Making Baking Powder
Find innovative production technology for making baking powder and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Baking powder is perhaps the best-known secret of baking. The leavening agent forms bubbles in dough and batter to give muffins, cakes, and no-yeast pizza their tempting lift. First developed in the 19th century, baking powder production turned baking into the home activity we know today.
Select your baking powder process
Tell us about your production challenge
Baking powder production begins with sodium bicarbonate
Baking powder is produced by combining a mild acid and a buffer with a base of sodium bicarbonate (baking soda).
Crystallized sodium bicarbonate starts as ammonia and carbon dioxide mixed through a saline solution in an absorption tower. The reaction with salt produces a compound of sodium bicarbonate and ammonium chloride. The result is centrifugated to filter out the sodium bicarbonate, which goes through heating and cooling to reach its crystalline form.

Add cornstarch to buffer sodium bicarbonate from acids
The buffer in the baking powder formula acts as an inert filler, adding bulk to the baking powder. But this additive does more than thicken the product.
It favors flowability by preventing mixture powders from binding together during processing. A buffer keeps the acids and bases separate during storage and stops them from reacting. Thanks to its moisture-absorption ability, cornstarch is almost invariably used. Sodium bicarbonate, acid, and cornstarch are blended in mixing containers and combined into a homogeneous blend.

Industrial acid blends determine the reaction time of baking powder
There is a broad spectrum of acid leaveners to choose from, depending on the action the baking powder is designed for. The acids blended in the mixture are either slow-reacting or fast-reacting.
On the slow-reaction side, anhydrous monocalcium phosphate (AMCP) is a stable ingredient and releases about 15% of carbon dioxide at the mixing stage. Dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (DCP) is even slower and only reacts with sodium bicarbonate when the temperature of the batter reaches 60°C.
A popular fast-reacting acid is monocalcium phosphate (MCP), letting off 60%-70% of carbon dioxide by the end of the mixing stage. This action produces batters with high viscosity and high volume.
Mix acids to produce a double reaction in baking powder
Most commercial baking powders contain acid types and are known as double-acting ingredients. A fast-reacting acid such as cream of tartar dissolves quickly and releases carbon dioxide as soon as it comes into contact with the recipe’. The second acid, a slow-reacting leavener, produces a second burst of CO2 when the batter hits the oven’s heat.
Processing steps involved in baking powder making
Which baking powder technology do you need?

Powder unloading systems for food and dairy applications
Streamline your powder handling with customizable unloading syst...

Industrial bag tie-wrapping solution
Ensure your bulk packaging is reliably sealed with a tamper-evident tie-wrap, allowing...

Automated bag sealing for packaging lines
Enhance your packaging efficiency by seamlessly integrating an automated bag sea...

Accurate powder filling solution
When precision is paramount, this solution offers exceptional accuracy, filling powders up ...
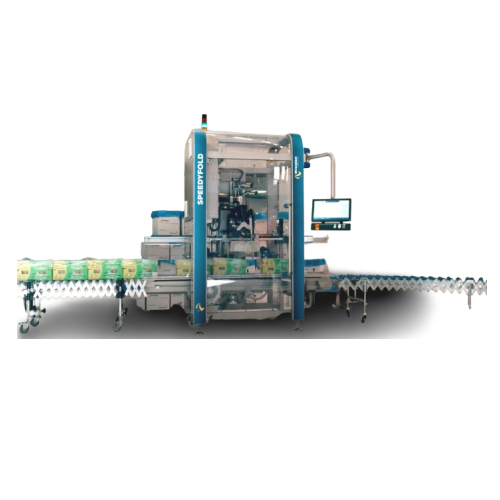

Bag folding solution for high-speed packaging
Effortlessly enhance your packaging line efficiency with this high-speed bag...
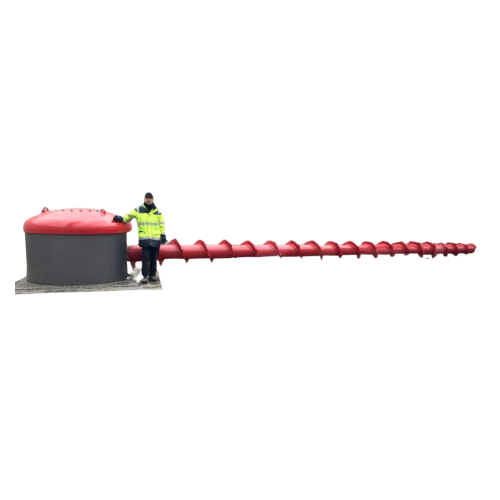

Unloader for non-free-flowing materials in flat bottom silos
Facing challenges unloading non-free-flowing materials? Thi...
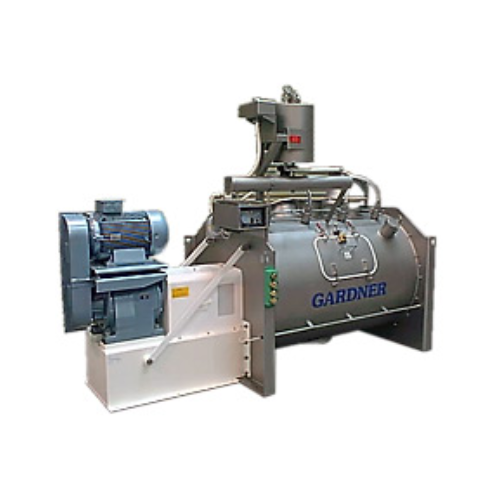

High shear plough mixer for powders, granules, and pastes
Achieve rapid and efficient blending with high shear mixers de...
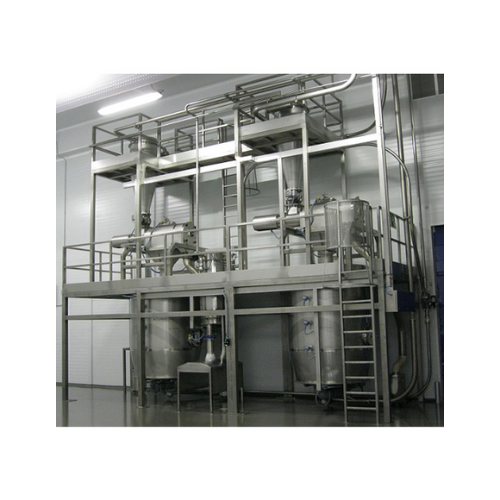

Buffer tanks for powdered or granulated solids storage
Enhance your production line with buffer tanks designed for precis...

Powder dosing system for big-bags
Efficiently dose and fill various powdered materials directly from big-bags into your pro...
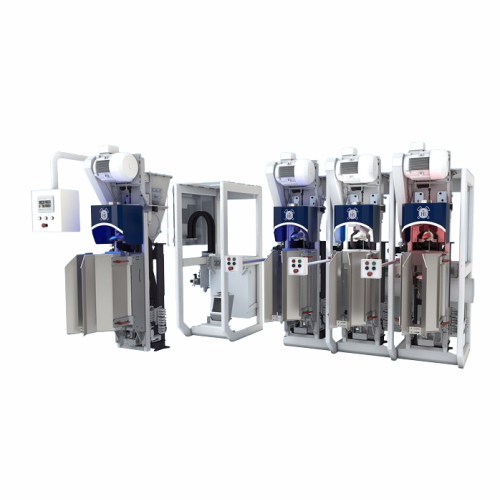

