Paper Pulp Making Equipment
Find innovative production technology for making paper pulp and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Few inventions in the history of civilizations have been as pervasive and impactful as that of paper, some 2,000 years ago. But the sheets used in documents just a few centuries ago seem like a different material compared with the paper products of our times. The refined stock that makes anything from egg trays and tissue paper to diaper linings needed other inventions to come about. These innovations are their own class of process equipment: paper pulp manufacturing technology.
Stories about paper pulp
Tell us about your production challenge
Grade the wood chips into even sizes
Paper pulp is derived from wood cores obtained from harvested forest products. Timber-based pulp can be produced from all kinds of heartwood and sapwood, but coniferous trees like pines, firs, and spruce contain longer fibers.
Start by debarking the wood and chipping the core material. Use specialized shredding technology for paper pulp to grade your final wood chips to a consistent size. Uniform chips facilitate a homogeneous separation process that translates into higher-quality paper.

Separate cellulose fibers from lignin to obtain the pulp
Half of the mass of chipped wood is water. The other half is divided mainly between cellulose fiber and lignin. All of which get processed in a blender.
Lignin serves a vital function in holding the cellulose fibers together in the tree. But for papermaking purposes, the fibers need to be loose. Paper pulp equipment is precisely designed to separate cellulose fibers from lignin.

Digesters are critical manufacturing technology for chemical paper pulping
A method of removing lignin involves cooking the wood chip slurry in a digester. The paper pulp process subjects the raw pulp to heat pressure, typically using steam. Add an alkaline solution to dissolve the lignin while the mixture is heating up.
Known as ‘white liquor’, this solution is formulated from chemicals like sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide that react with the lignin and break it down. Conventional digester systems operate batch processing, but continuous solutions have become more widely available.
Recover cooking chemicals with the Kraft paper pulp method
A variant of this chemical process is called the Kraft technique and is suitable for high-strength paper and board products, often used for packaging applications.
Kraft pulping recovers the cooking chemicals and the dissolved lignin as black liquor. Evaporate the water to turn the mixture into a green liquor, leaving behind the base chemicals. Treated with lime, the ingredients may be reused as white liquor in a new cycle of chemical pulping.

Add limited chemicals to prepare wood for mechanical abrasion
Besides chemical pulping, wood chips may also be defibrated mechanically. The raw pulp is pressed against rotating disks at atmospheric temperature, separating the cellulose fibers by abrasion.
Although primarily mechanical, this technique may incorporate thermal or chemical processes to soften the wood. Thermomechanical pulping injects pressurized steam to force out the lignin, while the chemi-mechanical process introduces additives to enhance the hydrophilic properties of the fibers.

Bleach away the lignin residues after the pulping process
Neither chemical nor mechanical separation processes remove all lignin content from the raw pulp. To obtain free fibers, the pulped material is bleached with chemicals to transform lignin into an alkali-soluble form.
The use of chlorine in the paper industry, for this purpose, was traditionally widespread. But modern paper mills employ total chlorine-free (TCF) bleaching methods using oxygen and alternative chemicals.
Correct the color of the material if it’s manufactured for print quality
Mechanical paper pulping forms strong bonds between the fibers, producing crisper paper products. However, the natural color range is grey to brown. Bleaching the processed pulp adds whiteness and brilliance to produce printing-grade paper and boards.
If the final product is intended for applications that do not require high brightness, such as cartridge paper for newsprint, you may forgo the bleaching process.

Bring water content down to 10% with industrial drying solutions
At every step of the way, the paper pulp is washed with water to remove any impurities. In the end, the cellulose material forms a wet web with excess water content.
There are several techniques for drying the moisture down to 90% fiber and 10% water. Standard drying techniques include drum dryers, fluidized-bed driers, and flash driers. Each method is suitable for different production parameters such as capacity and product type.

