Making Water For Injection
Find innovative production technology for making water for injection and connect directly with world-leading specialists
If you've ever heard the acronym WFI spoken, know that we're not talking about wireless technology to connect your computer. WFI stands for water for injection, a sterile water used as a solvent to dilute other solutions for injections to the body. Traditionally, WFI was only produced through the distillation process using water for injection equipment until other methods such as reverse osmosis, electrodeionization, and ultrafiltration were developed.
Select your water for injection process
Tell us about your production challenge
Achieving high purity water through different water for injection equipment
Achieving high purity water for injection requires complex equipment that depends on the preferred method to be used. The three common methods for WFI production are multiple effect distillation, vapor compression distillation, and reverse osmosis, electrodeionization, and ultrafiltration. They all use water softening and carbon filtration as a means of scale control and dechlorination of the water source.
Starting with the multiple effect distillation method, your feedwater is preheated before going to a column containing a heat exchanger. As the feedwater is heated, the cyclone separator separates the pure steam which is then used to heat more feedwater.
The condensate of pure steam collected in the condenser that goes to the holding tank is your water for injection.
The second method is vapor compression distillation. Feedwater is preheated before going to the decarbonator which removes non-condensable gases from the feedwater. It then goes to the evaporator tubes where steam-heating coils at the bottom further heat the feedwater to convert it to vapor. A demister removes water droplets from the vapor before the vapor goes to evaporator bank where it condenses, forming distillate. This distillate is collected in a box and pumped through a cooler to produce water for injection.
The third method combines multiple processes such as reverse osmosis, electrodeionization, and ultrafiltration using different water for injection equipment such as filters and membranes. Reverse osmosis uses membranes to remove most of the unwanted molecules and particles. Electrodeionization removes positive and negative ions using electric power and is considered as a polisher after performing reverse osmosis. Ultrafiltration uses ultra-fine membrane filters to further remove contaminants.
Bacteriostatic water or sterile water for injection?
Water for injection, in general, should be pure. Though in some applications, it may be necessary to add antimicrobial agents to minimize the chance of contamination once opened. Bacteriostatic water is sterile water containing 0.9% benzyl alcohol used to dissolve or dilute medications administered through intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous injection.
The container can be re-entered multiple times by sterile needles for injection because benzyl alcohol stops the growth of a possible contaminating bacteria, making it applicable for multi-dose medications. However, not all drugs are compatible with bacteriostatic water. Sterile water is purified water and does not contain any preservative or antimicrobial agent, making it only applicable for single-dose applications.
Standard criteria for qualifying water as WFI
Pharmacopeias develop standards to ensure that water for injection is pure and safe for its intended application. There are differences in the criteria used by Europe, the USA, and Japan Pharmacopoeias for the production of WFI. Europe requires using distillation processes only while the US and Japan allow membrane and other purification processes.
They all have similarities for some criteria such as for conductivity which should be less than 1.3 mS/cm or total organic carbon (TOC) in organic compounds found in aqueous systems, should not be more than 500 ppb. Endotoxins that are considered as pyrogens that can cause fever to patients should be less than 0.25 EU/mL. In contrast, bacteria or total aerobic microbial count should be less than 10 CFU/ 100mL and pH level between 5.0 to 7.0. These ranges in the criteria are considered safe for applications as water for injection.
Processing steps involved in water for injection making
Which water for injection technology do you need?
Membrane filtration system for bioburden and water testing
Ensure accurate microbial detection and efficient filtration ...
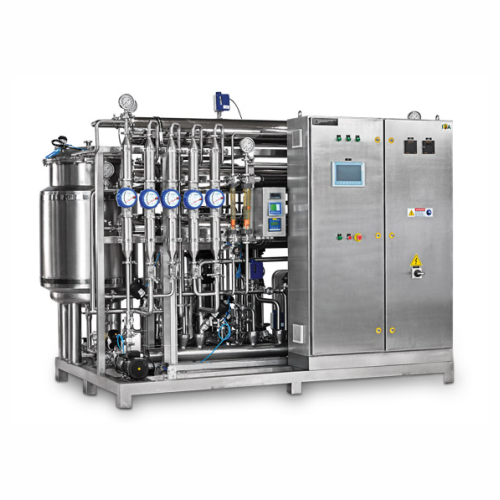

Purified water generation system for pharma applications
Ensure consistent purity in your therapeutics production with a ...
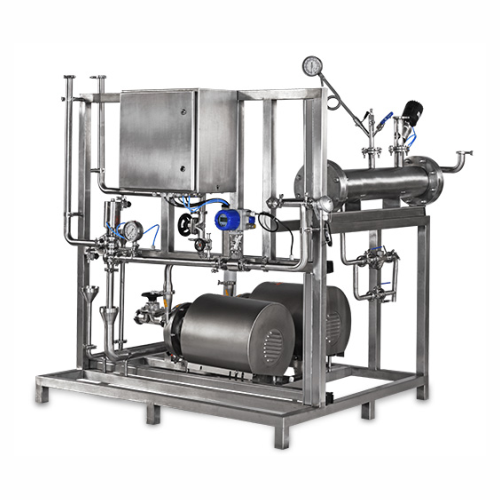

