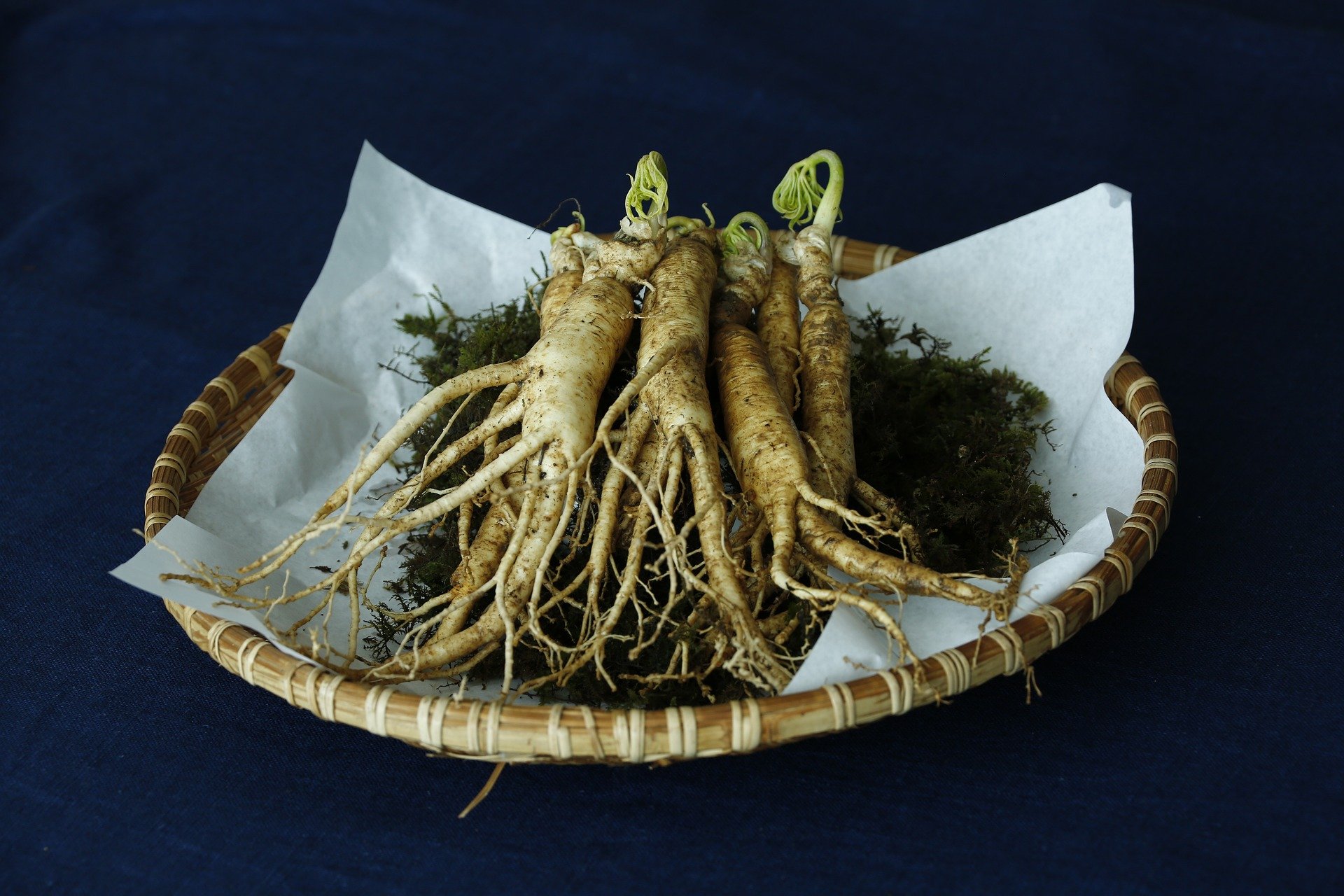
Making Ginseng Extract
Find innovative production technology for making ginseng extract and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Panax ginseng is a medicinal plant with a long history steeped in myth. The term “panax” itself is derived from a Greek word for “panacea” or “cure all”. As ginseng processing technology continues to develop, this famous traditional extract keeps finding new applications.
Stories about ginseng extract
Select your ginseng extract process
Tell us about your production challenge
