Making Metal Powders
Find innovative production technology for making metal powder and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Forged metal objects appear seamless, simple items. But as the use of metals changed over time and constructions became more intricate with additive manufacturing, a new way of processing materials surfaced. Metal powder manufacturing replaces the classic blacksmithing techniques, reducing scrap waste in the meantime. The final metal products, however, retain that shiny allure of the archetypal metal pieces.
Select your metal powder process
Tell us about your production challenge
Atomize molten metal to produce powder metallurgy
Metals with low melting points such as aluminum, brass, and iron are atomized into powders. The technique disintegrates the metal into solid droplets.
Melt the metal feed in a furnace and lead it through the narrow opening of the atomizer to form a thin stream. A jet of air or water within the chamber subjects the liquid metal to high pressure, splitting it into drops. The rapid reduction of temperature solidifies the material into a fine powder.

Obtain spongy particles by reducing oxygen in the raw material
Although new manufacturing processes were developed since metal powder production emerged in the 1940s, the traditional method is still applied. Solid-state reduction involves mixing crushed metal with carbon and passing through a continuous furnace.
The heat reduces the oxygen and carbon in the mixture and leaves a sponge metal. Mill the remaining material and sieve it to produce a homogeneous powder size.
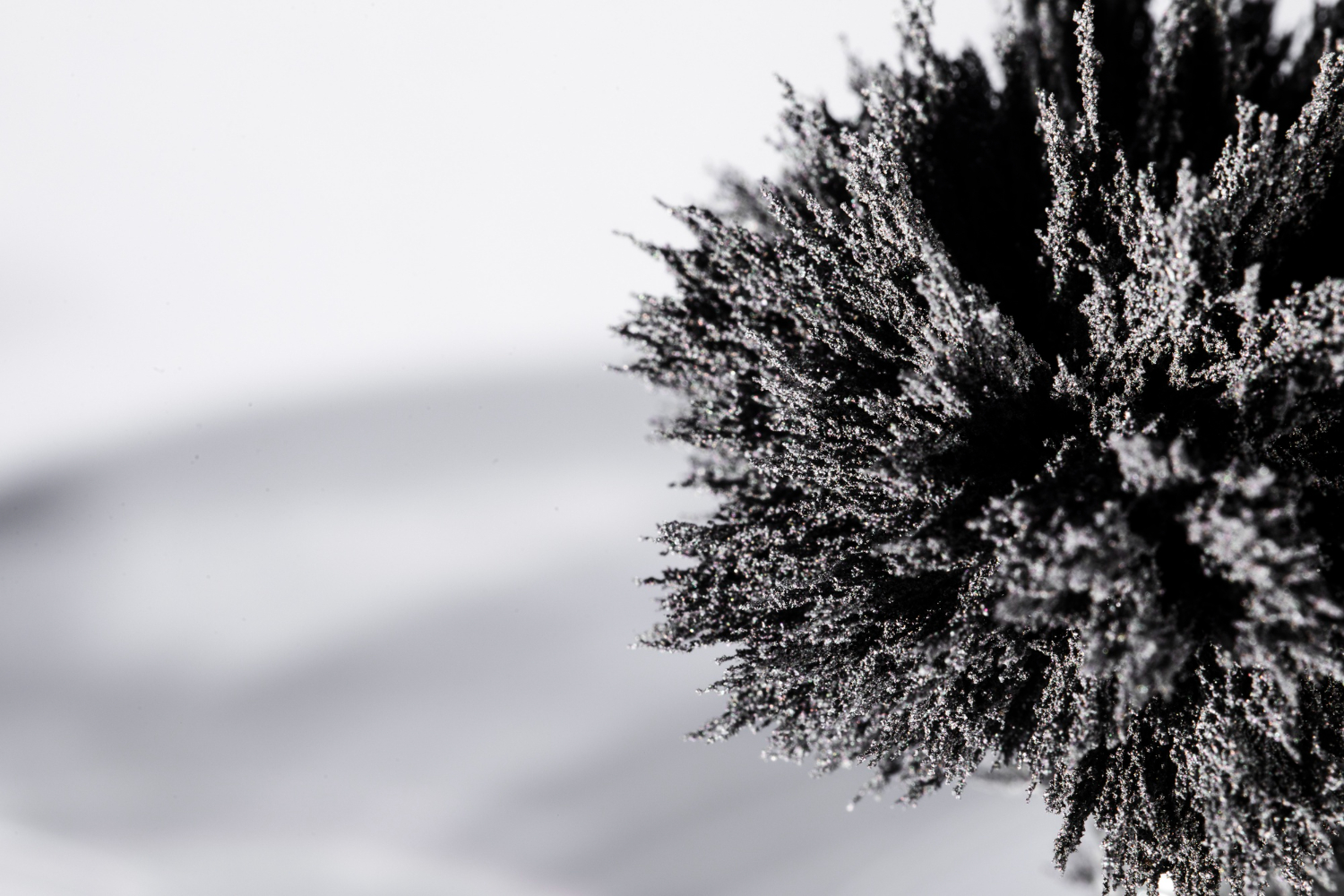

