Yeast Processing Equipment
Find innovative production technology for making yeast and connect directly with world-leading specialists
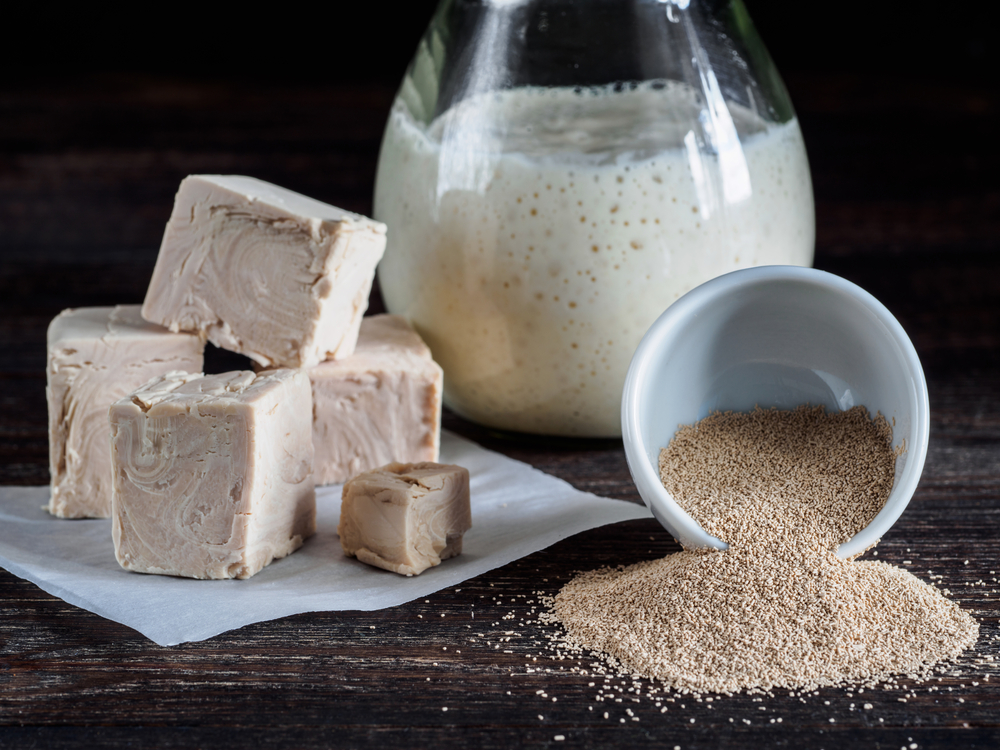
Ancient civilizations were using yeast as it naturally occurred in bread-making and brewing. But yeast processing equipment wasn't developed and fully commercialized until the end of the 18th century. Today, this industrialized micro-organism is critical in producing biofuels and other products beyond food and drinks.
Select your yeast process
Tell us about your production challenge
Yeast Production: Time and space in a controlled environment are important factors for yeast to grow
As yeast is a living micro-organism, you need time to feed it and space to let it grow. Its quality is affected by oxygen, microbes, temperature, pH, nutrients and other ingredients. Ensure a controlled environment where it can eat and grow while preserving its purity., through the different fermentation stages.
Begin the yeast propagation with a lab-scale start liquid culture and added molasses, then wait from 1 to 2 hours for the yeast to grow. Transfer your yeast to an industrial scale fermentation tank and add more molasses, aeration, and nutrients so it can eat and grow as the size of the tank. Yeast will eat everything and grow in between 3 to 4 hours in each stage. It will take about a week to grow from 10 mg to 150 tons.