Lower processing temperatures with ultrasound-assisted extraction
Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) performs at a lower temperature than conventional ginseng processing technology. Besides increasing yield, lower operating heat protects thermally unstable ingredients in plant materials.
Another advantage of UAE is that it requires less solvent than most solvent extraction techniques. The technology applies acoustic cavitation to disrupt the cell walls and release the target compounds.
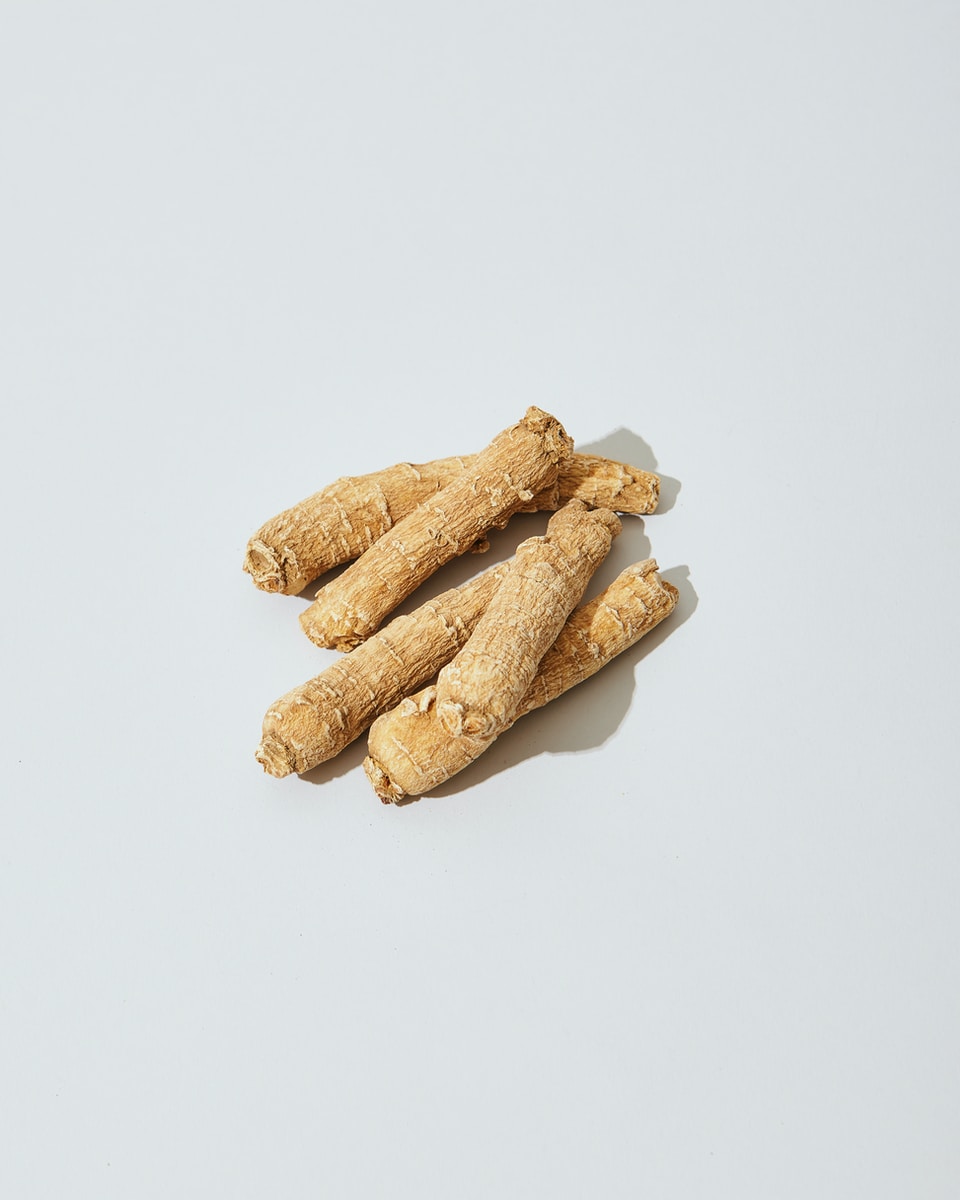

