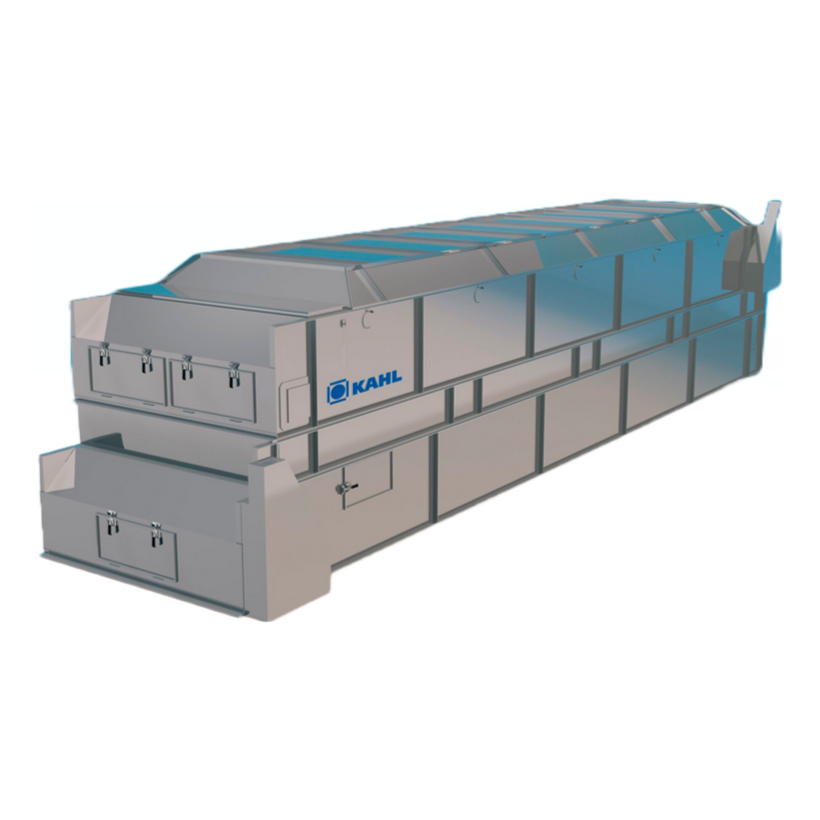
Making Gelatin Powder
Find innovative production technology for making gelatin powder and connect directly with world-leading specialists
In 1682, Denis Papin found a method to remove collagen from animal bones, discovering gelatin. But it was the inventor Peter Cooper who developed gelatin powder processing. In 1845 he secured his invention with US patent 4084 for a dessert of gelatin powder called “portable gelatin”.
Select your gelatin powder process
Tell us about your production challenge
Use vacuum evaporation to increase the concentration of gelatin
Gelatin is derived from the bones and tissues of healthy pigs, cows, chickens, and fish. These animals must have been first approved for human consumption.
Gelatin powder processing is complex and requires specialized equipment. First, you need steam vessels with increasing temperatures. This will separate the collagen from the tissues. Using hot water, you then extract the collagen from the material. Temperature is the key to the gel strength or bloom value: the lower temperature, the higher the gel strength.
Use separators or centrifuges to remove traces of fat and fibers and further filtering to eliminate unwanted microparticles. A vacuum evaporation system gives the gelatin thickness and concentration. Your process ends with sterilizing, cooling, drying, and grounding to make gelatin powder.

Gelatin powder processing for pharma and nutraceutical products
There are two types of gelatin forms: powder and leaves. Gelatin powder is more common and generally comes in small sachets. But it can also come in big bags to use in industrial processes. In addition, gelatin powder is more commercial and easier to use than leaf gelatin.
Gelatin doesn’t have color, taste, or odor. But you can make magic with it, turning liquids into a gel. It has thickening, emulsifying, binding, and adhesive properties. Moreover, it is a source of protein. It also attracts impurities and clarifies juices, wines, and vinegar. Gelatin can be used to make desserts, gummy candies, and marshmallows. As well as low-fat yogurts, broth, consommé, aspic, and many other food products.
Jelly isn’t only valuable for the food industry. Gelatin powder processing is critical to the pharma and nutraceutical industries. For example, to make softgel vitamin capsules and hard gelatin capsules that are easier to swallow.
Dietary restrictions of animal-based gelatin
Agar-agar and guar gum are among the main plant-based substitutes to gelatin derived from animals.
Agar-agar is made from cooked and pressed algae. Carrageenan, another alternative, is made from dried seaweed named Irish moss. The guar gum is extracted from guar beans and pectin. This last is a fiber found in fruits and vegetables. When heated in a liquid solution, it expands and turns into a gel. These materials are dried and ground to make plant-based gelatin powder.
Processing steps involved in gelatin powder making
Which gelatin powder technology do you need?
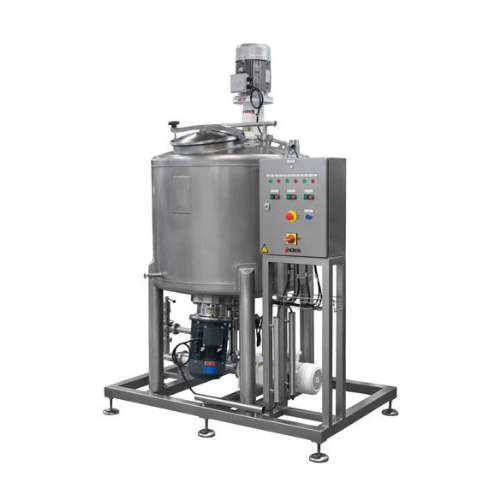

Hydroalcoholic gel mixing system
Ensure seamless production of hydroalcoholic gels with an advanced mixing system designed f...
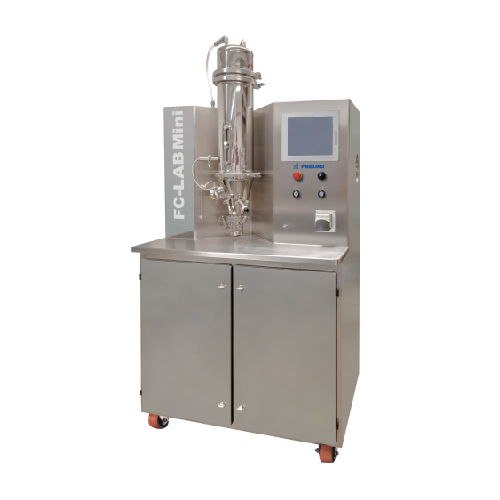

Laboratory fluid bed system for solvent processing
Optimize your laboratory scale operations with a versatile fluid bed s...
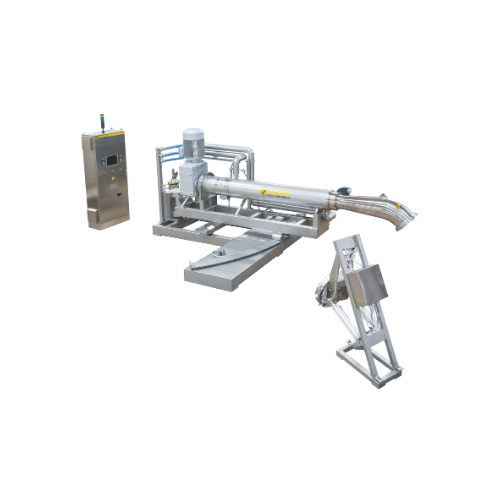

