Processing Sugar Beet Seeds
Find innovative production technology for making sugar beet seeds and connect directly with world-leading specialists
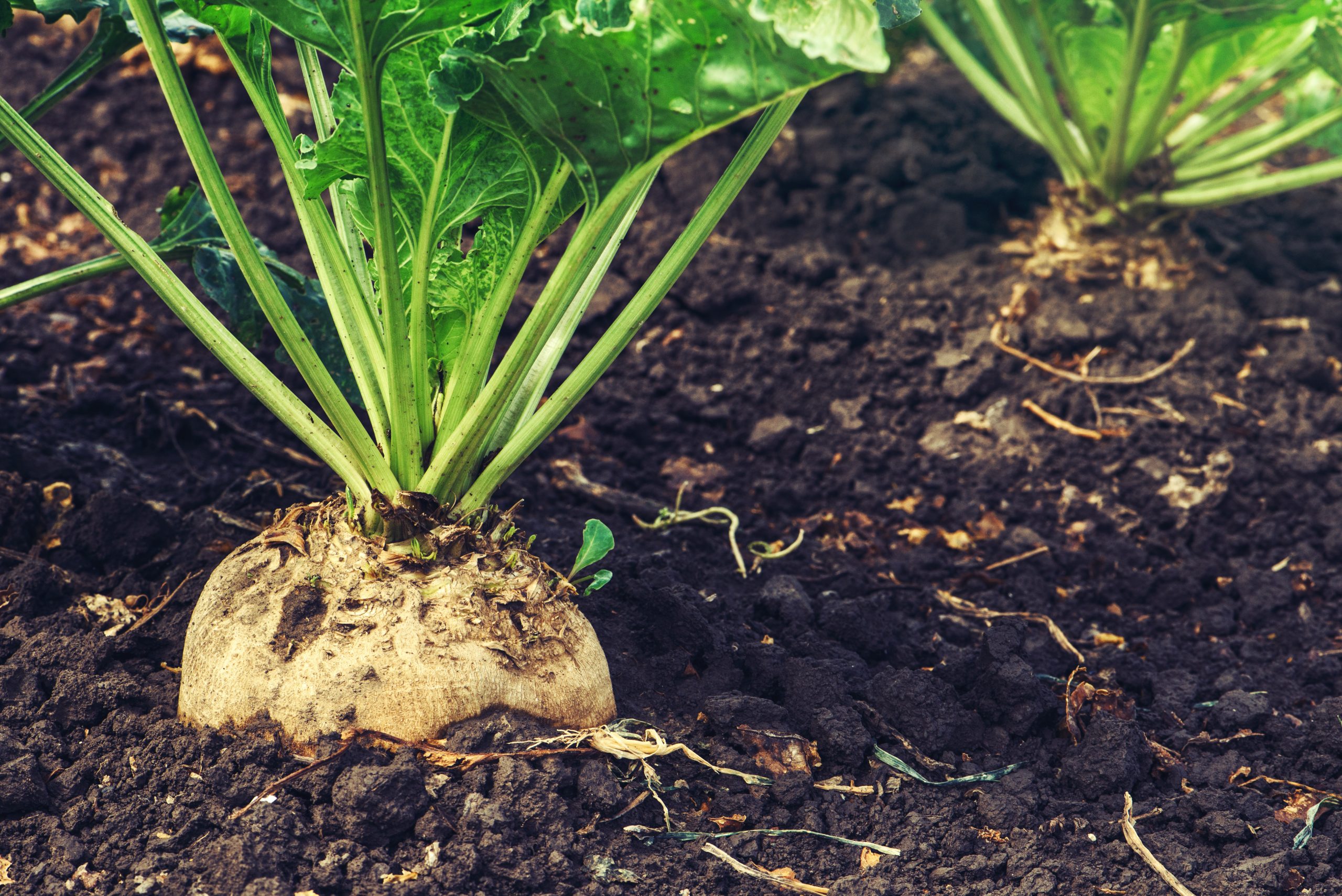
Extracting sugar from beets became popular in continental Europe during the Napoleonic Wars due to the British blockades of cane sugar. This is thanks to the high sugar content derived from this crop. Also known by its scientific name, "beta vulgaris", The beets’ popularity steadily rose afterwards and today, 20% of all sugar in the world comes from beets. But all of this can't be possible without its seeds. The production and processing of sugar beet seeds includes different steps such as cleaning, priming, pelleting and coating.
Stories about sugar beet seeds
Select your sugar beet seeds process
Tell us about your production challenge
First steps in processing: cleaning and priming