Centrifuge your liquid culture to produce cream yeast
To obtain liquid cream yeast, you need a centrifuge to separate the biomass from the culture medium. But yeast processing can go further. Using a vacuum filter to compress the yeast and drain the liquid, you make a fresh yeast paste. When passed through an extruder, the paste and a cutter can be turned into blocks. If you want to make dry yeast, take the extruded paste into a fluid bed dryer.
In this further processing, you need to add oils and emulsifiers. Oils help the yeast pass through the openings of the extruder and other yeast processing equipment. Emulsifiers help to texturize the yeast and facilitate rehydration. Refrigerate the cream yeast, and the blocks and vacuum pack your dry yeast to preserve its shelf life.
Yeast processing equipment in biotechnological industrial development
Yeast processing is also called yeast biotechnology because its applications in the food and beverage sector are signaled as the primary stage of the biotechnological industry.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the yeast of choice for baking, brewing, winemaking, and more recently for producing biofuels, probiotics, and vitamins. Biotechnologists are using conventional and non-conventional yeast, different from S. cerevisiae, to explore new applications in biofuels, recombinant proteins, enzymes, derived compounds, and others. What would you be making?
Processing steps involved in yeast making
Which yeast technology do you need?

Cylindrical-conical tanks for yeast propagation in wine and grape juice
Optimize your fermentation process with efficie...

Wrap-around cartoning solution for butter and yeast
Optimize your packaging line with a high-speed cartoning system that ...

Pulsed electric field system for olive oil processing
Enhance extraction efficiency and product quality with this advance...

Modular pulsed electric field system for food processing
Enhance your food processing efficiency with a modular system th...

High solids crossflow filter for beer sediment removal
Achieve high-quality, sediment-free beer with minimal oxygen uptak...
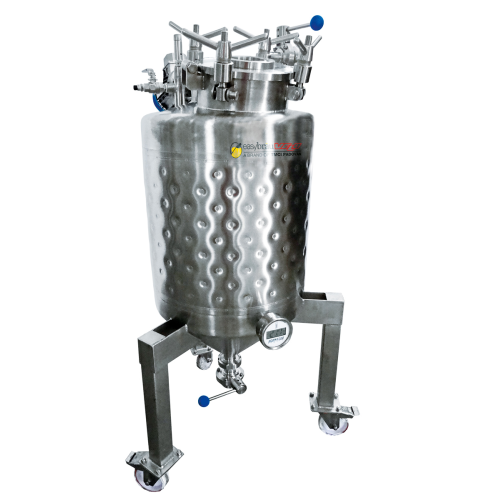

Yeast rehydration system for beer brewing
Optimize your beer production with a mobile, single-block system that automates ...
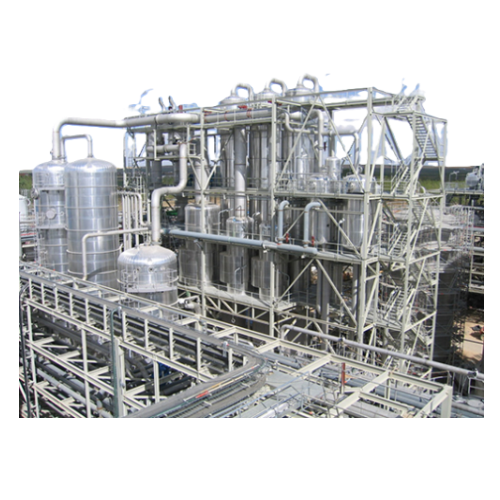

Industrial evaporators for diverse applications
Maximize energy efficiency and reduce operational costs with cutting-edge ...
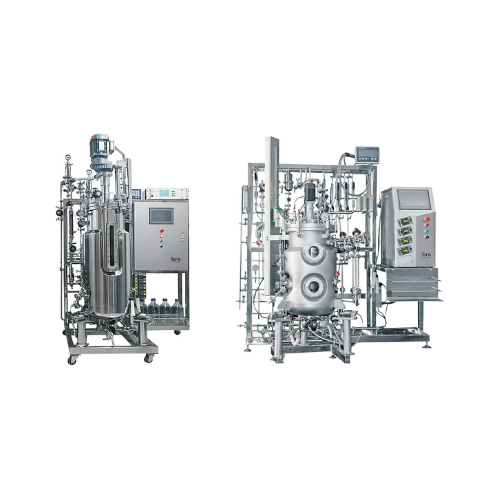

Industrial fermentors for large-scale bioprocessing
Enhance yield and consistency in fermentation processes with precise ...
Contact drum dryer for industrial food and chemical processing
Optimize your drying process with a contact drum dryer th...

