Agar-Agar Processing Equipment
Find innovative production technology for making agar-agar and connect directly with world-leading specialists
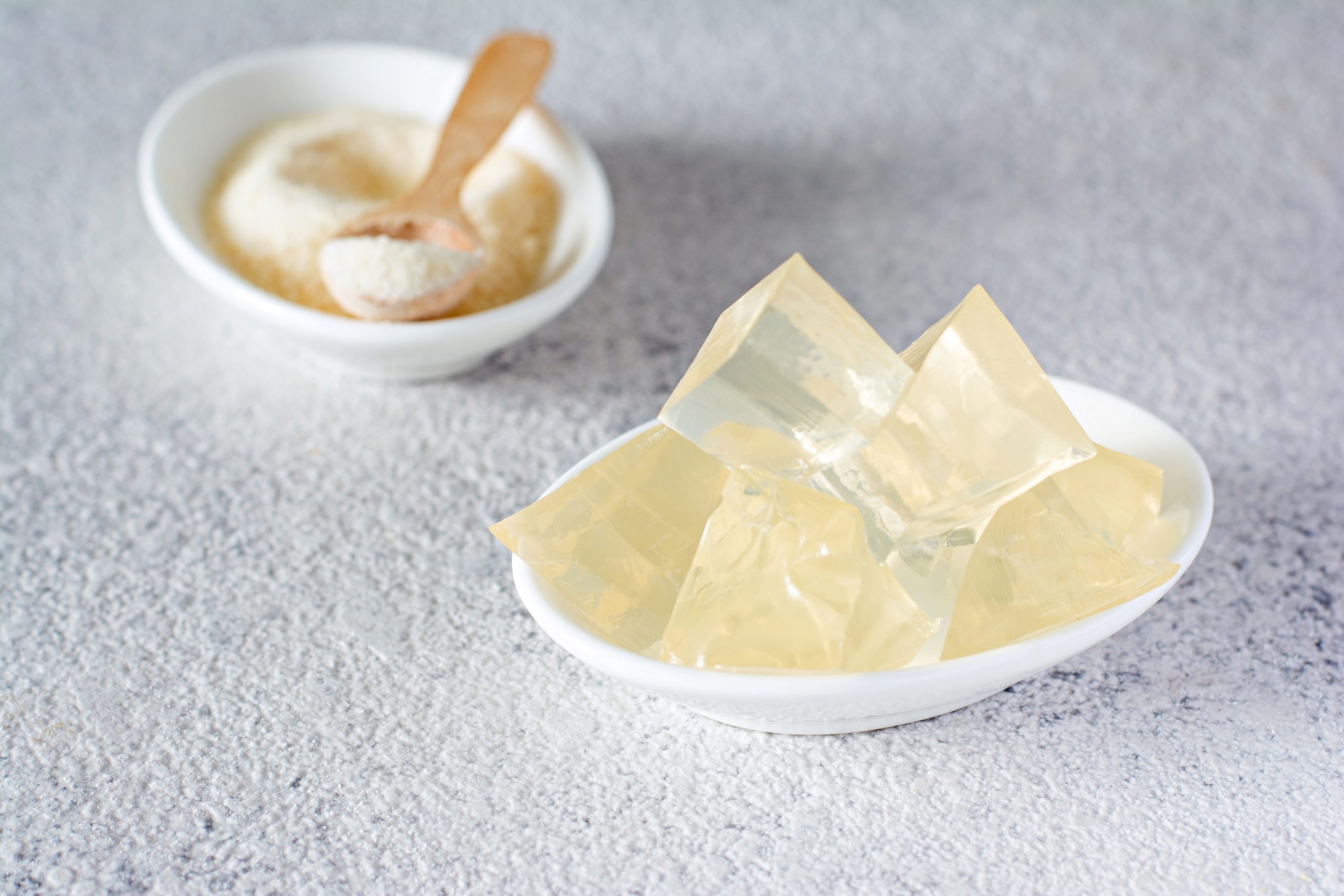
When it comes to vegan alternative plant-based sources, we always think about replacing meat and dairy. But have you ever thought of replacing food additives such as gelatine, an animal-derived ingredient? Agar-agar is emerging as a seaweed-based alternative. The appeal of agar-agar is that it doesn't need to be refrigerated and can stay at room temperature; it is insoluble in cold water and dissolves well in liquids at over 90° Celsius. You find it in powder format for most industrial applications. But agar-agar processing also delivers flakes or threads for food production.