This production occurs in many steps. Raw seeds are contaminated with sticks, dirt and weed so they must be cleaned before priming. The sugar beet seed has an odd shape and they are lined with the pericarp, a hardened membrane that protects it within; however, it also restricts hydration and inhibits germination.
A crop and vegetable seeds polisher and brushing machine carefully remove both the debris and the pericarp.
To make sure the seeds are of a similar size and undamaged, manufacturers use blowing machines for separation. This equipment provides similarly-sized seeds and eliminates the ‘duds’. For instance, a seed coming from your crop that is too large, too small or empty are rejected.
priming is a process that stimulates germination by carefully hydrating the seed. By using priming equipment, the seeds are soaked in water to slowly germinate, which ensures uniform emergence in the field.
From irregular seeds to coated pellets
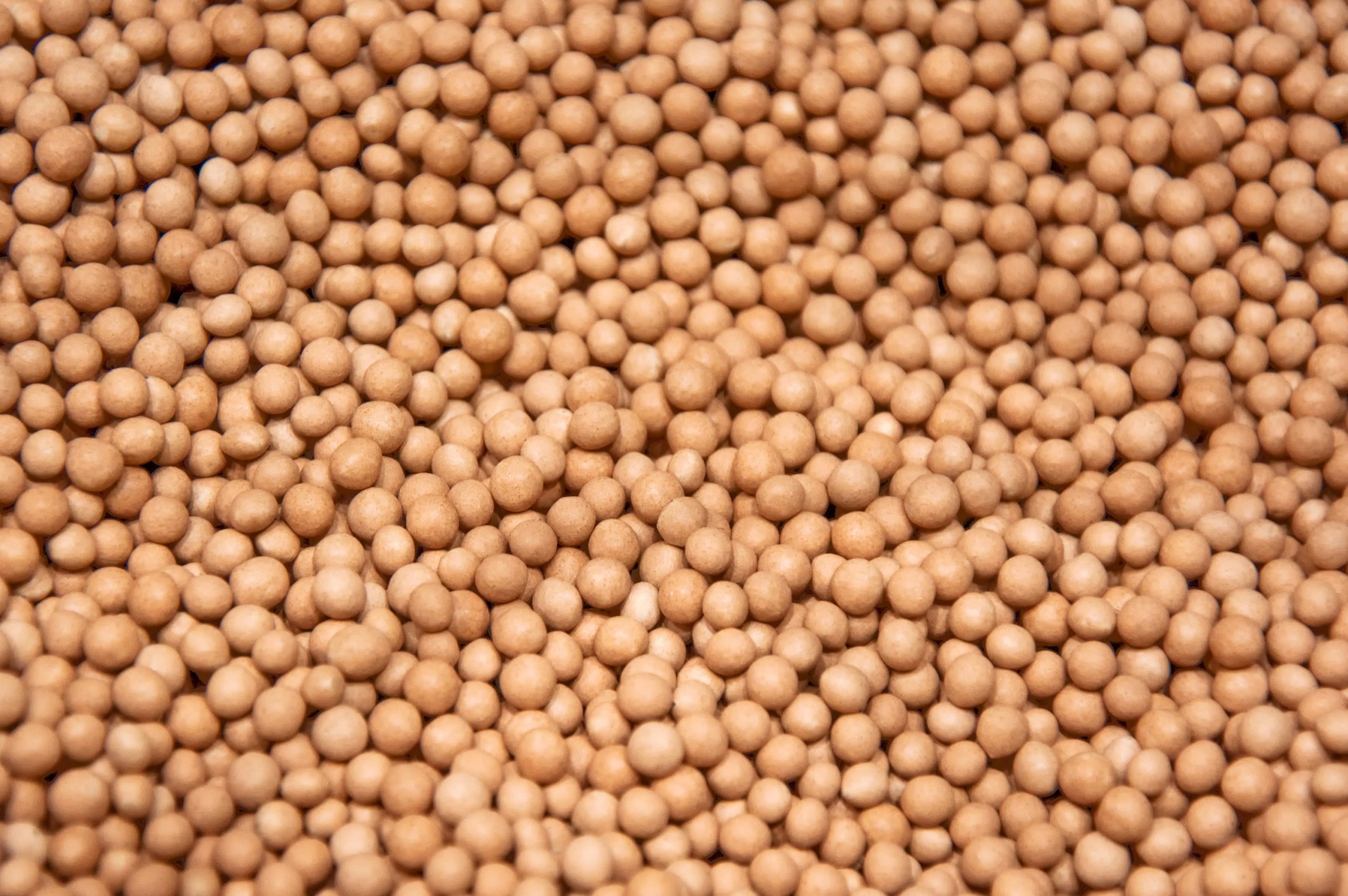

