Making Oatmeal
Find innovative production technology for making oatmeal and connect directly with world-leading specialists
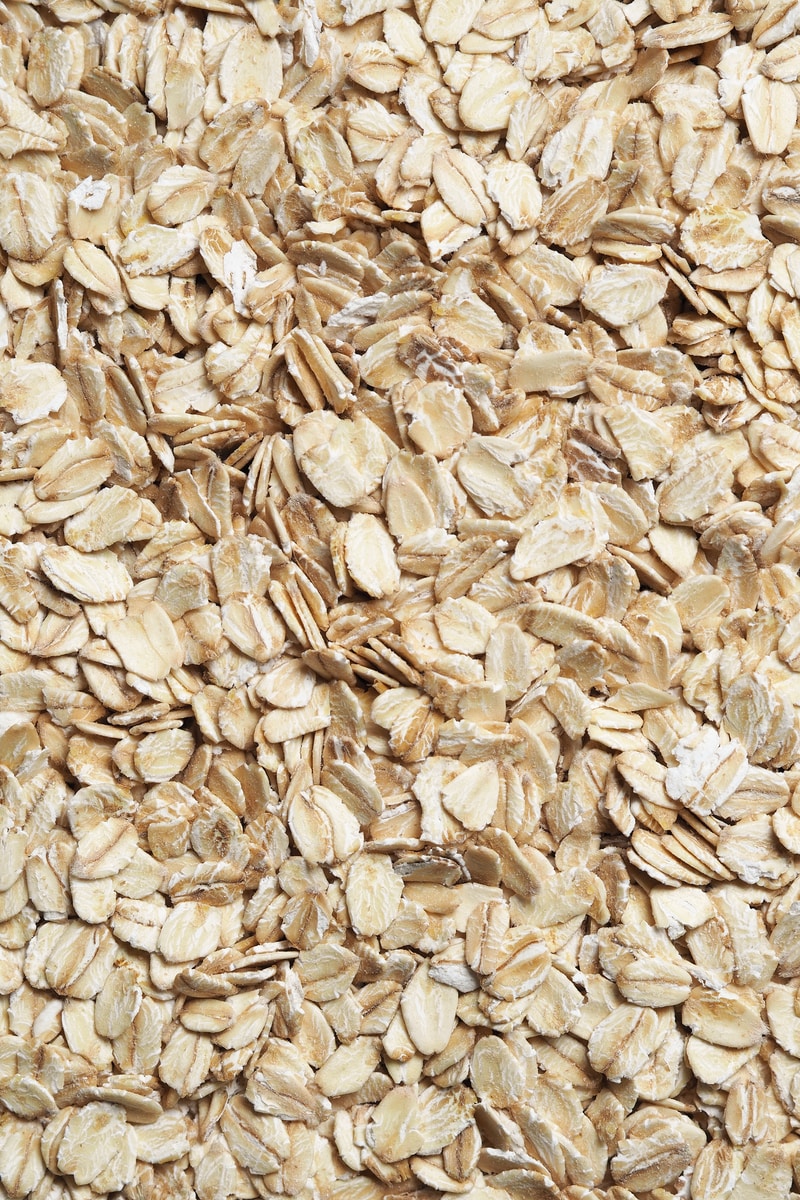
If you like a warm and easy breakfast, oatmeal can be a great option for you. Oatmeal, most commonly known as rolled oats, is prepared oats ready to consume in a form of porridge or cereal. Other than rolled oats, there are other types of oatmeal - such as steel-cut oats, quick oats, and instant oats. You first need to prepare clean oat groats - the hulled kernels of wild oats, and you can decide which oatmeal processing equipment you would like to set up and depending on the oatmeal of your choice.
Select your oatmeal process
Tell us about your production challenge

Preparing your oat groats for different types of oatmeals
Multiple different types of end products can be produced when it comes to oats. From oat groats to rolled oats, steel-cut oats, quick oats, and instant oats, the possibility of wild oats is limitless. To produce all of these products, however, you need to clean and process groats – the base of all oat products.
Once the wild oats are checked for their quality, they first have to be cleaned. During this cleaning process, any impurities are removed, and the oats are then graded for their qualities. Then, it is the dehuller’s turn to shine; during the dehulling process, the husk that covers the inside of the kernel – called the hull – is detached. These dehulled kernels now go through a kilning machine, a machine that heats up and dries the moisture from the oats. This process reduces microbial spoilage and develops a nutty flavor of groats. After this, the groats go through another grading process depending on their weight and damage.

Oatmeal processing equipment for steel-cut oats (Irish oats), rolled oats (old fashioned oats), quick oats and instant oats
Once you have prepared the clean and hulled groats, you can now decide which end product you would like to make. For manufacturing steel-cut oats, you simply need to cut the groats. You first need to transfer the groats into the rotary granulator, which has a drum-shaped rotational piece with steel knives that allows you to cut the kernels in the shape you would prefer. Depending on the speed of rotation and the position of the knives you set, the size of the cut groat can vary after the process.
If you want to make rolled oats, as known as old-fashioned oats, you first need a set of rotating rollers that can flatten the whole or steel-cut groats. This process is called flaking. During the flaking, it is important to use a steamer and release some additional steam to the groats – 3-5% of additional moisture to be accurate – because if they are too dry, they will become powder. A slight increase in temperature can optimize this flaking process. After this, a drying and cooling process is followed. Instant oats or quick oats have the same production steps as rolled oats, except they are additionally cut into smaller flakes – instant oat flakes are smaller than the quick oat flakes. Instant oats also include additional ingredients such as sweetener (sugar), salt, and flavorings, which are mixed in the mixer after the cutting process.

Making the "diet food" - oat processing and its influence on the nutritional aspects
We all know that oats are amazing for their nutritional benefits – especially with their high soluble fiber. But, how can the processing of wild oat influence the nutritional component of any oat product? Firstly, the dehulling process allows oats to be digestible and makes human bodies easily absorb the nutrients in the oats. The heating extrusion process of oats disables the enzymes to rancidify and improves the general nutrition properties of oats; the oat brans that went through the heating process have a higher solubility and swelling capacity with viscosity. This character allows the human stomach to digest the oats slower and gives a “fuller for longer” feeling.
Processing steps involved in oatmeal making
Which oatmeal technology do you need?