Fluidized bed spray granulators for liquid to solid conversion
Transform liquid suspensions into stable, dust-free granu...

Yeast centrifuge separator for pharmaceutical applications
Optimize microorganism recovery with high purity and efficien...

Centrifuge separator for food and beverage clarification
Ensure high efficiency and minimal product loss in your producti...

Industrial fermentation separator with nozzle bowl
Optimize your industrial fermentation process with advanced separation...

Hygienic centrifugal pump for beverage applications
Ensure gentle handling and efficient transfer of sensitive liquids wi...

Hygienic pump for beverage and pharmaceutical industries
Engineered to meet stringent hygiene demands, this versatile pum...

Centrifugal pumps for hygienic applications
Ensure precise liquid handling for high-stakes applications with this hygienic...

Yeast management for brewing high-quality beer
Ensure consistent beer quality and optimize your brewing process with advan...
Spray drying system for heat sensitive products
For heat-sensitive products requiring precision drying, this spray drying ...

Brick forming and wrapping system for food products
Optimize your production line with seamless forming and wrapping of v...
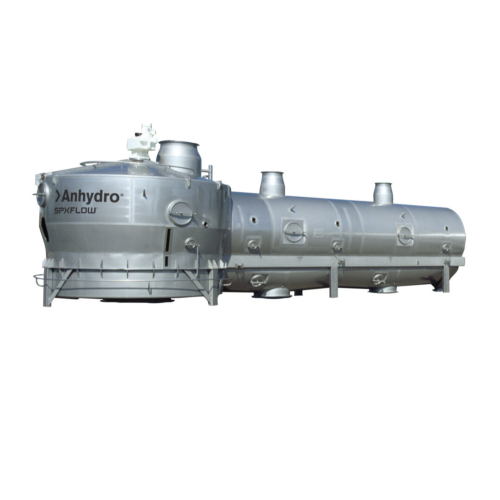

Industrial fluid bed dryers for powder processing
Enhance moisture control and uniformity in powder products with dynamic...
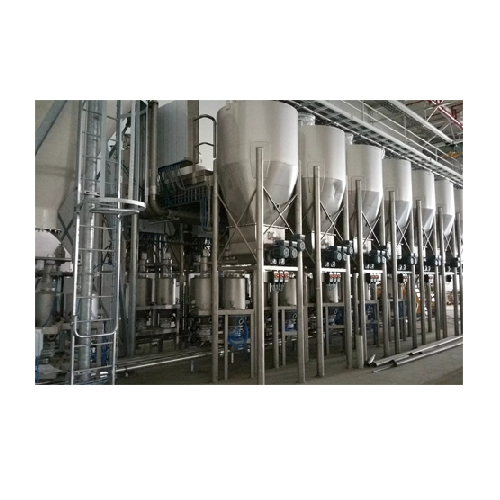

Industrial storage silos for food ingredients
Optimize your food processing operation with robust storage solutions that s...

Flexible laboratory bead mill for vaccines
For precise, efficient, and reproducible cell disruption, optimization of proce...

