Making Collagen Powder
Find innovative production technology for making collagen powder and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Around a third of your natural protein composition is collagen. But the human body still finds good use for more of it, whether to reinforce joints or aid digestion. Collagen powder processing breaks the chains of amino acids into smaller units, allowing them to be consumed at higher concentrations without changing your diet.
Stories about collagen powder
Tell us about your production challenge
Treat the raw material with mild chemicals to cleave the collagen
Collagen is, by nature, cross-linked to other molecules in the living organism. Freeing it up before extraction will increase the substance purity of your collagen powder processing line.
Pre-treating the material with a solution of diluted chemicals breaks up the tissue. But a partial hydrophilization afterward ensures that collagen chains are held together. Delicate organisms like porcine skins may be immersed in acidic agents. More rigid materials such as bovine ossein require a more aggressive pre-treatment using alkaline solutions.

Organic acids achieve better chemical hydrolyzation than inorganic acids
Hydrolyzing your pre-treated material can be done using both organic and inorganic acids. The former types, however, show more efficiency in solubilizing collagen.
Once filtered from residues, the liquid collagen is typically precipitated with sodium chloride to obtain a powder. Purification is the final but critical step in your collagen powder process. The material is dialyzed in acetic acid and distilled water ideally replaced at 12-hour intervals.

Activate enzymes to reduce collagen powder processing time
Biological hydrolyzation offers an attractive extraction method, particularly in the food industry. Products made with enzymatically hydrolyzed collagen report a higher concentration of beneficial nutrients after ingestion.
This technique solubilizes collagen in an acetic acid mixture containing enzymes. The method accelerates the process with lower salt content. Although the method incurs a higher processing cost, it leads to higher yield and lower waste.
Marine collagen mitigates health risks associated with animal-based collagen
Fish provide an alternative source for collagen powder processing. By-products such as scales, skin, and bones contain an appreciable amount of this protein that can be safely extracted. Marine collagen fibers tend to be less intertwined and more fragile than other animals, making acid pre-treatment more suitable.
Fish-based collagen overcomes concerns such as disease transmissibility associated with cattle or poultry. But with a low denaturation temperature of 25–30 ◦C, the properties of the substance can be disrupted by average body temperatures.
Processing steps involved in collagen powder making
Which collagen powder technology do you need?
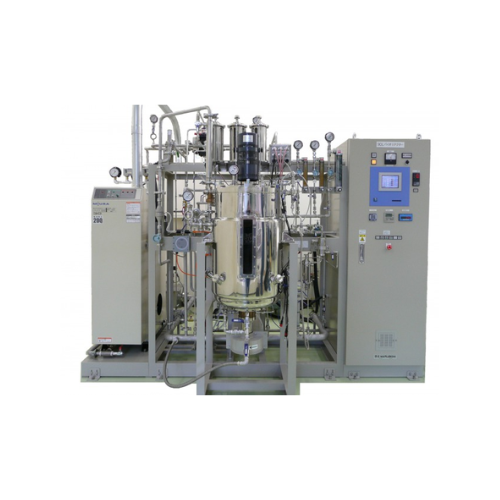

Sterilization in place fermentor for bioprocess applications
Optimize your fermentation processes with seamless integrat...
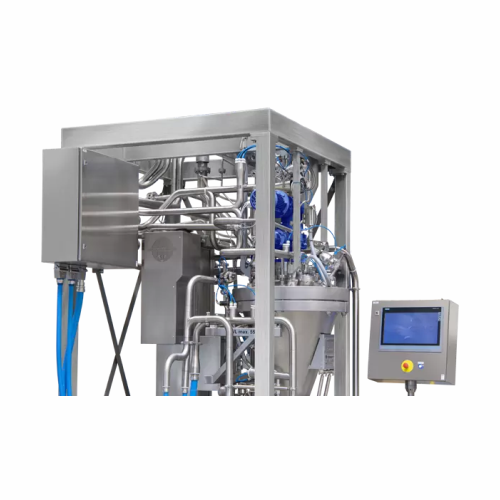

Pharmaceutical freeze dryer
Achieve contamination-free, high-quality pharmaceutical powders through an innovative freeze-dry...
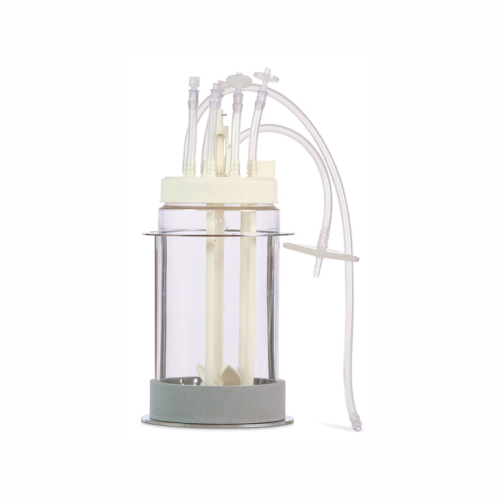

Single-use lab-scale bioreactor for upstream bioprocessing
Streamline your bioprocess development with a customizable, s...
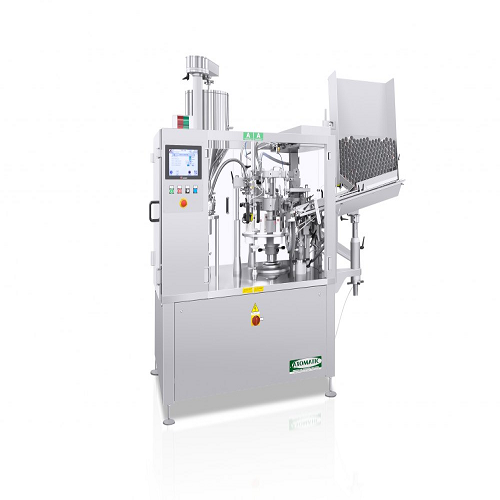

Automatic tube filling and closing solution
Optimize your production line with a high-speed machine for precise tube filli...
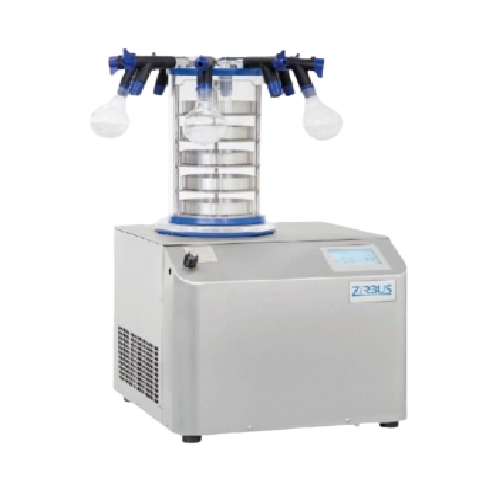