The next steps in processing and producing seeds from sugar beets are pelleting and coating. The seed is pelleted because the irregular and oddly-shaped ones cannot be planted in standardized intervals with industrial sowing equipment. The pelleting machine equally distributes the liquids and powders on the seeds to create perfectly round pellets. It is because of the irregular shape they come with that their production process is more challenging than other crops. High-capacity and high-speed industrial equipment can shorten this process significantly.
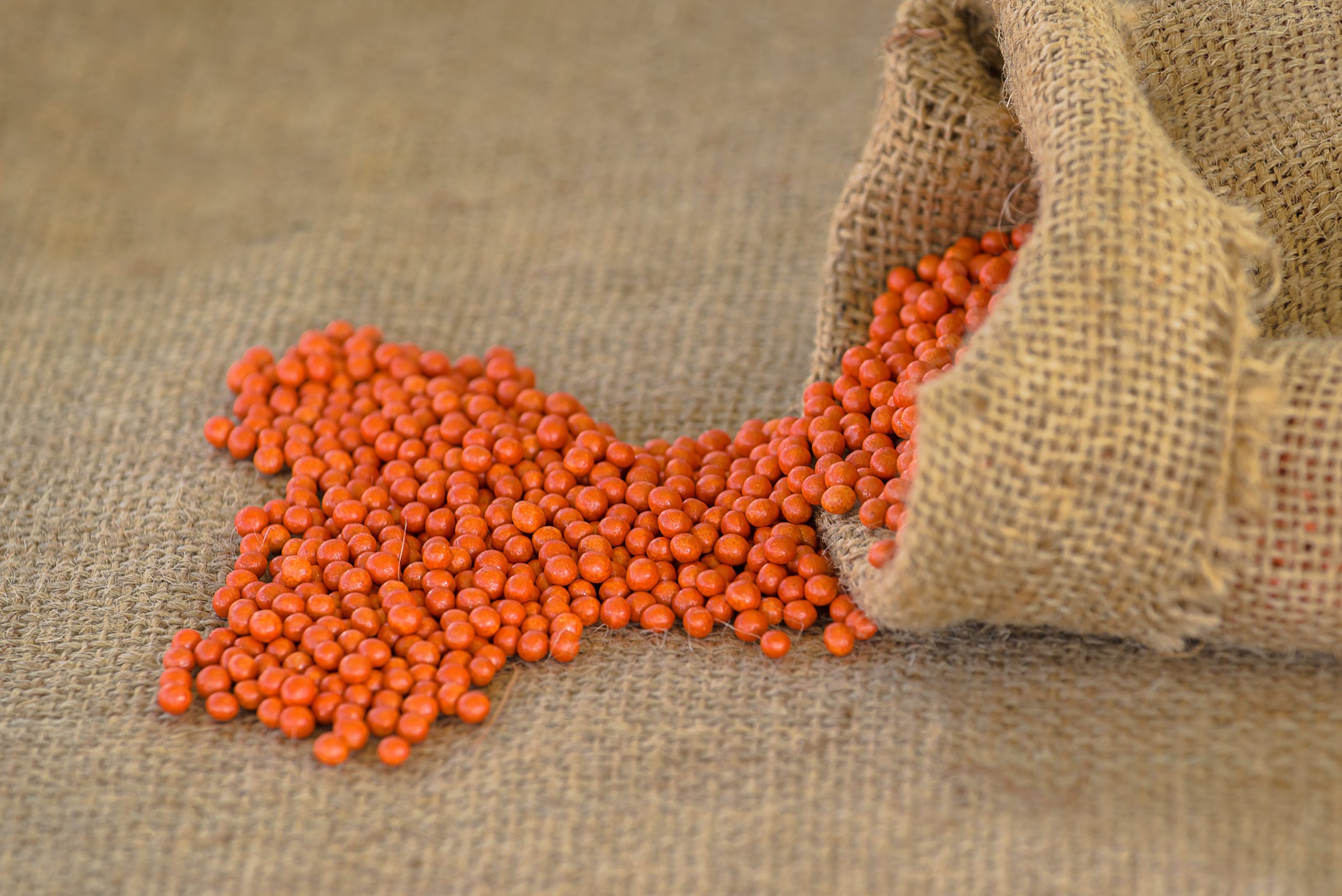

The final step is seed coating, which reduces the amount of pesticides used in the fields by applying a smaller amount directly onto the pellets. The coating machine distributes various protective fluids, like insecticides and fungicides, for an added layer of protection. Coating further supports germination and shields the seeds from pests. The color of the pellet’s coating indicates which treatment was used and it can also help track the placement and depth of each individual seed when sowing.
From beets to biofuel
Sugar beets are not only used for sugar production but also to derive bioethanol, a biofuel. Producing bioethanol is a carbon-neutral process, and bioethanol itself is easily biodegradable or diluted in case of spills. First developed by DSD and ACRRES, the Betaprocess shortened the amount of time needed to extract bioethanol from biomass. That’s because it is no longer necessary to extract sugar from the beets first.

Before they can be used to produce bioethanol, sugar beets have to be harvested, washed and crushed. The crushed sugar beets are then transferred into the Betaprocess, where they are placed in vacuum conditions and the temperature is set between 60 and 65°C. Here, the sugar beet cell explodes immediately releasing the sugars, so the pulp, along with yeast, is fermented. After fermentation, the mixture can be distilled. This entire process only lasts two days and costs 35% less than traditional extraction of ethanol from sucrose.
Processing steps involved in sugar beet seeds making
Which sugar beet seeds technology do you need?
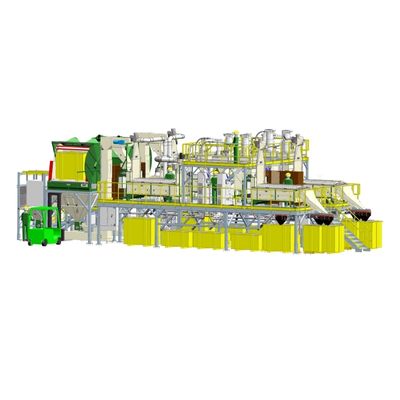

Automatic processing line for field crop seeds
The quality of field crops (ROW crops) is determined by their seeds. The br...