Apply superheated steam drying systems for fully sterile results
Conventional drying equipment does a job for generalist products like cardboard or paper bags. More delicate paper materials, however, such as those used for sanitary purposes or food products, demand stricter hygiene processes.
Superheated steam dryers keep the slurry away from direct heat. The technology treats the slurry with superheated steam that instantly vaporizes water molecules trapped in the pores of the wet web. This solution generates no smells or tastes, producing a dry, sterilized pulp ready for the most demanding applications.
Paper pulp processing from recycled materials
Besides fresh sawdust or wood chips, paper pulp may be sourced from existing paper products. The process converts used paper and board back to cellulose fibers.
Separate the collected material into a clean stock and mix it with water into a slurry. Specialized paper pulp processing technology (a repulper) separates the fibers into individual strands. Rewash the final product to remove residues, and remove the water content with an industrial dryer.
Processing steps involved in paper pulp making
Which paper pulp technology do you need?
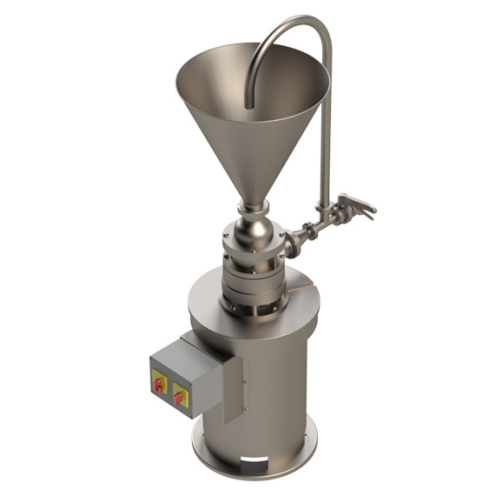

Perforated disc mill for pre-comminution and mashing
Achieve precise granulating and mashing of diverse materials with th...
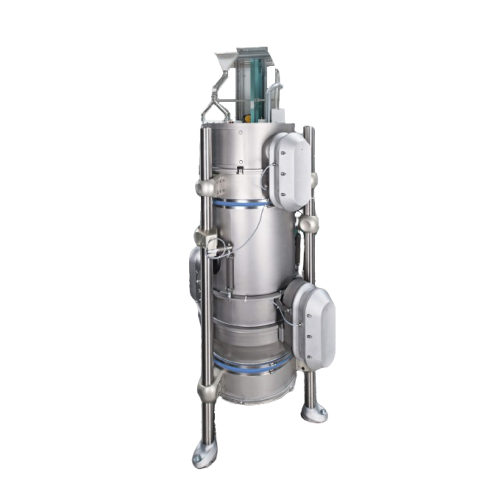

Advanced superheated steam drying solution
Harness the power of consistent drying technology to achieve optimal moisture c...
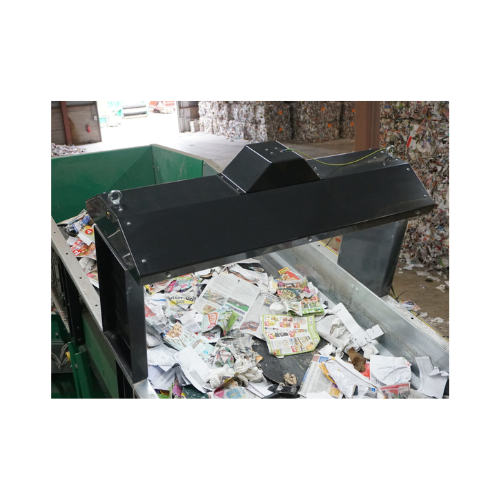