Cryloc rotary screens for grain processing
Efficiently sort and separate fine particles with high precision to enhance pro...

X-ray inspection system for large bulk products
Ensure consumer safety and product quality by efficiently detecting contam...

Metal detector for conveyorized applications
Enhance your production line by ensuring product safety with advanced metal d...
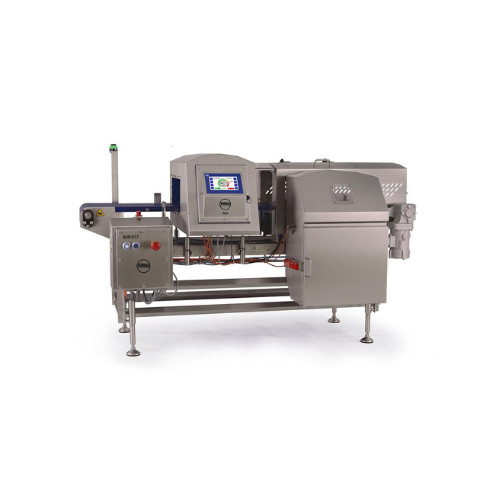

Conveyorized food metal detector for high-care environments
Ensure food safety with advanced metal detection tailored fo...
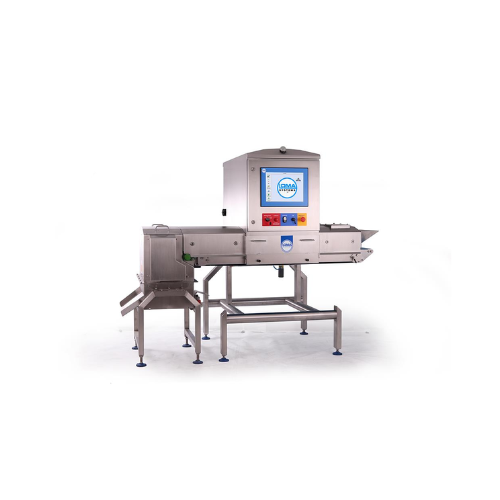

X-ray food inspection system for loose products
Ensure contaminant-free loose products by integrating a versatile inspecti...
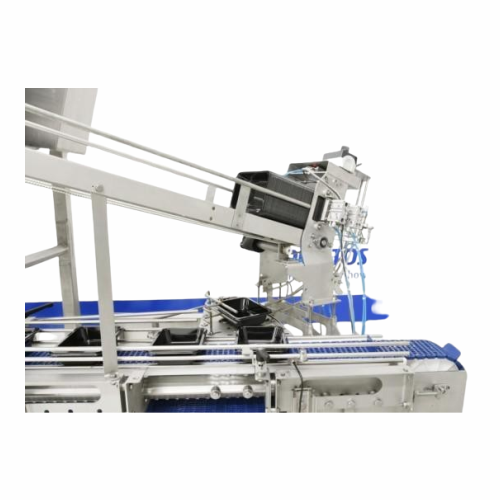

Tray handling equipment for food packaging
Optimize your food production with adaptable tray handling units that streamlin...
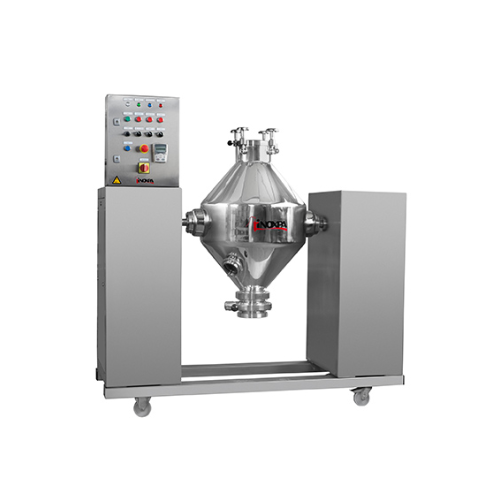

Double cone blender for homogeneous solid-solid mixtures
Need uniform blending for complex solid mixtures with diverse de...
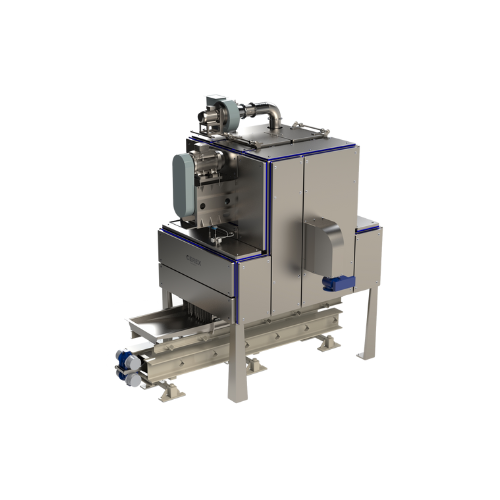

Single-zone toasters for raw grain processing
Optimize your cereal and snack food production by achieving consistent toast...
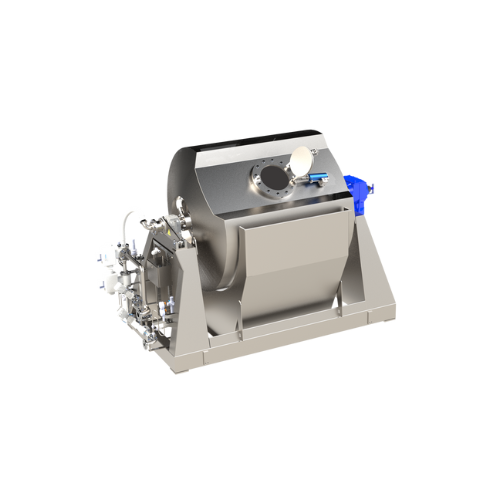