Oscillating heat exchanger for gelatin production
Ensure hygienic transfer in gelatin production with an innovative oscil...
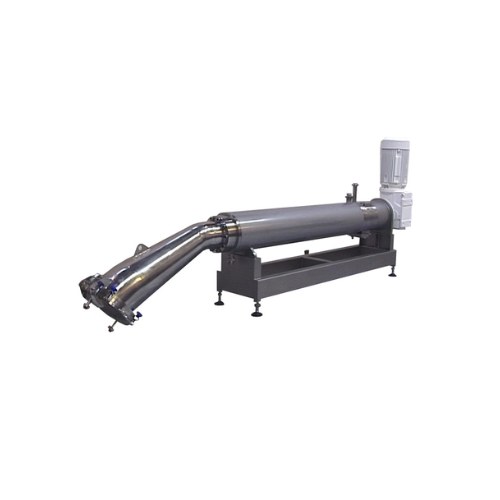

Scraped surface heat exchangers for gelatine processing
Effortlessly manage the cooling, gelling, and extrusion of gelati...
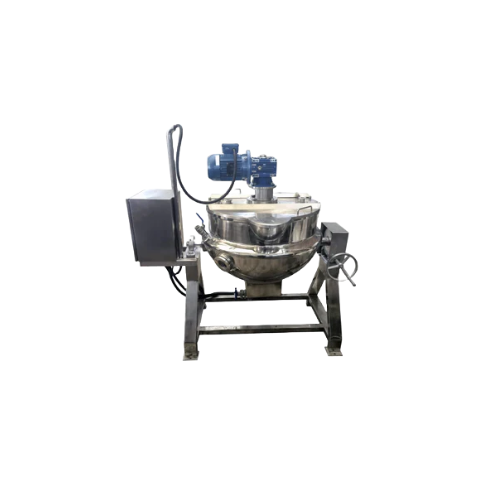

Dissolving tilt kettle for gummy candy production
Optimize your gummy candy production by melting and dissolving ingredie...
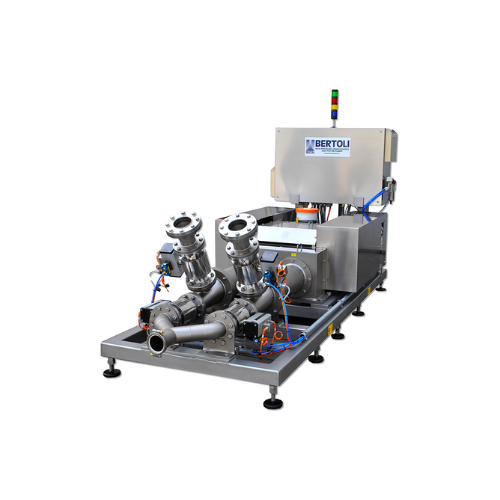

Industrial homogenizer for food and beverage applications
For manufacturers seeking consistent quality, this homogenizer...
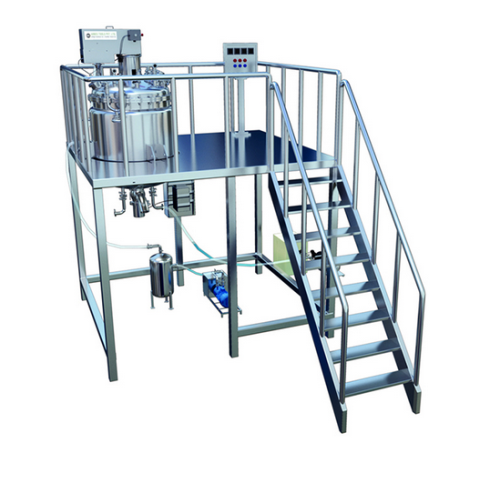

Gelatin melters for softgel production
Optimize your softgel production with a solution that ensures precise gelatin meltin...
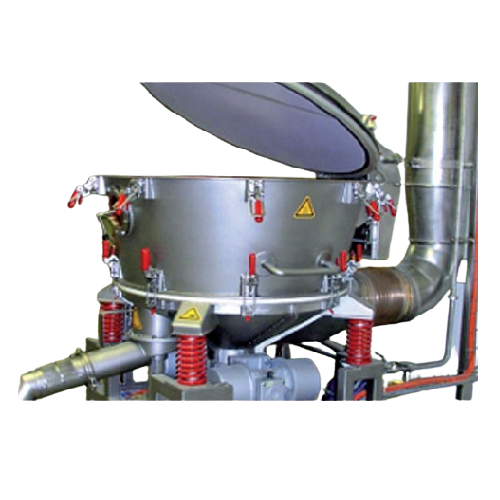

Vibration batch dryer for difficult solids
Ensure efficient drying of complex solids prone to sticking and shape irregular...
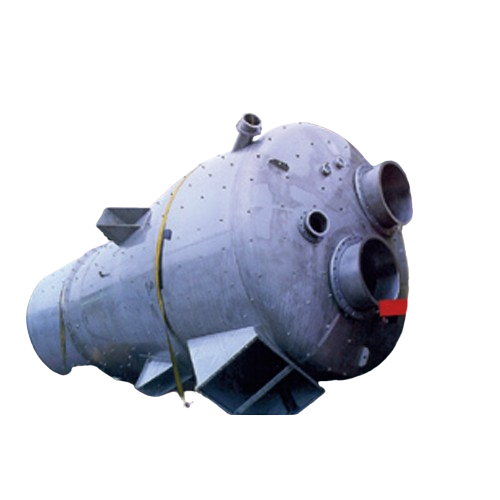

Fluidized bed spray granulators for liquid to solid conversion
Transform liquid suspensions into stable, dust-free granu...
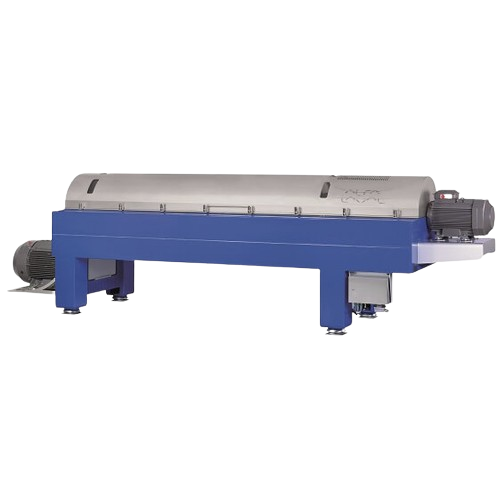

Decanter centrifuge for protein extraction
Efficiently enhance your recovery of valuable proteins and fats with customizab...
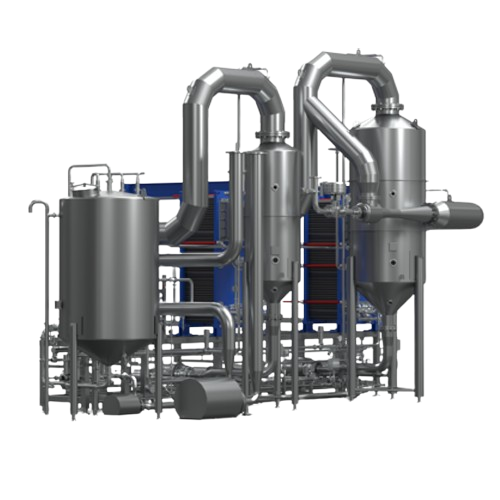

Rising film evaporator for concentration of viscous liquids
Effortlessly concentrate low-to-medium fouling and highly vi...
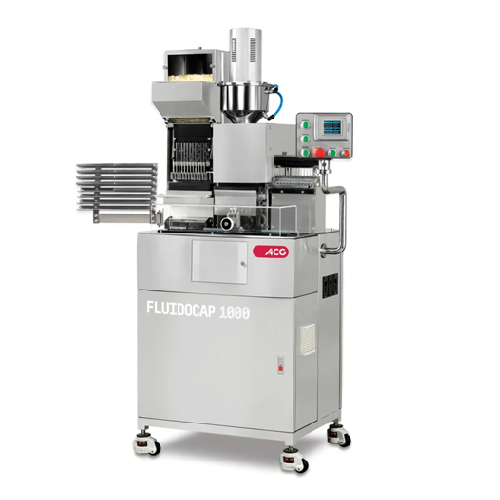

