Cultured Meat Technology
Find innovative production technology for making cultivated meat and connect directly with world-leading specialists
What does a $300,000 burger taste like? Meat. The first lab-grown burger took two years and 20,000 strands of muscle tissue to produce. But with rapid advances in cultivated meat processing technology, non-animal meat alternative products can now take a lot shorter to prepare. And cost much less.
Stories about cultivated meat
Select your cultivated meat process
Tell us about your production challenge
Collect healthy cells for your production starter kit
Like live animals, cultured meat starts with an animal cell. The first time, cells are extracted through a biopsy or from an egg in the case of poultry products. Isolate the tissue cells that make up the end product, such as fats or muscle tissue.
This starter cell kit can be stored indefinitely in a cell bank, producing multiple cycles of meat cultivation without further extraction.
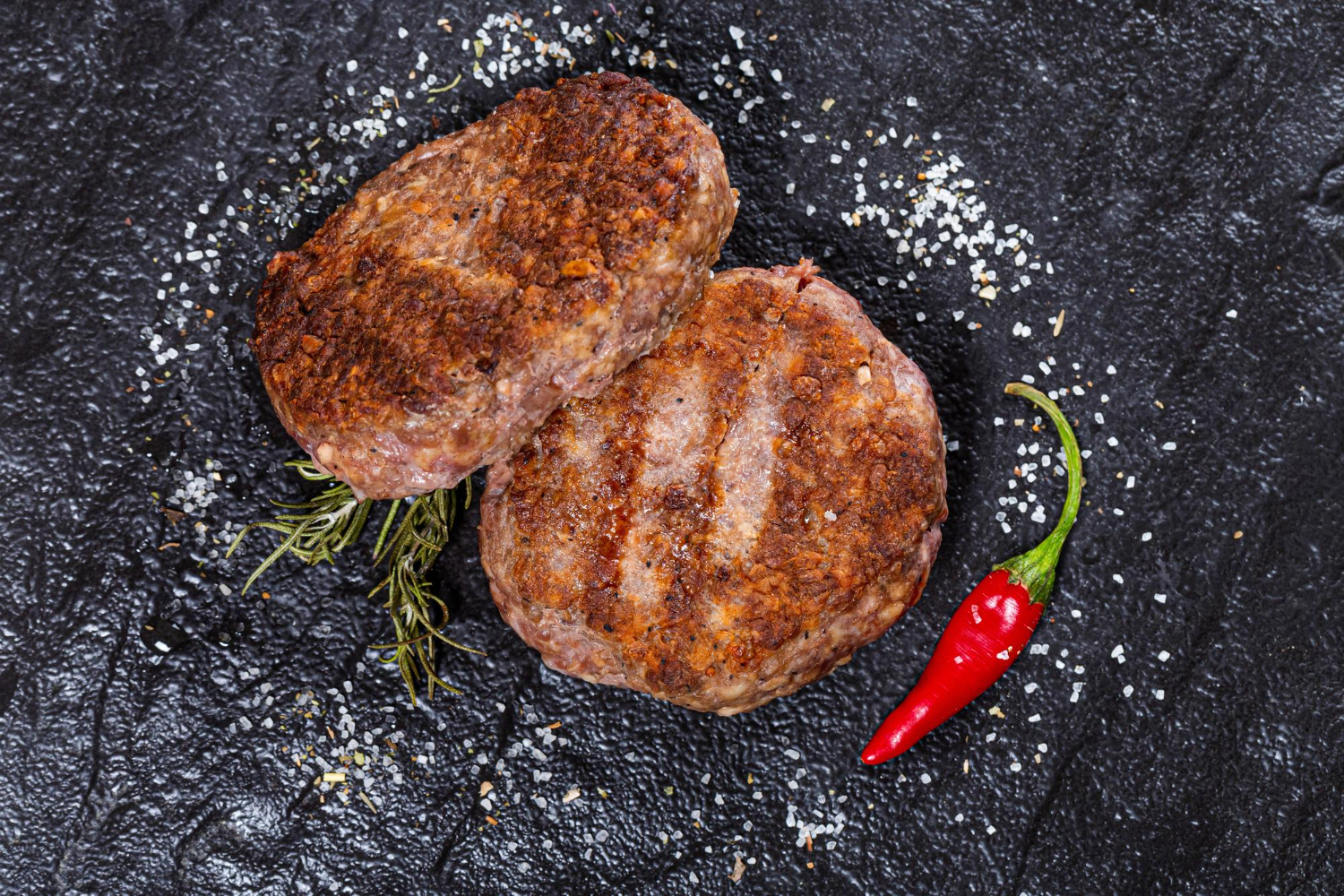