Applying ginseng processing technology to produce black extract
Ginseng extracts can be further processed into black ginseng. The type can be prepared from either the red or white variety by repeated steaming and drying. The process gelatinizes the ginseng, reducing moisture levels.
But the biochemical reactions also increase the concentration of benzopyrene, a carcinogen.
The drying phase has a more significant impact on the presence of benzopyrene than steaming. The optimum drying temperature is 100 °C for a period of 8 hours.
Novel ginseng extract finds new application in pharmacology
Ginsenosides are the primary bioactive compounds in ginseng extracts. But the plant contains several other bioactives such as ginsenosides, polyacetylenes, and acidic polysaccharides.
One of the novel compounds identified in ginseng, gintonin, promises a broad application as an active pharmaceutical ingredient. Gintonin binds with the proteins on cell surface membranes and transmits cellular information. The ingredient has the potential for the treatment of geriatric brain diseases.
Processing steps involved in ginseng extract making
Which ginseng extract technology do you need?

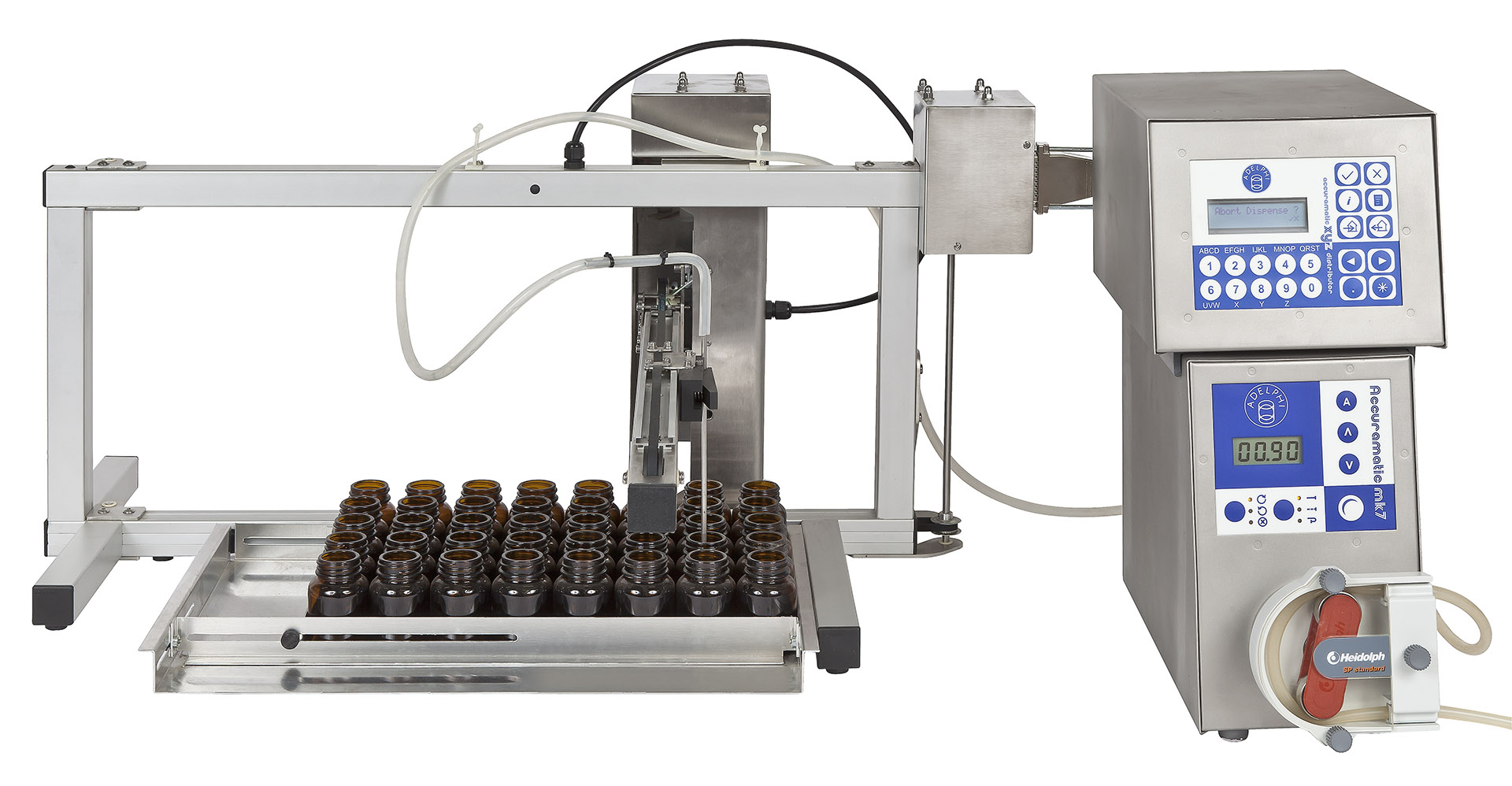
Benchtop peristaltic dispenser
When you fill vials and ampoules, high standards of hygiene are required to avoid the risk of...