Exergy pressurized superheated steam dryer
Traditional dryers and heat transfer systems, like belt-, drum- or bed dryers a...
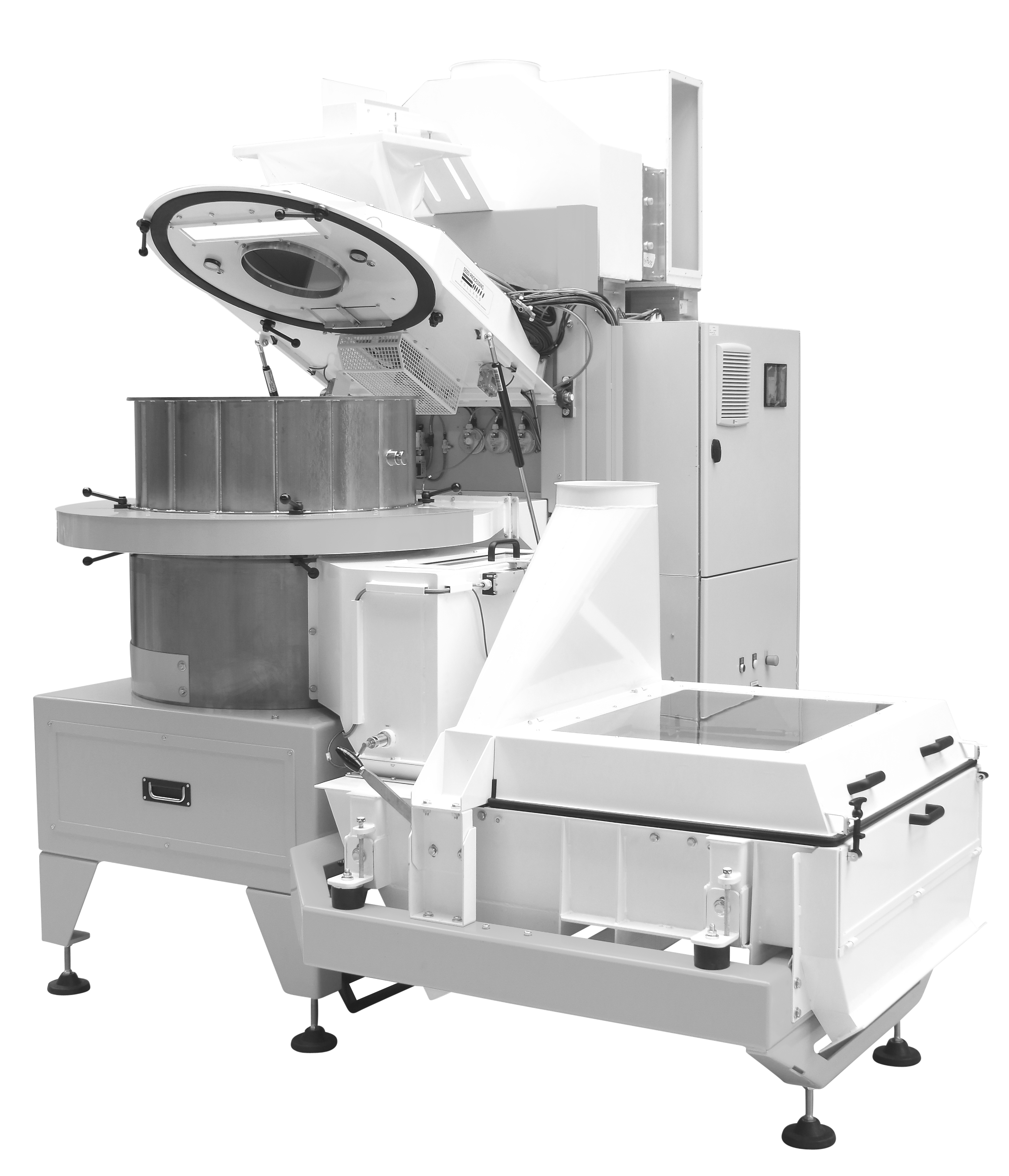

Rotary Seed Dryer Coater
Large-volume vegetable and field crop seeds manufacturers may prefer a fully automated coating and d...
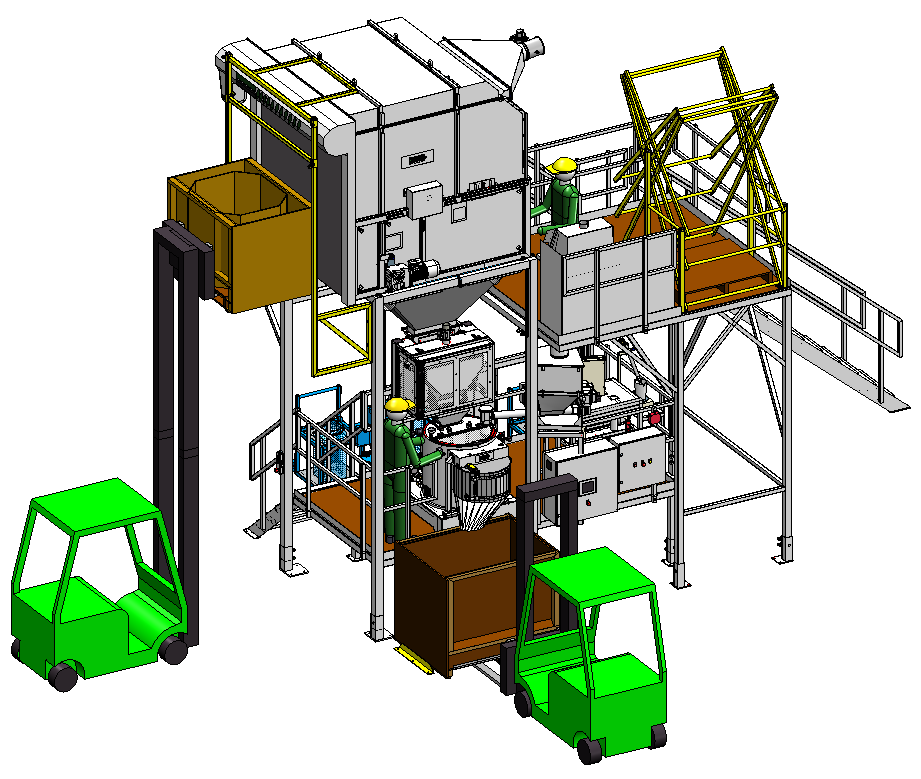
Rotary Seed Pelleting Machine
When pelleting large batches of seeds like flower, vegetable, or agricultural types, it is imp...