Liquid capsule filling for r&d and pilot-scale production
Optimize liquid capsule production with a compact machine that...
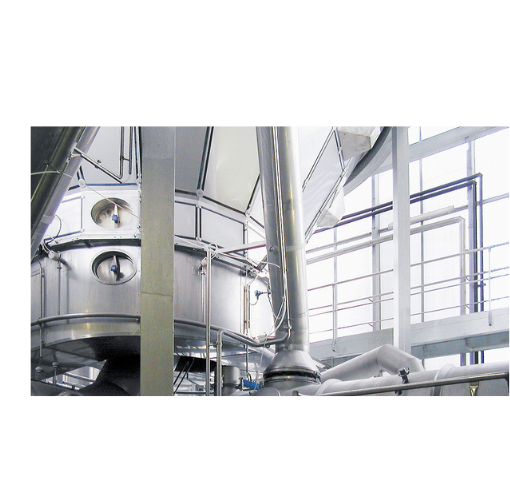

Spray dryer for whey and milk powders
Optimize your drying process for dense, agglomerated whey and milk powders with a spa...
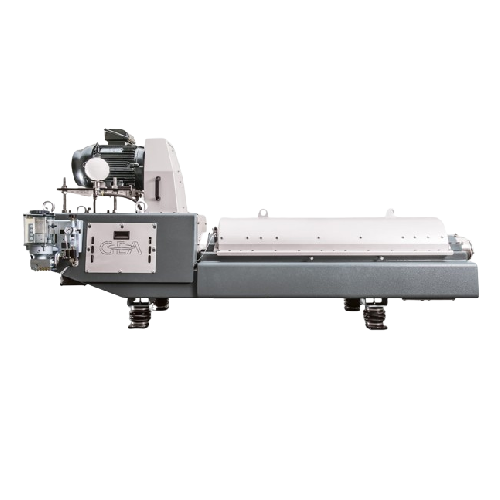

3-phase centrifuge for animal and fish by-products
Optimize your by-product processing with a 3-phase centrifuge that eff...
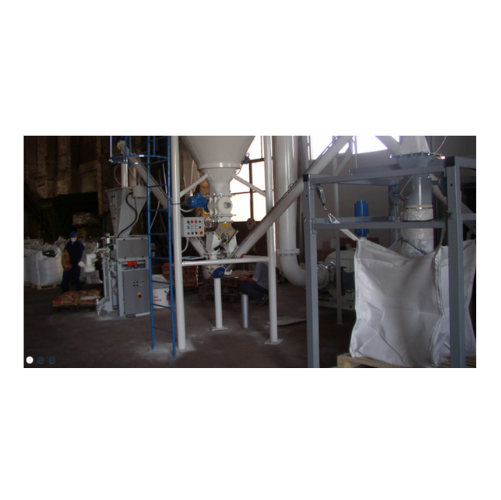

Manual Fibc bag filling station
Achieve dust-free filling of bulk bags with an efficient system designed to handle compacted...
Temperature control system for bioprinting with gelatin
Ensure precise bioprinting outcomes by maintaining accurate tempe...
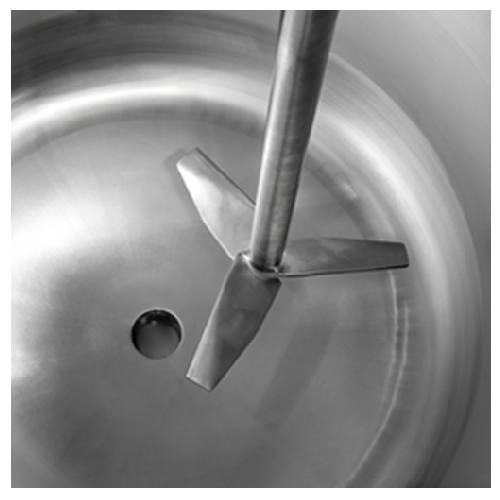

Static impellor mixer for homogeneous gelatin solutions
Achieve lump-free mixtures in your bakery production line with pr...
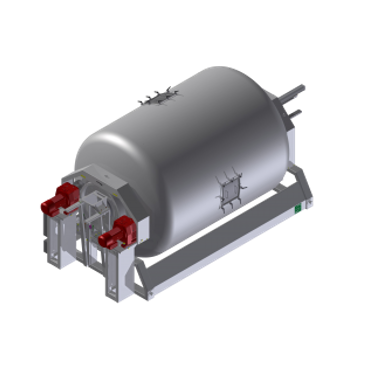
Gentle mixing solution for gelatin powder
The fragile nature of gelatin makes it a challenging material to blend homogeneo...
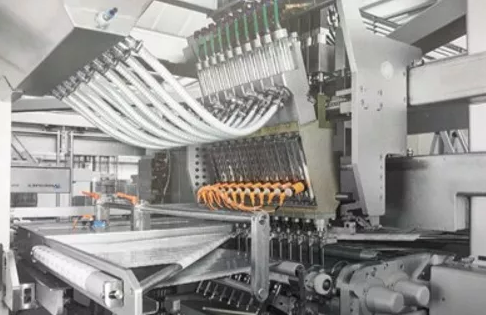
Accurate multiple dosing system for powders
Dosing multiple powders in a batch process is time inefficient, especially whe...
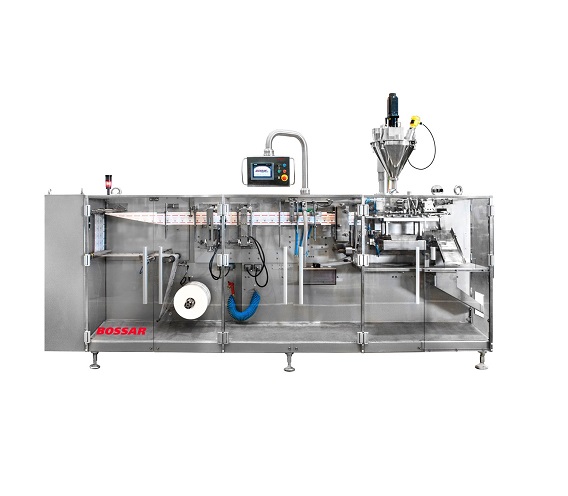

Entry level HFFS Machine for flat sachets
Traditional horizontal form fill and seal sachet machines for lower volume lines...
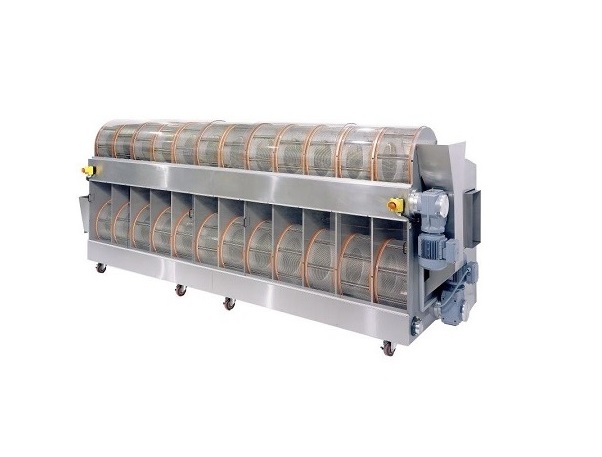

Softgel tumble dryer
Softgel (or soft gelatin) capsules are a very popular means of delivering oral doses in the pharmaceutic...

Continuous in-line softgel drying system
High output softgel (or soft gelatin) capsule encapsulating machines can operate b...

