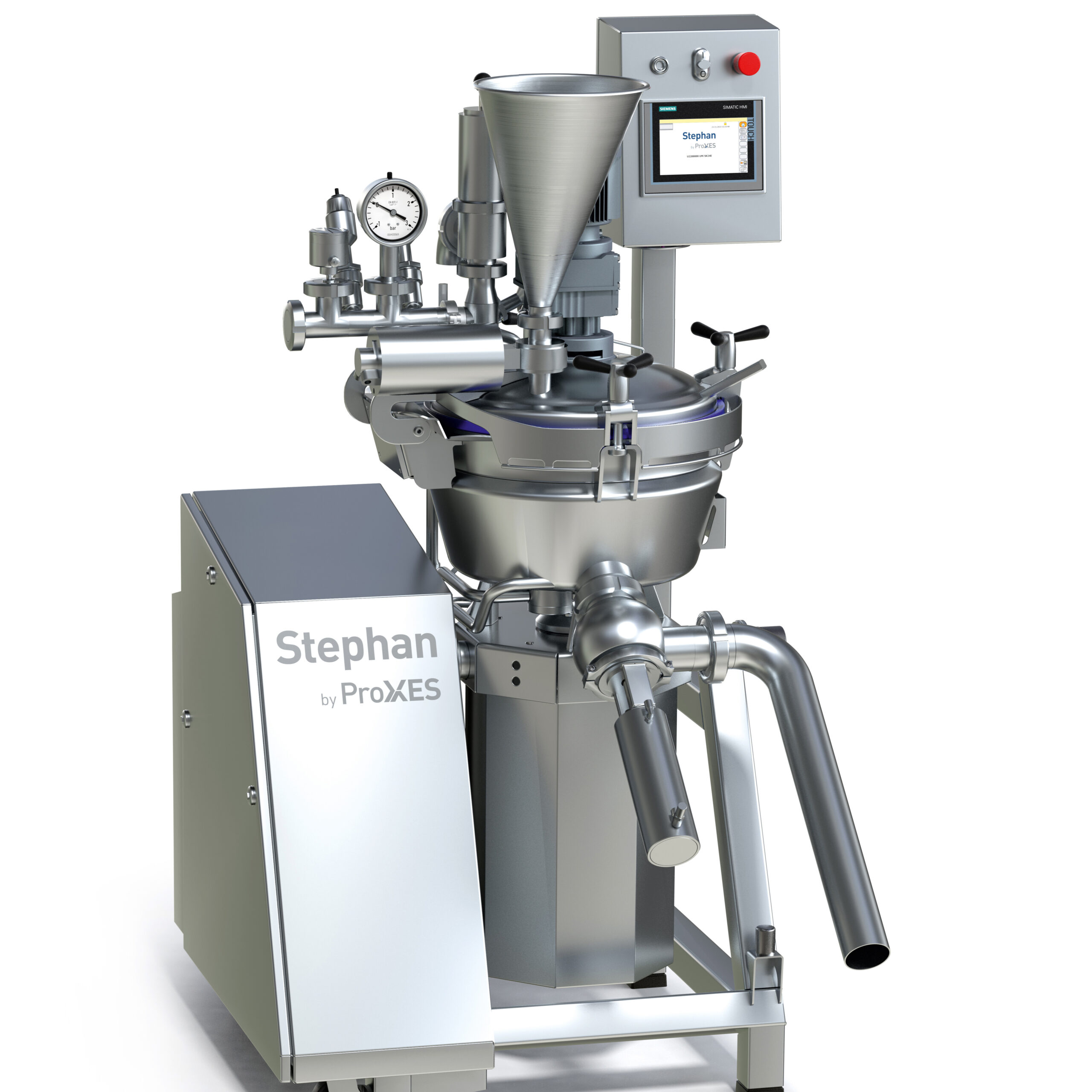

Flexible mixing system for whipped cream and pastries
Delicacies such as meringue, ganache, and marzipan undergo various ...