Add nutrients to grow the cells in a bioreactor
Biotechnology is the driving force that makes large scale lab-grown meat a possibility. As a result, bioreactors are fundamental cultured meat processing technology. Place the cells in a bioreactor where they will divide and multiply, just like in the natural process. The cell cultures feed on a medium of nutrients, including fibers and amino acids, fats, and vitamins. The mix is based on natural feed products extracted from crops, yeasts, and minerals.
This phenomenon mimics the organic process but cuts the growth period significantly. Depending on the final product, harvesting typically takes four to six weeks from immersion in the medium.
Avoid cell aggregation in the cultivation step
The bioreactor cultivates the sourced cells, providing energy and a conducive temperature. But failing to control the process risks depleting the growth factors and degrading the cells. The cultivator needs to keep a uniform environment for the cell population to thrive.
Another manufacturing challenge at this stage is the lumping of cells. Aggregation hinders development, causing cells to die out.
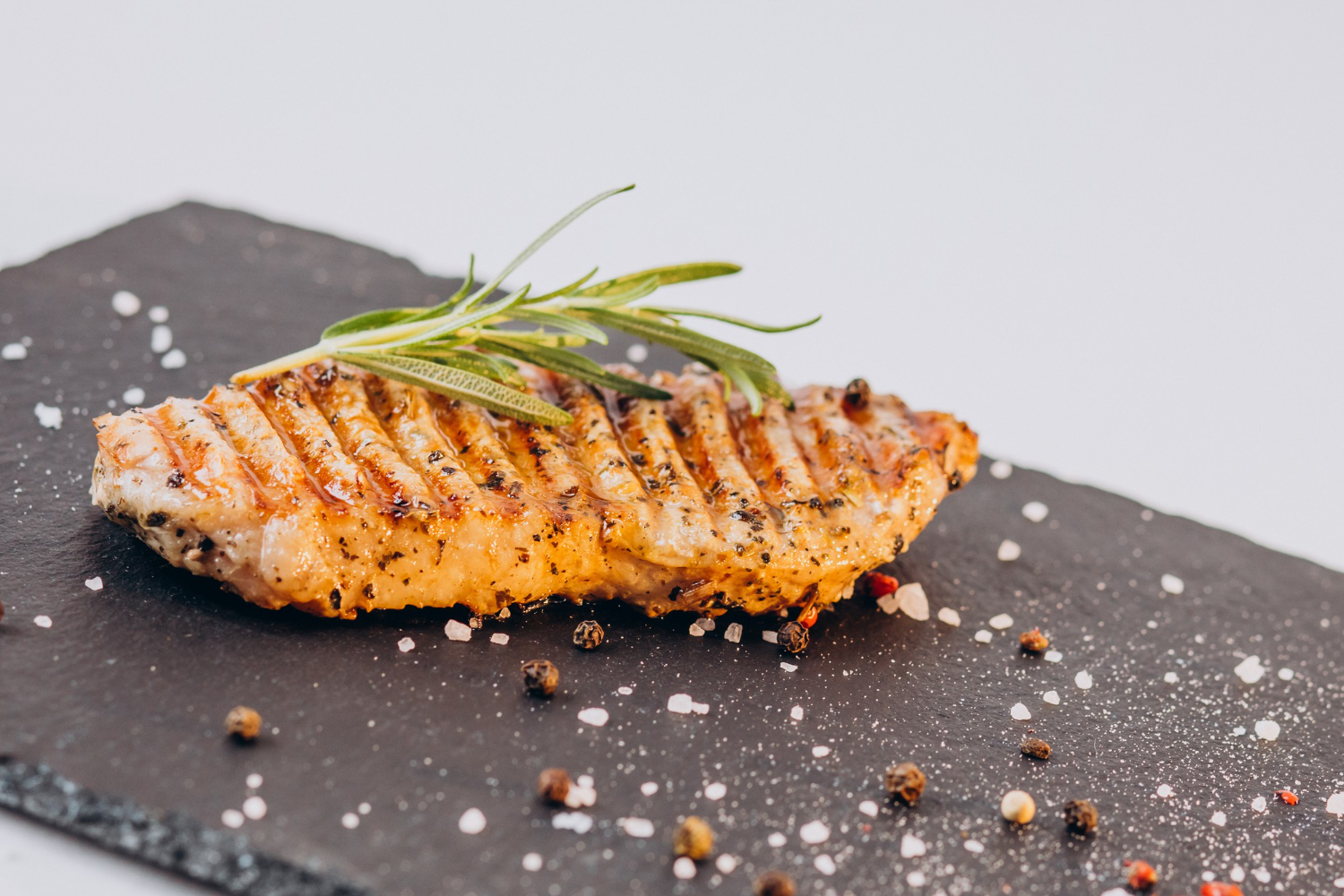

