Making Plant-Based Cheese
Find innovative production technology for making plant-based cheese and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Cheese is the most demanding food in the entire dairy family to emulate using non-animal and dairy free ingredients. The complex physical and taste profiles of animal-derived milk products make plant-based cheese manufacturing challenging to pull off. But the growing appetite for lactose-free and non dairy products is serving alternative platters of cheese.
Stories about plant-based cheese

#Changemaker: developing your recipe to success in the vegan market

Innovator or perfector – what kind of plant-based food maker are you?

From the kitchen counter to industrial production: How to master texturing of vegan specialties

#Changemaker: A divine alternative to synthetic preservatives

#Changemaker: From Scotland, the award-winning vegan cheese that is taking the market by storm
Select your plant-based cheese process
Tell us about your production challenge
Avoid sedimentation of large particles to produce a cheesy mouthfeel
The sensory attributes present a formidable challenge to the preparation of plant-based cheese. The flavors, taste, and aroma of plant ingredients do not match those of dairy products. Blend your base mix with nutritional yeast, tapioca starch and/or different types of alternative milk such as soymilk and nut milk to obtain a dairy-like sensory profile.
Similarly, plant material gives a different mouthfeel, usually produced by the sedimentation of larger particles. Adding sodium bicarbonate softens the plant material to reduce the gritty texture often associated with cheese made from dairy free ingredients.
Cheesemaking without dairy is difficult for many reasons. But the biggest challenge was finding a dairy free ingredient that contained enough fat to make vegan cheese a possibility. However, Food manufacturers found that cashew nuts, coconut and almonds would solve the problem.
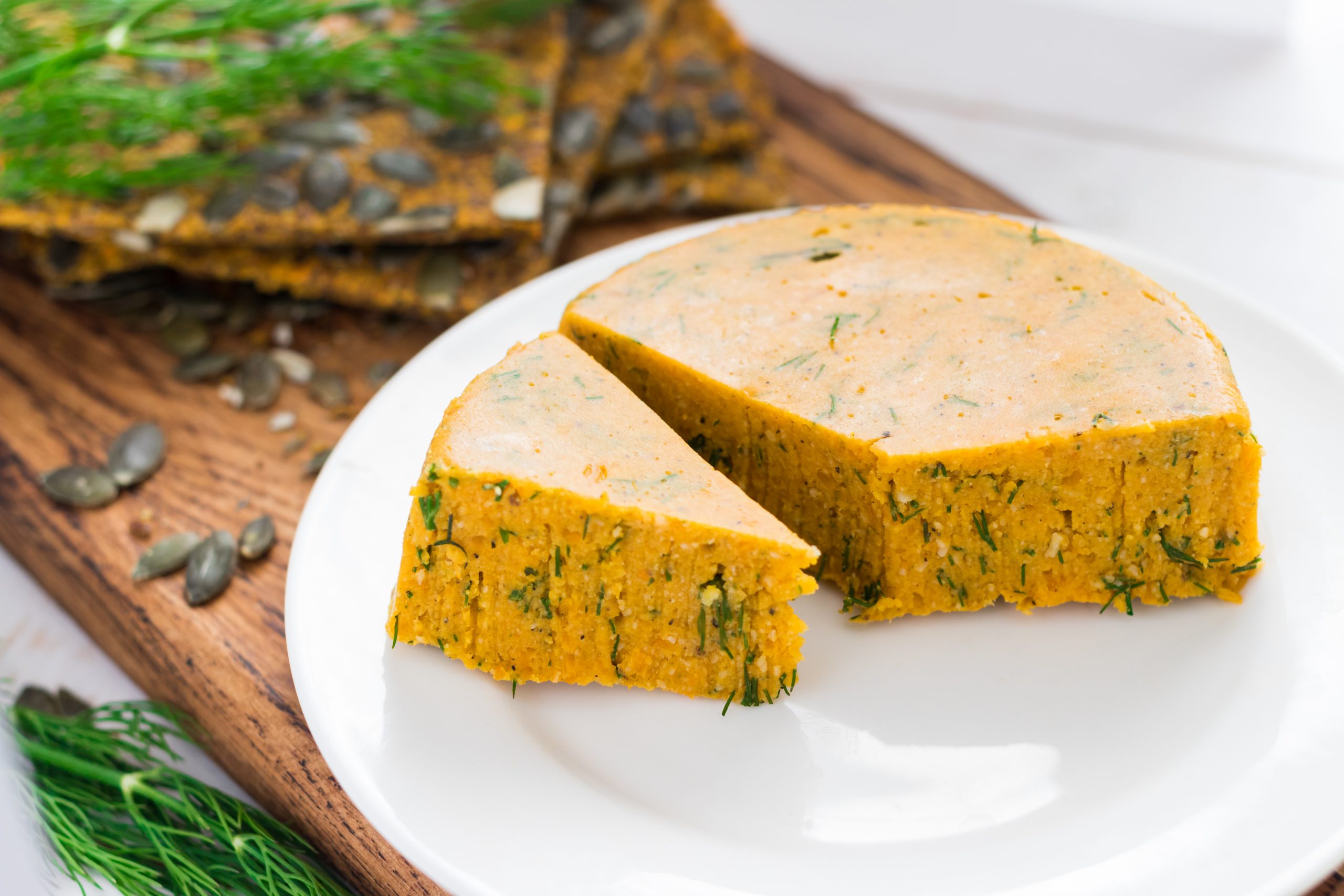