React metals with a chemical solution to increase purity
One of the main drawbacks of solid-state reduction is that it has a lower threshold for impurities. To raise the purity rate, treat the material with a chemical agent.
React with a reducing agent to strip the metal of its electrons and form highly-adherent porous particles. Grind the resulting material into a finer powder and anneal it to obtain metal powder purity of up to 99.5%. Purity is particularly crucial for new high-tech industries like lithium-ion battery manufacturing.
Complete metal powder manufacturing with sintering
Metal powder blends are delivered for fabrication in the form of briquettes. Blend the alloys and materials in a mixer to ensure a uniform particle distribution. Then compact the mixture at a temperature lower than the melting point of the metals.
A widespread technique is sintering. Heating the mixture allows the atoms to diffuse and bond with those from other particles. This process establishes the green strength of the block.
Processing steps involved in metal powder making
Which metal powder technology do you need?

Precision sieve shaker for particle size analysis
Achieve precise particle size separation with a sieve shaker designed f...

Sample divider for on-site reduction of bulk materials
Ensure consistent sample analysis with precise on-site material di...

Laser diffraction particle size analyzer
Achieve precise particle size analysis with laser diffraction technology, ensuring...
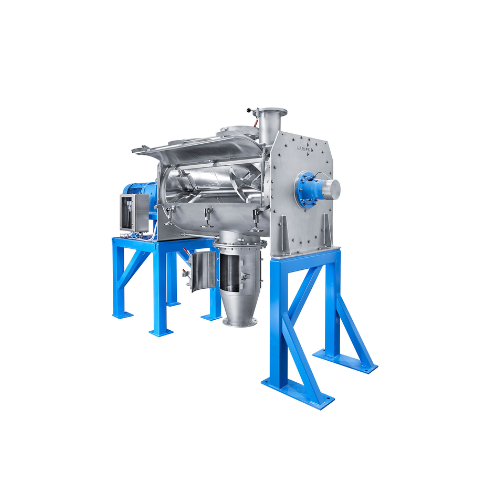

Ploughshare mixer for batch operation
Achieve superior mixing quality with a system designed for rapid batch operations. Ex...
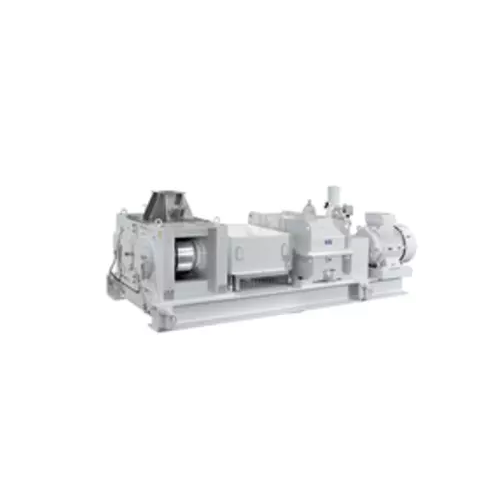

High pressure roller mill for medium-fine crushing
Achieve precision in particle size with high-pressure roller mills, id...
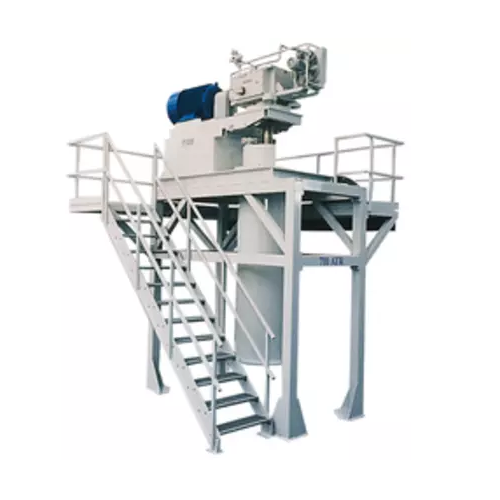

Ultra-fine grinding with ball mills and agitated media mills
Achieve precision in ultra-fine grinding for demanding mate...
Powder belt feeder for accurate powder metering
Achieve precise powder metering with a specialized feeder that maintains d...

Oxygen / nitrogen / hydrogen analyzers for inorganic samples
Quickly and accurately measure oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrog...

Vertical flash dryer for industrial drying applications
Optimize your production line with an energy-efficient vertical f...

Automated de-oiling centrifuge system for metalworking chips
Enhance metal recovery and efficiency with a de-oiling cent...