Purified water storage and distribution for pharmaceuticals
Ensure seamless water quality for critical pharmaceutical pr...
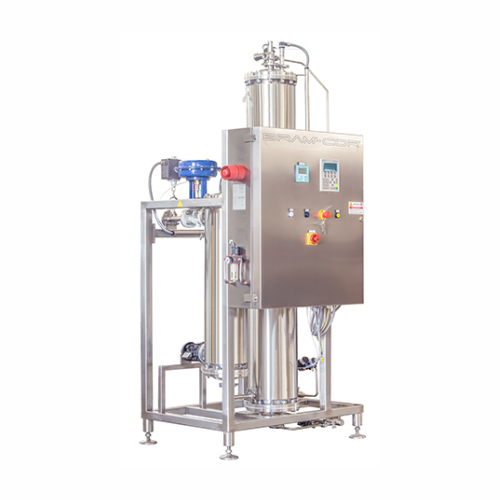

Pure steam generation and distribution system
Ensure reliable sterilization with pure steam that’s free from contami...
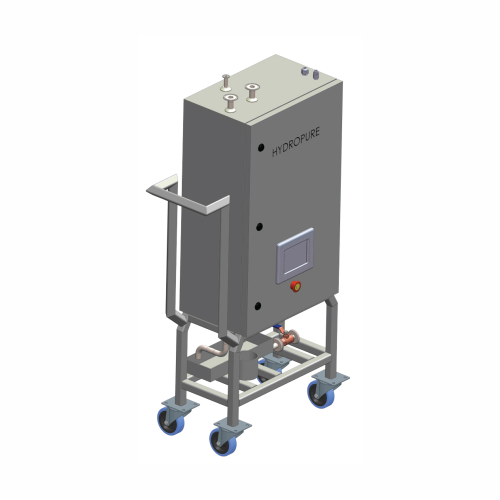

Pure steam sample cooler for pharmaceutical industry
Ensure sterile sampling of pure steam while maintaining precise cool...
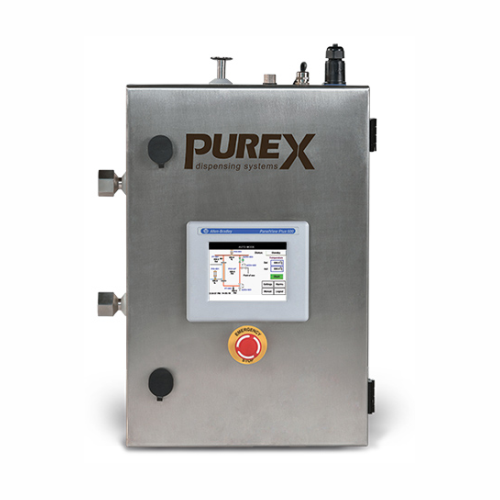

Wfi cooler
Ensure precise temperature control and contamination-free dispensing for high-value liquid formulations with this a...
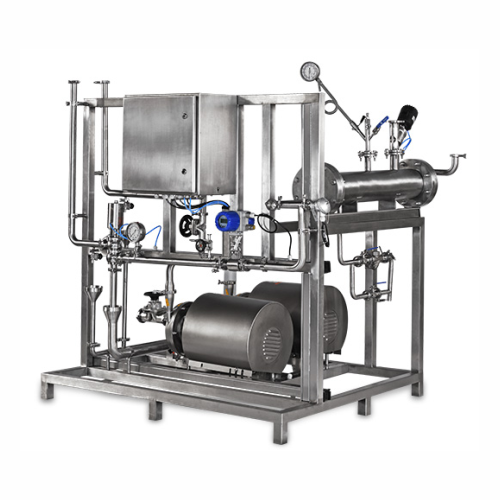

Water for injection storage and distribution system
Ensure the integrity and sterility of injectable solutions with this ...
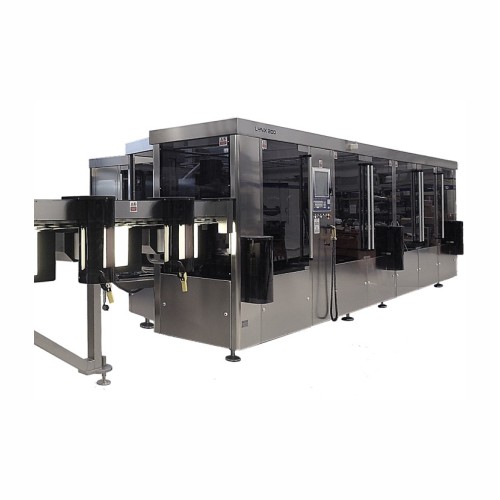

Optical inspection system for large parenteral containers
Ensure the quality and safety of liquid pharmaceutical product...
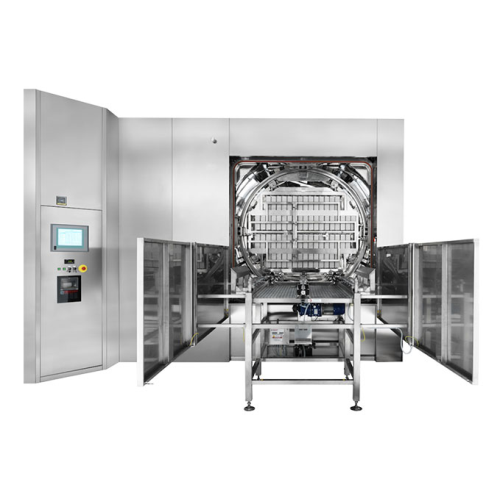