Valve bag filling system for cement and chemicals
Optimize your material handling with precision filling and sealing, ens...
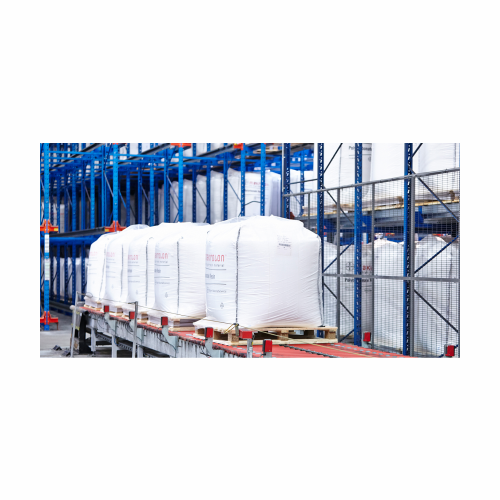

Stationary entry packaging system for valve bags
Optimize your packaging workflow with a high-speed, modular filling syste...
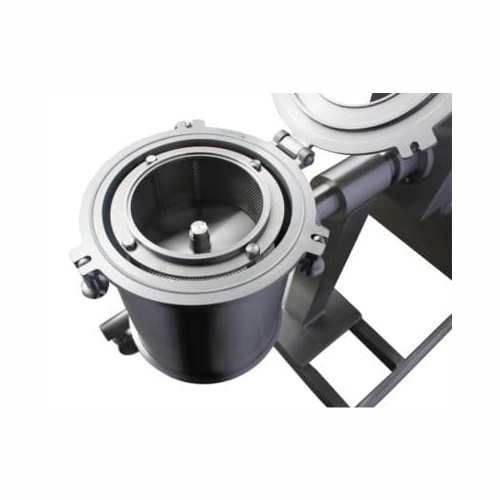

Centrifugal powder sifter for particle separation
Achieve consistent material quality with efficient powder sifting and d...
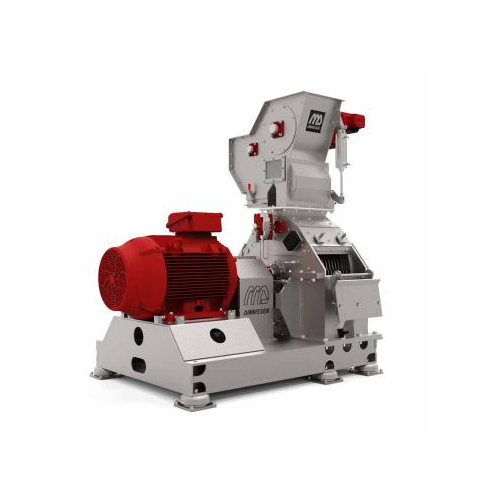

Industrial hammer mill for grinding and sifting
Ensure precise particle size reduction and consistent product quality with...

Centrifugal mill for fine grinding in industrial processes
Achieve exceptional fineness without overheating your materia...

Evaporative crystallizers for chemical processing
Optimize your crystallization process with state-of-the-art evaporative...

Moisture analyzer for flour and tobacco
Optimize your moisture measurement process with precision and speed, ensuring quali...

Release agent sprayer for baking trays and moulds
Achieve perfect results in baking by ensuring efficient and uniform gre...
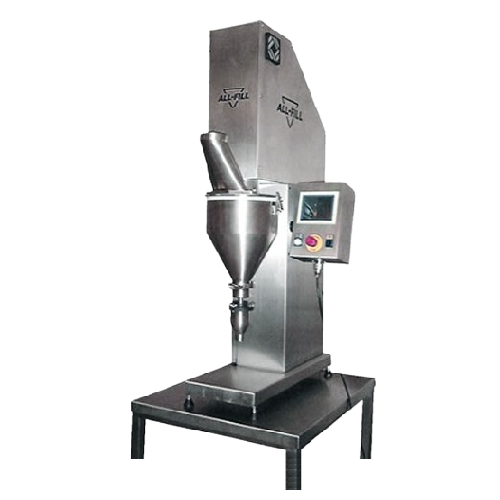

Miniature auger filler for precise powder filling
Achieve precision filling with a compact, bench-top auger solution desi...
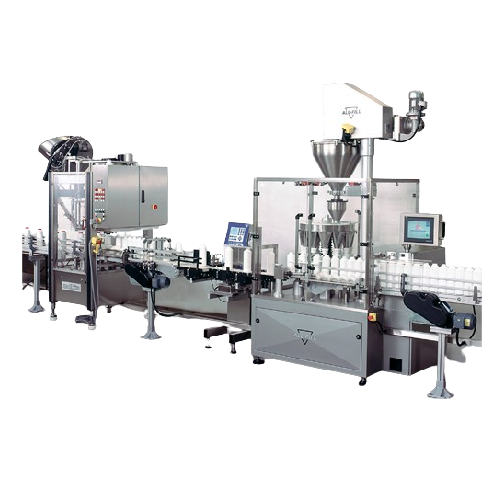

Turnkey filling lines for packaging solutions
Optimize your production line with our turnkey filling solutions, designed t...
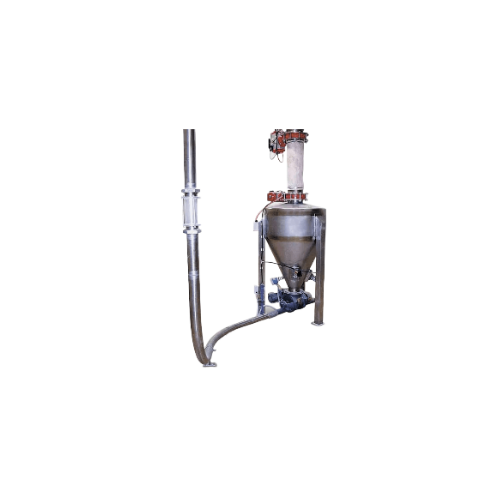

Lean phase vacuum conveying system for powder handling
Efficiently transport and separate powders and granules with preci...

25kg bag tipping station for powder discharge
Efficiently discharge and sieve 25kg bags of powder while minimizing dust em...
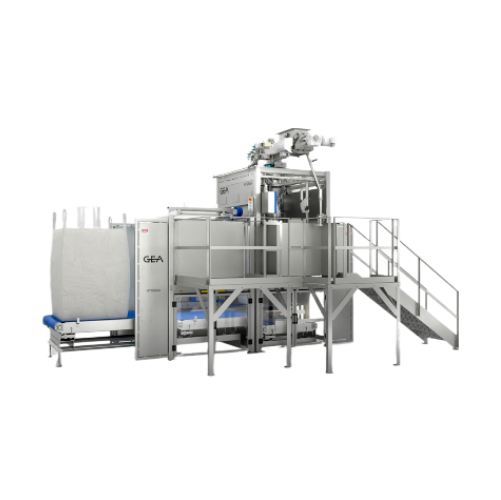

Bulk powder filler for food, dairy, and nutraceuticals
Optimize your bulk powder filling process with a system designed t...
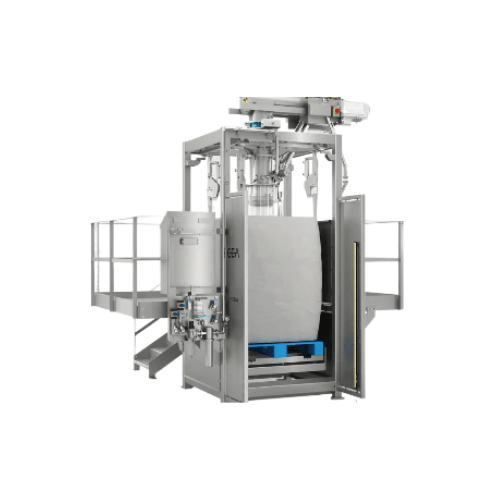

Low care bulk powder fillers
Optimize your production efficiency by accurately filling flexible bulk containers with dry pow...