Tell us about your production challenge
From sea to industry, through the gel press
The red seaweed is subjected to an extraction treatment to obtain the agar content after harvesting. The extract is then cooked, turning it into agar gel which can be used as a gelling agent in the food industry.
Although the traditional freezing method can accomplish the same task, you will need a gel press for dewatering. Finally, dry the agar-agar to get the flakes and grind them if you want them powdered.
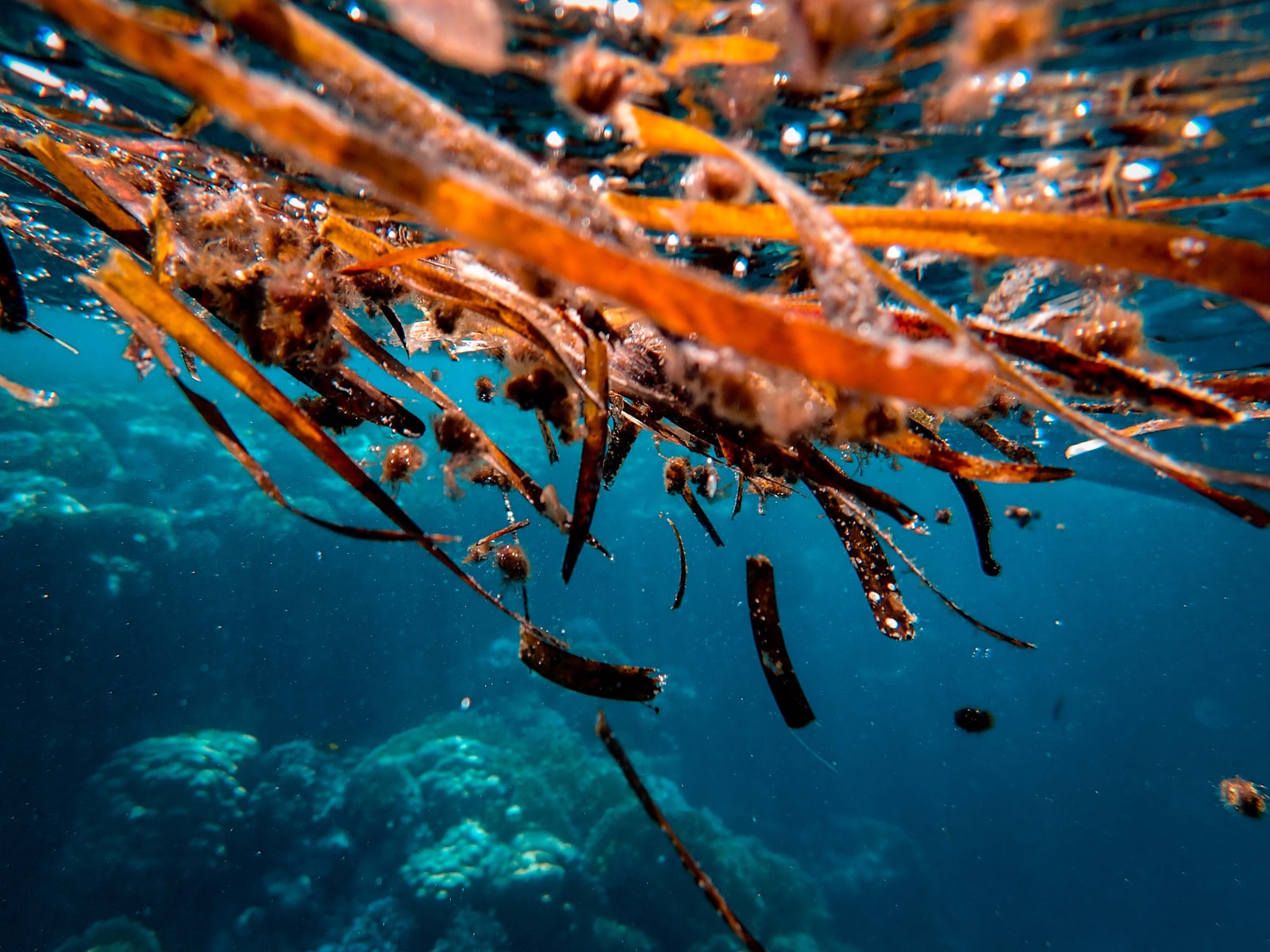

Climate conditions determine the quantity of agar-agar in red seaweeds
Agar is found in the cell walls of red algae from the Rhodophyceae class. The most common species are Gelidium and Gracilaria. These agarophyte seaweeds are typically harvested in the wild, although Gracilaria is also cultivated on a commercial scale in warm seawaters.