Laboratory freeze dryer for small batch processing
Ensure precise moisture control and stability in sensitive samples wit...
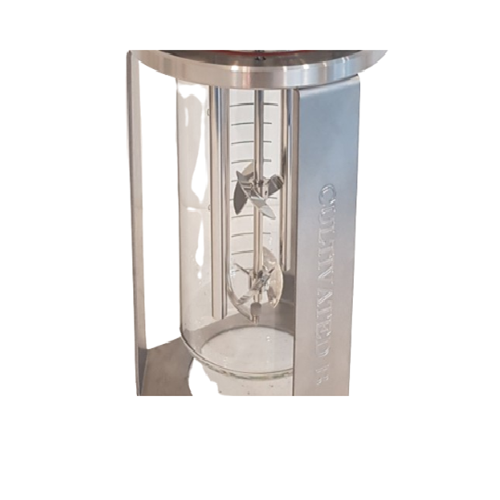

Benchtop bioreactor for research and development
Achieve precise control over fermentation and cultivation processes with ...
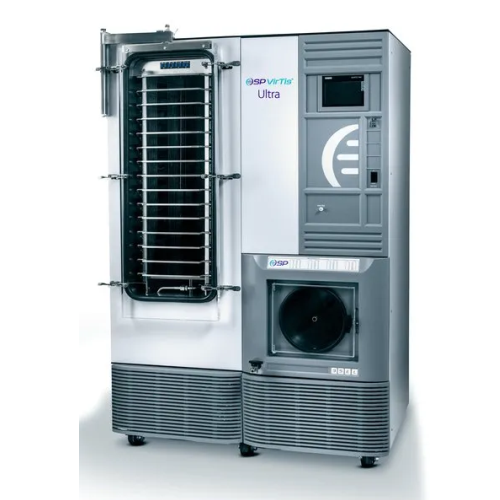

Pilot-production freeze dryer for diagnostic kits and Api
Optimize your lyophilization process with this versatile freez...
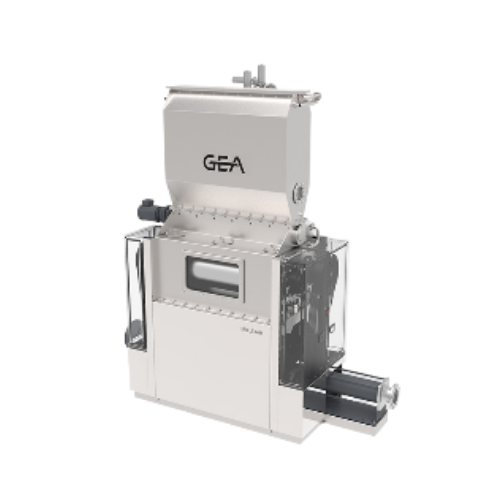
Gentle mixing solution for gelatin powder
The fragile nature of gelatin makes it a challenging material to blend homogeneo...
Accurate multiple dosing system for powders
Dosing multiple powders in a batch process is time inefficient, especially whe...

Big bag discharger
Big bags offer suitable material handling for powder products from pharma and food ingredients to bulk and...
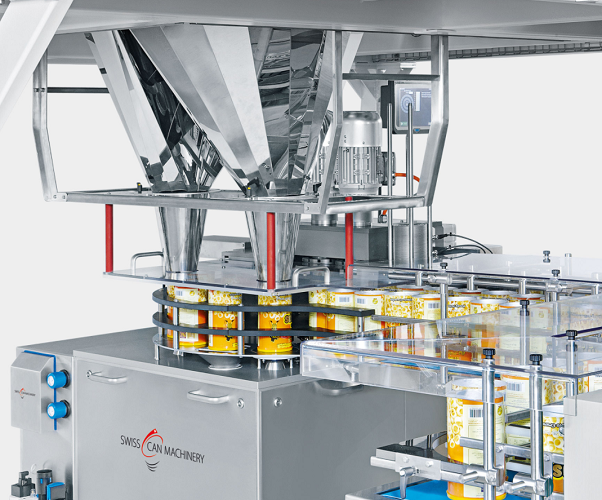

Filling and weight checking machine for food cans
Making sure the right quantity of product is in the packaging can be a ...

Gravimetric powder microdosing 2 - 100 g
Powders and granules are commonly dosed for the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, ...
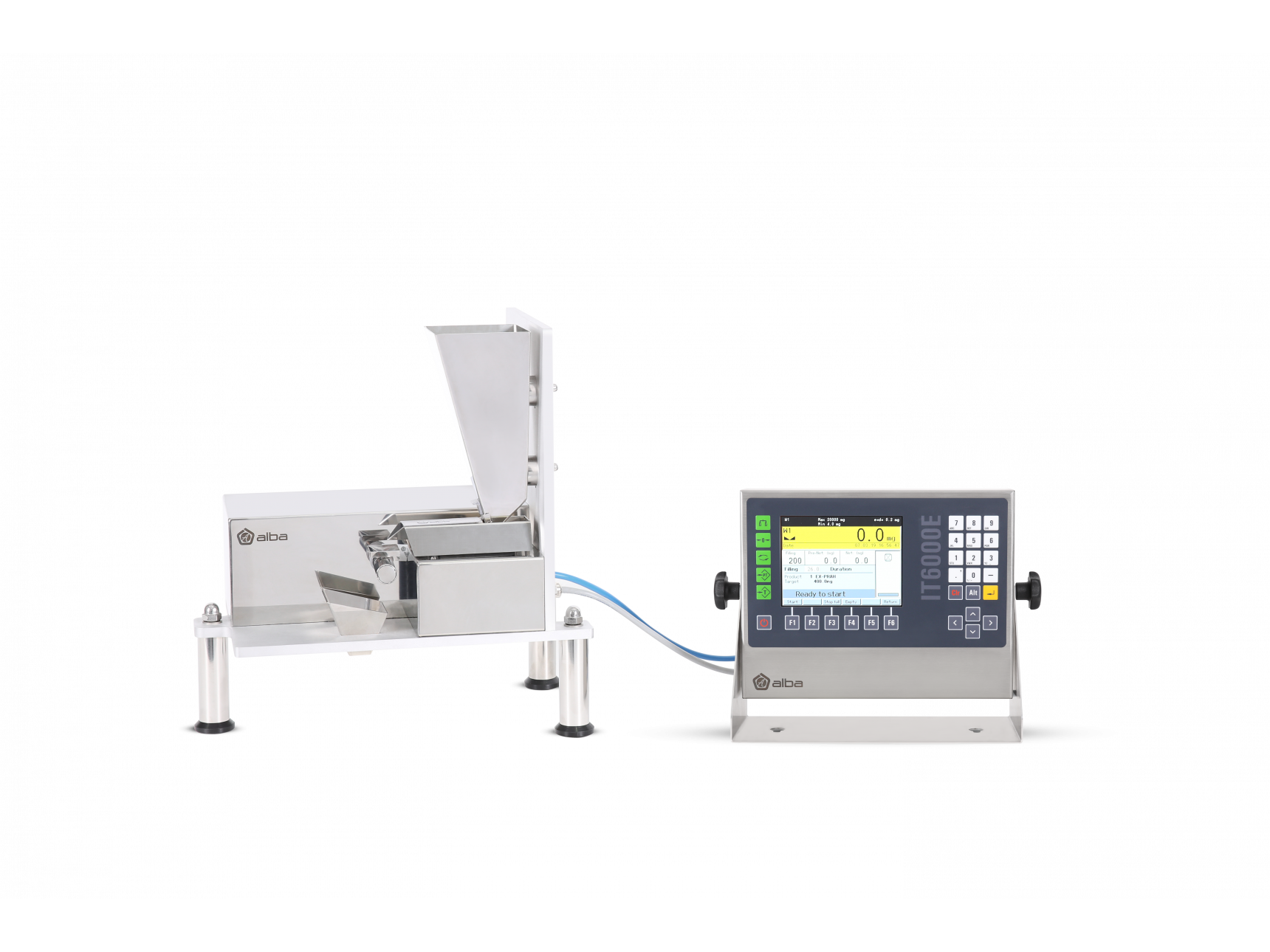