Superheated water sterilizer for large volume parenterals
When sterilizing large volumes of liquid products, achieving p...
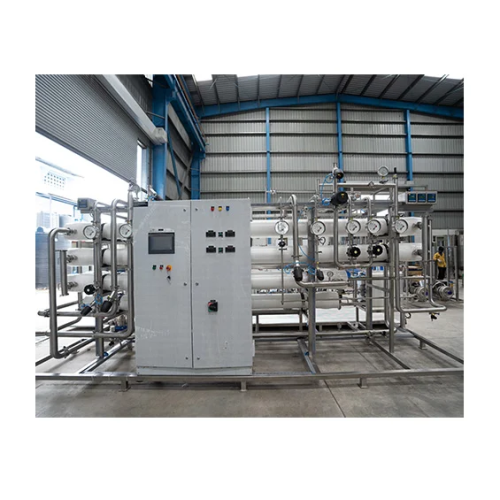

Purified water generation system for pharmaceutical applications
Ensure consistent water purity for critical drug formul...
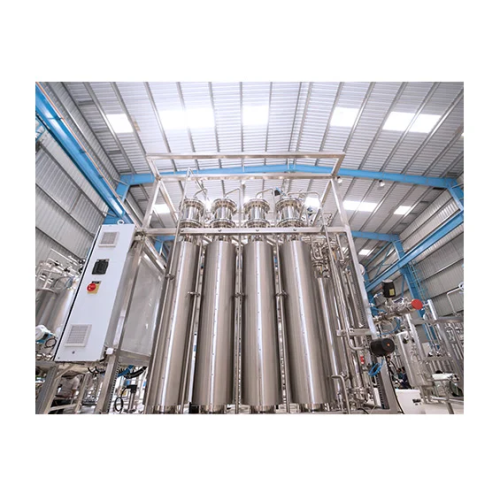

Water for injections generation system
Ensure compliance with strict regulatory standards while providing pyrogen-free wate...
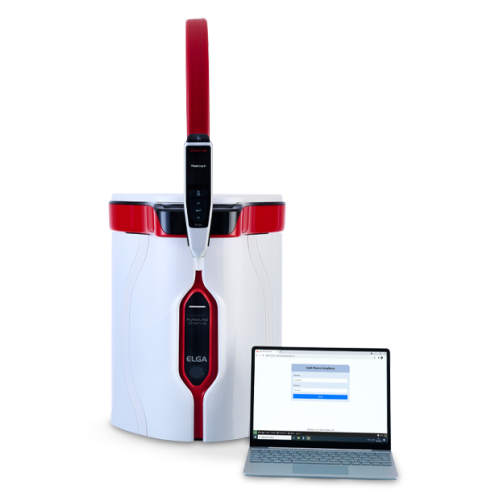

Pharmaceutical water purification system
Ensure compliance with stringent pharmaceutical standards by integrating a reliabl...
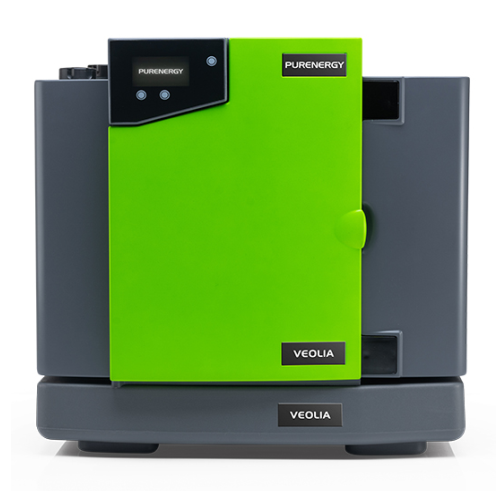

Water purification system for Pem electrolyser
Achieve premium water purity essential for hydrogen electrolysers with this...

Ultrapure water system for laboratory applications
Ensure uncompromised water purity for critical applications with a sys...

Centralized water purification system for laboratories
Ensure consistent purity and reliability for your laboratory proce...

Preparation tank isolator for reactor charging
Ensure aseptic conditions for sterility testing and safe handling of sensit...