The content of agar in red seaweeds depends on the environmental conditions. Water temperature, oxygen, solar radiation intensity, and the concentration of carbon dioxide; all combined, increase or decrease agar levels in algae.
Agar-agar cultivation is in global bloom
A recent publication about aquaculture and fisheries (FAO, 2021) shows that in 2019, 3.6 million tonnes of Gracilaria were farmed. 3.4 million of this came from China. Indonesia, Chile, and Vietnam also boast large agar-agar processing industries.
Meanwhile, agar-agar farming is flourishing worldwide in countries including the Republic of Korea, Taiwan, Morocco, the Philippines, Brazil, Tunisia, and Spain.
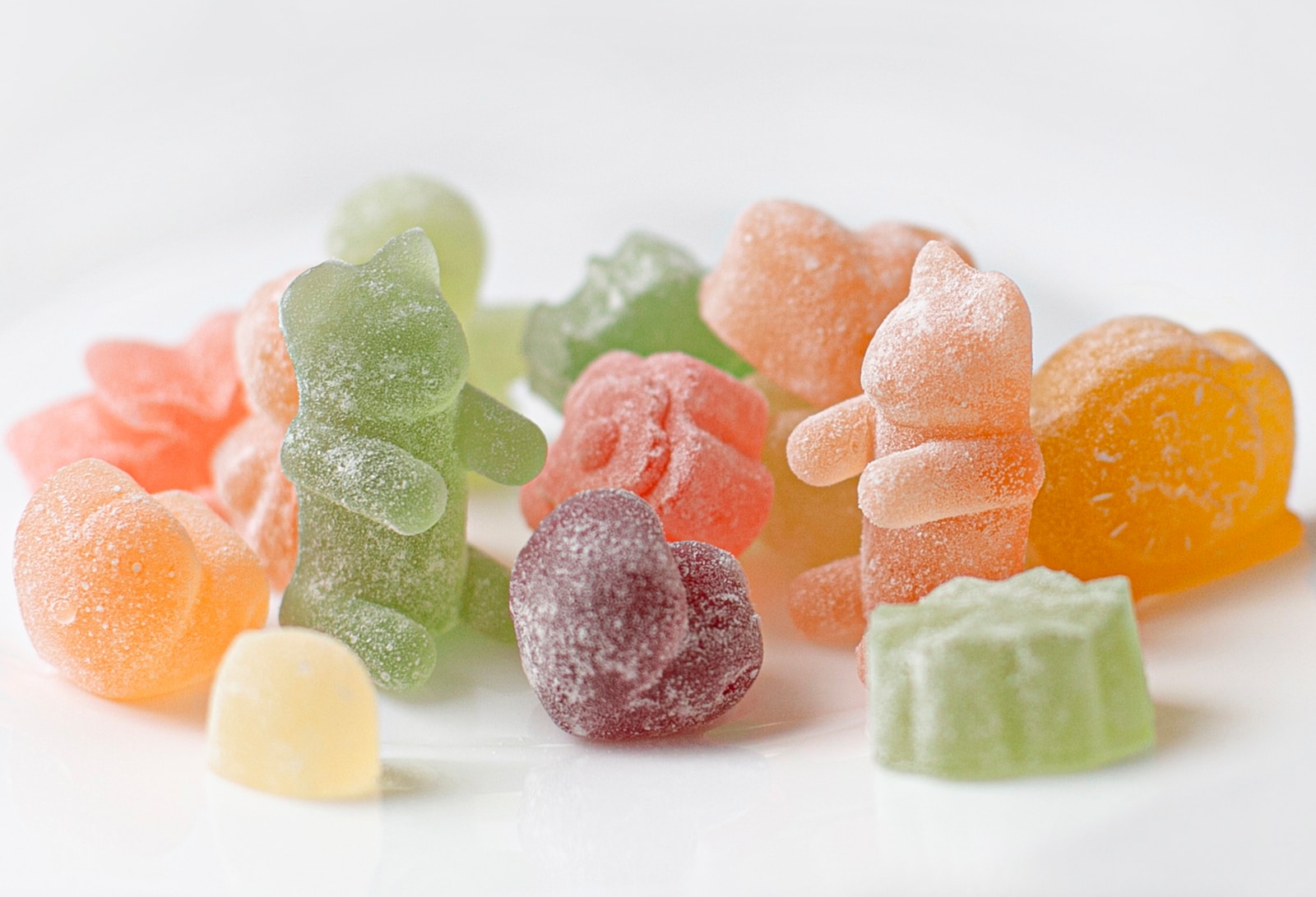

Applications of agar-agar go beyond food production
Using Agar is often applied in food preparations, replacing gelatin in products from gummies to ice cream. But it has broader applications in the manufacturing industry, such as culture media for plant tissues and microorganisms in petri dishes. As well as gels for molding dentures and fingerprints.
Manufacturing more soluble agar recipes that dissolves at temperatures below the water boiling point promises new applications in the future.