Seed Gravity Separator
In large-scale production, separating quality seeds from empty seeds and other debris – such as ...
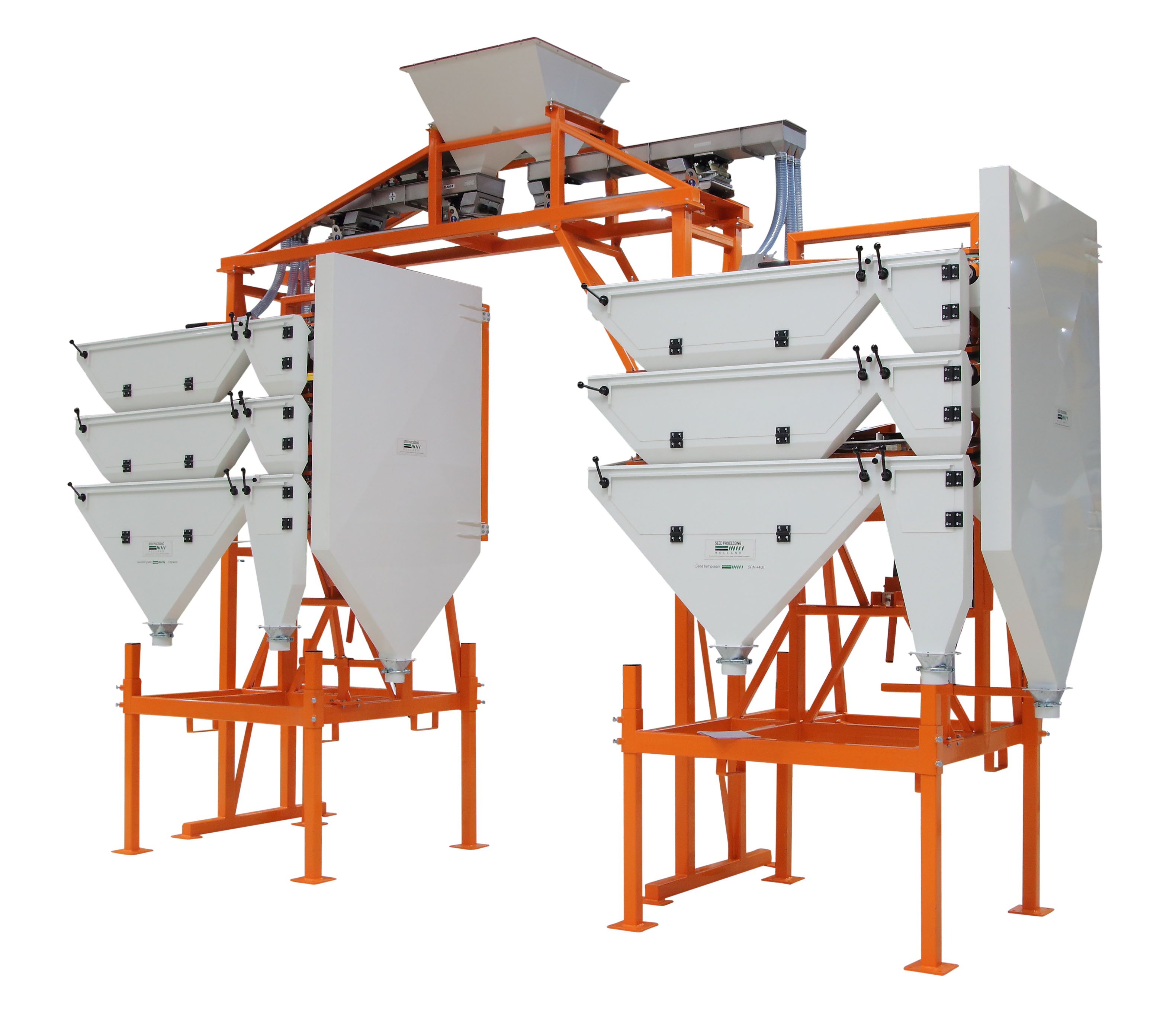
Seed Belt Grader
Large volume seed producers require high-capacity grading equipment to separate the good seeds from the bad o...
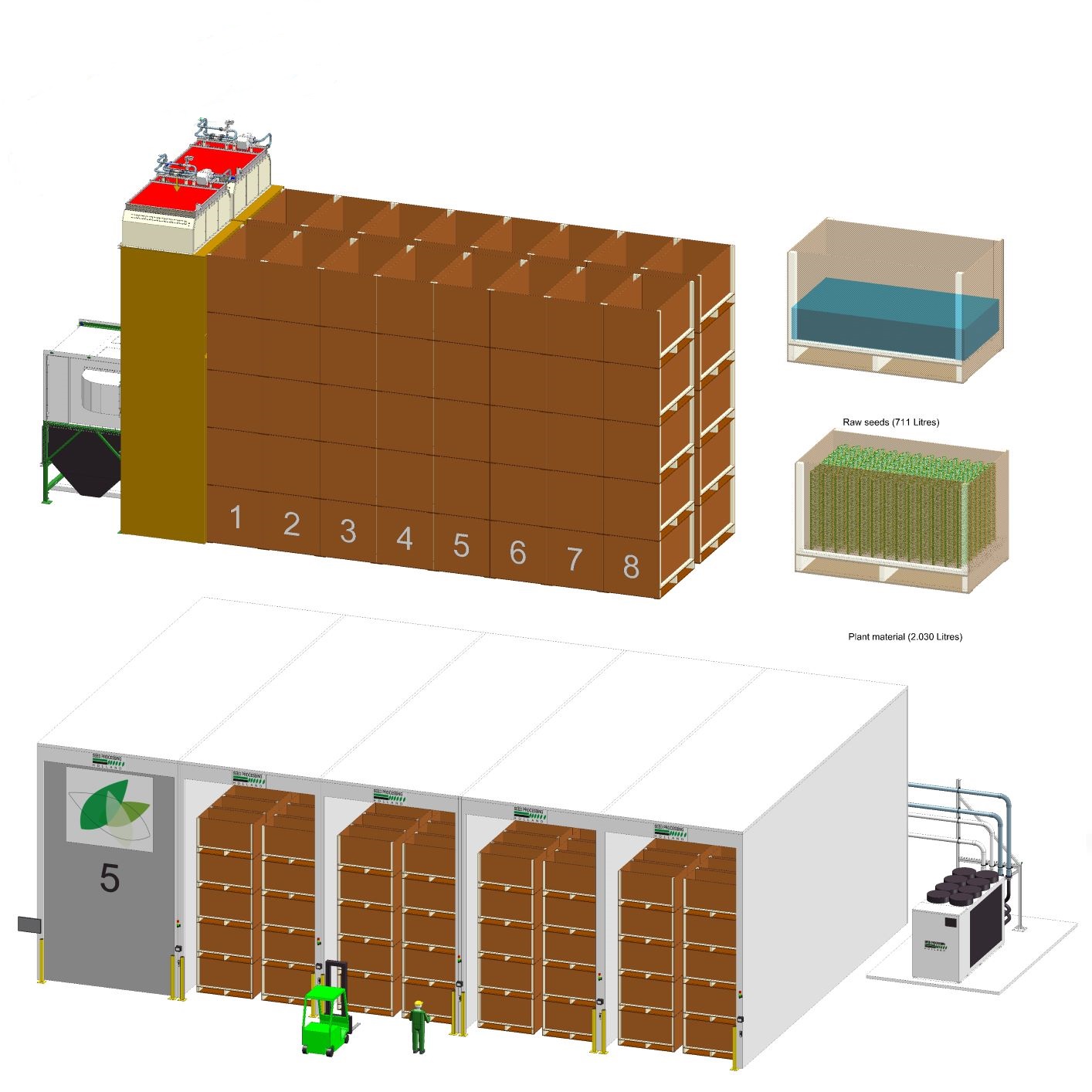
Conditioned Box Dryer
Seeds that are harvested are dried as part of their initial process of cleaning. Having huge quantities...
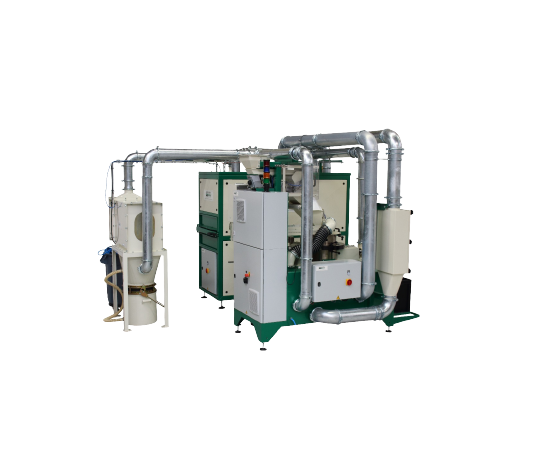

