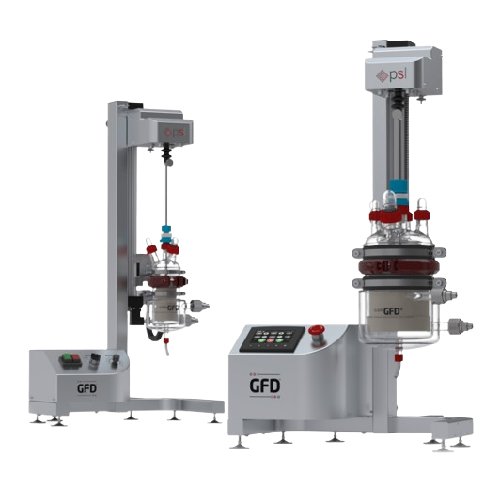
Echinacea Extraction Equipment
Find innovative production technology for making echinacea extract and connect directly with world-leading specialists
Echinacea, also known as coneflowers, are brightly hued flowers with distinguished, cone-shaped flower heads. Over 200 medicines in the world are derived from coneflower extracts. Echinacea processing was introduced by Native Americans who were interested in the plant's medicinal qualities.
Stories about echinacea extract
Select your echinacea extract process
Tell us about your production challenge
Use high dielectric solvents for microwave-assisted extraction
In microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), the heat of microwave radiation reaches the plant material directly without being absorbed by the microwave transparent solvent in which the solid is placed. Meanwhile, most MAE operations use solvents with a high dielectric constant that absorbs microwave energy.
Heating generates a high vapor pressure breaching the cell wall and releasing the echinacea extract into the solvent. The same heat causes the residual moisture in the solid to evaporate.

Maceration with glycerol as an alternative echinacea extraction technique
Maceration is soaking the plant material in a liquid to extract its phenolic acids without subjecting it to thermal treatment.
A non-toxic polyol, Glycerol offers a viable extraction fluid option for extracts designed for pharmacological or dietary products. However, the compound registers a high level of viscosity, and 90% mass concentration is sufficient for echinacea processing.

Chicoric acid shows promise in functional foods preparation
Echinacea is rich in chicoric acid, a hydroxycinnamic acid with several pharmacological applications. The extract is used as an active ingredient in anti inflammatory and anti-viral formulations.
Meanwhile, chicoric acid is also being explored as a base in preparing functional foods and supplements.
Echinacea extracts contain 38 taxa of bacteria
Echinacea Purpurea is the only species of the Echinacea plant with the capacity to bolster the immune system in humans. For example, improving the immune system against flu.
This species, known as the purple coneflower, carries 38 different taxa of bacteria in its extracts. These bacteria help the plant’s extracts stimulate macrophages (a type of white blood cell) that strengthen immunity.
However, there is still debate surrounding the differences between Echinacea Angustifolia and Purpurea. Many believe that the Angustifolia contains more effective medicinal properties and thus used for medications, tinctures and herbal extracts. The reason Purpurea is used instead is that it is a lot more common to obtain and also easier to grow.
Processing steps involved in echinacea extract making
Which echinacea extract technology do you need?