Optical analytics tool for material flow and composition
Optimize your waste management with real-time data analysis and ...
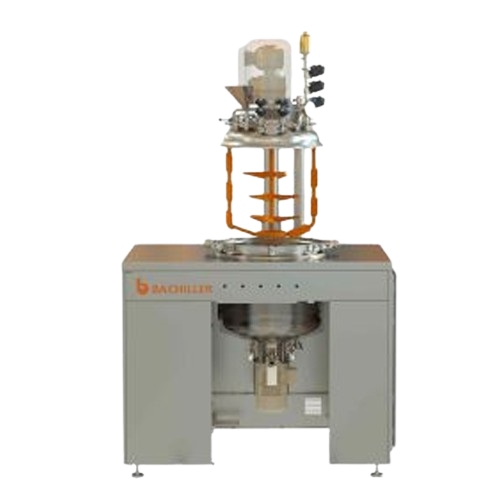

Laboratory vacuum mixer reactor for liquids and semi-solids
Achieve precise emulsification and mixing for high-viscosity...
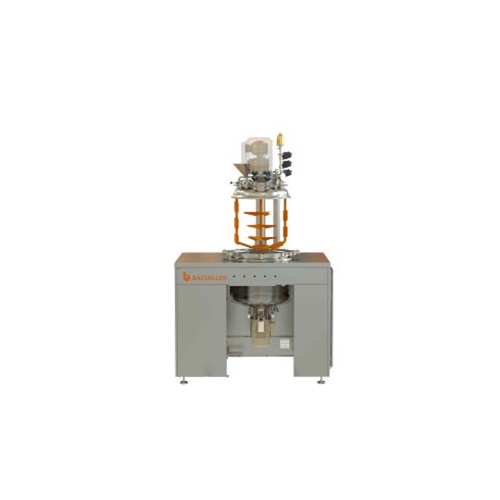

Vacuum mixer for liquid and cream processing
When dealing with high-viscosity liquids and creams, achieving uniform consis...
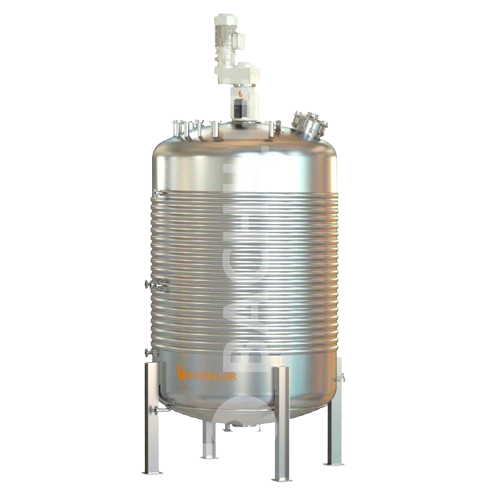

Stirred reactors with heating and cooling system
Optimize your production line with versatile stirred reactors, designed t...
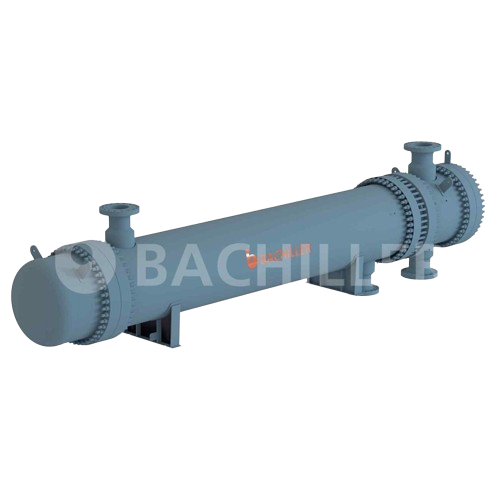

Shell and tube heat exchangers
Efficiently manage heat transfer in your production line with custom-engineered shell and tub...