Seed Coating Machine With Integrated Dryer
Seed coating, also known as seed dressing, refers to the covering of seeds with...
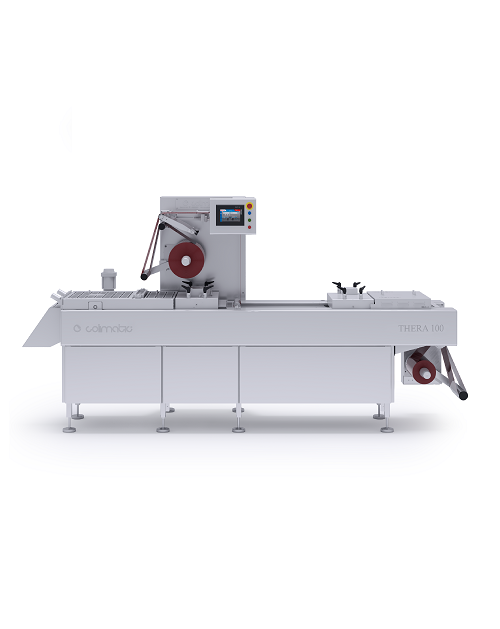

Form fill seal thermoforming machine
As the name suggests, a Form Fill Seal machine is one that forms, fills, and seals a p...
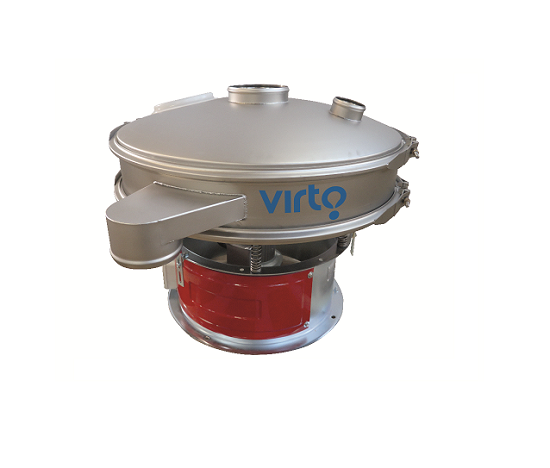

