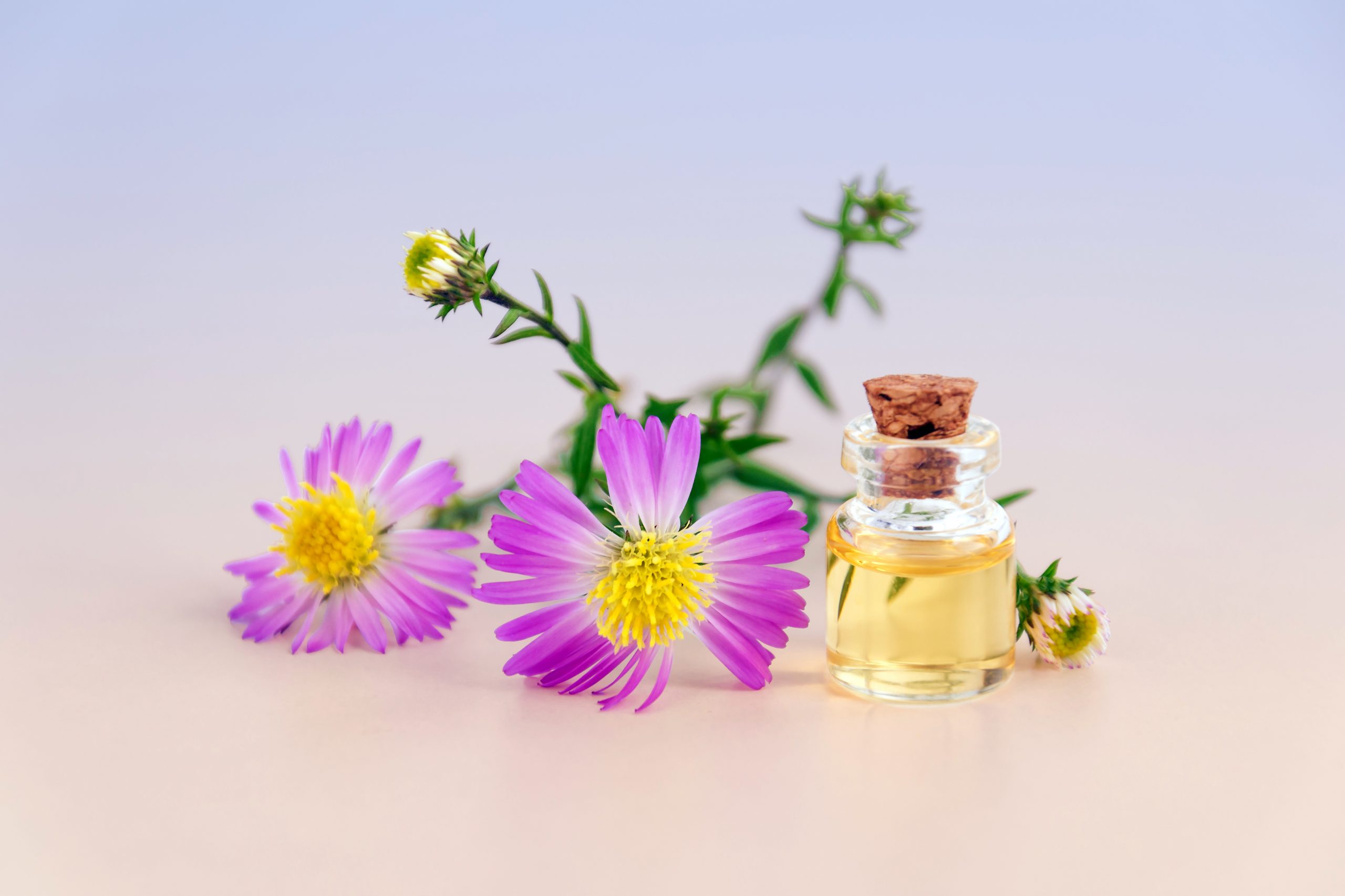
Making Flower Extract
Find innovative production technology for making flower extract and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Only one percent of the entire plant species on the planet produces essential oils, but that amount has found its way into various products, from perfumes to foods. Flower extraction systems are similarly diverse, and picking the right ones depends on the organic material and the final product.
Select your flower extract process
Tell us about your production challenge
Apply volatile solvents to extract oils from fragile flowers
Conventional steam extraction methods can thermally destabilize delicate flower materials such as tuberose, hyacinth, or jasmine. On the other hand, flower extraction systems by solvent,
on the other hand, are performed at low and uniform temperatures that preserve the oils.
Use volatiles such as hexane and petroleum to evaporate the solvents out of the essential oil filtrate and concentrate the extract into a resinoid or concrete.