Gravimetric powder microdosing 0.400 - 2 g
If you need to process high value food, pharmaceuticals or chemicals, there is ...
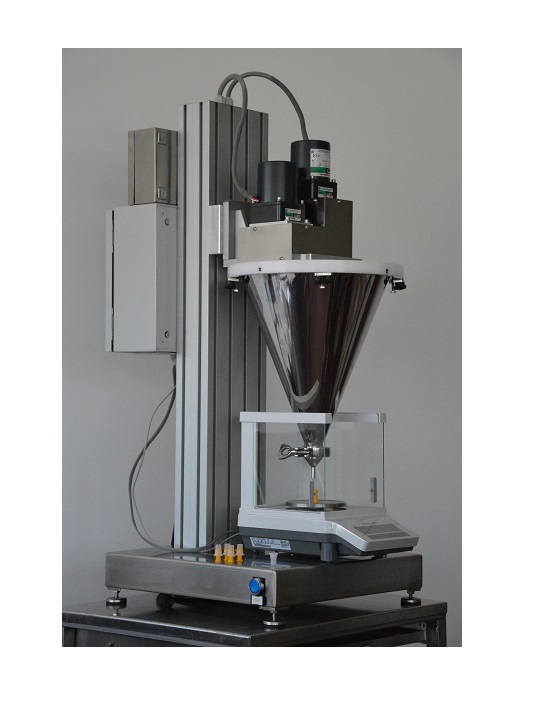

Semi-automatic powder dosing machine
Powders or granules are common dose types used in many pharmaceutical and nutraceutica...
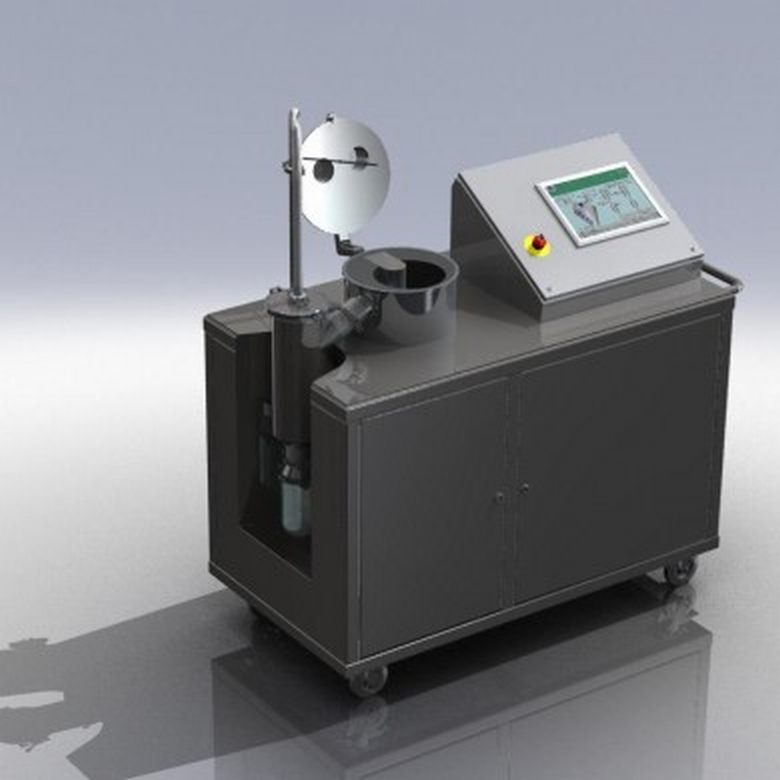

Laboratory scale active freeze dryer
The laboratory-scale active freeze-drying is used for dehydrating high-value products ...
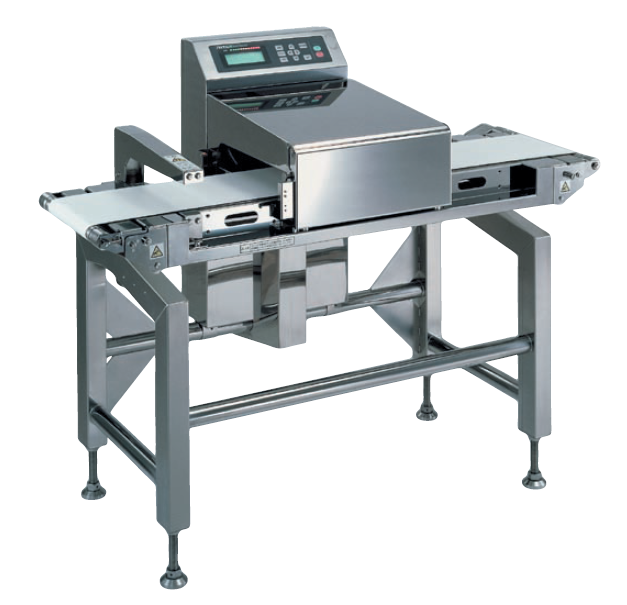

Metal detection system for aluminum packages
The magneto reflection system is ideal for detection of metals in aluminium f...
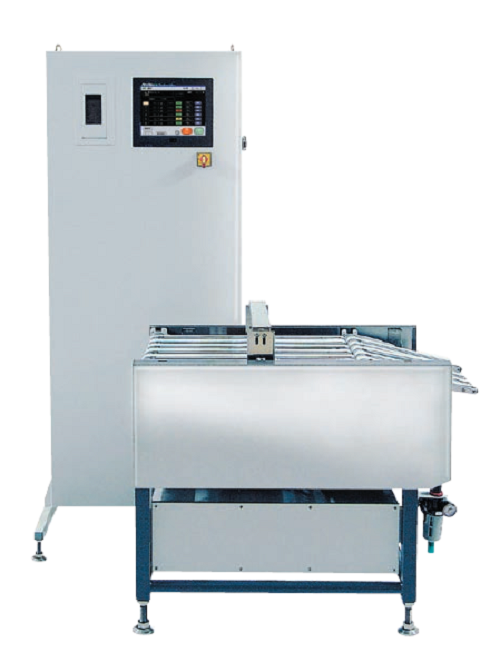