Vibrating sieve for liquid solid separation
Many industrial processes require the efficient separation of solids from a sl...
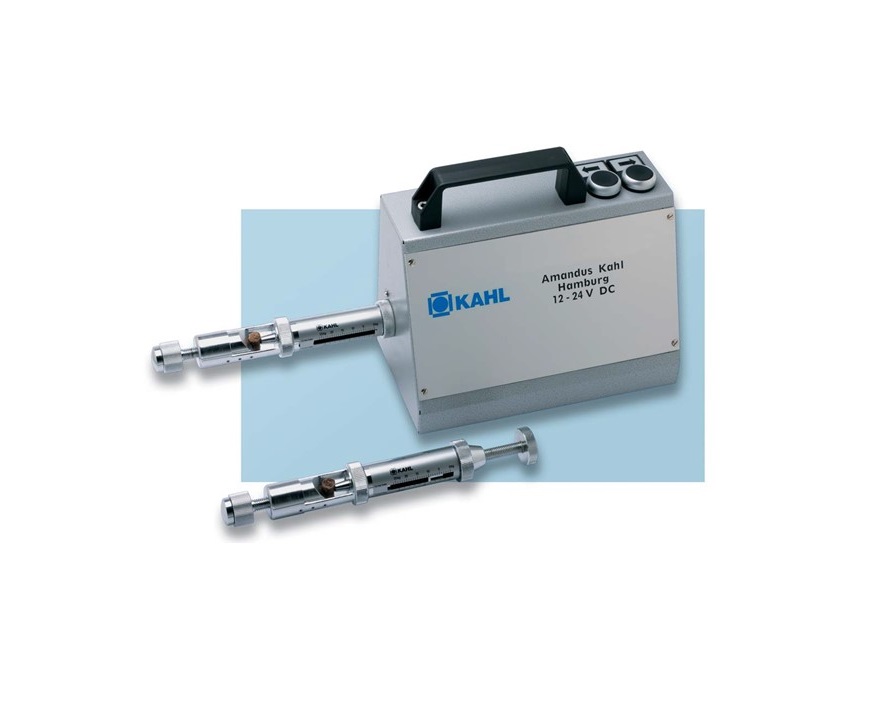

Pellet hardness tester
Control the quality of your pelletizing processes using a pellet hardness tester. Pellet hardness is o...
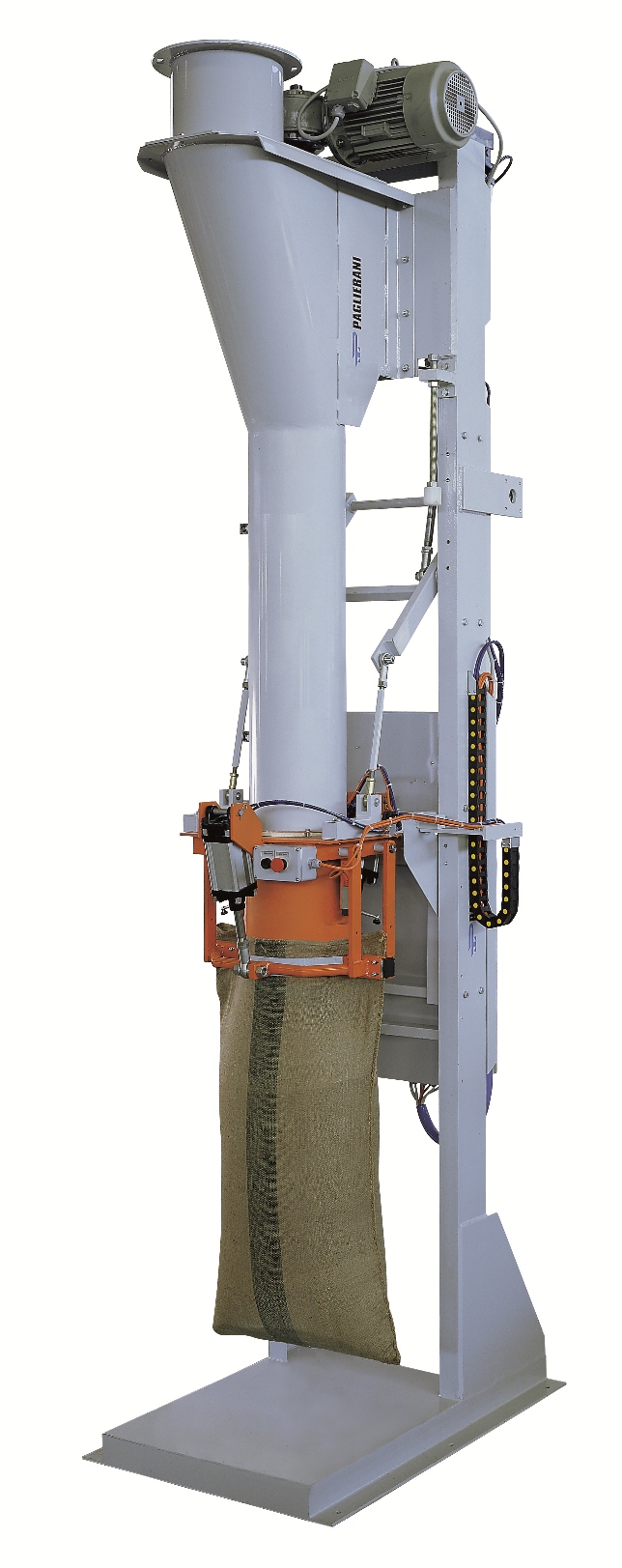