Benchtop piston filling equipment for vials in trays
Vials are difficult to fill individually through manual methods due ...

Semi-automatic vial crimper
In a small production line, crimping vials manually can cause fatigue to your operator due to mu...
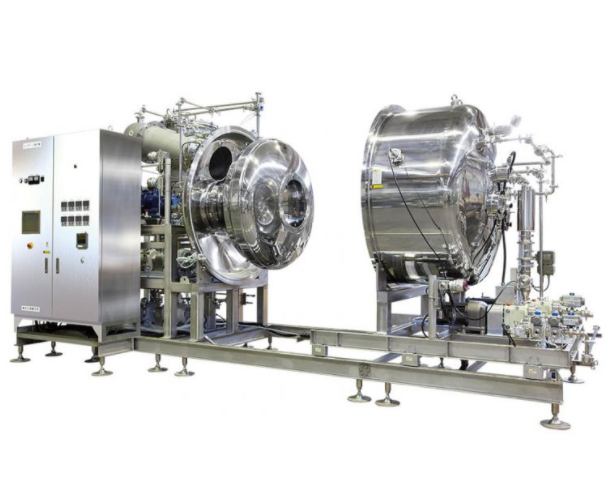

Evaporator for heat sensitive products
The removal of solvents when making products in industries like food, cosmetics, pha...

Ultrasonic barbell for extraction
Conventional extraction methods are time-consuming, labour-intensive and can sometimes be...
Vacuum belt dryer for instant drink powders
Extracting the essential acids and compounds from fruits and plants is a compl...

Cosmetic cream filler
From thin liquid baby oils and perfumes to thicker lotions and creams for hair and skincare, cosmetic p...

Flower oil extraction machine
The production of “essential oils” has traditionally involved using heat and distillation to e...