Gelatin melters and tanks
When producing high quality softgels its important that the gelatin base is processed and stored c...
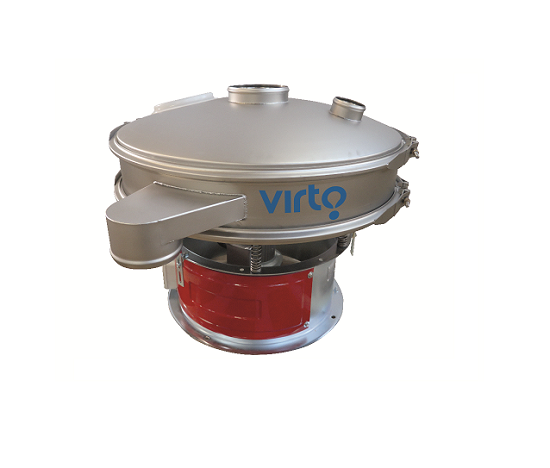

Vibrating sieve for liquid solid separation
Many industrial processes require the efficient separation of solids from a sl...
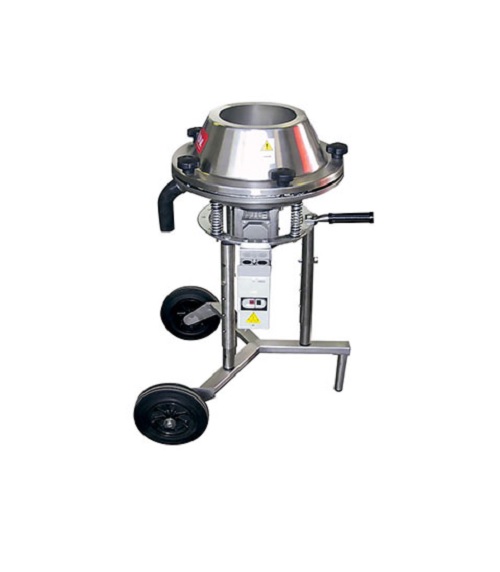

Screener and separator of dry powder
Many industries require the effective screening and separating of a range of dry powde...
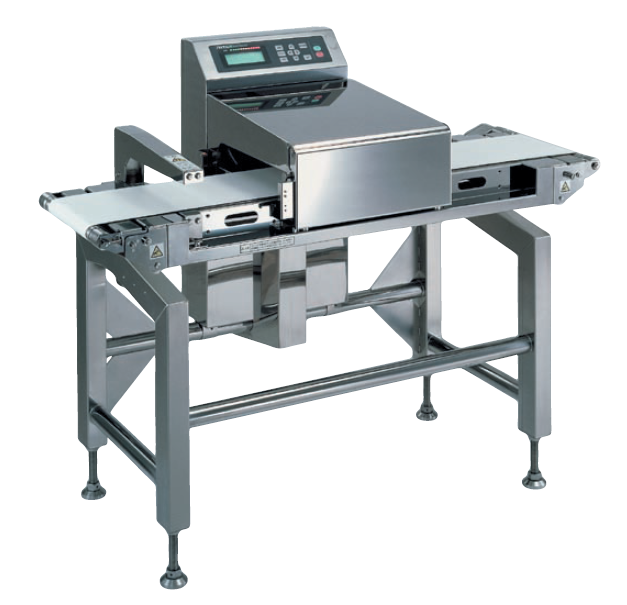

Metal detection system for aluminum packages
The magneto reflection system is ideal for detection of metals in aluminium f...
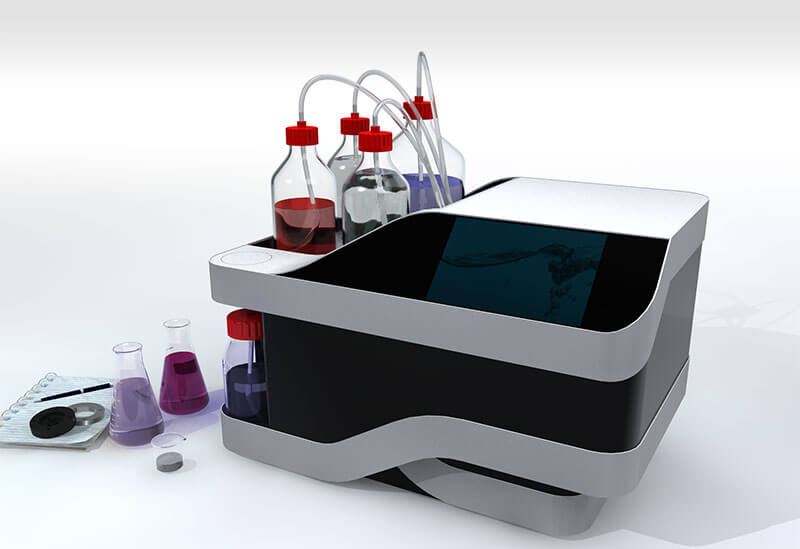
Microencapsulation system for your drug delivery system
Whether you want to improve the stability of nutrients, protect a...
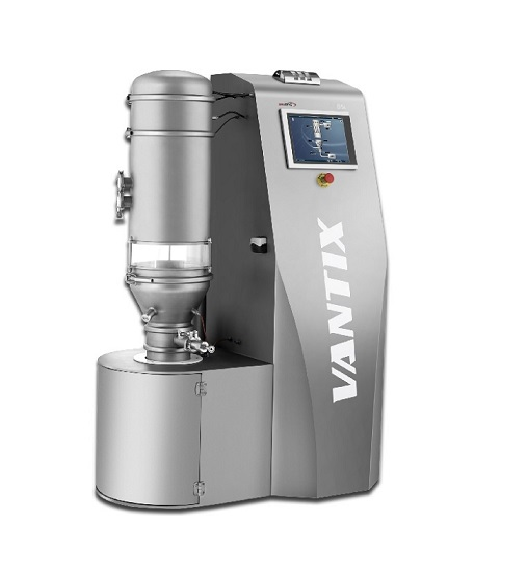

Fluid bed dryer for lab scale
Fluidised bed drying (FBD) is a common process in the pharmaceutical industry for drying compo...
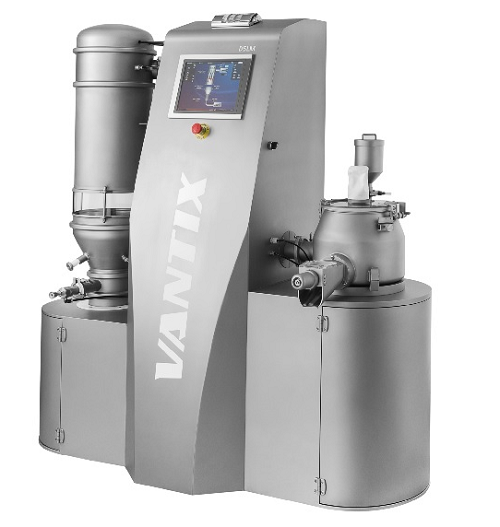