Bagger for open mouth bags
Where a stand-alone bagger is required for filling large, open mouth bags, a delivery method is n...
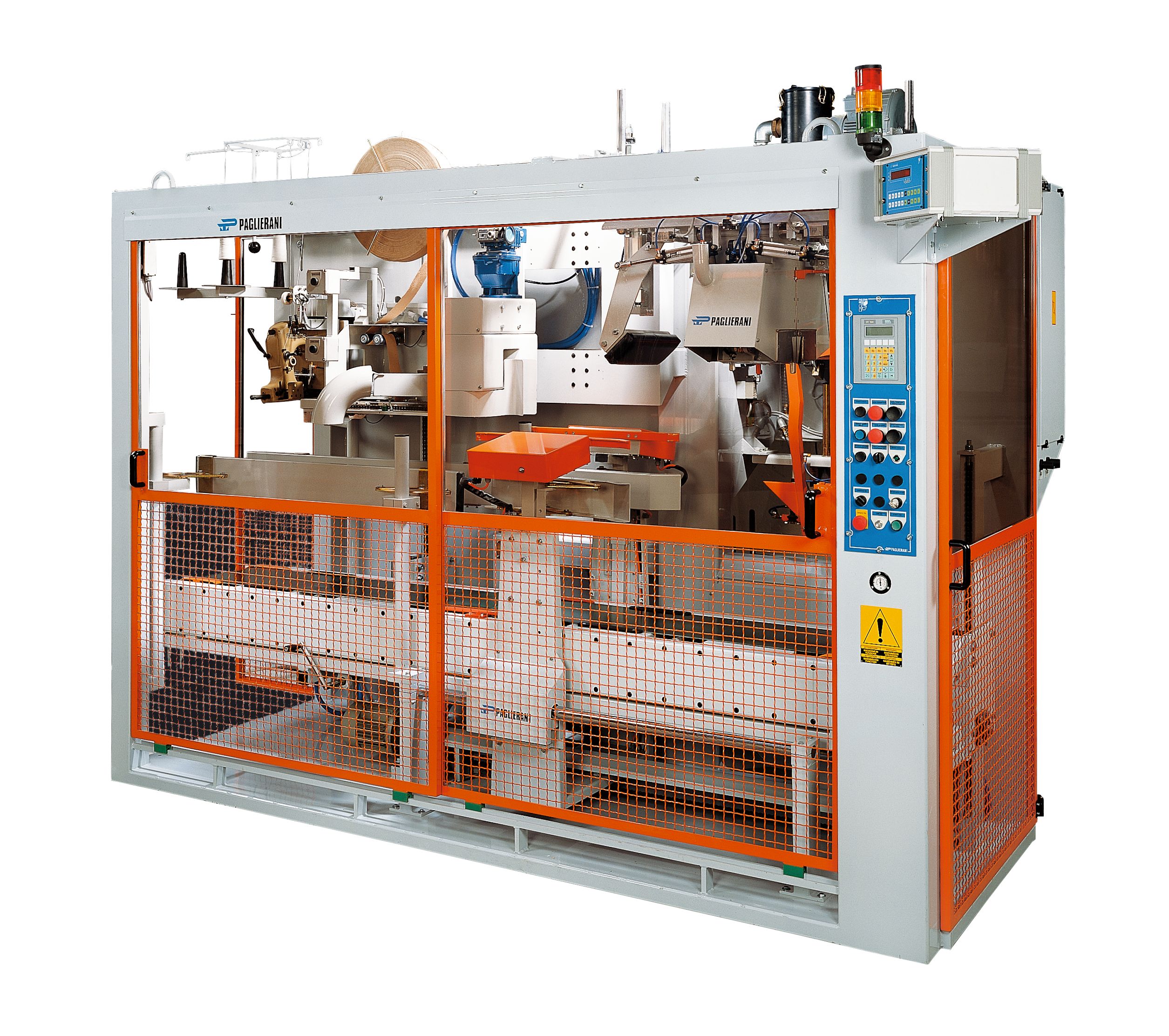

Automatic bagging machine for open mouth bags
Open mouth bags allow for a variety of different products to be packaged, wi...
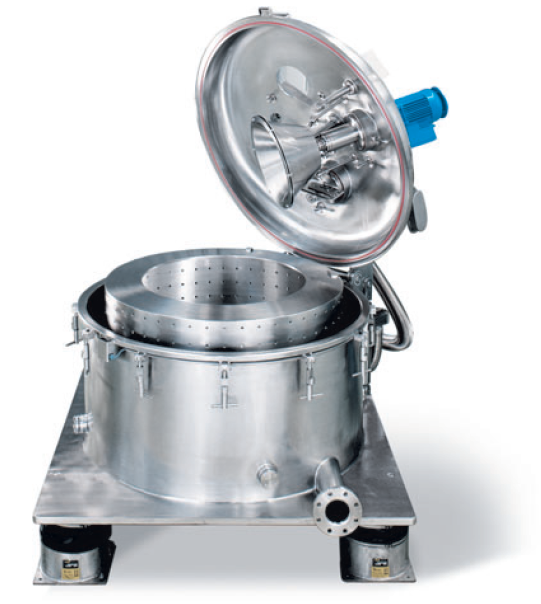

Vertical scraper centrifuges
Vertical Bottom discharge Centrifuges work discontinuously, discharging the solids to the botto...