Explosion protection vents for spray dryers
Optimize safety and hygiene in your spray drying operations with advanced expl...
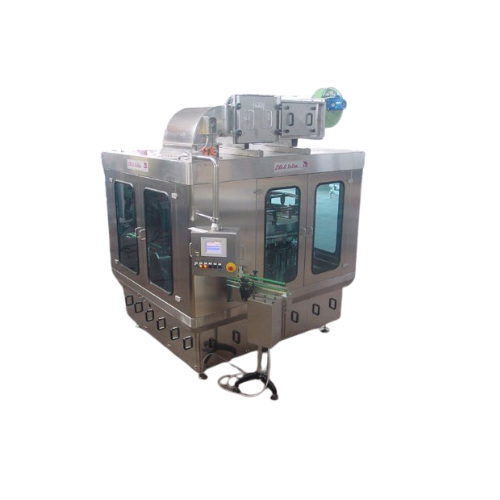

Industrial powder fillers for various containers
Optimize your packaging line with high-speed powder fillers that handle d...

Pneumatic mixer for fluidizable bulk materials
Achieve uniform and gentle mixing of powdered ingredients with minimal effo...
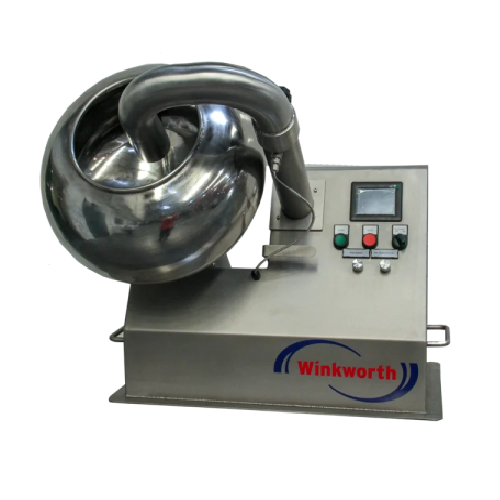

Industrial coating pan for food and pharmaceutical products
Optimize your production with precision mixing and coating, ...
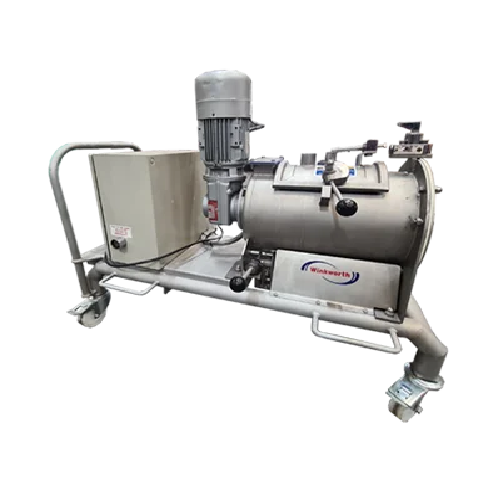

Industrial mixers for hire
Optimize your production line with versatile mixers designed for precision blending, heating, and...
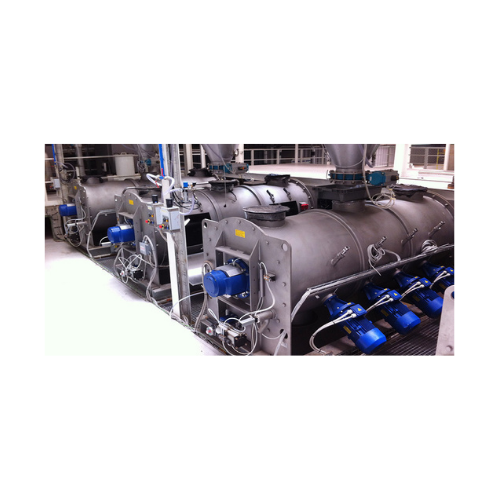

Batch-type single shaft mixer for industrial mixing
Achieve precise and uniform mixing with high-speed, single-shaft mixe...
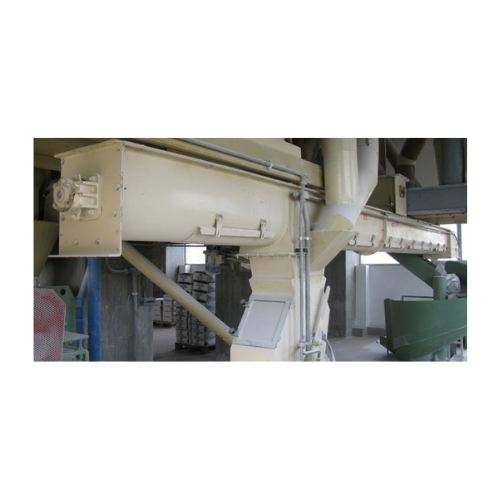

Trough screw conveyor for flour mills
Optimize your flour processing with efficient material handling, precisely designed f...
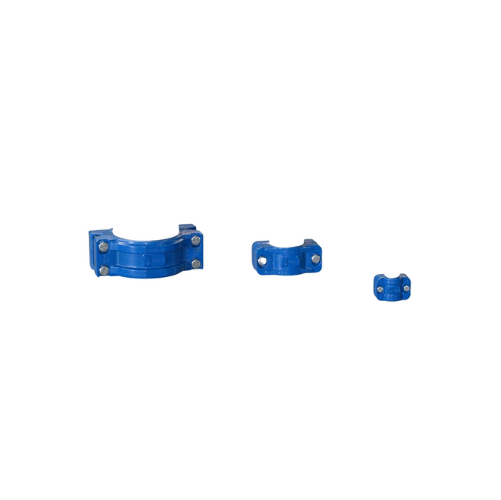

Pipe couplings for pneumatic conveying lines
Ensure a secure and quick connection for your pneumatic lines with these pipe...
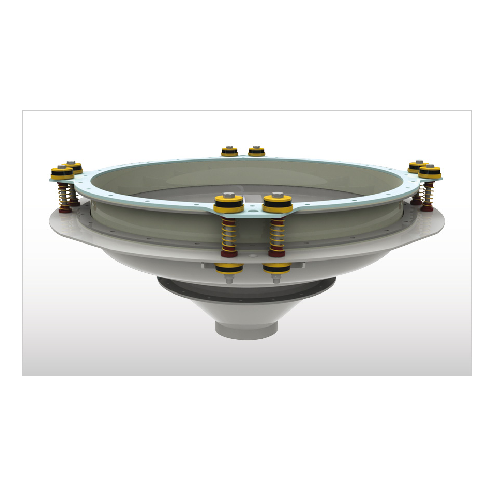
Industrial bin activator for smooth material flow
Enhance your material handling process with a solution that ensures con...
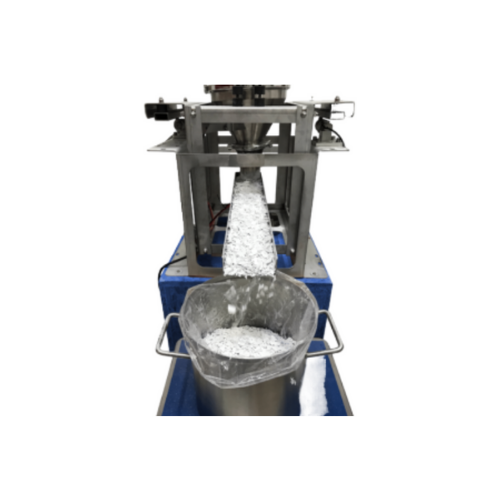

Vibratory feeder for dosing powders and bulks
Ensure precise feeding of powders and bulk materials with a system that inte...
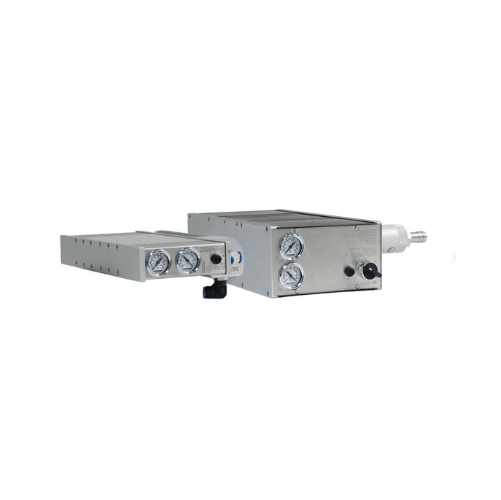