Checkweigher for sachets and sticks
The checkweighers for multiple lanes have a 1.5 times faster response speed and 2 times...
Microencapsulation system for your drug delivery system
Whether you want to improve the stability of nutrients, protect a...
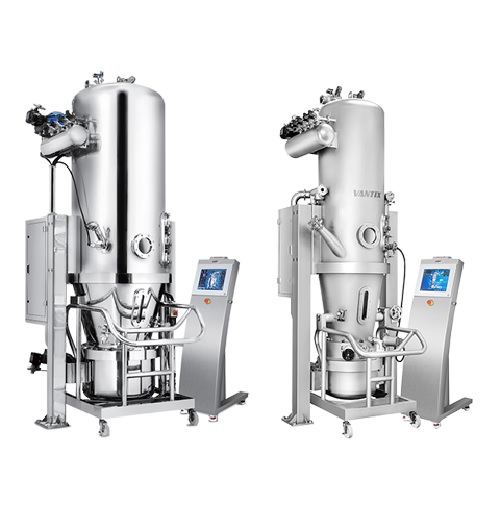

Fluid bed dryer for production scale
Fluidized bed drying (FBD) is a common process in the pharmaceutical industry for dryi...
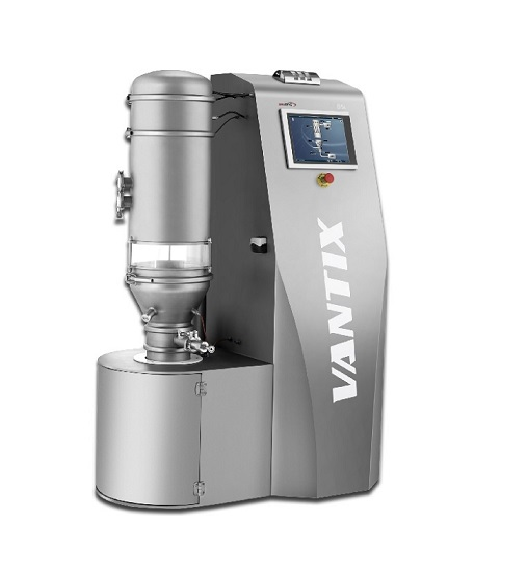

Fluid bed dryer for lab scale
Fluidised bed drying (FBD) is a common process in the pharmaceutical industry for drying compo...
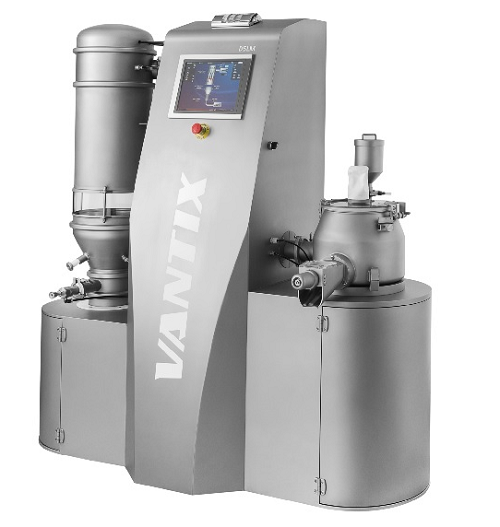

Fluid bed dryer and mixer for lab scale
Designed for pharmaceutical R&D, a lab-scale fluid bed dryer and mixer/granulat...
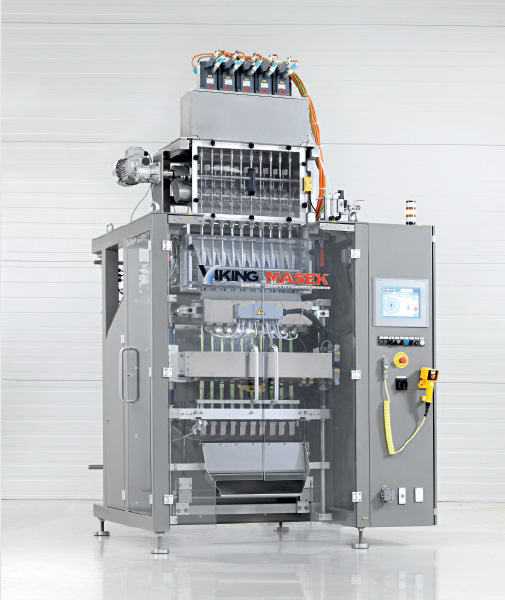

Stickpack Machine
If you are looking to pack your product into stick packs from 17 x 40 mm to 100 x 200 mm in size, you may b...
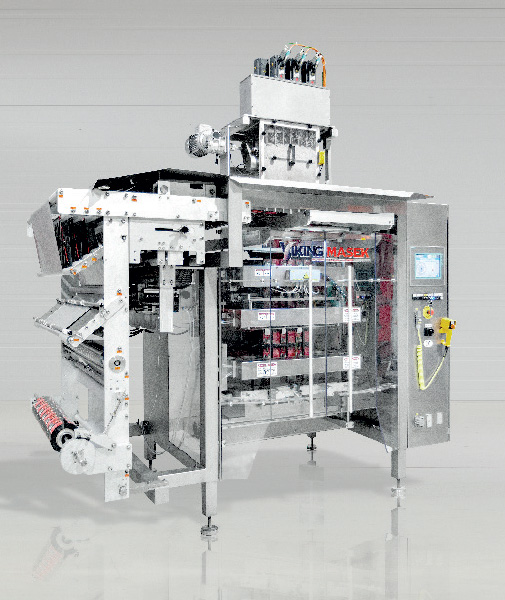

Sachet Machine
If you want to pack into eye-catching 4-side sealed sachets between 40×50 mm and 250×200 mm in size, ...
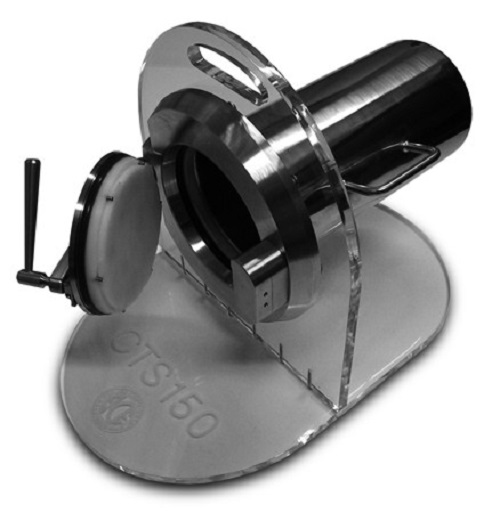