Integrate red seaweeds cultivation into aquaculture for sustainable processing
Harvesting red seaweeds in the wild has environmental and manufacturing implications. First, the agar content may be less than optimal since natural growing conditions are not controlled. Second, harvesting activities risk damaging underwater ecosystems.
To obtain an optimal agar content, Gracilaria species are being cultivated. Meanwhile, alternative cultivation methods may be explored to make agar-agar processing sustainable. For example, integrating seaweed farming into aquaculture leads to an efficient, economic, and environmentally responsible production system. This integrated multitrophic aquaculture (IMTA) system has successfully been applied in shrimp ponds to grow Gracilaria.
Processing steps involved in agar-agar making
Which agar-agar technology do you need?

Precast agarose gels for Dna electrophoresis
Achieve precise DNA separation and purification effortlessly with bufferless ...

Agitator bead mill for functional foods and flavors
Fine-grinding solid flavors to improve taste properties and integrati...
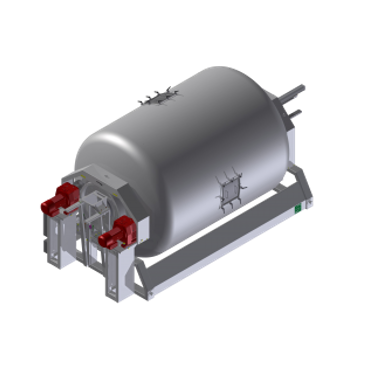
Gentle mixing solution for gelatin powder
The fragile nature of gelatin makes it a challenging material to blend homogeneo...