Full-membrane water for injection (wfi) generation system
Ensure consistent high-quality injections by integrating real-...
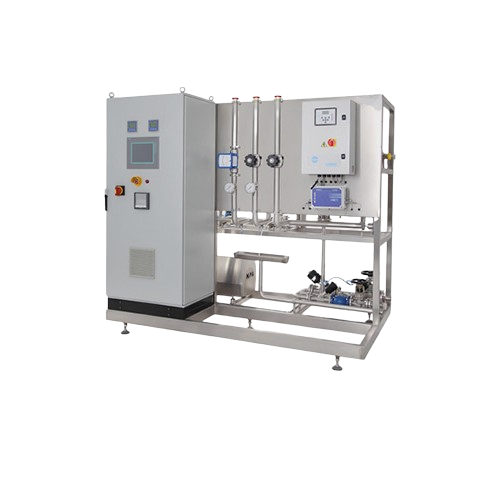

Pharmaceutical-grade Pw storage and distribution system
Ensure consistent purity and compliance in your pharmaceutical wa...
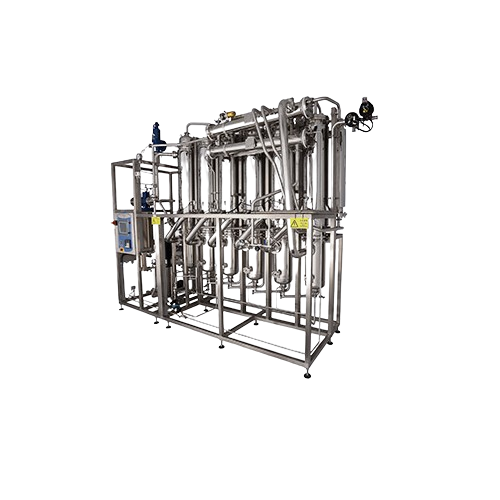

Multi-effect water distiller for pharmaceutical and biological applications
Achieve unmatched water purity for sterile...

Pure steam generator for pharmaceutical sterilization
Achieve ultra-pure steam for critical sterilization tasks, ensuring...
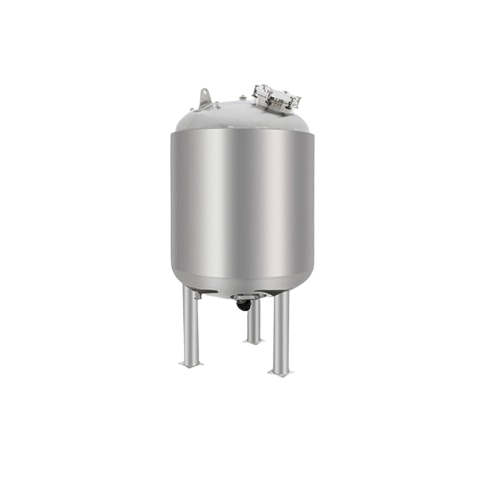

Purified water storage tank for pharmaceutical use
Ensure the integrity of your pharmaceutical formulations with precisio...
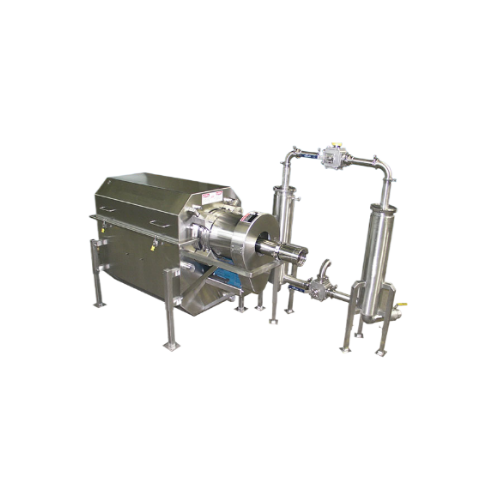

Water reuse system for poultry processing
Optimize your poultry processing with a customizable water reuse system designed...

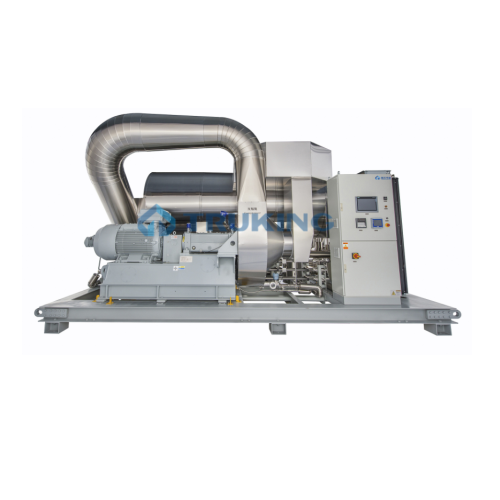
Cip for pharmaceutical process plants
Streamline your cleaning processes with integrated CIP systems to ensure precise and ...

Pharmaceutical isolator system for aseptic production
Ensure aseptic conditions and operator safety with a robust isolati...

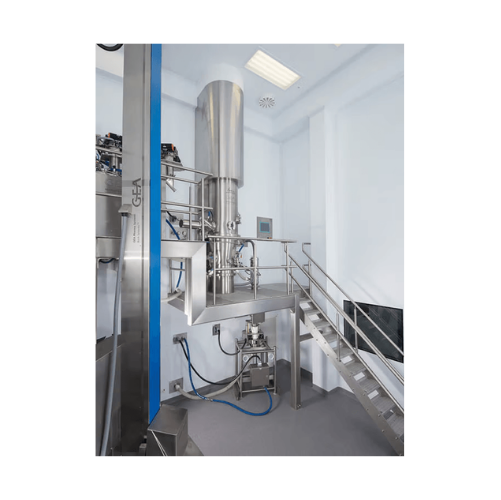
Ultra-pure water preparation system for pharmaceutical industry
Ensure your pharmaceutical production line meets stringe...