Fluid bed dryer and mixer for lab scale
Designed for pharmaceutical R&D, a lab-scale fluid bed dryer and mixer/granulat...
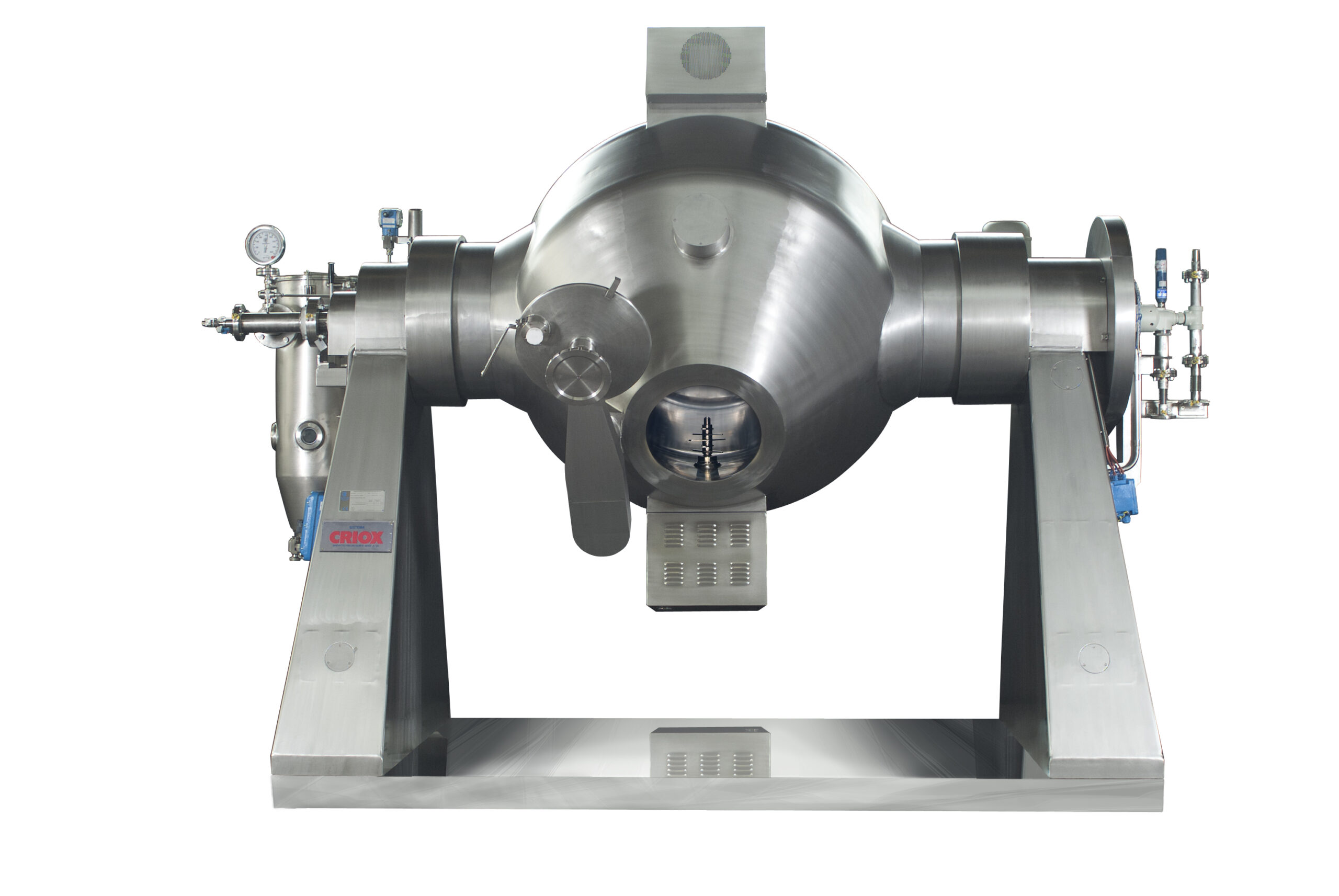

Rotary vacuum dryer
Powdered products tend to agglomerate during vacuum drying. This adds an additional step to the productio...
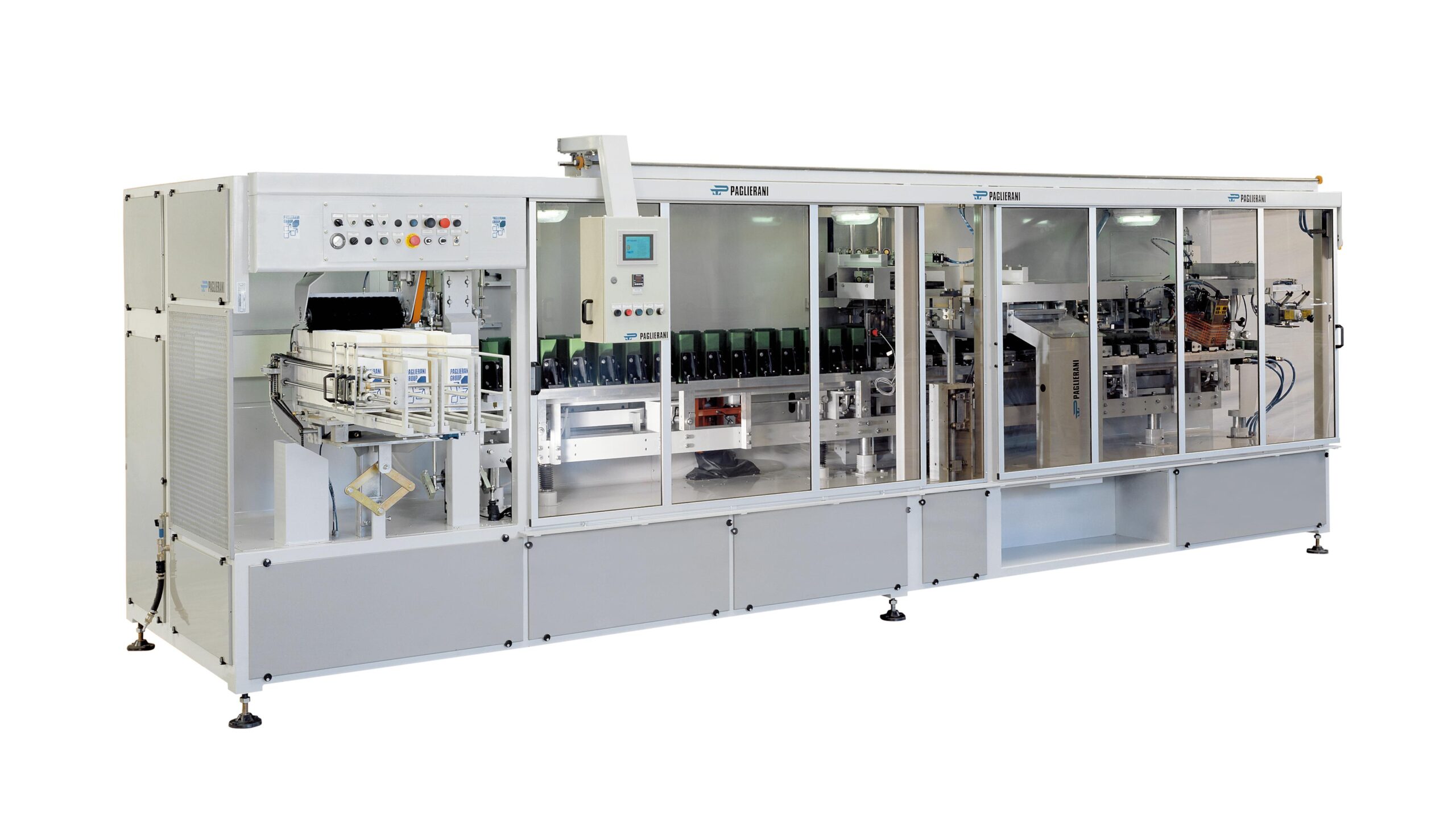