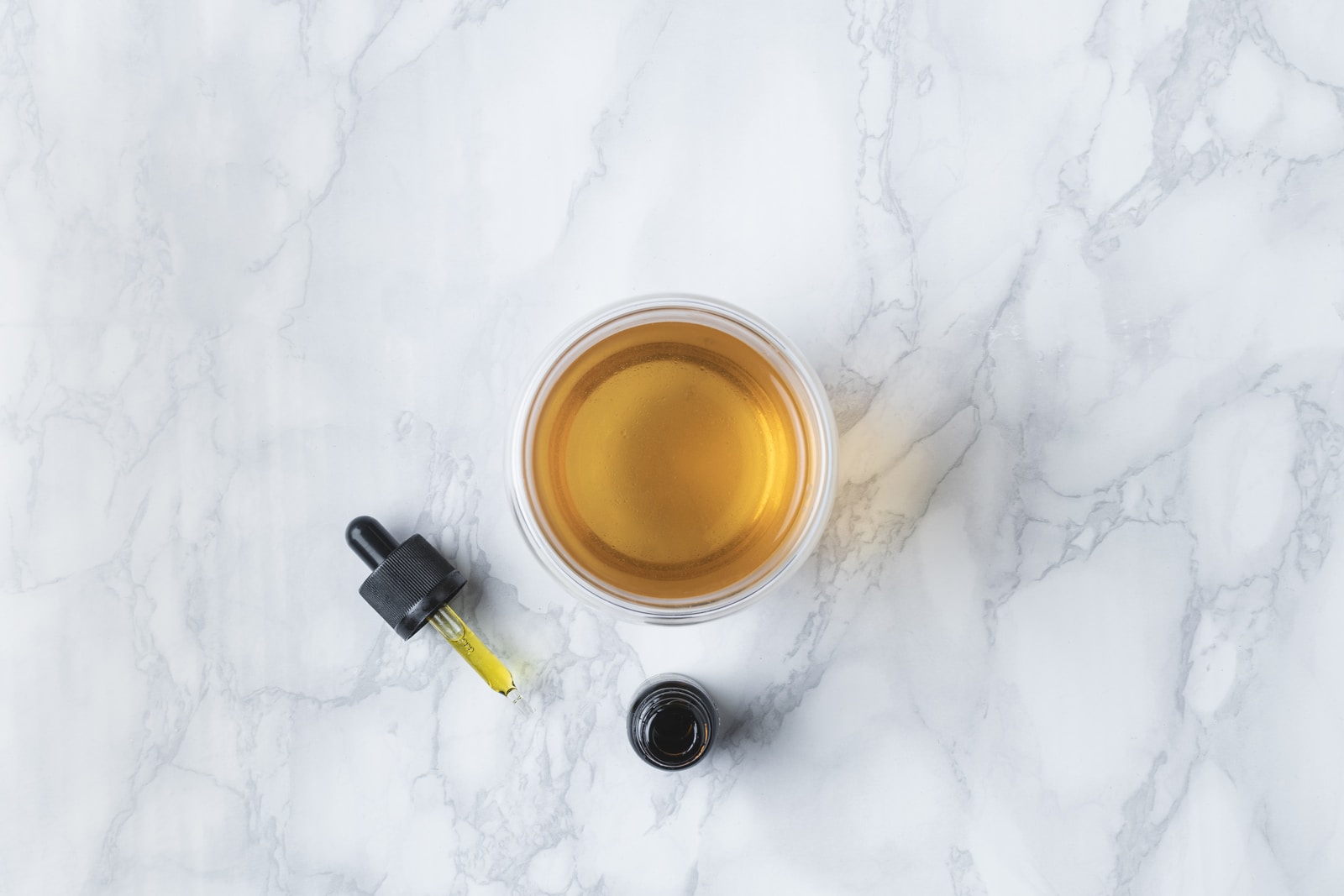
Pressurize carbon dioxide to above its supercritical point in supercritical fluid extraction
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) is emerging as an alternative flower extraction process. The technique heats fluids above their critical temperatures to diffuse through the flower walls and dissolve the target oils.
CO2 is a typical substance in SFE because it is inert and transforms into liquids under high pressure. Under normal atmospheric pressure and temperatures, the fluid reverts to a gas and evaporates, leaving no solvent behind in the final completed product.

Use silica gel in adsorbent chromatography to separate oils
Conventional hydrodistillation techniques require further separation of oils from the extracted compounds.
Column chromatography typically uses silica gel as an adsorbent to perform this process. As a polar absorbent, silica gel has a higher retention rate for other materials with a polar profile, like essential oils.
Coumarin extract in pharmacological applications
Flowers have a high concentration of coumarin. The extract offers antioxidant and antibacterial properties, making it a substance of pharmacological interest.
Among other applications, coumarin is used to treat ailments from cancer to thrombosis to leukemia. The compound is also used to counteract the side effects of radiotherapy.
Processing steps involved in flower extract making
Which flower extract technology do you need?
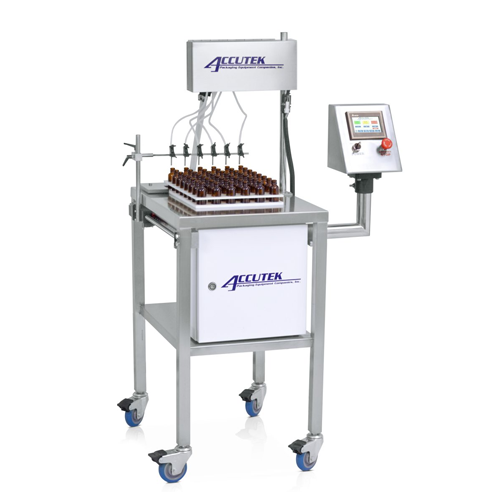