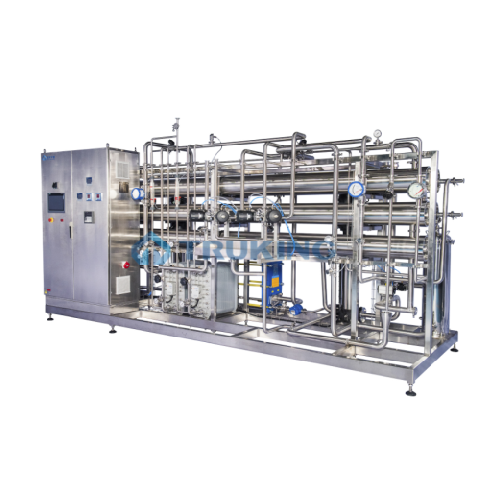
Hot press distilled water unit for pharmaceutical applications
Ensure superior water purity in pharmaceutical production...
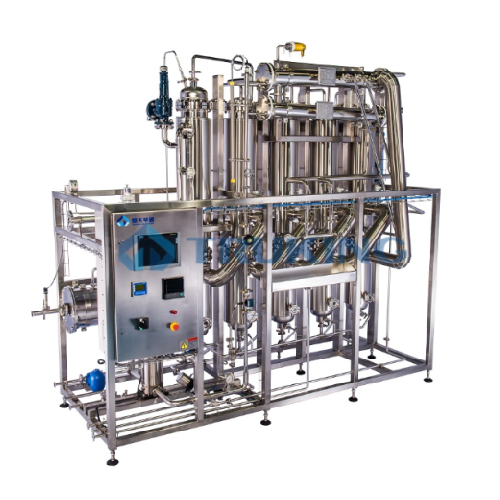

Multi-effect water distillator for pharmaceutical applications
Ensure your production line meets stringent regulatory st...

Pharmaceutical ultra pure water distribution system
Ensure stringent purity standards with a modular water distribution s...
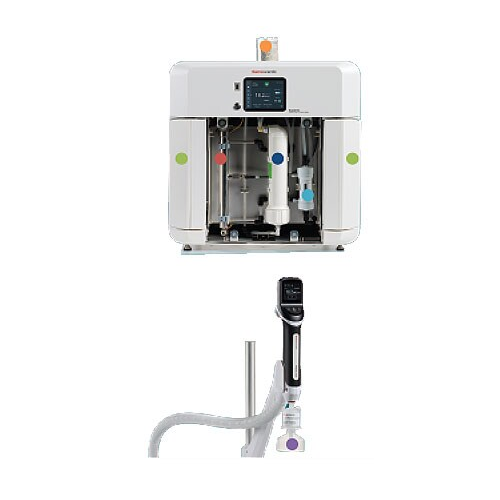

Ultrapure water purification system for laboratories
Achieve consistent high-purity water essential for sensitive laborat...
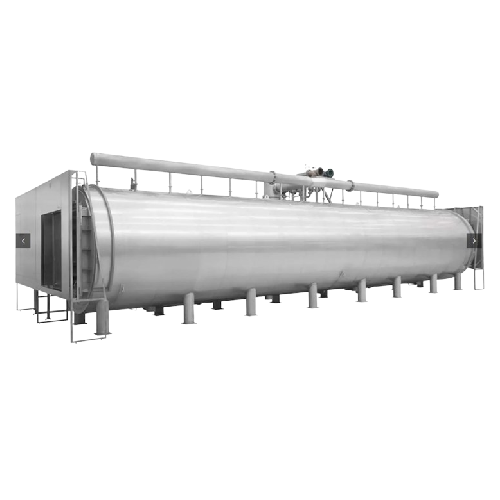

Superheated water shower sterilizers for parenteral solutions
Optimize sterilization cycles for liquid pharmaceuticals w...
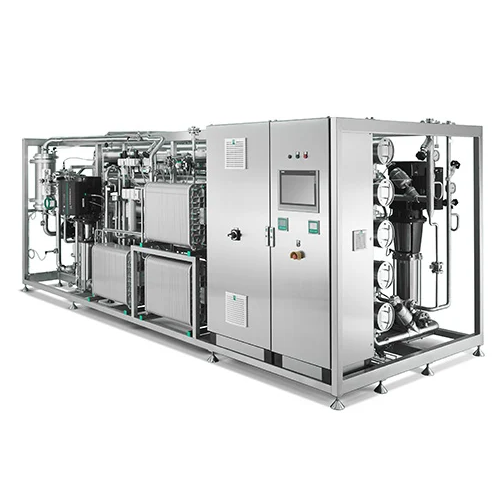