Synthesis gas cooler for partial oxidation of oil or natural gas
Optimize high-temperature gas streams efficiently by em...
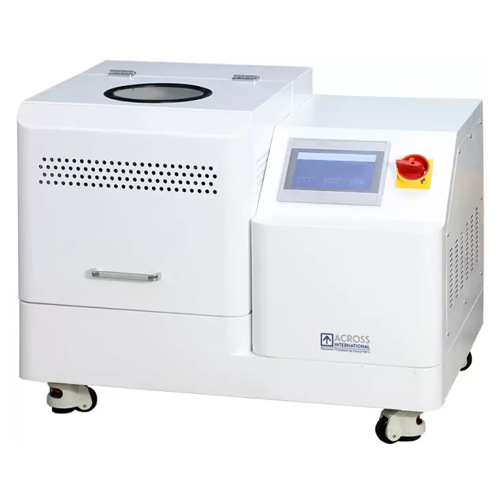

Planetary ball mill for powder material mixing and alloying
Achieve precise control in particle size reduction and homog...

High-temperature top-open tube furnace for laboratory applications
Achieve precise thermal processing with this high-te...
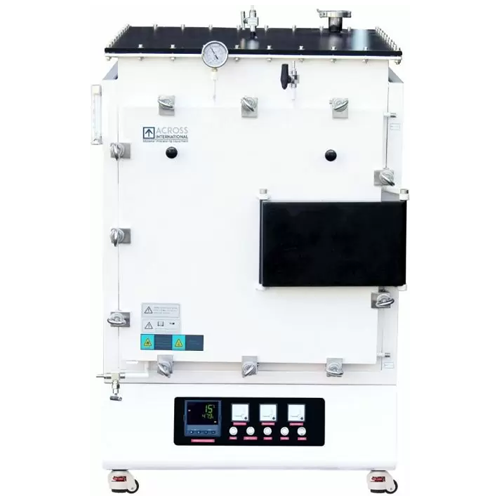

Controlled atmosphere muffle furnace
Achieve precise temperature and atmosphere control for critical processes like sinteri...
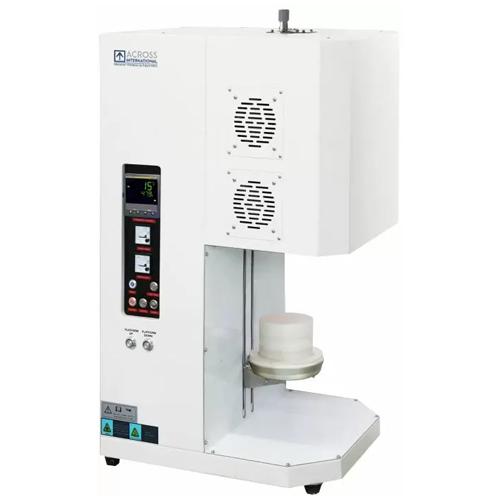

Table-top bottom loading furnace for high-temperature applications
For precise thermal processing and advanced experime...
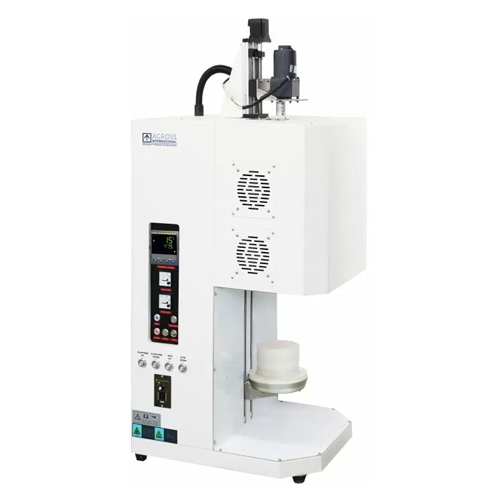

Table-top bottom loading furnace with stirring capability
Achieve precise thermal processing with controlled heating and...

1200°c benchtop muffle furnace
Ensure precise thermal processing and testing with this high-capacity benchtop furnace, ideal...

High-temperature tube furnace for laboratory applications
Achieve precise thermal treatment with this high-temperature t...

24-ton laboratory pellet press
Achieve precise pellet formation with reliable 24-ton pressing power, ideal for compaction of...

Controlled atmosphere top-open tube furnace
Achieve precise thermal processing and sintering with this versatile tube furn...
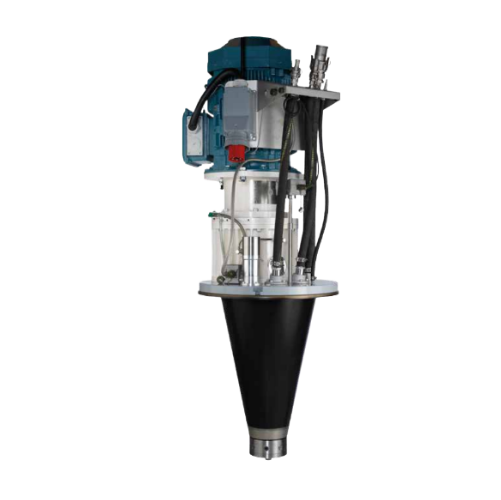

Spray drying evaporation for wastewater treatment
Achieve efficient zero liquid discharge with this spray drying evaporat...