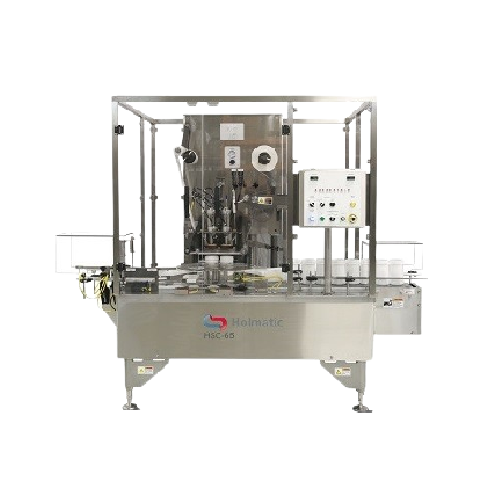
Auto-indexing filler for aqueous solutions and light oils
Streamline your bottling process with this six-head filler, pe...
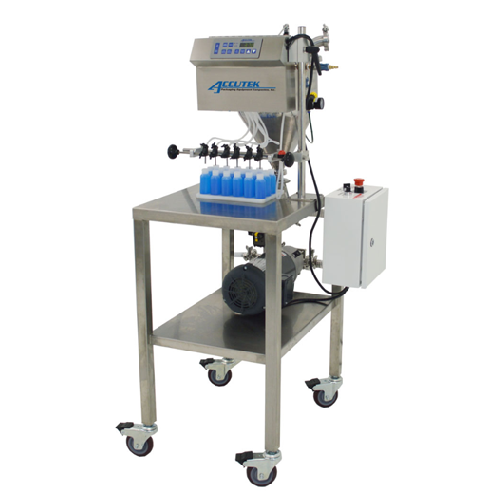

Semi-automatic timed flow filler for aqueous solutions
Handle diverse liquid filling needs with precision, from thin oils...

Benchtop peristaltic dispenser
When you fill vials and ampoules, high standards of hygiene are required to avoid the risk of...
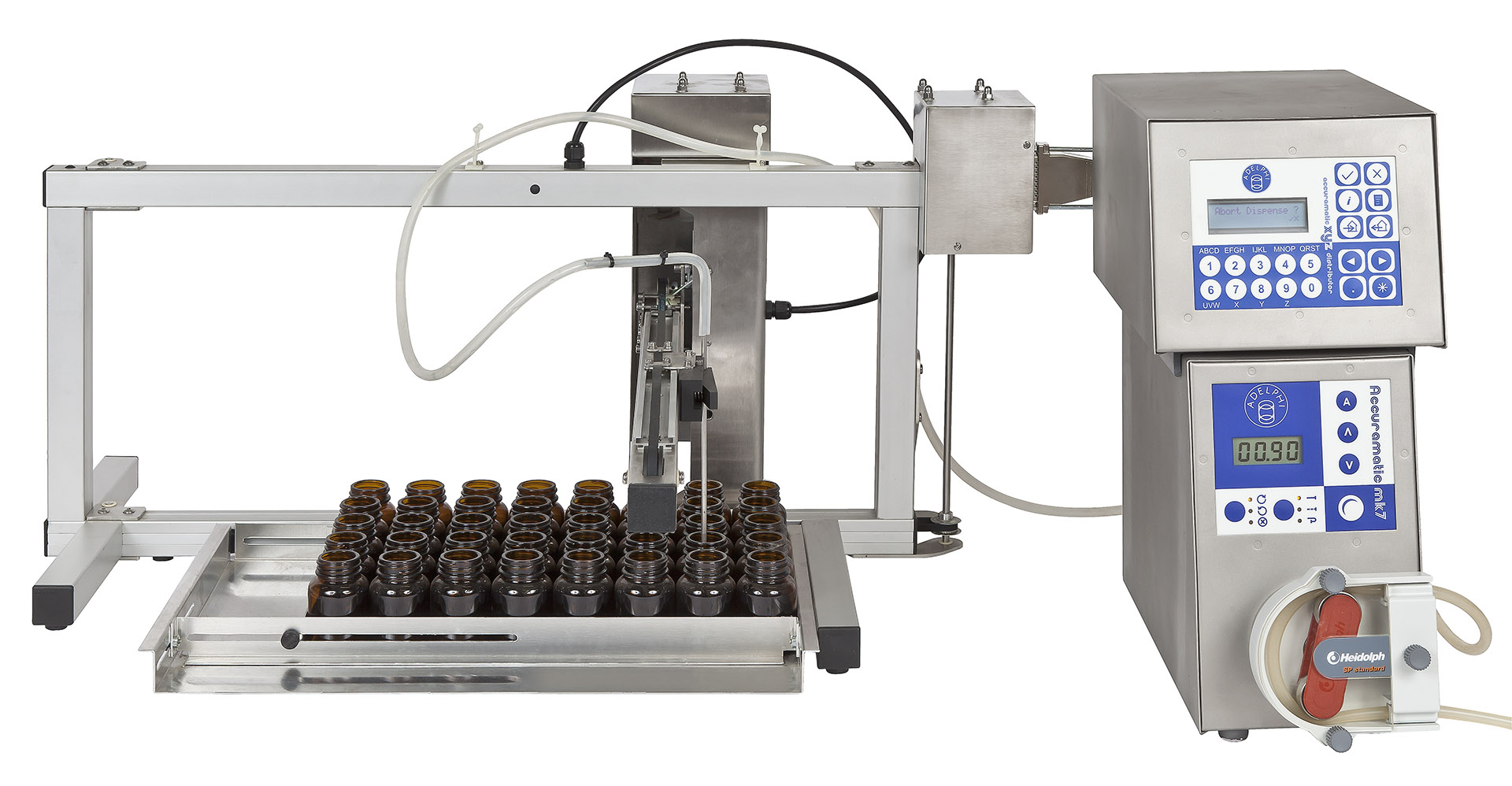

Benchtop piston filling equipment for vials in trays
Vials are difficult to fill individually through manual methods due ...