Medicinal plant extraction machine
Traditional methods for extracting active compounds from medicinal plants or herbs use h...
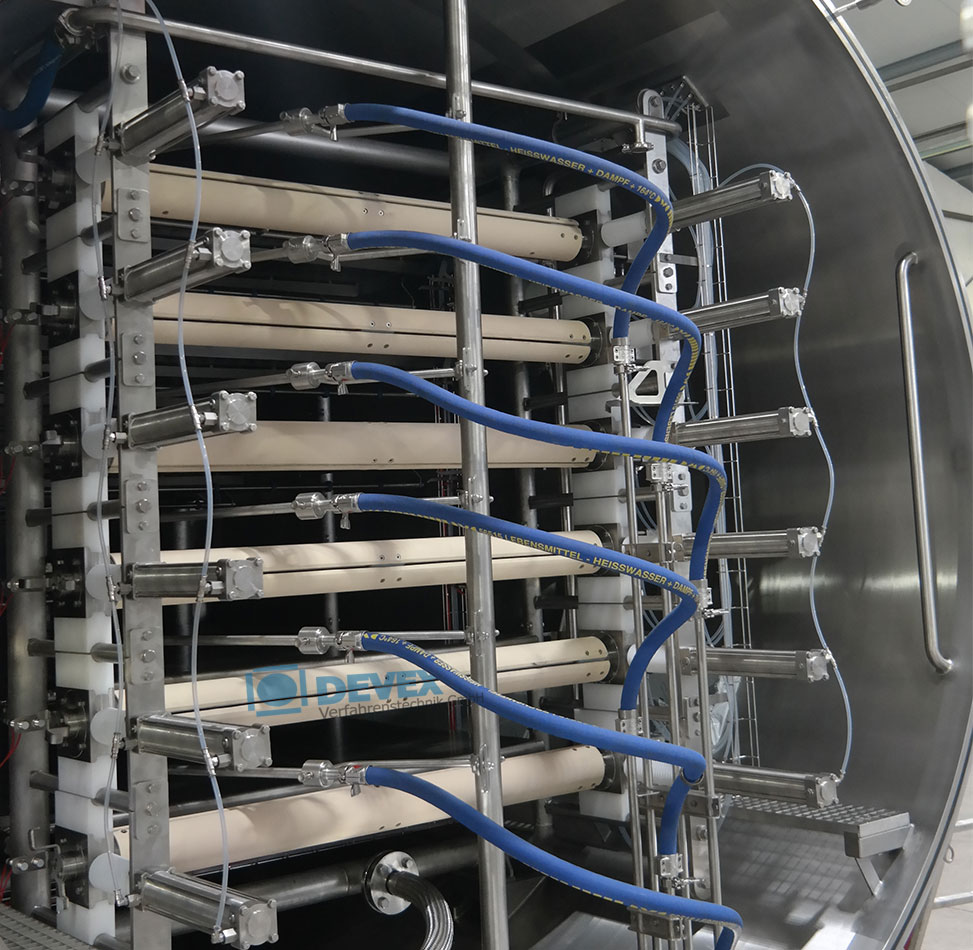