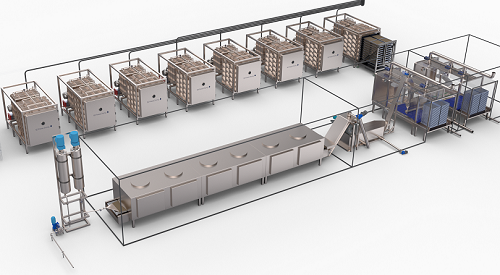
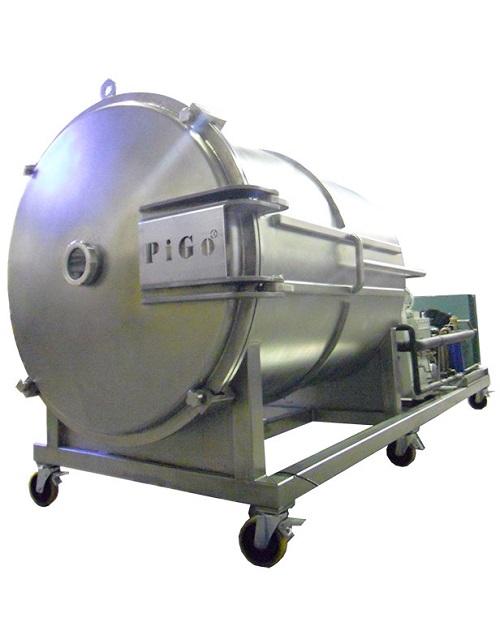
Automatic freeze drying system
Freeze drying can be an expensive and cumbersome process. When dealing with nutraceuticals it...
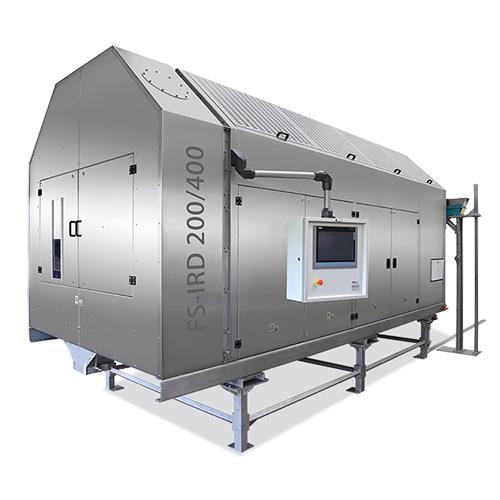

Infrared rotating drum dryer
Traditional drying methods are often slow and can actively damage ingredients, reducing the fin...
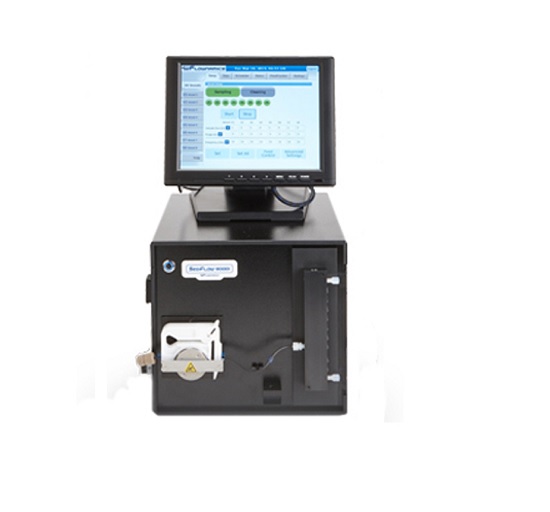

Online sampling system for larger scale bioprocesses
Accurate sampling is vital for improving a wide variety of industria...