Rotary cooker for uniform steam heating in cereals production
Achieve consistent product quality in high-volume cereal p...
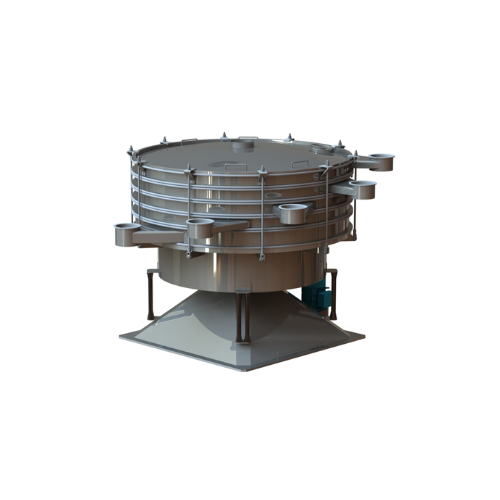

Industrial screeners for grain product processing
Optimize your cereal production line with specialized industrial screen...
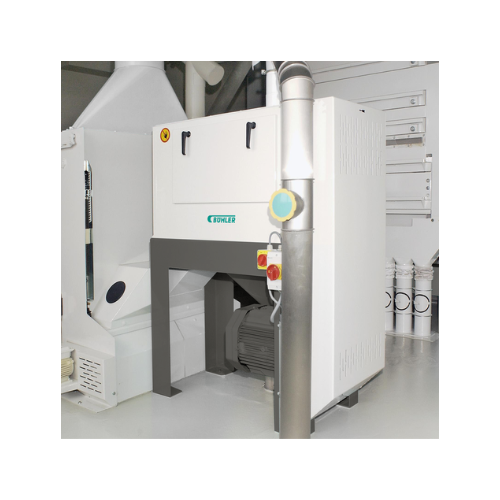

Grain scourer for wheat, durum, and rye
Enhance grain processing by efficiently removing impurities like dust, sand, and so...

Control systems for wet grinding industry
Enhance precision and efficiency in your production line with advanced control s...

Efficient destoner for wheat and rye
Achieve optimal grain purity with a high-speed destoning solution that efficiently rem...

Industrial fat extraction system for food and feed analysis
Optimize your laboratory workflow with a versatile fat extra...

Coffee roasting system
Optimize your coffee production from green beans to finely ground espresso with this versatile system,...

Gluten quality testing solution
Ensure optimal flour quality by rapidly assessing gluten properties, allowing you to refine ...

Aseptic filler for bag in drum or box
Enhance product shelf life and maintain quality without preservatives by employing as...

Industrial shear pump for high-viscosity food applications
Optimize your high-viscosity food processing with a shear pum...

Bulk storage silos for food products
Ensure optimal powder storage and handling with versatile silos designed for efficient...
Vibratory spiral elevator for vertical transport
Achieve efficient vertical transport with precise temperature control, su...
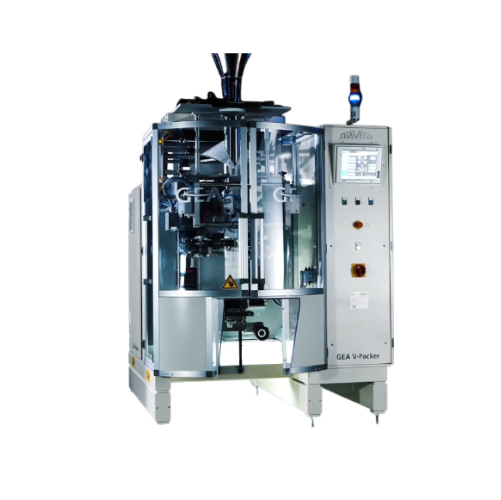

Eco-friendly vertical packaging for pasta
Reduce plastic waste and enhance sustainability in pasta packaging with high-spe...
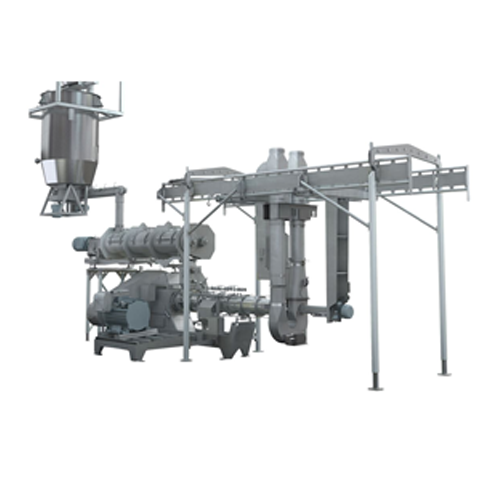

Single screw extruder for pet food and aquatic feed
Maximize production capacity and optimize product quality with advanc...
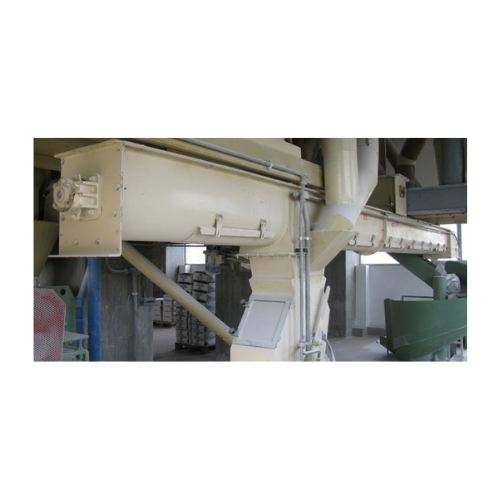