Cip system for process tanks
Ensure high-level cleanliness and compliance in your production line with an efficient in-place...
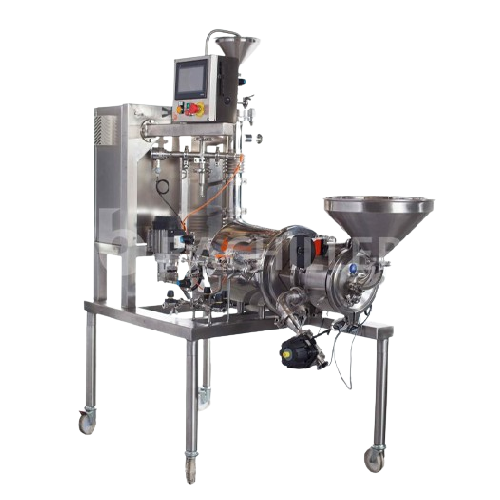

Colloidal mill for fine grinding and homogenisation
Optimize your liquid and semi-solid processing by achieving precise p...

Industrial columns and towers for chemical processing
Optimize your chemical production with robust columns and towers, d...

Flash dryer for high-moisture bulk materials
Tackle high-moisture challenges head-on with rapid drying solutions that effi...

Ultrafiltration and microfiltration module for low to medium viscosity products
Streamline the separation and concentr...

Heat exchanger for fibrous and coarse particle fluids
For operations involving fibrous and coarse particle fluids, this a...

Welded plate heat exchangers for high-pressure applications
Boost your production line’s energy efficiency and rel...

Oil and gas-fired industrial boiler
Enhance steam production efficiency with a robust three-pass combustion system designed...

Sifter for pet food, fish feed, and animal feed
Achieve precise particle separation and enhance feed quality with this vib...

Heavy metal removal system for industrial flue gas
Effectively remove harmful heavy metals from industrial emissions whil...

Clarifying decanter for starch recovery
Ensure optimal dewatering and separation of starch, pulp, and fibers with this high...

Shaftless spiral conveyor for difficult waste handling
Efficiently tackle complex waste handling challenges with a design...

Pulp and paper horizontal screw press separator
Optimize your pulp recycling and manure treatment with high-efficiency sol...

Screw press separator for biogas digestate treatment
Optimize your biogas plant’s efficiency with a robust solution...

Sub-vertical mechanical bar screens for wastewater treatment
Optimize your wastewater treatment process by capturing coa...

Grit classifier for wastewater treatment
Optimize your wastewater treatment process with a grit classifier that efficiently...

Laboratory and production agitator for medium-sized containers
Streamline your mixing and agitation processes with a ver...

Industrial mixer for facade paint and plaster
Optimize your facade paint and plaster production with this mixer designed f...

Industrial mixer for product-critical processes
When dealing with high-hygiene requirements and complex mixing tasks acros...

Fibrous material dewatering press
Efficiently remove excess moisture from a variety of fibrous materials, enhancing process...

Drying and cooling classifier for plastic pellets
This solution enhances efficiency by combining drying, cooling, and cla...

Sanitary separator for food processing applications
Ensure efficient separation and prevent contamination in food product...

Dual-motion rectangular separator for pulp and paper industry
Optimize your production line with a versatile separation ...
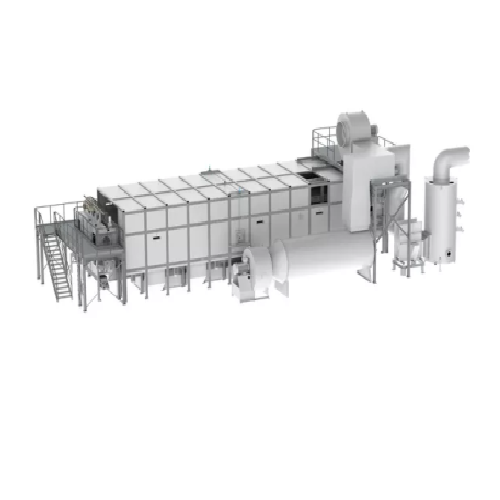
Slat conveyor dryer for industrial drying processes
Optimize your drying process with a robust slat conveyor system that ...

Stationary drying system for agricultural products
Optimize moisture control and energy efficiency in your drying process...

Low-emission belt drying systems for timber industry
Optimize moisture control and energy efficiency in drying processes ...