Form the ingredients into natural lookalikes
Shaping the mature cells into standard dimensions presents a key challenge for lab grown meat technology. One technique is to form a scaffolding from natural materials like textured vegetable protein, allowing the splitting cells in the bioreactor to grow onto it.
Another method is to mold the material following cultivation. The product is then treated with coloring and seasoning techniques to bring it closer to a conventional meat cut derived from live animal farming.
Different cultivated meat technology to achieve the right texture
The test of cultivated meat is how faithfully it can reproduce the textures of the farmed products from the traditional meat industry. One solution is to extrude the cultivated ingredients. The pressure applied to the cell material develops a more fibrous consistency reminiscent of meat products from slaughtered animals. An alternative way is to model the separate meat strands and create the product in 3D using additive manufacturing equipment.
All in all, cultivated meat is gaining in popularity around the world as people are moving towards sustainability and reducing greenhouse gases. Lastly, this technology gives meat lovers a way to enjoy their favorite foods without any harm to animals as well as the plant. And, provides them with the real thing instead of plant-based meat alternatives.
Processing steps involved in cultivated meat making
Which cultivated meat technology do you need?
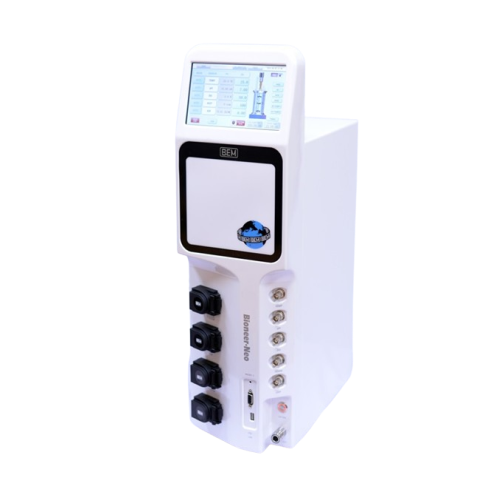

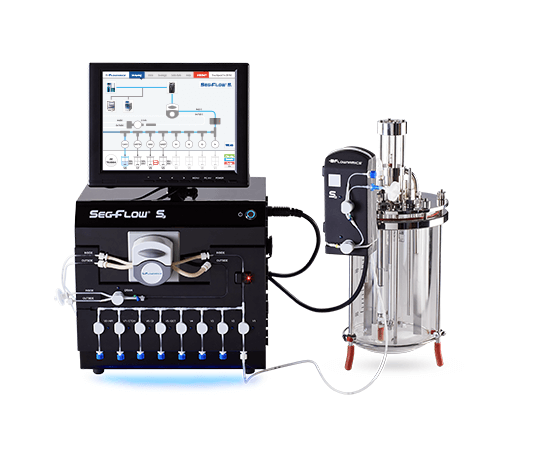
Compact fermentor for research and scale-up studies
Optimize your bioprocess development with a desktop fermentor that of...
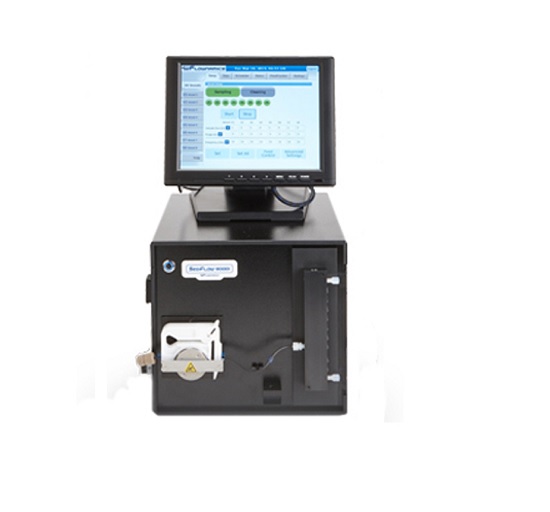