Industrial vacuum pumps for efficient powder conveyance
Harness the power of efficient vacuum generation to streamline th...
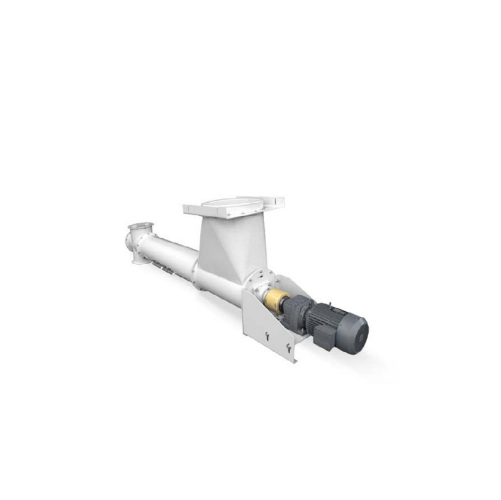

Tube screw conveyor for flour and fine-milled materials
Optimize your production line by efficiently transporting flour a...
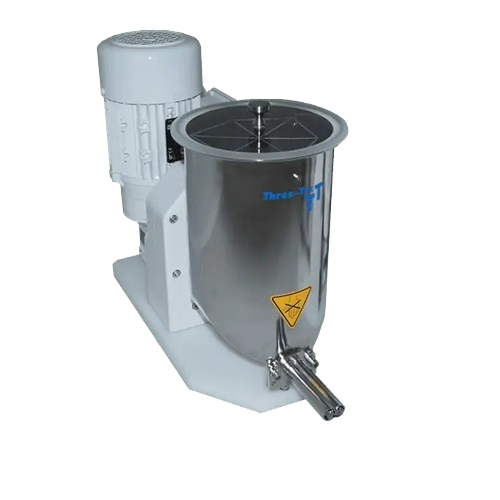

Twin-screw feeder for powders and micro-granules
Ideal for handling poorly flowing powders and granules, this advanced twi...
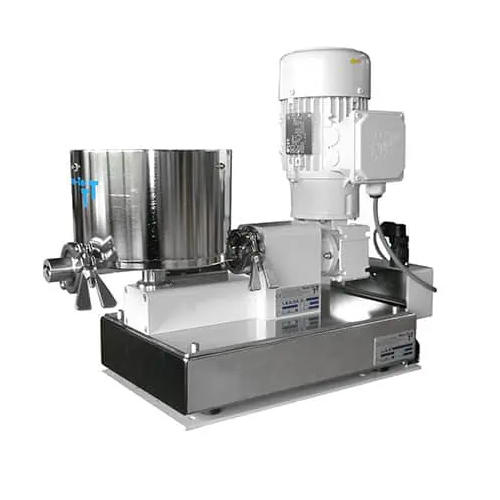

Volumetric flat-bottom twin-screw feeder for powders
When handling powders prone to clumping, a reliable feeder ensures u...
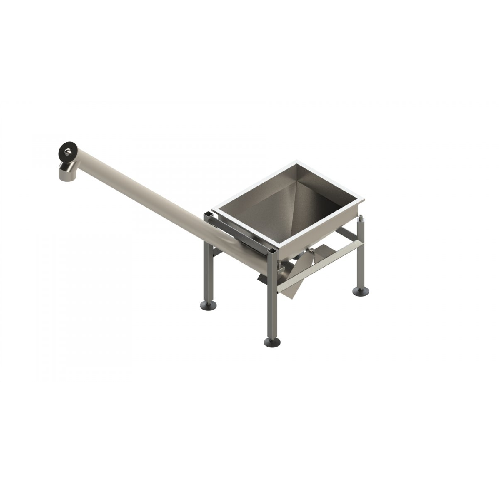

Vibratory storage hopper with inclined screw conveyor
Enhance your production line efficiency with a vibratory storage ho...
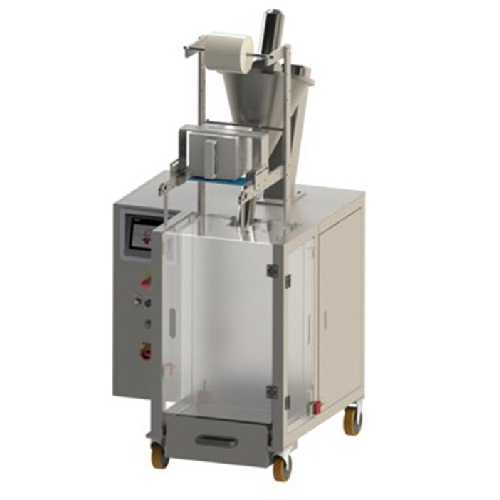

Sachet powder filling machine
Optimize your packaging line with this efficient solution for precise powder filling, ensuring...
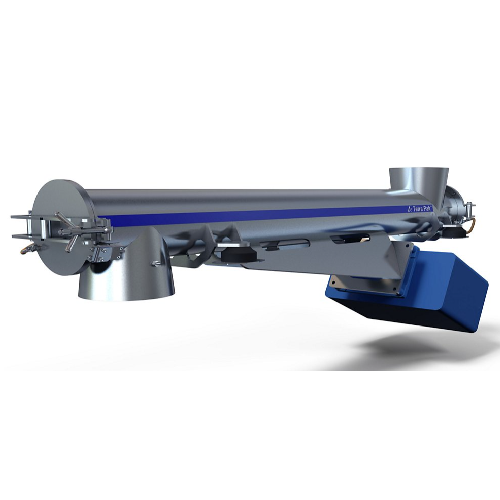

Vibrating conveyor for short-distance powder transport
Achieve precise and hygienic powder conveying and dosing with this...
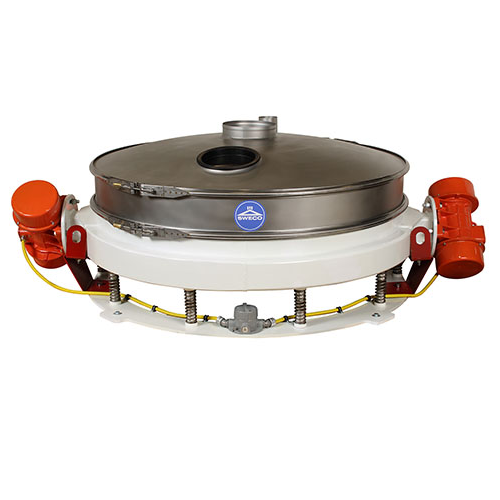

Low profile flow-thru separator for wet or dry scalping
Efficiently handle high-capacity separation with a compact design...
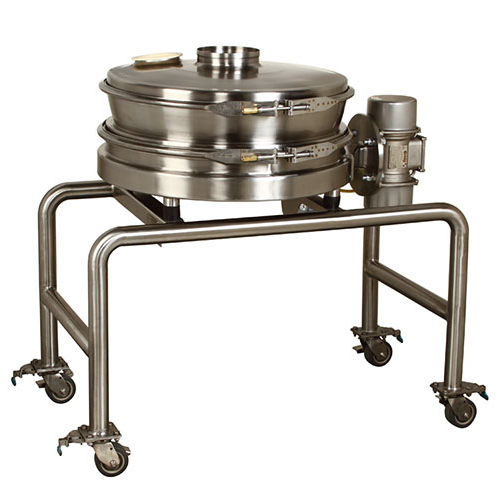

Sanitary separator for food processing applications
Ensure efficient separation and prevent contamination in food product...