Belt dryer for timber industry
Optimize moisture removal and ensure consistent drying in your production line with advanced ...
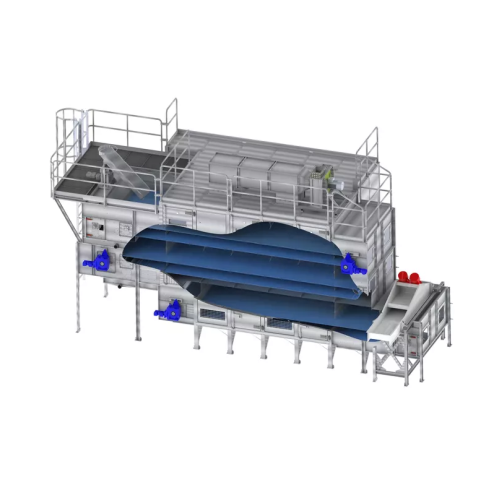
Layer dryer for food and pet food applications
Optimize drying efficiency with multi-layer technology that minimizes space...
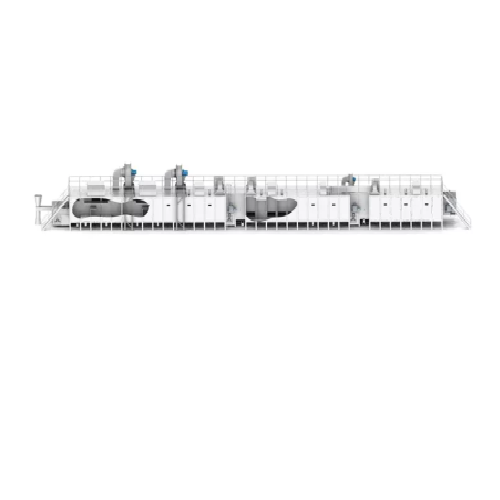

Belt dryer for food and pet food products
Optimize drying processes with customizable belt dryers, engineered to handle ro...
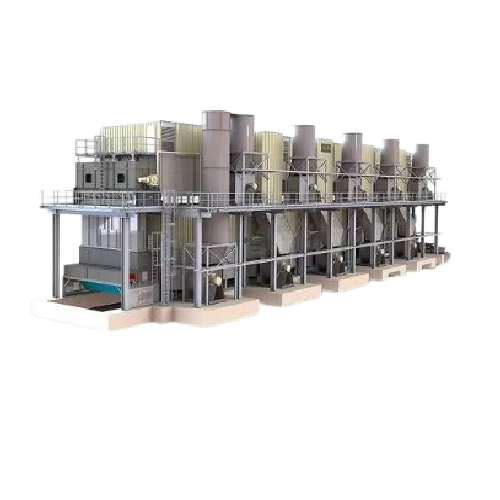

Belt dryer for sawdust
Optimize your drying process with advanced technology engineered for precise moisture reduction in div...
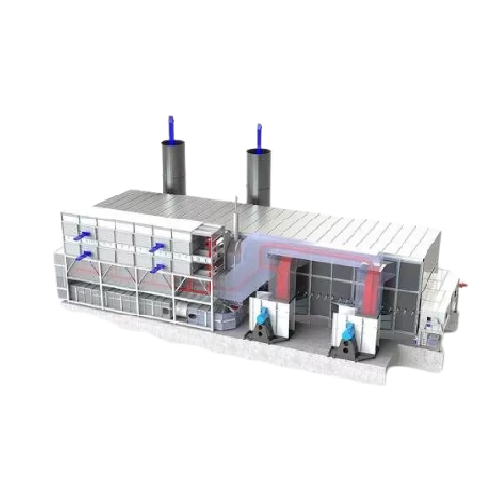
Low-emission belt dryer for timber industry
Achieve maximum drying efficiency and significant energy savings in your proce...
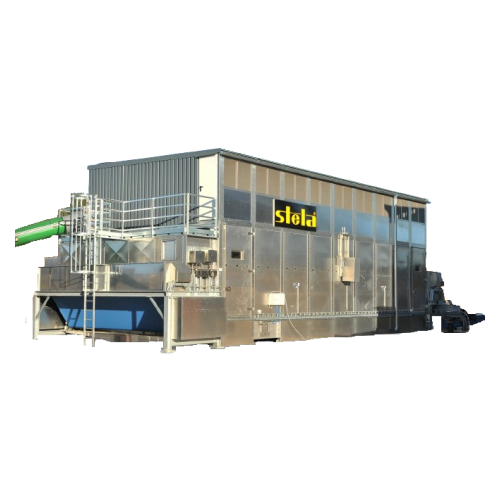