Trough screw conveyor for flour mills
Optimize your flour processing with efficient material handling, precisely designed f...
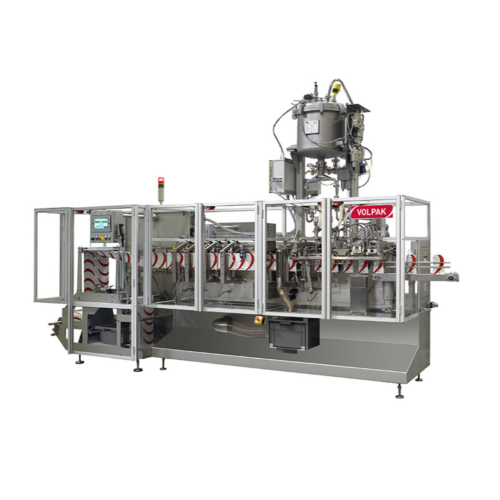

Stand-up pouch packaging for various products
For manufacturers seeking versatile packaging solutions, this machine delive...
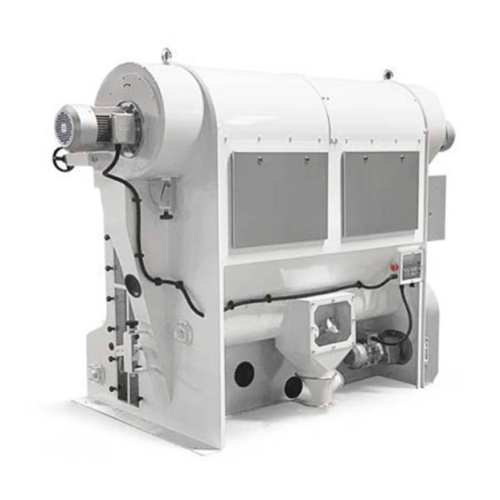

Separation system for low-density materials from grains
Efficiently separate lightweight impurities from dense grains to ...
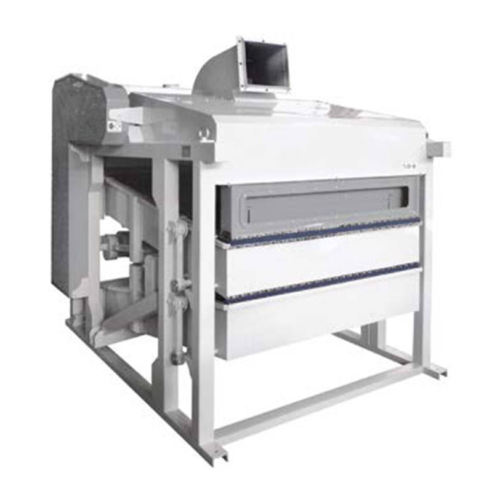

Double story paddy sieve for rice cleaning
Efficiently cleanse and separate impurities from rice, lentils, and grains, ens...
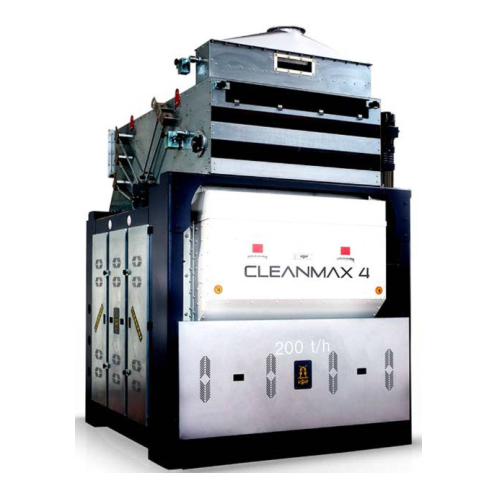

High capacity grain sifter
Efficiently separate and clean a variety of grain types with minimal space requirements, ensuring...
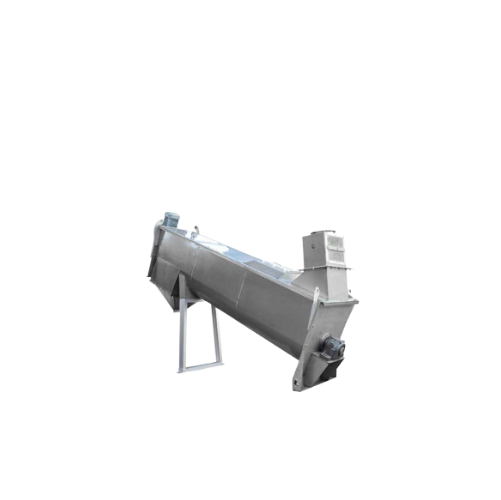

Inclined intensive dampener for grain processing
Ensure consistent moisture levels for optimal grain processing and enhanc...
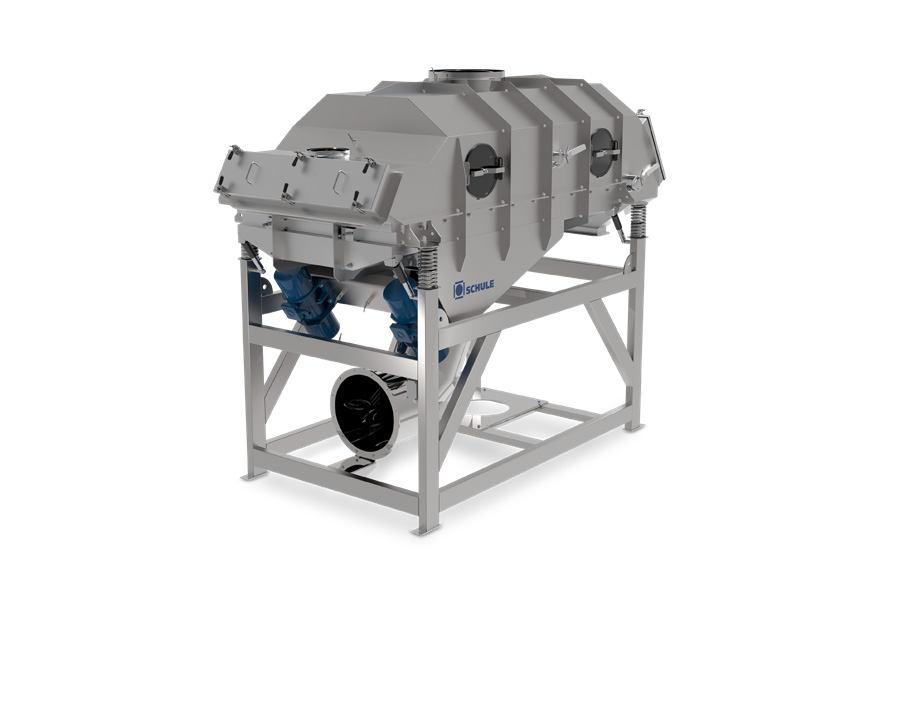