Metal detection system for powders & granules
Ensure product integrity and protect your machinery from metallic contaminan...
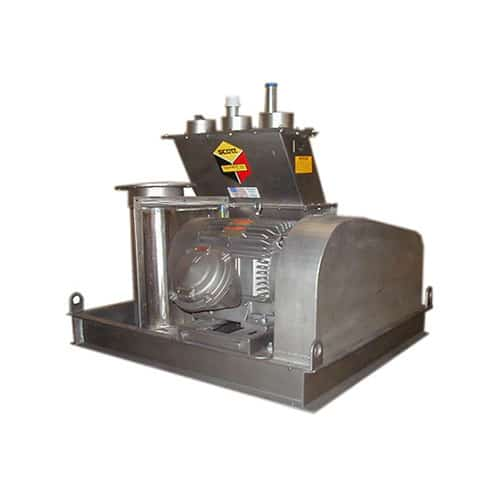

Shredder for fine particle size reduction
Optimize your production line with high-speed shredding technology designed for ...
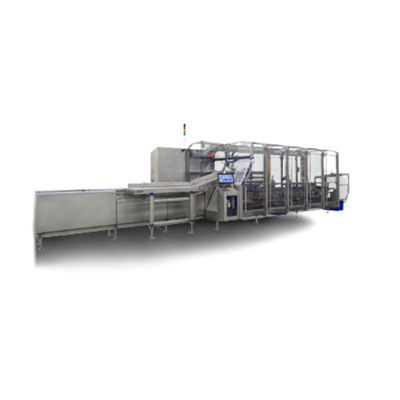

Intelligent Continuous Food Cartoner
Fully automated robotic packing solutions enable larger-scale food producers to pack a...
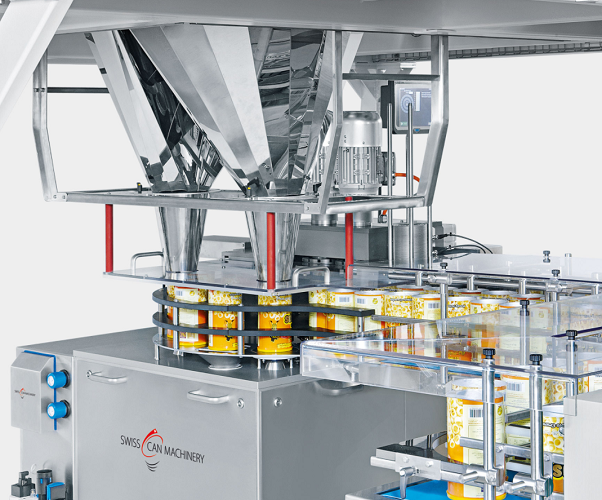

Filling and weight checking machine for food cans
Making sure the right quantity of product is in the packaging can be a ...
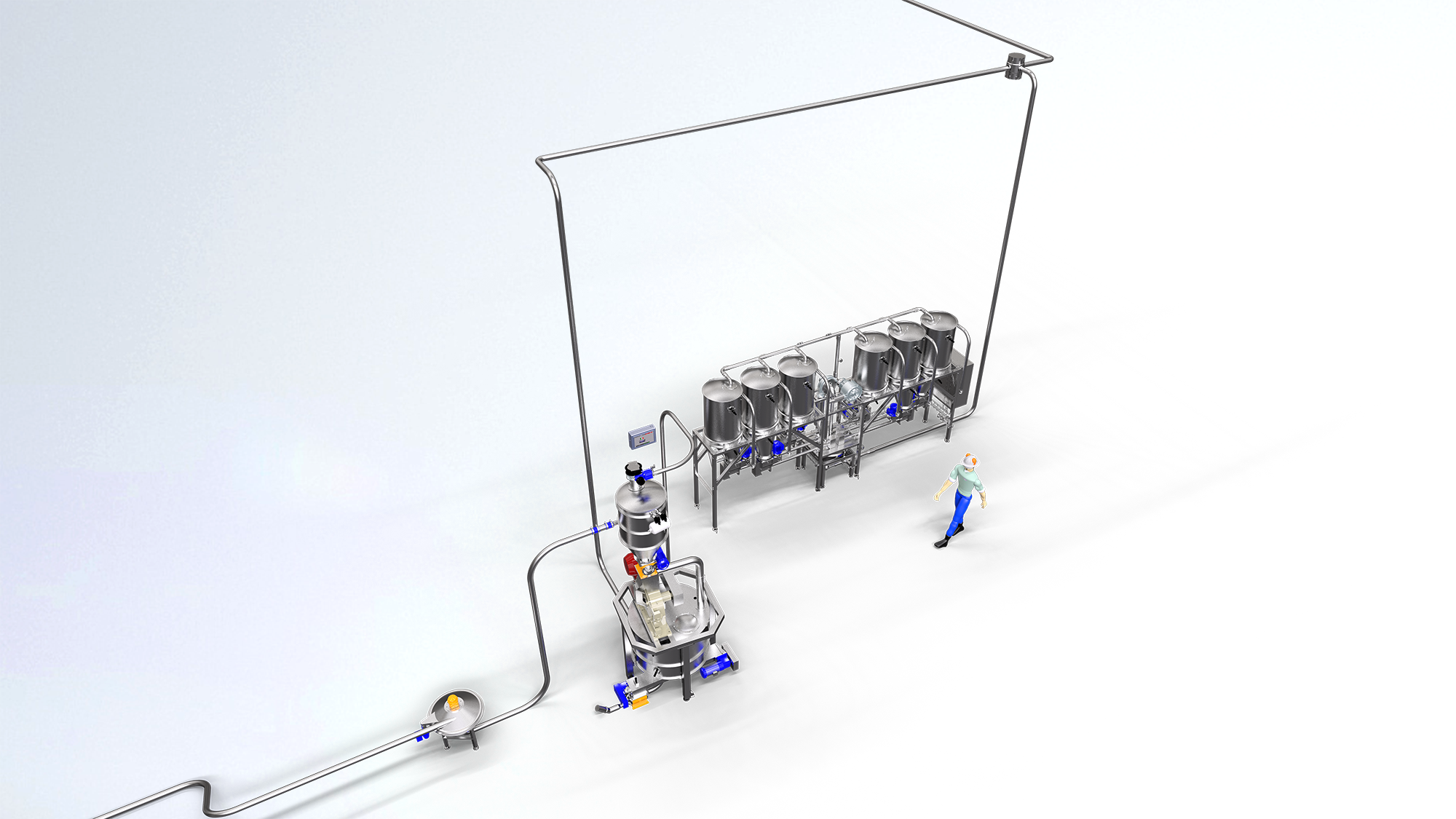

Microdosing system for bakery industry
Storage and dosing of powdered minor ingredients such as flavourings, colours and si...
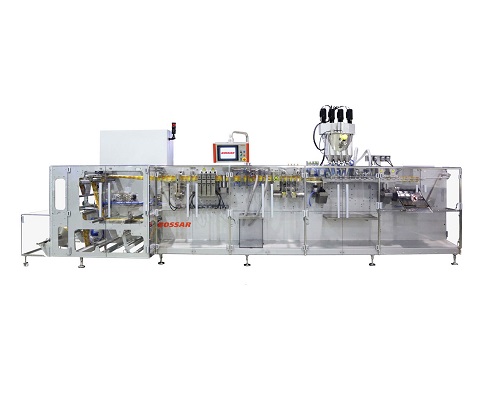