Pure water generation system for pharmaceutical manufacturing
Ensure high-purity water and steam production with precisi...
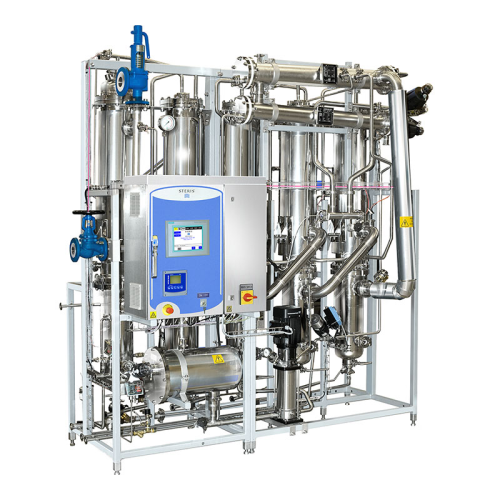

Multiple-effect water still for pharmaceutical applications
Optimize your pharmaceutical water production with a system ...
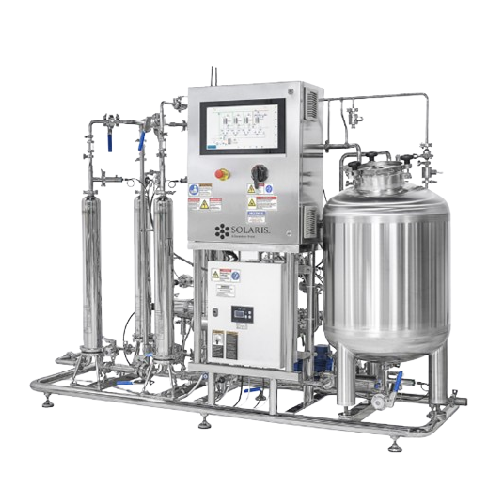

Full flow filtration system for bioprocess applications
Ensure sterile filtration of process liquids and aseptic chemical...
Soft bag form-fill-seal system for large volume injection
Streamline your production of intravenous and nutritional flui...
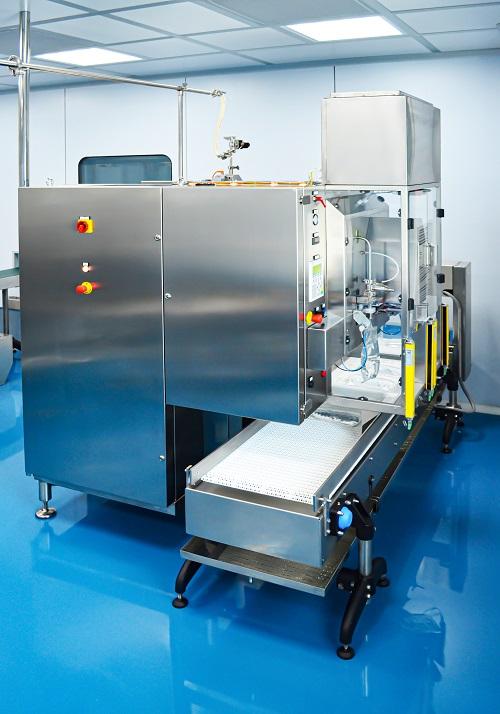

IV bag filling machine
Filling machines for intravenous bags require highly polished surfaces where they contact the bags or ...
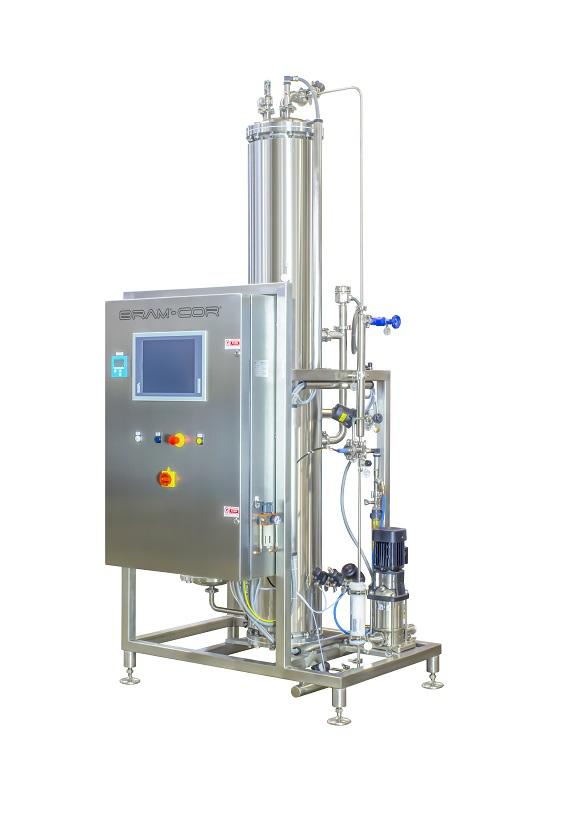