Fluidized bed drier/cooler for grains
Processed grains absorb moisture throughout the production line. Lowering that water ...
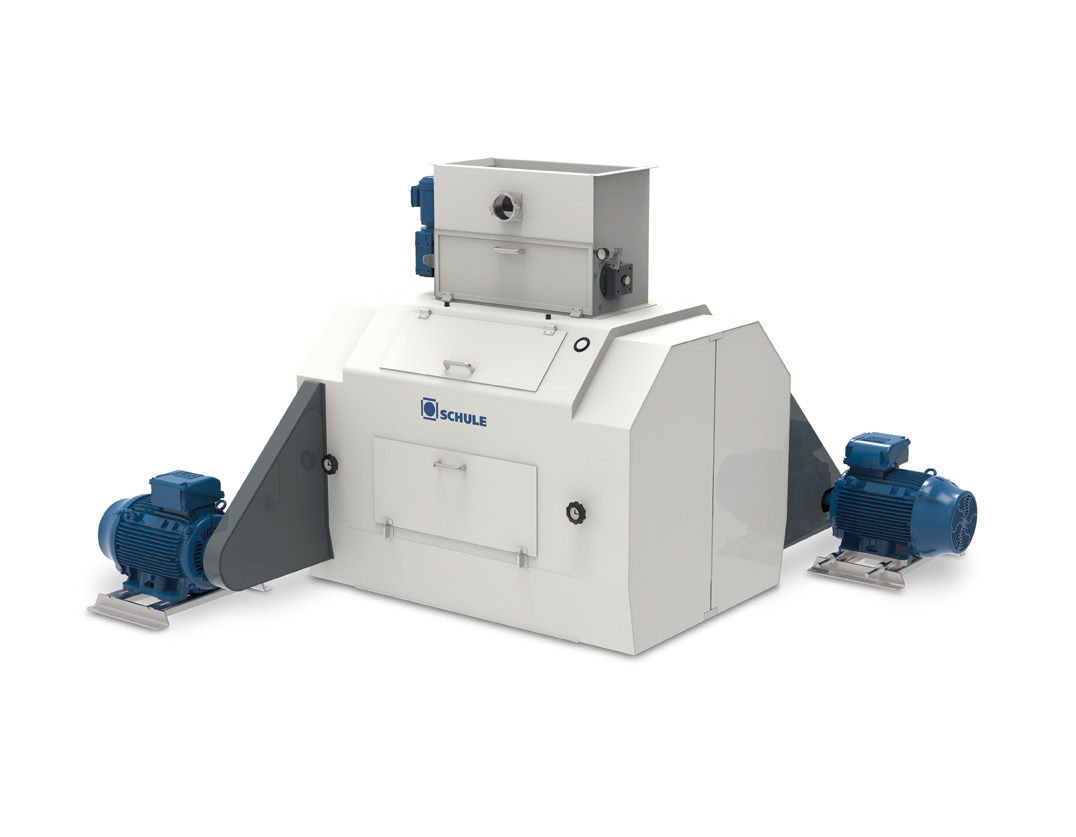

Flaking roller mill for oats
Consistent flake size is one of the main contributors to processed oat quality. But producing a...
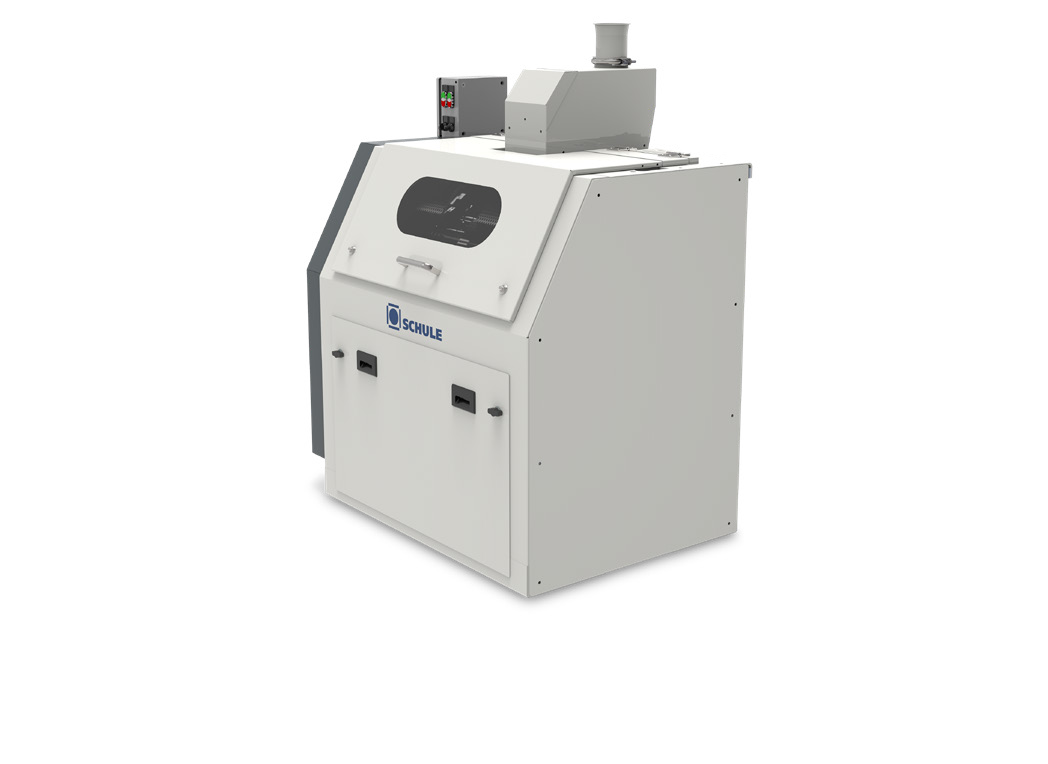