High precision mixer for metallic powder paints
Achieve unparalleled precision and uniformity in producing high-gloss and ...
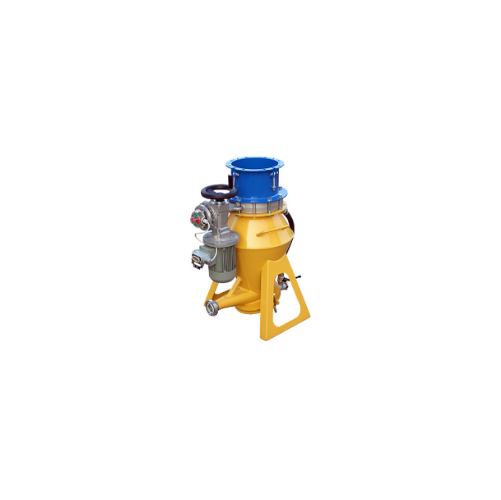

Butterfly valves for dry powder and granule flow interception
Ensure precise control over material flow in your processi...
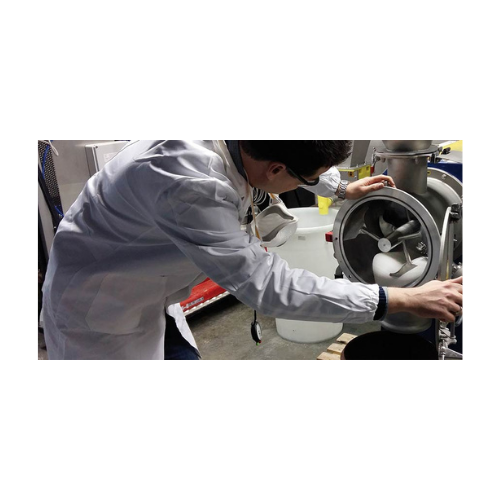

Laboratory batch mixer for small scale production
Achieve rapid and reproducible mixing results with this laboratory batc...

Closed powder handling loop for Eos metal Am printers
Effortlessly manage metal 3D printing powders with a solution that ...
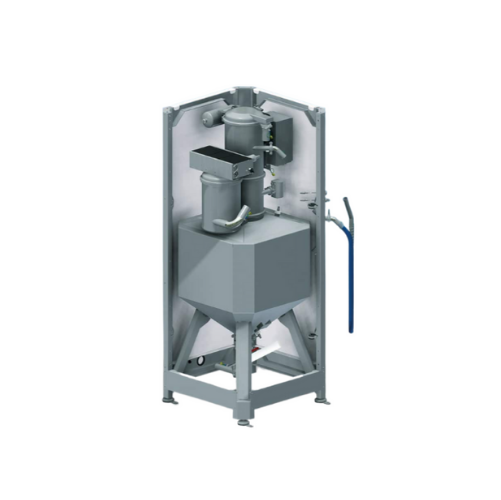

Metal powder buffer storage for additive manufacturing
Streamline your additive manufacturing workflow with our advanced ...
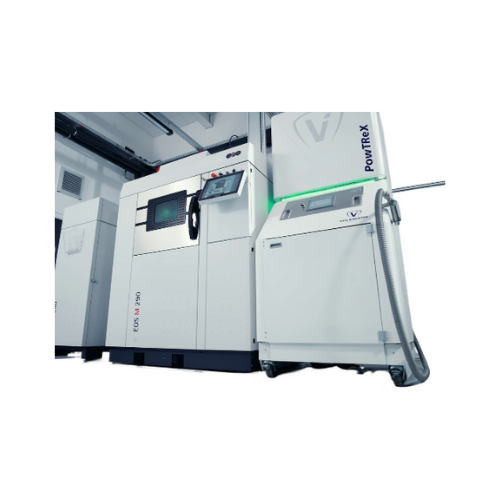

Metal powder recovery system after 3d printing
Effectively reclaim and purify metal powders after 3D printing to enhance c...
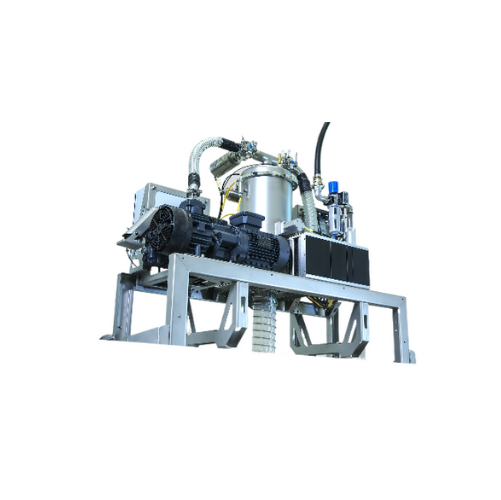