Manipulate stretchability with moisture content
The famous Caprese salad or a classic pizza Margherita would be something else without mozzarella. The high water content emulsifies the milk protein to give the cheese its signature stretchability.
But plant protein has a narrow amino acid profile, so water content needs to be adjusted accordingly. Extruded fava protein requires between 40 and 50 weight percentage to achieve a similar stretchability. Moreover, oil and starch content of around 20 wt% each produce mozzarella-like meltability in vegan cheese.
Labeling restrictions for plant-based cheese processing
Many jurisdictions restrict the term ‘cheese’ to animal-derived items. The European Union forbids the term for products made from plant ingredients but stopped short of banning related dairy terms like ‘creamy’ or ‘vegan alternative to cheese’.
In the United States, the standards of identity of cheese products include animal-based dairy products. But the Food and Drugs Administration is assessing proposals to update the definition and applicability of terms.
Processing steps involved in plant-based cheese making
Which plant-based cheese technology do you need?

Inline high shear mixing for dairy and condiments
Streamline your production line with innovative inline high shear mixin...

Cooling system for vegetables and meat
Optimize cooling efficiency with dual counterrotating agitators and expansive surfac...

Heating solution for vegetable and meat products
Achieve efficient heating and optimal heat transfer for sauces and dairy ...
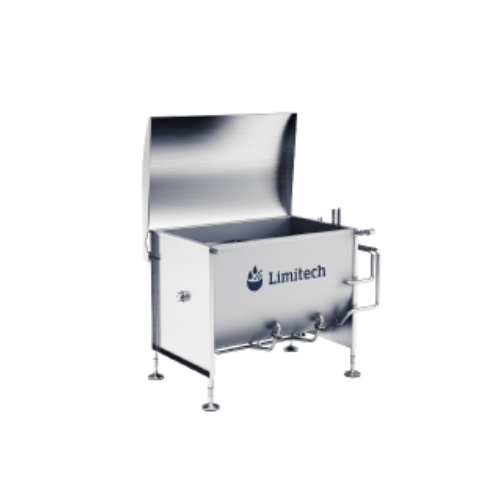

Food mixing and blending system
Enhance your production line with a versatile system designed for gentle processing needs, o...
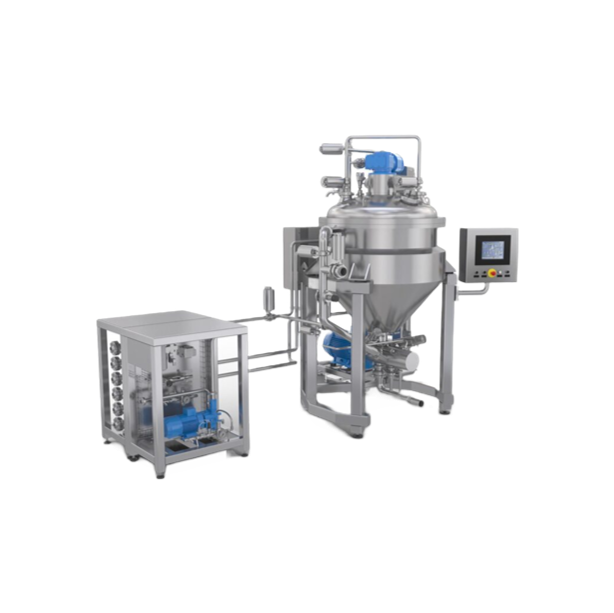
Batch processing system for processed cheese and sauces
Optimize your food processing line with a versatile batch process...
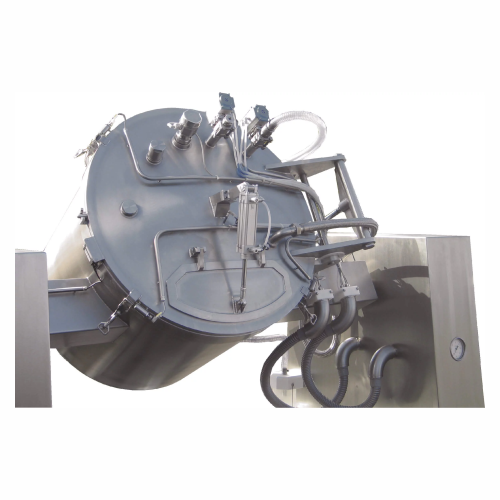