Benchtop peristaltic dispenser
When you fill vials and ampoules, high standards of hygiene are required to avoid the risk of...
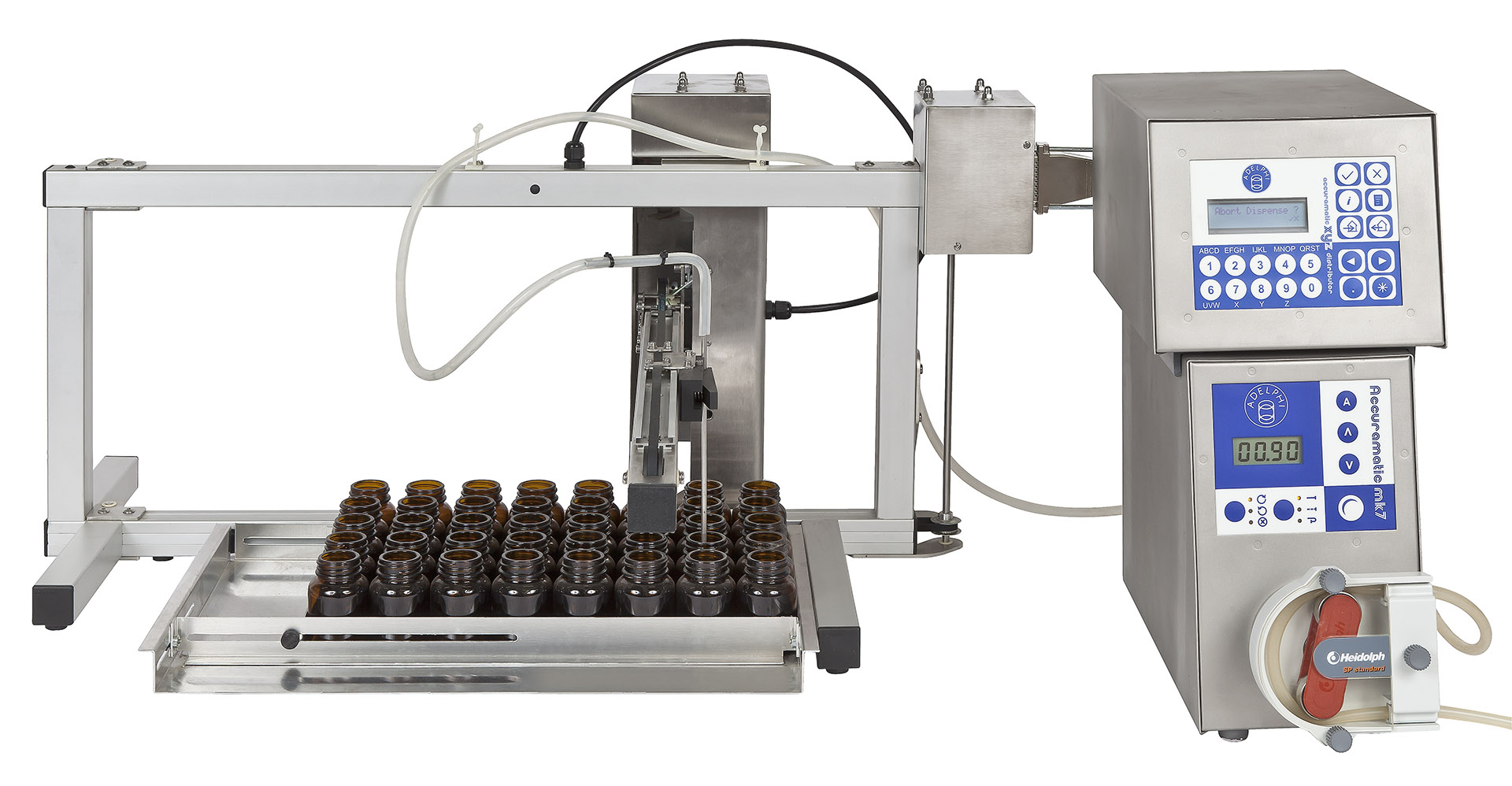

Benchtop piston filling equipment for vials in trays
Vials are difficult to fill individually through manual methods due ...

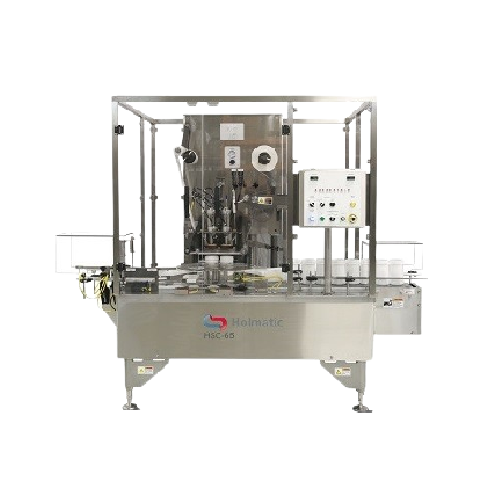
Semi-automatic vial crimper
In a small production line, crimping vials manually can cause fatigue to your operator due to mu...
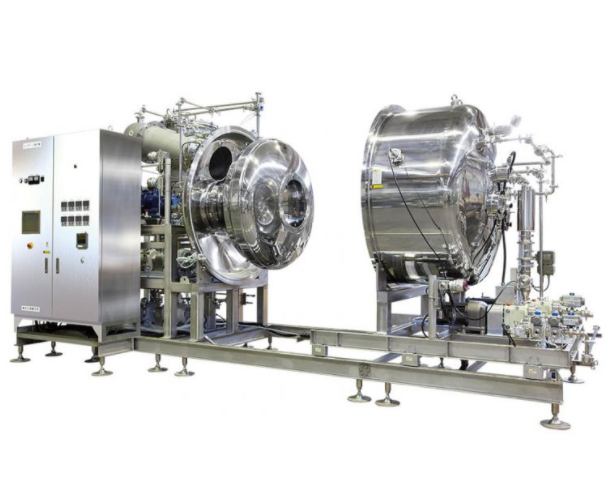