Packaging machine for preformed paper bags from 500 g to 5 kg.
Paper bag filling and closing for larger quantities of ma...
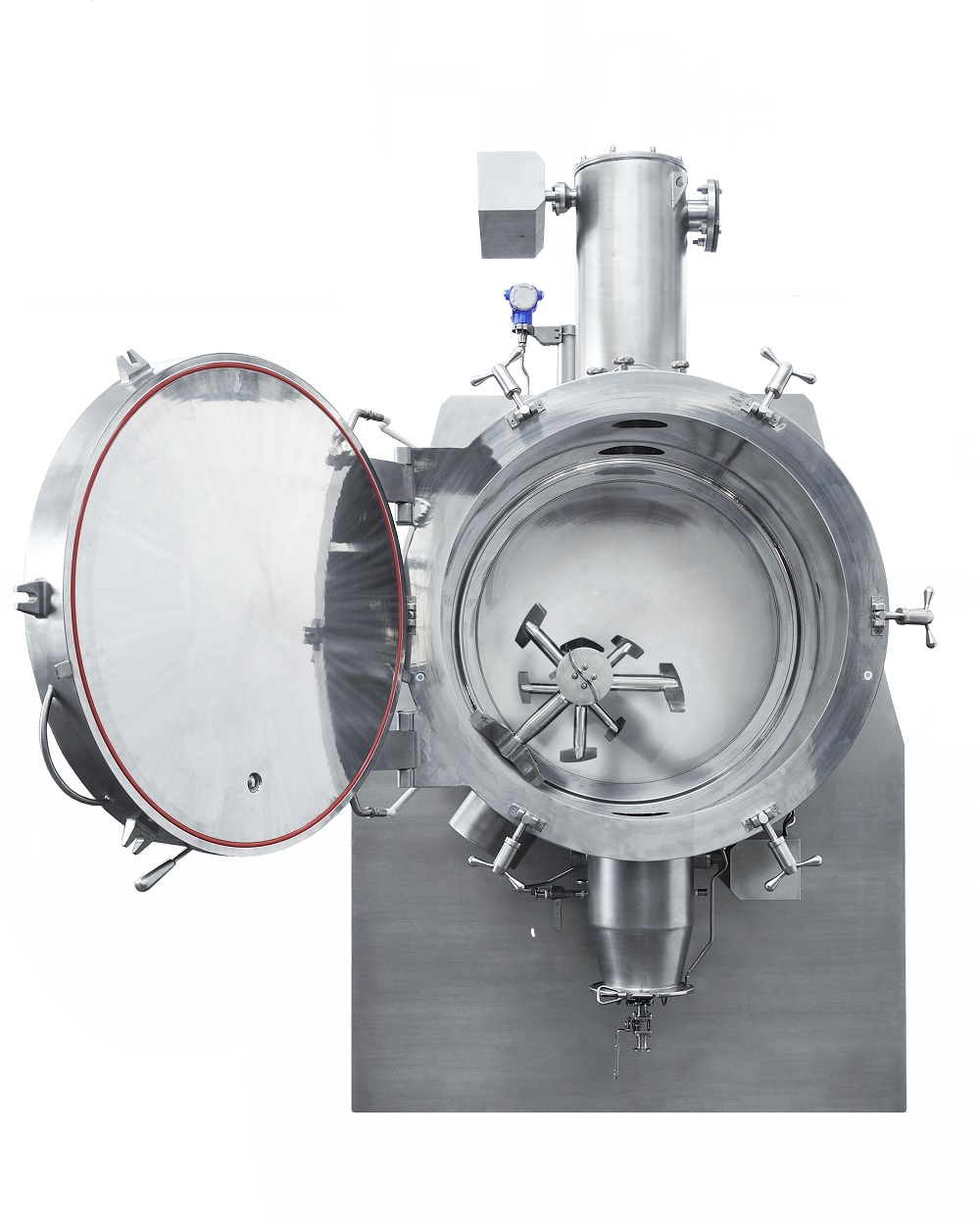

Horizontal vacuum dryer with eccentric agitator
Conventional dryers are inefficient and can lead to significant mechanical...
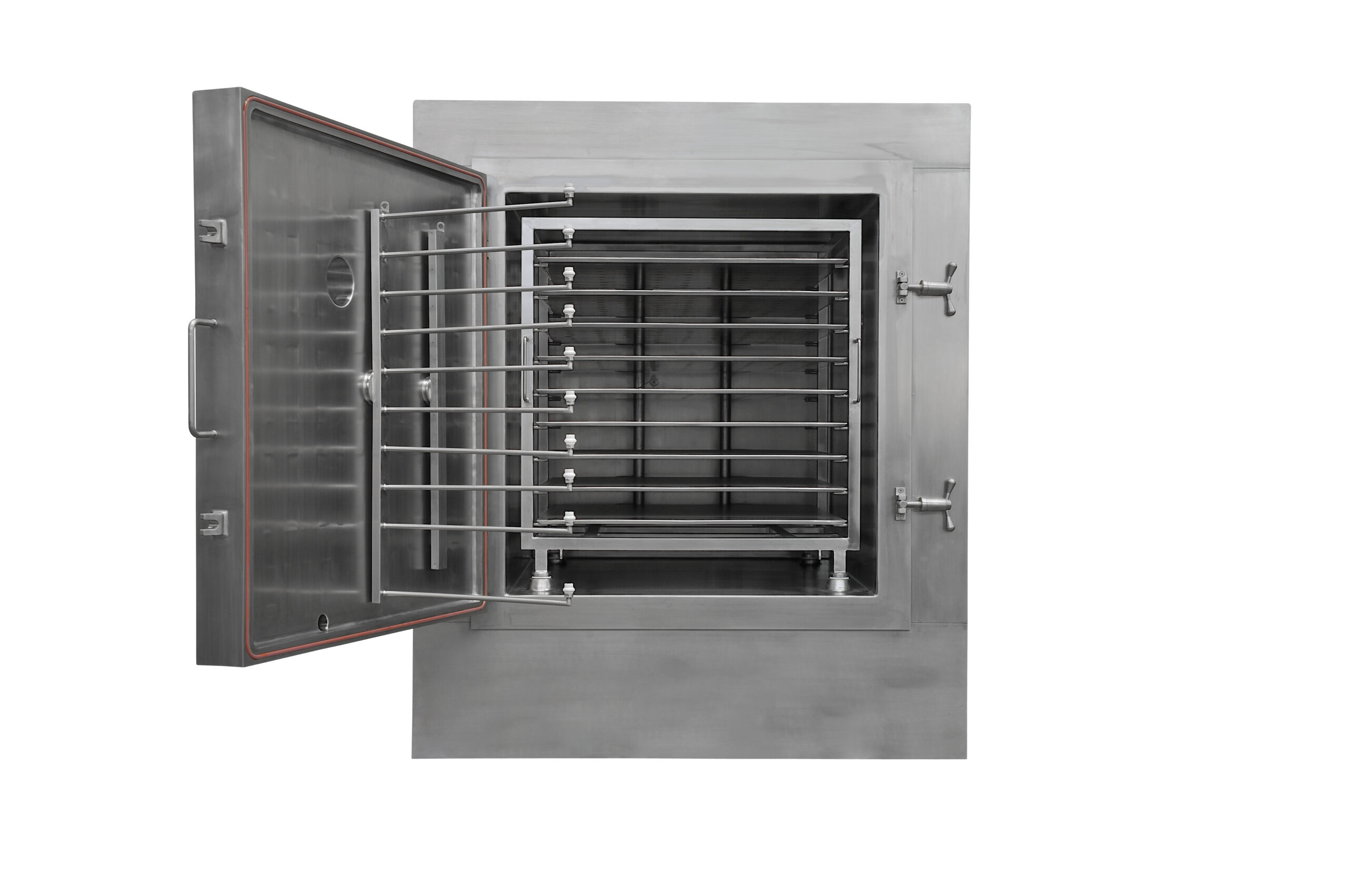