Mobile belt dryer for sawdust and biomass
Efficiently reduce moisture in a variety of materials, from sawdust to cereal sn...

Vacuum belt filter for sludge and suspension filtration
Optimize your production line with efficient filtration and dewat...

Twin shaft horizontal batch mixers for homogenous material mixing
Achieve consistent and rapid mixing of diverse materi...

Energy saving vertical steam dryer for paper pulp
Apart from soil and water pollution with cholates, chlorine, and metal ...

Solid biomass screening and crushing equipment
Biomass fuels come in many forms and often include impurities that can dama...
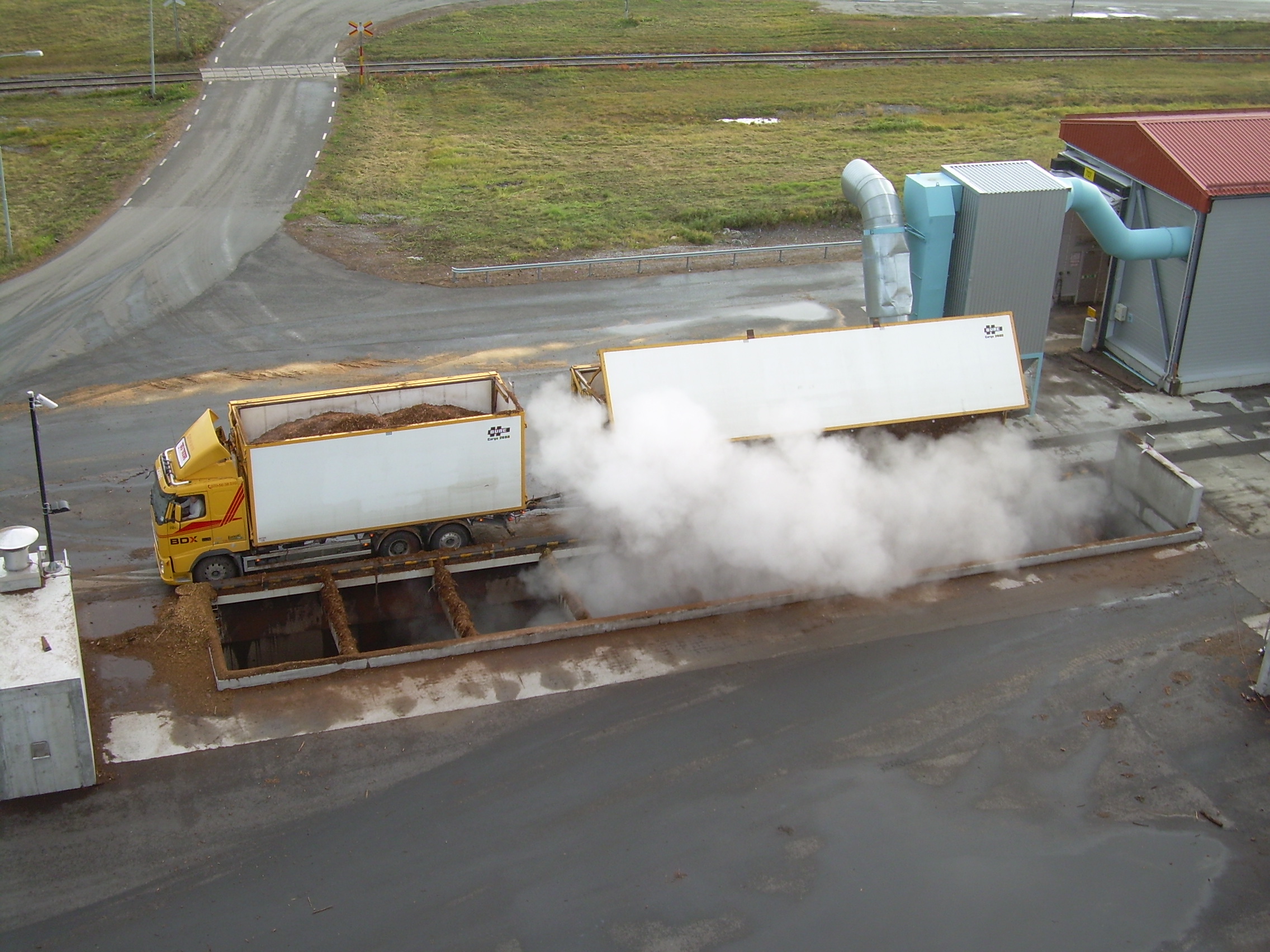