Continuous vacuum belt dryer
For gently drying liquid concentrates into granulates or powders, a vacuum drying solution is t...
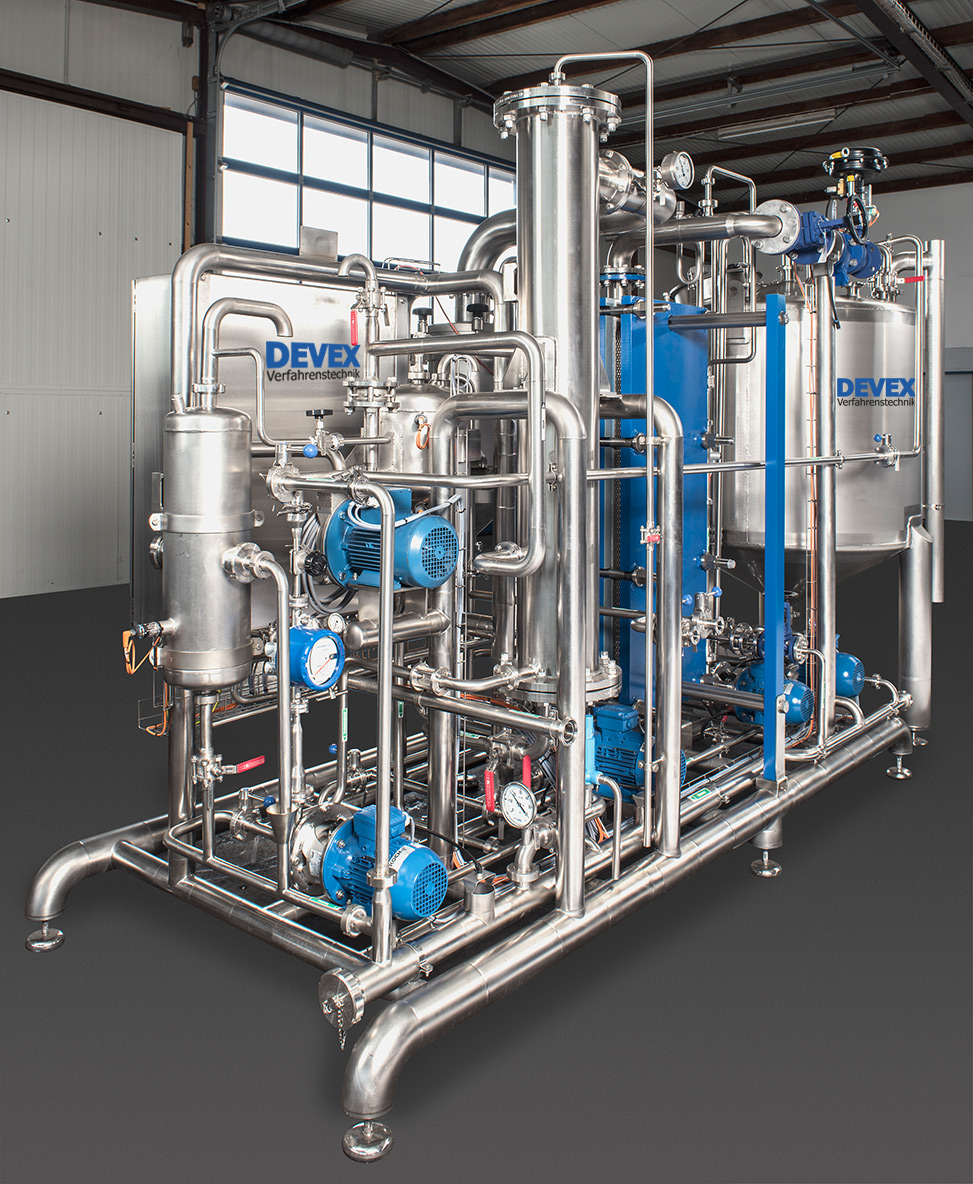

Evaporation plant for the recovery of extracts
Bespoke evaporation plants using the latest plate evaporation technology ca...
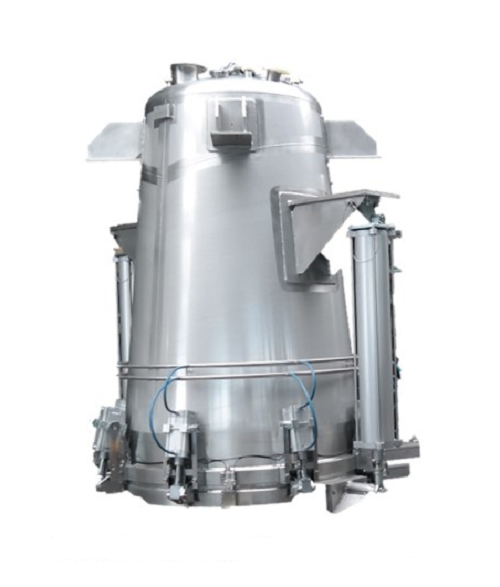