Vacuum tumblers for food processing
Optimize your production line with vacuum tumblers designed to enhance flavor infusion,...
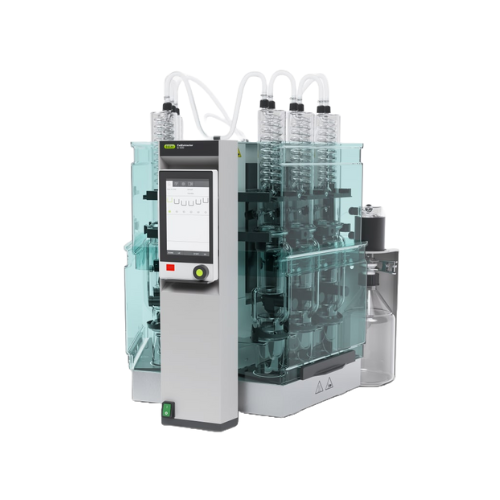

Industrial fat extraction system for food and feed analysis
Optimize your laboratory workflow with a versatile fat extra...
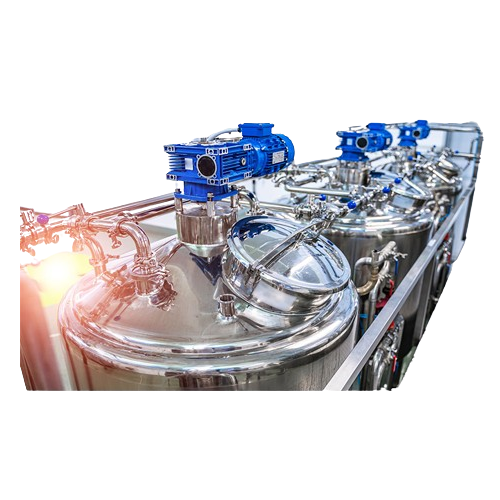

Plant-based protein extraction technology
Achieve optimal purity in plant-based milk, yogurt, and cheese production with c...
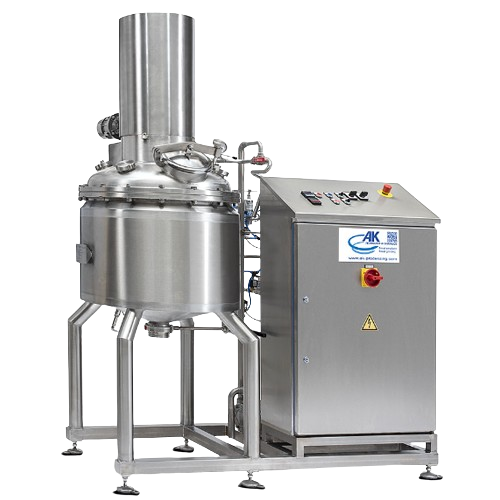

Hydro grind reactor for meat, vegetable, and vegan product processing
Achieve precision grinding and emulsification of ...
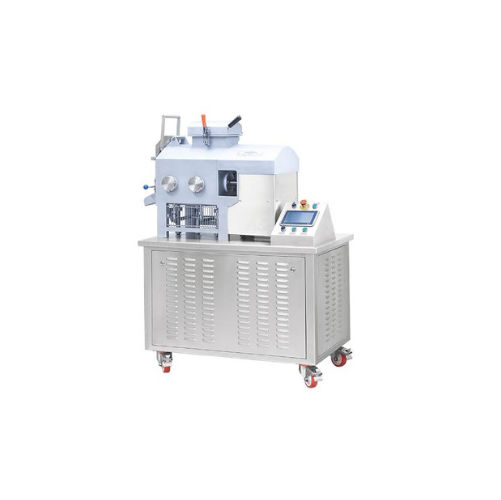

Steam cooker and stretcher for cheese processing
Optimize your cheese production with a versatile solution designed to eff...
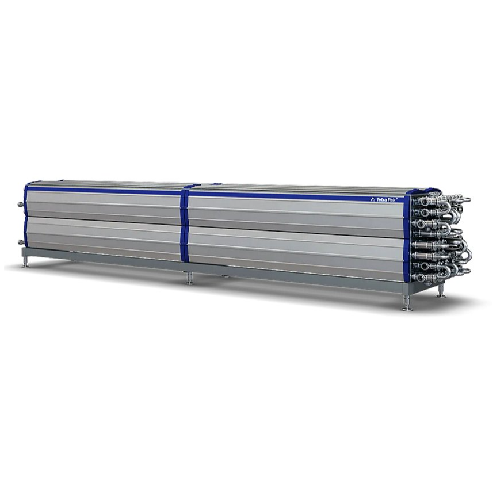

Tubular heat exchanger for food products
Achieve precise temperature control and energy efficiency with this innovative tub...
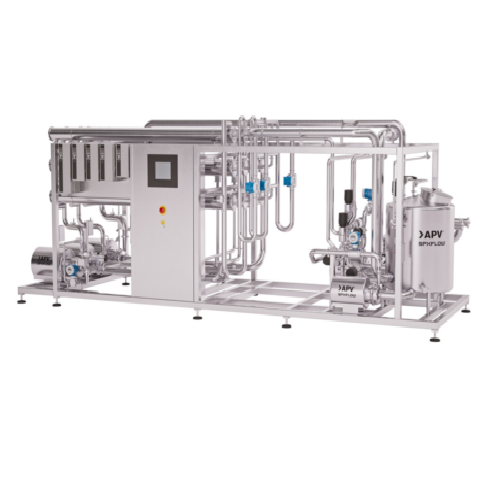

Ultrafiltration for dairy and plant-based protein concentration
Optimize your production capacity and increase yield wit...