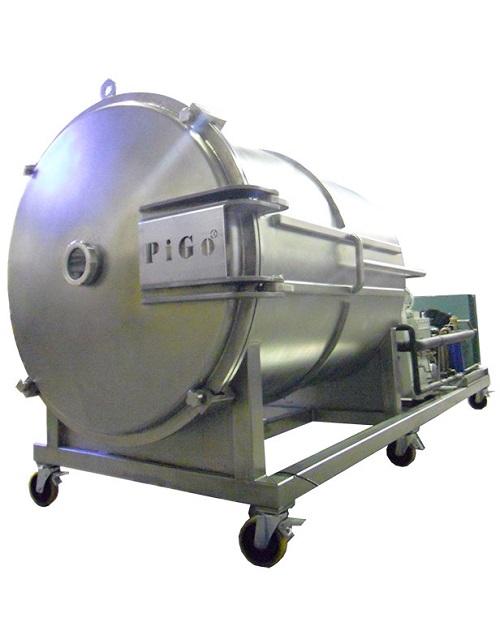
Evaporator for heat sensitive products
The removal of solvents when making products in industries like food, cosmetics, pha...

Cosmetic cream filler
From thin liquid baby oils and perfumes to thicker lotions and creams for hair and skincare, cosmetic p...
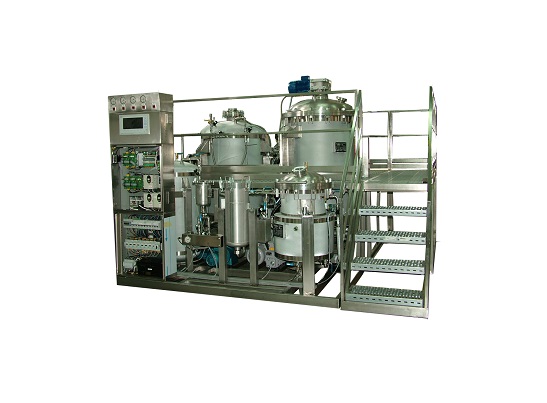

Flower oil extraction machine
The production of “essential oils” has traditionally involved using heat and distillation to e...