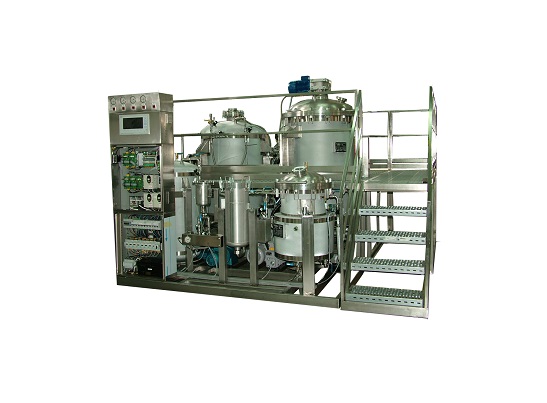
Extraction plant for natural ingredients
Bespoke extraction plants using the latest technology can improve your efficiency ...
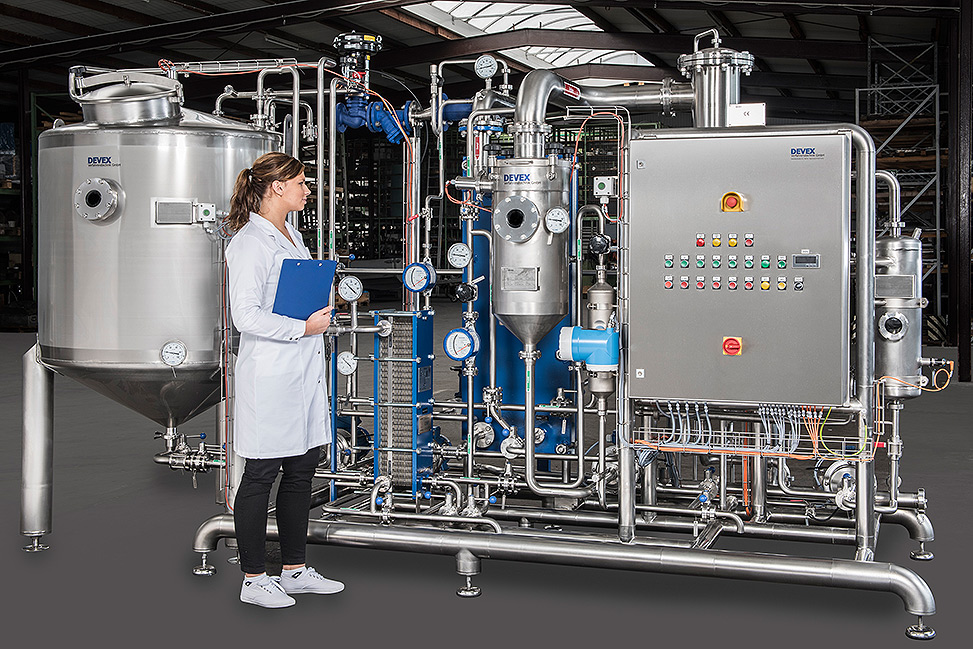

Pilot evaporation plant for the recovery of extracts
For development of concentrates of extracts based on water or ethano...
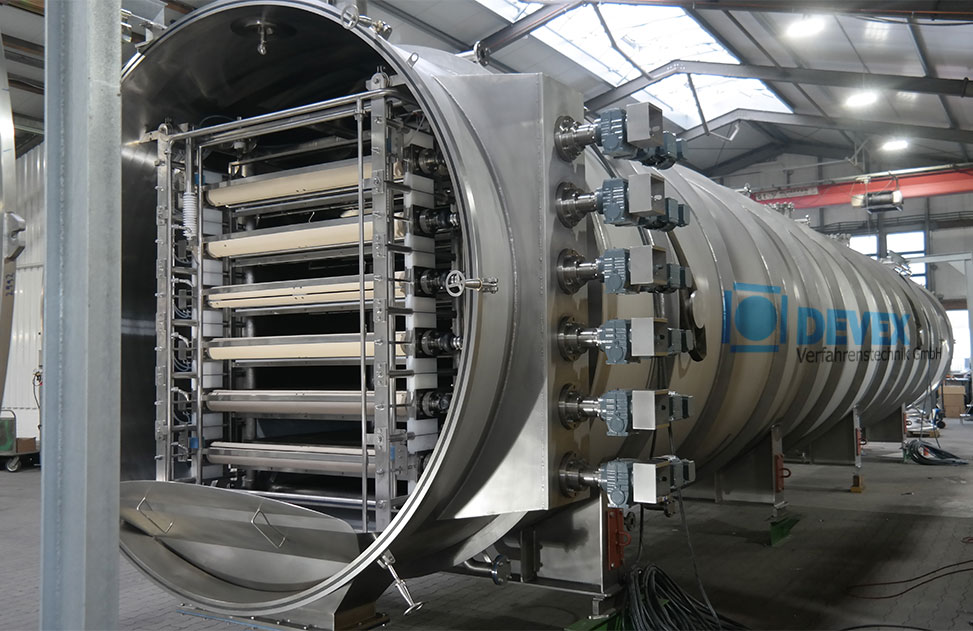