Vacuum tray dryer with clean-in-place system
Cabinet tray dryers can be difficult to clean, making their use difficult for...
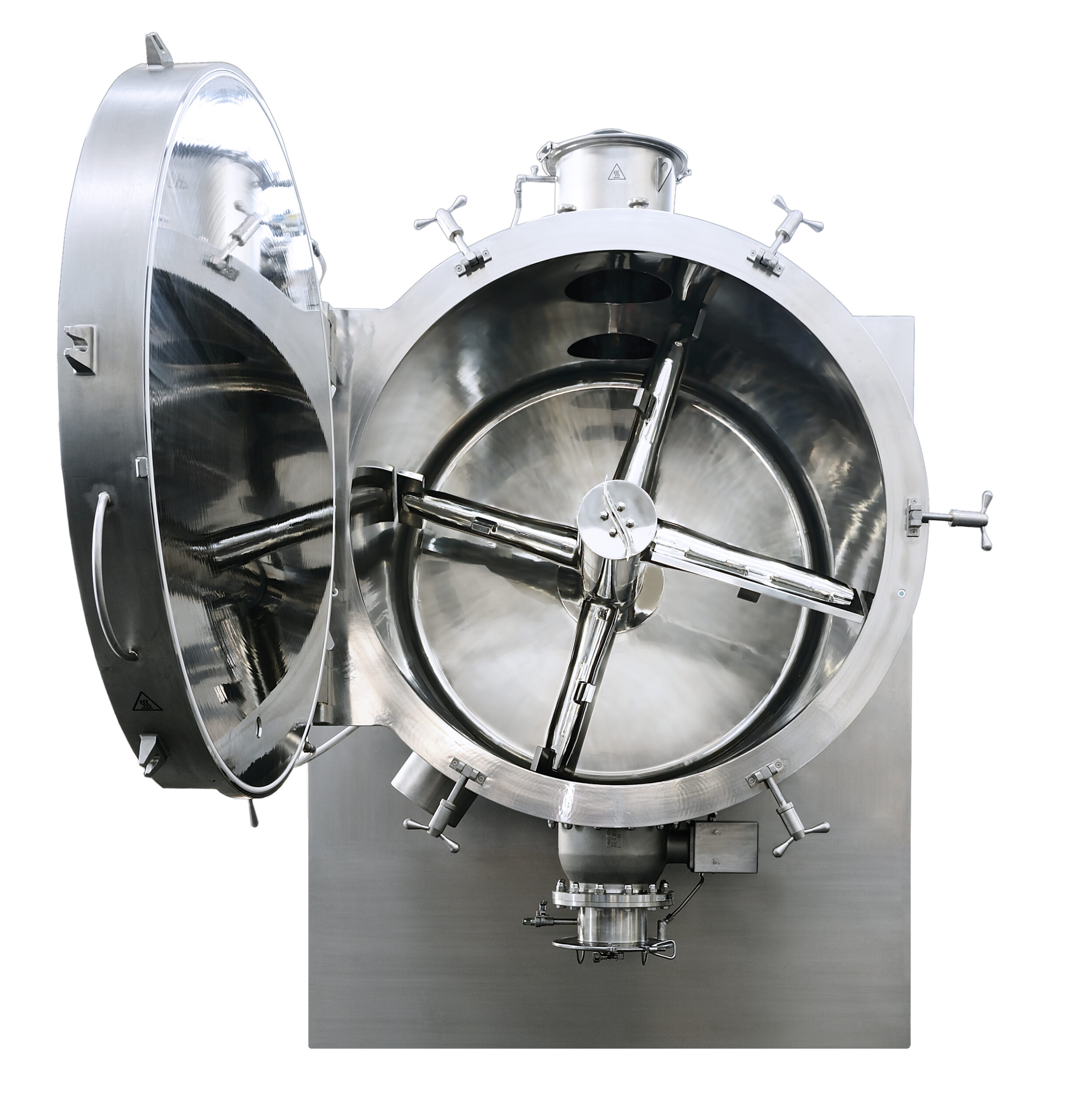

Horizontal paddle vacuum dryer
Agitated vacuum dryers can be difficult to clean which makes them unsuitable for multi-produc...
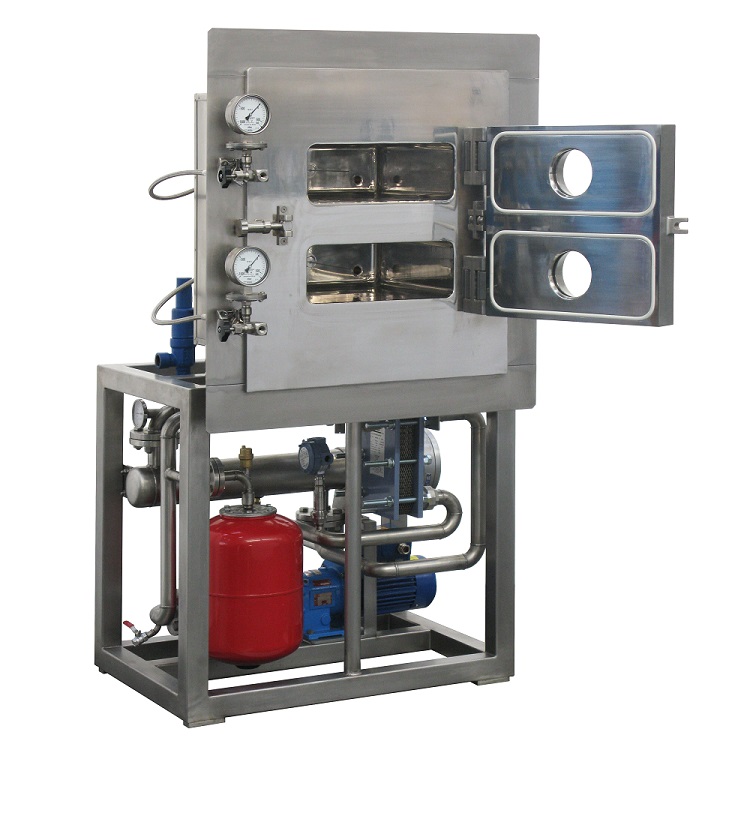

Laboratory-scale vacuum tray drying oven
Vacuum drying is used to remove moisture from sensitive materials. Drying small ba...
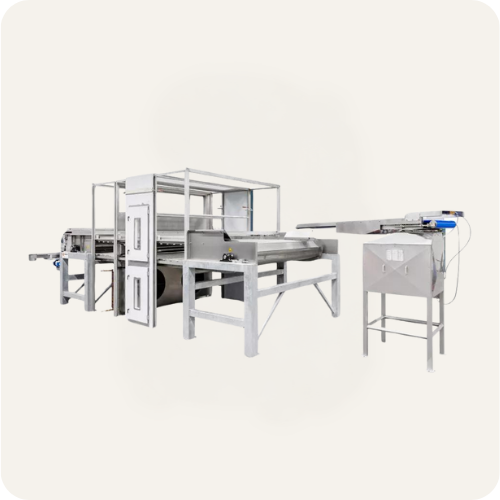

Hygienic belt dryer
A belt dryer typically applies the product through an infeed chamber onto a perforated horizontal belt, w...
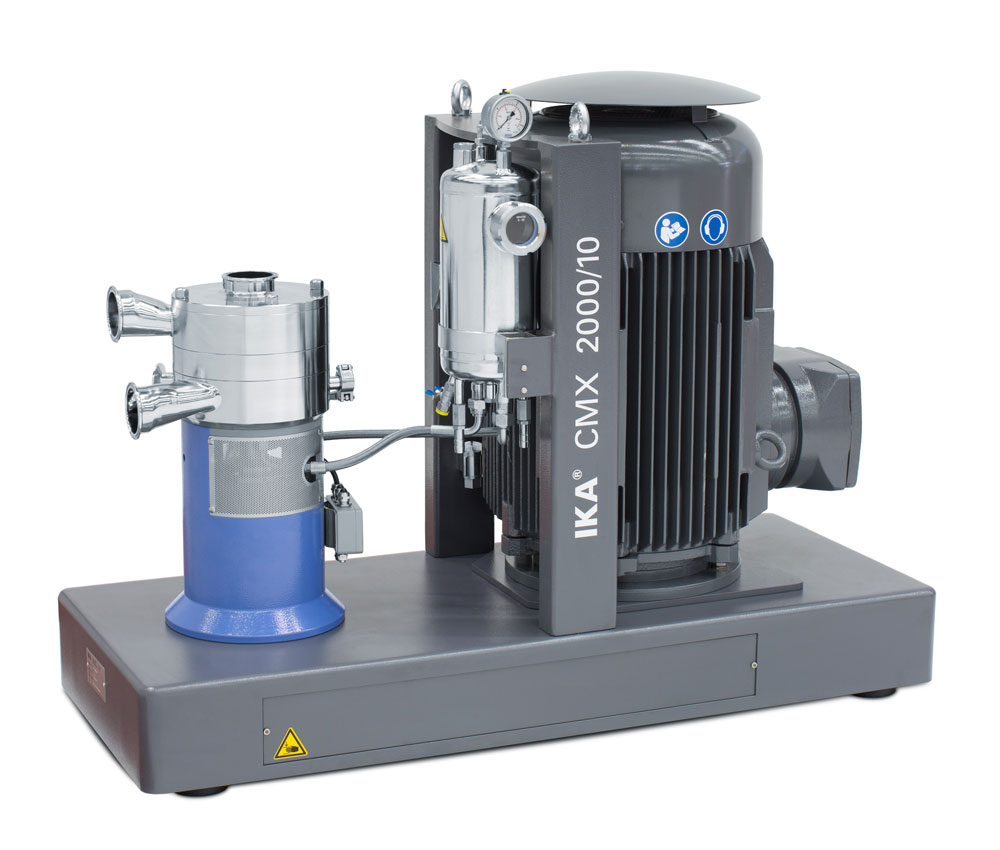