Sterile Filtration System for GMP-grade products
Processing equipment used in industries regulated by GMP must ensure full...
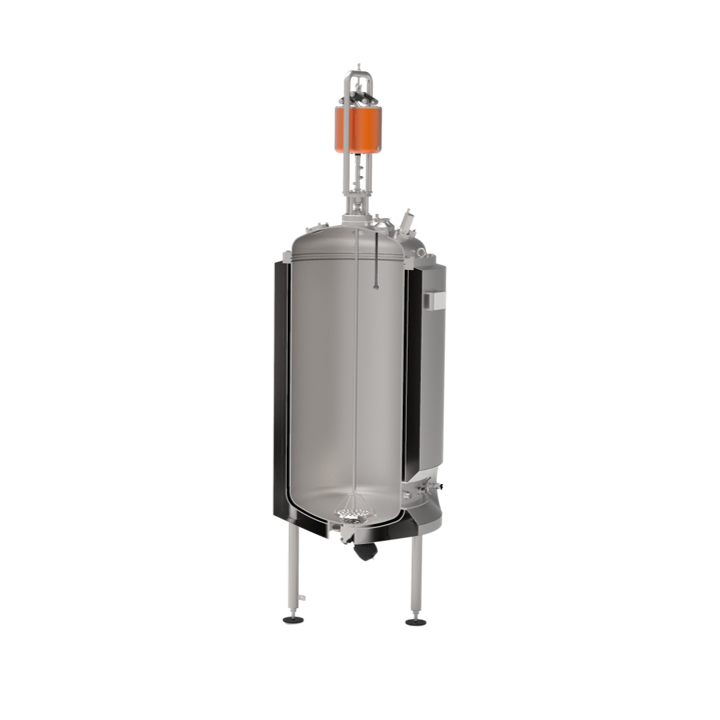

High-frequency vibratory mixer
Mixing liquid products by stirring method generates heat from friction and shear forces. This...
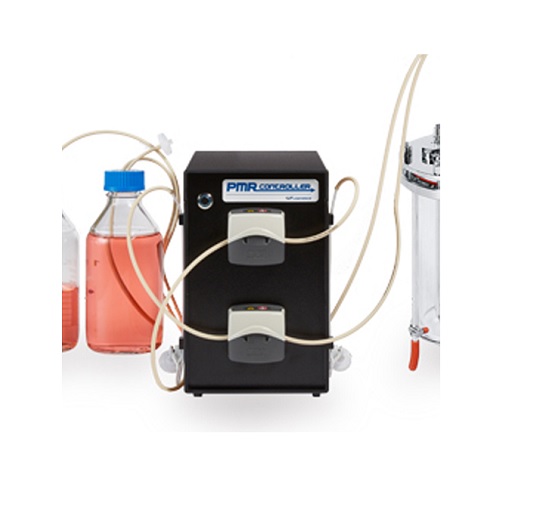

Perfusion process controller
Advanced biopharmaceutical and lab systems involving microcarrier and stem cell applications re...
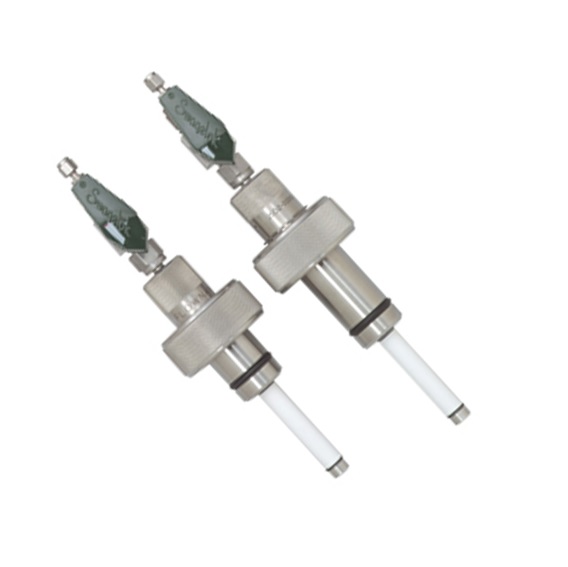