Continuous belt freeze dryer
Freeze drying is the most gentle and aroma protective method of drying, widely used in the coff...
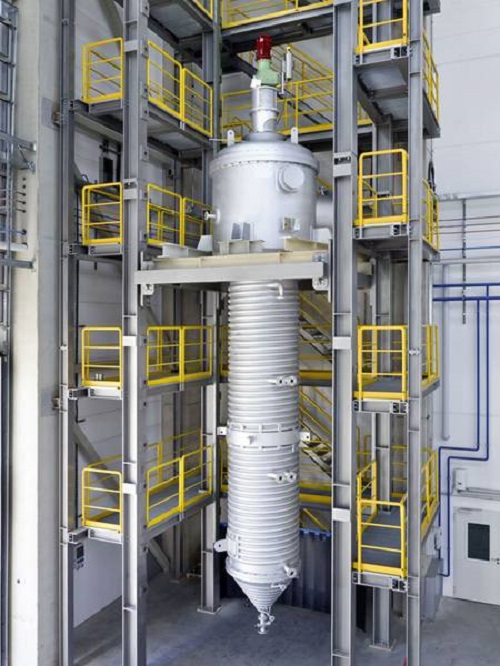

Wiped film evaporator
With wiped film distillation, a substantial decrease of boiling temperature is obtained by reducing the...
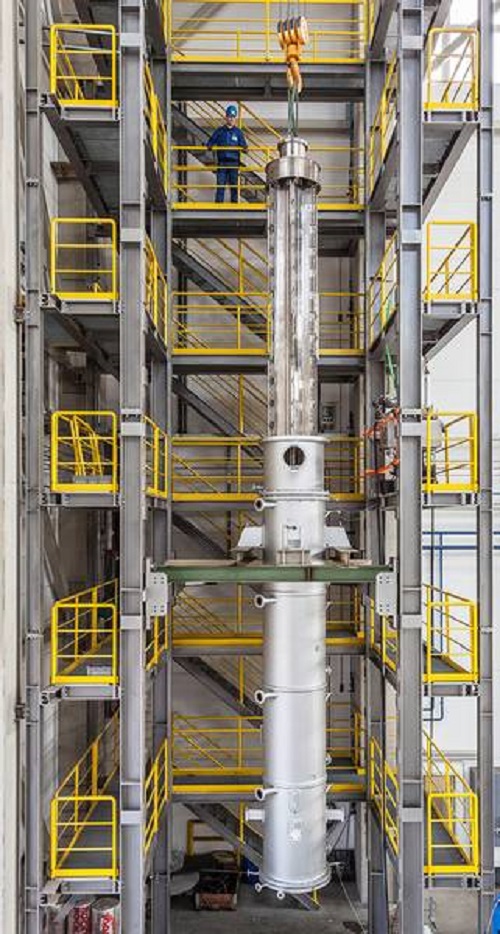

Thin film dryers
Dry dissolved or slurried crystallizing or amorphous products to a pourable powder.