Sanitary gasketed plate heat exchangers for clean applications
Ensure product purity and maintain hygienic standards wit...

Foil wrapping machine for cream cheese
When producing cream cheese and selling them in foil wrapped bricks you need a relia...

Homogenization and emulsifying system for fine foods
Texture and consistency are critical to foods with delicate composit...

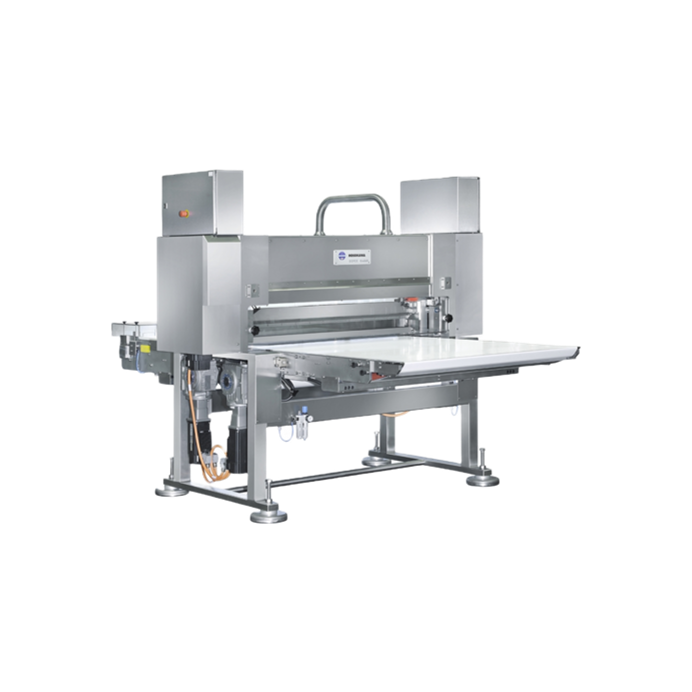
Industrial guillotine machine for extruded foods
Textured vegetable proteins made from soy, wheat, and oats are extruded i...
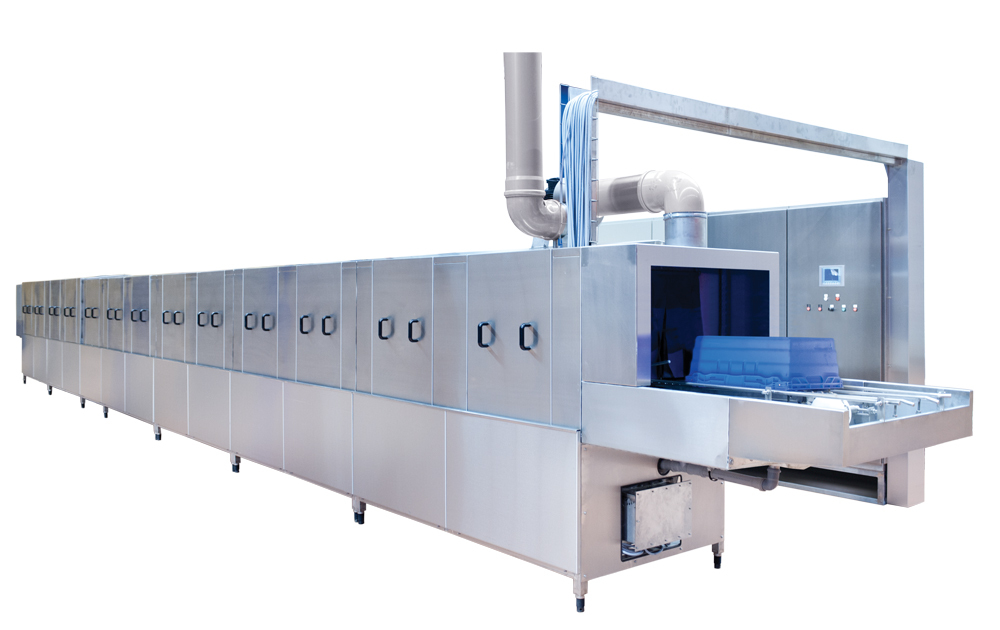