Automatic metal powder filling system for 3d printers
Ensure seamless operation of your 3D printing process with a system...
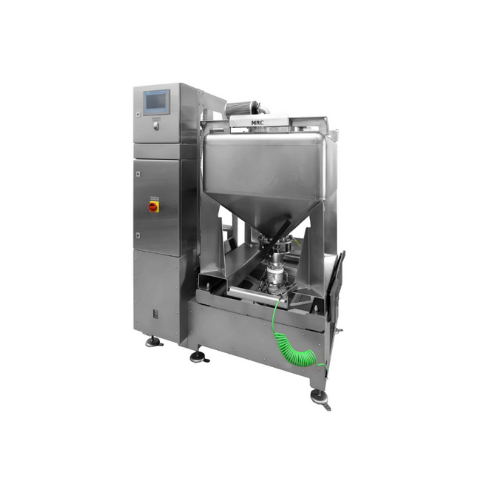

Docking station for intermediate bulk container (ibc)
Streamline your metal powder management by efficiently connecting a...
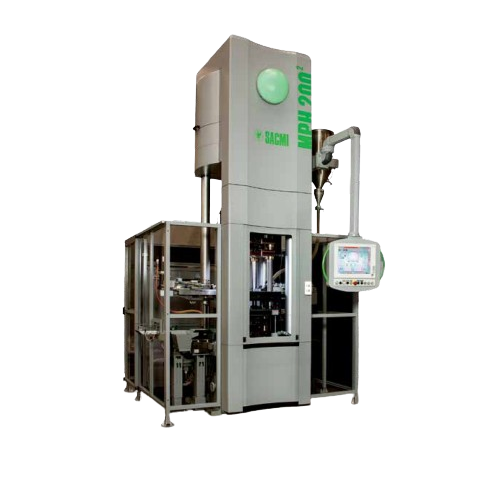

Presses and furnaces for metal powder components
Achieve precise forming and consistent quality in metal components produc...

High volume 3D shaker mixer for ceramics
Achieving consistent homogeneity and the logistics of handling and introducing lar...

R&D shaker mixer for battery powders and chemicals
Material heterogeneity, agglomeration, and contamination are key param...
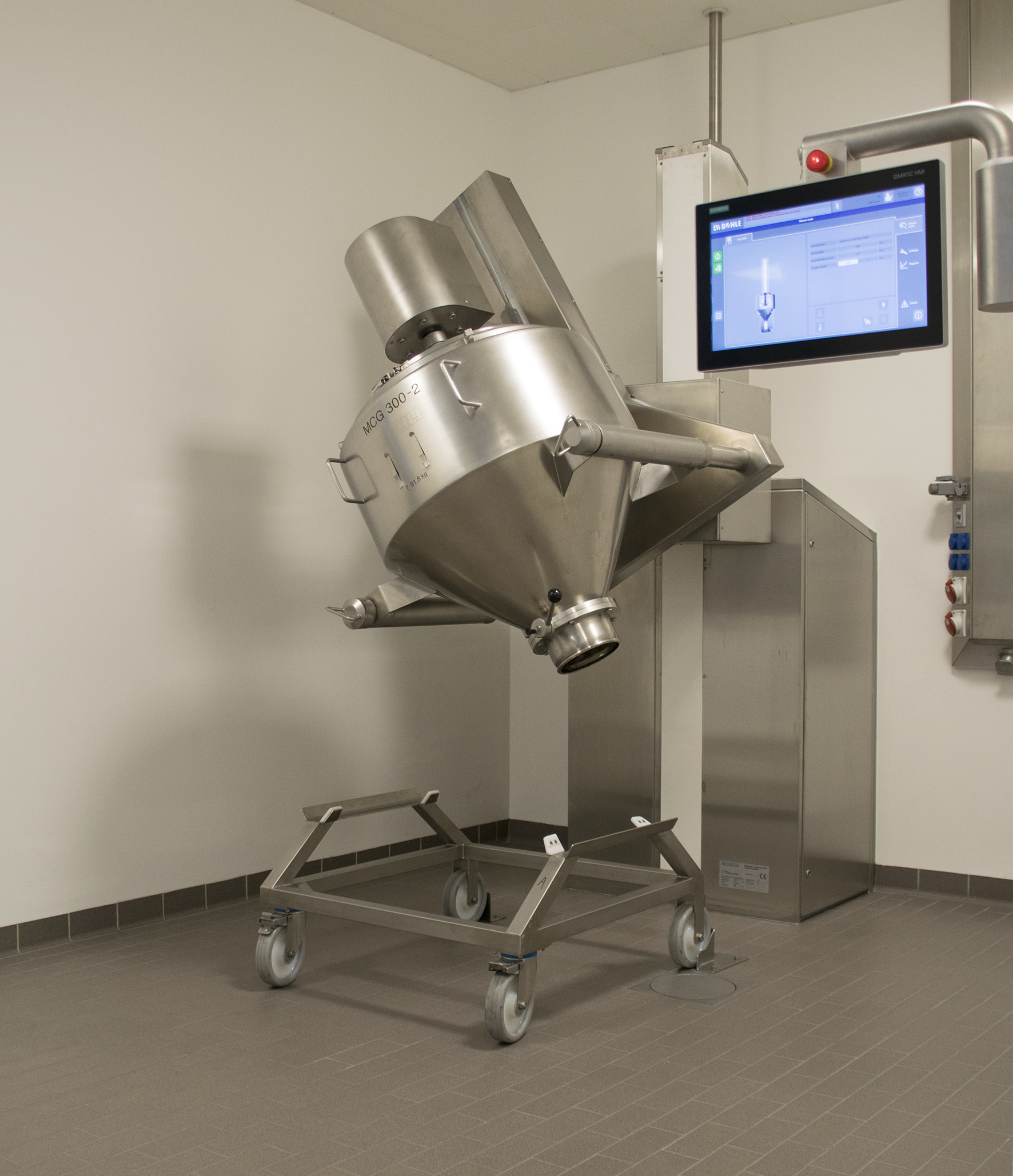