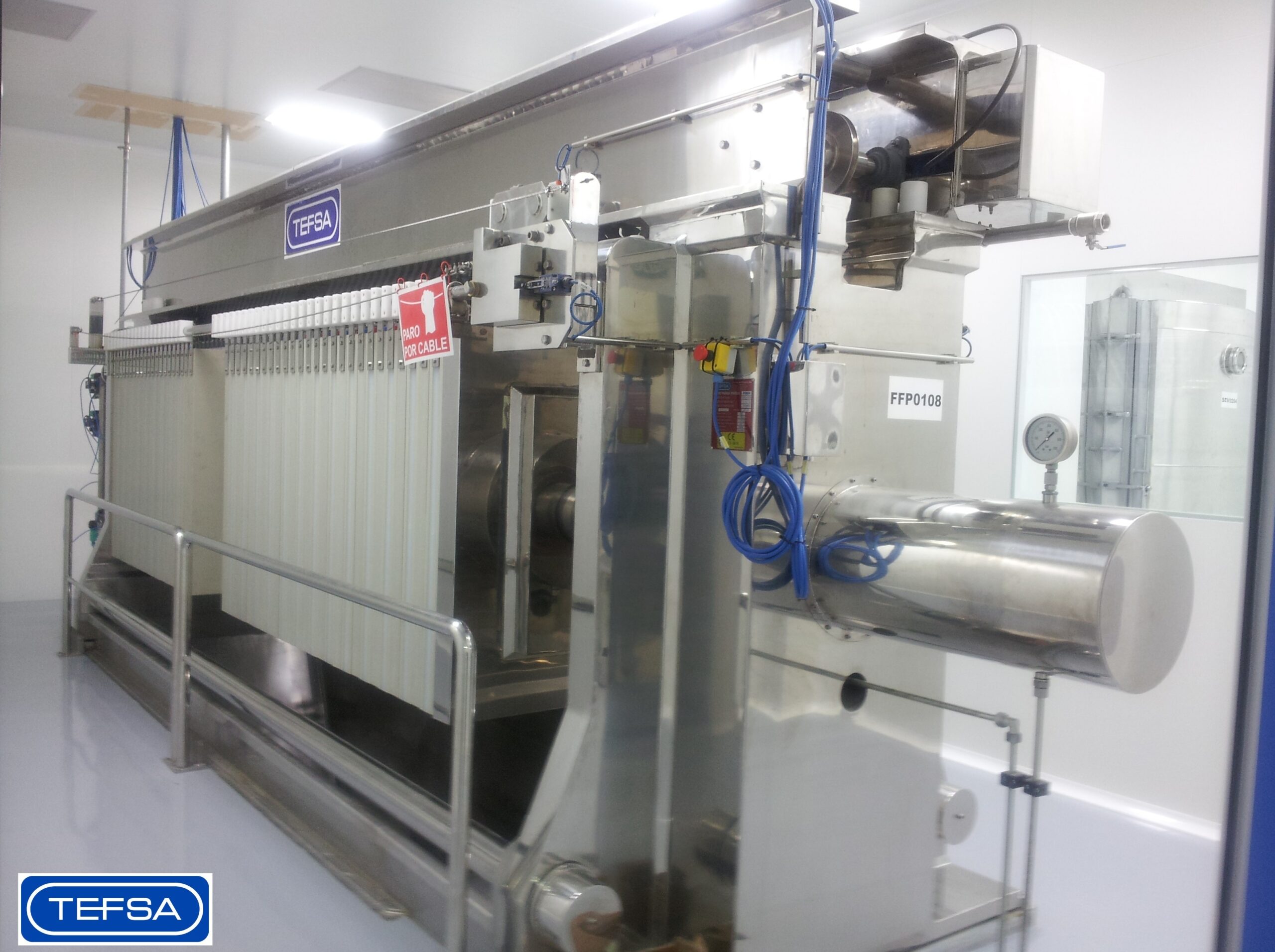

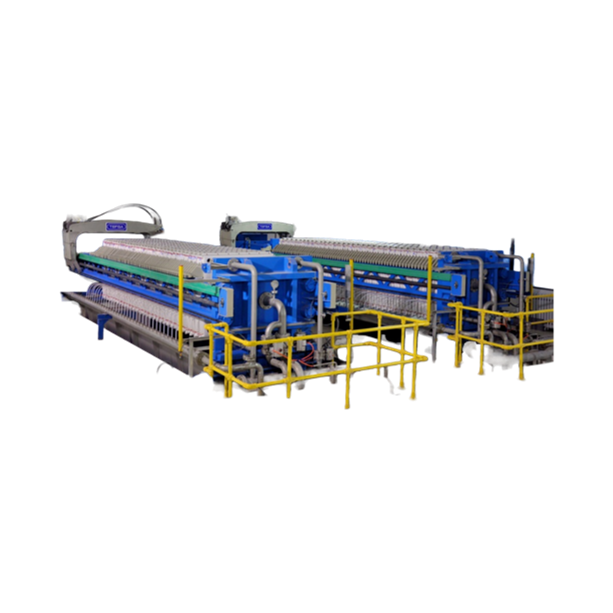
Hygienic filter press
Food and pharmaceutical plant managers need equipment designed for easy access to all components for cl...