Industrial washer for plastic crates
In the food production sector, hygiene regulations are getting stringent by the day. E...
Grated cheese case packing machine
Large-scale cheese manufacturers process and handle products of different sizes and volu...
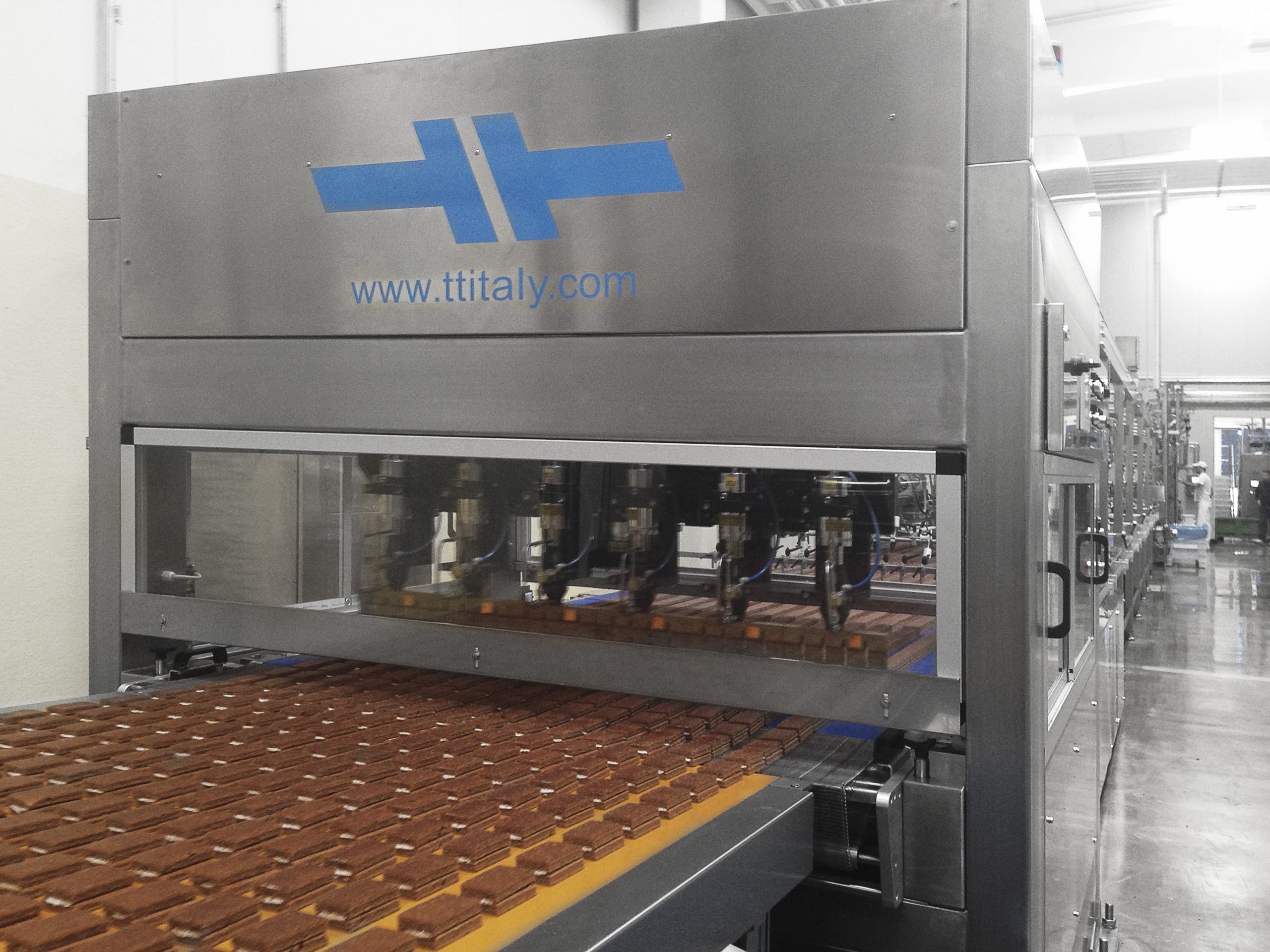

Cake ultrasonic cutter
Some cake items you may wish to cut can feature substantial amounts of cream. But that cream could sme...
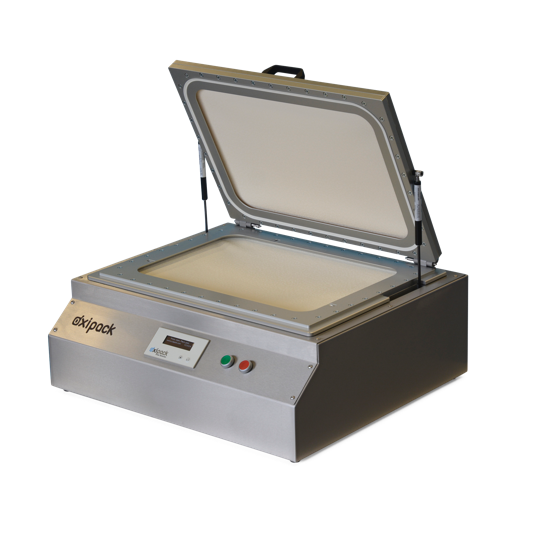