Solid biomass receiving systems
Biomass fuels come in many forms and are often handled in very large quantities. Shipment m...
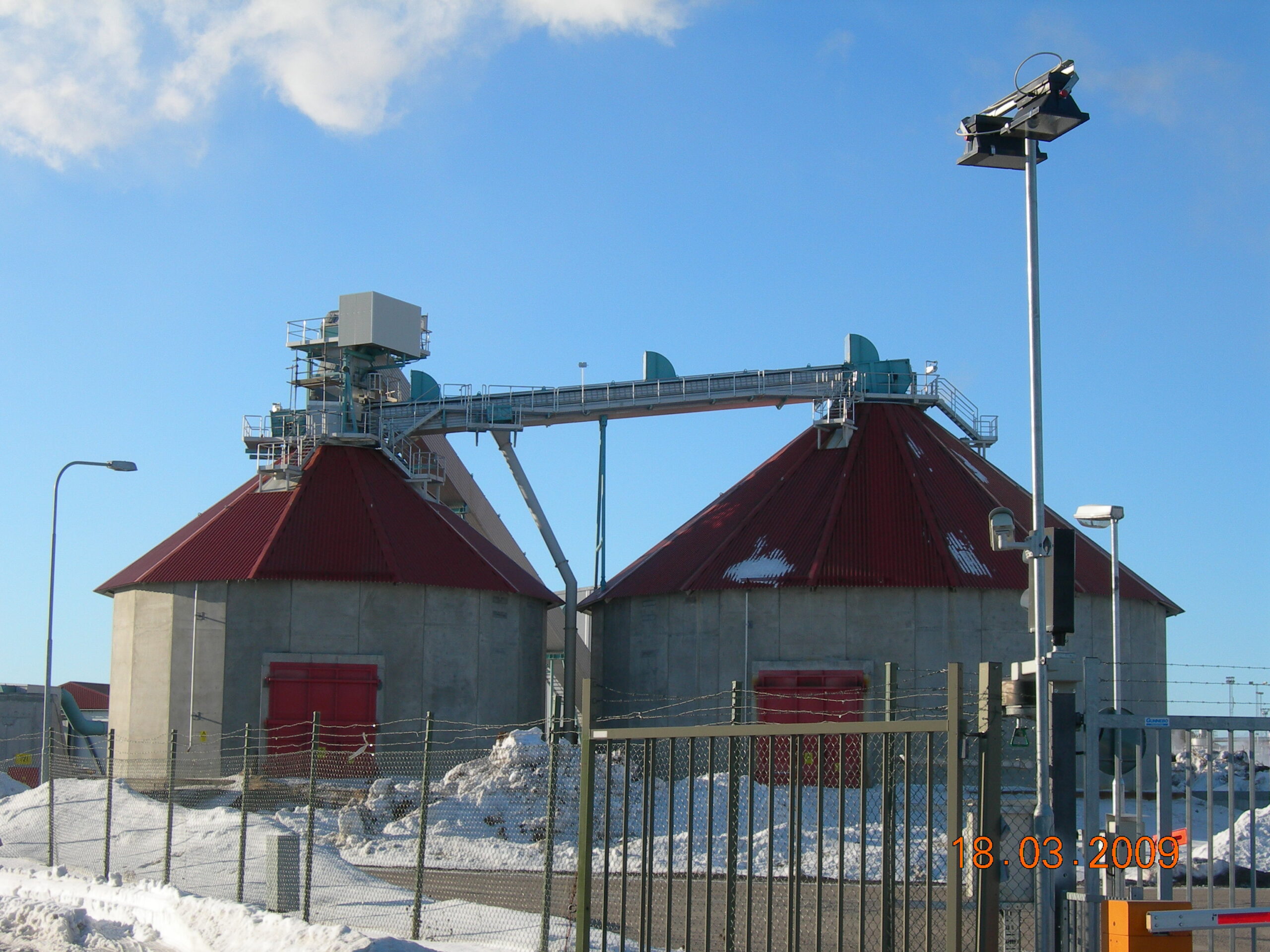