Semi-automatic vial crimper
In a small production line, crimping vials manually can cause fatigue to your operator due to mu...
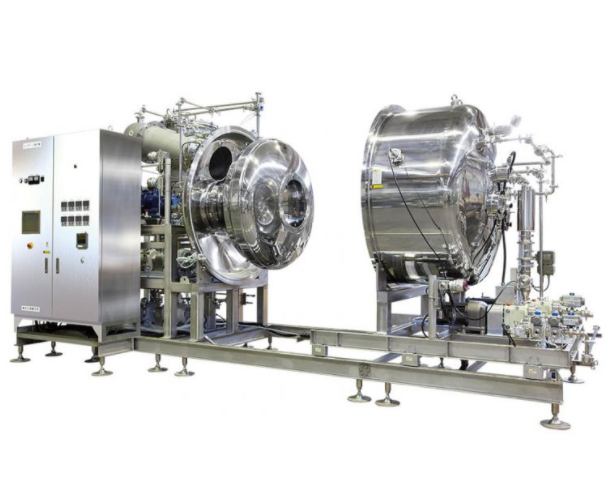

Evaporator for heat sensitive products
The removal of solvents when making products in industries like food, cosmetics, pha...

Ultrasonic barbell for extraction
Conventional extraction methods are time-consuming, labour-intensive and can sometimes be...
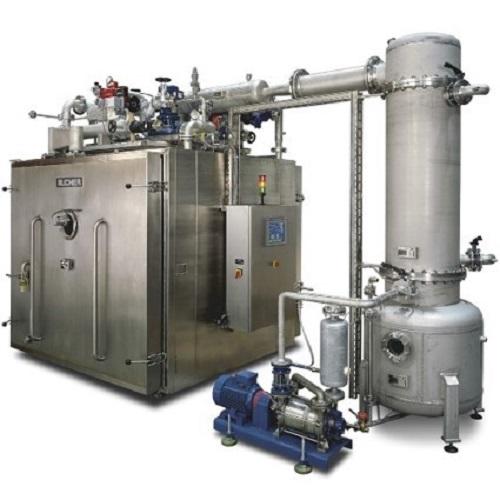

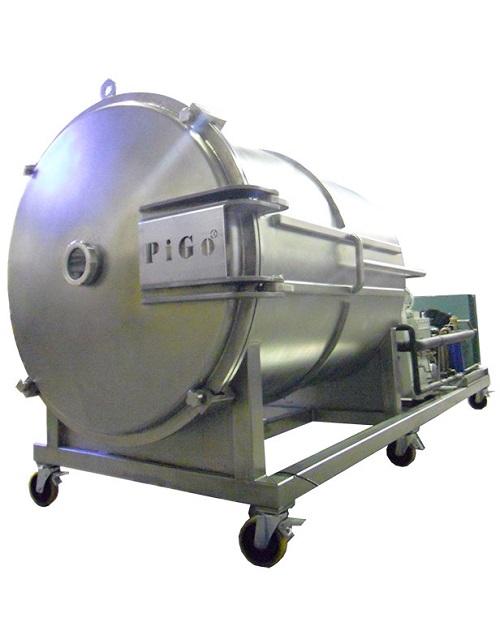
Vacuum cabinet dryer for plant extracts and functional foods
Plant extracts are vital to functional food preparations. B...
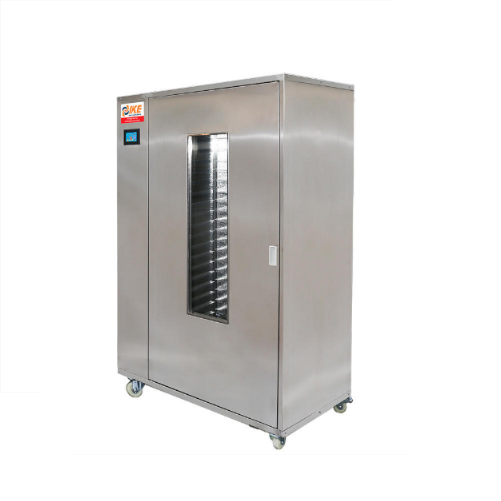

Industrial drying cabinet
The production of high-quality biltong and similar dried meat products can pose problems with main...