Leak tester for pouches and MAP packaging
Nuts are packed with unsaturated fatty acids, which means they are prone to oxid...
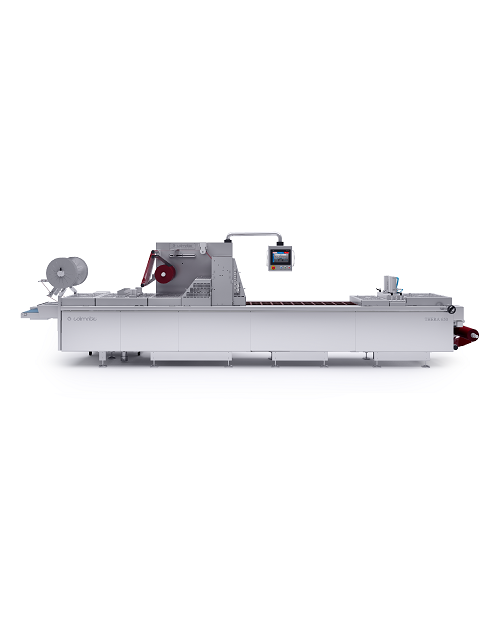

Skin packaging machine
Skin packaging is when a product is placed on a tray or a paperboard with a thin layer of plastic plac...
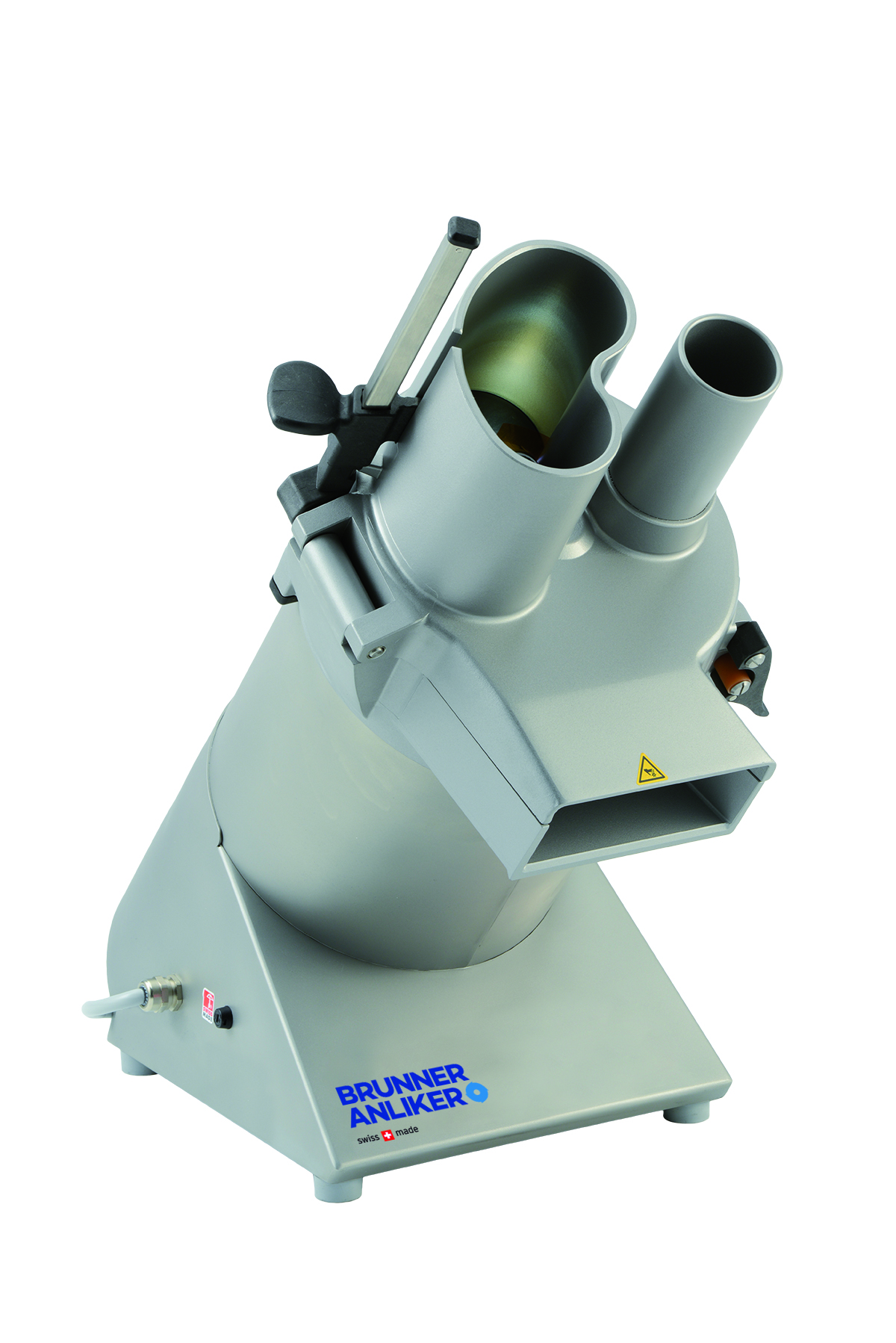