Solid biomass storage and reclaiming equipment
Biomass fuels must often be stored for additional preprocessing or prior to...
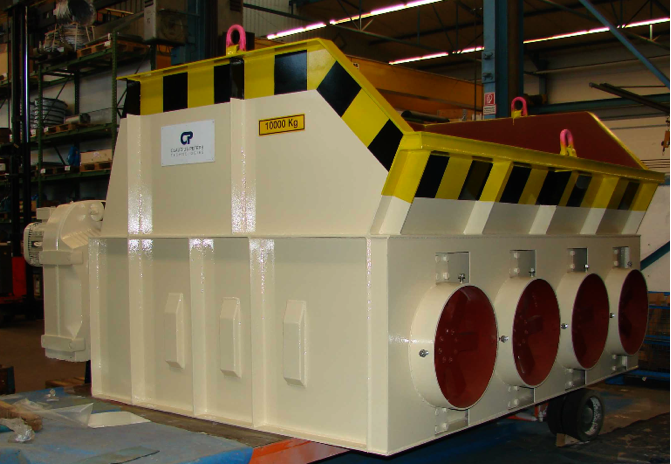

Reclaim crusher
Waste products and rejected materials are inevitably generated from any gypsum products manufacturing process....
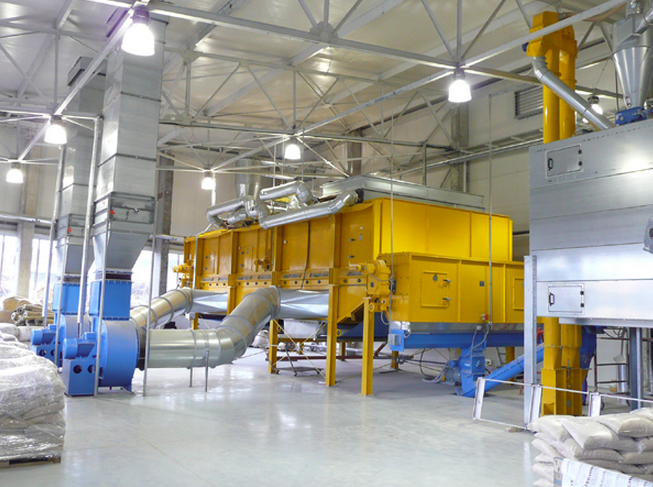

Belt dryer for wood
Processing of wood and biomass into pellets or other volume reduced products requires careful and consist...