Sampling probe suitable for fermenter samples
Accurate, sterile sample collection is vital across a range of biopharmaceut...
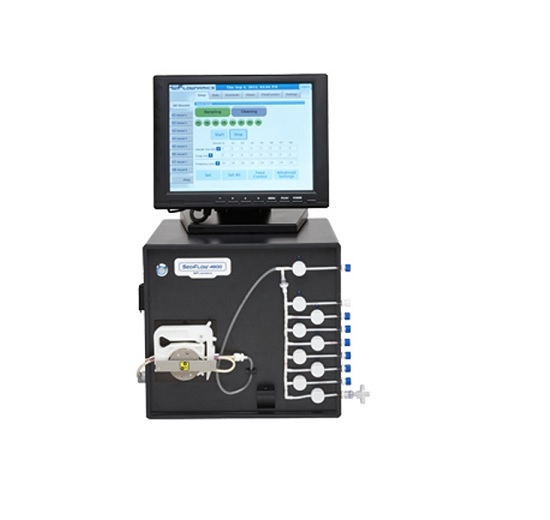

Automatic sampling system for bioprocess monitoring
An accurate, automated sampling of cultures is a key requirement in t...
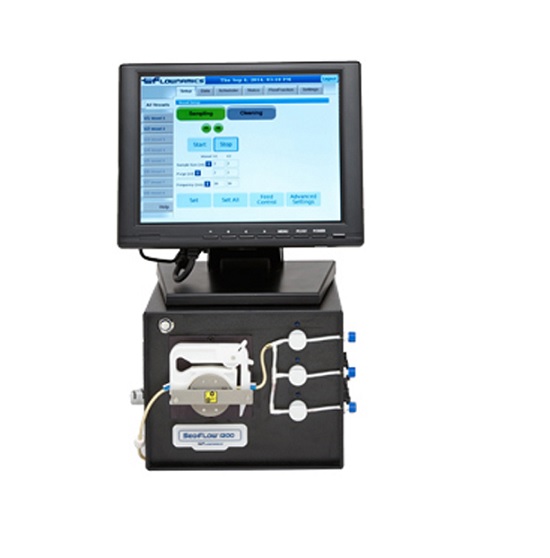