Cosmetic cream filler
From thin liquid baby oils and perfumes to thicker lotions and creams for hair and skincare, cosmetic p...
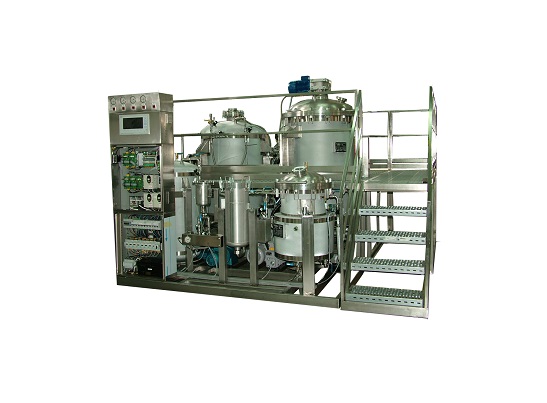

Flower oil extraction machine
The production of “essential oils” has traditionally involved using heat and distillation to e...

Medicinal plant extraction machine
Traditional methods for extracting active compounds from medicinal plants or herbs use h...
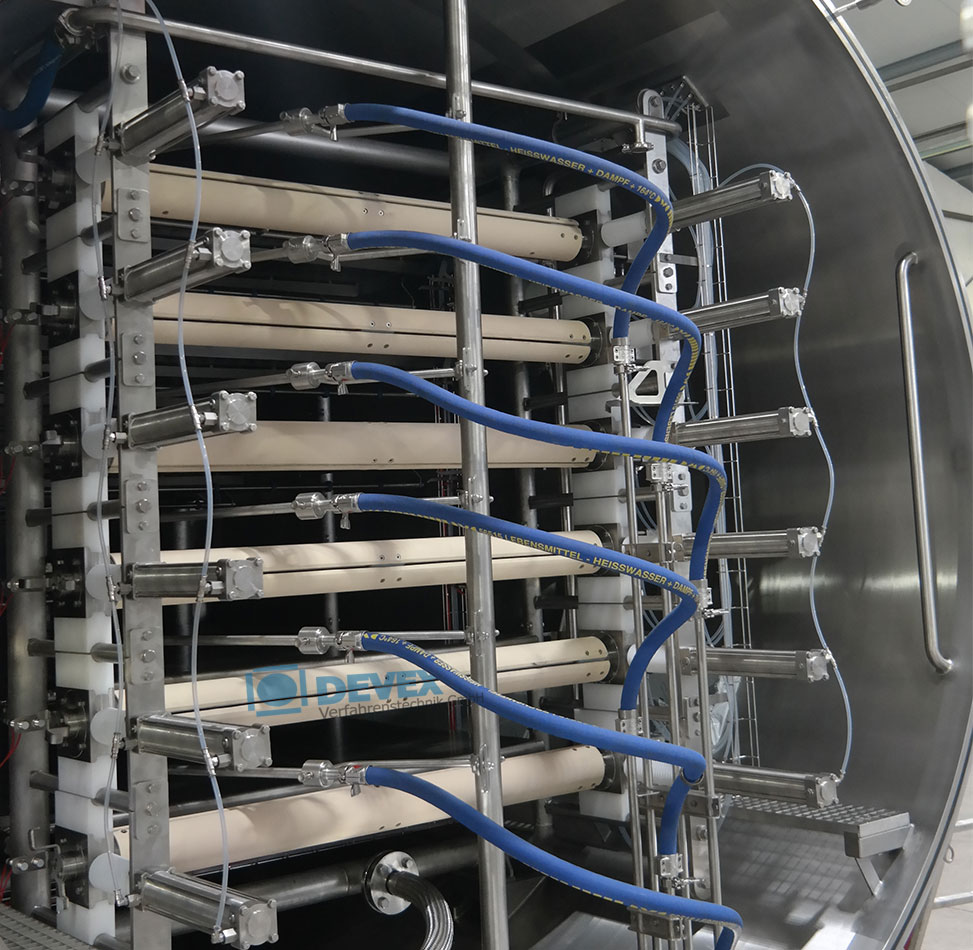