Container blender for pharmaceuticals
Manufacturing pharmaceutical solids like tablets requires using a proper blender to b...
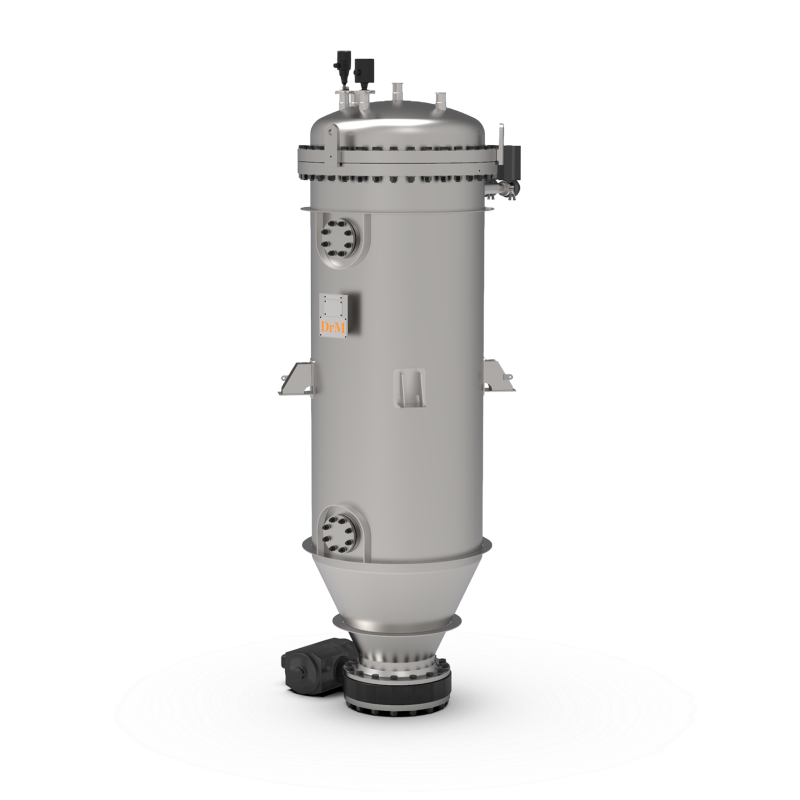

Self-cleaning candle filtration system
Separating solids from liquids by filtration requires frequent cleaning or replaceme...

Powder transfer system
Loading powder from a container source to vessels, tanks, or mixers that are under pressure may be haz...
Classifier mill for powder coating
High-quality powder coatings are often required to manufacture equipment, appliances, an...

Macro ingredient dosing system
Traditional dosing systems do not have a very long operational life and are hard and expensiv...
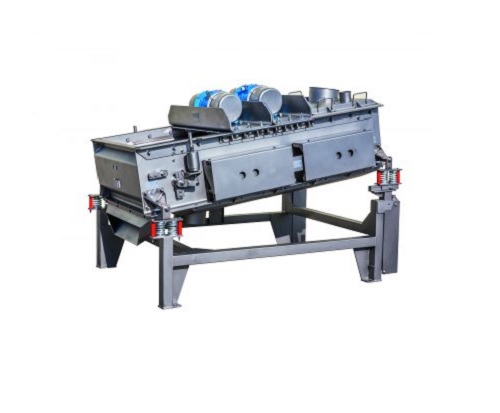

High volume particles separation sieve
For large scale production processes in the chemicals or food industries that requir...
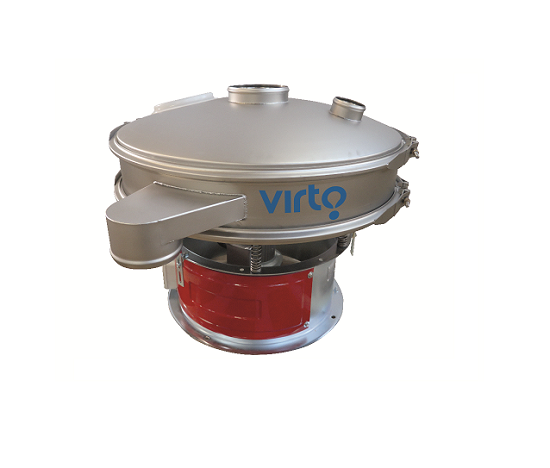