Entry-level automated online sampling system
An accurate and sterile sampling of cultures is vital throughout the biopharm...
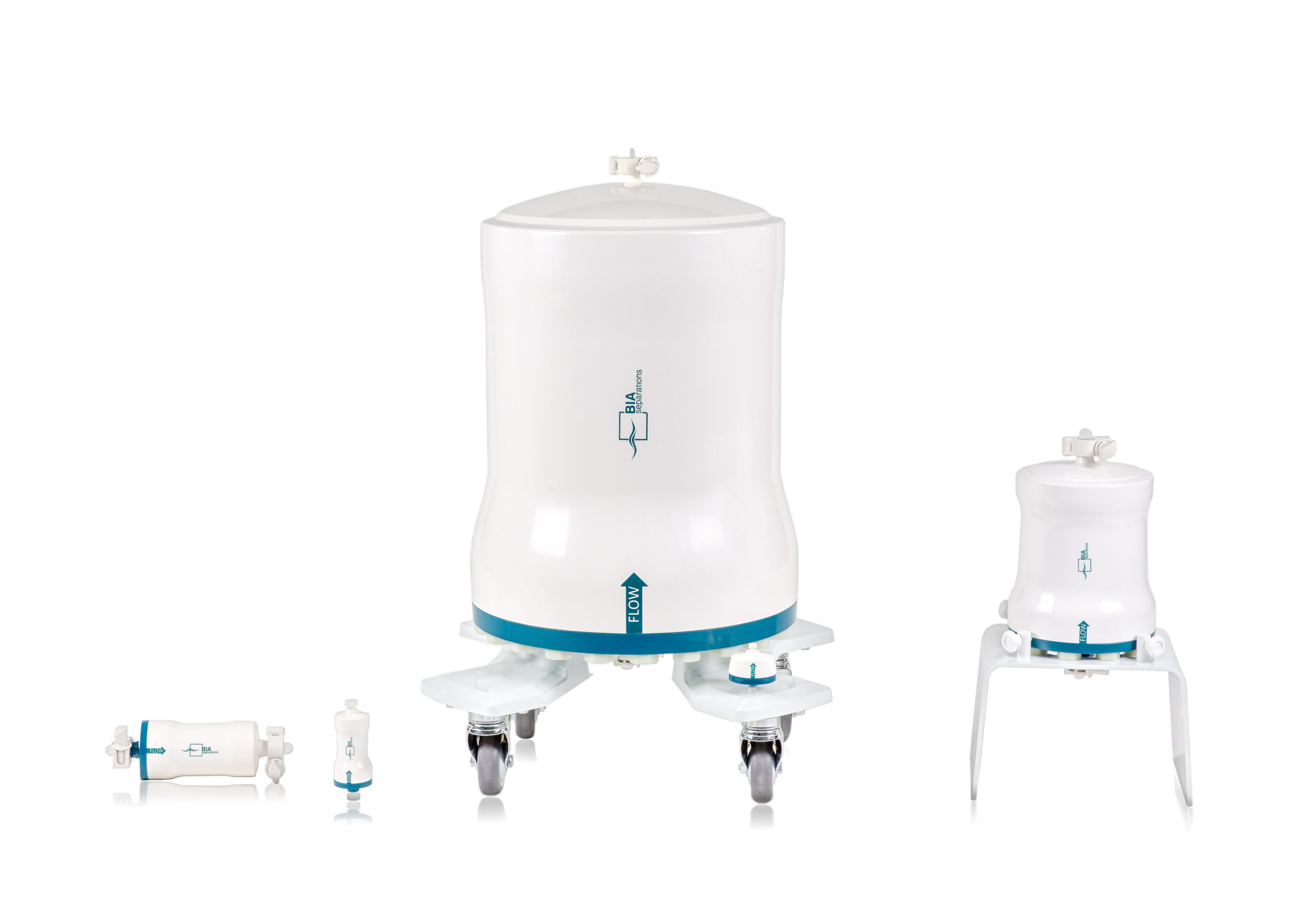