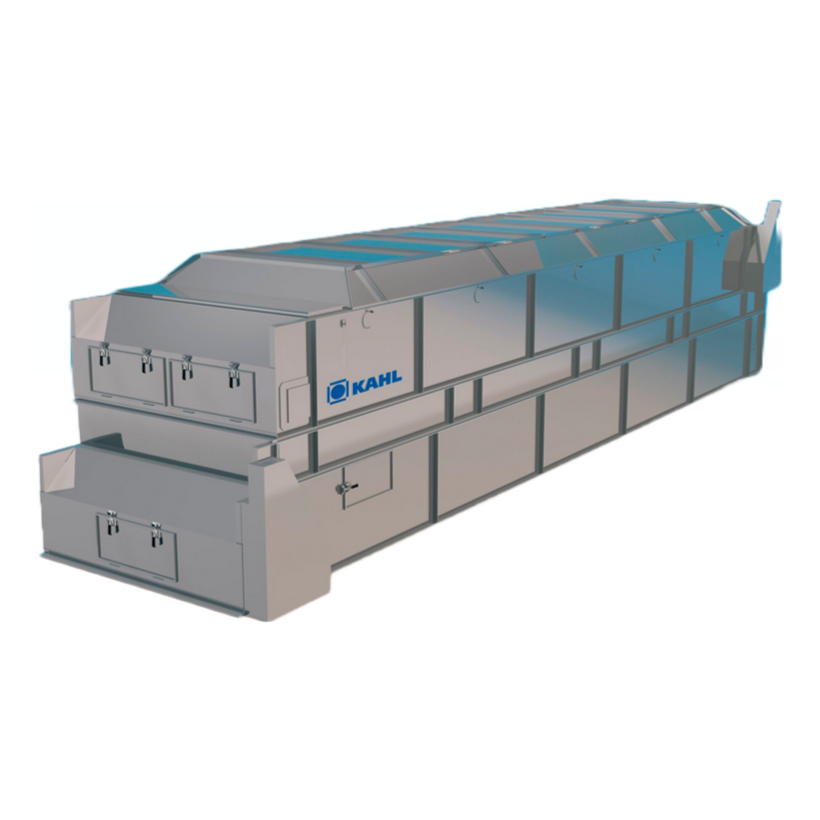
Continuous vacuum belt dryer
For gently drying liquid concentrates into granulates or powders, a vacuum drying solution is t...
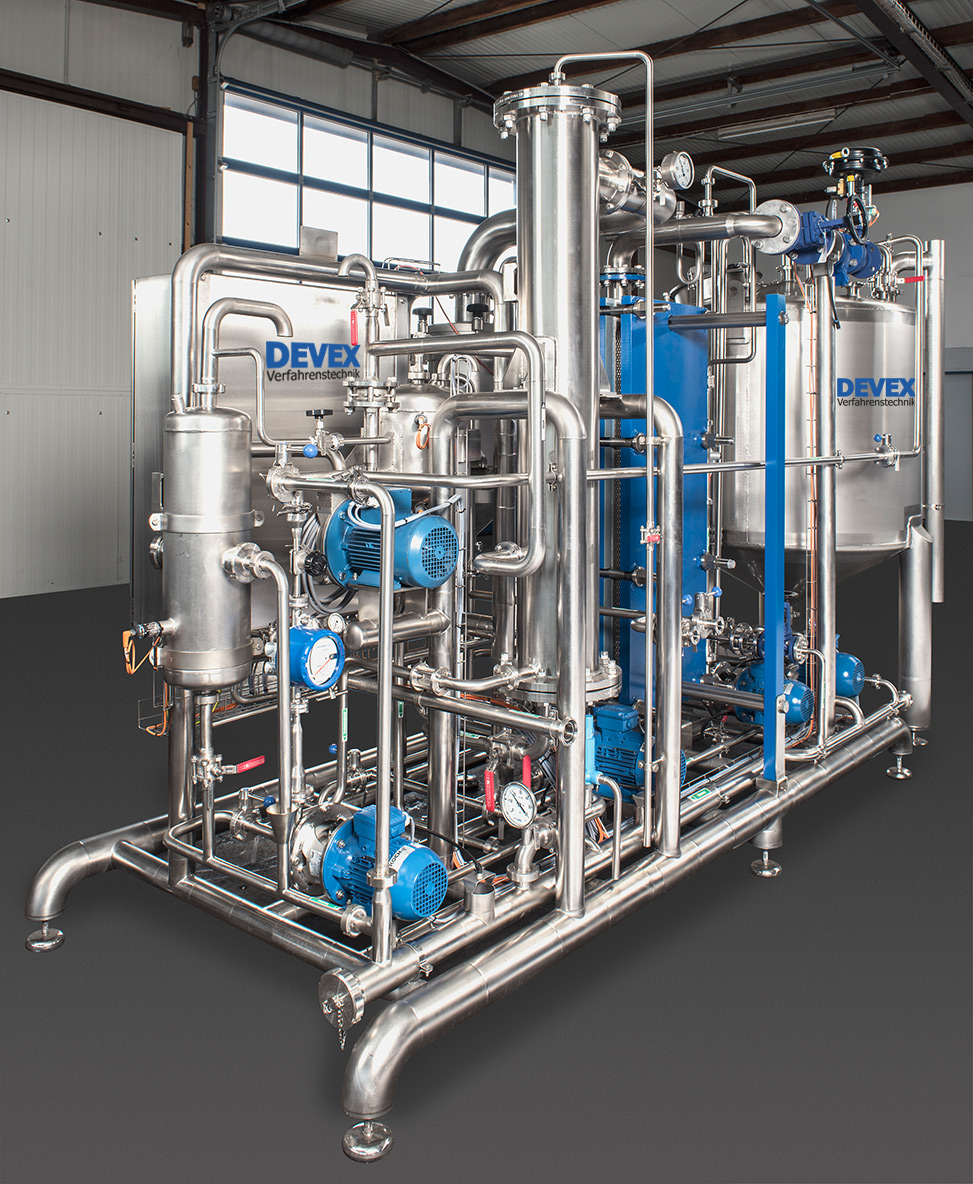