High-Speed Pouch Packaging Machine
For large scale production of powders and liquids in a wide range of industry sectors, a...
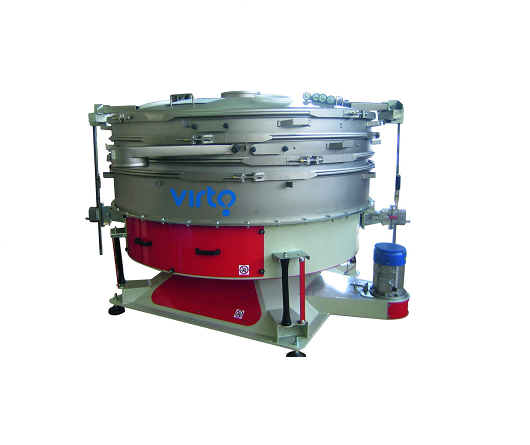

Tumbler sieve for classifying and dedusting granular materials
For the classification of delicate granular material, scr...
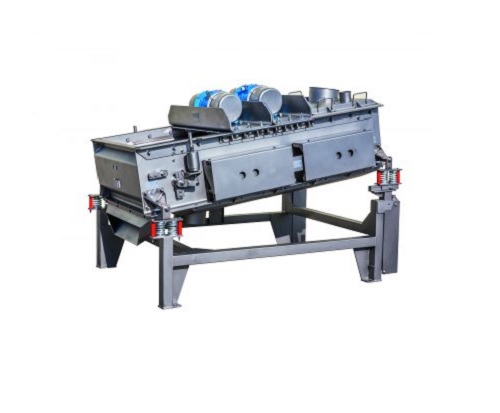

High volume particles separation sieve
For large scale production processes in the chemicals or food industries that requir...
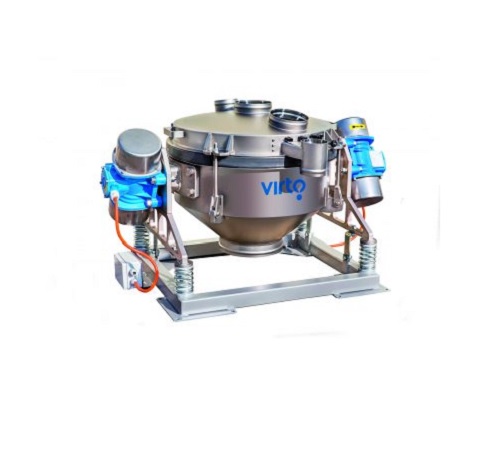

Multifrequency sieve for separation of difficult particles
Separating particles in difficult-to-process materials for pr...
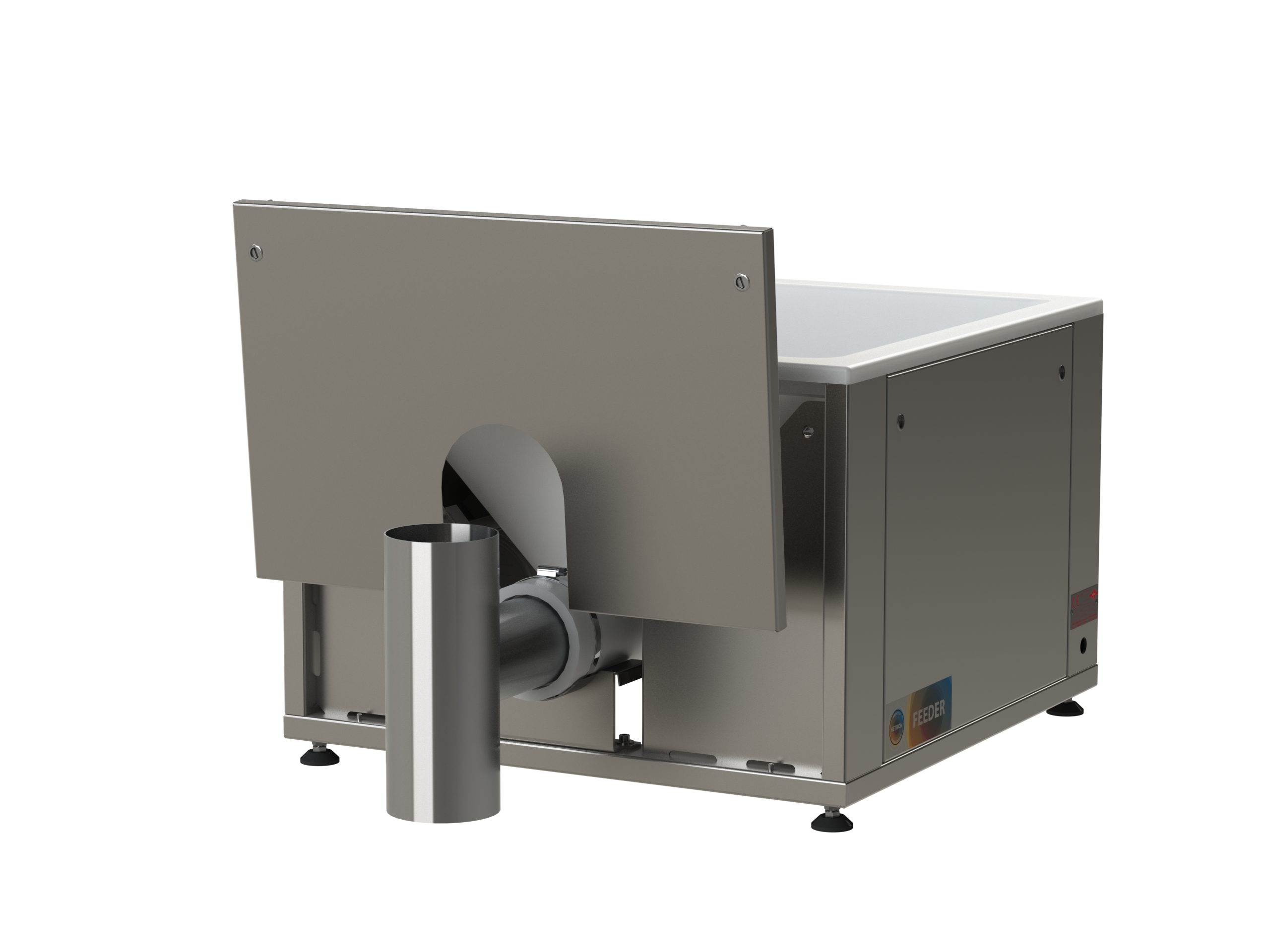

Feeder with flexible wall hopper
The varying properties of dry powder products mean that specialized feeders are required fo...
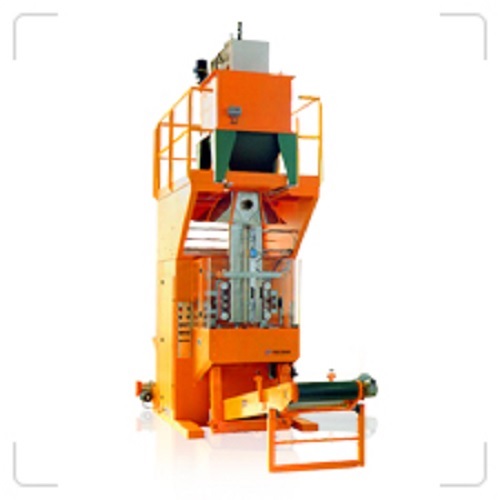