Drum groat cutter for baby oats
Used as food thickeners and toppings, baby oat flakes must adhere to a consistent size. But ...
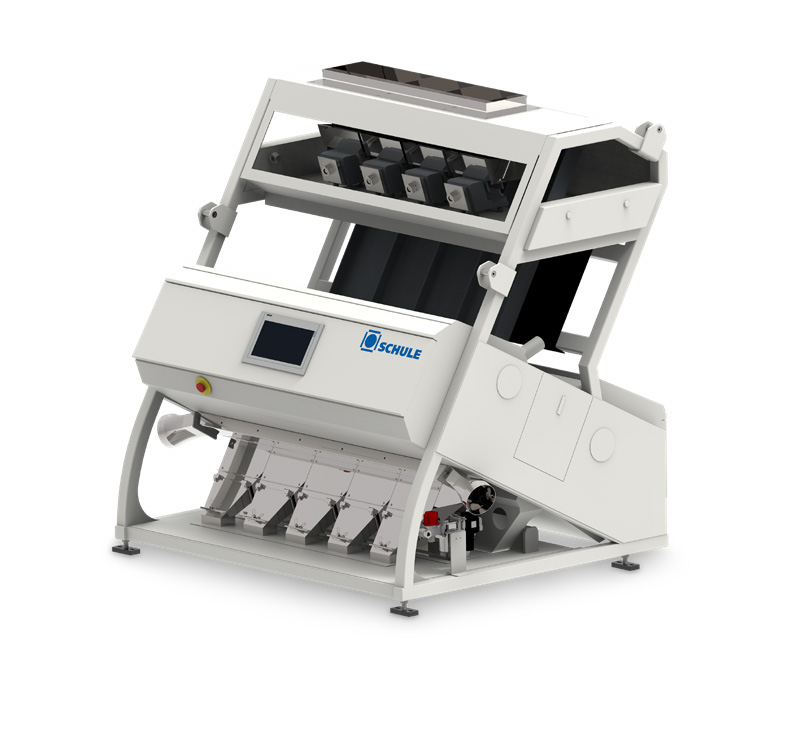

Color sorting machine for grains
Detecting impurities in processed grain becomes more challenging as the output increases. B...
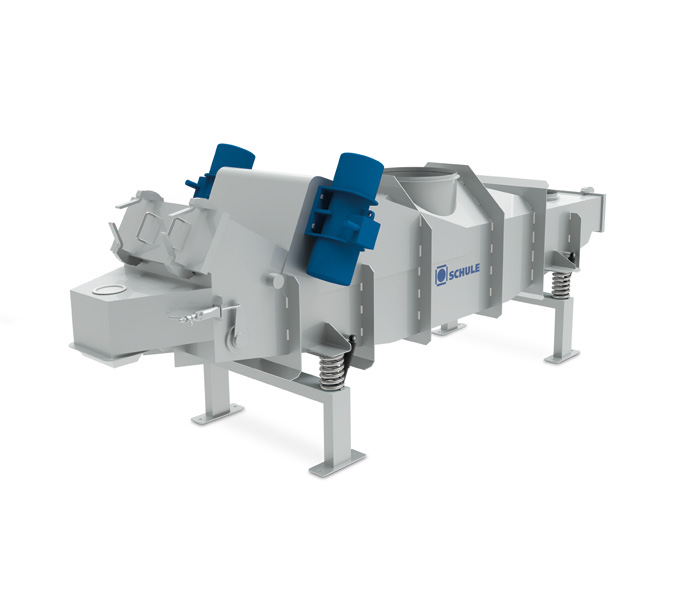
Kiln and cooler for oats and fatty cereals
Grains such as oats and parboiled rice have a high fat content and must be stab...

Table separator for grains
Imprecise sorting of oats and other grains brings down the yield. To avoid wastage, hulled and un...
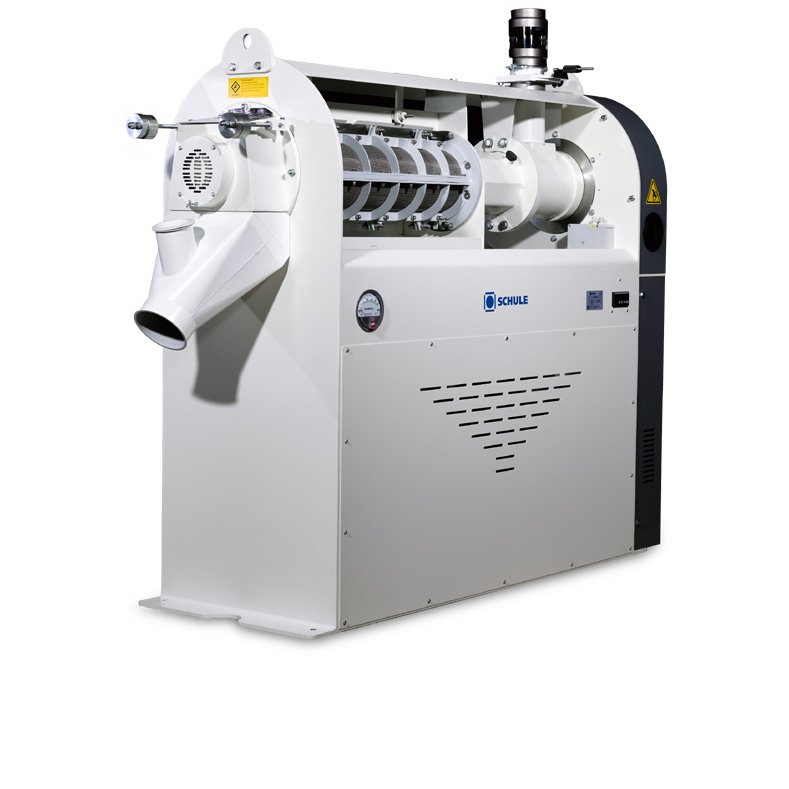