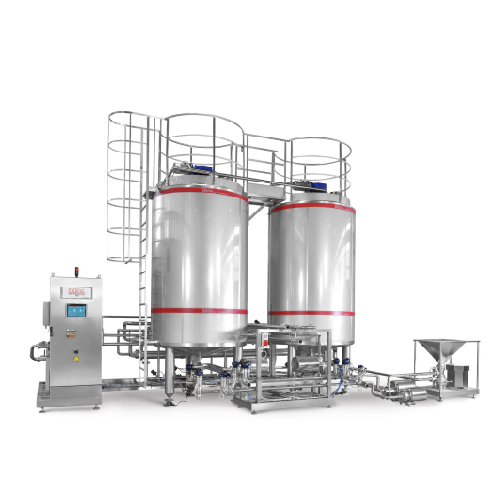
Evaporation plant for the recovery of extracts
Bespoke evaporation plants using the latest plate evaporation technology ca...
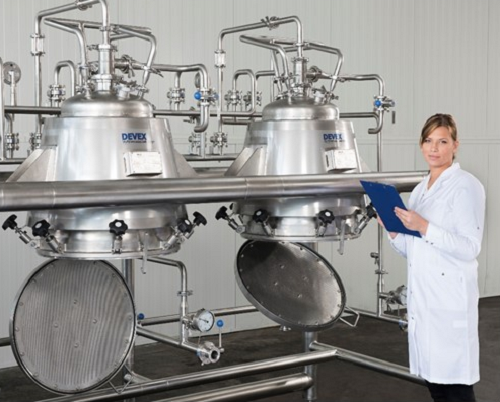

Pilot extraction plant for natural ingredients
Before purchasing a full-scale extraction plant you need to exactly determi...
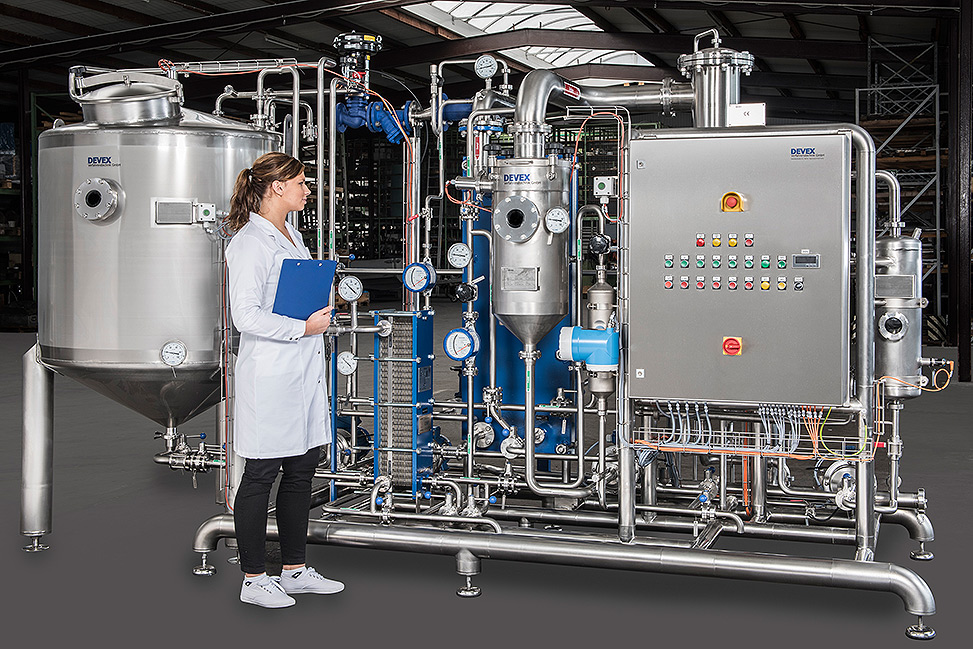

Pilot evaporation plant for the recovery of extracts
For development of concentrates of extracts based on water or ethano...
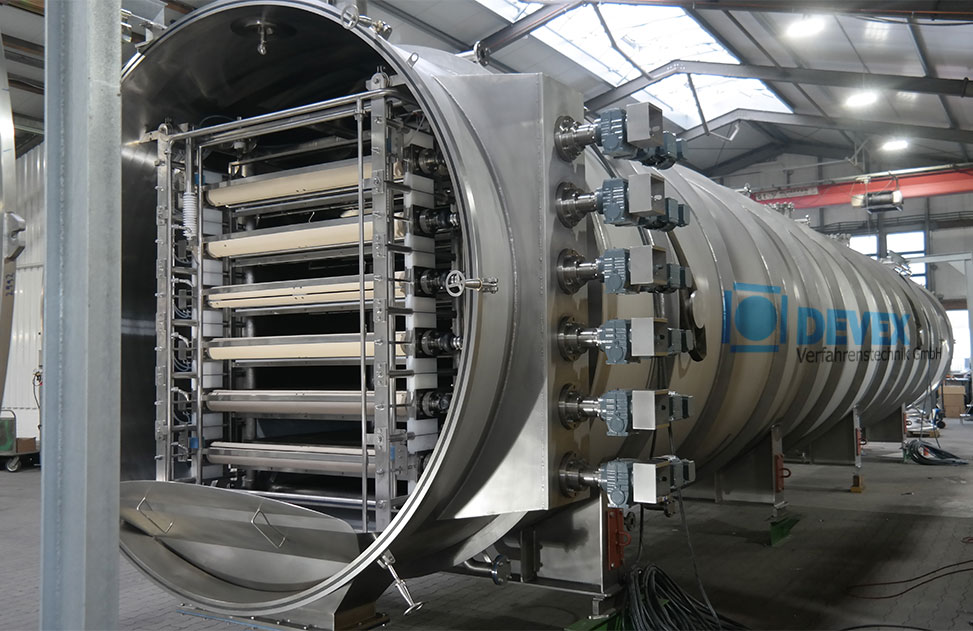