Pharmaceutical pure steam generator
Dry, saturated steam can be used to sterilise pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment, a...
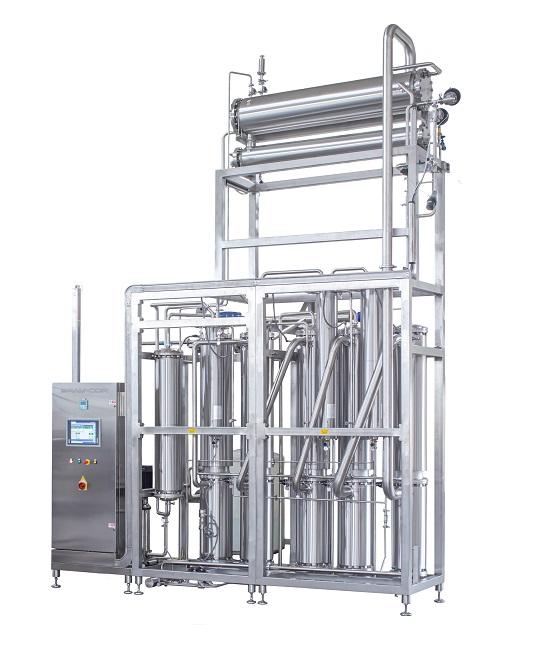

Water distillation system
Water used in pharmaceutical processes must meet high standards of regulatory bodies. These includ...
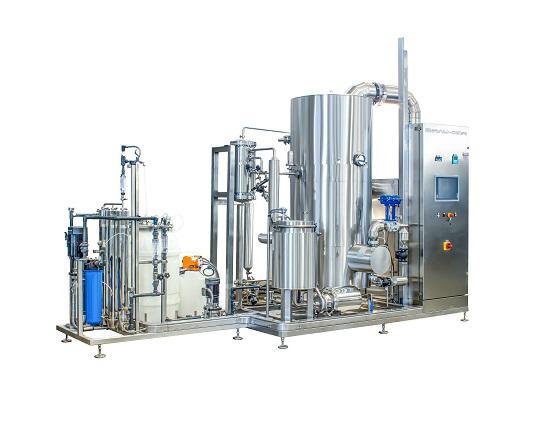

Vapor compression distiller
Water for injections must be of highest achievable quality to eliminate the possibility of conta...
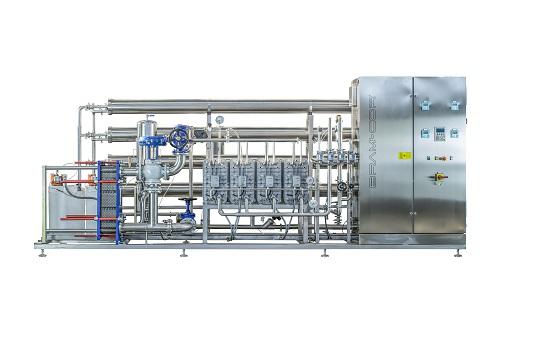
Reverse Osmosis water filtration system
Reverse osmosis uses a partially permeable membrane to remove undesirable molecules...
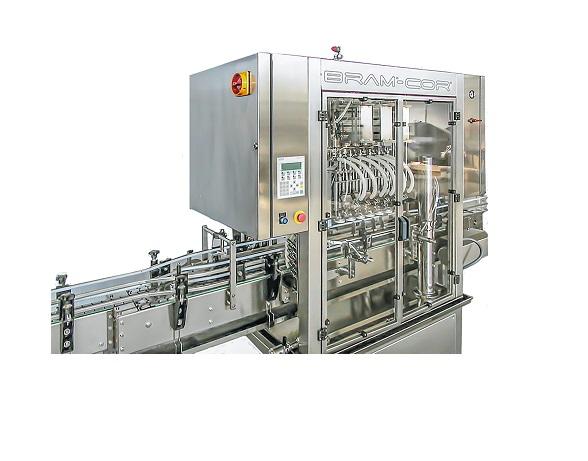

Pharmaceutical bottle filling machine
Filling machines for pharmaceutical bottles must achieve high production speeds while...
Shell and tube heat exchanger
Heating, cooling and tempering are important processes in the production of many products acro...
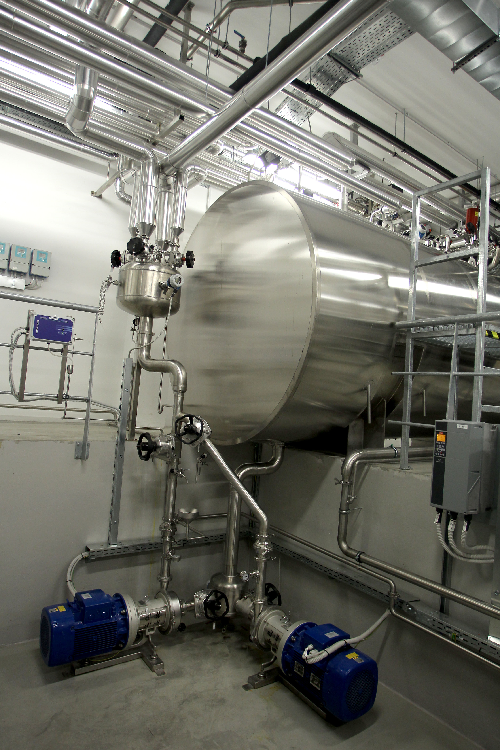