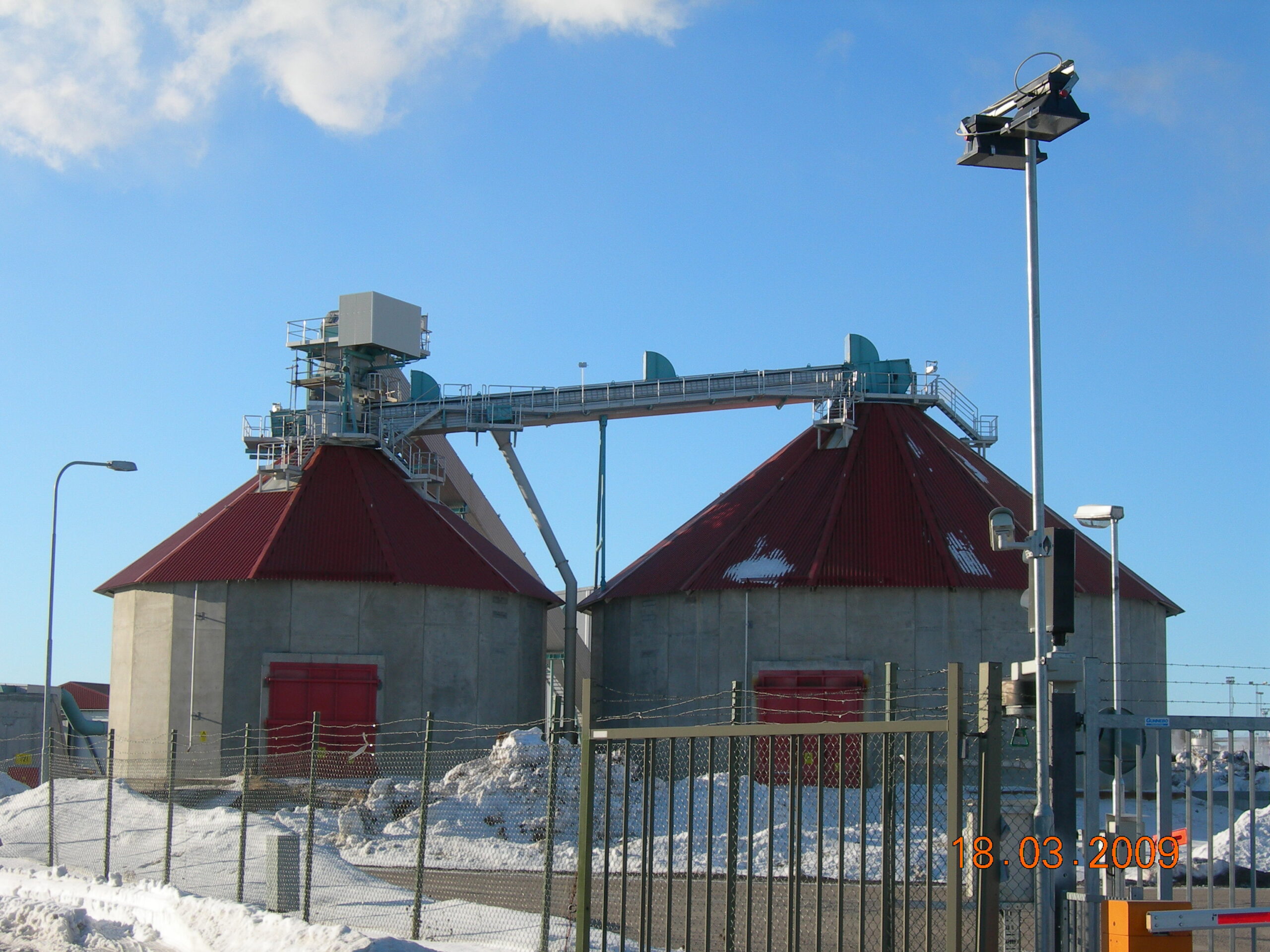

Solid biomass storage and reclaiming equipment
Biomass fuels must often be stored for additional preprocessing or prior to...