Gentle polisher for oats
The fine fluff covering oat grains complicates the cleaning of processing equipment. The hair-like f...
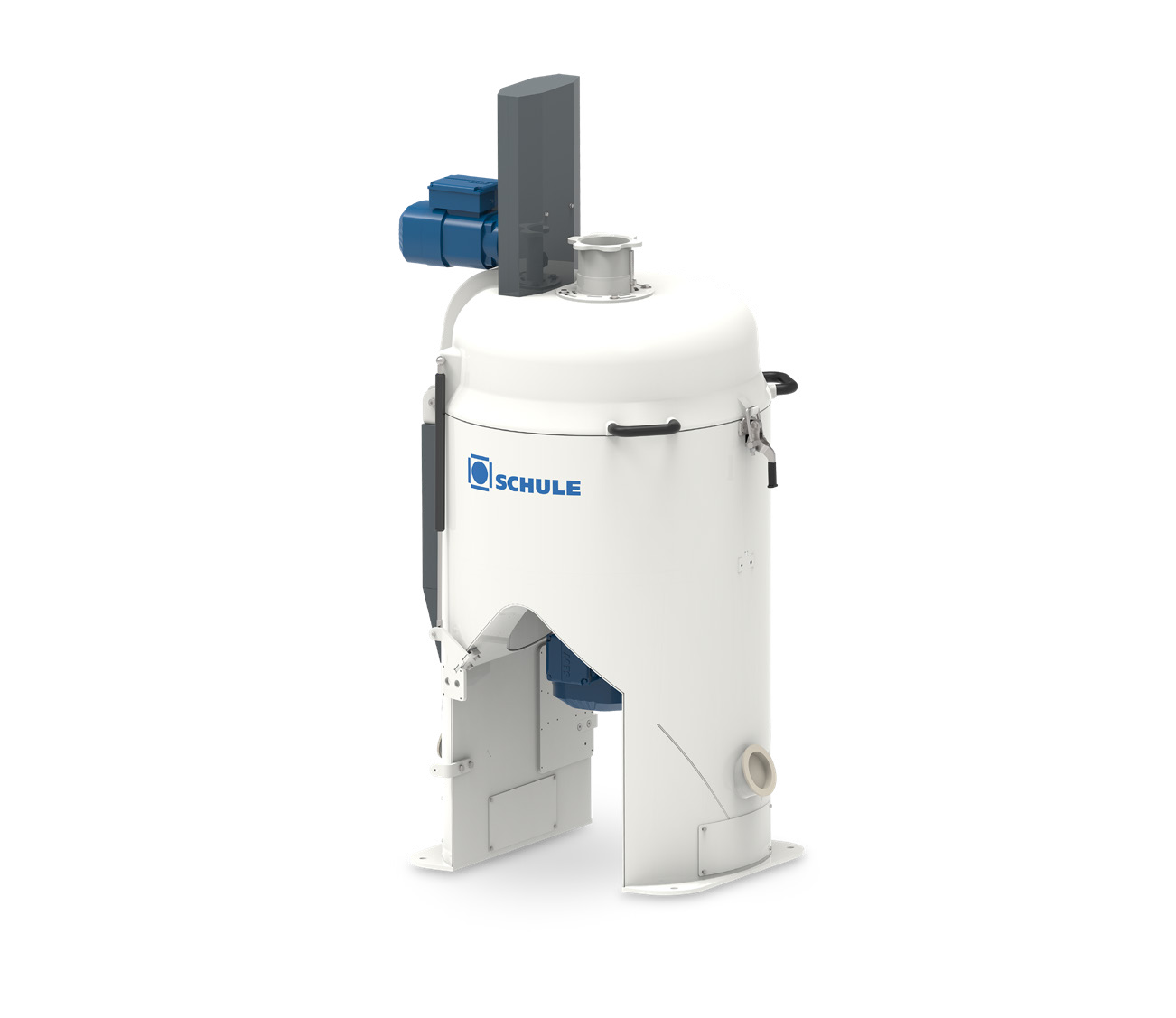

Impact huller for oats
Hulling technology risks breaking oat grains if the system is not adjustable to fragile materials. Agg...

Gentle de-awner for grains
Husking is a fundamental step in grain processing, but it lowers the yield if it’s not carefully ...

Box erector and bag inserter
If you are looking to improve your throughput and eliminate labor associated with manual box er...
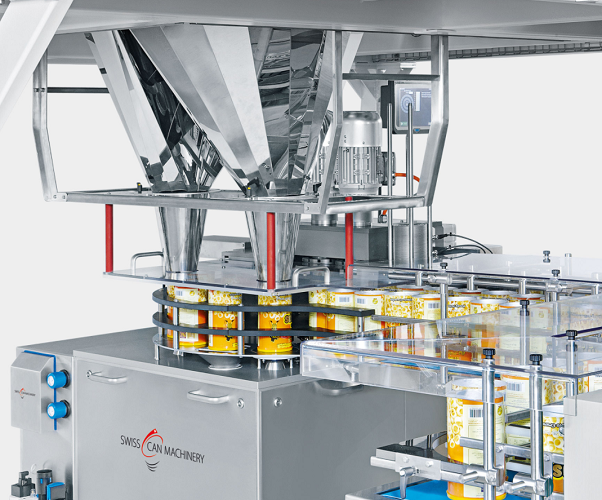

