Making Glycerine
Find innovative production technology for making glycerine and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Glycerine is a water-soluble liquid mix of alcohol and sugar. It is a by-product of the oil and fats industry that offers added value to various industries. There are three ways to process it: transesterification, saponification, and fat splitting (hydrolysis). In 2020 these 3 forms of glycerine production reached around 4 million metric tons, with a global market of $1.68 billion.
Tell us about your production challenge
Glycerine production from by-products of biodiesel, soap, or fat-splitting
Glycerine production starts with the transformation of by-products from different industrial processes and feedstock. The main industries are biodiesel production, soap production, and fat splitting. To obtain crude or refined glycerine, you need storage tanks, evaporators centrifuges, hydrolizers, and distillers.
Crude glycerine can be obtained by transesterification of natural oils or biodiesel. Here, fatty acid methyl esters are separated from sweet water. The concentration of the latter results in crude glycerol. It can also be obtained by hydrolysis or fat splitting, separating fatty acids from sweet water concentration. Last but not least is the saponification method. In this process, alkali solutions separate oils and fats from glycerol and convert the triglycerides into soap. If you’re making refined glycerine, crude glycerine must undergo subsequent refining and distillation.
Glycerine has multiple applications across industries
The natural origins, water solubility, and non-toxicity make glycerol a versatile option across industries. It’s used as a moisture retention agent, humectant, and lubricant in personal care products and cosmetics. Due to its smoothening, moisturizing, and sweetening properties, pharmaceutical and health care, glycerine is used to manufacture skin creams, eye drops, syrups, toothpaste, suppositories, and other products.
Food and beverages producers use it as a humectant, solvent, sweetener, or preserver, to make a range of foodstuffs including candies, low-fat products, cheese, margarine, and pet food.
Moreover, other industries use glycerine to make products such as anti-freeze, lubricant additives, coatings, paints, foams, and solid rocket fuels. The chemical and physical properties of glycerine, give it flexibility in its applications and compatibility with many ingredients.
Processing steps involved in glycerine making
Which glycerine technology do you need?

Spray cooler for food and chemical industry applications
Achieve precise particle size control and encapsulation for melt...

Agitator bead mill reactor for molecular synthesis by mechanochemistry in continuous flow
To achieve cleaner, safer,...

Refining plant for vegetable oil and animal fats
The main problems arising from refining process of vegetable oil and anim...
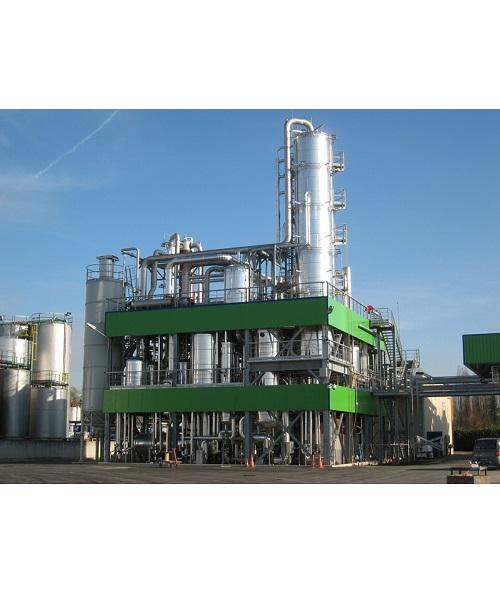

Production plant for biodiesel
As a biofuel producer, making biodiesel from several types of treated vegetable oils or anima...
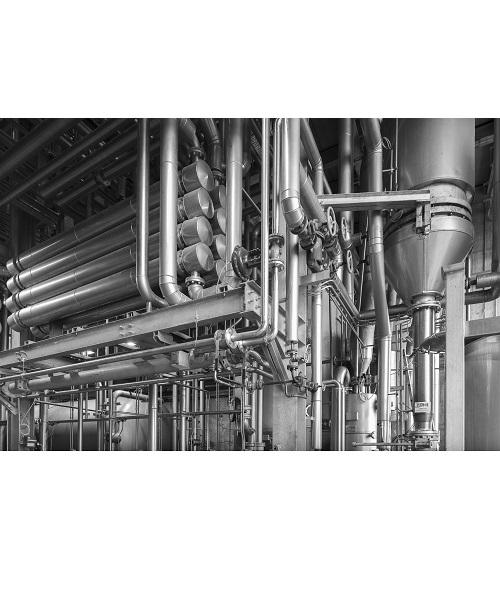

Glycerine manufacturing plant
Glycerol or glycerin is the major by-product generated in the biodiesel production process. Bu...

Fluid sensor technology for flow rate measurement
For many bioprocesses, precise measurement of media flow rates is vital...
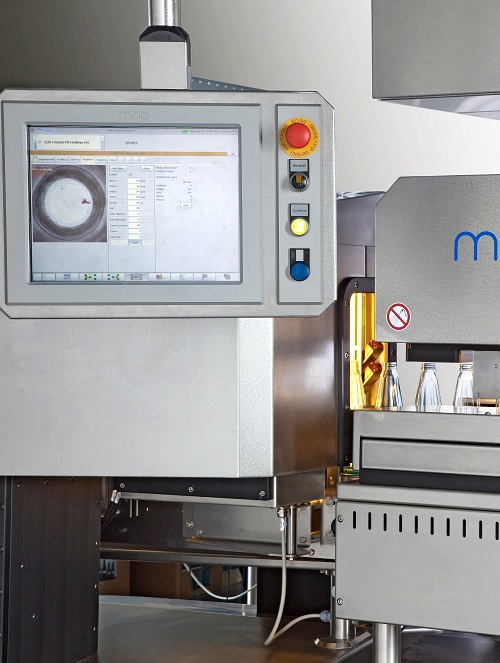

High-end empty bottle inspection system
If you are looking for a system with empty bottle inspection; base, residual liquid...
Disposable mixer bags for bioprocesses
Bioprocessors must use ingredients of known high quality and consistency. Inconsist...

Pusher centrifuge
Pusher centrifuges are continuously operating filter centrifuges and can have several basket stages dependi...