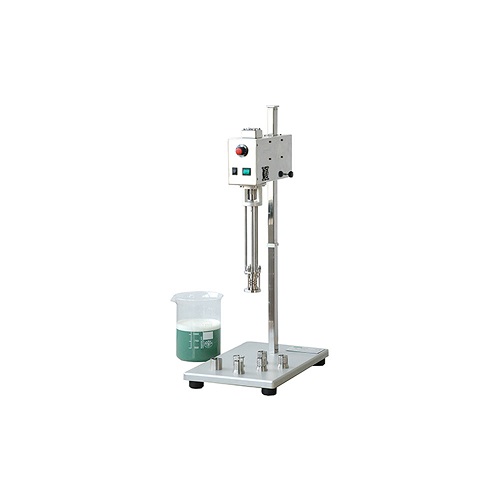
Medicinal plant extraction machine
Traditional methods for extracting active compounds from medicinal plants or herbs use h...
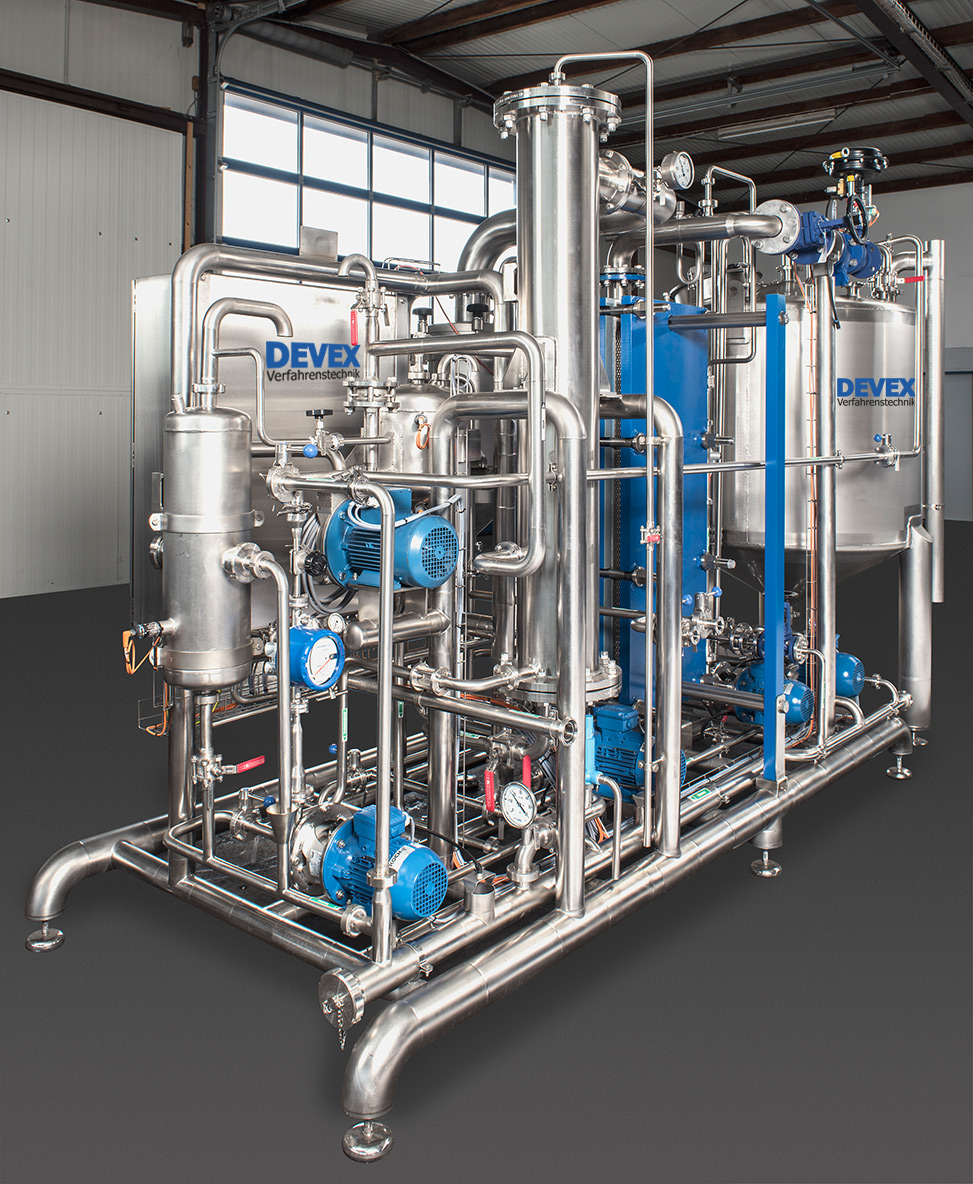