Purified water storage tank
Many pharmaceutical and cosmetic production lines require holding vessels for the storage of liq...
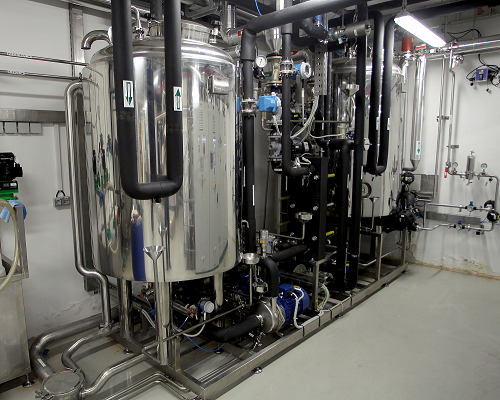

Cleaning and sterilization systems
An increasingly vital part of high quality pharmaceutical production is a dedicated Clea...
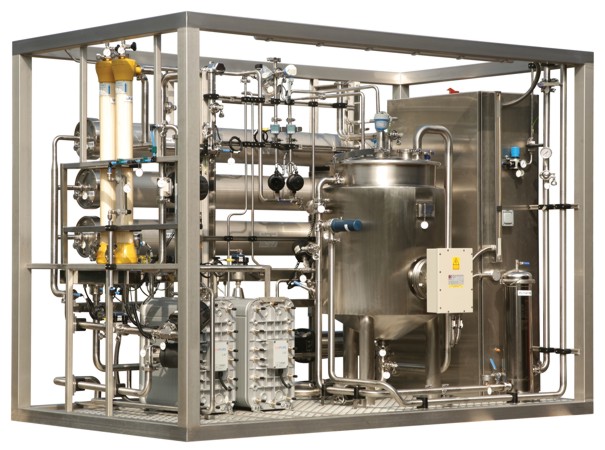

Purified water systems
Highly Purified water is used in the preparation of medicinal products where bacterial endotoxins need...
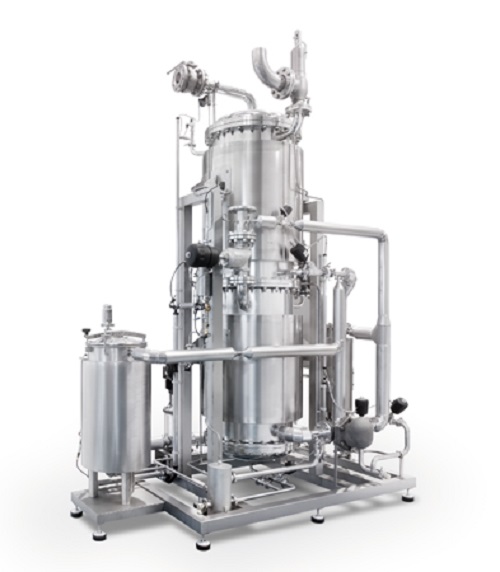

Pure steam generator
Pure steam is mainly used in the pharmaceutical industry and in biotechnology for sterilization, water f...
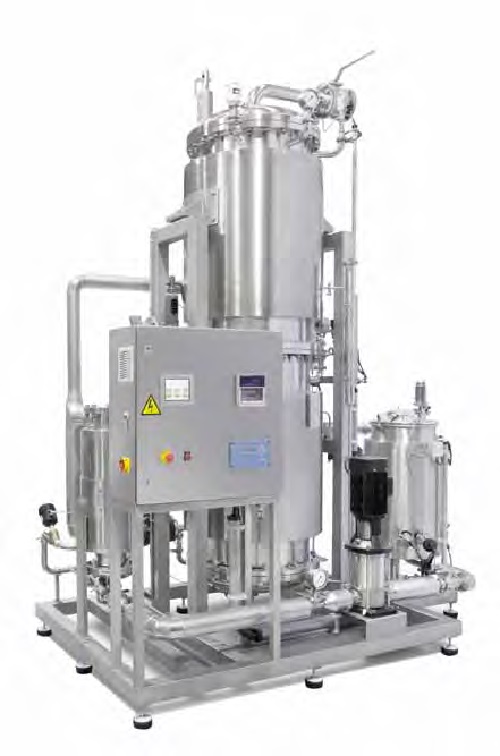

Electrical pure steam generator
Pure steam is defined as the steam which when condensed becomes WFI quality water in accorda...
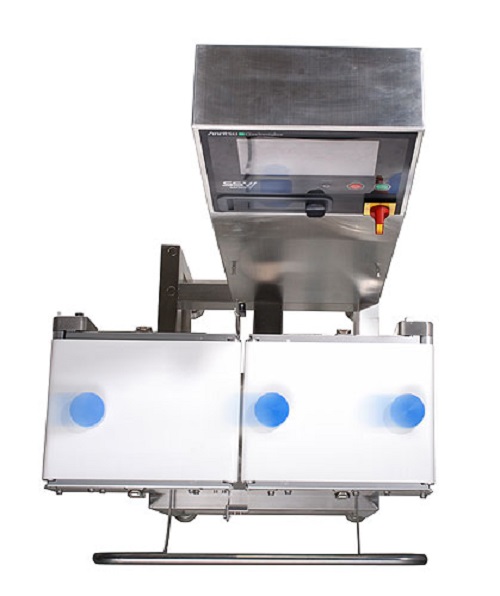

Versatile checkweigher
This Versatile checkweigher is equipped with a highly versatile strain gauge load cell. It is also sui...