Transfer system for high-containment environments
A high-performance transfer port system that combines ultimate safety, ...
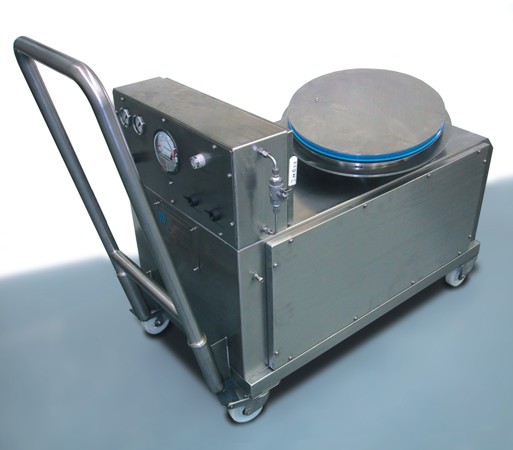

Half-suit tester
Designed to allow operators to perform sterility testing in an aseptic environment providing assurance of mat...
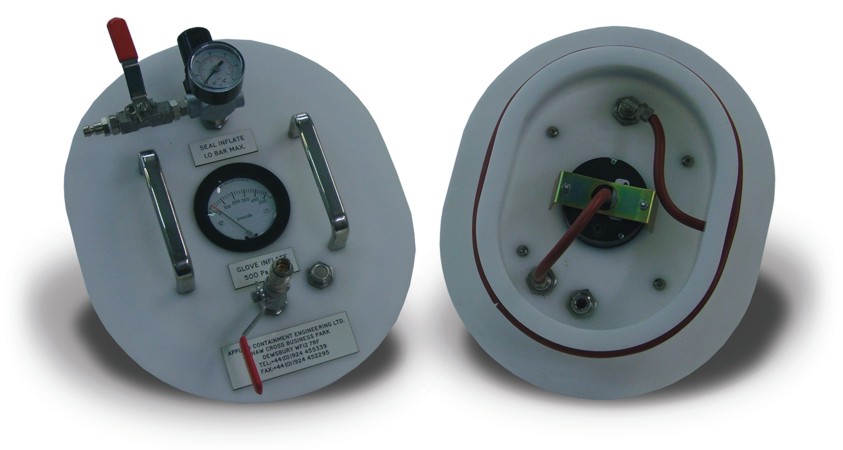

Glove tester
Testing device of the containment capability of gloves, which is as important as the other parts of the integrate...
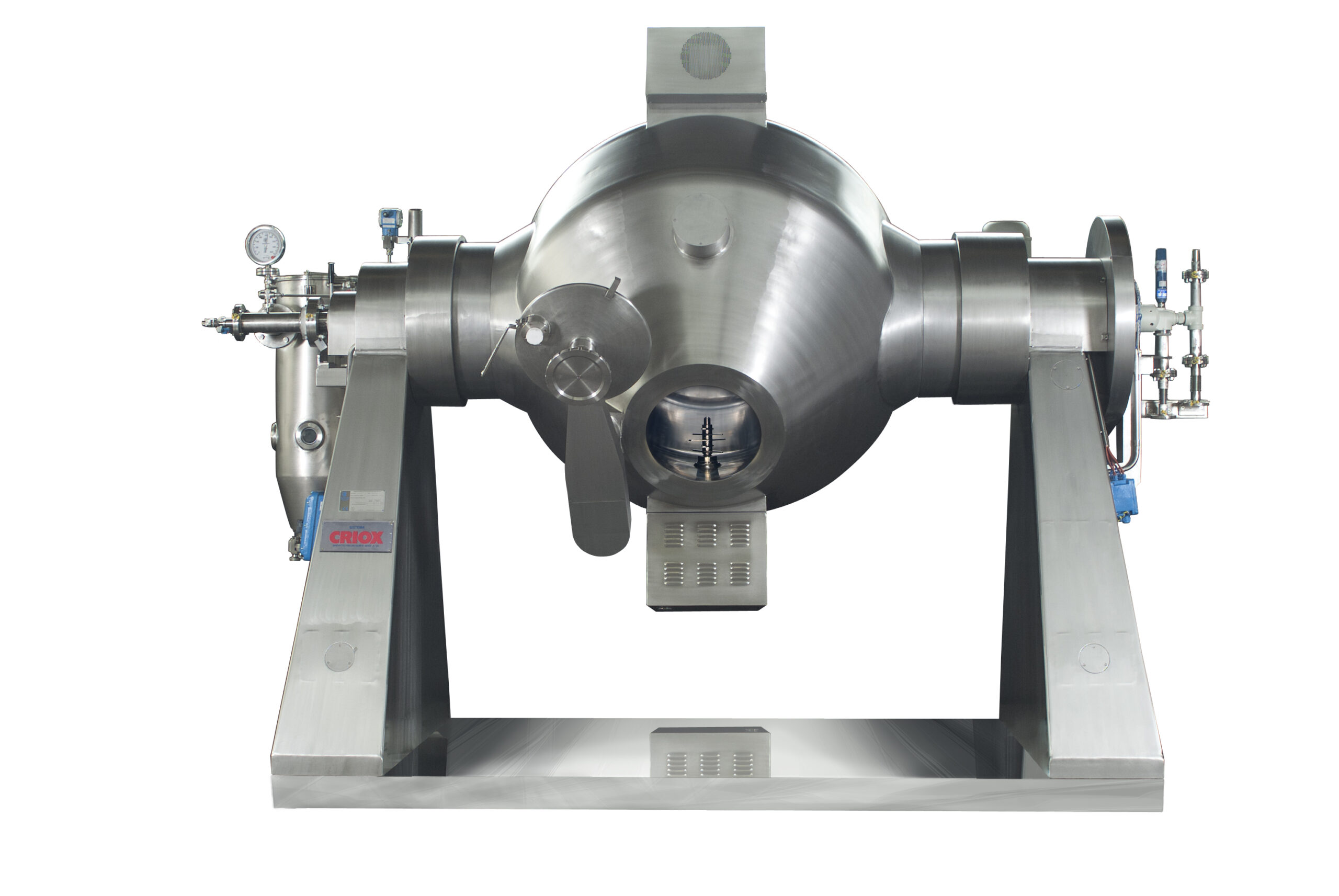

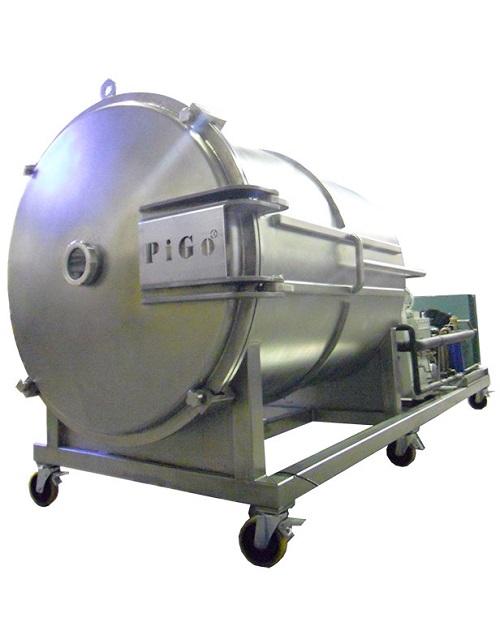
Rotary vacuum dryer
Powdered products tend to agglomerate during vacuum drying. This adds an additional step to the productio...
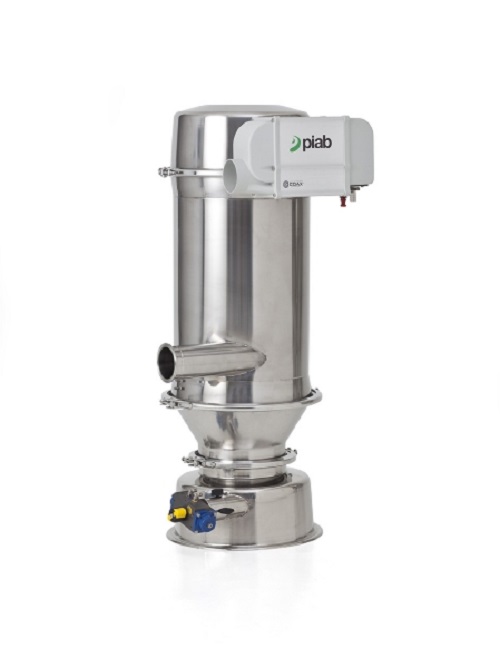