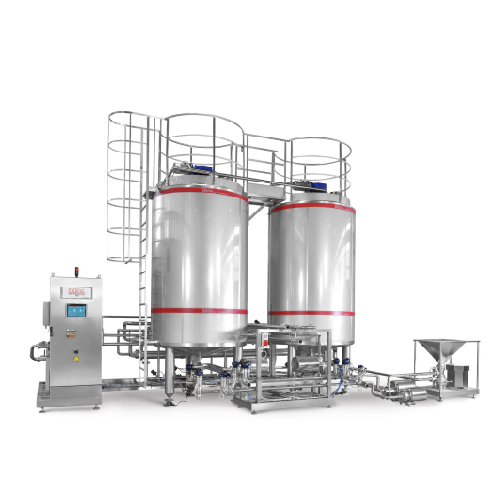
Evaporation plant for the recovery of extracts
Bespoke evaporation plants using the latest plate evaporation technology ca...
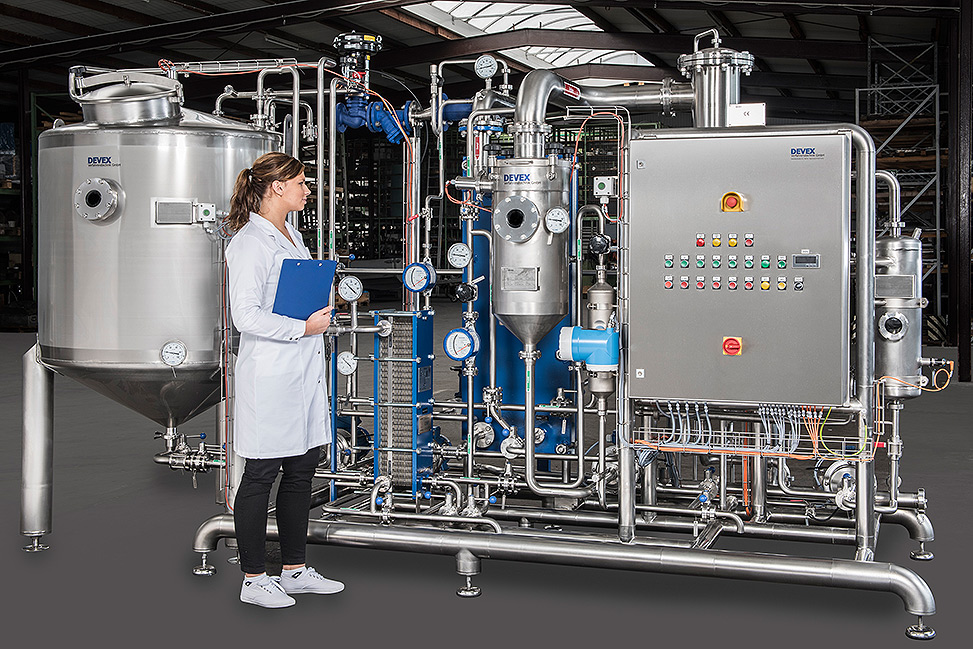

Pilot evaporation plant for the recovery of extracts
For development of concentrates of extracts based on water or ethano...
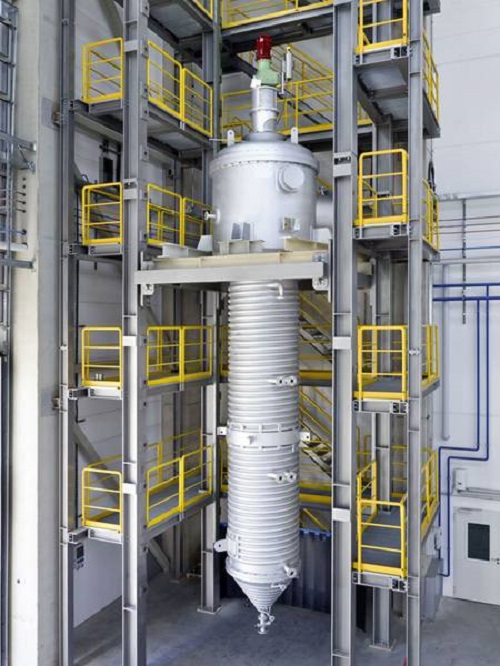

Wiped film evaporator
With wiped film distillation, a substantial decrease of boiling temperature is obtained by reducing the...
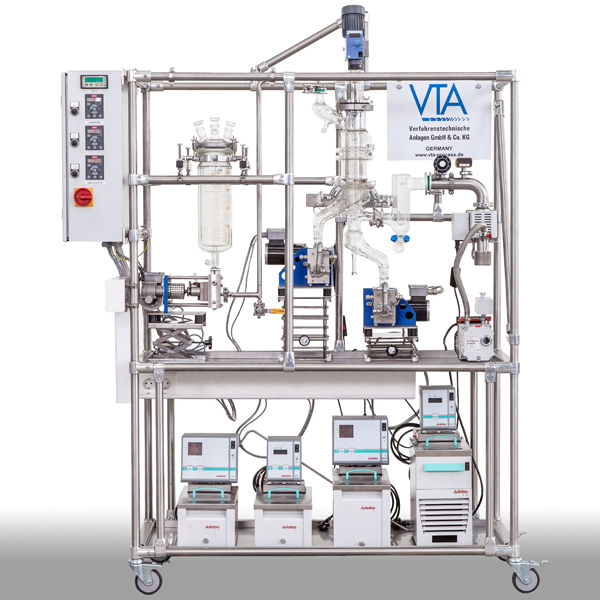

Laboratory short path distiller
Get to reliable conclusions for the separation of high-boiling and heat-sensitive products u...