Cheese grater
Breaking down large blocks into grated, shredded, powdered or planed cheese requires multiple graded discs that ...
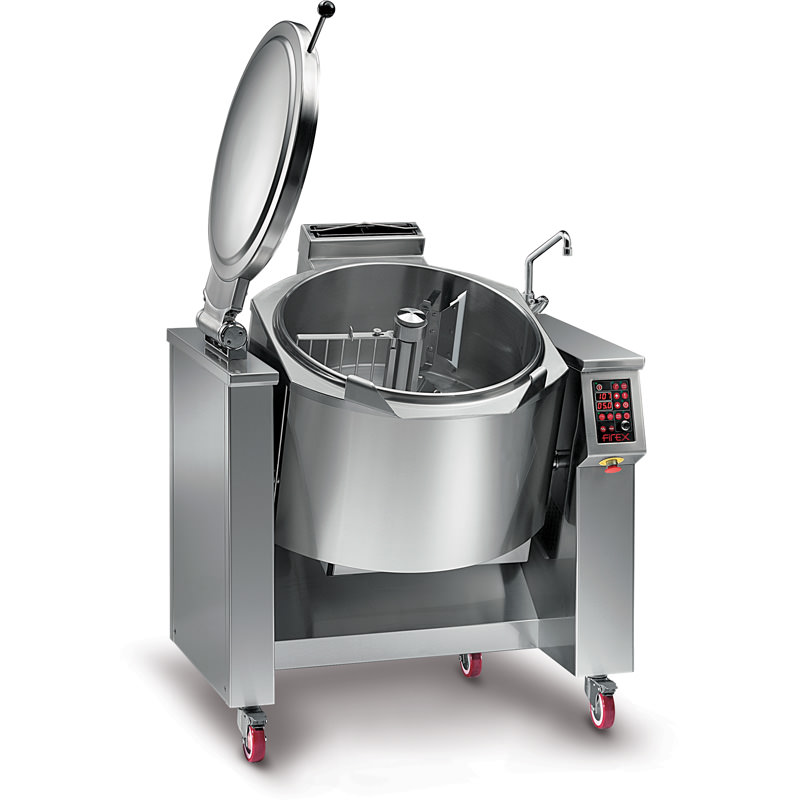

Industrial sauce pan
For the small and medium food industry, economical use of time, space and human resources is critical wh...
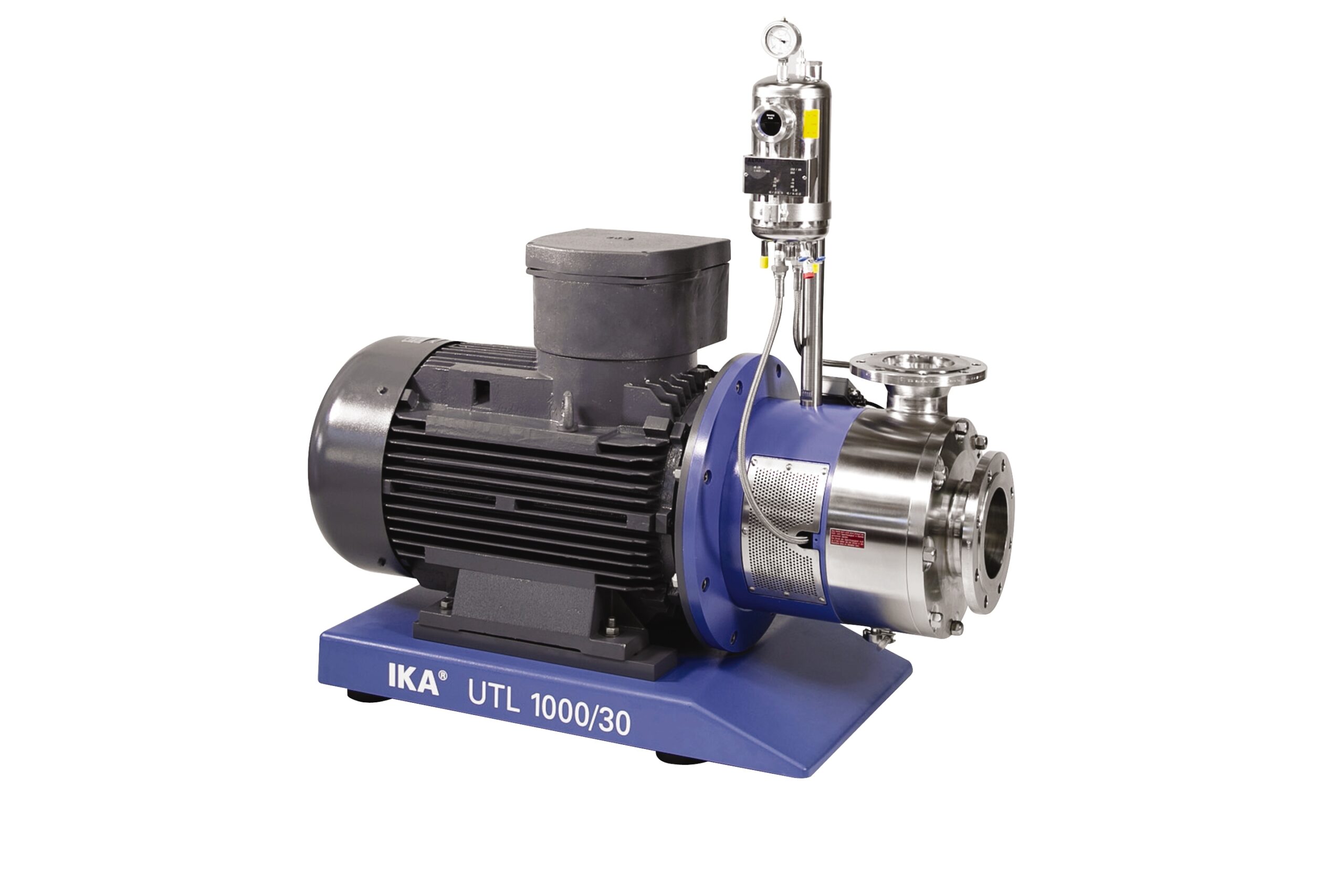