Premium vacuum conveyor
When you have a need to tailor make your conveyor and still have the high requirement on hygiene, e.g...
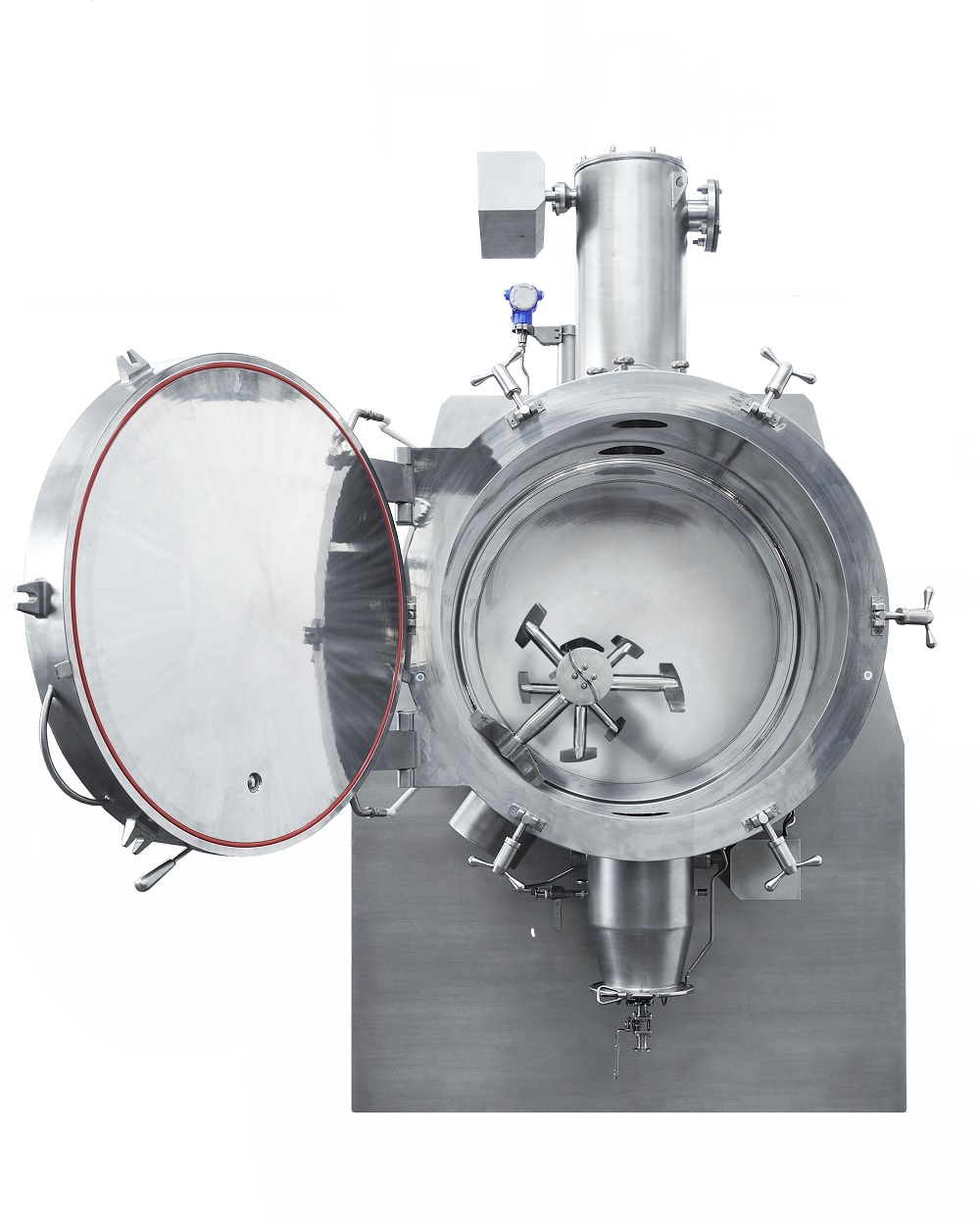