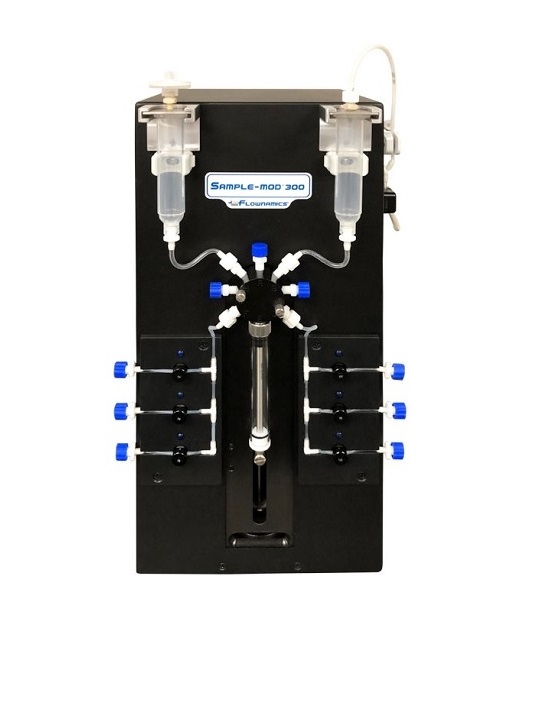
Online sampling system for larger scale bioprocesses
Accurate sampling is vital for improving a wide variety of industria...
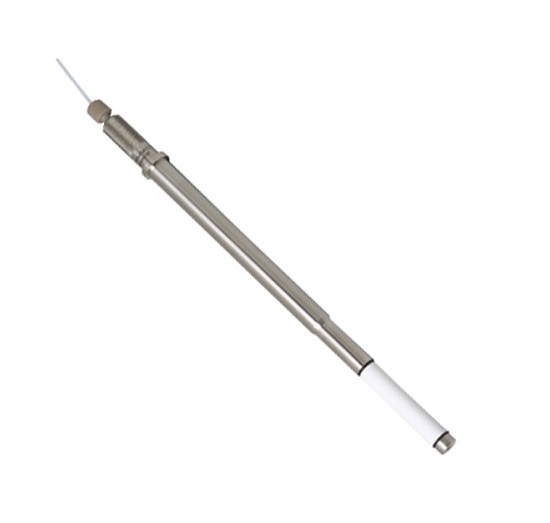

Sampling probe for bioreactor samples
In biopharmaceutical and chemical industries, sampling is vital to develop, maintain,...
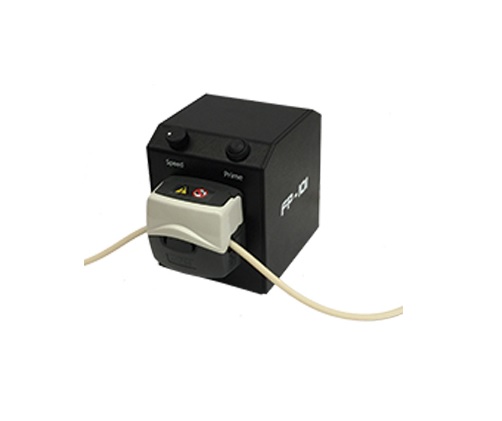

Accessory feed pump for various applications
In many biopharmaceutical or chemical development processes, lab work can be ...

Fluid sensor technology for flow rate measurement
For many bioprocesses, precise measurement of media flow rates is vital...
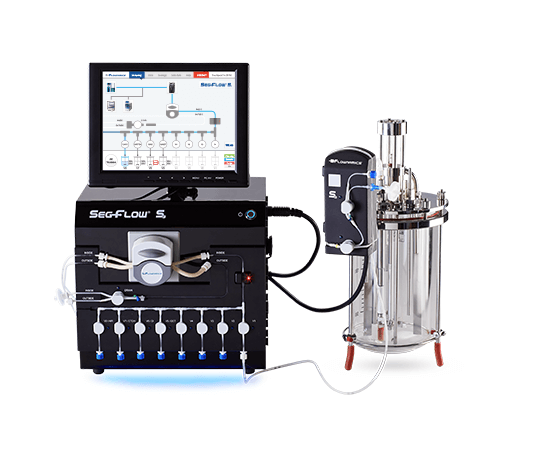

Fully Automated On-Line Sampling for Bioprocesses
Accurate sampling is a critical tool in the design and improvement of a...
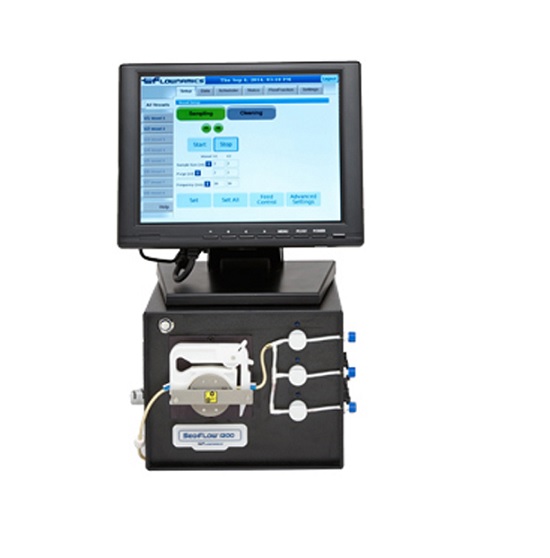

Entry-level automated online sampling system
An accurate and sterile sampling of cultures is vital throughout the biopharm...

Liquid nitrogen freezer for safe and dry storage of your samples
Remove the risks of cross-contamination and liquid nitr...

Automated dispensing system for bioprocesses
Biopharmaceutical manufacturers require precisely known liquid quantities for...

Laboratory extruder
Products can be extruded with a variety of shapes and characteristics by controlling the nozzle geometry ...