Economic dispersing machine for emulsions and suspensions
For products of medium viscosity and relatively consistent par...
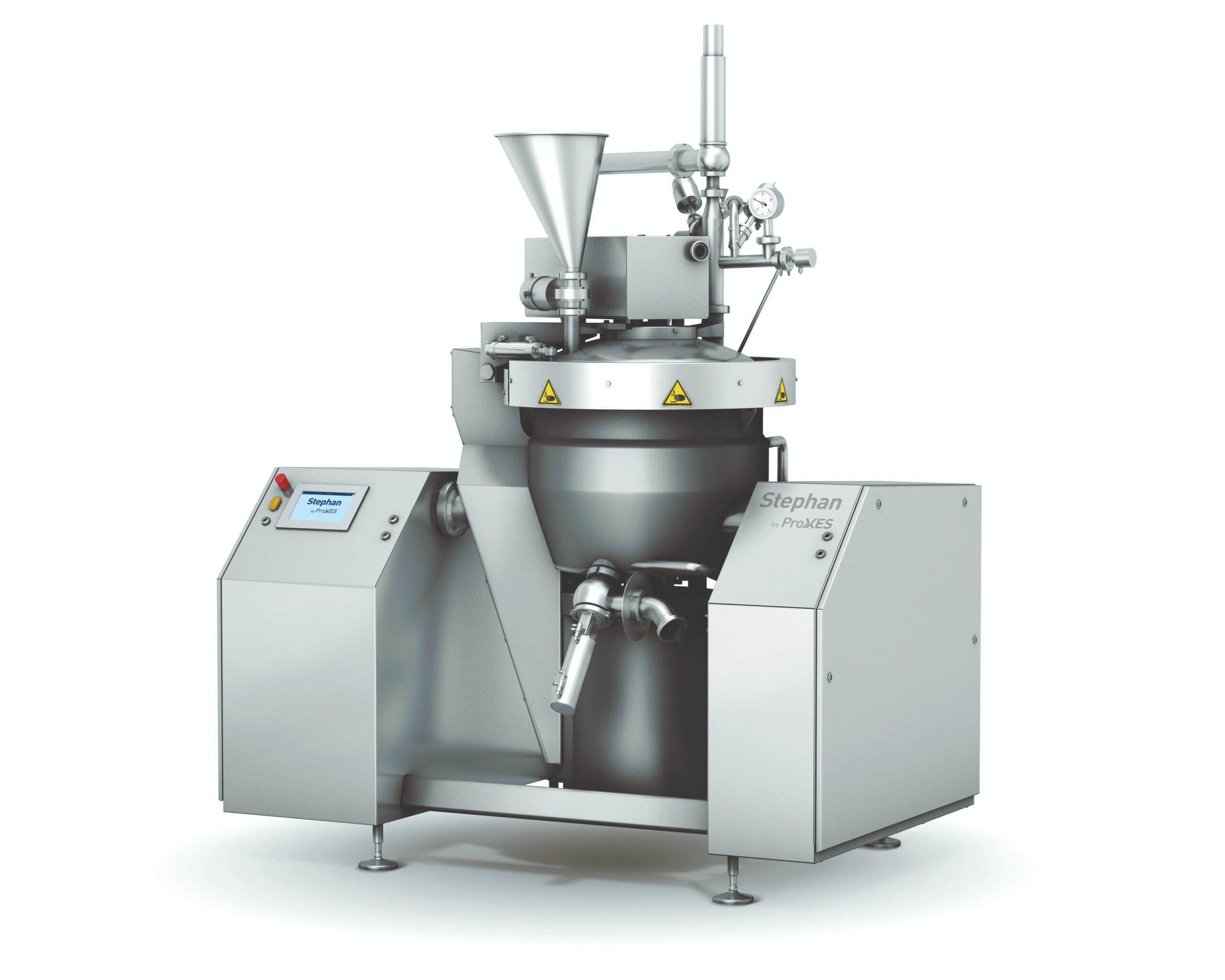

Complete cutting, mixing, emulsifying and heating system
From laboratory scale to large volume food or cosmetic productio...