Horizontal vacuum dryer with eccentric agitator
Conventional dryers are inefficient and can lead to significant mechanical...
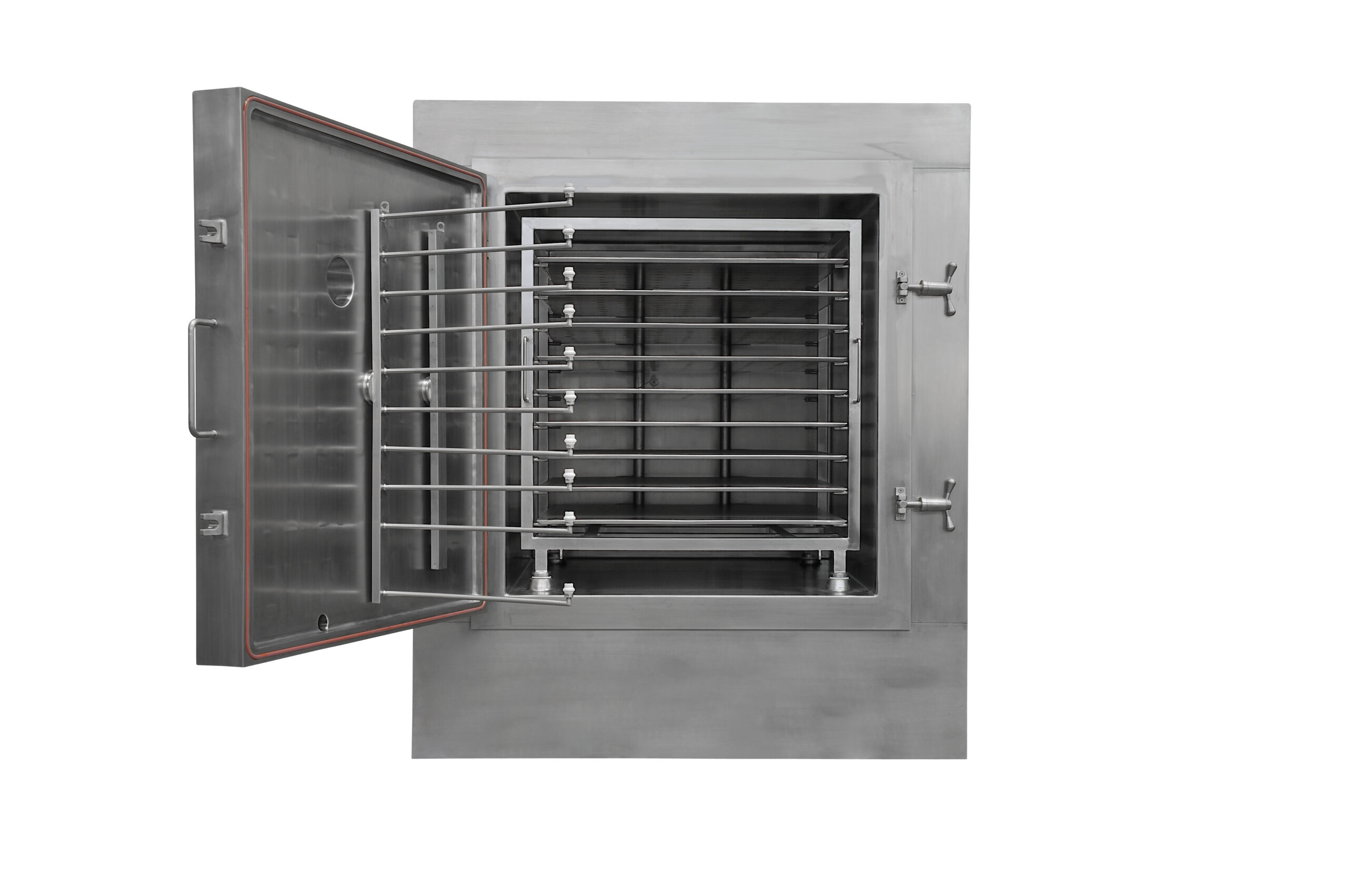

Vacuum tray dryer with clean-in-place system
Cabinet tray dryers can be difficult to clean, making their use difficult for...
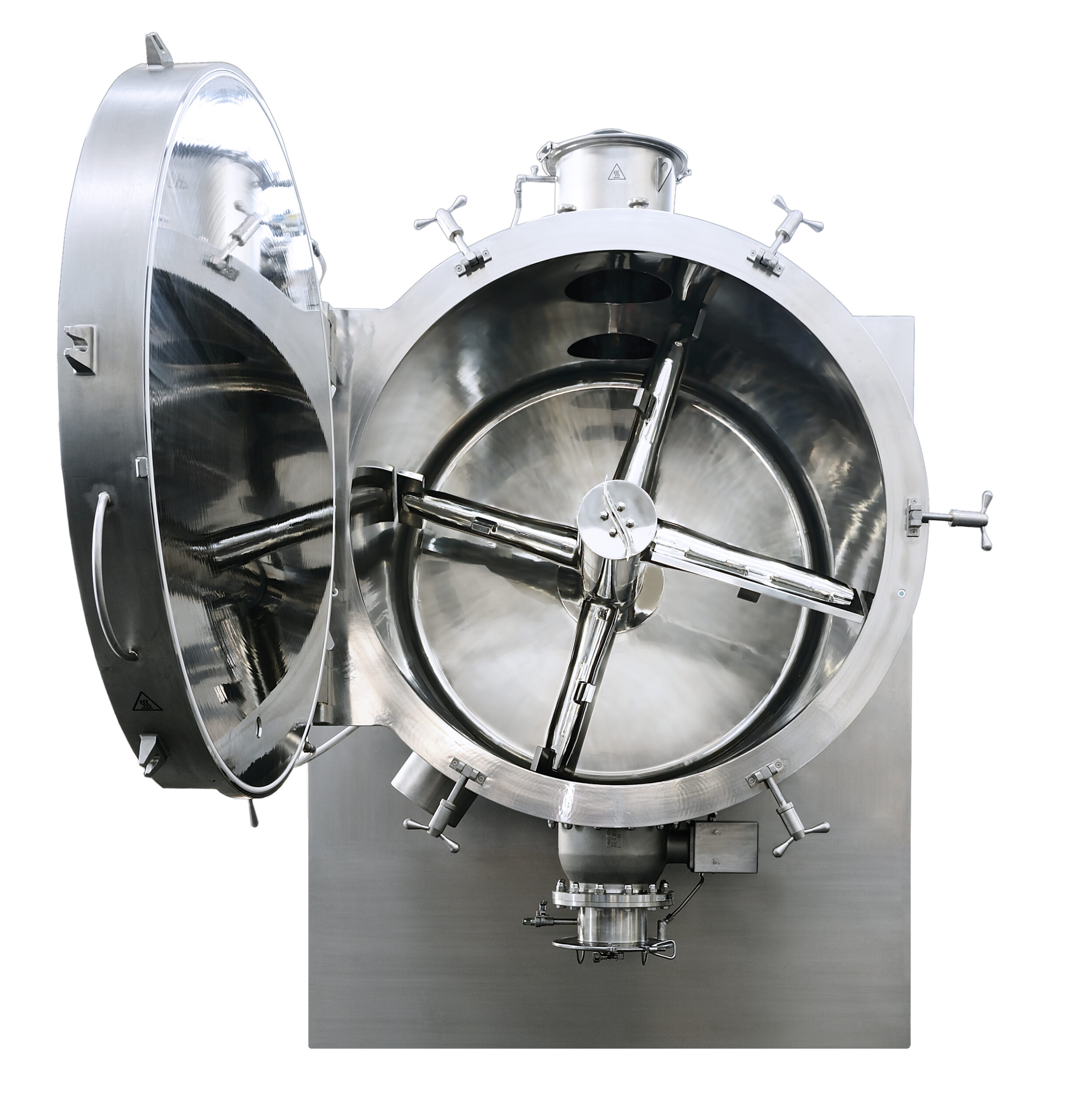