Vibrating sieve for liquid solid separation
Many industrial processes require the efficient separation of solids from a sl...
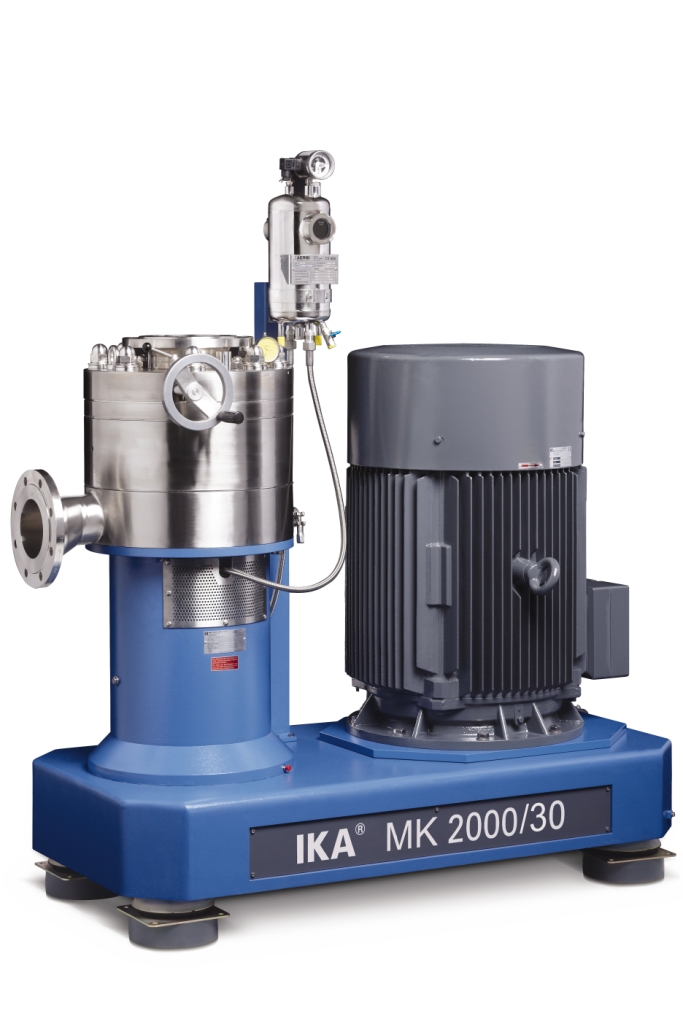

Colloid mill
For creating extremely fine emulsions and high quality dispersions a high pressure homogenizer is often chosen. ...
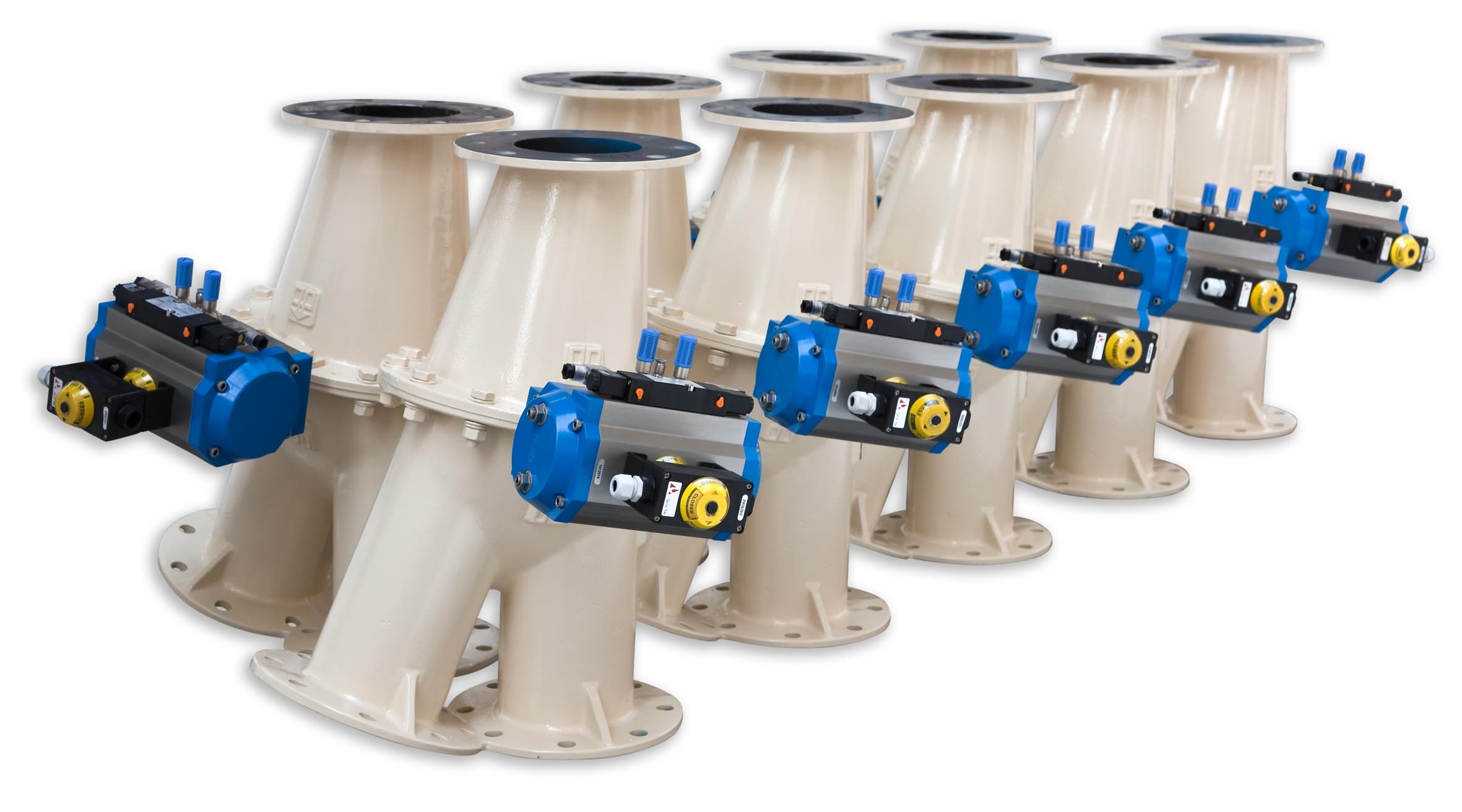