Vertical form, fill and seal machine for bags from 5 to 50 kg
To securely create, dose and pack larger quantities of mat...
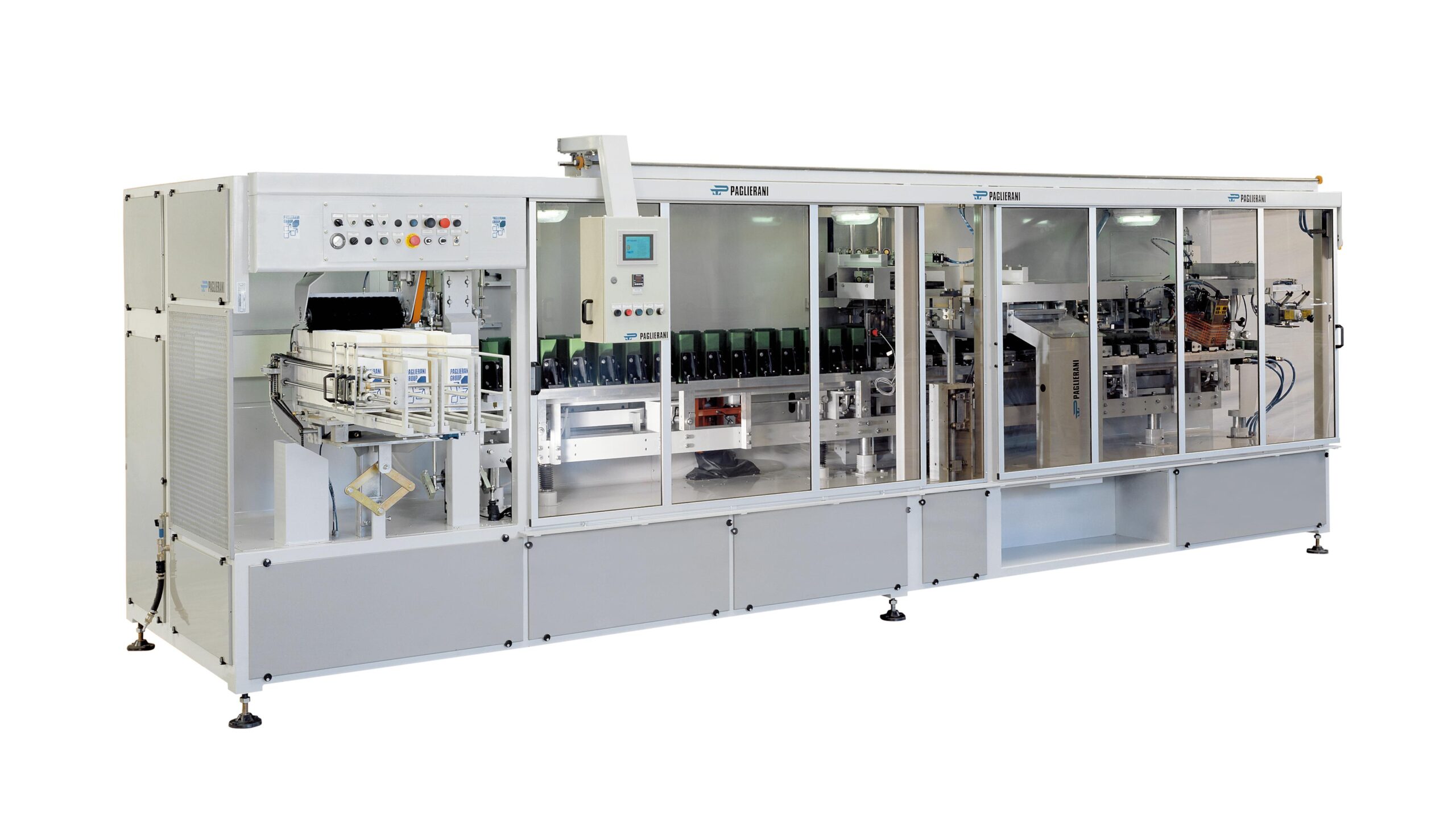

Packaging machine for preformed paper bags from 500 g to 5 kg.
Paper bag filling and closing for larger quantities of ma...
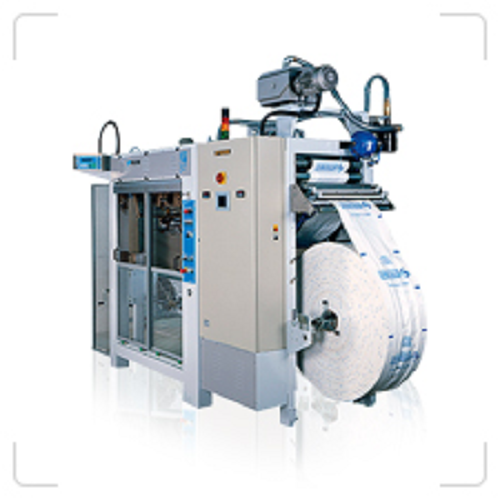

Horizontal form, fill and seal machine for bags up to 10kg
Bagging small quantities of solids or liquids, whether in pap...
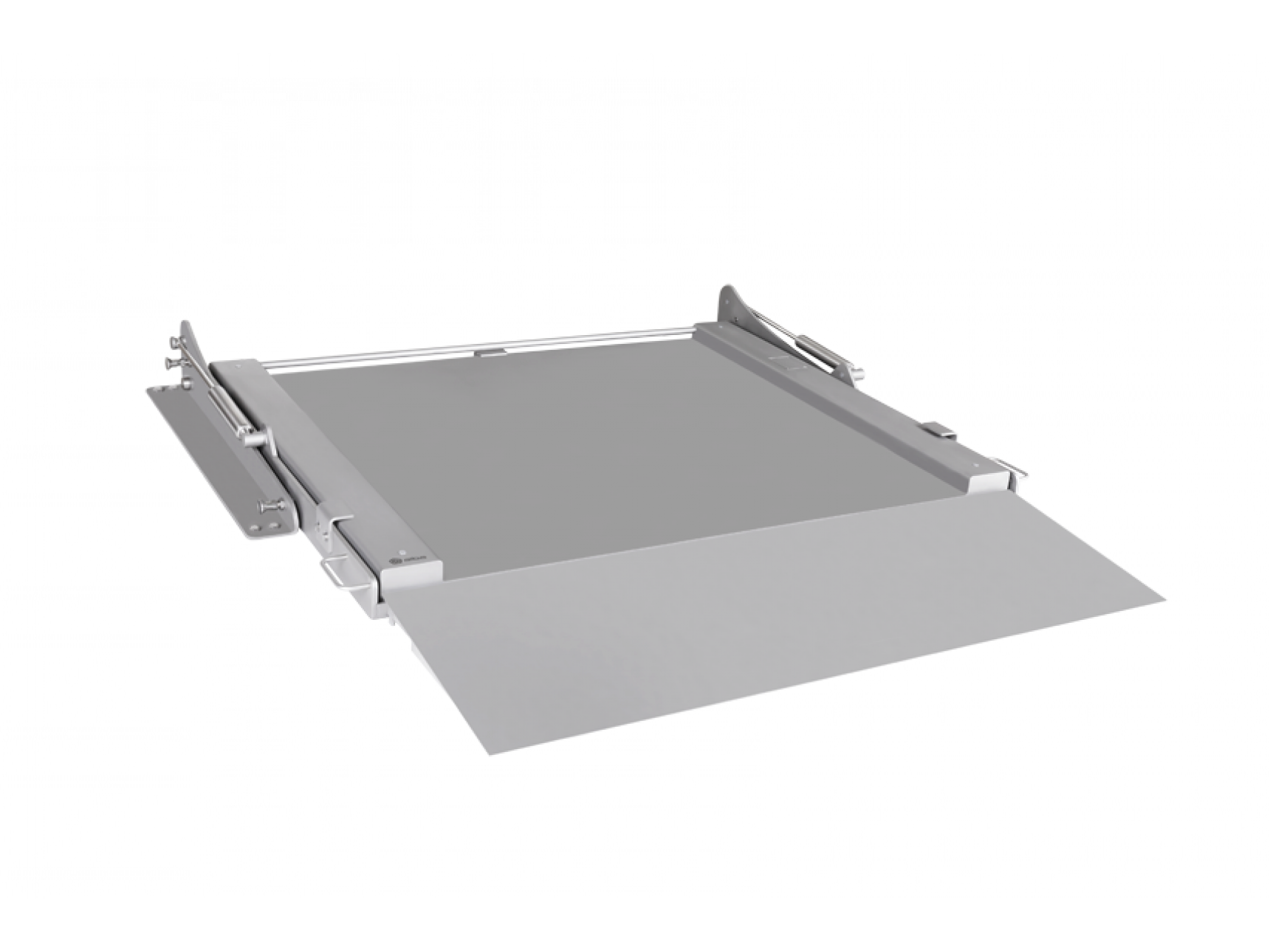
Hygienic floor scale with lifting device
The food and pharmaceutical industries require maintaining high levels of sanitati...
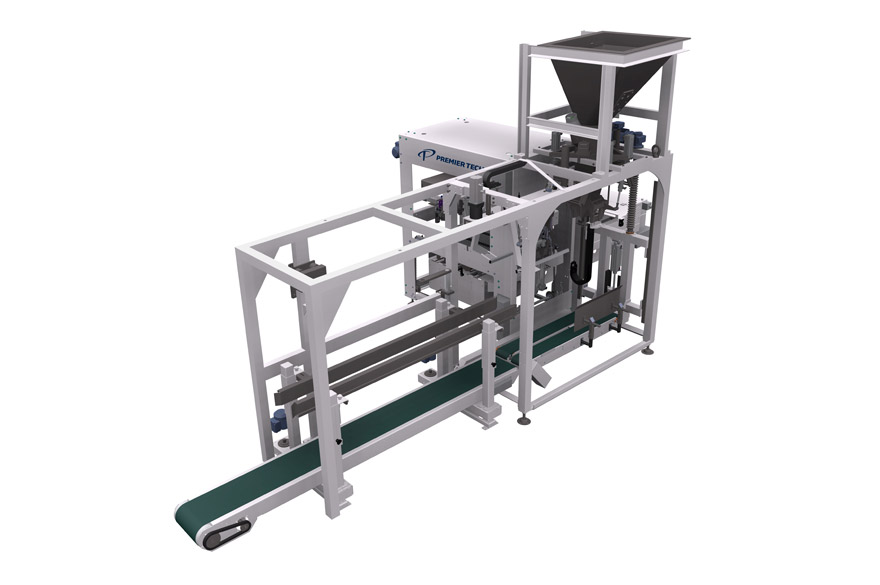