Horizontal paddle vacuum dryer
Agitated vacuum dryers can be difficult to clean which makes them unsuitable for multi-produc...
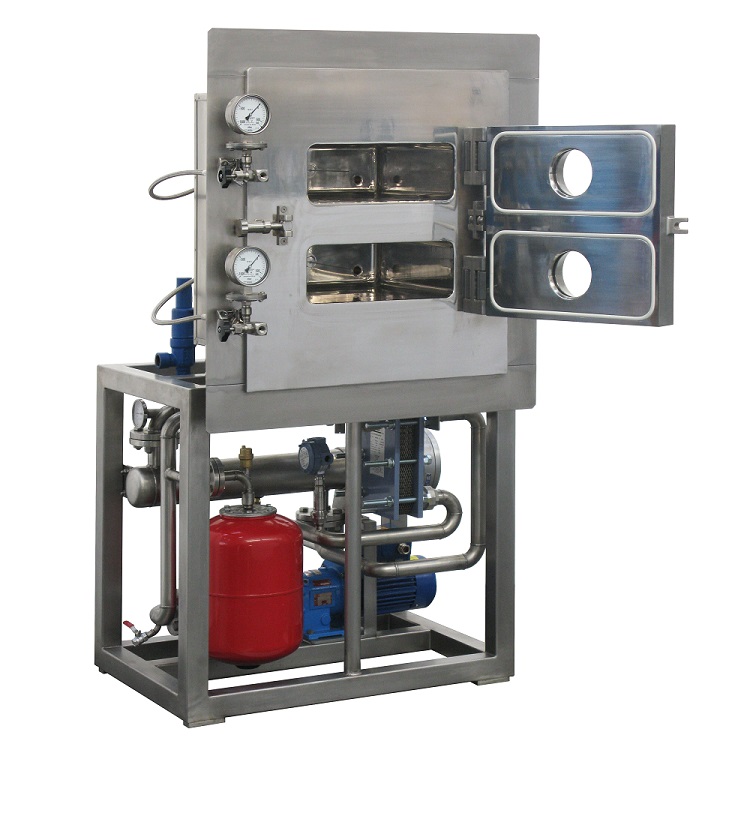

Laboratory-scale vacuum tray drying oven
Vacuum drying is used to remove moisture from sensitive materials. Drying small ba...
Hygienic floor scale with lifting device
The food and pharmaceutical industries require maintaining high levels of sanitati...
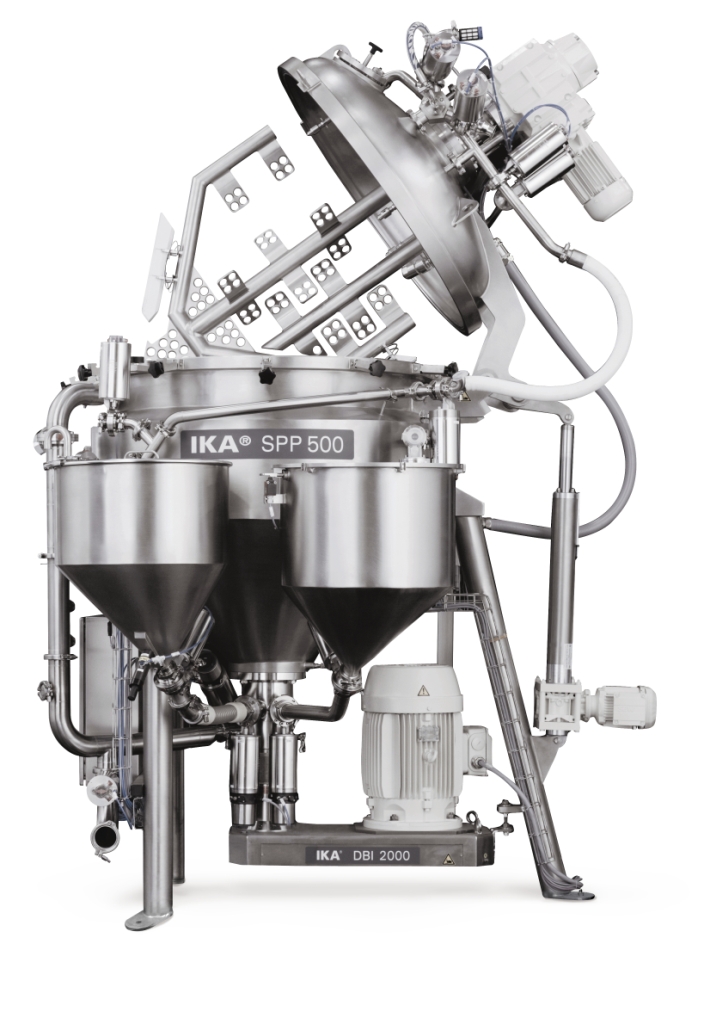

Cost-effective homogenizing and emulsifying system
Manufacturers of cosmetic products need mixing equipment that is capab...
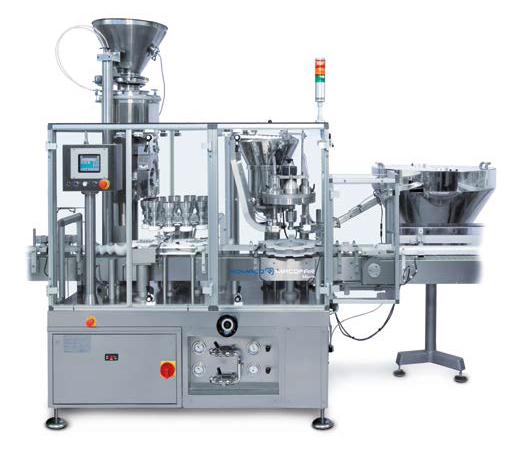

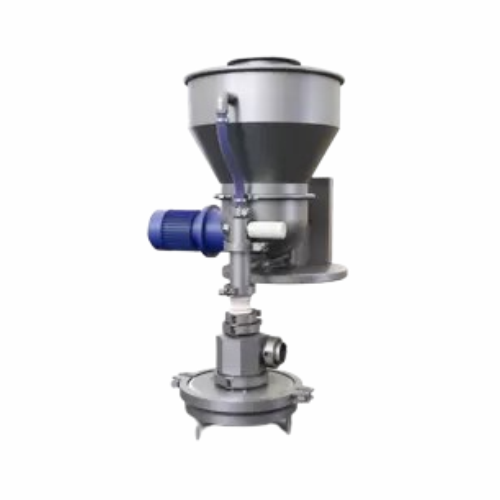
Dosing machine for nonfree-flowing powders
Fill poorly flowing powders, dry syrups and similar substances into various gla...
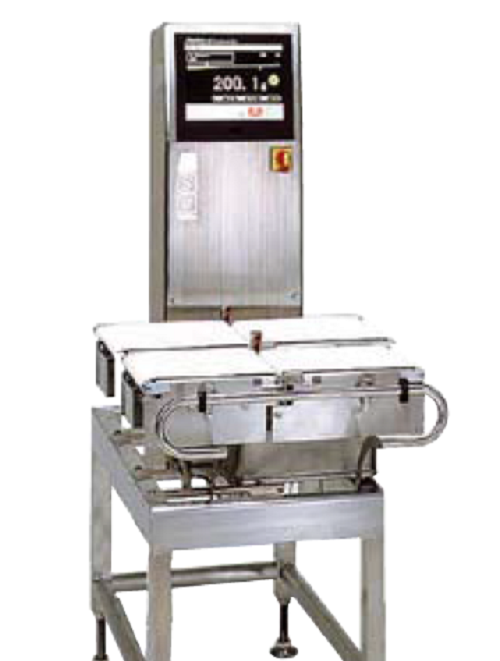

Checkweigher for stand-up pouches
When working with several lines of stand-up pouches, you can benefit from controlling the...