Two-way flap type diverter valve
Routing powder, pellets or granules from a product source to two receiving points must be d...
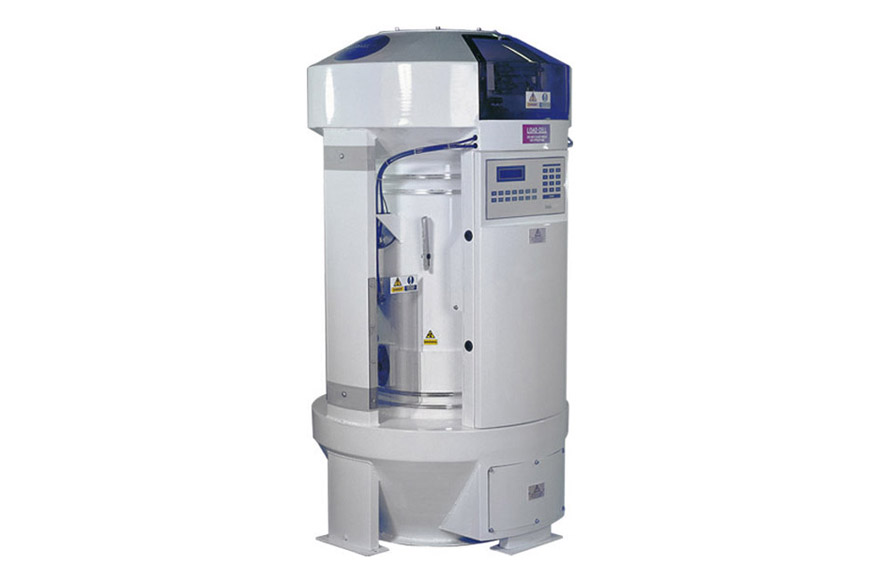

In-process weighing system for mills
When you need a throughput weigher for modern flour/grain milling applications, the we...
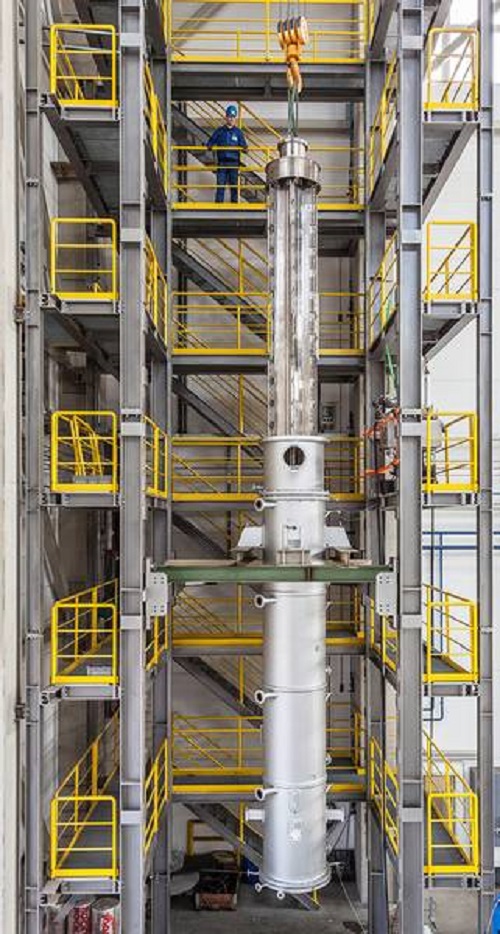

Thin film dryers
Dry dissolved or slurried crystallizing or amorphous products to a pourable powder.