Filling and weight checking machine for food cans
Making sure the right quantity of product is in the packaging can be a ...
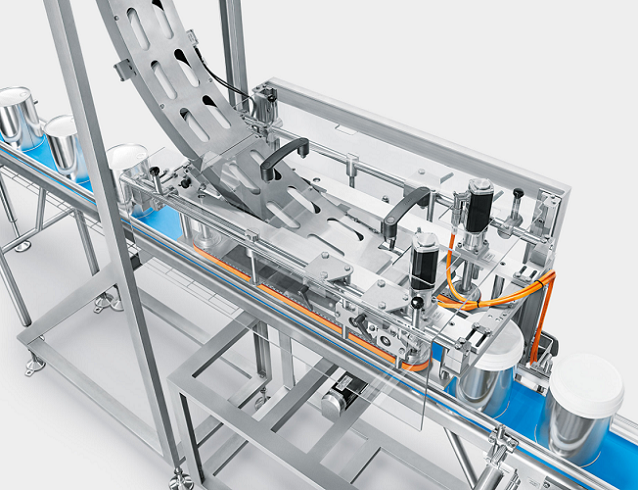
Capping machine for plastic lid oatmeal tins
Some products ask for a plastic reusable lid after the can has been sea...
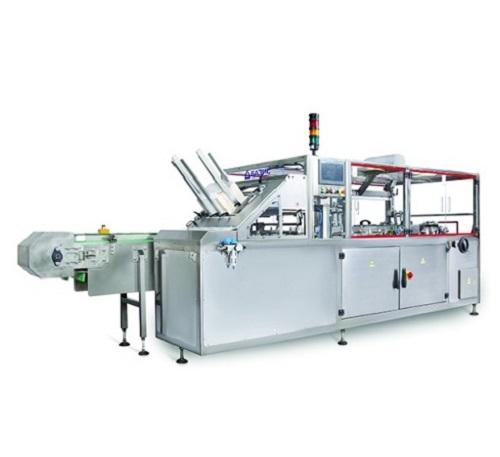

Horizontal cartoner for food products
Depending on the primary product packages, food products like confectionery (biscuits...
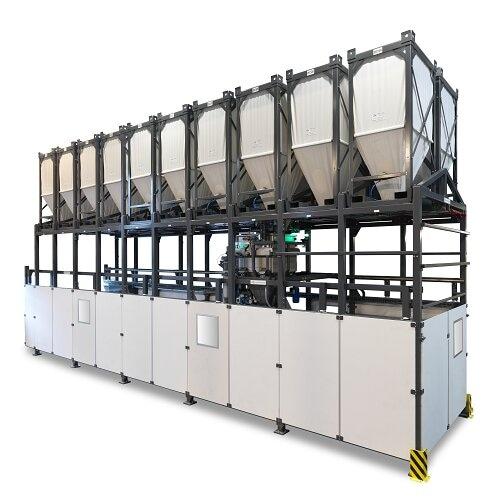

Exchangeable silo dosing system
Rarely used bulk ingredients, like grains, agricultural feed or silage, can get spoilt if th...
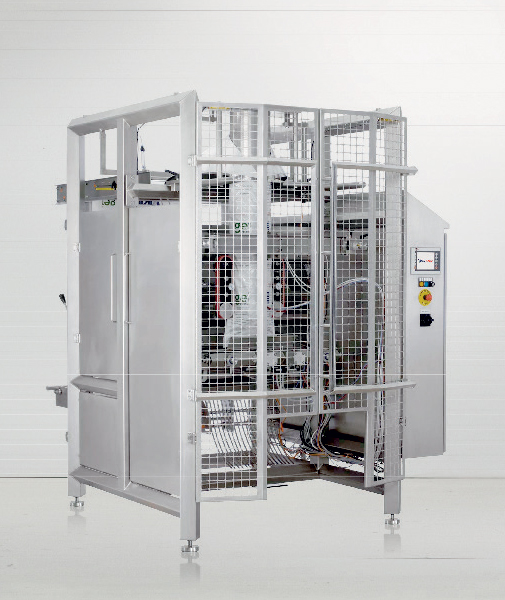

Hygienic vertical bagging machine
Hygienic bagging with a compact packing machine that can withstand the harshest wash down...
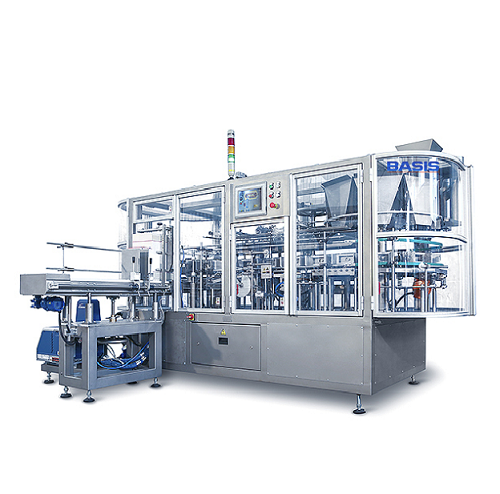

Continuous vertical cartoner
When producing cereals, it is paramount to stay on top of market trends. New packaging forms ca...
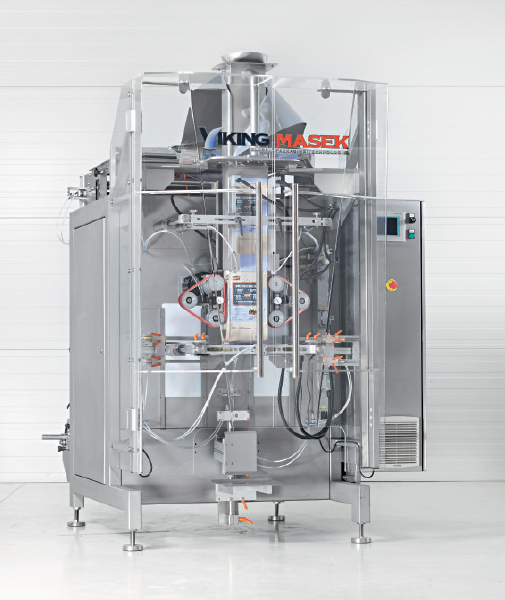

Continuous vertical bagger
Want a machine to pack unique bag styles such as quad-seal and Doy-pack bags at incredible speeds...