Continuous belt freeze dryer
Freeze drying is the most gentle and aroma protective method of drying, widely used in the coff...
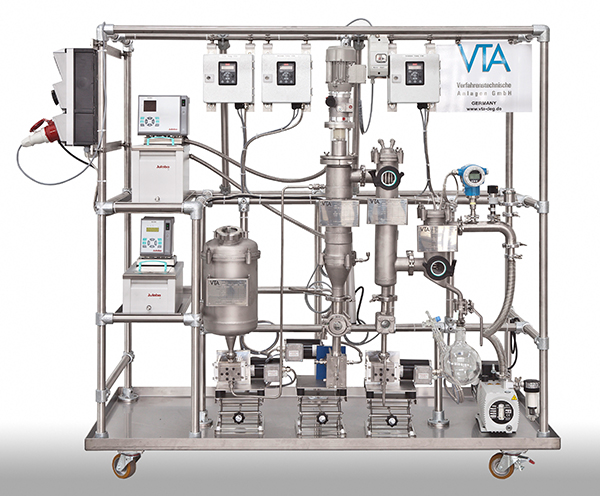
Pilot wiped film distiller
Generate scalable data and results during the pilot tests with wiped film distillation, distill ...
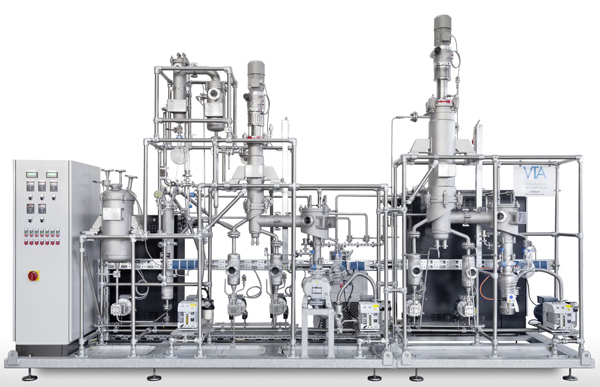
Pilot short path distiller
Generate scalable data and results during the pilot tests with short path distillation, distill o...

Laboratory wiped film distiller
Reach reliable conclusions testing the distillation of high-boiling or highly viscous materi...
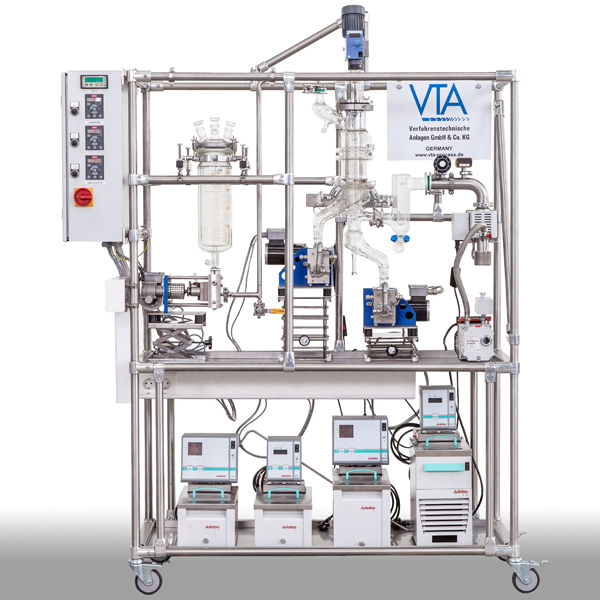

Laboratory short path distiller
Get to reliable conclusions for the separation of high-boiling and heat-sensitive products u...

Horizontal thin film evaporators
Horizontal thin film evaporators can increase the residence time of the product and achieve...
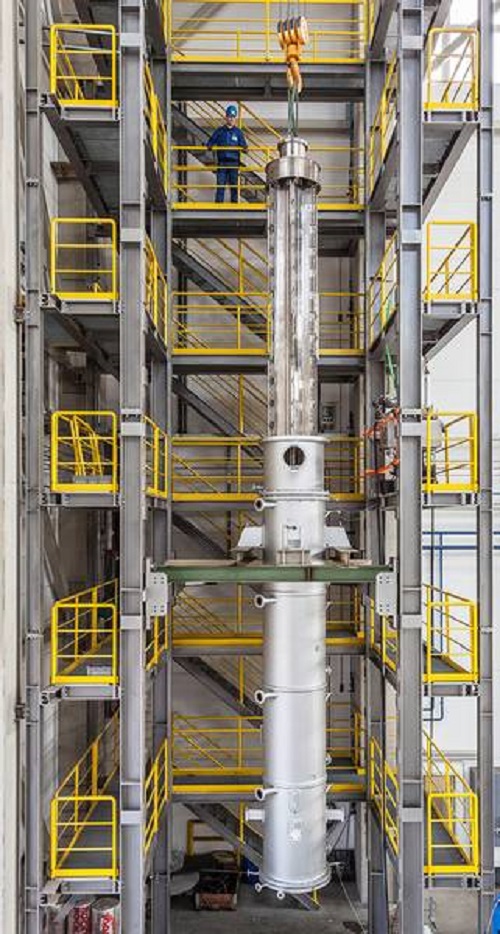

Thin film dryers
Dry dissolved or slurried crystallizing or amorphous products to a pourable powder.