Disposable monolithic columns
Chromatographic monolithic columns for working with large proteins, viruses, VLPs and pDNA req...
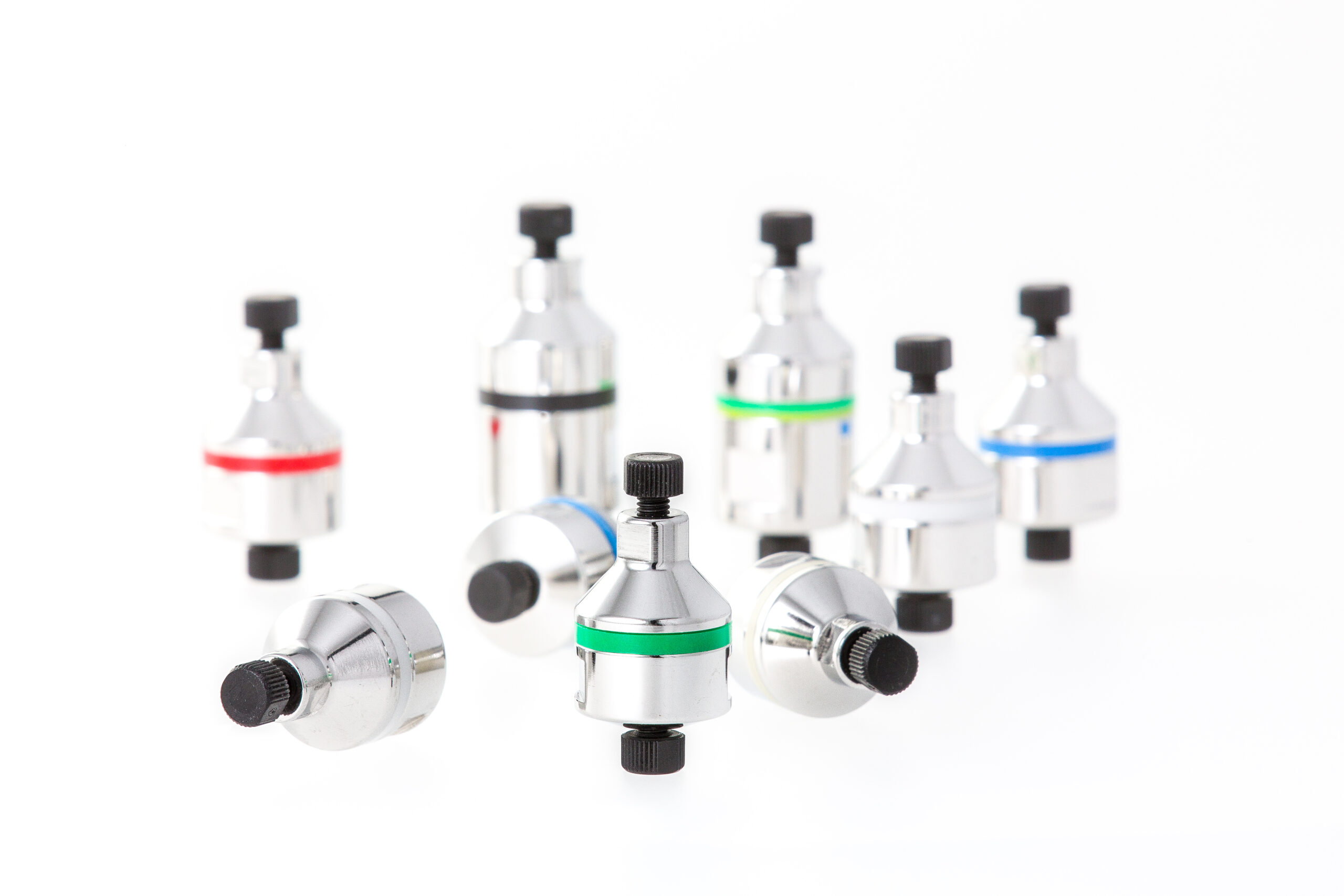

Short bed monolithic columns for analytics
Samples taken at various process steps need to be analysed quickly and accurate...
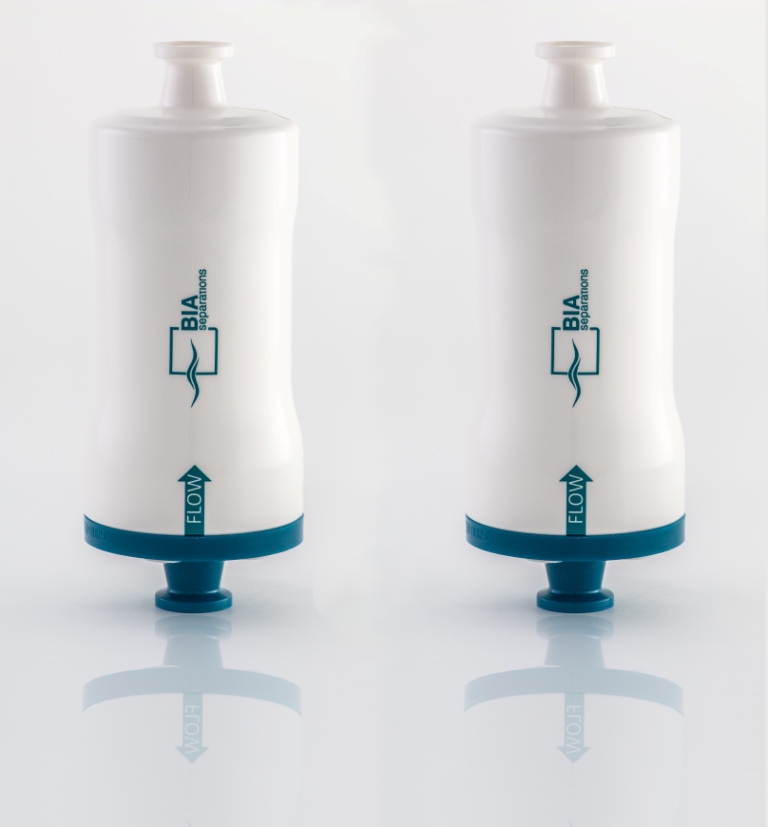