Inline batch mixer for solids and liquids
Several issues often arise when your process requires batch-wise mixing of powde...
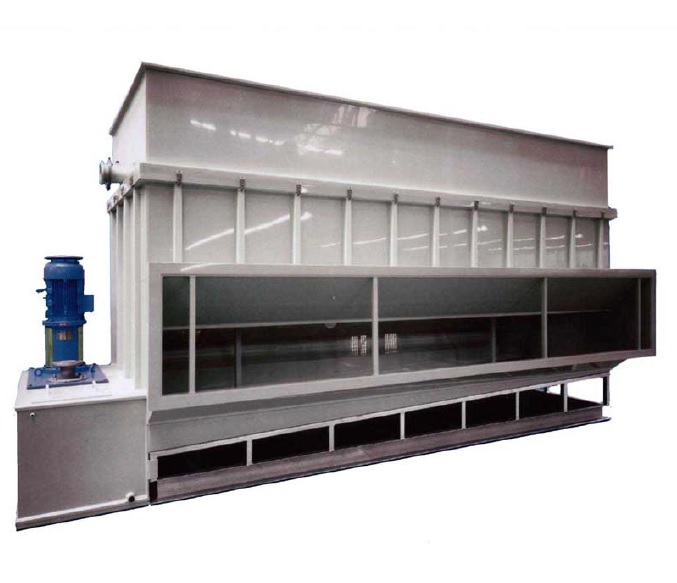

Air dehumidifier for bulk products
When your product or process is sensitive to humidity, using an air dehumidifier may res...
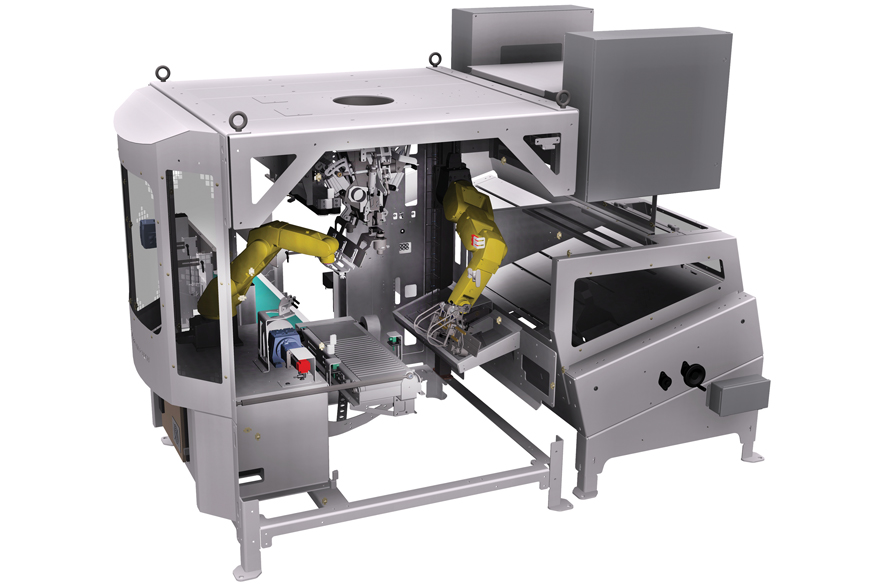
Versatile open-mouth bagger
If you want highly precise bagger for bagging multiple bag materials, here you go. This versatil...
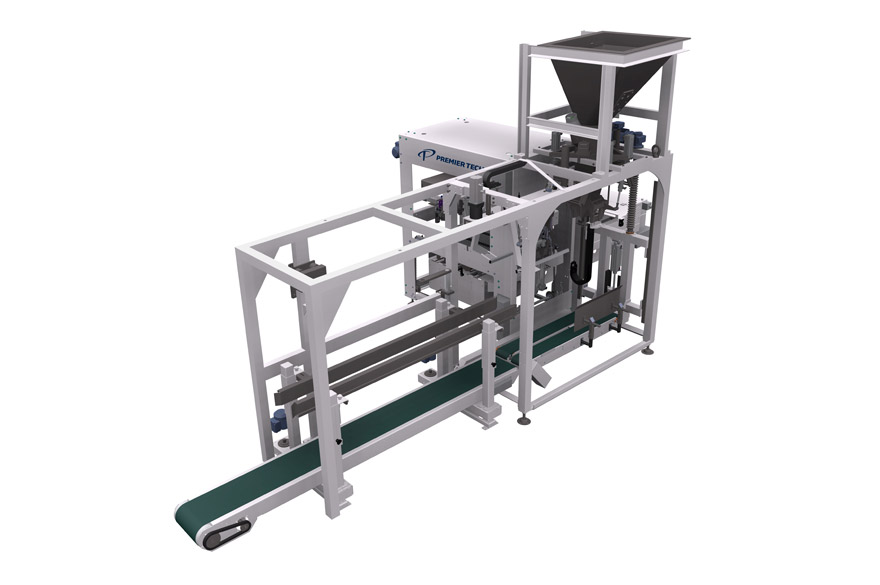

Open-mouth baggers for free flowing powders
For bagging free flowing materials into open mouth bags, this system is ideal....
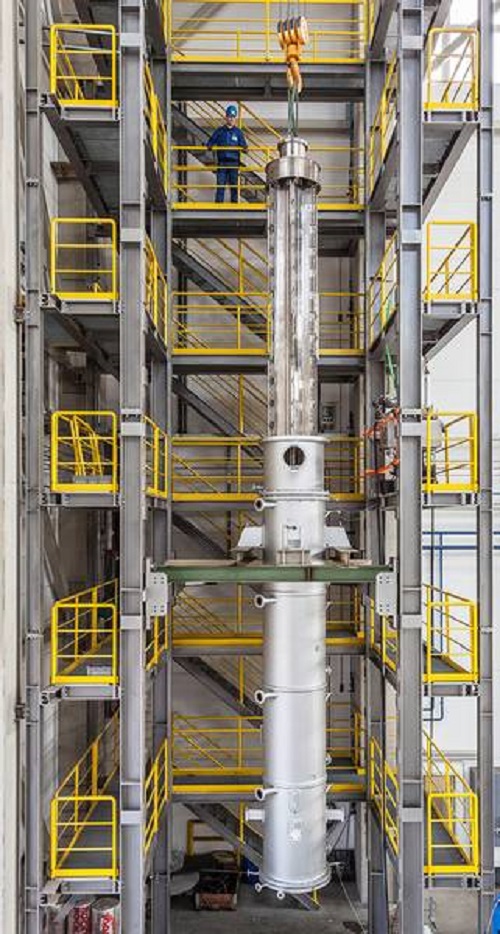

Thin film dryers
Dry dissolved or slurried crystallizing or amorphous products to a pourable powder.