Open-mouth baggers for free flowing powders
For bagging free flowing materials into open mouth bags, this system is ideal....
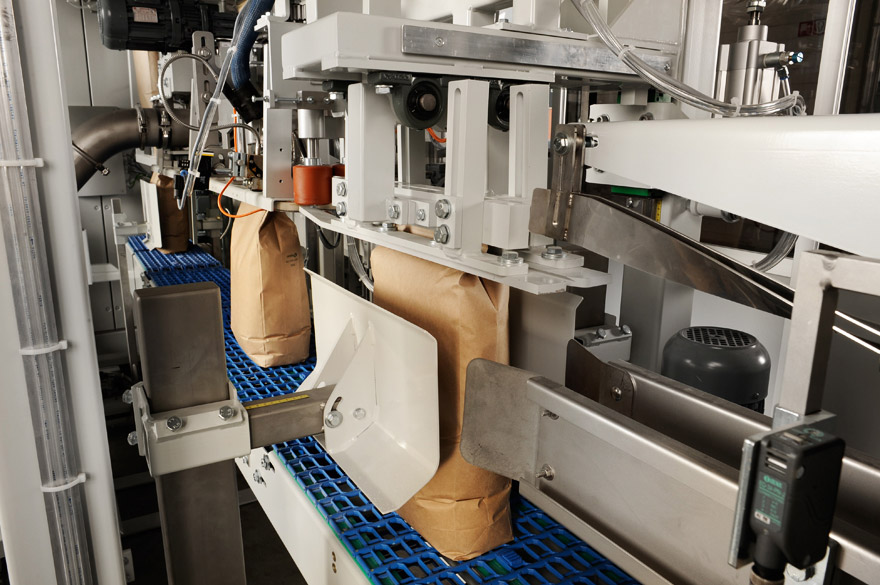

Open-mouth bottom-up baggers
Innovative bottom-up baggers for high-speed industrial packaging will help you create a dust-fr...
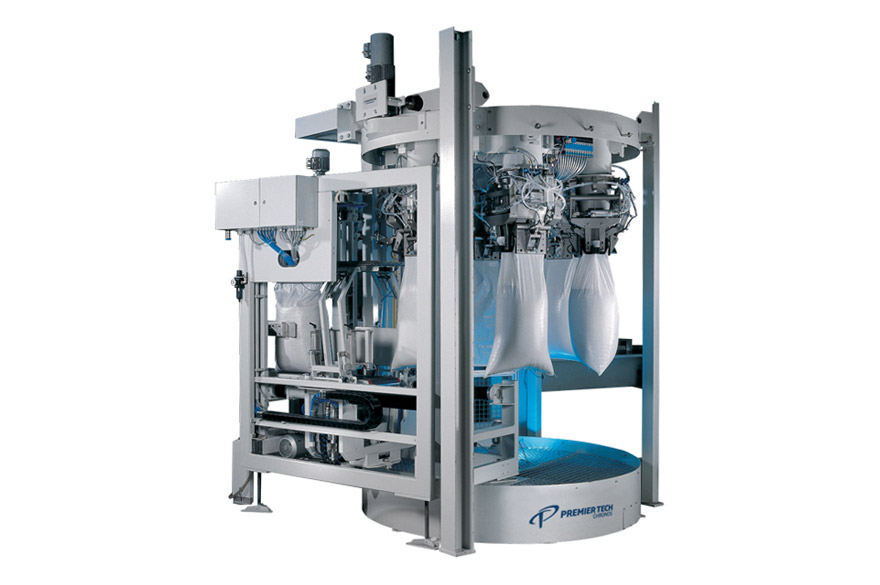

Open-mouth bagging carousel for flour
When you need a carousel for packing powdery bulk materials, the bagging carousel tha...
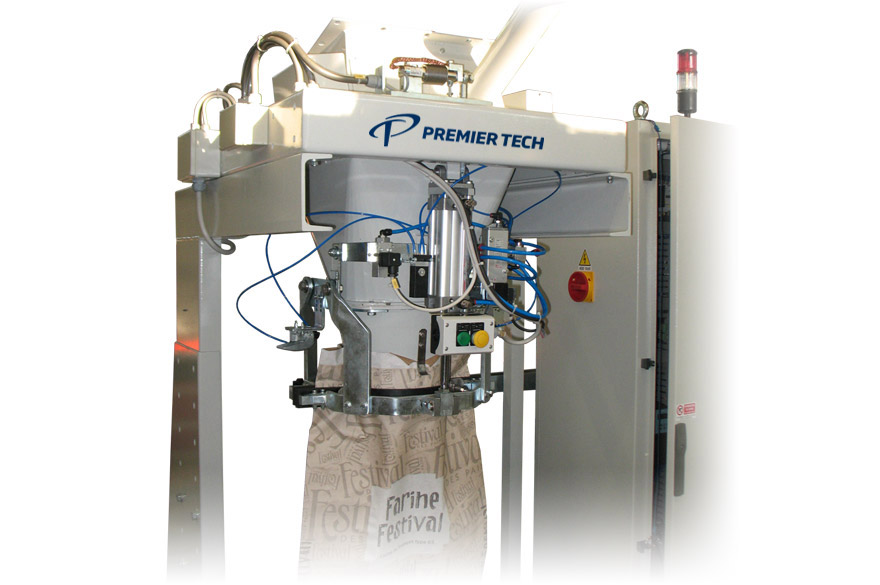

Manual bagger with gross weigher
This is a manual bagging set with an electronic gross weighing system to meet international...