Plasmid process pack for your pDNA purification process
When developing a pDNA purification process for eventual transfer...
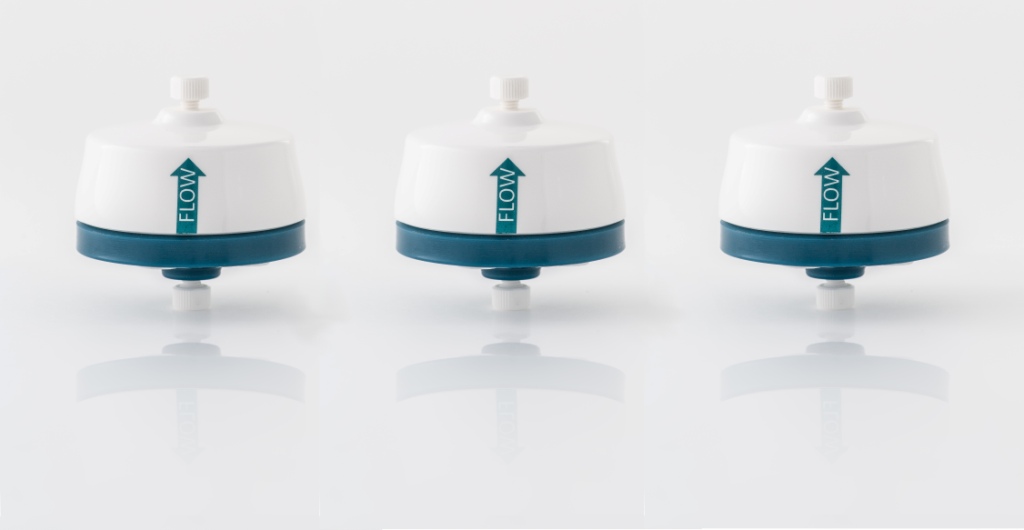

Purification screening kit for large biomolecules
To purify a specific large biomolecule, for example IgM or a virus or v...
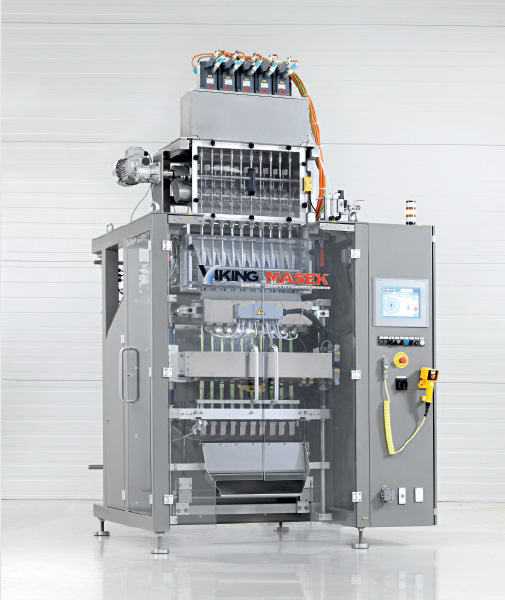

Stickpack Machine
If you are looking to pack your product into stick packs from 17 x 40 mm to 100 x 200 mm in size, you may b...